Electrically controlled polarization rotator based on liquid crystal optical waveguide
-
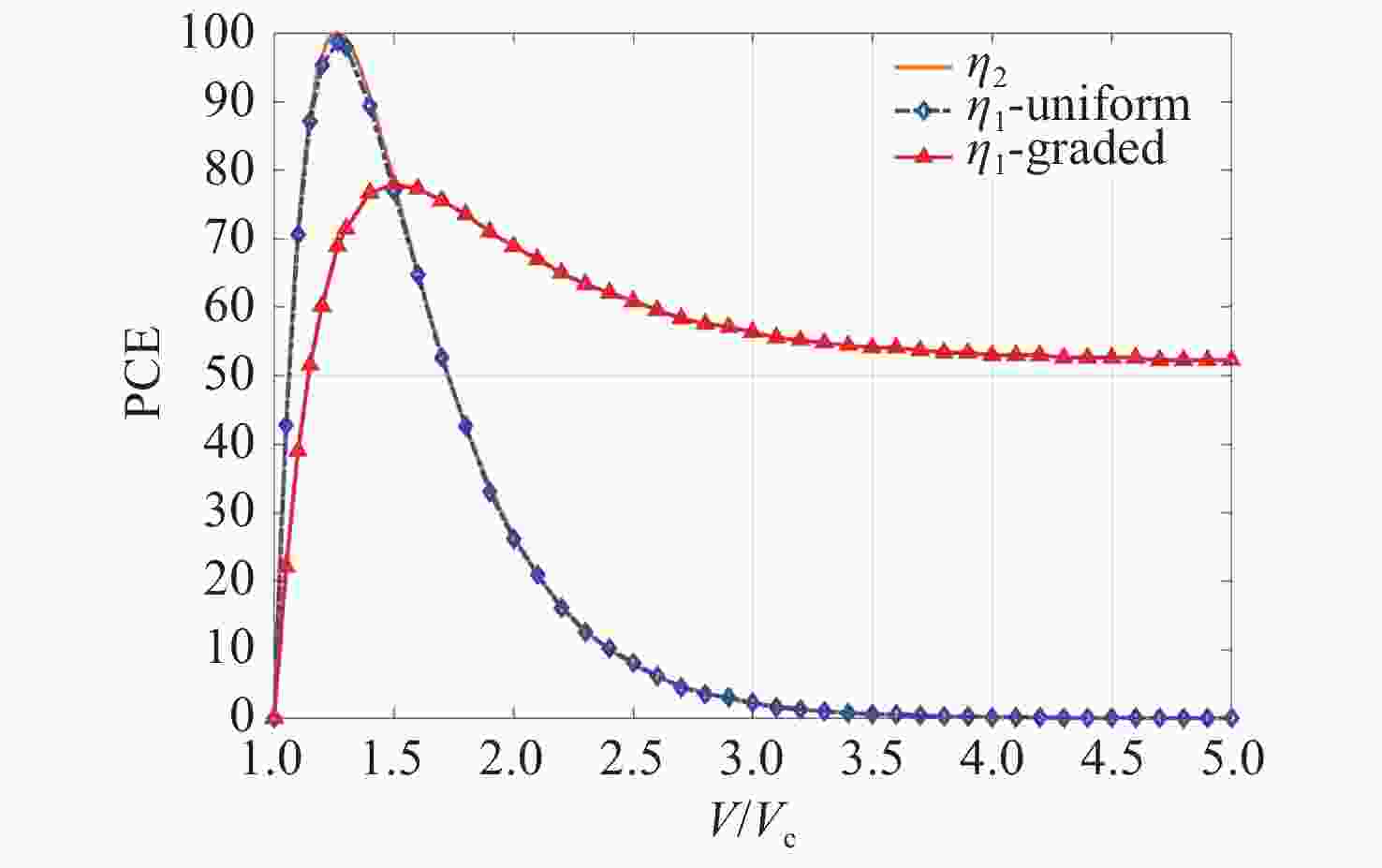
摘要: 为了更准确地分析基于液晶光波导的电控偏振旋转器的偏振转换长度和偏振转换效率,研究了向列相液晶场致重新取向的渐变特性。首先,根据液晶磁场耦合方程组得出的本征值方程构建偏振转换长度与外加电压的对应关系。然后通过对电场传输方程进行横向有限差分离散得到了交替方向隐式束传播法迭代方程组的显式表达,用于求解液晶光波导中的传播场,进而计算偏振转换效率。最后,通过仿真实验求解了本征模式以及传播场,进而分析液晶指向矢的渐变特性对偏振转换长度和偏振转换效率的影响。结果表明,液晶指向矢的渐变对偏振转换长度的影响可以忽略,但其得出的最大偏振转换效率相较于液晶重新取向均匀的求解结果低大约20%。这一结果将为基于液晶光波导的电控偏振旋转器的实际开发提供理论参考。Abstract: In this study, the gradient characteristic of field-induced reorientation of nematic liquid crystal was investigated to accurately analyze the Polarization Conversion Length (PCL) and Polarization Conversion Efficiency (PCE) of an electronically controlled polarization rotator based on a liquid crystal optical waveguide. Firstly, according to the eigenvalue equation obtained from the liquid crystal magnetic field coupling equations, the corresponding relationship between PCL and the applied voltage was constructed. Then, the explicit expression of the iterative equations of the Alternating Direction Implicit Beam Propagation Method (ADI-BPM) was obtained by transverse finite-difference discretization of the electric field transmission equation, which was used to solve the propagation field in the liquid crystal optical waveguide and calculate the PCE. Finally, the eigenmode and propagation field were solved through a simulation experiment, and then the effects of the gradient characteristics of the liquid crystal director on PCL and PCE were analyzed. The results show that the effect of the gradient of the liquid crystal director on the PCL can be ignored, but the maximum PCE is about 20% lower than that of the uniform reorientation of the liquid crystal. This result will provide a certain theoretical reference for the practical development of an electronically controlled polarization rotator based on a liquid crystal optical waveguide.
-
Key words:
- liquid crystal /
- optical waveguide /
- polarization rotator /
- electric tuning
-
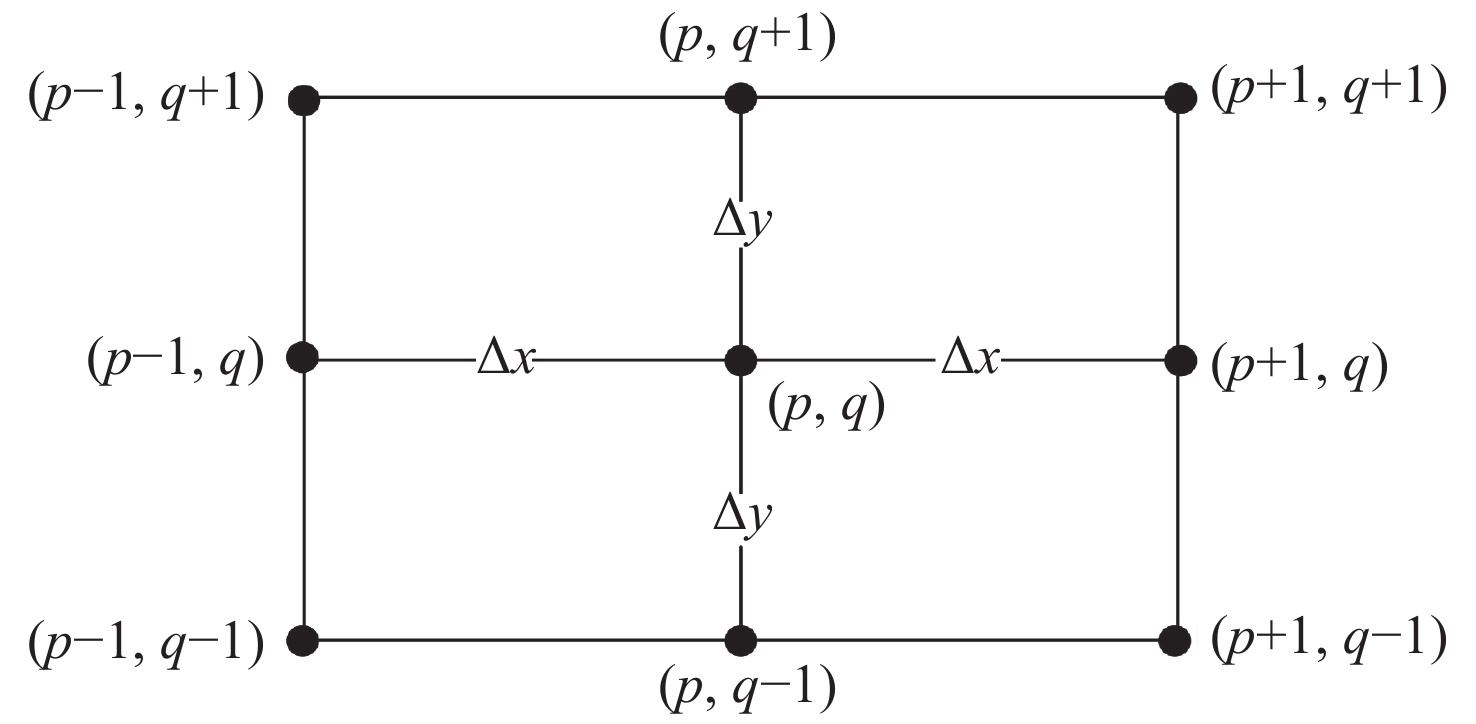
图 2 有限差分法中使用的网格节点示意图。(p, q) 表示中心节点,其余节点为距离其最近的8个节点。
${\Delta }x$ ,${\Delta }y$ 分别表示x和y方向上的网格间距Figure 2. Diagram of mesh nodes used in the finite difference method. (p, q) represent the central node, and the other nodes are the 8 nodes closest to the central node.
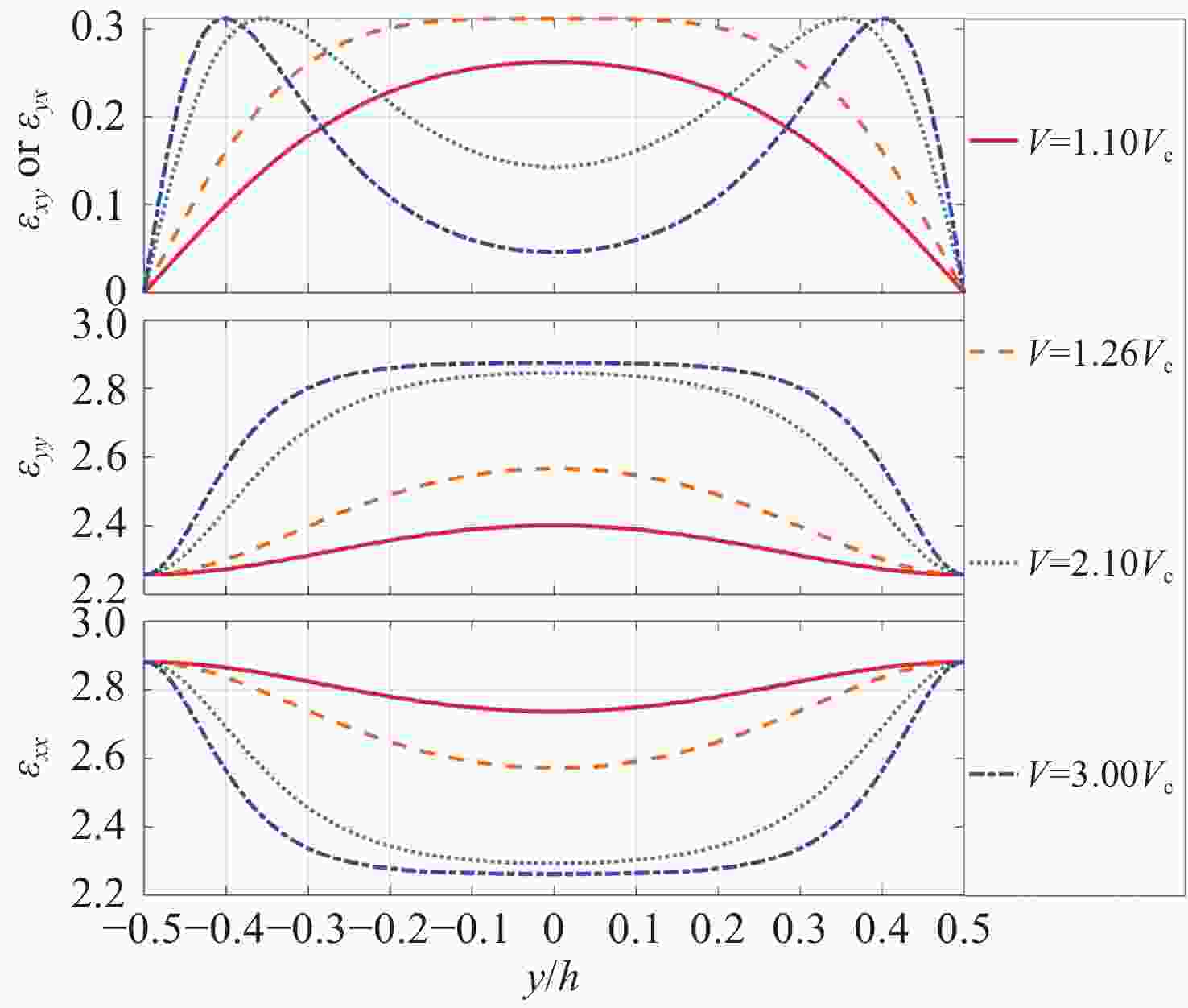
${\Delta }x$ and${\Delta }y$ are the mesh spacing in the x and y direction, respectively图 3 不同外加电压下
$ {\varepsilon _{xx}} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{yy}} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{xy}} $ (或$ {\varepsilon _{yx}} $ )随y的一维渐变曲线Figure 3. One-dimensional gradual change curves of
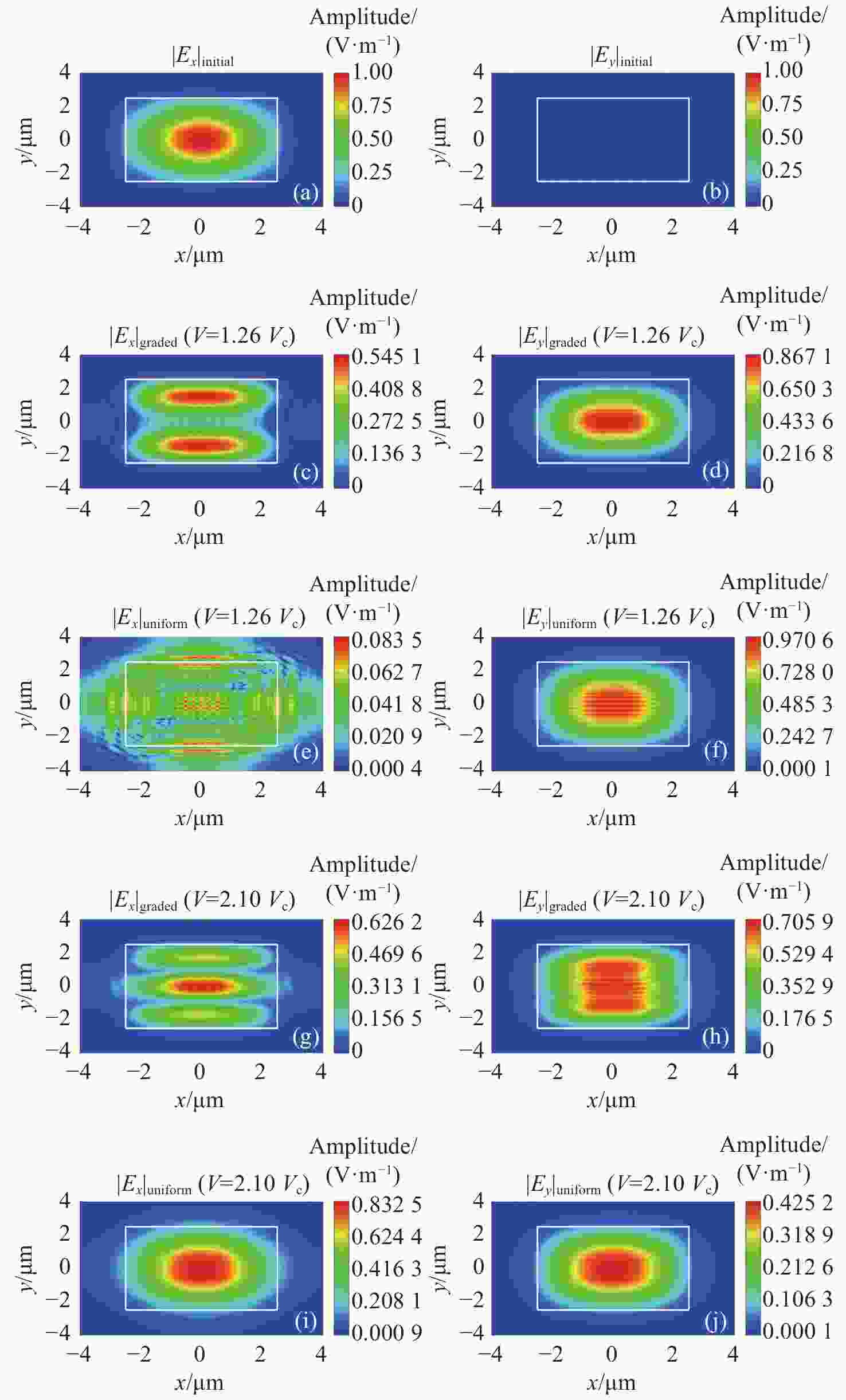
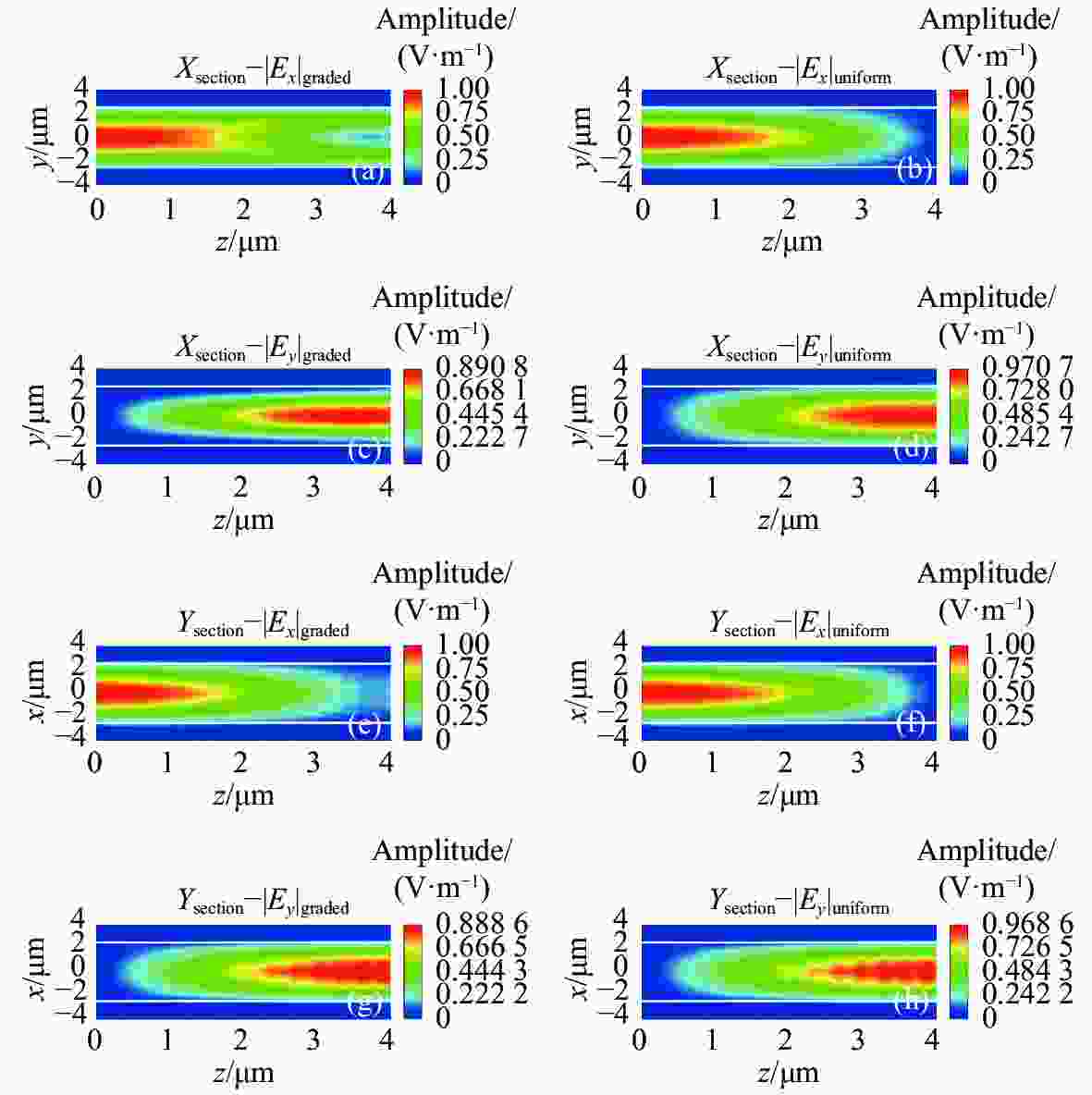
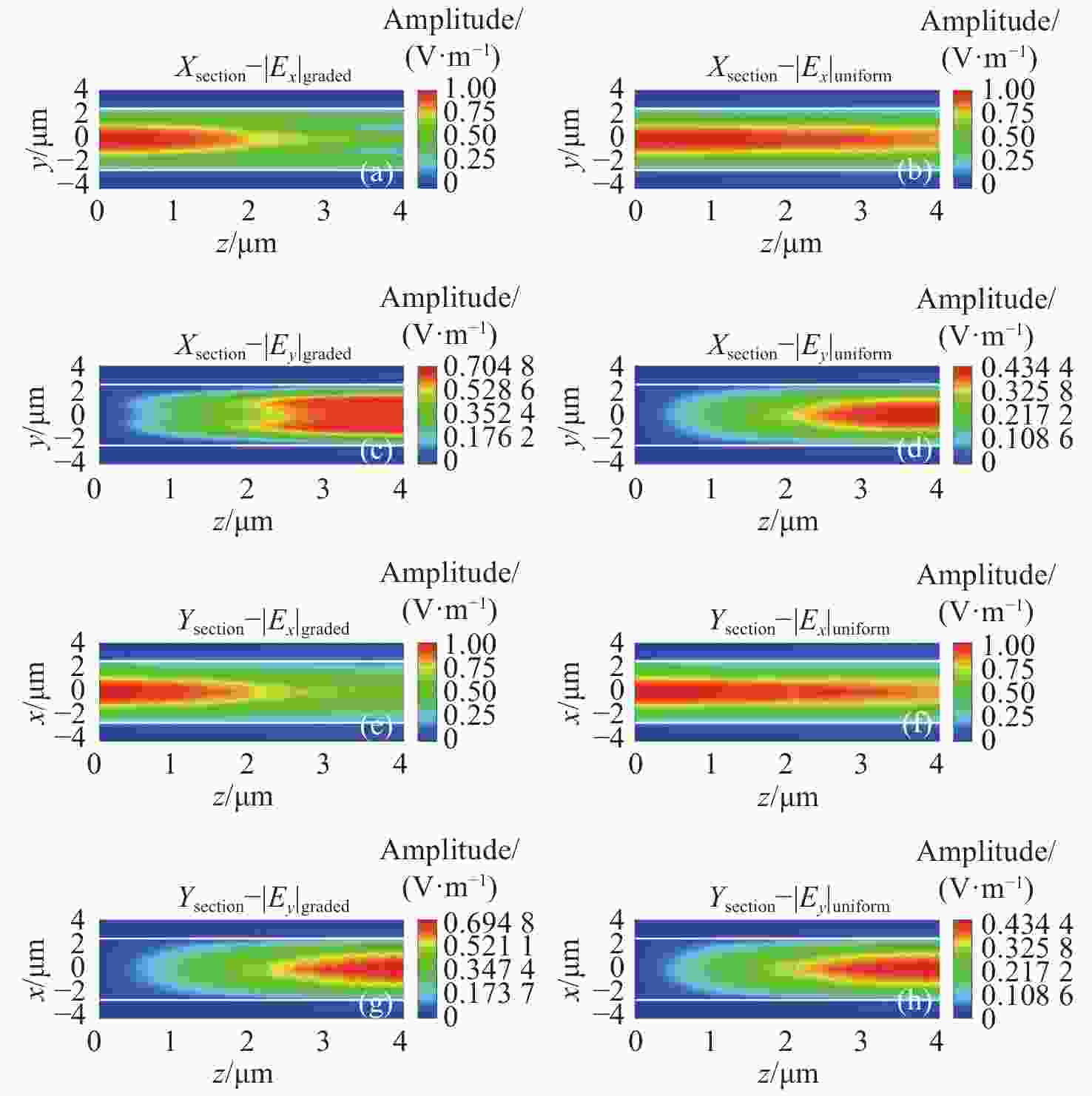
$ {\varepsilon _{xx}} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{yy}} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _{xy}} $ (or$ {\varepsilon _{yx}} $ ) with y at different applied voltages图 5 初始和输出位置处的电场分布。(a)~(b)初始激励;(c)~(f) 外加电压为1.26倍阈值时输出端的传播场分布;(g)~(j) 外加电压为2.1倍阈值时输出端的传播场分布
Figure 5. Electric field distribution at initial and output positions. (a)−(b) Initial excitation; (c)−(f) propagation field distribution at the output when the applied voltage is 1.26 times the threshold; (g)−(j) propagation field distribution at the output when the applied voltage is 2.1 times the threshold
-
[1] WANG ZH CH, DAI D X. Ultrasmall Si-nanowire-based polarization rotator[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2008, 25(5): 747-753. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.25.000747 [2] 戴道锌, 王健, 陈思涛. 硅基片上复用—解复用技术与器件[J]. 电信科学,2015,31(10):9-21.DAI D X, WANG J, CHEN S T. Silicon-based-chip multiplexing technologies and devices[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2015, 31(10): 9-21. (in Chinese) [3] ONO T, YANO Y. Key technologies for terabit/second WDM systems with high spectral efficiency of over 1 bit/s/Hz[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1998, 34(11): 2080-2088. doi: 10.1109/3.726596 [4] INOUE Y, TAKAHASHI H, ANDO S, et al. Elimination of polarization sensitivity in silica-based wavelength division multiplexer using a polyimide half waveplate[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1997, 15(10): 1947-1957. doi: 10.1109/50.633599 [5] LI T H, CHEN Q M, YU W X, et al. Planar polarization-routing optical cross-connects using nematic liquid crystal waveguides[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(1): 402-418. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.000402 [6] SHANI Y, ALFERNESS R, KOCH T, et al. Polarization rotation in asymmetric periodic loaded rib waveguides[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1991, 59(11): 1278-1280. doi: 10.1063/1.105474 [7] VAN DER TOL J J G M, HAKIMZADEH F, PEDERSEN J W, et al. A new short and low-loss passive polarization converter on InP[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 1995, 7(1): 32-34. doi: 10.1109/68.363385 [8] OBAYYA S S A, RAHMAN B M A, GRATTAN K T V, et al. Beam propagation modeling of polarization rotation in deeply etched semiconductor bent waveguides[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2001, 13(7): 681-683. doi: 10.1109/68.930413 [9] OBAYYA S S A, RAHMAN B M A, GRATTAN K T V, et al. Improved design of a polarization converter based on semiconductor optical waveguide bends[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(30): 5395-5401. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.005395 [10] CHEN L, ZHANG W G, ZHOU Q, et al. Polarization rotator based on hybrid plasmonic photonic crystal fiber[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(22): 2291-2294. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2352356 [11] BEGGS D M, MIDRIO M, KRAUSS T F. Compact polarization rotators for integrated polarization diversity in InP-based waveguides[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(15): 2176-2178. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.002176 [12] HAMEED M F O, HUSSAIN F F K, OBAYYA S S A. Ultracompact polarization rotator based on liquid crystal channel on silicon[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(11): 2190-2199. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.032317 [13] DAVIS S R, ROMMEL S D, FARCA G, et al. . A new electro-optic waveguide architecture and the unprecedented devices it enables[C]. SPIE Defense and Security Symposium. Orlando, United States: International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2008: 697503. [14] TRIPATHI U S, RASTOGI V. Liquid crystal based rib waveguide[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2020, 38(15): 4045-4051. [15] 杨登科, 吴诗聪. 液晶器件基础[M]. 郭太良, 周雄图, 译. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.YANG D K, WU S T. Fundamentals of Liquid Crystal Devices[M]. GUO T L, ZHOU X T, trans. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [16] KHOO I C. Liquid Crystals[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience, 2007. [17] AGRAWAL O P. Formulation of Euler-Lagrange equations for fractional variational problems[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2002, 272(1): 368-379. [18] 查正桃,张谦述. 液晶光波导中本征模内场分量间的关系[J]. 液晶与显示,2022,37(1):14-20.ZHA ZH T, ZHANG Q SH. Relationship of field components in the liquid crystal optical waveguide eigenmode[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystal and Displays, 2022, 37(1): 14-20. (in Chinese) [19] FALLAHKHAIR A B, LI K S, MURPHY T E. Vector finite difference modesolver for anisotropic dielectric waveguides[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2008, 26(11): 1423-1431. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2008.923643 [20] KAWANO K, KITOH T. Introduction to Optical Waveguide Analysis: Solving Maxwell's Equations and the Schrödinger Equation[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2001. [21] YAMAMOTO S, KOYAMADA Y, MAKIMOTO T. Normal‐mode analysis of anisotropic and gyrotropic thin‐film waveguides for integrated optics[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1972, 43(12): 5090-5097. doi: 10.1063/1.1661077 [22] YAMAUCHI J, TAKAHASHI G, NAKANO H. Full-vectorial beam-propagation method based on the McKee-Mitchell scheme with improved finite-difference formulas[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1998, 16(12): 2458-2464. doi: 10.1109/50.736638 [23] ALCANTARA L D S, TEIXEIRA F L, CÉSAR A C, et al. A new full-vectorial FD-BPM scheme: application to the analysis of magnetooptic and nonlinear saturable media[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2005, 23(8): 2579-2585. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2005.850811 [24] HADLEY G R. Transparent boundary condition for beam propagation[J]. Optics Letters, 1991, 16(9): 624-626. doi: 10.1364/OL.16.000624 [25] HOLMES B M, HUTCHINGS D C. Realization of novel low-loss monolithically integrated passive waveguide mode converters[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2006, 18(1): 43-45. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2005.859987 [26] BULJA S, MIRSHEKAR-SYAHKAL D, JAMES R, et al. Measurement of dielectric properties of nematic liquid crystals at millimeter wavelength[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2010, 58(12): 3493-3501. [27] LI J, WU S T, BRUGIONI S, et al. Infrared refractive indices of liquid crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 97(7): 073501. doi: 10.1063/1.1877815 [28] 查正桃,张谦述,张耀进,周琪.液晶平板光波导中耦合模式的研究[J/OL].西华师范大学学报(自然科学版): 1-7. [2021-12-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1699.N.20211130.1830.008.html.ZHA ZH T, ZHANG Q SH, ZHANG Y J, et al. Coupling modes in liquid crystal slab optical waveguide[J/OL]. Journal of China West Normal University (Natural Sciences): 1-7. [2021-12-04]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1699.N.20211130.1830.008.html. [29] 杨文晨, 秦增光, 刘兆军, 等. 基于希尔伯特-黄变换的双马赫-曾德分布式光纤传感振动定位方法[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1410-1416. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0065YANG W CH, QIN Z G, LIU ZH J, et al. A Hilbert-Huang transform method for vibration localization based on a dual Mach-Zehnder distributed optical fiber sensor[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1410-1416. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0065 [30] 刘野, 刘宇, 肖辉东, 等. 638nm光栅外腔窄线宽半导体激光器[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1249-1256. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0249LIU Y, LIU Y, XIAO H D, et al. 638 nm narrow linewidth diode laser with a grating external cavity[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1249-1256. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0249 [31] DENG H H, YEVICK D O, BROOKS C, et al. Design rules for slanted-angle polarization rotators[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2005, 23(1): 432-445. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2004.834477 -






 下载:
下载: