Brightness correction and color restoration of seabed image obtained by active optical detection
-
摘要:
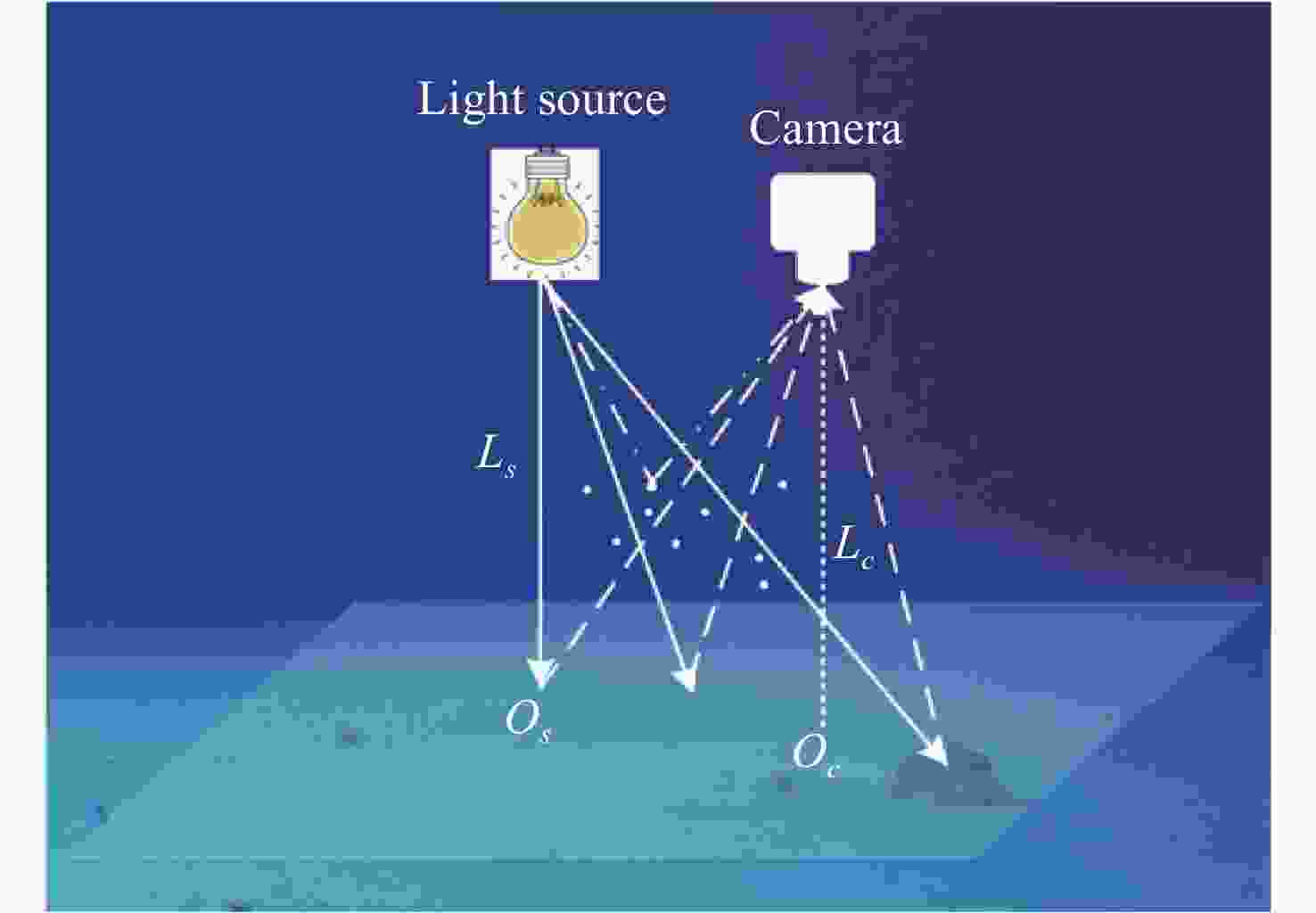
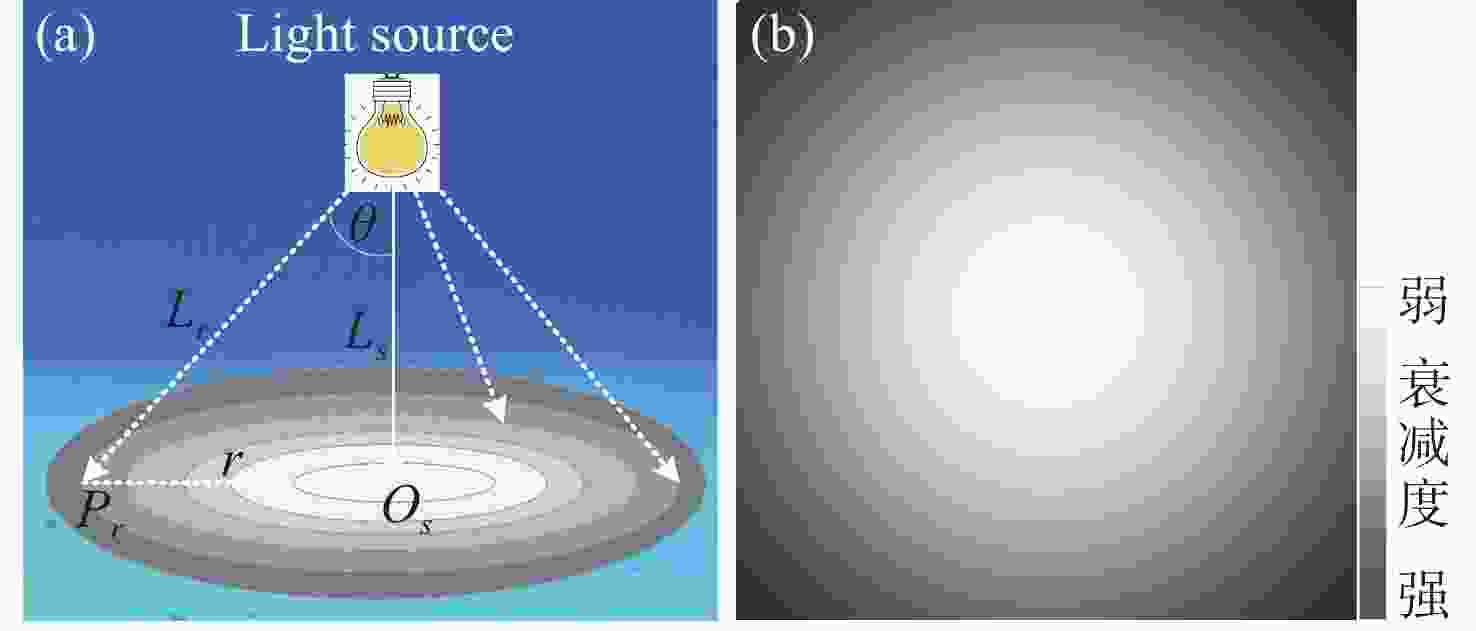
主动光学成像探测是海底形貌与环境探测的重要方式,广泛应用于大洋勘探、海底探测等领域。然而,由于海水对光的衰减作用,造成光学影像照度不均、颜色失真、对比度低等质量退化问题。本文依据水下主动光学成像探测的特点,提出了一种基于相对辐射校正原理的水下图像增强方法。该方法将增强过程分为亮度补偿和色彩恢复两个阶段。在亮度补偿阶段,依据水下点光源的成像特点和辐射衰减机制,采用相对辐射校正原理对水下图像分通道进行补偿,消除因光源不均、光程不同等因素造成的亮度畸变。在色彩恢复阶段,首先对红通道图像进行自适应补偿和色彩粗平衡,在此基础上进一步利用Retinex模型对图像进行色彩恢复。利用实际的海底勘探图像进行实验验证,结果表明本文方法的增强结果亮度均匀、色彩自然,有效提升了图像质量。相较现有方法,本文方法的结果无论主观感受还是客观评价整体更优。同时,由于本文方法不需要光源、相机等特性参数,仅利用实际观测图像本身进行校正,因而具有更好的适应性。
Abstract:Active optical imaging detection is an important method for seabed topography and environment detection, which is widely used in ocean exploration. However, due to the attenuation effect of light in seawater, the optical images often suffer uneven illumination, color distortion and low contrast. According to the property of underwater active optical imaging, an underwater image enhancement method based on relative radiometric correction is proposed in this paper. The procedure is divided into brightness compensation and color restoration. In brightness compensation, according to the imaging characteristics and radiation attenuation mechanism of a point light source, the relative radiation correction is used to compensate for the channels of underwater images. This stage eliminates the brightness distortion caused by an uneven light source, varying optical paths and so on. In the color restoration, adaptive compensation and rough color balance are performed first on the red channel. Then, the Retinex model is used to restore colors. The real seabed images are used for experiments. The results show that the enhanced images by the proposed method have uniform brightness and natural look. Compared with the other methods, the results of the proposed method are better overall both subjectively and objectively. At the same time, the method proposed in this paper does not need the properties of light source, camera and others. Only the real detection images themselves are used for correction, and achieve better adaptability.
-
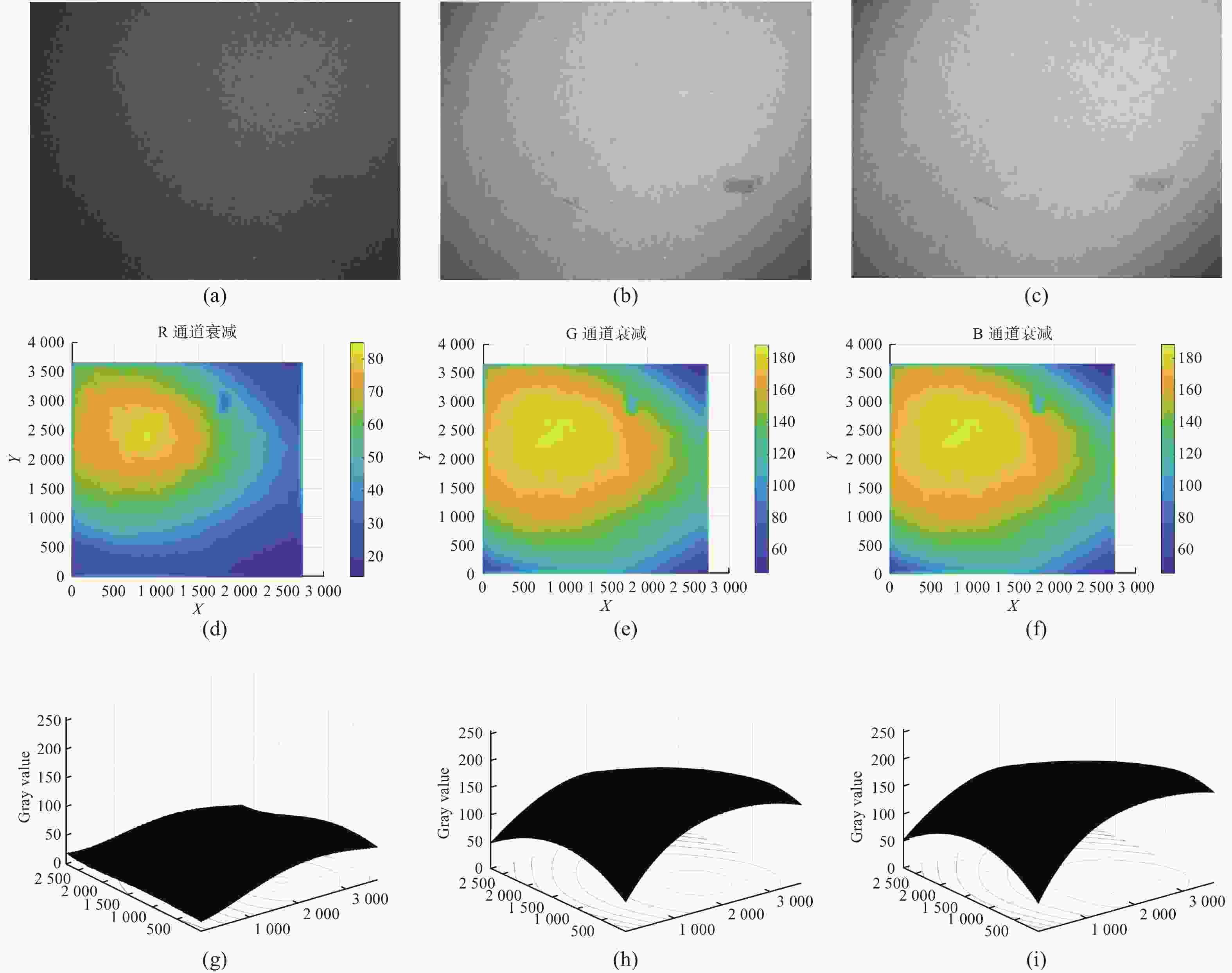
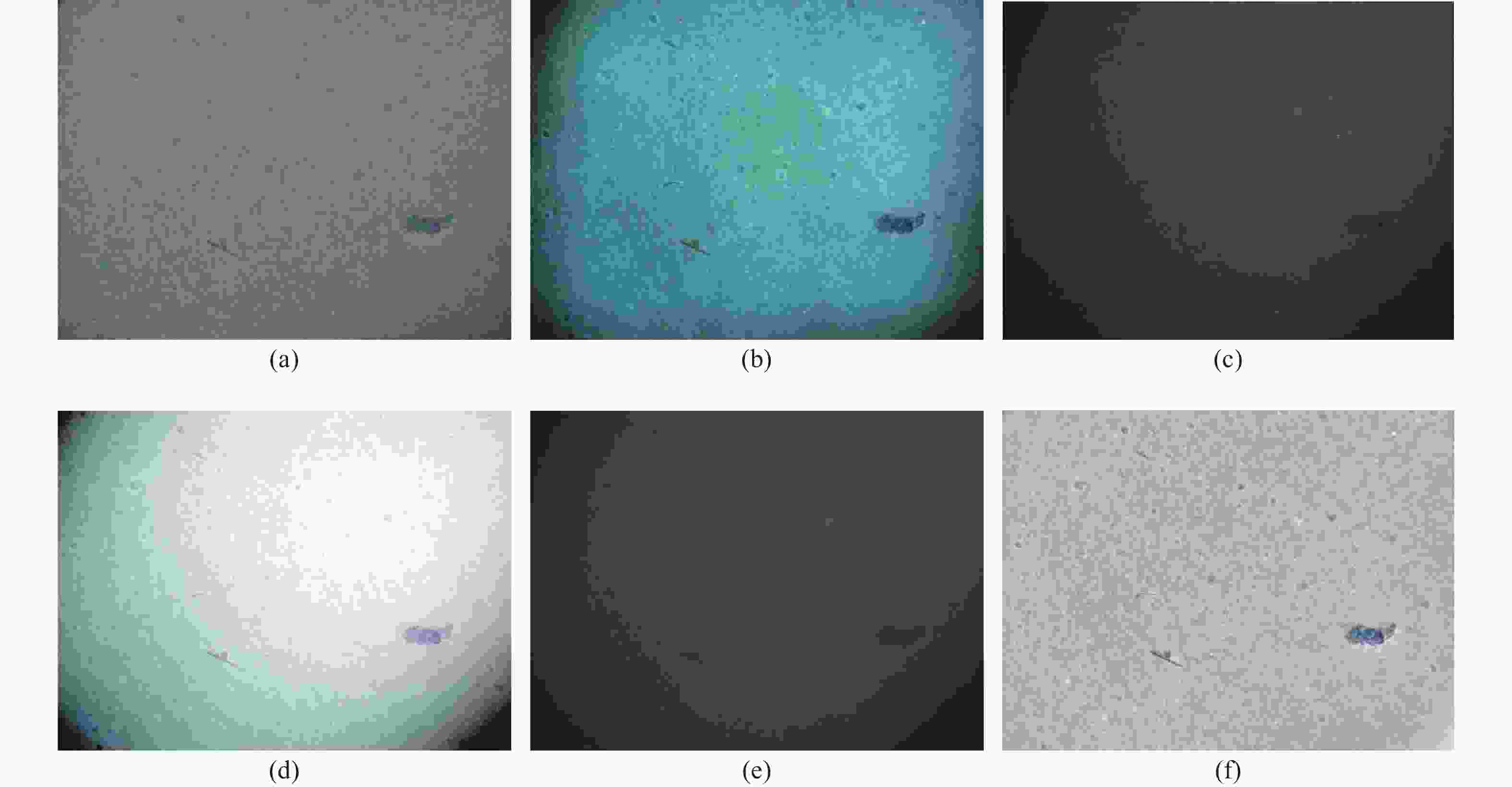
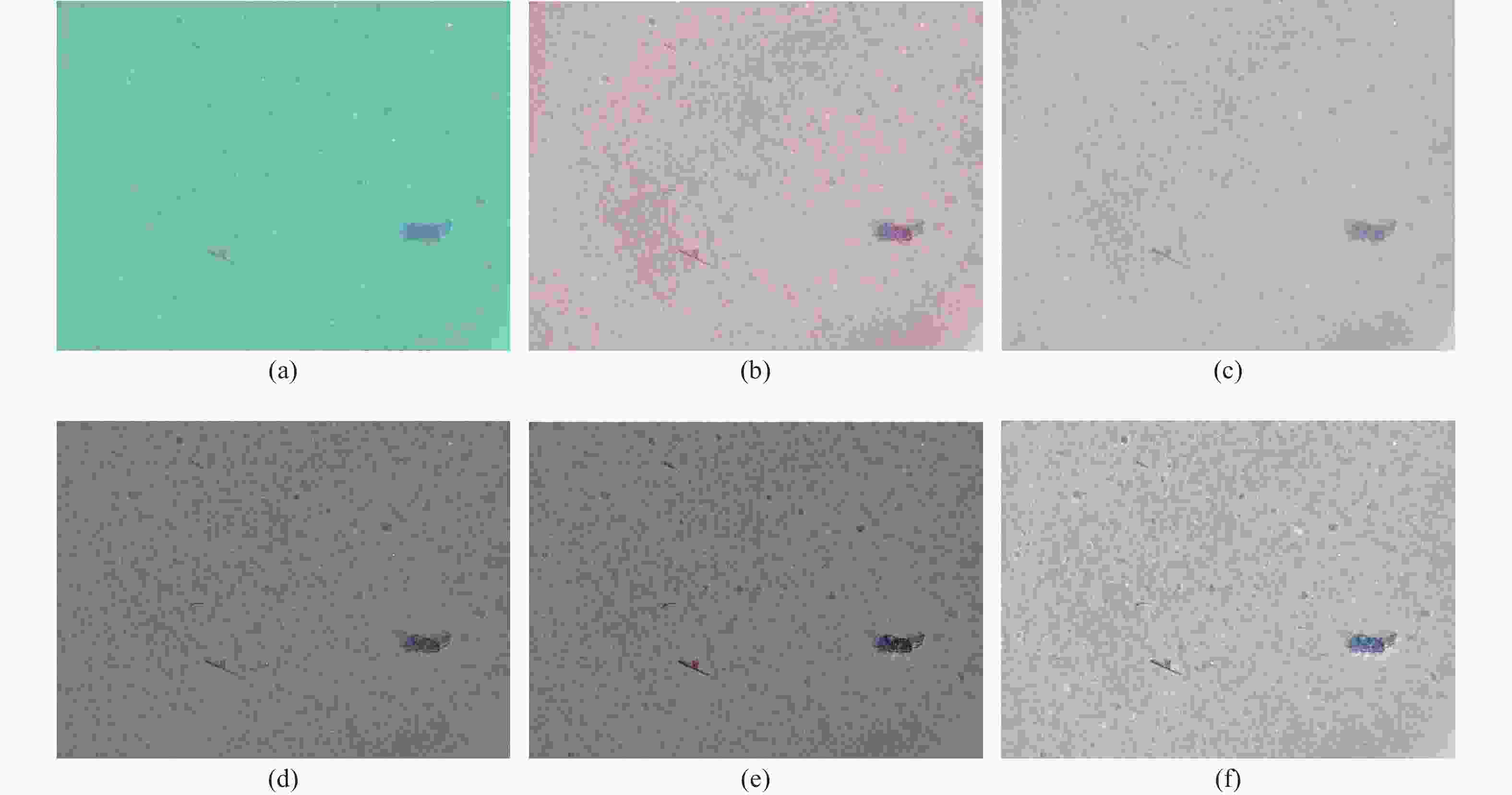
图 4 参考图像的各通道图像及其亮度拟合曲面。(a)~(c)参考图像的红、绿、蓝通道;(d)~(f)红、绿、蓝通道的三维俯视图;(g)~(i)红、绿、蓝通道的拟合曲面
Figure 4. Each channel of the reference image and their brightness fitting surface (a)−(c) red, green, blue channels of the reference image; (d)−(f) 3D top view of the red, green and blue channels; (g)−(i) fitting surface of the red, green, blue channels
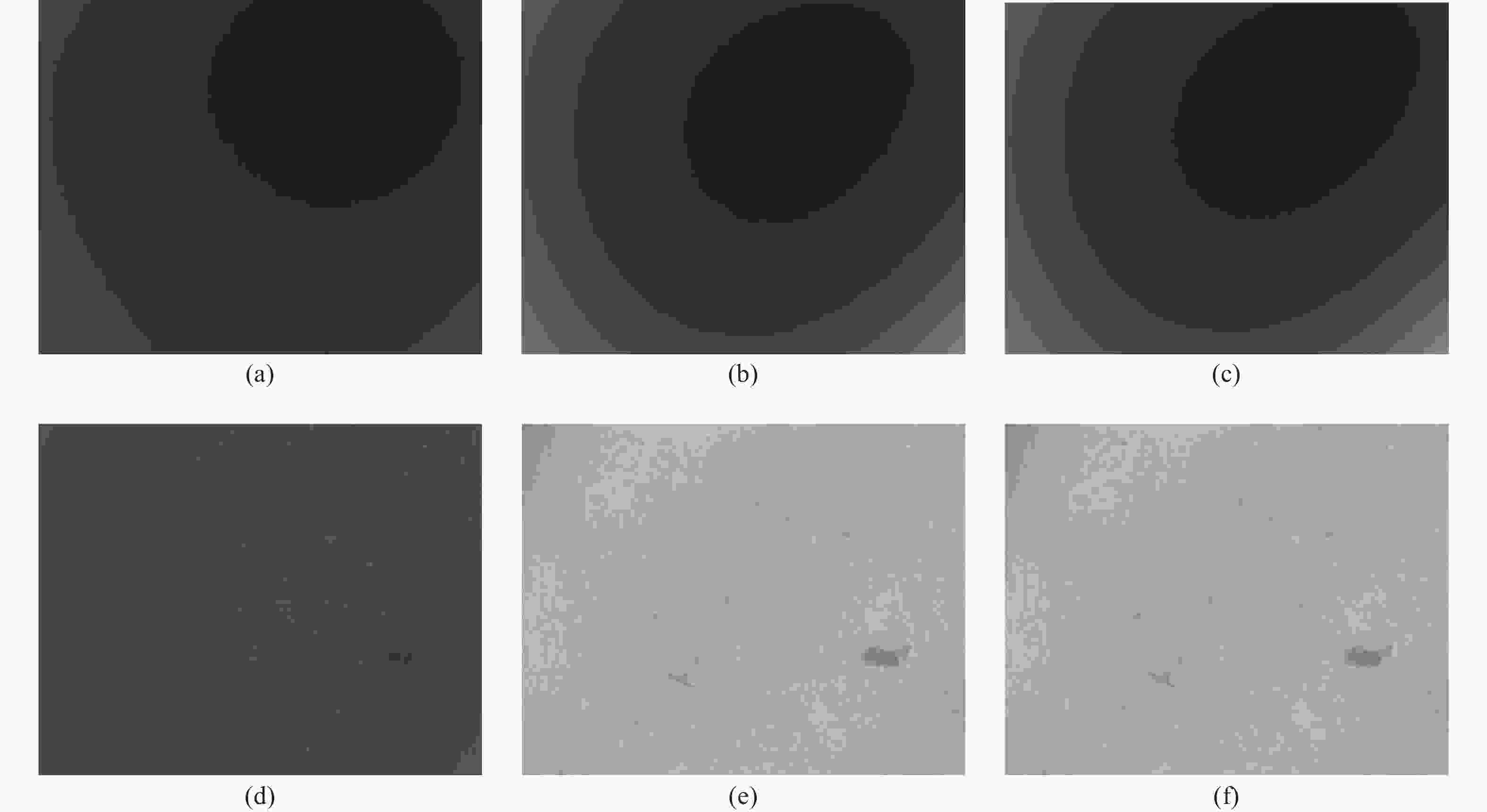
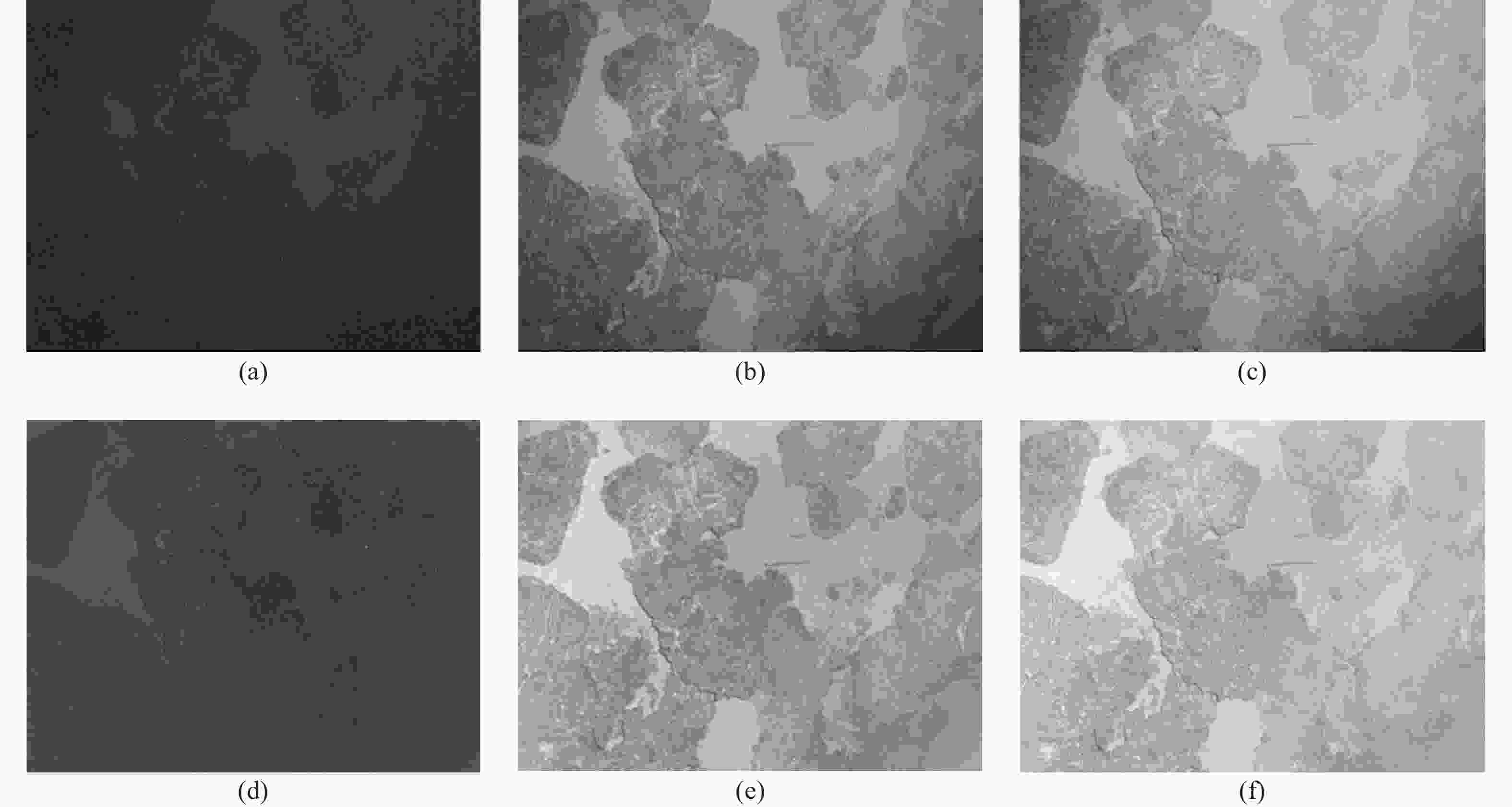
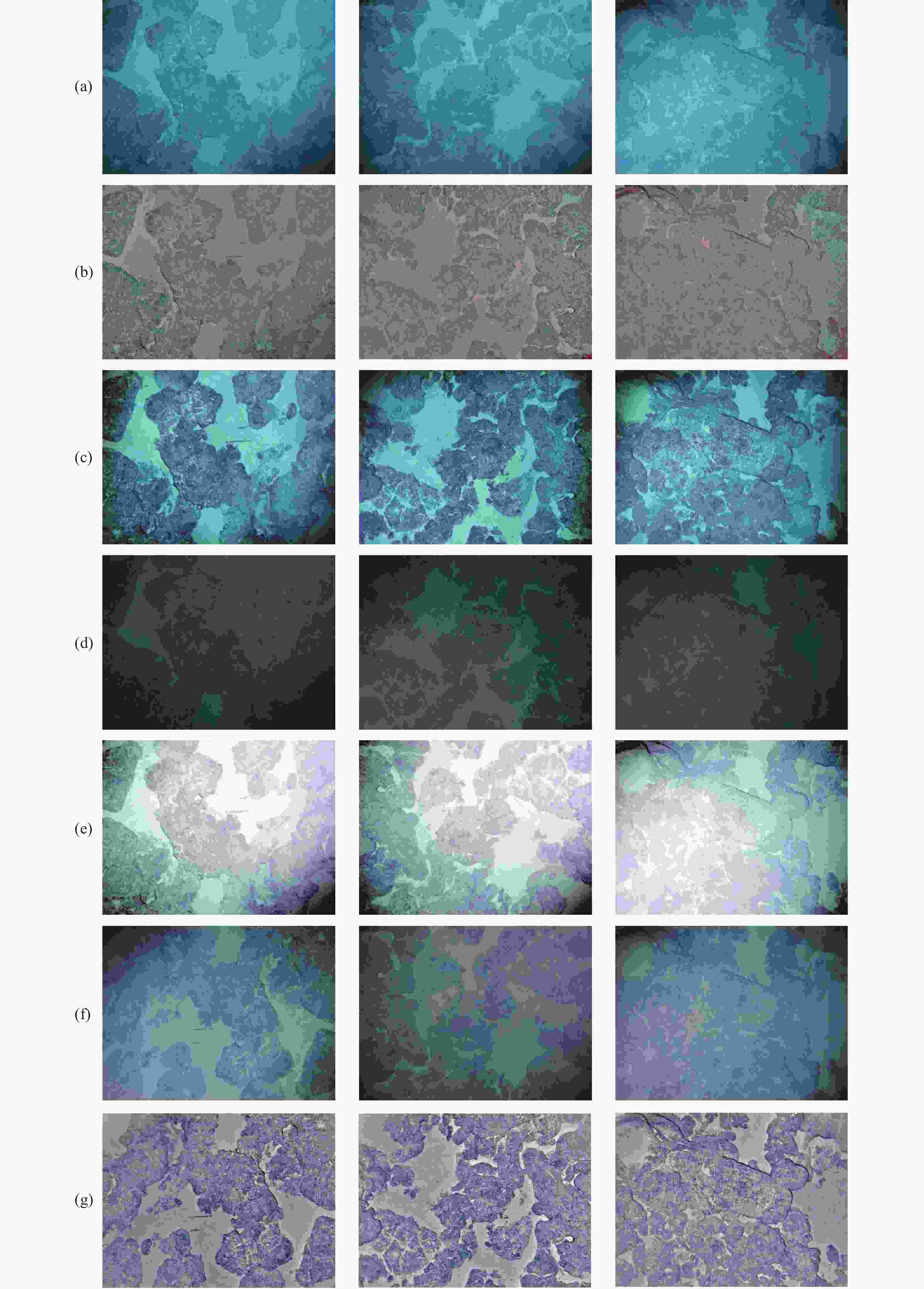
图 7 不同图像增强方法效果对比。(a)预补偿输入图像;(b)~(f)分别是灰色世界、本文预处理方法、MSR、灰色世界算法+MSR、本文预处理方法+MSR方法结果
Figure 7. Comparison of image enhancement with different pre-processing methods. (a) Pre-compensation image; (b)−(f) compensated results with Gray world, the proposed pre-processing method, MSR, Gray world + MSR, and the proposed pre-processing method + MSR methods
表 1 参考图像各通道灰度曲面四次多项式拟合参数
Table 1. Quartic polynomial fitting parameters of the gray surface of each channel of the reference image
参数 R通道 G通道 B通道 a00 19.25 46.32 50.18 a10 −0.1006 0.4208 0.4696 a01 −0.1152 0.3904 0.4299 a20 1.005×10−3 −4.915×10−4 −7.192×10−4 a11 1.038×10−3 −6.395×10−4 −8.548×10−4 a02 1.002×10−3 −4.785×10−4 −6.328×10−4 a30 −2.241×10−6 1.353×10−7 6.774×10−7 a21 −1.584×10−6 −2.121×10−7 −1.141×10−7 a12 −7.252×10−7 2.581×10−6 3.145×10−6 a03 −2.75×10−6 −8.219×10−7 −5.752×10−7 a40 1.391×10−9 −8.548×10−10 −1.382×10−9 a31 3.485×10−10 3.321×10−9 4.136×10−9 a22 2.072×10−9 −4.899×10−9 −6.476×10−9 a13 −1.332×10−9 4.571×10−10 1.053×10−9 a04 2.382×10−9 3.993×10−10 7.139×10−11 表 2 参考图像及其在不同算法处理后的客观评价结果
Table 2. Objective image quality evaluation results of the reference image and images processed by different algorithms
指标 参考图像 MSR CLAHE RCP RWCGC UWCNN Ours UIQM 0.9322 3.809 2.3193 3.3535 3.1508 1.4238 4.0546 UCIQE 20.3988 24.9813 25.6173 24.0433 28.7847 21.4546 28.2705 注:加粗字体为每行最优值。 表 3 对于图9第一列影像不同算法的客观评价结果
Table 3. Objective image quality evaluation results of the first column of Fig. 9 processed by different algorithms
指标 图9第一列原图 MSR CLAHE RCP RWCGC UWCNN Ours UIQM 1.0147 3.8557 2.9908 2.6969 3.6444 3.0211 4.5062 UCIQE 18.2575 28.0713 24.3802 22.4397 29.3778 21.9017 29.8468 注:加粗字体为每行最优值。 表 4 对于图9第二列影像不同算法的客观质量评价指标
Table 4. Objective image quality evaluation indexes of the second column of Fig. 9 processed by different algorithms
指标 图9第二列原图 MSR CLAHE RCP RWCGC UWCNN Ours UIQM 1.0147 3.8557 2.9908 2.6969 3.6444 3.0211 4.5583 UCIQE 20.5561 27.6709 27.5439 24.2877 29.0778 20.9523 29.5887 注:加粗字体为每行最优值 表 5 对于图9第三列影像不同算法的客观质量评价指标
Table 5. Objective image quality evaluation indexes of the third column of Fig. 9 processed by different algorithms
图9第三列原图 MSR CLAHE RCP RWCGC UWCNN Ours UIQM 0.6739 3.7142 2.8359 2.4611 3.12146 2.6183 4.3095 UCIQE 20.0312 28.1392 25.5831 23.8943 29.0996 22.8868 29.1635 注:加粗字体为每行最优值 -
[1] 邓翔宇, 王惠刚, 张永庆. 基于主动光照的深海图像增强算法[J]. 光子学报,2020,49(3):0310001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204903.0310001DENG X Y, WANG H G, ZHANG Y Q. Deep sea image enhancement method based on the active illumination[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(3): 0310001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204903.0310001 [2] 郭继昌, 李重仪, 郭春乐, 等. 水下图像增强和复原方法研究进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报,2017,22(3):273-287.GUO J CH, LI CH Y, GUO CH L, et al. Research progress of underwater image enhancement and restoration methods[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2017, 22(3): 273-287. (in Chinese) [3] HENKE B, VAHL M, ZHOU ZH L. Removing color cast of underwater images through non-constant color constancy hypothesis[C]. 2013 8th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis (ISPA), IEEE, 2013. [4] FU X Y, ZHUANG P X, HUANG Y, et al.. A retinex-based enhancing approach for single underwater image[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), IEEE, 2014. [5] 杨卫中, 徐银丽, 乔曦, 等. 基于对比度受限直方图均衡化的水下海参图像增强方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6):197-203. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.027YANG W ZH, XU Y L, QIAO X, et al. Method for image intensification of underwater sea cucumber based on contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(6): 197-203. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.027 [6] XIANG W D, YANG P, WANG SH, et al. Underwater image enhancement based on red channel weighted compensation and gamma correction model[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2018, 1(10): 180024. [7] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [8] CHIANG J Y, CHEN Y C. Underwater image enhancement by wavelength compensation and dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1756-1769. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2179666 [9] GALDRAN A, PARDO D, PICÓN A, et al. Automatic red-channel underwater image restoration[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 26: 132-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.11.006 [10] 谢昊伶, 彭国华, 王凡, 等. 基于背景光估计与暗通道先验的水下图像复原[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(1):0101002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0101002XIE H L, PENG G H, WANG F, et al. Underwater image restoration based on background light estimation and dark channel prior[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 0101002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0101002 [11] 王一斌, 尹诗白, 吕卓纹. 自适应背景光估计与非局部先验的水下图像复原[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(2):499-510. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192702.0499WANG Y B, YIN SH B, LÜ ZH W. Underwater image restoration with adaptive background light estimation and non-local prior[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(2): 499-510. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192702.0499 [12] 林森, 刘世本, 唐延东. 多输入融合对抗网络的水下图像增强[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(5):20200015. doi: 10.3788/irla.28_2020-0015LIN S, LIU SH B, TANG Y D. Multi-input fusion adversarial network for underwater image enhancement[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(5): 20200015. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/irla.28_2020-0015 [13] LI CH Y, ANWAR S, PORIKLI F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107038 [14] 刘群, 刘崇, 朱小磊, 等. 星载海洋激光雷达最佳工作波长分析[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(1):148-155. doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0148LIU Q, LIU CH, ZHU X L, et al. Analysis of the optimal operating wavelength of spaceborne oceanic lidar[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(1): 148-155. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0148 [15] 全向前, 陈祥子, 全永前, 等. 深海光学照明与成像系统分析及进展[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):153-165. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0153QUAN X Q, CHEN X Z, QUAN Y Q, et al. Analysis and research progress of deep-sea optical illumination and imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 153-165. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0153 [16] 吕宝林, 佟首峰, 徐伟, 等. 基于配准的机载红外非均匀性校正技术应用[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):1124-1137. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0109LV B L, TONG SH F, XU W, et al. Non-uniformity correction of airborne infrared detection system based on inter-frame registration[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 1124-1137. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0109 [17] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, DE VLEESCHOUWER C, et al. Color balance and fusion for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 379-393. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2759252 [18] LAND E H, MCCANN J J. Lightness and retinex theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1971, 61(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.61.000001 [19] RAHMAN Z, JOBSON D J, WOODELL G A. Multi-scale retinex for color image enhancement[C]. Proceedings of 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 1996. [20] PANETTA K, GAO CH, AGAIAN S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(3): 541-551. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2015.2469915 [21] YANG M, SOWMYA A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 6062-6071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2491020 -





 下载:
下载: