Lunar long-wave infrared radiation characteristics based on space-based quantitative measured data
-
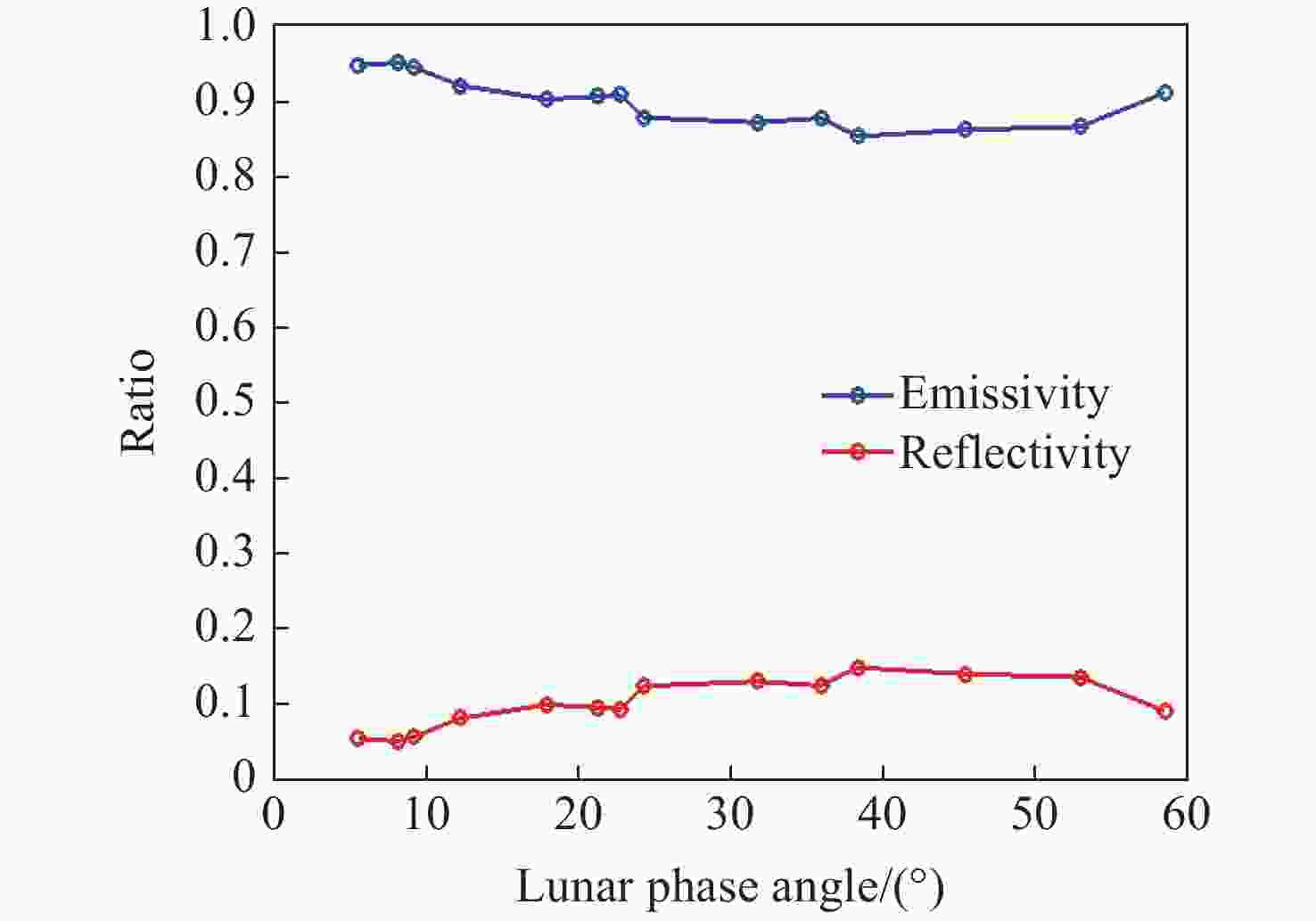
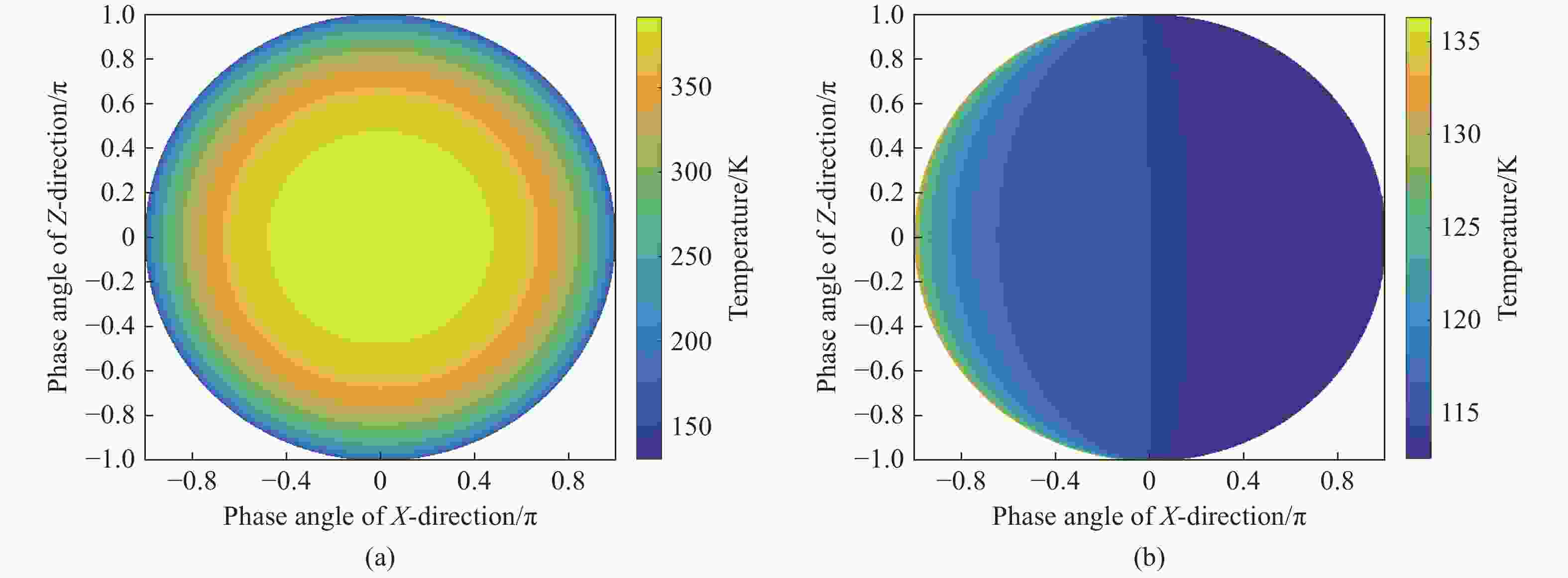
摘要: 月球是理想的在轨辐射定标源,为提高卫星等在轨航空器的长波红外辐射测量精度,本文开展了月球长波红外辐射特性研究。通过分析月球辐射来源类型、辐射探测机理和建立辐射探测模型,探寻点目标/圆盘目标模式下月球的长波红外辐射规律,并依据天基实测数据计算其定标应用精度。首先,从月球自身辐射和反射太阳辐射两方面研究月球辐射,精确拟合月表温度,建立月球红外辐射模型,仿真两部分天基卫星辐射探测结果与月相角的数学关系;其次,对卫星红外载荷进行地面辐射定标,获得图像灰度-辐照度之间转换的关键参数,进而建立了月球长波红外辐射探测模型;最后,通过“吉林一号”对月拍摄实测数据,反演计算了探测模型中月表的反射率和发射率。实验结果表明:本文所得的月表长波红外辐射特性结果准确、鲁棒性高,与Apollo 12070实验室测量结果、Diviner实测数据拟合结果相比,月球发射率和反射率的误差分别约为7.18%和5.71%。Abstract: The moon is an ideal on-orbit radiation calibration source. In order to improve the measurement accuracy of long-wave infrared radiation for satellites and other on-orbit aircrafts, the characteristics of lunar long-wave infrared radiation are studied in this paper. The law of lunar long-wave infrared radiation is explored taking the moon as a point target or disk target, and the calibration accuracy is calculated based on the measured space-based data by analyzing the types of lunar radiation sources and radiation detection mechanism, and by establishing a radiation detection model. First, the lunar radiation is studied from two aspects of lunar self radiation and reflected solar radiation. The lunar surface temperature is fitted accurately, the lunar infrared radiation model is established, and the mathematical relationship is simulated between the radiation measurement results of space-based satellites and the lunar phase angles. Second, the key parameters of conversion between gray-scale and irradiation images are obtained through calibrating the radiation of satellite infrared loads in the ground. The lunar long-wave infrared radiation measurement model is then established. Finally, the reflectance and emissivity of the lunar surface are calculated based on the measured data taken by the “Jilin-1” satellite on the moon. The experimental results show that the long-wave infrared radiation characteristics of the lunar surface obtained by the proposed menthod are accurate and robust. Moreover, there are nearly 7.18% and 5.71% of the fitting errors in the obtained data compared with Apollo 12070 laboratory measurement results and diviner measured data, respectively.
-
表 1 “吉林一号”长波红外相机的主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the long-wave infrared camera of “Jilin-1” satellite
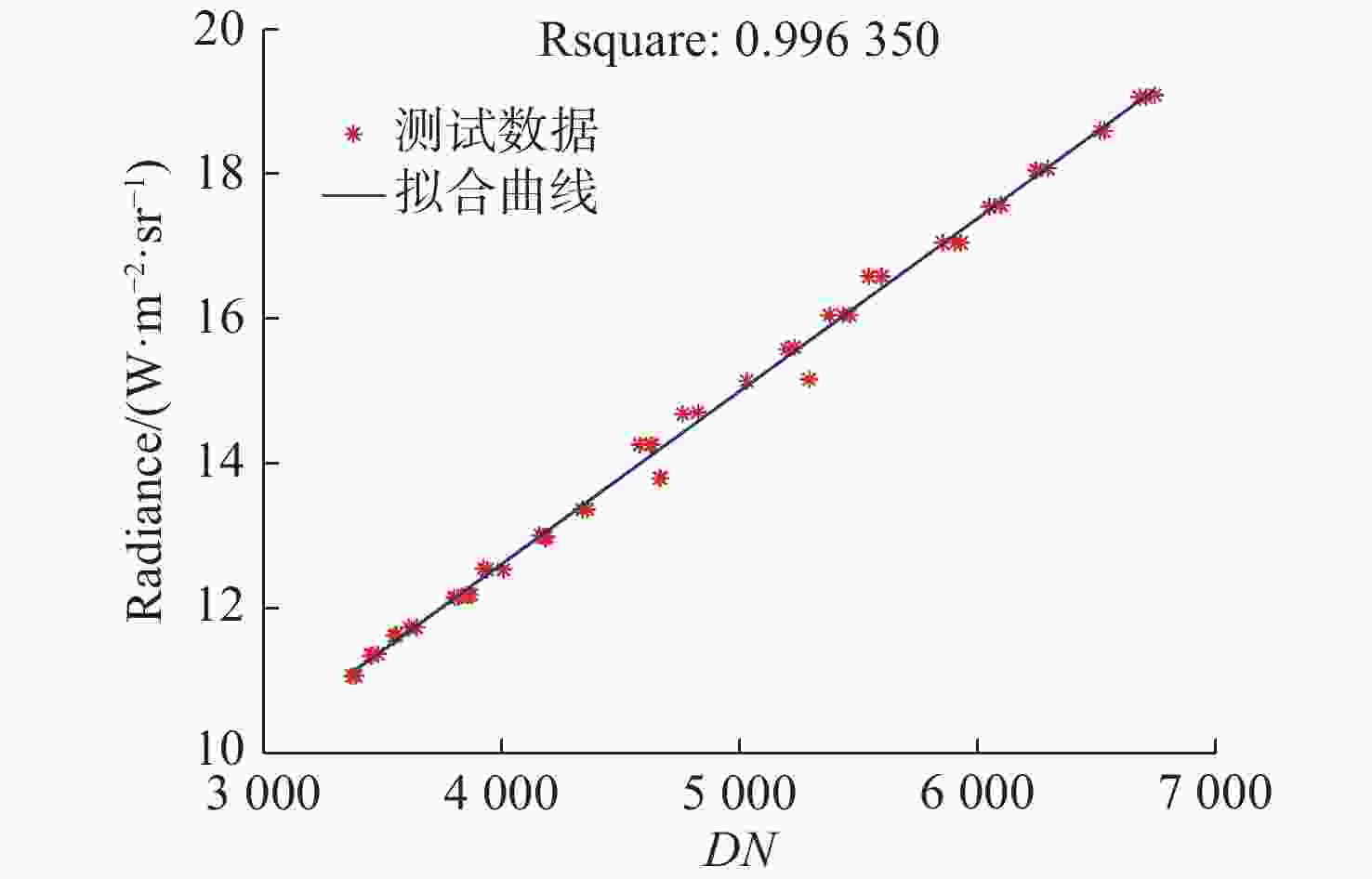
波段/μm 焦距/mm 相对孔径 分辨率 视场角/(°) 帧频/(frame·s−1) 像元尺寸/μm NETD/mK 8-12.5 60 1.17 640×512 13.3 7.49 17 ≤50 表 2 “吉林一号”对月拍摄信息参数
Table 2. Information parameters of Moon captured by the “Jilin-1” satellite
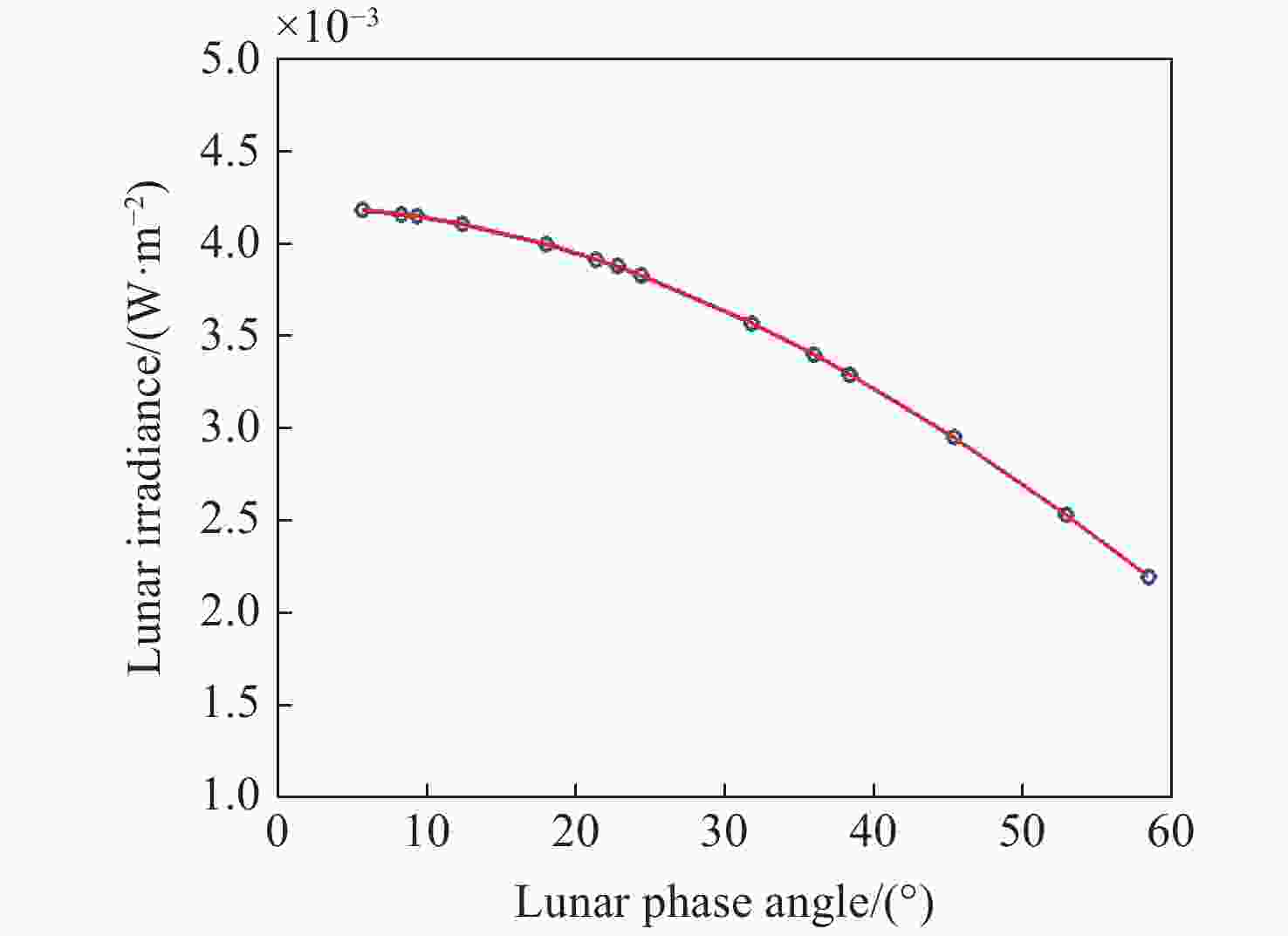
次序 观测相位角(°) 拍摄时间(北京时间) 日-月距离(km) 卫星-月距离(km) 1 5.72 2020年4月8日7:43:23 150155484.4 350339.7 2 8.27 2020年3月9日6:39:14 148890326.3 351319.3 3 9.31 2020年3月10日14:28:26 148927699.1 350427.7 4 12.38 2020年4月7日7:54:26 150106457.9 350231.5 5 18.04 2020年4月9日7:32:23 150185032.4 352748.4 6 21.36 2020年3月8日6:50:16 148834109.5 354435.4 7 22.75 2020年3月11日6:17:15 148946142.6 351837.0 8 24.35 2020年4月6日11:15:29 150048417.8 352037.6 9 31.79 2020年4月10日7:21:23 150196149.6 357210.6 10 35.91 2020年3月7日5:25:19 148754960.4 359974.6 11 38.34 2020年4月5日11:25:29 149964953.0 356162.6 12 45.33 2020年4月11日7:11:23 150191076.5 363431.2 13 52.86 2020年4月4日10:01:29 149859532.7 362171.6 14 58.38 2020年4月12日7:00:23 150172914.8 370550.0 表 3 “吉林一号”长波辐射实测反演结果
Table 3. Measured inversion results of the long-wave radiance from the “Jilin-1” satellite
次序 观测相位角/(°) 长波红外辐射照度实测反演结果/(W·s−2) 1 5.72 0.00493332 2 8.27 0.00492300 3 9.31 0.00487956 4 12.38 0.00470402 5 18.04 0.00449120 6 21.36 0.00441650 7 22.75 0.00438659 8 24.35 0.00418648 9 31.79 0.00387823 10 35.91 0.00371954 11 38.34 0.00350546 12 45.33 0.00317342 13 52.86 0.00273809 14 58.38 0.00493332 -
[1] 朱军, 李永昌, 白照广, 等. 低轨高分辨率遥感卫星姿态机动对月定标方法[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(9):1913-1923. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202809.1913ZHU J, LI Y CH, BAI ZH G, et al. Lunar calibration method through attitude maneuver of low-earth-orbit and high-resolution remote sensing satellites[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(9): 1913-1923. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202809.1913 [2] NODA H, ARAKI H, GOOSSENS S, et al. Illumination conditions at the lunar polar regions by KAGUYA(SELENE) laser altimeter[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(24): L24203. doi: 10.1029/2008GL035692 [3] BUSSEY D B J, MCGOVERN J A, SPUDIS P D, et al. Illumination conditions of the south pole of the Moon derived using Kaguya topography[J]. Icarus, 2010, 208(2): 558-564. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2010.03.028 [4] KIEFFER H H. Photometric stability of the lunar surface[J]. Icarus, 1997, 130(2): 323-327. doi: 10.1006/icar.1997.5822 [5] EPLEE R E JR, SUN J Q, MEISTER G, et al. Cross calibration of SeaWiFS and MODIS using on-orbit observations of the Moon[J]. Applied Optics, 2011, 50(2): 120-133. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.000120 [6] EPLEE R E JR, BARNES R A, PATT F S, et al. SeaWiFS lunar calibration methodology after six years on orbit[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5542: 1-13. doi: 10.1117/12.556408 [7] 吴荣华, 张鹏, 杨忠东, 等. 基于月球反射的遥感器定标跟踪监测[J]. 遥感学报,2016,20(2):278-289.WU R H, ZHANG P, YANG ZH D, et al. Monitor radiance calibration of the remote sensing instrument with reflected lunar irradiance[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(2): 278-289. (in Chinese) [8] 张璐, 张鹏, 胡秀清, 等. 月球辐射照度模型比对及地基对月观测验证[J]. 遥感学报,2017,21(6):864-870.ZHANG L, ZHANG P, HU X Q, et al. Comparison of lunar irradiance models and validation of lunar observation on Earth[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(6): 864-870. (in Chinese) [9] LEBLANC F, CHAUFRAY J Y. Mercury and moon he exospheres: analysis and modeling[J]. Icarus, 2011, 216(2): 551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2011.09.028 [10] HURLEY D M, SARANTOS M, GRAVA C, et al. An analytic function of lunar surface temperature for exospheric modeling[J]. Icarus, 2015, 255: 159-163. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2014.08.043 [11] MEEUS J. Astronomical Algorithms[M]. Richmond: Willmann-Bell, 2005. [12] 路鹏, 陈圣波, 崔腾飞, 等. 月球表面矿物二向性反射特性实验研究[J]. 岩石学报,2016,32(1):107-112.LU P, CHEN SH B, CUI T F, et al. Experimental study on bidirectional reflectance characteristics of minerals on lunar surface[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(1): 107-112. (in Chinese) [13] 高帅, 李元, 白廷柱, 等. 交叉定标中的不确定度分析及定标系数计算改进[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(3):568-576.GAO SH, LI Y, BAI T ZH, et al. Uncertainty analysis in cross-calibration and optimization calculation of calibration coefficients[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(3): 568-576. (in Chinese) [14] 李元, 张勇, 胡丽琴, 等. 中国遥感卫星辐射校正场敦煌戈壁场区光环境变化研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(5):1231-1242. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0129LI Y, ZHANG Y, HU L Q, et al. Investigation of optical environment changes in the Dunhuang Gobi site of the Chinese radiometric calibration sites[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(5): 1231-1242. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0129 [15] 刘群, 刘崇, 朱小磊, 等. 星载海洋激光雷达最佳工作波长分析[J]. 中国光学,2021,13(1):148-155.LIU Q, LIU CH, ZHU X L, et al. Analysis of the optimal operating wavelength of spaceborne oceanic lidar[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 13(1): 148-155. (in Chinese) [16] 牛明慧. 光学遥感仪器月球定标技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海技术物理研究所), 2018: 54-58.NIU M H. Research on the lunar calibration technologies of optical remote sensing radiometers[D]. Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018: 54-58. (in Chinese) [17] REN H ZH, NIE J, DONG J J, et al. Lunar surface temperature and emissivity retrieval from diviner lunar radiometer experiment sensor[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2021, 8(1): e2020EA001436. -





 下载:
下载: