Ultrafast fiber laser based on bismuth telluride evanescent field mode-locked device
-
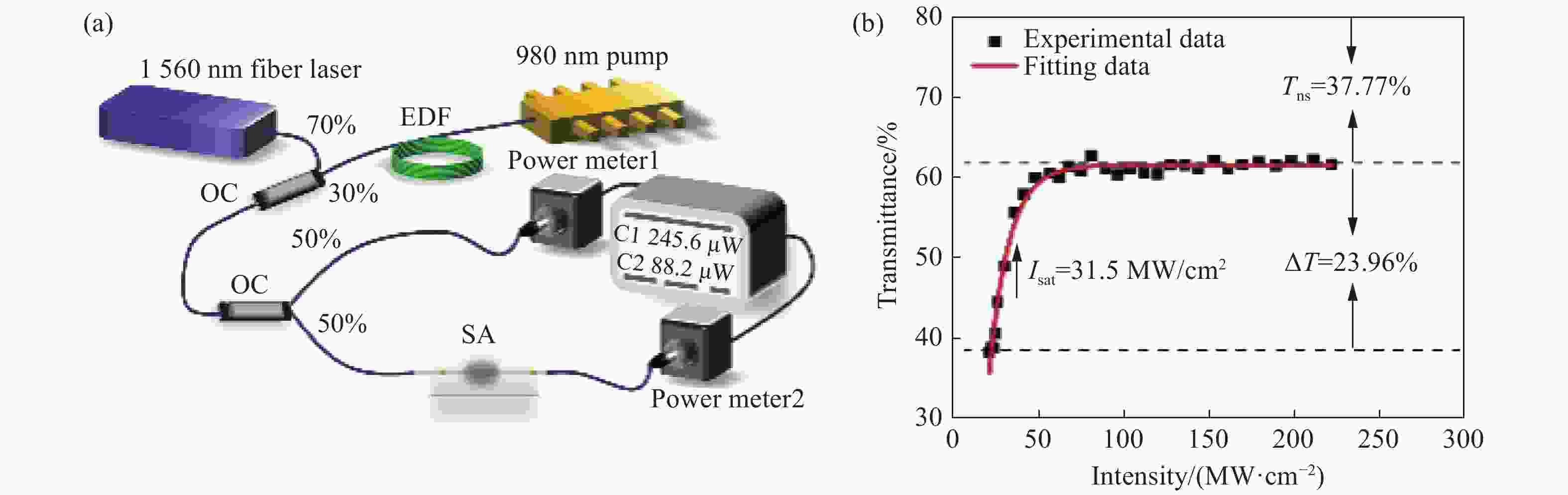
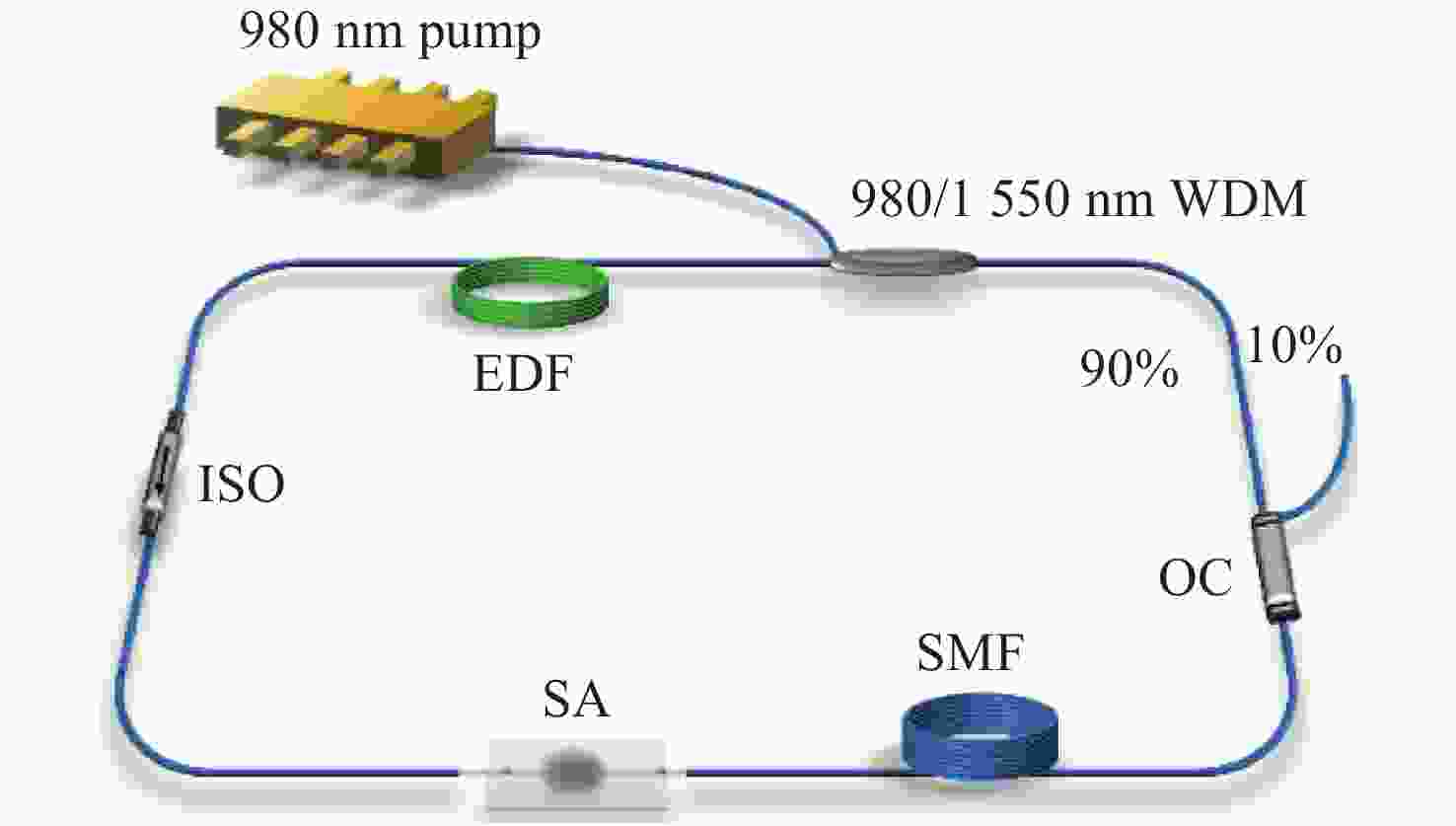
摘要: 为使光纤激光器在被动谐波锁模状态下实现锁模脉冲高重复频率输出,本文通过激光沉积法制备了一种基于非线性拓扑绝缘体材料碲化铋与侧面抛磨光纤相结合的可饱和吸收体锁模器件,该器件调制深度、非饱和损耗、饱和强度分别为23.96%、37.77%、31.5 MW/cm2。将其应用在掺铒光纤激光器中,通过对整个腔内色散参数的调整,以及利用材料自身良好的非线性可饱和吸收能力,成功实现了锁模自启动,其中心波长为1555.67 nm,脉冲宽度为487 fs,重复频率为47.87 MHz,信噪比为58 dB。当泵浦功率超过150 mW时出现锁模脉冲的谐波分裂,持续对泵浦功率进行微调,增加直至最高功率250 mW时,出现了11阶谐波锁模脉冲,重复频率最高达到528 MHz,此时的信噪比为41.5 dB。本文结果证明利用侧面抛磨光纤结构的倏逝场,能够辅助材料提升一定的激光抗损伤能力,便于其在基本锁模状态下进一步实现被动谐波锁模,满足锁模脉冲高重频的产生及探究,对材料在高重频超快光纤激光器中的应用具有重要意义。Abstract: In order to realize the passively harmonic mode-locking with high repetition rate in the fiber laser. A saturable absorber (SA) based on two dimensional (2D) topological insulators material of Bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3), combining with a side-polished fiber, was fabricated by laser deposition technology in this study. This device has a modulation depth of 23.96%, nonsaturable loss of 37.77% and saturable intensity of 31.5 MW/cm2. According to the adjustment of dispersion in the whole cavity and the excellent nonlinear saturable absorb character in topological insulator materials, a self-starting mode-locking is realized successfully when this SA device is applied in the Er-doped fiber laser, with a central wavelength of 1555.67 nm, pulse duration of 487 fs, repetition rate of 47.87 MHz and signal-to-noise ratio of 58 dB. A harmonic mode-locking is achieved when the pump power is over 150 mW. When we adjust and increase slightly the pump power till 250 mW, the harmonic mode-locking of 11 orders is achieved with the repetition rate of 528 MHz and the signal-to-noise ratio of 41.5 dB. These results demonstrate that with the evanescent field produced by the side-polished fiber, the damage threshold of materials can be improved and the passively harmonic mode-locking with high repetition rate is realized, which has a great significance for the materials in the application of ultrafast fiber laser with high repetition rate.
-
Key words:
- tow dimensional material /
- saturable absorber /
- evanescent field /
- ultrafast fiber laser
-
图 1 (a)碲化铋样品扫描电镜(SEM)图;(b)碲化铋粉末X射线衍射图谱;(c)碲化铋样品拉曼光谱;(d)碲化铋样品原子力显微镜图;(e)碲化铋样品光学线性吸收图
Figure 1. (a) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) image of bismuth telluride sample; (b) X-ray diffraction pattern of bismuth telluride powder; (c) Raman spectrum of bismuth telluride sample; (d) atomic force microscope image of bismuth telluride sample; (e) optical linear absorption of bismuth telluride sample
图 2 (a) D型光纤结构图;(b) 激光沉积装置图;(c) 激光沉积原理图;(d) D型光纤沉积前金相显微照片;(e) D型光纤沉积后金相显微照片;(f) D型光纤电子显微镜表征图;(g) D型光纤抛磨区域内材料元素分布图
Figure 2. (a) D-shaped optical fiber structure; schematic diagram of (b) laser deposition device and (c) laser deposition principal; metallographic microscope image of D-shaped optical fiber (d) before deposition and (e) after deposition; (f) SEM image of D-shaped fiber; (g) mapping image of elements distribution in polishing area of D-shaped fiber
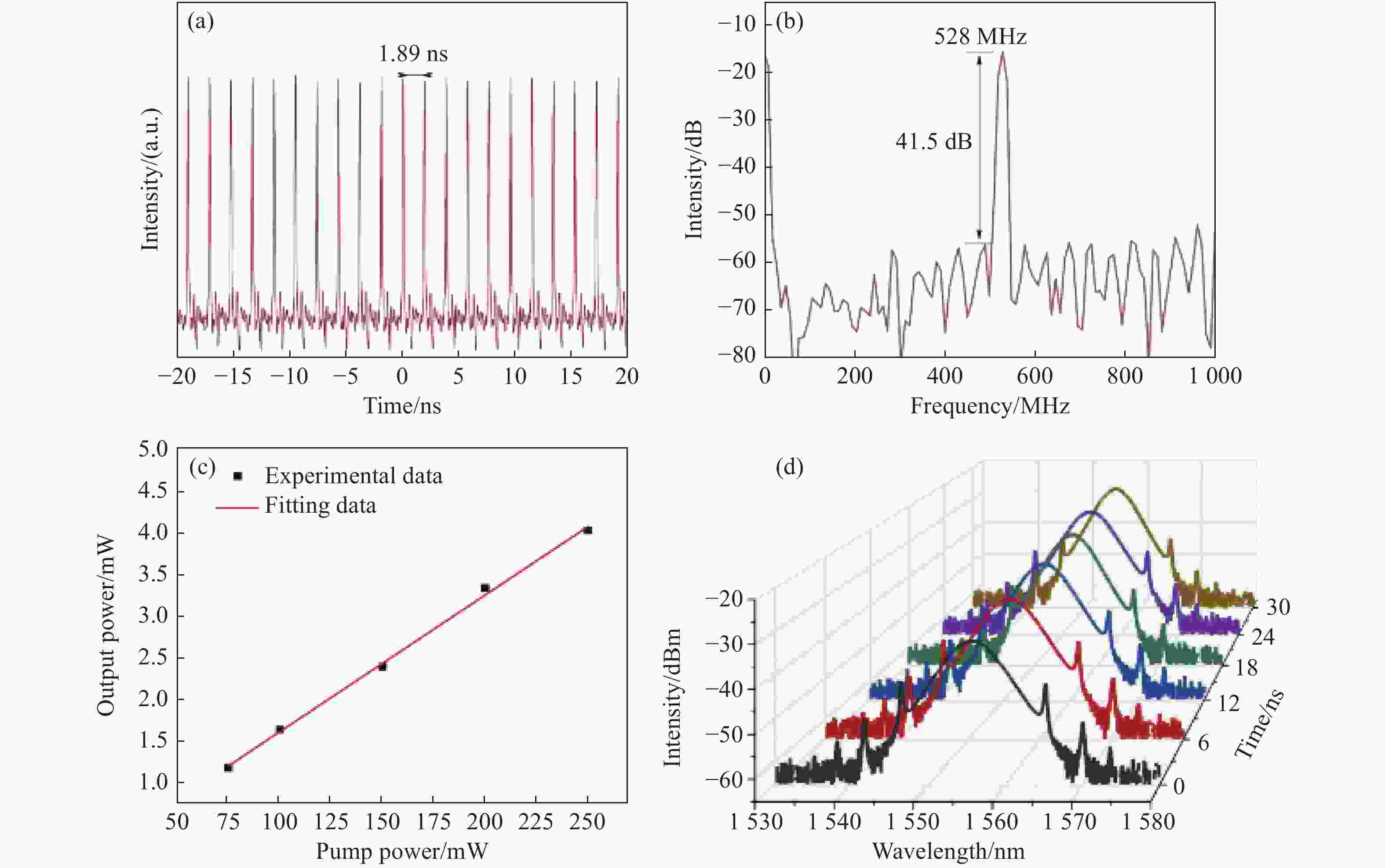
图 6 (a)11阶谐波锁模运作下的时域图;(b)11阶谐波锁模运作下的频域图;(c)泵浦功率与平均输出功率关系图;(d)30 h长时间锁模运作光谱图
Figure 6. (a) Time domain diagram under 11th-order harmonic mode-locking operation; (b) frequency domain diagram under 11th-order harmonic mode-locking operation; (c) relationship between pump power and average output power; (d) spectrum of 30 h long-time mode-locking operation
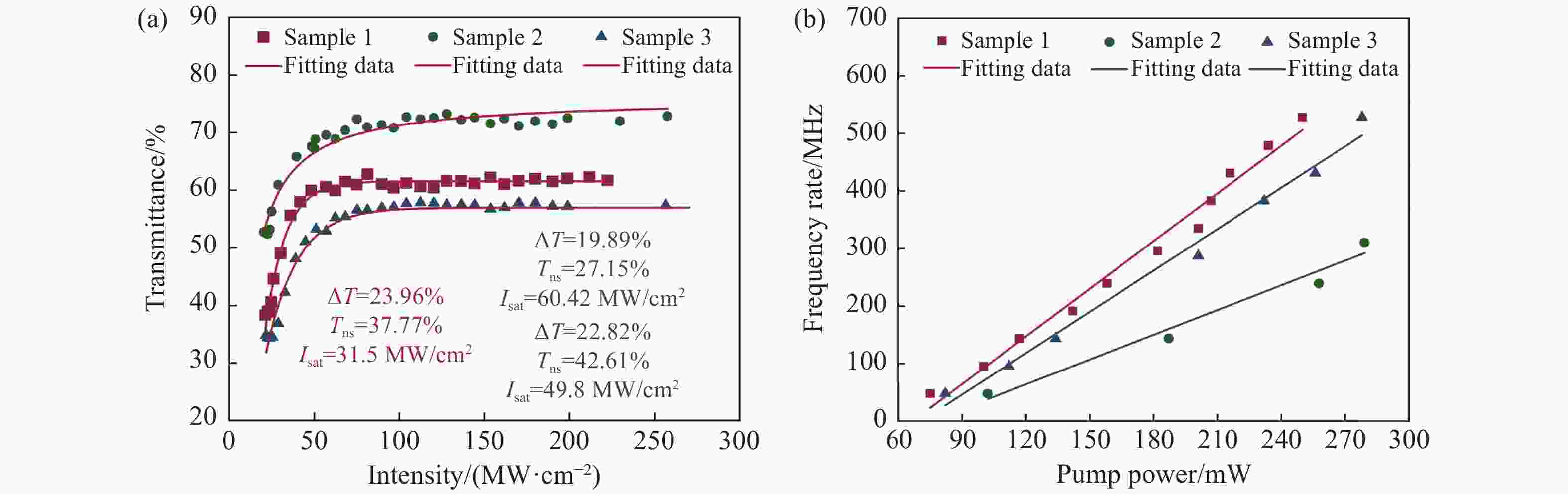
图 7 (a)同一制备参数下3个可饱和吸收器件的调制深度对比;(b)同一制备参数下3个可饱和吸收器件在光纤激光器中高重频输出性能比较
Figure 7. (a) Comparison of modulation depth for three saturated absorbers with same preparation parameters; (b) comparison of high repetition rate output performance of three saturated absorbers in the fiber laser with same preparation parameters
表 1 几种基于拓扑绝缘体材料的可饱和吸收器件用于1.5 μm光纤激光器时的非线性及脉冲输出性能的对比
Table 1. The nonlinear characteristics and pulse output characteristics of different saturated absorbers based on the topological insulator material used in a 1.5 μm fiber laser
Material type Integration method Modulation depth Saturable intensity/(MW·cm−2) Pulse energy/pJ Pulse width/fs Repetition rate/MHz Ref Sb2Te3 D-shaped fiber 6.0% 31 29.0 270 34.50 [34] Sb2Te3 D-shaped fiber 3.9% 106 39.6 449 22.13 [35] Sb2Te3 D-shaped fiber 6.0% 31 − 128 22.32 [6] CoSb3 D-shaped fiber 5.0% 16 6.9 833 14.48 [36] Bi2Te3 D-shaped fiber 15.7% 81 52.9 600 15.11 [37] Bi2Te3 polyvinyl alcohol(PVA) thin film 2.0% 180 46.3 1080 8.64 [23] Bi2Te3 D-shaped fiber 23.9% 32 7.6 487 528.00 This work -
[1] BAO Q L, ZHANG H, WANG Y, et al. Atomic-layer graphene as a saturable absorber for ultrafast pulsed lasers[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(19): 3077-3083. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200901007 [2] MOUCHEL P, SEMAAN G, NIANG A, et al. High power passively mode-locked fiber laser based on graphene nanocoated optical taper[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(3): 031106. doi: 10.1063/1.4994026 [3] 公爽, 田金荣, 李克轩, 等. 新型二维材料在固体激光器中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(1):18-30. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181101.0018GONG SH, TIAN J R, LI K X, et al. Advances in new two-dimensional materials and its application in solid-state lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1): 18-30. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20181101.0018 [4] 丁蓉, 常建华, 孔春霞, 等. 基于石墨烯量子点的被动调Q Nd: YVO4激光器[J]. 发光学报,2020,41(1):63-70. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20204101.0063DING R, CHANG J H, KONG CH X, et al. Passively Q-switched Nd: YVO4 laser based on graphene quantum dots[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 41(1): 63-70. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20204101.0063 [5] ZHAO CH J, ZHANG H, QI X, et al. Ultra-short pulse generation by a topological insulator based saturable absorber[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(21): 211106. doi: 10.1063/1.4767919 [6] SOTOR J, SOBON G, ABRAMSKI K M. Sub-130 fs mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser based on topological insulator[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(11): 13244-13249. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.013244 [7] ZHANG H, LU S B, ZHENG J, et al. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) as a broadband saturable absorber for ultra-fast photonics[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(6): 7249-7260. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.007249 [8] LUO ZH Q, LI Y Y, ZHONG M, et al. Nonlinear optical absorption of few-layer molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) for passively mode-locked soliton fiber laser [Invited][J]. Photonics Research, 2015, 3(3): A79-A86. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.3.000A79 [9] 孙有生, 端木庆铎, 林鹏, 等. 1.6μm波段锁模光纤激光器[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1387-1394. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0128SUN Y SH, DUANMU Q D, LIN P, et al. 1.6 μm band mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1387-1394. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0128 [10] 孙俊杰, 陈飞, 何洋, 等. 新型过渡金属硫化物在超快激光中的应用[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(4):647-659. doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0241SUN J J, CHEN F, HE Y, et al. Application of emerging transition metal dichalcogenides in ultrafast lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(4): 647-659. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0241 [11] 付鑫鹏, 付喜宏, 姚聪, 等. 基于超薄层MoS2可饱和吸收体的被动调Q固体Nd: YAG激光器[J]. 发光学报,2021,42(5):668-673. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210030FU X P, FU X H, YAO C, et al. Passive Q-switched solid-state Nd∶YAG laser based on ultrathin MoS2 saturable absorber[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2021, 42(5): 668-673. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210030 [12] CHEN Y, JIANG G B, CHEN SH Q, et al. Mechanically exfoliated black phosphorus as a new saturable absorber for both Q-switching and mode-locking laser operation[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(10): 12823-12833. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.012823 [13] JIN X X, HU G H, ZHANG M, et al. 102 fs pulse generation from a long-term stable, inkjet-printed black phosphorus-mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(10): 12506-12513. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.012506 [14] JHON Y I, KOO J, ANASORI B, et al. Metallic MXene saturable absorber for femtosecond mode-locked lasers[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(40): 1702496. doi: 10.1002/adma.201702496 [15] JIANG X T, LIU SH X, LIANG W Y, et al. Broadband nonlinear photonics in few-layer MXene Ti3C2TX (T = F, O, or OH)[J]. Laser &Photonics Reviews, 2018, 12(2): 1700229. [16] ZHANG M Y, CHEN H, YIN J D, et al. Recent development of saturable absorbers for ultrafast lasers [Invited][J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(8): 081405. doi: 10.3788/COL202119.081405 [17] MA CH Y, WANG C, GAO B, et al. Recent progress in ultrafast lasers based on 2D materials as a saturable absorber[J]. Applied Physics Reviews, 2019, 6(4): 041304. doi: 10.1063/1.5099188 [18] 张明霞, 袁振, 杜晓娟, 等. 被动调Q锁模运转Tm: LuScO3陶瓷激光器特性[J]. 发光学报,2021,42(7):1049-1056. doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210165ZHANG M X, YUAN ZH, DU X J, et al. Characteristics of passively Q-switched mode locked Tm: LuScO3 ceramic laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2021, 42(7): 1049-1056. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJL.20210165 [19] MOORE J E. The birth of topological insulators[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7286): 194-198. doi: 10.1038/nature08916 [20] ZHANG H J, LIU CH X, QI X L, et al. Topological insulators in Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3 with a single Dirac cone on the surface[J]. Nature Physics, 2009, 5(6): 438-442. doi: 10.1038/nphys1270 [21] DOU ZH Y, SONG Y R, TIAN J R, et al. Mode-locked ytterbium-doped fiber laser based on topological insulator: Bi2Se3[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(20): 24055-24061. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.024055 [22] JUNG M, LEE J, KOO J, et al. A femtosecond pulse fiber laser at 1935 nm using a bulk-structured Bi2Te3 topological insulator[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(7): 7865-7874. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.007865 [23] MAO D, JIANG B Q, GAN X T, et al. Soliton fiber laser mode locked with two types of film-based Bi2Te3 saturable absorbers[J]. Photonics Research, 2015, 3(2): A43-A46. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.3.000A43 [24] WEI Q, HAN X L, ZHANG H N, et al. CVD-Bi2Te3 as a saturable absorber for various solitons in a mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(26): 7792-7800. doi: 10.1364/AO.397625 [25] YAN P G, LIN R Y, RUAN SH CH, et al. A practical topological insulator saturable absorber for mode-locked fiber laser[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8690. doi: 10.1038/srep08690 [26] JIANG T, YIN K, WANG C, et al. Ultrafast fiber lasers mode-locked by two-dimensional materials: review and prospect[J]. Photonics Research, 2020, 8(1): 78-90. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.8.000078 [27] WANG F, ZHOU H, LI N, et al. Mesoporous carbon nanospheres deposited onto D-shaped fibers for femtosecond pulse generation[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(21): 11621-11626. doi: 10.1039/C9RA01082C [28] LIU M, WEI ZH W, LUO A P, et al. Recent progress on applications of 2D material-decorated microfiber photonic devices in pulse shaping and all-optical signal processing[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(9): 2641-2671. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0564 [29] CHI C, LEE J, KOO J, et al. All-normal-dispersion dissipative-soliton fiber laser at 1.06 µm using a bulk-structured Bi2Te3 topological insulator-deposited side-polished fiber[J]. Laser Physics, 2014, 24(10): 105106. doi: 10.1088/1054-66/24/10/105106 [30] YIN K, ZHANG B, LI L, et al. Soliton mode-locked fiber laser based on topological insulator Bi2Te3 nanosheets at 2 μm[J]. Photonics Research, 2015, 3(3): 72-76. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.3.000072 [31] WANG Y ZH, LI J F, MO K D, et al. 14.5 GHz passive harmonic mode-locking in a dispersion compensated Tm-doped fiber laser[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 7779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06326-5 [32] BOGUSŁAWSKI J, SOBOŃ G, ZYBAŁA R, et al. Towards an optimum saturable absorber for the multi-gigahertz harmonic mode locking of fiber lasers[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(9): 1094-1100. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.001094 [33] TAO SH, XU L X, CHEN G L, et al. Ultra-high repetition rate harmonic mode-locking generated in a dispersion and nonlinearity managed fiber laser[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2016, 34(9): 2354-2357. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2528304 [34] SOTOR J, SOBON G, GRODECKI K, et al. Mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser based on evanescent field interaction with Sb2Te3 topological insulator[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(25): 251112. doi: 10.1063/1.4885371 [35] BOGUSLAWSKI J, SOTOR J, SOBON G, et al. Mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser based on liquid phase exfoliated Sb2Te3 topological insulator[J]. Laser Physics, 2014, 24(10): 105111. doi: 10.1088/1054-660X/24/10/105111 [36] LEE J, KIM Y, LEE K, et al. Femtosecond mode-locking of a fiber laser using a CoSb3-skutterudite-based saturable absorber[J]. Photonics Research, 2018, 6(10): C36-C43. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000C36 [37] LEE J, KOO J, JHON Y M, et al. A femtosecond pulse erbium fiber laser incorporating a saturable absorber based on bulk-structured Bi2Te3 topological insulator[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(5): 6165-6173. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.006165 -






 下载:
下载: