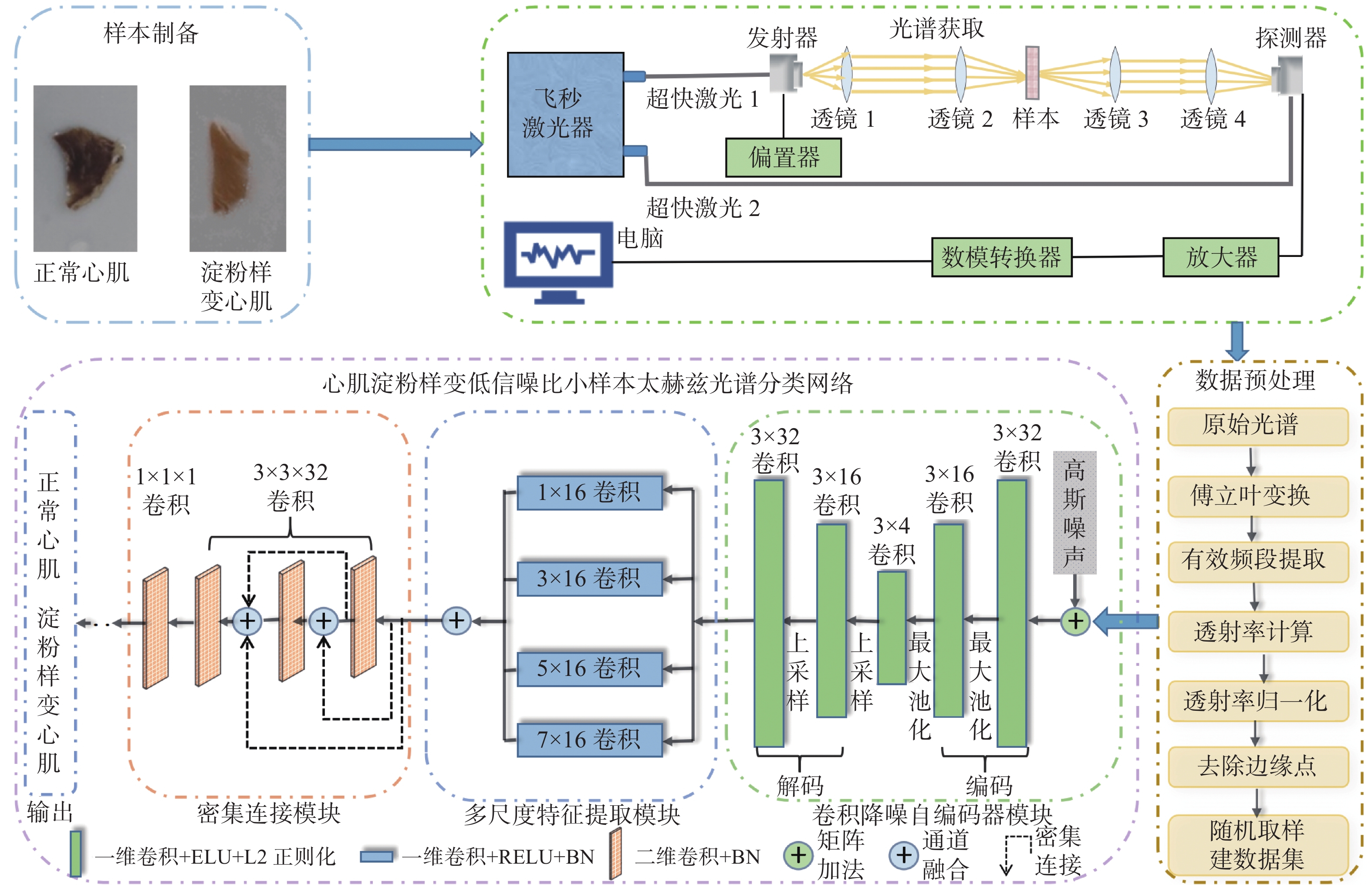
Detection of myocardial amyloidosis by a small number of terahertz spectra with low signal-to-noise ratio
-
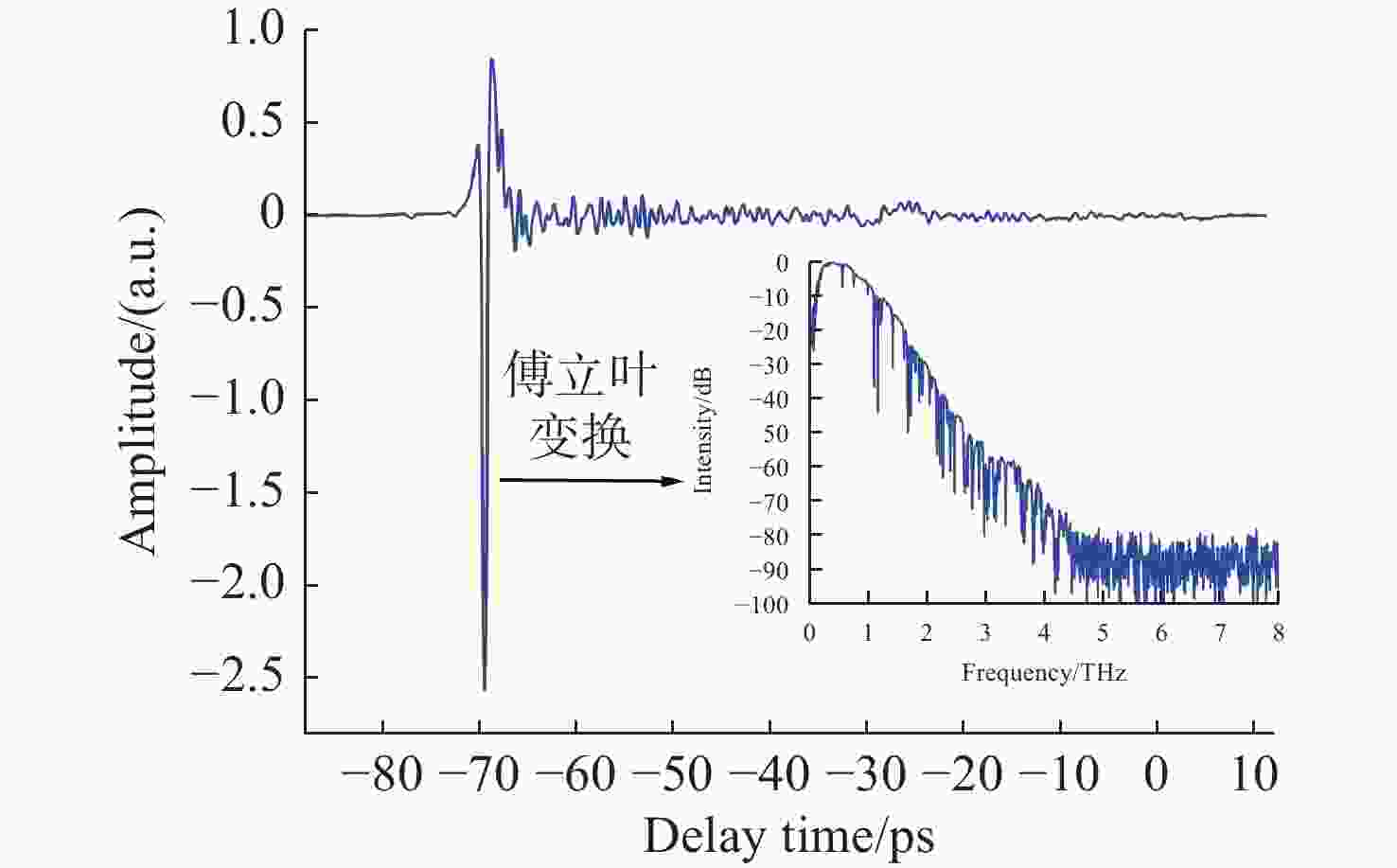
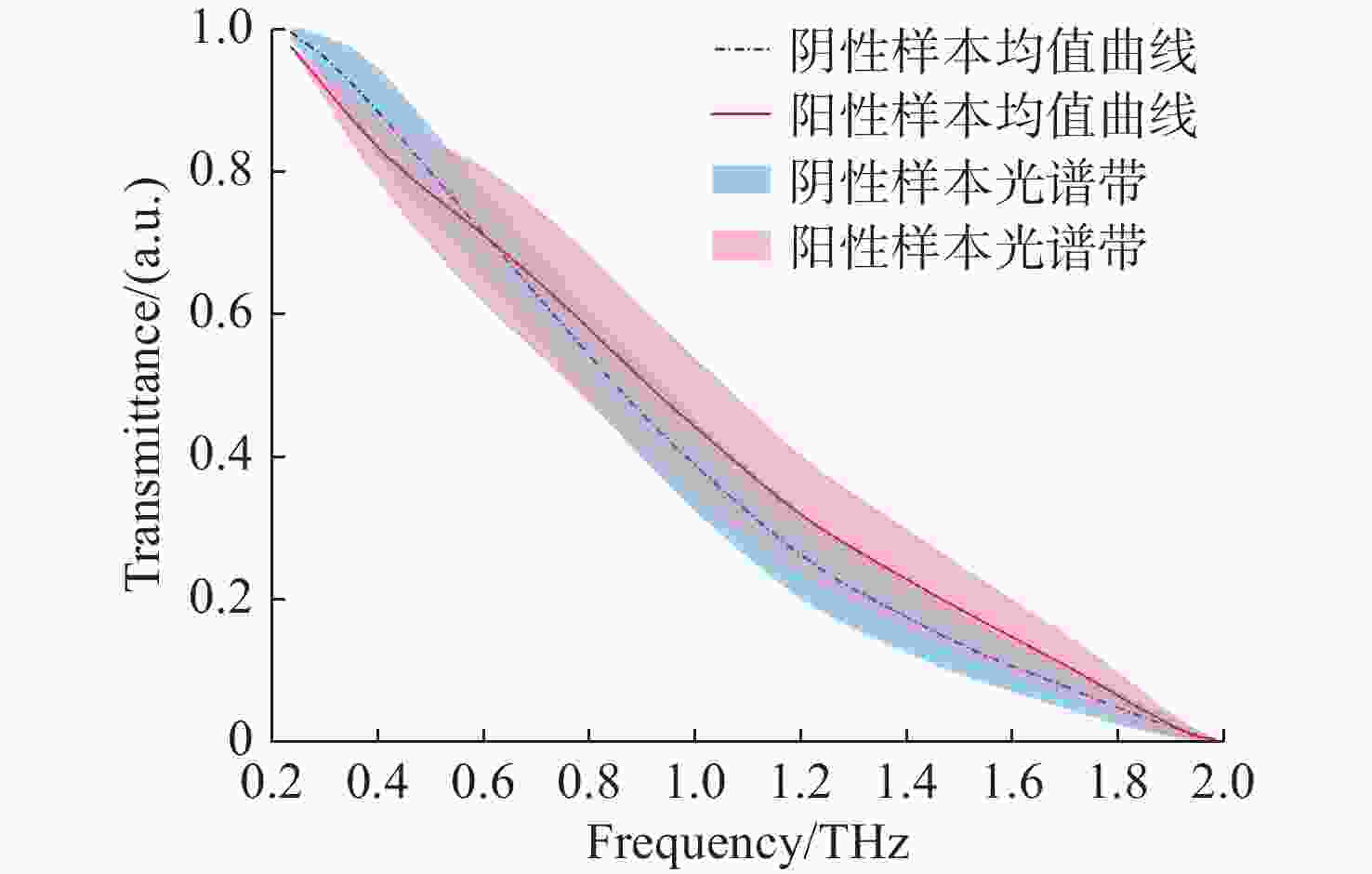
摘要: 由于低信噪比的小样本太赫兹光谱的可区分性特征提取困难和样本量过少带来的深度学习模型自身的过拟合问题,将太赫兹光谱与深度学习相结合应用于心肌淀粉样变检测仍面临挑战。本文提出了一种基于多模块顺序级联的分类模型,用于心肌淀粉样变在算法层面的实时检测。首先,采集了少量的低信噪比太赫兹光谱并对其进行预处理。其次,构建了一个基于卷积降噪自编码器、多尺度特征提取模块、密集连接模块的深度学习模型。最后,通过五折交叉验证策略进行病变预测,以获得稳定、可靠的结果。 10次独立重复实验和对比实验结果表明,该方法能对含噪光谱进行准确、稳定的分类,且其综合指标更优。不同样本量下的实验表明,本方法对样本量变化具有适应性:数据量为100时可达到95%的准确率;数据量仅为20时,该模型仍能取得70%的准确率。该项工作对心肌淀粉样变的实时、高效、安全诊断具有重要意义。Abstract: Due to the difficulty of extracting the distinguishable features of a small number of terahertz spectra with low signal-to-noise ratio; second and the over fitting problem of the deep learning model itself caused by too few samples, the application of terahertz spectra and deep learning in myocardial amyloidosis detection exists some challenges. In this paper, we propose a classification model based on multi-modules sequential cascade for real-time detection of myocardial amyloidosis at the algorithm level. Firstly, we collect a small number of low SNR terahertz spectra and preprocess them. Secondly, we construct a deep learning model based on denoising autoencoder, multi-scale feature extraction module and dense connection module. Finally, we use the 5 folds cross validation strategy to predict the lesions to obtain stable and reliable results. The results of 10 times independent repeated experiment and comparative experiment show that this method can classify the spectra with noise accurately and stably, which possesses of a better performance. Experiments under different number of samples show that this method is adaptive to the change of dataset size: an accuracy of 95% is achieved corresponding to 100 samples; when the amount of samples is only 20, the model can still achieve an accuracy of 70%. Therefore, the proposed method is of great significance for the real-time, efficient and safe diagnosis of myocardial amyloidosis.
-
表 1 10次独立重复实验结果
Table 1. Results of 10 times of independent repeated tests
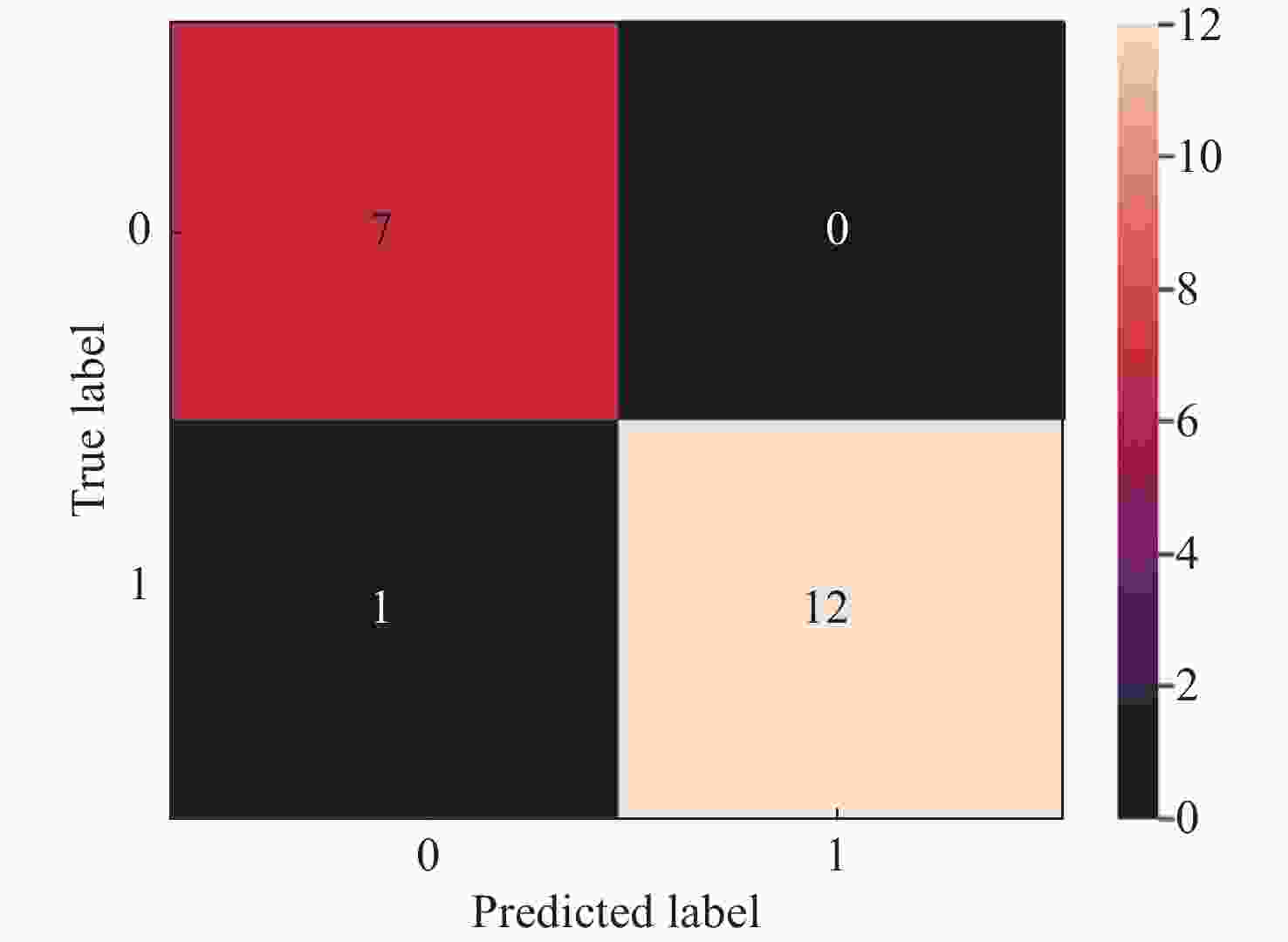
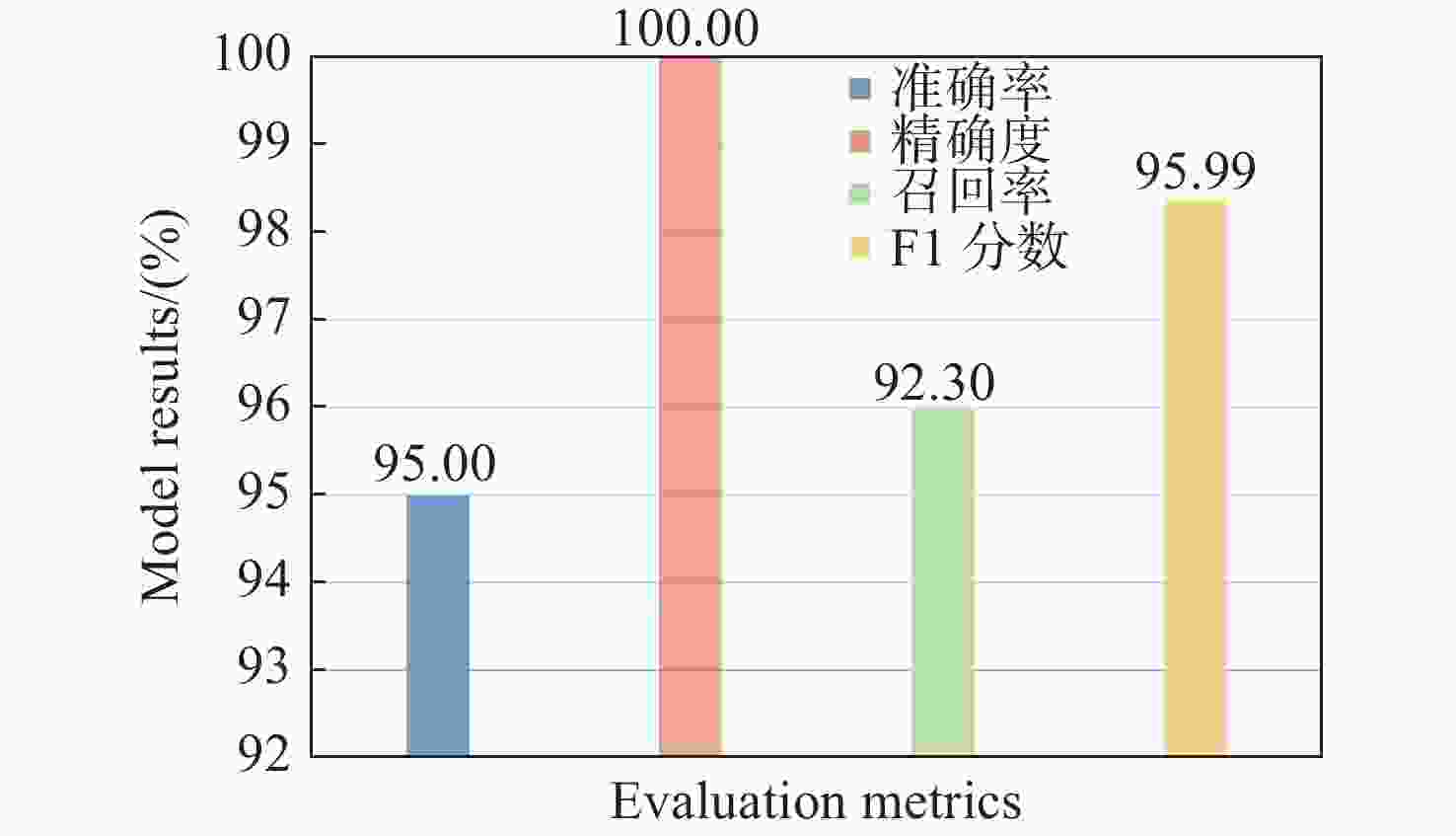
实验序号 准确率(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1分数(%) 1 95.00 100.00 91.66 95.65 2 95.00 100.00 92.30 95.99 3 94.85 99.76 92.32 95.89 4 94.93 99.86 91.75 95.63 5 95.04 100.00 92.28 95.98 6 94.66 99.80 92.25 95.87 7 95.12 99.75 91.84 95.63 8 95.06 99.66 92.25 95.81 9 94.75 99.62 92.32 95.83 10 94.84 99.82 91.75 95.61 极差(%) 0.46 0.38 0.66 0.38 表 2 不同参数对模型分类效果的影响
Table 2. Effects of different parameters on model classification
学习率/
批大小准确率(%) 精确度
(%)召回率
(%)F1分数(%) 0.001/3 85.00 81.81 90.00 85.71 0.001/5 86.21 90.00 81.81 85.71 0.001/10 90.00 98.56 84.61 91.05 0.0001/3 85.00 90.90 83.33 86.95 0.0001/5 90.00 91.66 91.66 91.66 0.0001/10 95.00 100.00 92.30 95.99 表 3 样本量对本文模型分类效果的影响
Table 3. Influence of the number of sample on model classification effect
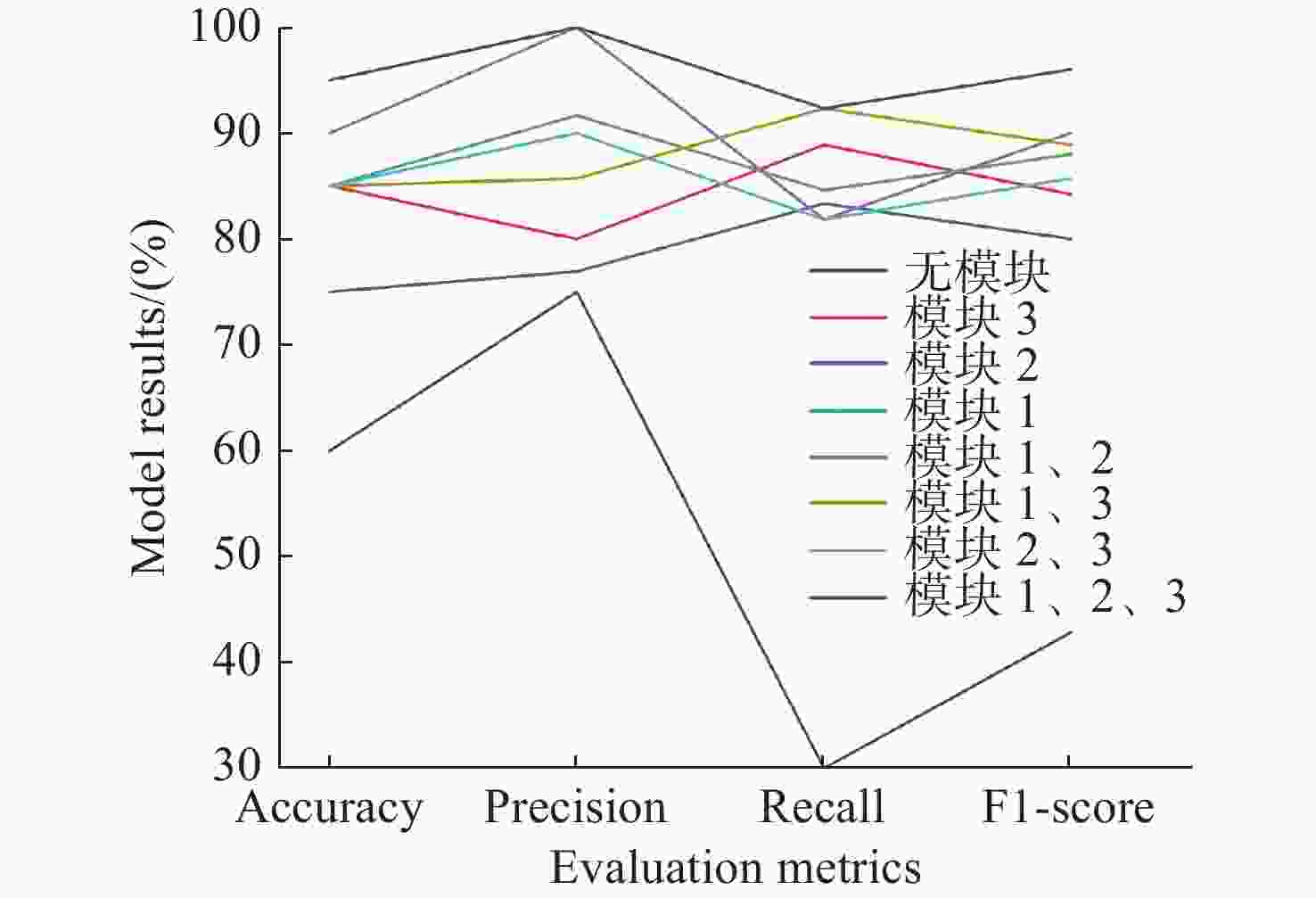
样本量 准确率(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1分数(%) 20 70.00 72.35 64.23 68.04 40 76.54 78.25 75.00 76.59 60 83.33 86.80 82.78 84.74 80 93.75 100.00 85.71 92.30 100 95.00 100.00 92.30 95.99 表 4 扩增样本量对模型分类效果的影响
Table 4. Influence of the number of expanded samples on model classification effect
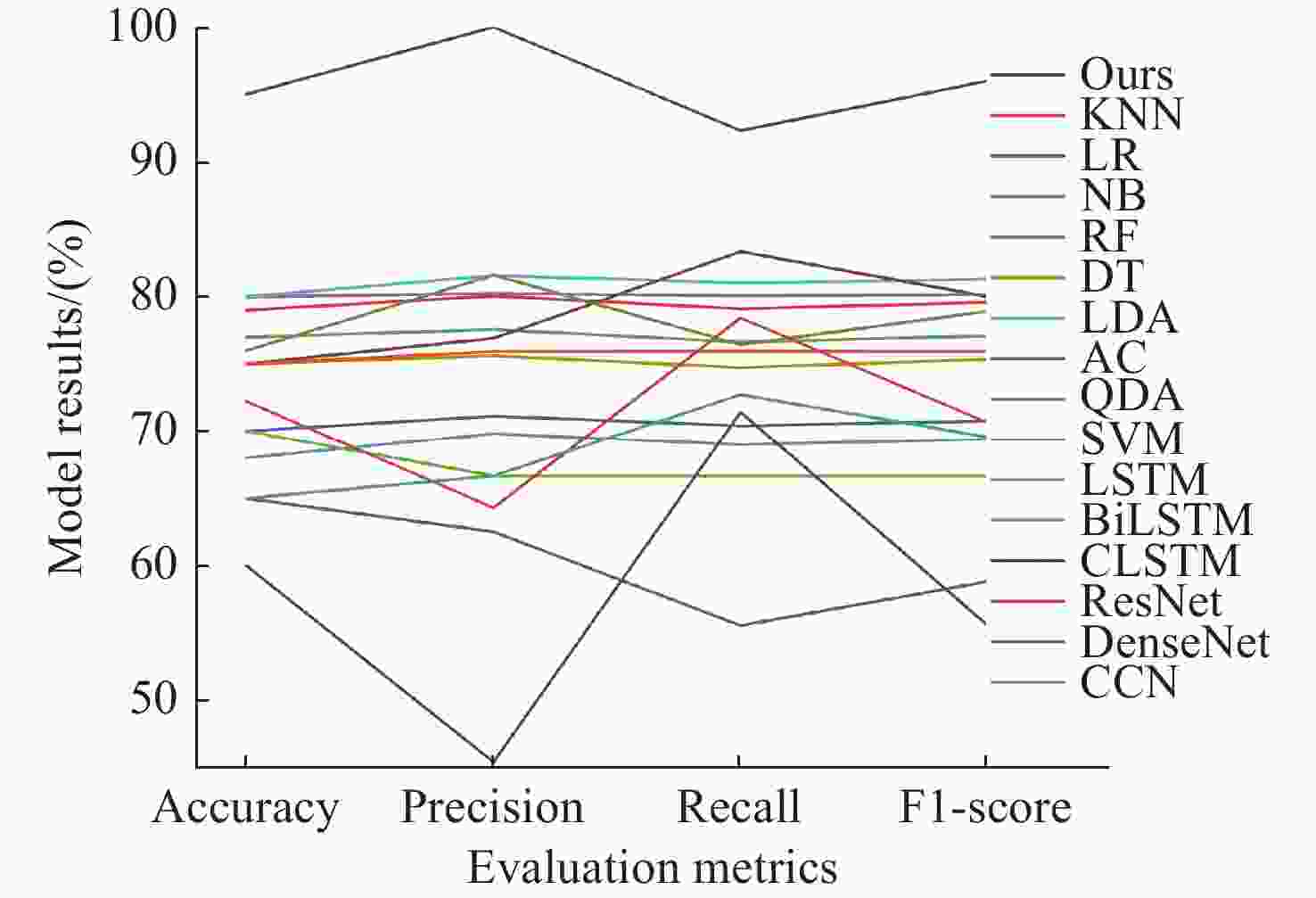
模型 准确率(%) 精确度(%) 召回率(%) F1分数(%) ResNet 64.57 60.31 64.59 62.37 DenseNet 63.66 65.87 68.30 67.06 CNN 64.83 66.05 65.66 65.85 本文模型 66.50 71.47 68.35 69.87 -
[1] CHATZANTONIS G, BIETENBECK M, ELSANHOURY A, et al. Diagnostic value of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in comparison to endomyocardial biopsy in cardiac amyloidosis: a multi-centre study[J]. Clinical Research in Cardiology, 2021, 110(4): 555-568. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01771-1 [2] GARCIA-PAVIA P, RAPEZZI C, ADLER Y, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis: a position statement of the ESC working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases[J]. European Heart Journal, 2021, 42(16): 1554-1568. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab072 [3] ASH S, SHORER E, RAMGOBIN D, et al. Cardiac amyloidosis—a review of current literature for the practicing physician[J]. Clinical Cardiology, 2021, 44(3): 322-331. doi: 10.1002/clc.23572 [4] LI W J, UPPAL D, WANG Y CH, et al. Nuclear imaging for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis in 2021[J]. Diagnostics, 2021, 11(6): 996. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11060996 [5] BAGGIANO A, BOLDRINI M, MARTINEZ-NAHARRO A, et al. Noncontrast magnetic resonance for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis[J]. JACC:Cardiovascular Imaging, 2020, 13(1): 69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.03.026 [6] DORBALA S, CUDDY S, FALK R H. How to image cardiac amyloidosis: a practical approach[J]. JACC:Cardiovascular Imaging, 2020, 13(6): 1368-1383. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.07.015 [7] 阎春生, 黄晨, 韩松涛, 等. 古代纸质文物科学检测技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(5):936-964. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0010YAN CH SH, HUANG CH, HAN S T, et al. Review on scientific detection technologies for ancient paper relics[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(5): 936-964. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0010 [8] 王晓东, 颜伟, 李兆峰, 等. 平面天线在场效应晶体管太赫兹探测器中的应用[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(1):1-13. doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0001WANG X D, YAN W, LI ZH F, et al. Application of planar antenna in field-effect transistor terahertz detectors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(1): 1-13. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0001 [9] ZHANG Y Y, WANG CH T, HUAI B X, et al. Continuous-wave THz imaging for biomedical samples[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(1): 71. [10] 蔡莉, 王淑婷, 刘俊晖, 等. 数据标注研究综述[J]. 软件学报,2020,31(2):302-320.CAI L, WANG SH T, LIU J H, et al. Survey of data annotation[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 31(2): 302-320. (in Chinese) [11] BARZ B, DENZLER J. Deep learning on small datasets without pre-training using cosine loss[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, IEEE, 2020: 1360-1369. [12] LIU S D, SHAN Z, SAV A, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) status prediction in histopathology images of gliomas using deep learning[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 7733. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64588-y [13] WANG Z S, ZOU C, CAI W W. Small sample classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images based on sequential joint deeping learning model[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 71353-71363. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2986267 [14] 王德文, 魏波涛. 基于孪生变分自编码器的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 智能系统学报,2021,16(2):254-262.WANG D W, WEI B T. A small-sample image classification method based on a Siamese variational auto-encoder[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2021, 16(2): 254-262. (in Chinese) [15] 崔向伟, 沈韬, 刘英莉, 等. 小样本太赫兹光谱识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2021,58(1):0130001.CUI X W, SHEN T, LIU Y L, et al. Recognition of small-sample terahertz spectrum[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(1): 0130001. (in Chinese) [16] 赵凯琳, 靳小龙, 王元卓. 小样本学习研究综述[J]. 软件学报,2021,32(2):349-369.ZHAO K L, JIN X L, WANG Y ZH. Survey on few-shot learning[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(2): 349-369. (in Chinese) [17] 张申华, 杨延西, 秦峤孟. 针对光栅图像的快速盲去噪方法[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(3):596-604. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0166ZHANG SH H, YANG Y X, QIN Q M. A fast blind denoising method for grating image[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 596-604. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0166 [18] 代磊超, 冯林, 尚兴林, 等. 基于深度网络的快速少样本学习算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2021,34(10):941-956.DAI L CH, FENG L, SHANG X L, et al. Fast few-shot learning algorithm based on deep network[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 34(10): 941-956. (in Chinese) [19] YU P, ZHENG J P, ZHAO M, et al. Myocardial amyloidosis detection with terahertz spectroscopy[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(3): 2389-2398. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3133294 [20] 李泽田, 雷志春. 基于局部期望最大化注意力的图像降噪[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(4):350-359. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203504.0350LI Z T, LEI ZH CH. Local expectation-maximization attention network for image denoising[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(4): 350-359. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203504.0350 [21] 来杰, 王晓丹, 向前, 等. 自编码器及其应用综述[J]. 通信学报,2021,42(9):218-230. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021160LAI J, WANG X D, XIANG Q, et al. Review on autoencoder and its application[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(9): 218-230. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021160 [22] 张墺琦, 亢宇鑫, 武卓越, 等. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的肝脏组织病理图像语义分割网络[J]. 模式识别与人工智能,2021,34(4):375-384.ZHANG A Q, KANG Y X, WU ZH Y, et al. Semantic segmentation network of pathological images of liver tissue based on multi-scale feature and attention mechanism[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 34(4): 375-384. (in Chinese) [23] 史健锋, 高治明, 王阿川. 结合ASPP与改进HRNet的多尺度图像语义分割方法研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(11):1497-1505. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2021-0093SHI J F, GAO ZH M, WANG A CH. Multi-scale image semantic segmentation based on ASPP and improved HRNet[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(11): 1497-1505. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2021-0093 [24] 魏丙财, 张立晔, 孟晓亮, 等. 基于深度残差生成对抗网络的运动图像去模糊[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(12):1693-1701.WEI B C, ZHANG L Y, MENG X L, et al. Motion image deblurring based on depth residual generative adversarial network[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(12): 1693-1701. (in Chinese) [25] WANG Y Y, WANG G Q, XU D G, et al. Terahertz spectroscopic diagnosis of early blast-induced traumatic brain injury in rats[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11(8): 4085-4098. doi: 10.1364/BOE.395432 [26] ZHU H Q, WANG H R, LIU J L, et al. Application of terahertz dielectric constant spectroscopy for discrimination of oxidized coal and unoxidized coal by machine learning algorithms[J]. Fuel, 2021, 293: 120470. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120470 [27] CAO C, ZHANG ZH H, ZHAO X Y, et al. Terahertz spectroscopy and machine learning algorithm for non-destructive evaluation of protein conformation[J]. Optical and Quantum Electronics, 2020, 52(4): 225. doi: 10.1007/s11082-020-02345-1 [28] LEBANOV L, TEDONE L, GHIASVAND A, et al. Random Forests machine learning applied to gas chromatography – mass spectrometry derived average mass spectrum data sets for classification and characterisation of essential oils[J]. Talanta, 2020, 208: 120471. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120471 [29] HUANG P J, CAO Y Q, CHEN J N, et al. Analysis and inspection techniques for mouse liver injury based on terahertz spectroscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(18): 26014-26026. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.026014 [30] WEI X, LI S, ZHU SH P, et al. Terahertz spectroscopy combined with data dimensionality reduction algorithms for quantitative analysis of protein content in soybeans[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2021, 253: 119571. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119571 [31] LIAQAT S, DASHTIPOUR K, ARSHAD K, et al. A hybrid posture detection framework: Integrating machine learning and deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9515-9522. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3055898 [32] AYGUL M A, NAZZAL M, EKTI A R, et al. . Spectrum occupancy prediction exploiting time and frequency correlations through 2D-LSTM[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), IEEE, 2020: 1-5. [33] DASHTIPOUR K, GOGATE M, ADEEL A, et al. Sentiment analysis of Persian movie reviews using deep learning[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23(5): 596. doi: 10.3390/e23050596 [34] HO C S, JEAN N, HOGAN C A, et al. Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman spectroscopy and deep learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4927. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12898-9 [35] DOAN V S, HUYNH-THE T, KIM D S. Underwater acoustic target classification based on dense convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 19: 1500905. [36] WANG C, SHI F, ZHAO M, et al. Convolutional neural network-based terahertz spectral classification of liquid contraband for security inspection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(17): 18955-18963. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3086478 -





 下载:
下载: