-
摘要:
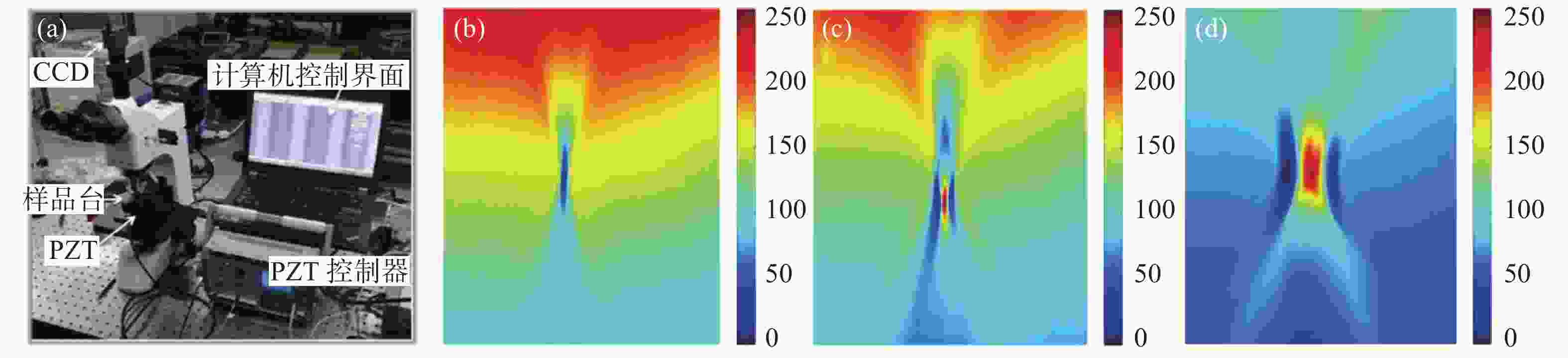
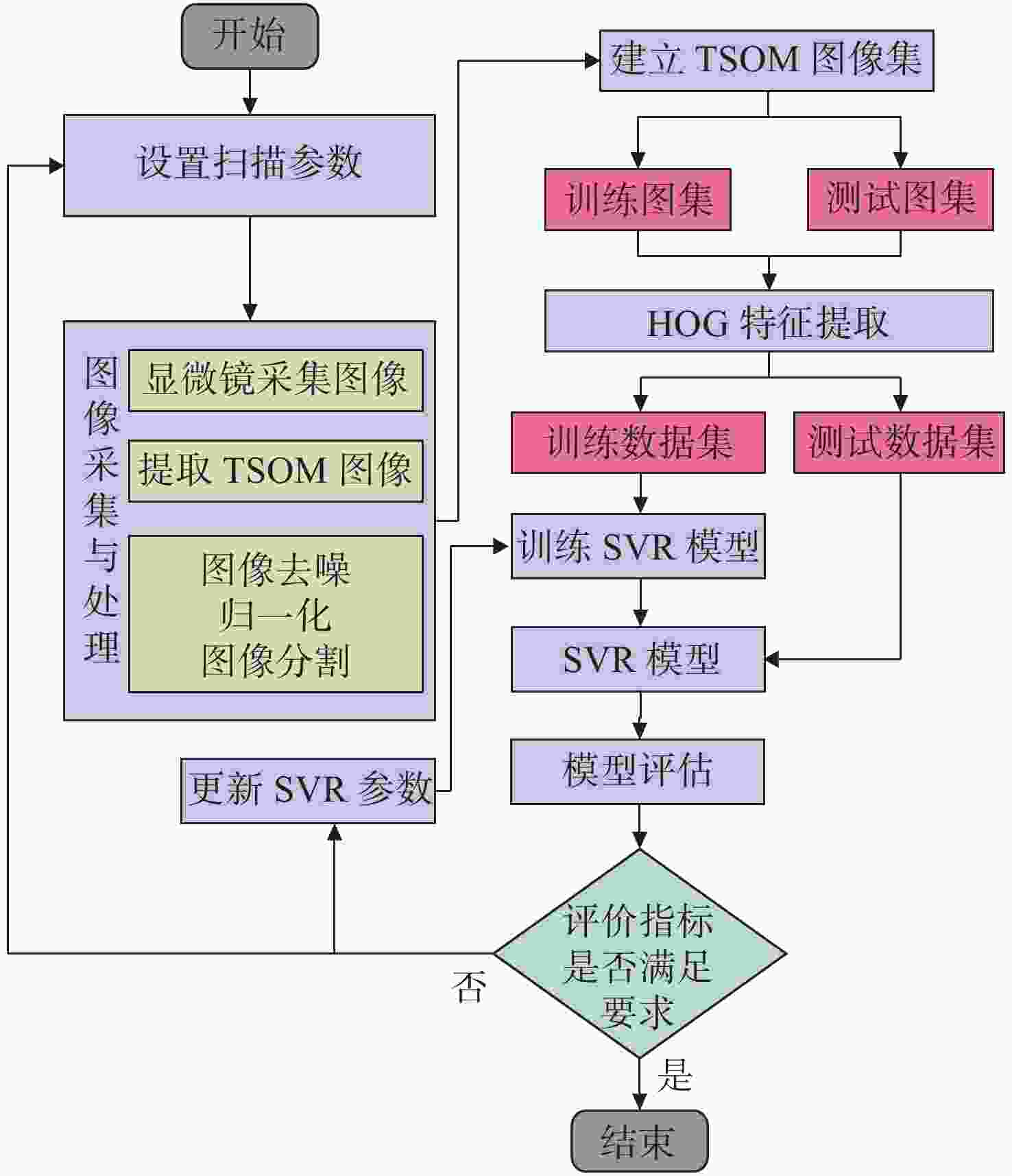
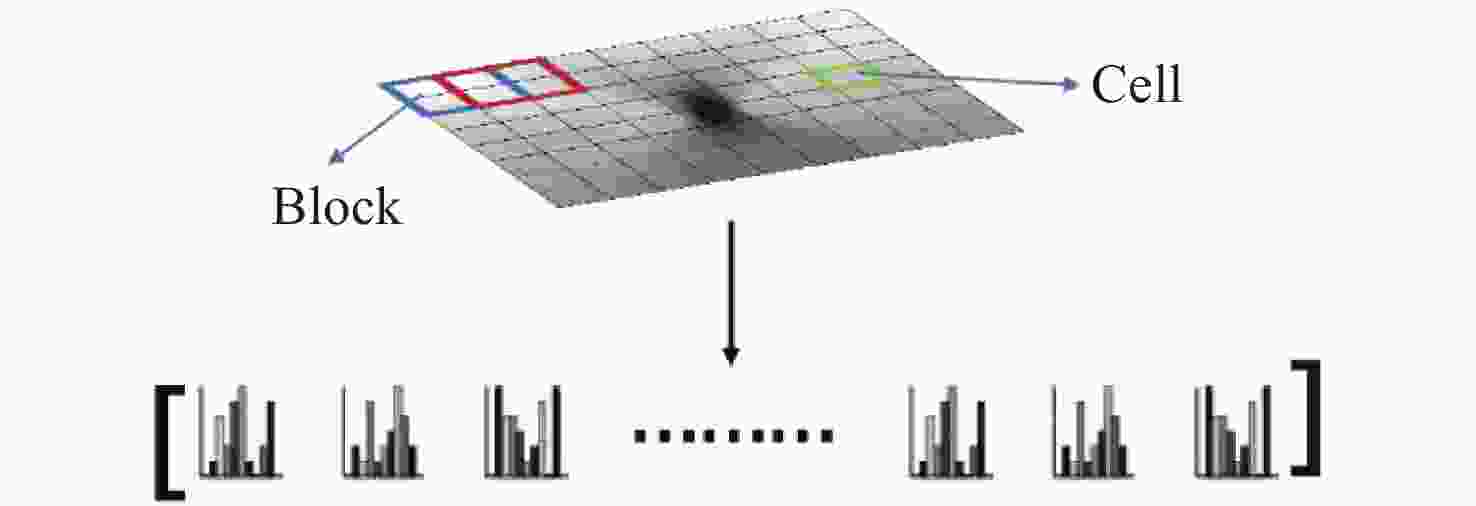
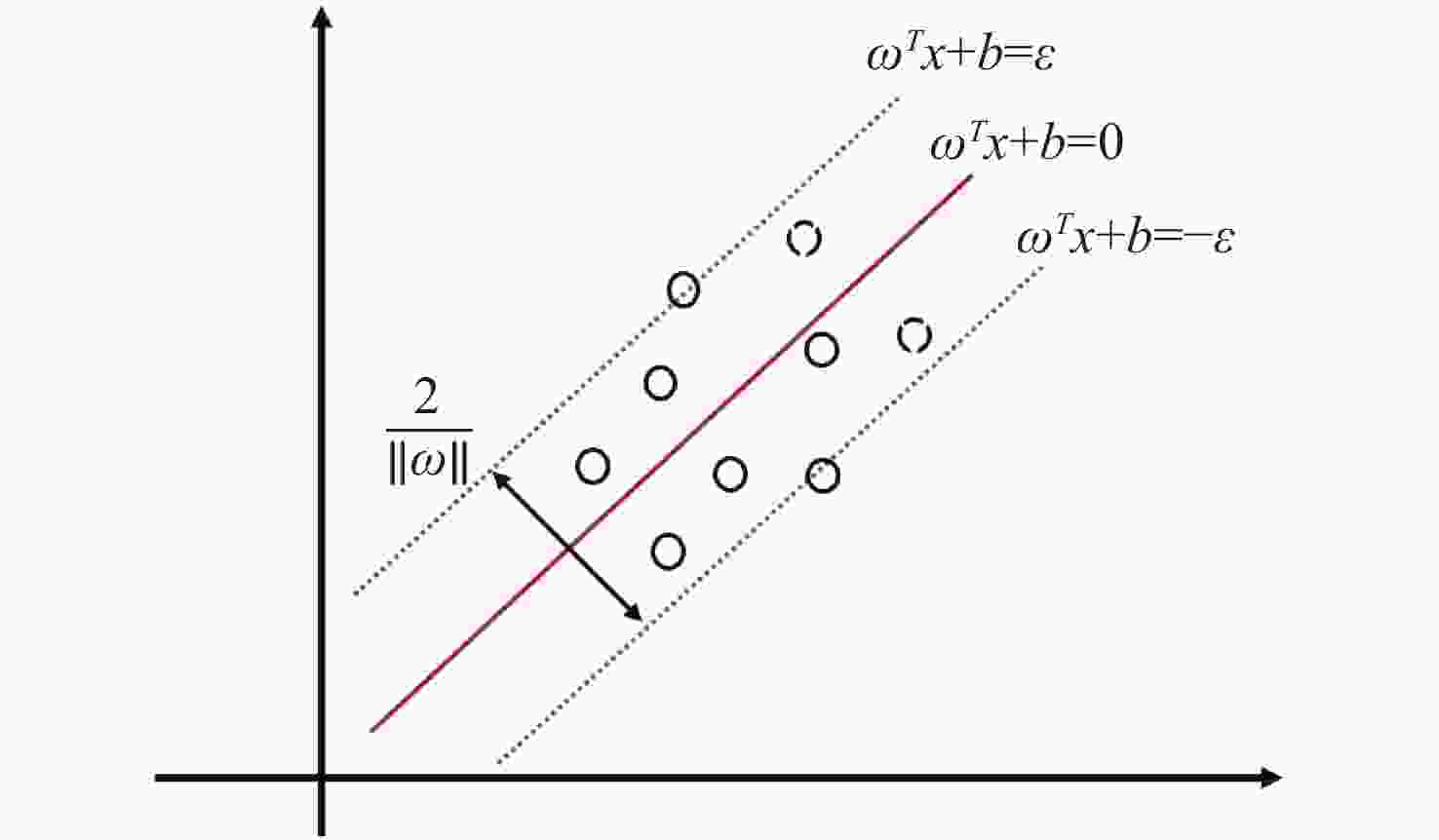
微电子机械系统(Micro-Electro-Mechanical System,MEMS)具有小型化、高集成度的特点,随着MEMS结构深宽比的不断增大,对MEMS结构尺寸的测量提出更高的要求。过焦扫描光学显微技术(Through-focus Scanning Optical Microscopy,TSOM)是一种高精度无损的光学测量方法,通过采集一组离焦图并沿扫描方向截取TSOM图像,利用库匹配的方法从中提取待测结构的尺寸信息。该方法对于纳米级结构测量有着极高的灵敏度,然而对于微米级特征尺寸存在建库困难且易受环境干扰的问题。本文针对微米级MEMS沟槽结构,在传统的光学显微镜基础上进行改造,建立了TSOM光学系统采集离焦图像,利用图像特征提取方法生成TSOM特征向量集,结合机器学习的方法建立不同槽宽尺寸的回归预测模型,对微米级MEMS槽宽尺寸实现纳米级测量精度,单点重复性测量2 μm槽宽的相对标准差(Relative Standard Deviation,RSD)在1%左右,10 μm和30 μm槽宽RSD分别低于0.2%和0.35%,结果表明该方法对于微米级MEMS沟槽测量具有极高的应用前景。
Abstract:Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) have the characteristics of miniaturization and high integration. As the high aspect ratio of MEMS increases, the measurement of MEMS feature size faces greater challenges. Through-focus Scanning Optical Microscopy (TSOM) technology is a high-precision and nondestructive optical measurement method. TSOM images are captured along the scanning direction by collecting a set of defocused images and the size information of the structure is extracted from TSOM images by the library matching method. This method is highly sensitive and suitable for nano-scale structure measurements, but it is difficult to build a database for micron-scale features and is susceptible to environmental interference. In this paper, a TSOM optical system is established and traditional optical microscopy is used to collect a set of defocused images. The TSOM’s feature vector set is obtained by the image feature extraction method and is combined with machine learning to establish MEMS groove regression prediction models with different feature sizes. The results show that the above method can achieve nano-scale high precision measurement of a MEMS groove width and the single point repeatability measurement has great performance. The Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) of 2 μm width is about 1%, and the RSD of 10 μm and 30 μm width are respectively lower than 0.2% and 0.35%. This method has very high application prospects for micron MEMS groove structure measurement.
-
Key words:
- MEMS /
- machine learning /
- TSOM /
- micro-nano measuring
-
表 1 样品参数
Table 1. Sample parameters
样品编号 设计槽宽/μm 槽深/μm 深宽比 电镜实测槽宽/μm 1 2 24 12∶1 2.21/2.52/2.61/2.86/3.06 2 2 200 100∶1 1.79/1.98/2.19/2.58 3 10 34 3.4∶1 10.5/10.7/10.8/11.1/11.3 4 10 106 10.6∶1 10.8/11/11.3/11.7 5 30 38 1.3∶1 30.6/30.9/31/31.2/31.5 6 30 236 7.9∶1 31.4/31.8/32.1/33.1 -
[1] 秦雷, 谢晓瑛, 李君龙. MEMS技术发展现状及未来发展趋势[J]. 现代防御技术,2017,45(4):1-5,23.QIN L, XIE X Y, LI J L. Development status and future development trend of MEMS technology[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2017, 45(4): 1-5,23. (in Chinese) [2] 穆继亮, 郭茂香, 刘冰, 等. 高深宽比硅基微纳结构制造方法及其应用[J]. 半导体技术,2013,38(5):321-327.MU J L, GUO M X, LIU B, et al. Fabrication methods and applications of silicon micro/nanometer structures with high aspect ratio[J]. Semiconductor Technology, 2013, 38(5): 321-327. (in Chinese) [3] 吴俊杰, 李源. 基于纳米测量机的微结构三维坐标测量[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(10):2252-2259. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202810.2252WU J J, LI Y. Three-dimensional coordinate measurement of microstructures based on Nano measuring machine[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(10): 2252-2259. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202810.2252 [4] 张冬至, 胡国清. 微机电系统关键技术及其研究进展[J]. 压电与声光,2010,32(3):513-520.ZHANG D ZH, HU G Q. Key technologies of micro-electromechanical system and its recent progress[J]. Piezoelectrics &Acoustooptics, 2010, 32(3): 513-520. (in Chinese) [5] OGURA T. A high contrast method of unstained biological samples under a thin carbon film by scanning electron microscopy[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2008, 377(1): 79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.09.097 [6] 冯斌, 王建华. 表面形貌光学法测量技术[J]. 计量与测试技术,2005,32(6):4-6.FENG B, WANG J H. The optical means used in measuring surface microtopography[J]. Metrology &Measurement Technique, 2005, 32(6): 4-6. (in Chinese) [7] SCHAPER A, RÖßLE M, FORMANEK H, et al. Complementary visualization of mitotic barley chromatin by field-emission scanning electron microscopy and scanning force microscopy[J]. Journal of Structural Biology, 2000, 129(1): 17-29. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1999.4203 [8] ATTOTA R, SILVER R, BARNES B M. Optical through-focus technique that differentiates small changes in line width, line height, and sidewall angle for CD, overlay, and defect metrology applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 6922: 69220E. doi: 10.1117/12.777205 [9] ATTOTA R. TSOM method for nanoelectronics dimensional metrology[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2011, 1395(1): 57-63. [10] ATTOTA R, DIXSON R G, VLADÁR A E. Through-focus scanning optical microscopy[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8036: 803610. doi: 10.1117/12.884706 [11] VARTANIAN V, ATTOTA R, PARK H, et al. TSV reveal height and dimension metrology by the TSOM method[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8681: 86812F. doi: 10.1117/12.2012609 [12] ATTOTA R. Noise analysis for through-focus scanning optical microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(4): 745-748. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.000745 [13] ATTOTA R K, KANG H, SCOTT K, et al. Nondestructive shape process monitoring of three-dimensional, high-aspect-ratio targets using through-focus scanning optical microscopy[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2018, 29(12): 125007. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aae4c2 [14] ATTOTA R. Through-focus or volumetric type of optical imaging methods: a review[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2018, 23(7): 070901. [15] LEE J H, PARK J H, JEONG D, et al. Tip/tilt-compensated through-focus scanning optical microscopy[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 10023: 100230P. [16] QU Y F, HAO J L, PENG R J. Machine-learning models for analyzing TSOM images of nanostructures[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(23): 33978-33998. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.033978 [17] PENG R J, JIANG J, REN J J, et al. Statistical character analysis for through-focus scanning optical microscopy in double floating variables measurement applications[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2021, 141: 106560. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2021.106560 [18] 葛德彪, 闫玉波. 电磁波时域有限差分方法[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2002.GE D B, YAN Y B. Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2002. (in Chinese) [19] DALAL N, TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2005: 886-893. [20] 张瑞琰, 姜秀杰, 安军社, 等. 面向光学遥感目标的全局上下文检测模型设计[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1302-1313. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0057ZHANG R Y, JIANG X J, AN J SH, et al. Design of global-contextual detection model for optical remote sensing targets[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1302-1313. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0057 [21] 耿庆田, 赵浩宇, 于繁华, 等. 基于改进HOG特征提取的车型识别算法[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):174-181. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0174GENG Q T, ZHAO H Y, YU F H, et al. Vehicle type recognition algorithm based on improved HOG feature[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 174-181. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0174 [22] CORTES C, VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273-297. [23] 闫国华, 朱永生. 支持向量机回归的参数选择方法[J]. 计算机工程,2009,35(14):218-220.YAN G H, ZHU Y SH. Parameters selection method for support vector machine regression[J]. Computer Engineering, 2009, 35(14): 218-220. (in Chinese) [24] 于连栋, 常雅琪, 赵会宁, 等. 基于支持向量回归机的机器人定位精度提高[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(12):2646-2654. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2646YU L D, CHANG Y Q, ZHAO H N, et al. Method for improving positioning accuracy of robot based on support vector regression[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 2646-2654. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2646 [25] 邹永宁, 张智斌, 李琦, 等. 基于Hessian矩阵和支持向量机的CT图像裂纹分割[J]. 光学 精密工程,2021,29(10):2517-2527. doi: 10.37188/OPE.2021.0349ZOU Y N, ZHANG ZH B, LI Q, et al. Crack detection and segmentation in CT images using Hessian matrix and support vector machine[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(10): 2517-2527. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.2021.0349 -






 下载:
下载: