Aberration coupling characteristics of axial and lateral misalignments of off-axis three-mirror telescopes
-
摘要:
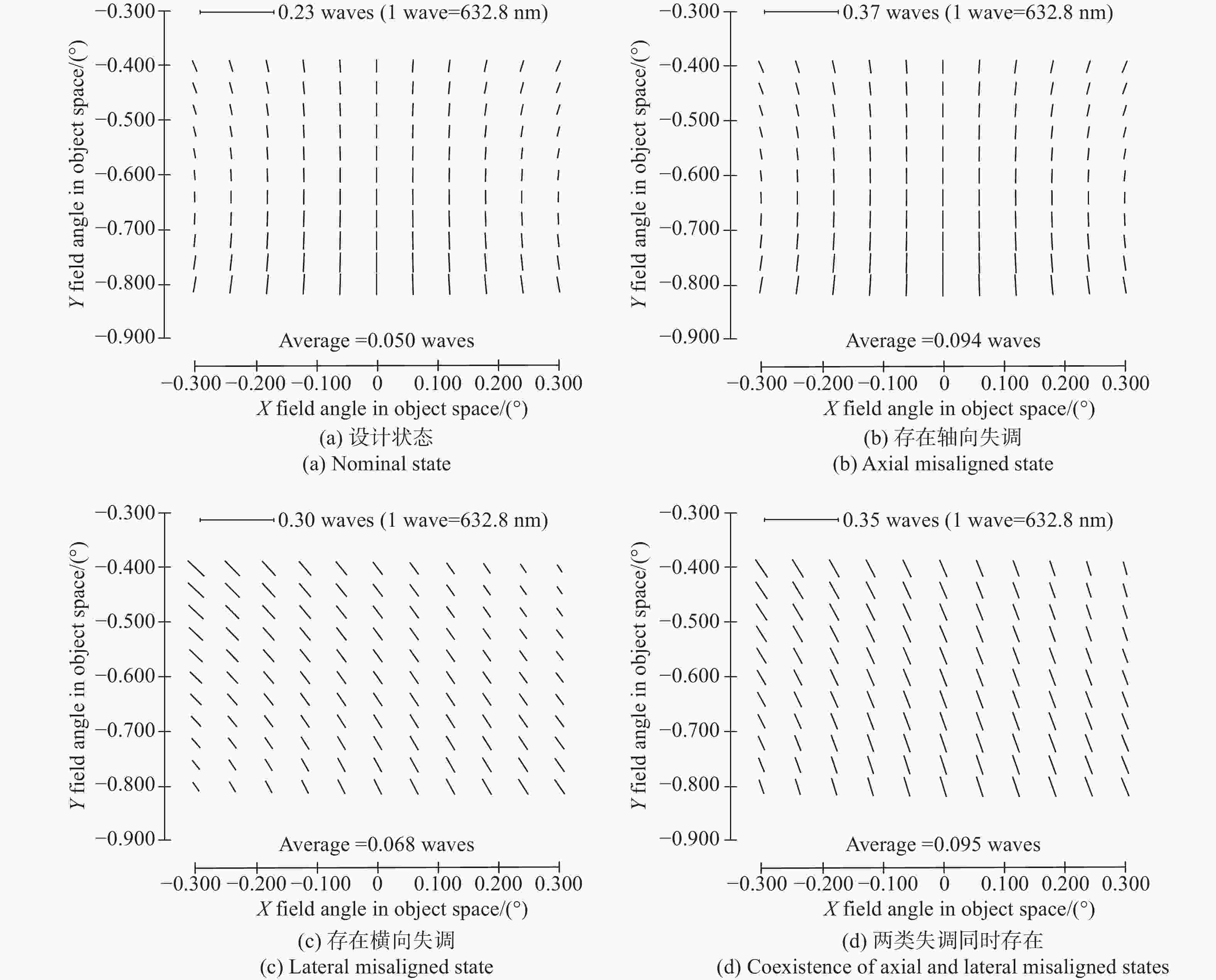
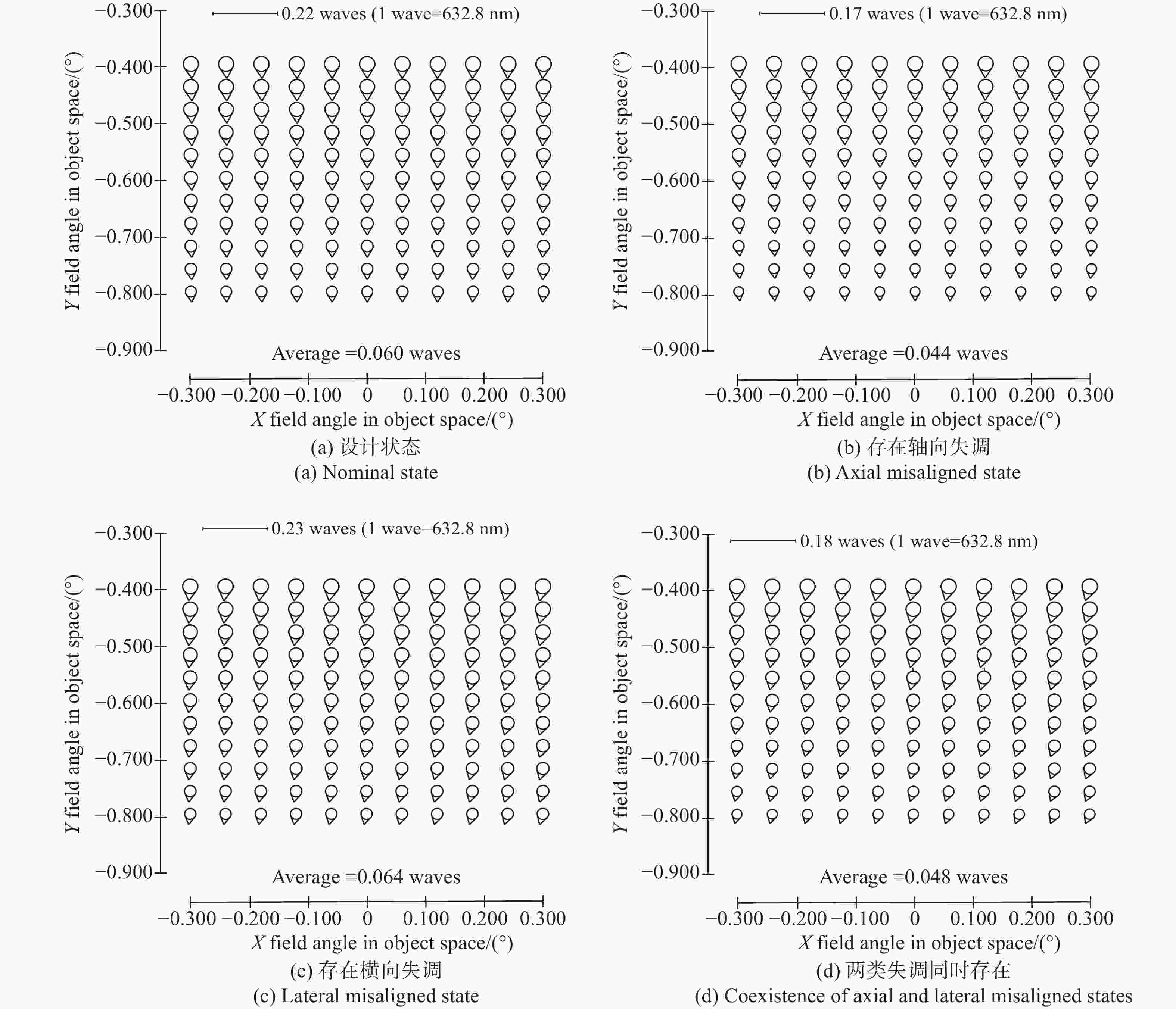
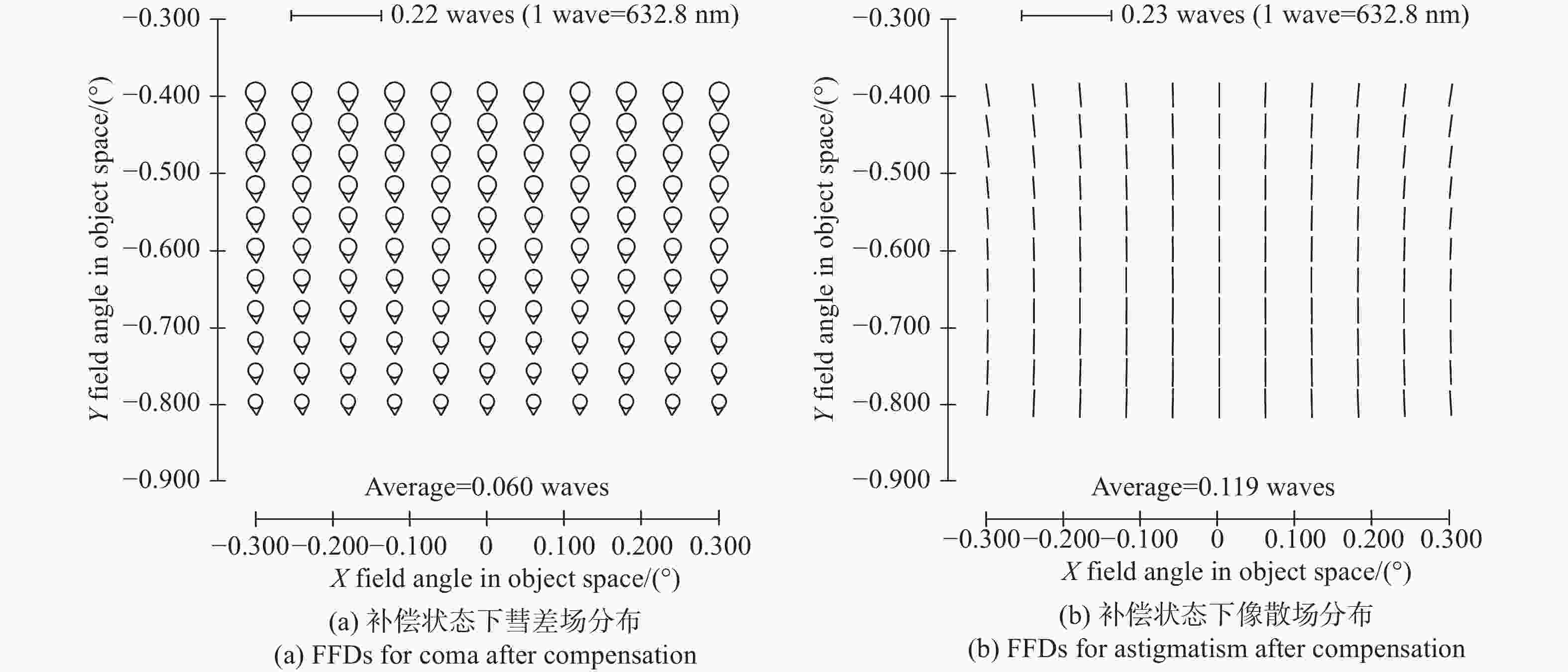
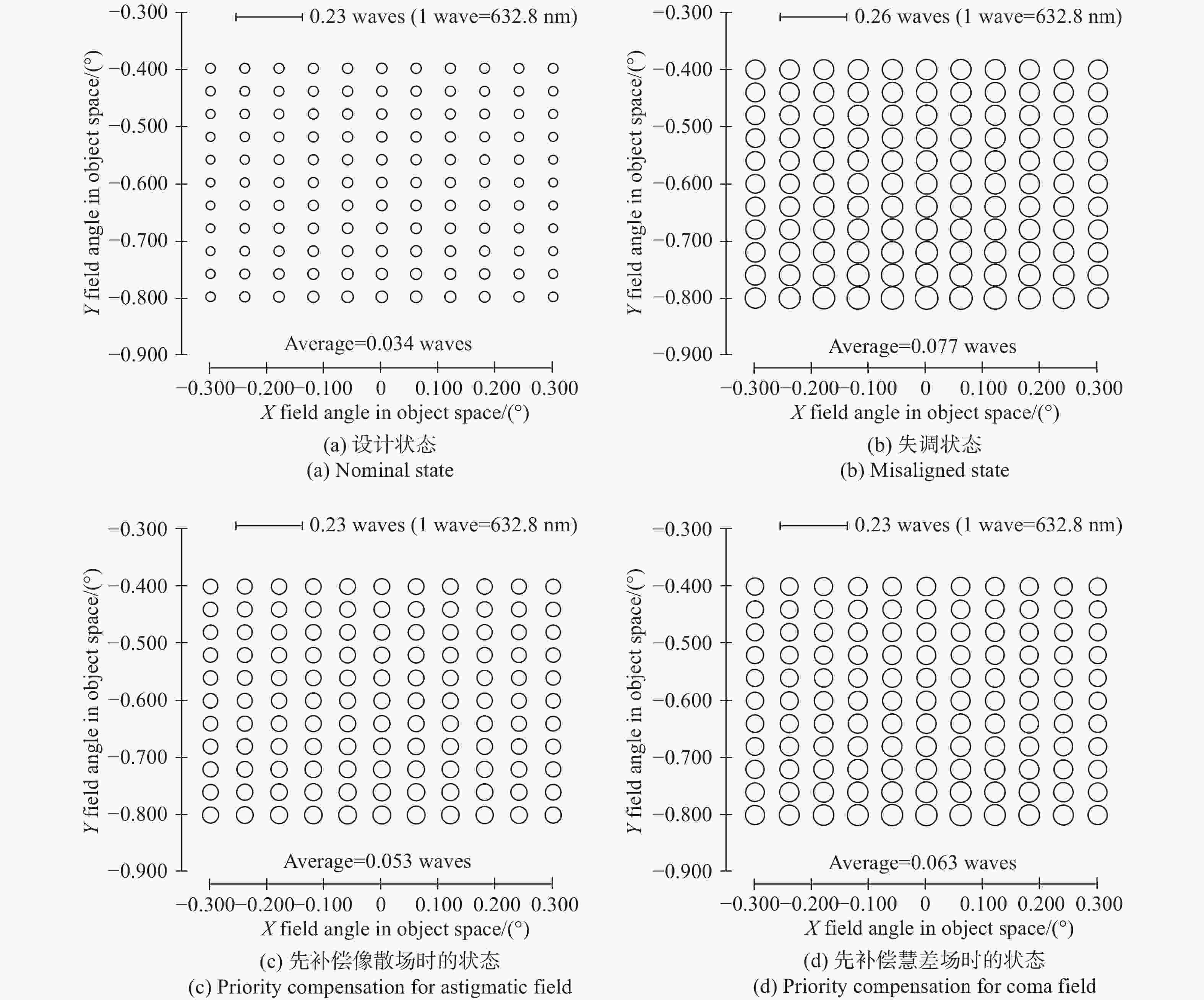
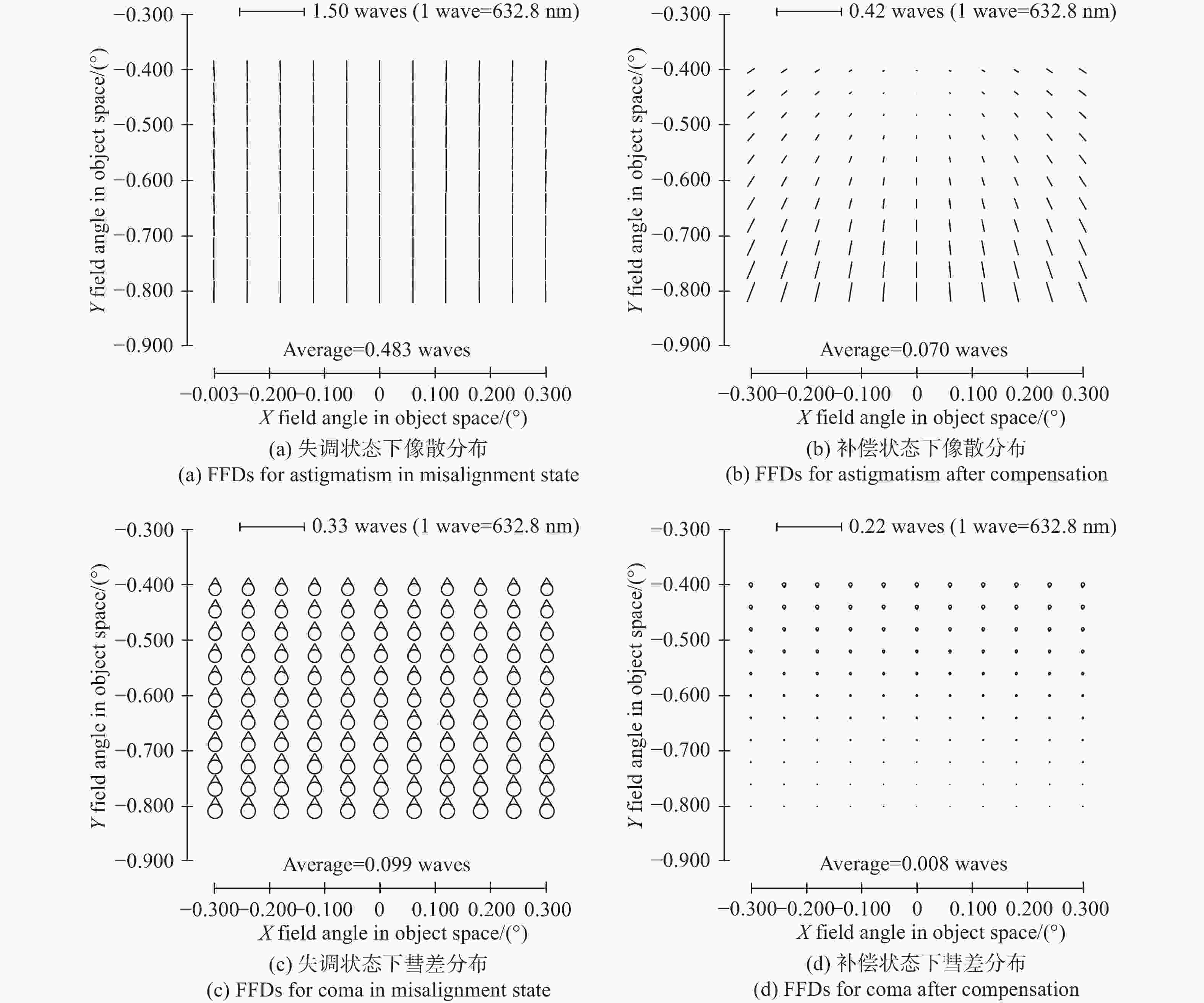
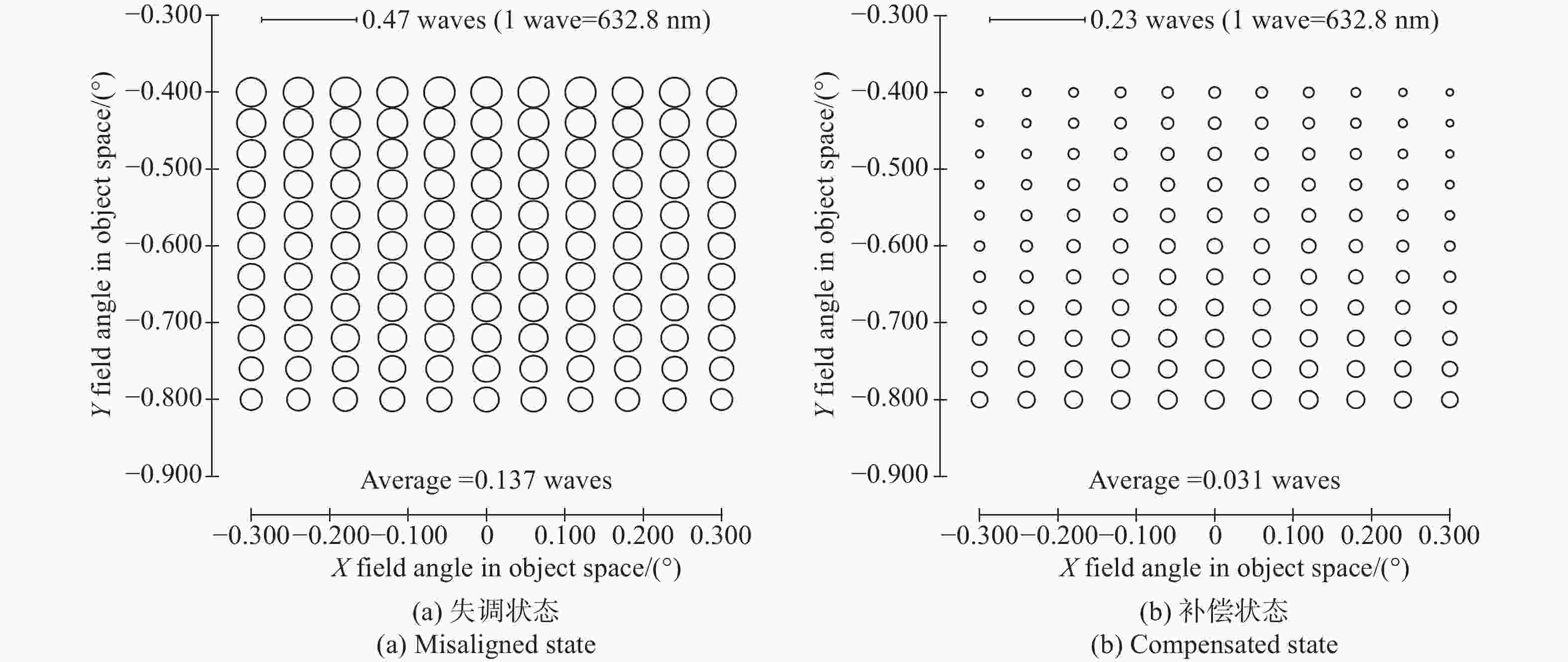
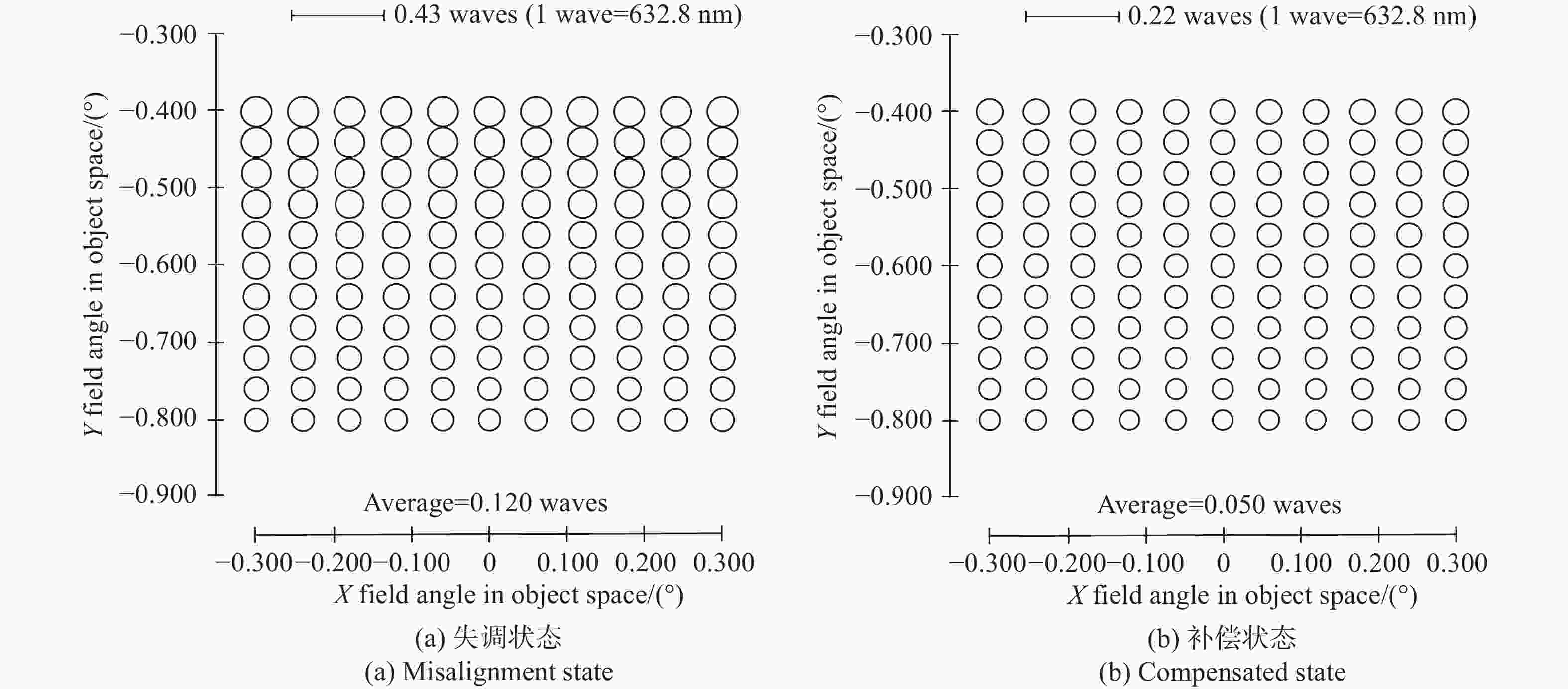
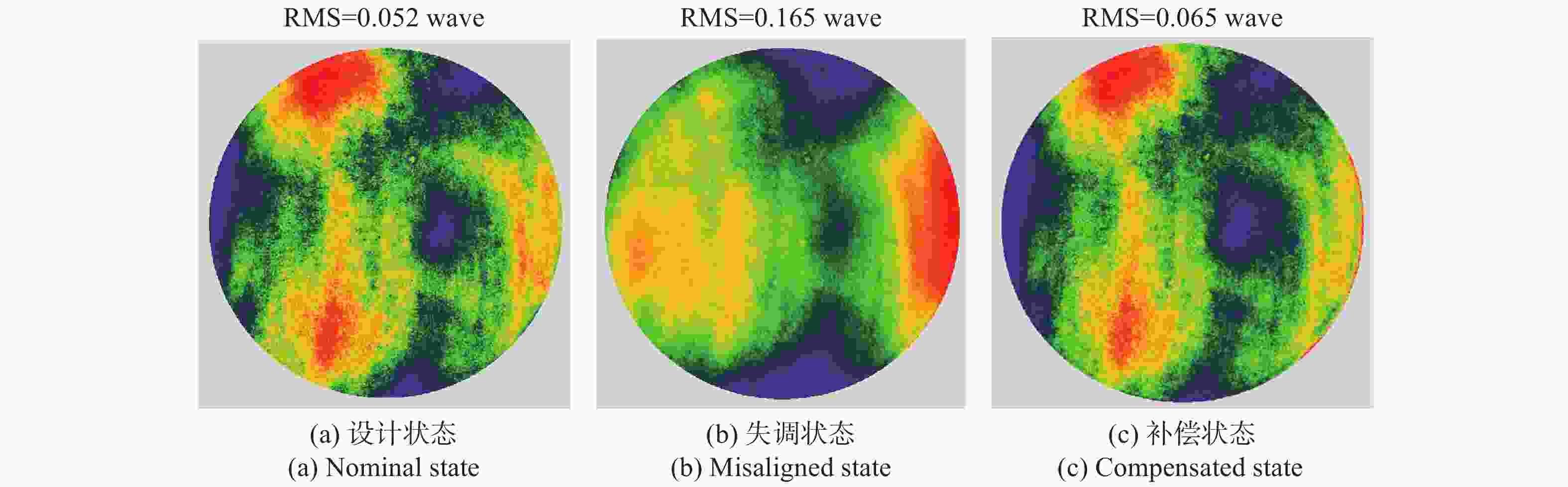
为了保证离轴三反空间望远镜地面装调阶段及在轨调整阶段的成像质量,本文基于矢量像差理论从内在机理层面揭示了轴向失调与横向失调对像差影响的耦合特性,重点分析了两类失调耦合特性产生的补偿关系:(1)针对轴向失调补偿横向失调,揭示了装调过程中系统像质可能处于局部极值的一类工况;(2)针对横向失调补偿轴向失调,提出利用在轨横向失调引入的像散、彗差补偿轴向失调引入的像散、彗差的补偿策略(离焦不能补偿)。本文以实验室现有的一套离轴三反系统为例,充分验证了解析关系的准确性。仿真和实验证明:当系统同时存在轴向失调和横向失调时,系统成像质量也可能达到衍射极限(1/14λ),但系统像质处于局部极小值;望远镜在轨处于失调状态且离焦较小时,可以优先通过校正横向失调以完成系统像质校正,RMS波前误差改变量小于0.02λ。
Abstract:To ensure the imaging quality of the off-axis three-mirror space telescope during the ground adjustment and on-orbit adjustment stages, we reveal the coupling characteristics of the effect of the axial misalignment and the lateral misalignment on aberration based on the Nodal aberration theory from the internal mechanism level. This paper focuses on the compensation relationship generated by the coupling characteristics of two types of misalignments: (1) axial misalignment compensates for lateral misalignment, which reveals a type of working condition where the system image quality may be at a local extreme during the alignment process on the ground; (2) lateral misalignment compensates for axial misalignment. A compensation strategy wherein astigmatisms and comas introduced by in orbit lateral misalignment can compensate for astigmatisms and comas induced by axial misalignment is proposed (defocus cannot be corrected). Taking the off-axis three-mirror system in the laboratory as an example, the accuracy of the analytical relationships can be verified. Simulations and experiments have proven that the imaging quality of the system may reach the diffraction limit (1/14λ), but the system’s image quality is at a local minimum in the presence of both axial and lateral misalignment. When the telescope is misaligned in orbit and the defocus is small, the system image quality can be corrected by properly aligning the lateral misalignment first. The RMS wavefront error after compensation changes less than 0.02λ compared with the design state (the best state of installation and alignment).
-
表 1 波像差系数对主次镜间距的敏感度
Table 1. Sensitivity of the wavefront aberration coefficient to the distance between primary and secondary mirrors (632.8 nm/mm)
像差系数 像差系数对主次镜间距的敏感度 $ {K_{040{d_1}}} $ 0.080 $ {K_{222{d_1}}} $ 0.239 $ {K_{131{d_1}}} $ −0.119 表 2 波像差系数对次三镜间距的敏感度
Table 2. Sensitivity of the wavefront aberration coefficient to the distance between the secondary and tertiary mirrors (632.8 nm/mm)
像差系数 像差系数对次三镜间距的敏感度 $ {K_{040{d_2}}} $ −0.006 $ {K_{222{d_2}}} $ −0.016 $ {K_{131{d_2}}} $ 0.028 表 3 不同方法获得的像散系数差值
Table 3. The difference in the astigmatism coefficient obtained by different methods (λ=632.8 nm)
视场 Zernike 像差系数 仿真软
件获取值公式
计算值(0.3°,−0.8°) $ \Delta {C_5} $ −0.0038 −0.0026 $ \Delta {C_6} $ −0.0495 −0.0388 (−0.3°,−0.8°) $ \Delta {C_5} $ 0.0109 0.0118 $ \Delta {C_6} $ −0.0659 −0.0618 表 4 不同方法获得的彗差系数差值
Table 4. The difference in the coma coefficient obtained by different methods (λ=632.8 nm)
视场 Zernike 像差系数 仿真软件获取值 公式
计算值(0.3°,−0.8°) $ \Delta {C_7} $ −0.0107 −0.0108 $ \Delta {C_8} $ 0.0115 0.0108 (−0.3°,−0.8°) $ \Delta {C_7} $ −0.0136 −0.0134 $ \Delta {C_8} $ 0.0113 0.0110 表 5 像差系数对失调量的敏感度
Table 5. Sensitivity of the aberration coefficient to misalignment (632.8 nm/mm and 632.8 nm/°)
C5 C6 C7 C8 XDE 0.053 1.419 0.290 -0.001 YDE −1.410 0.051 −0.0001 0.276 ZDE −0.240 0.031 0.0129 0.139 ADE 8.394 −2.396 −0.014 −2.600 BDE 2.351 8.190 2.522 −0.0165 -
[1] 张晓彬. 基于矢量像差理论的离轴反射系统失调校正研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018.ZHANG X B. Research on misalignment correction in off-axis reflective systems based on nodal aberration theory[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese) [2] 鞠国浩. 离轴反射式天文望远镜主动光学波前控制方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017.JU G H. Research on active optical wavefront control methods for off-axis reflective astronomical telescopes[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese) [3] 赵文才. 改进的离轴三反光学系统的设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2011,19(12):2837-2843. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111912.2837ZHAO W C. Design of improved off-axial TMA optical systems[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2011, 19(12): 2837-2843. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111912.2837 [4] 杨飞, 安其昌, 张静, 等. 大口径光学系统的镜面视宁度检测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(10):2572-2579. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172510.2572YANG F, AN Q CH, ZHANG J, et al. Seeing metrology of large aperture mirror of telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(10): 2572-2579. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172510.2572 [5] 沙巍, 陈长征, 许艳军, 等. 离轴三反空间相机主三镜共基准一体化结构[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(6):1612-1619. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152306.1612SHA W, CHEN C ZH, XU Y J, et al. Integrated primary and tertiary mirror components from common base line of off-axis TMA space camera[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(6): 1612-1619. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152306.1612 [6] 张磊, 刘东, 师途, 等. 光学自由曲面面形检测技术[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(3):283-299. doi: 10.3788/co.20171003.0283ZHANG L, LIU D, SHI T, et al. Optical free-form surfaces testing technologies[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(3): 283-299. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171003.0283 [7] 康健, 宣斌, 谢京江. 表面改性碳化硅基底反射镜加工技术现状[J]. 中国光学,2013,6(6):824-833.KANG J, XUAN B, XIE J J. Manufacture technology status of surface modified silicon carbide mirrors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(6): 824-833. (in Chinese) [8] BAI X Q, XU B Q, MA H C, et al. Aberration fields of pupil-offset off-axis two-mirror astronomical telescopes induced by ROC error[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(21): 30447-30465. doi: 10.1364/OE.403470 [9] BAI X Q, XU B Q, JU G H, et al. Aberration compensation strategy for the radius of curvature error of the primary mirror in off-axis three-mirror anastigmatic telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(21): 6199-6212. doi: 10.1364/AO.431908 [10] JU G H, YAN CH X, GU ZH Y, et al. Aberration fields of off-axis two-mirror astronomical telescopes induced by lateral misalignments[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(21): 24665-24703. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.024665 [11] JU G H, YAN CH X, GU ZH Y, et al. Nonrotationally symmetric aberrations of off-axis two-mirror astronomical telescopes induced by axial misalignments[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(6): 1399-1409. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.001399 [12] JU G H, MA H C, YAN CH X. Aberration fields of off-axis astronomical telescopes induced by rotational misalignments[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(19): 24816-24834. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.024816 [13] 顾志远, 颜昌翔, 李晓冰, 等. 改进的灵敏度矩阵法在离轴望远镜装调中的应用[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(9):2595-2604. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152309.2595GU ZH Y, YANG CH X, LI X B, et al. Application of modified sensitivity matrix method in alignment of off-axis telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(9): 2595-2604. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152309.2595 [14] HUANG Y F, LI L. Novel method of computer-aided alignment for large aperture space systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7655: 76550T. doi: 10.1117/12.867688 [15] SHACK R V, THOMPSON K. Influence of alignment errors of a telescope system on its aberration field[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1980, 251: 146-153. doi: 10.1117/12.959464 [16] THOMPSON K P. Aberration fields in tilted and decentered optical systems[D]. Tucson, Arizona: The University of Arizona, 1980. [17] BAI X Q, JU G H, MA H C, et al. Aberrational interactions between axial and lateral misalignments in pupil-offset off-axis two-mirror astronomical telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(28): 7693-7707. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.007693 [18] 潘君骅. 光学非球面的设计、加工与检验[M]. 苏州: 苏州大学出版社, 2004.PAN J H. The Design, Manufacture and Test of the Aspherical Optical Surfaces[M]. Suzhou: Suzhou University Press, 2004. (in Chinese) [19] WILSON R N. Reflecting Telescope Optics[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2004. [20] BAI X Q, JU G H, XU B Q, et al. Active alignment of space astronomical telescopes by matching arbitrary multi-field stellar image features[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(15): 24446-24465. doi: 10.1364/OE.432412 [21] SCHMID T, THOMPSON K P, ROLLAND J P. Misalignment-induced nodal aberration fields in two-mirror astronomical telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(16): D131-D144. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.00D131 -





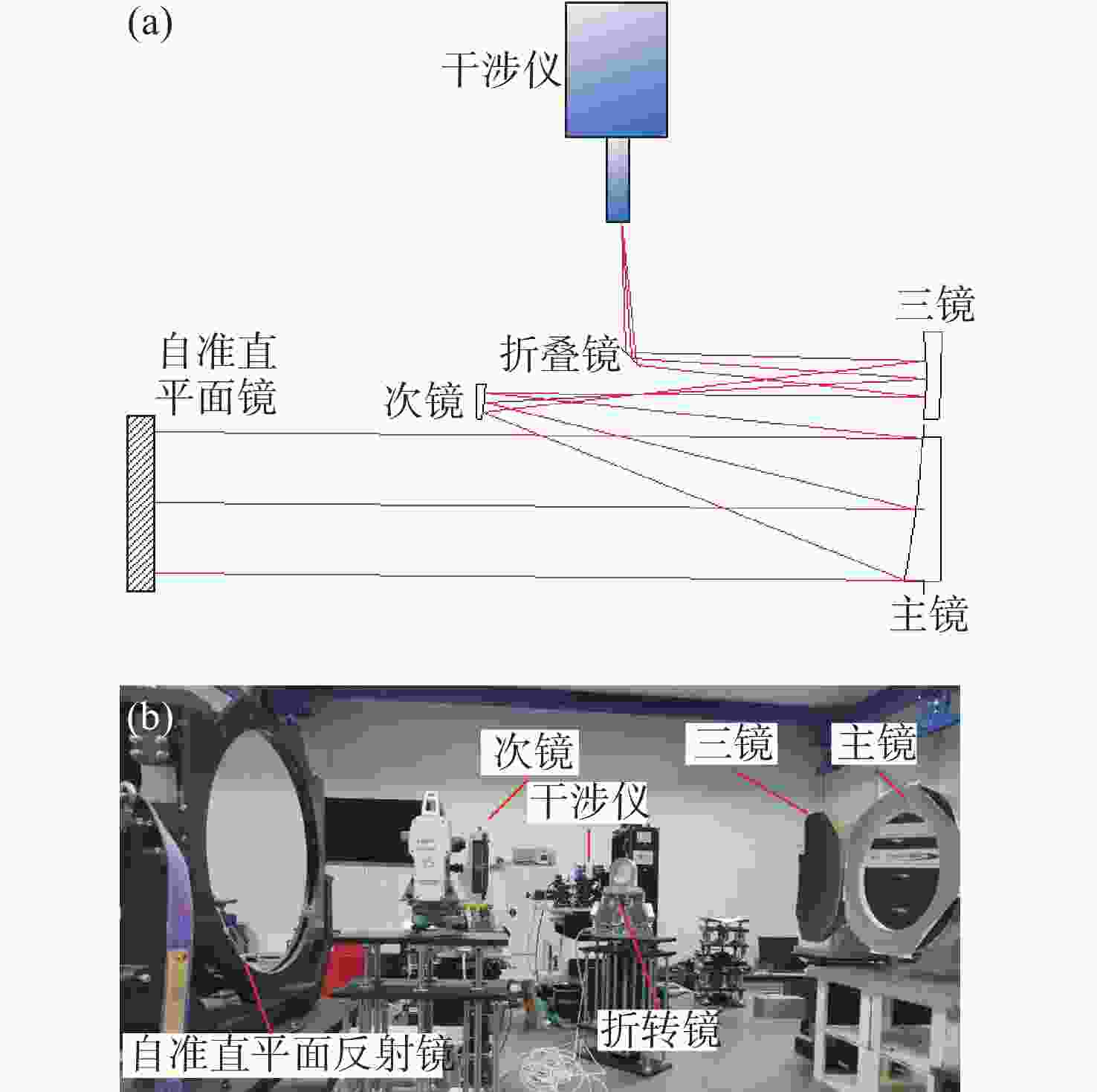
 下载:
下载: