-
摘要:
光学成像技术具备高分辨、多尺度、多维度、易集成以及低辐射等优势,在生物医学领域发挥重要的作用。在内窥镜领域,如何进行内窥图像信息的获取、处理及可视化是光学成像技术要解决的核心问题,在医学临床中获取内窥镜所观察部位的跨尺度图像有利于医师对于患者病情的诊断以及提升术中操作的精确程度。本文从跨尺度光学成像技术在内窥镜领域的应用入手,重点阐述了目前内窥镜临床中用于获取跨尺度图像的光学系统类型,包括跨尺度变焦光学系统、光纤扫描成像系统、多通道成像系统等,说明了这些跨尺度光学内窥镜系统如何获取跨尺度图像,并对跨尺度光学成像在内窥镜领域的未来发展做了展望。
Abstract:Due to the advantages of high resolution, multi-scale, multi-dimension, low radiation and easy to integrate, optical imaging technology plays an important role in biomedical field. In the field of endoscopy, how to obtain, process and visualize the endoscopic image information is the core of the problem what optical imaging technology need to solve. The obtaining of trans-scale endoscopic image of patients in the medical clinical is more advantageous to the surgeon for the diagnosis of patients and can improve in accuracy of the operation. The review starts with the application of trans-scale optical imaging technology in the field of endoscopy, focusing on the different optical systems to obtain trans-scale images in clinical endoscopy, including trans-scale optical zoom system, multi-channel imaging system, fiber-scanning imaging system, and expounds its progress and future trends.
-
Key words:
- endoscopic imaging /
- trans-scale imaging /
- optical zoom /
- scanning imaging /
- multichannel imaging
-
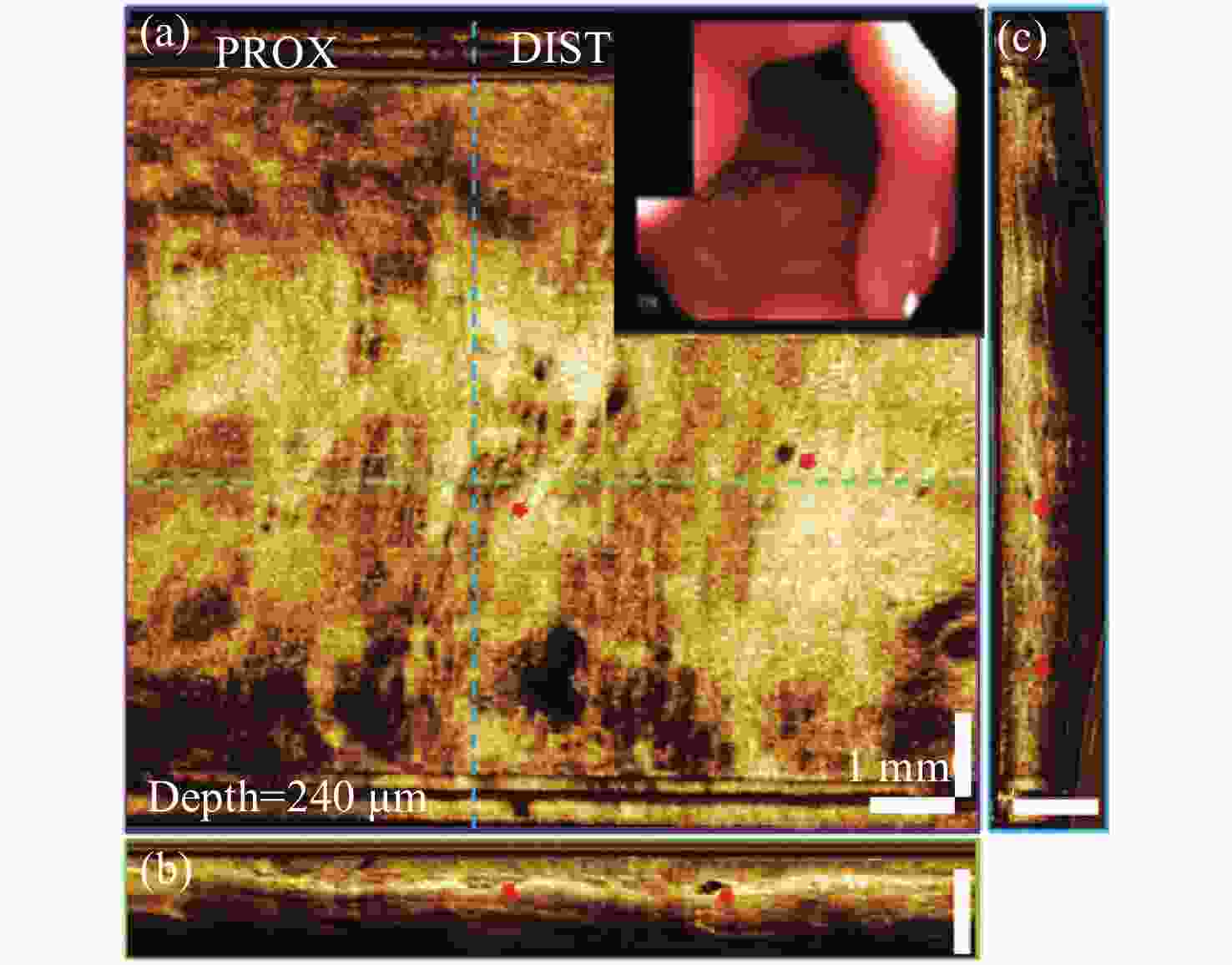
图 7 正常食管OCT。(a)240 μm组织深度的en face OCT图像;(b)沿回拉方向的横切面图像;(c)旋转方向横切面图像[45]
Figure 7. OCT of the normal esophagus.(a) En face OCT image at 240 μm depth. The inset shows an endoscopic view of the esophagus obtained prior to endoscopic OCT imaging; (b) cross-sectional image along the pullback direction; (c) cross-sectional image along the rotary direction[45]
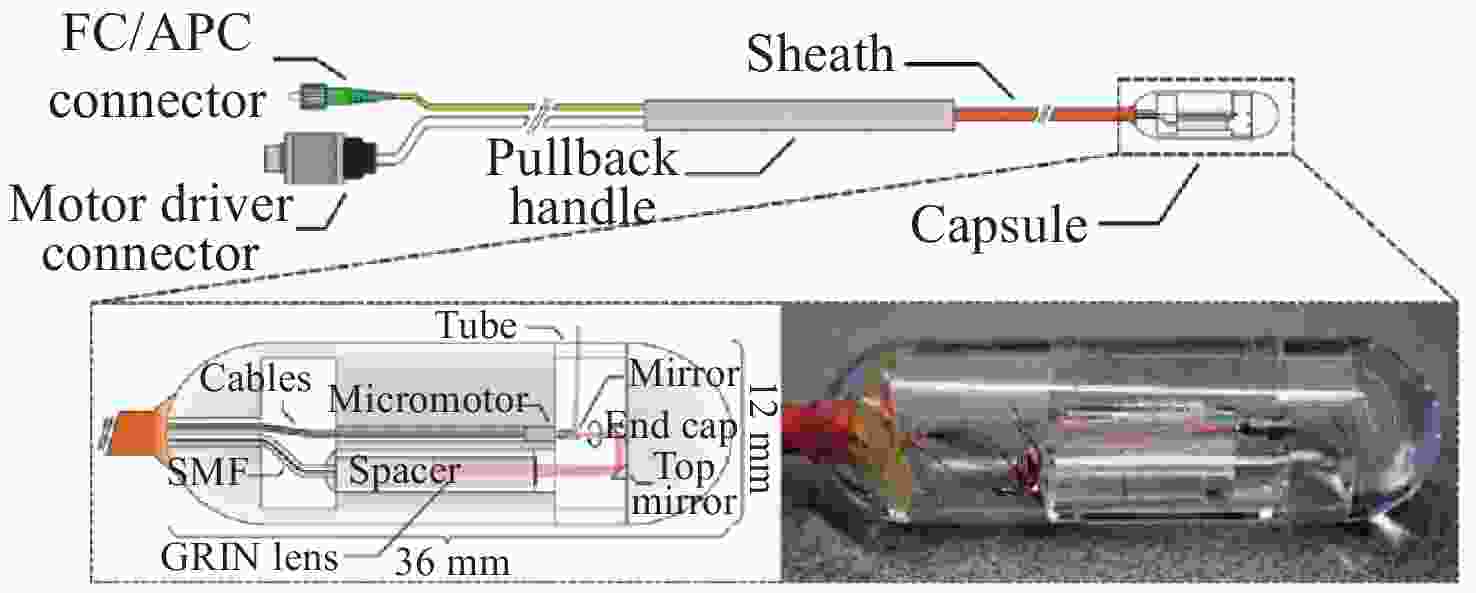
图 8 系线胶囊示意图和照片[47]
Figure 8. Schematic of the tethered capsule and photo of the capsule
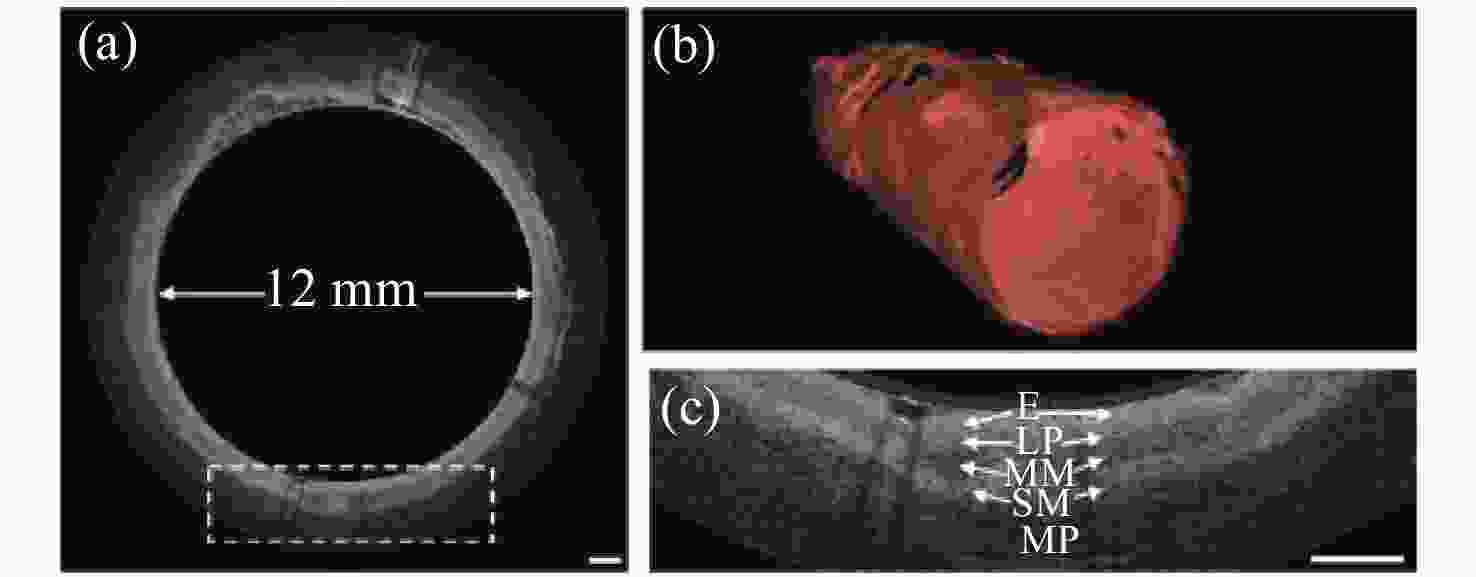
图 9 食管OCT图像。(a)猪食道代表性横切面图(剪去内壁);(b)沿4.5 cm拉回距离进行3D重建;(c)(b)中虚线框的放大区域。比例尺为1 mm[47]
Figure 9. OCT imageof esophagus. (a) Representative cross-sectional image of swine esophagus (inner wall of the tube is cropped out); (b) 3D reconstruction along a 4.5 cm pull-back distance; (c) zoomed-in area of the dotted box in (b). Scale bar is 1 mm[47]
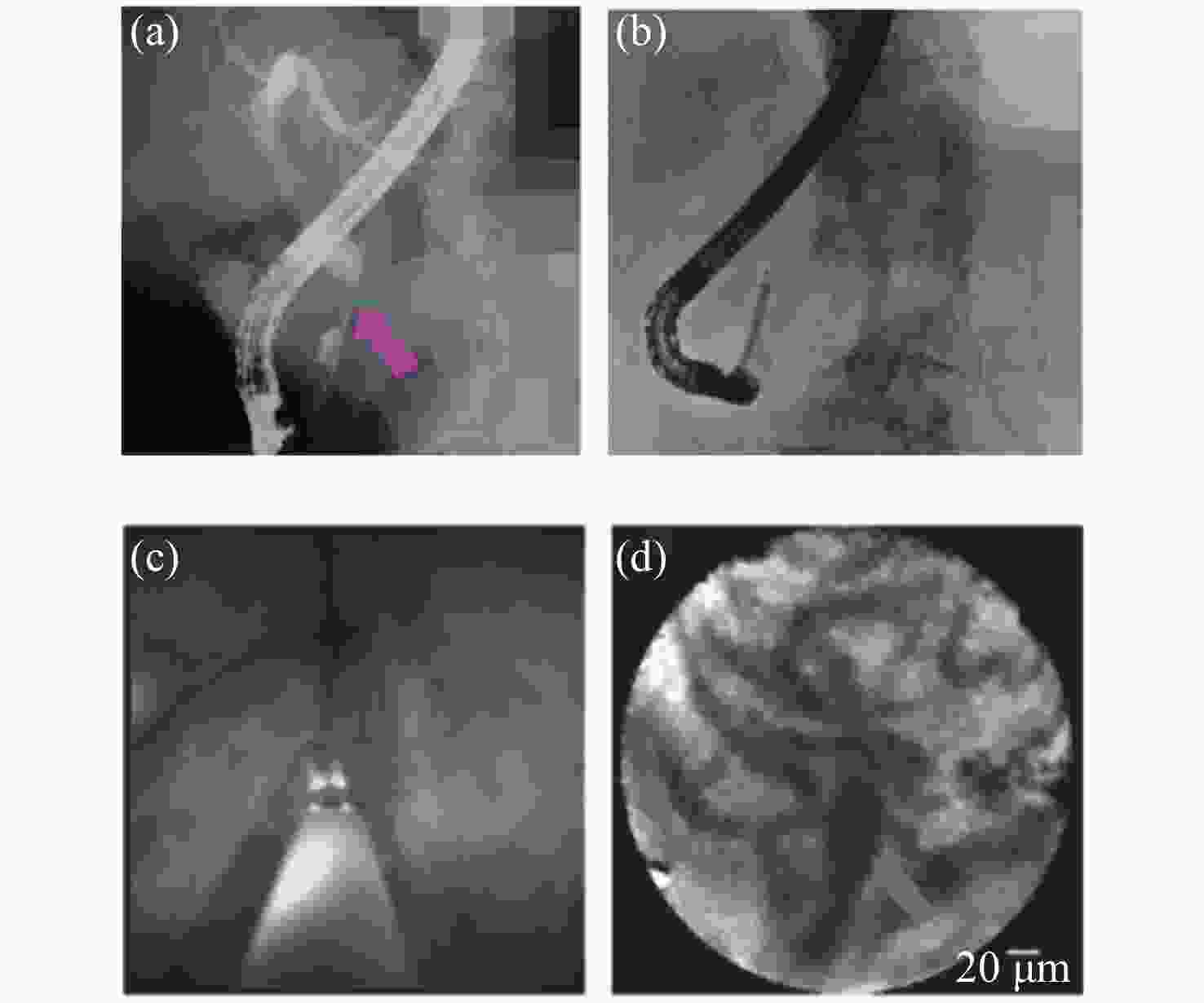
图 10 自身免疫性胆管炎。(a)胆管造影显示胆道狭窄(粉红色箭头);(b)POCS下的pCLE执行;(c)胆管镜显示微红色乳头状颗粒状表面;(d)pCLE显示Paris分类增厚网状结构[48]
Figure 10. Autoimmune cholangitis. (a) Cholangiography shows the biliary stricture (pink arrow); (b) pCLE under the direct view of POCS was performed; (c) cholangioscopy shows a reddish papillogranular surface; (d) pCLE shows a thickened reticular structure in the Paris classification[48]
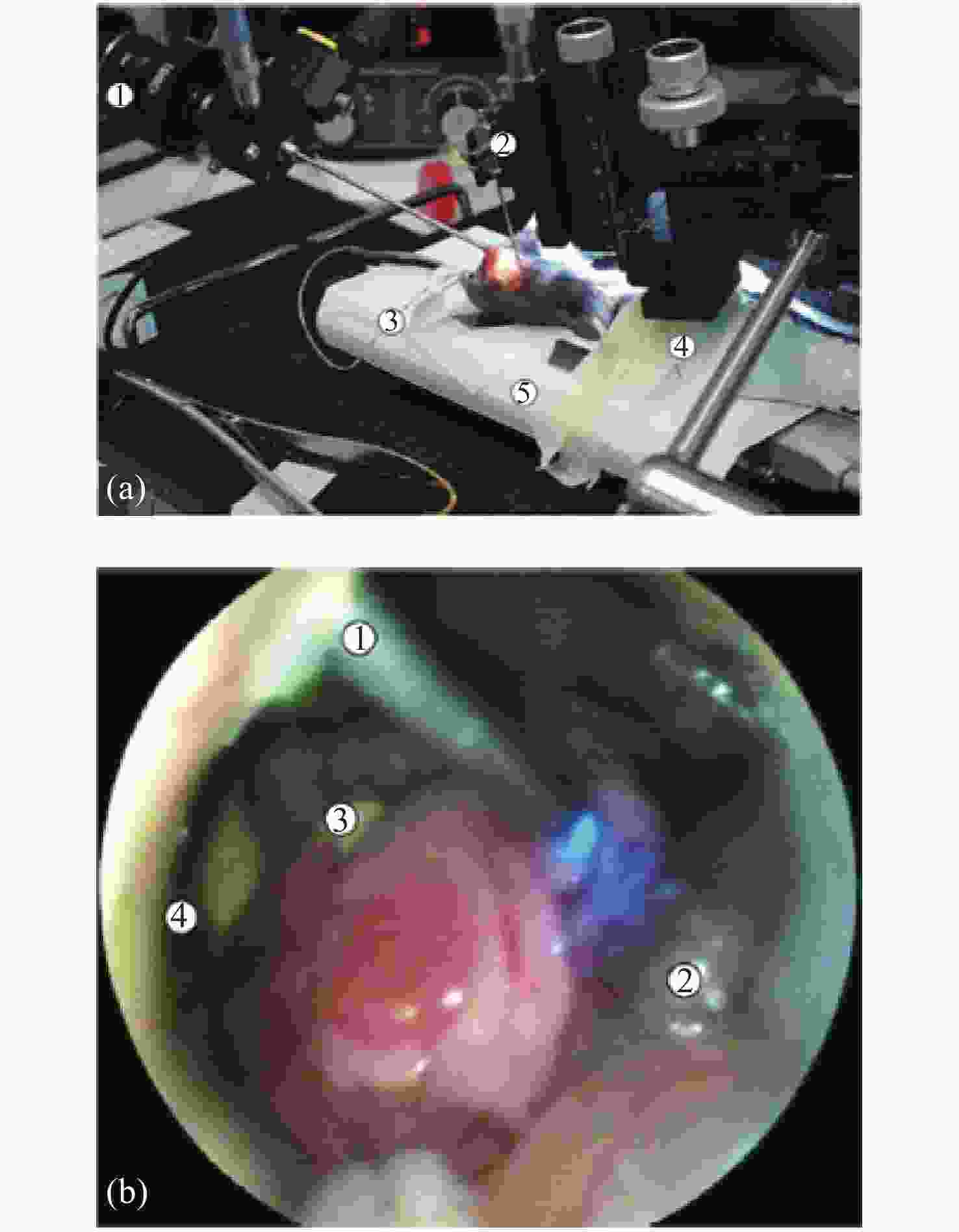
图 11 内窥镜系统。(a)手术过程照:1. 商用内窥镜;2. 具有用于光纤束的套管针的微操作器;3. 吹气管。(b)在活体成像过程中,通过商业内窥镜进行内窥镜观察:1. 用于光纤束和蓝色照明光纤的套管针;2. 肠套;3. 胰腺;4. 肝脏[49]
Figure 11. Endoscope system. (a) Photograph of the surgical procedure: 1. commercial endoscope; 2. micromanipulator with the trocar for the fiber bundle; 3. insufflation-pipe. (b) Endoscopic view through the commercial endoscope during the imaging procedure in vivo: 1. trocar for the fiber-optic with fiber bundle and blue illumination; 2. intestinal loop; 3. pancreas; 4. liver[49]
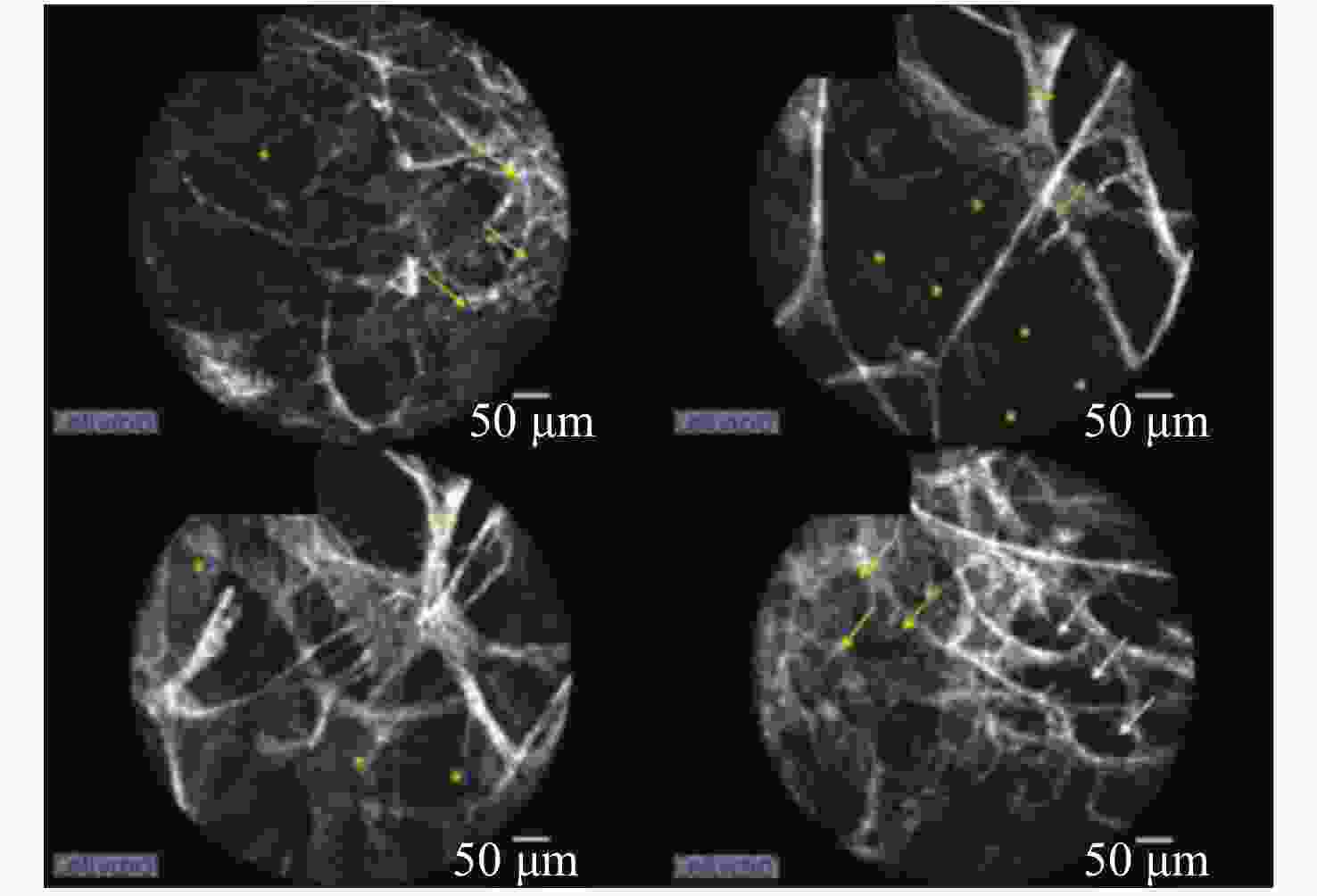
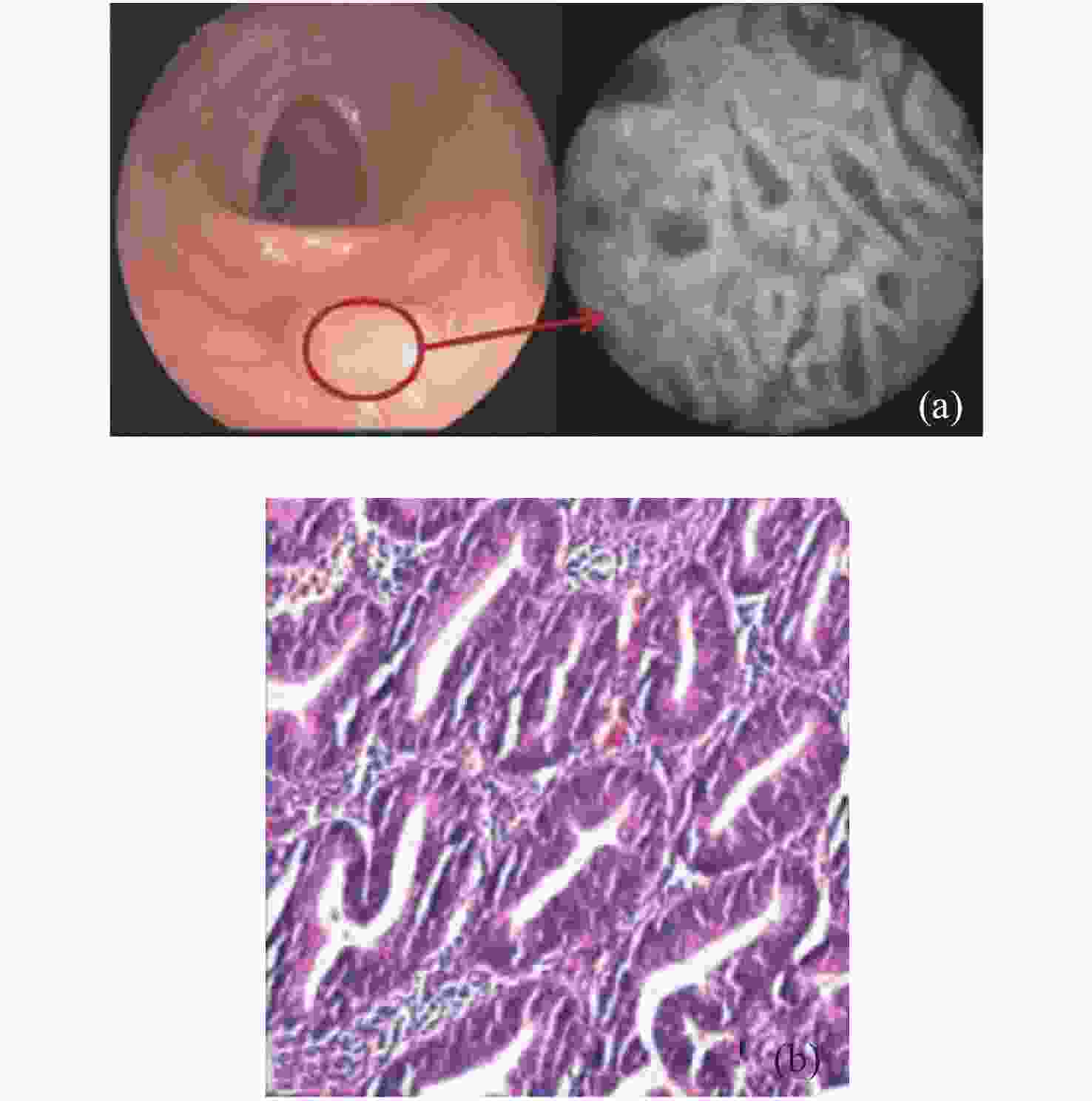
图 13 左上叶肺组织的pCLE图像。肺泡内纤维厚度(黄线),弹性结构密度增加(白箭头),直至肺泡结构消失(黄箭头),肺泡内分泌物大滴(*)[50]
Figure 13. pCLE images of lung tissue of the left upper lobe. Intra alveolar fiber thickness (yellow line), increased density of elastic structures (white arrow), up to disappearance of alveolar structures (yellow arrow), and large drops of intra alveolar secretions (*)[50]
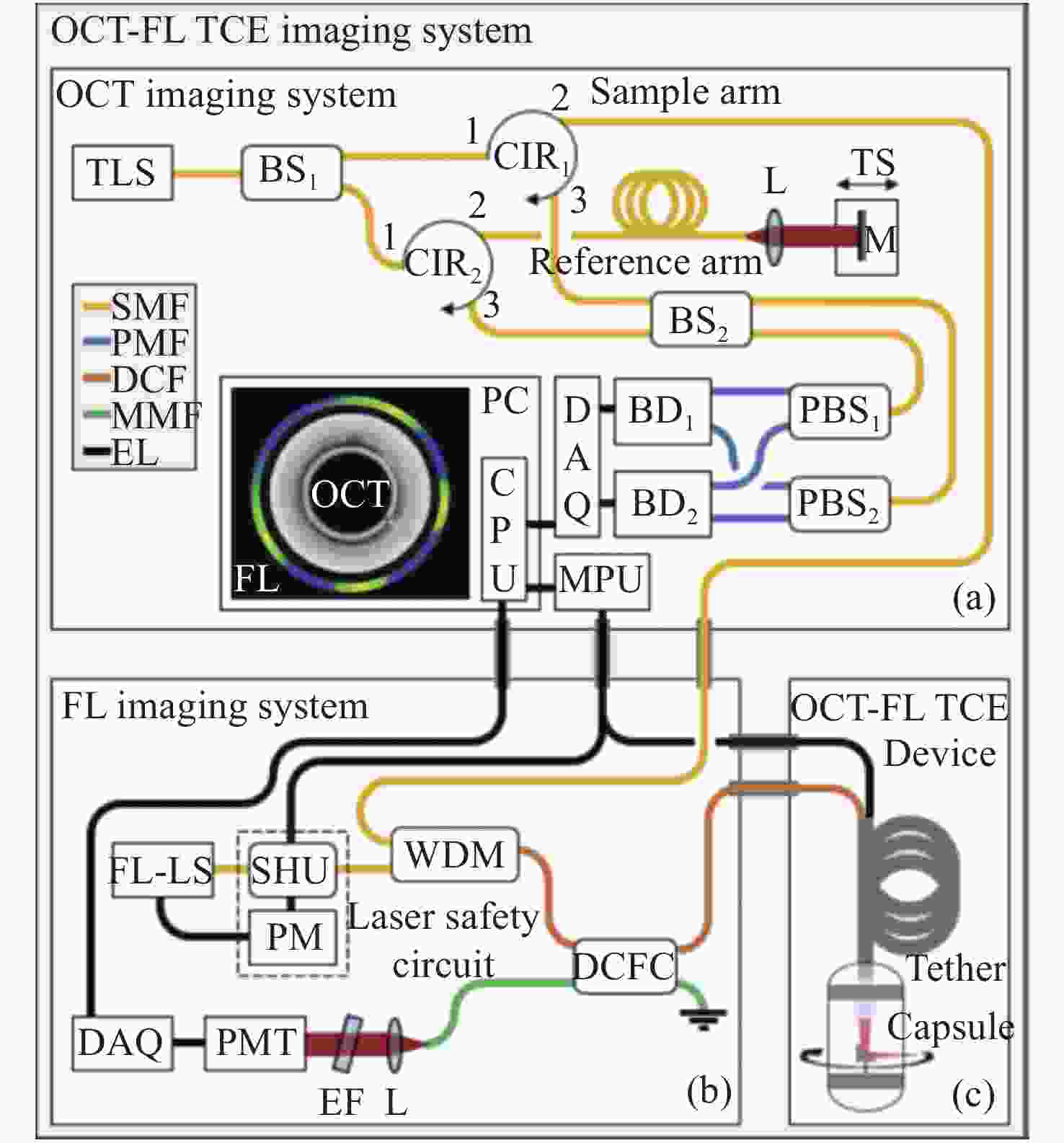
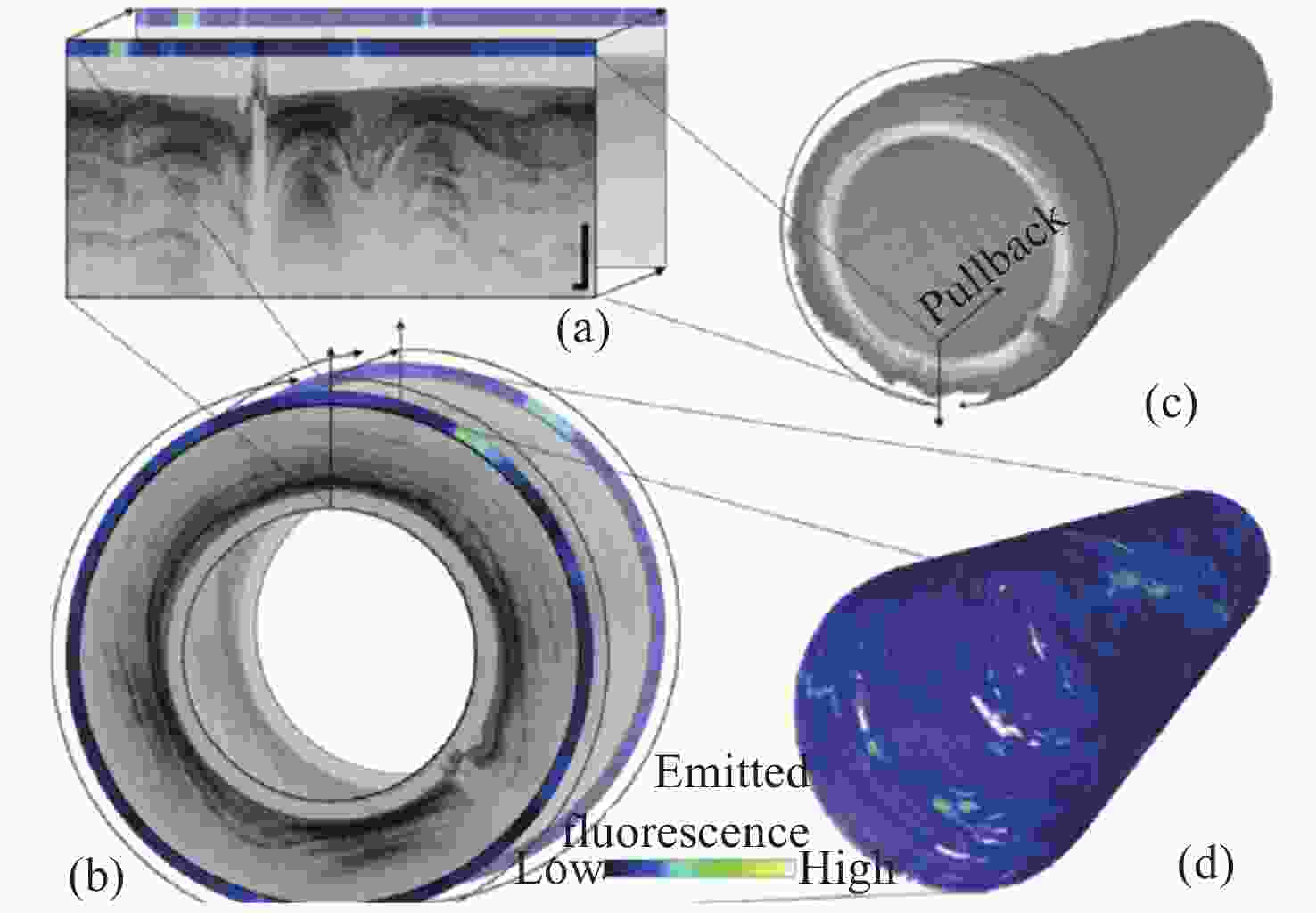
图 17 活体猪食管代表性图像的OCT-FL数据显示。在同一横截面扫描的极坐标表示(a)和笛卡尔表示(b),分别描述2D灰度OCT和1D假色FL数据。(c)沿食管轴向延伸的横截面的OCT图的3D表示(反转灰度:从低到高对应从黑到白)。(d)沿食道轴向延伸的FL表面图的3D表示。比例尺:1 mm。[55]
Figure 17. OCT-FL data display of representative images from swine esophagus, in vivo. (a) Polar and (b) cartesian representation of the same crosssectional scan, depicting 2D grayscale OCT and 1D false color FL data. (c) 3D representation of the cross-sectional OCT map along the axial extension of the esophagus (inverted grayscale: low-to-high as black-to-white). (d) 3D representation of the FL surface map along the axial extension of the esophagus. Scale bars: 1 mm.[55]
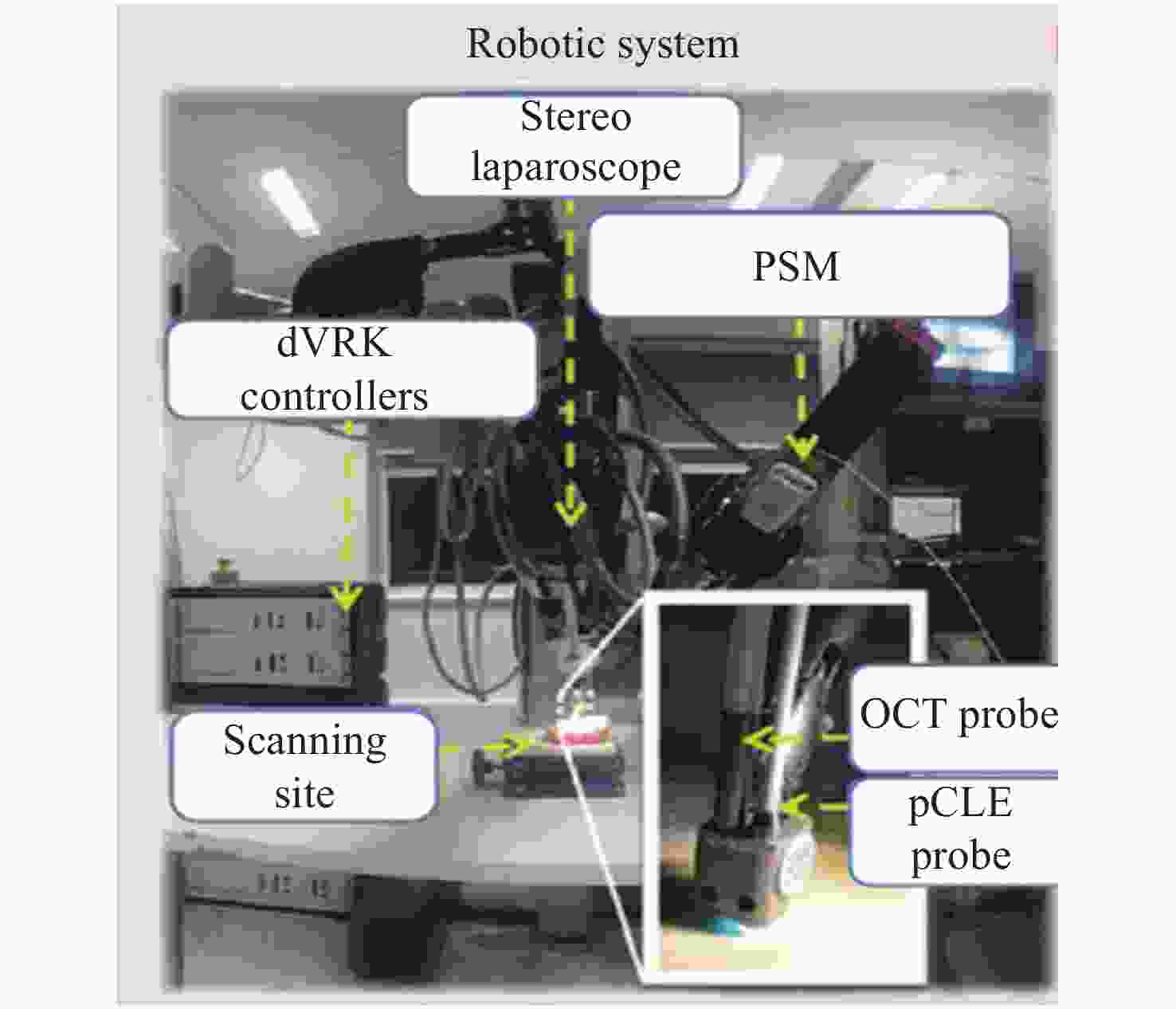
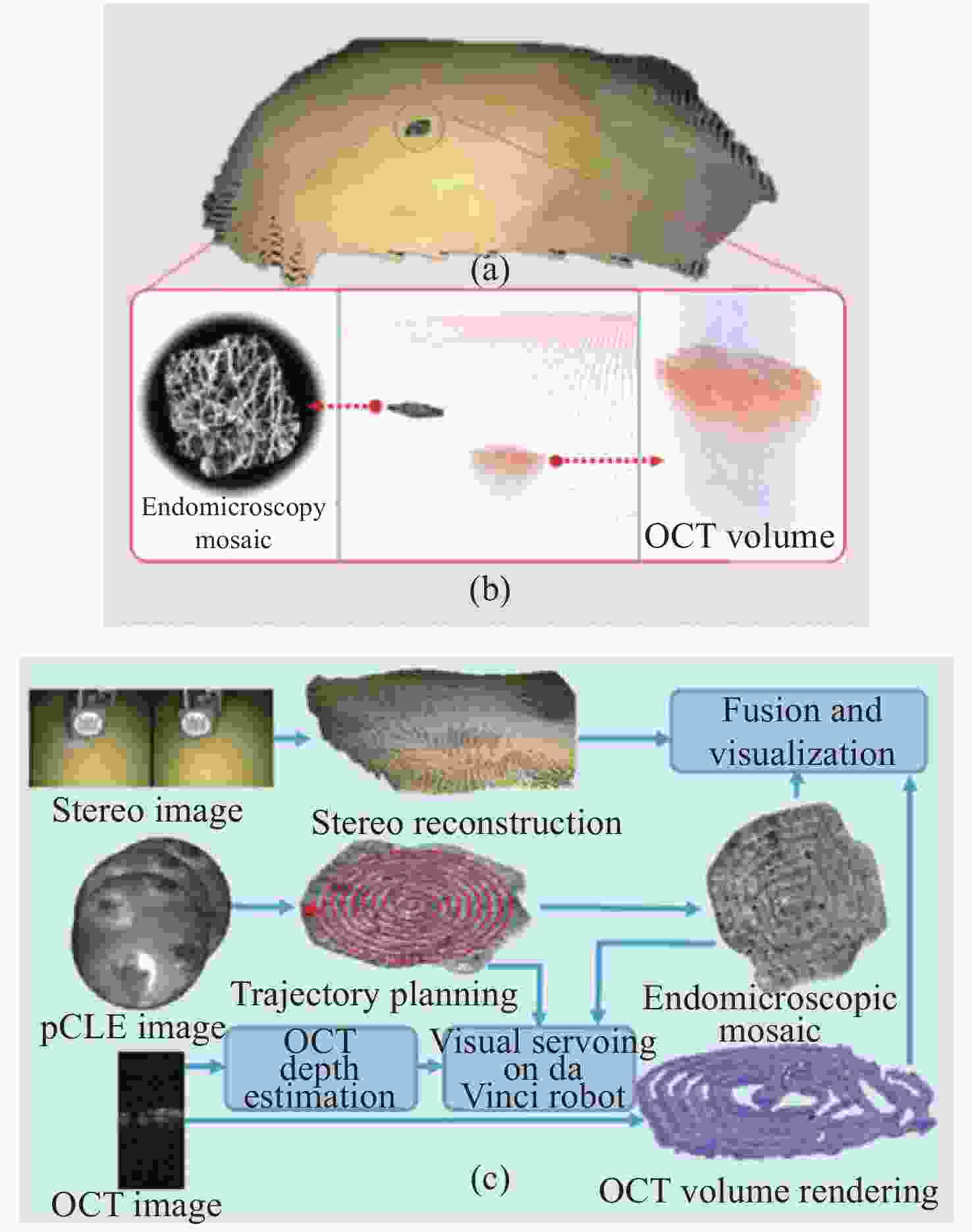
图 19 跨尺度融合案例。(a)宏观立体重建;(b)将拼接后的图像叠加在立体图像上,与微观尺度图像建立联系;(c)自主光学活检探针扫描和多尺度融合的实现步骤[57]
Figure 19. An example of trans-scale fusion. (a) A macroscale stereo reconstruction; (b) to link with the microscale, by adding the mosaic image to the stereo reconstruction; (c) implementation steps involved for autonomous optical biopsy probe scanning and multiscale fusion[57]
-
[1] 付玲, 骆清铭. 生物医学光学成像的进展与展望[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2020,50(11):1222-1236. doi: 10.1360/SSV-2020-0263FU L, LUO Q M. Progress and prospect of biomedical optical imaging[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2020, 50(11): 1222-1236. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/SSV-2020-0263 [2] ZAHRAN S A E S, SAEED R A H, ELAZIZY I M. Remote sensing based water resources and agriculture spatial indicators system[J]. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 2022, 25(2): 515-527. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrs.2022.02.002 [3] YANG L, CHEN M, ZHU Q, et al. Development of a small-diameter and high-resolution industrial endoscope with CMOS image sensor[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2019, 296: 17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2019.04.026 [4] PRENGÈRE L, KULCSÁR C, RAYNAUD H F. Zonal-based high-performance control in adaptive optics systems with application to astronomy and satellite tracking[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2020, 37(7): 1083-1099. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.391484 [5] 刘飞, 吴晓琴, 段景博, 等. 浅谈计算成像在光电探测中的应用(特邀)[J]. 光子学报,2021,50(10):1011001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20215010.1011001LIU F, WU X Q, DUAN J B, et al. An Introduction of application of computational imaging in photoelectric detection (invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(10): 1011001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20215010.1011001 [6] COSSAIRT O, NAYAR S. Spectral focal sweep: extended depth of field from chromatic aberrations[C]. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), IEEE, 2010: 1-8. [7] WANG X H, LI D Y, ZHANG G. Panoramic stereo imaging of a bionic compound-eye based on binocular vision[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(6): 1944. doi: 10.3390/s21061944 [8] WANG Y Y, SHI CH Y, XU H R, et al. A compact bionic compound eye camera for imaging in a large field of view[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2021, 135: 106705. [9] 裴红星, 刘金达, 葛佳隆, 等. 图像拼接技术综述[J]. 郑州大学学报(理学版),2019,51(4):1-10,29.PEI H X, LIU J D, GE J L, et al. A review on image mosaicing techniques[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Natural Science Edition) , 2019, 51(4): 1-10,29. (in Chinese) [10] LIU Y Y, LI Q W, LI Y, et al. High-resolution multi-wavelength lensless diffraction imaging with adaptive dispersion correction[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(5): 7197-7209. doi: 10.1364/OE.419128 [11] YIN W X, HE K J, XU D, et al. Significant target analysis and detail preserving based infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2022, 121: 104041. [12] LEE M H, LEE T K. Application of fusion-fluorescence imaging using indocyanine green in endoscopic endonasal surgery[J]. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 2022, 98: 45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2022.01.023 [13] VANI V, PRASHANTH K V M. Image enhancement of wireless capsule endoscopy frames using image fusion technique[J]. IETE Journal of Research, 2021, 67(4): 463-475. doi: 10.1080/03772063.2018.1554459 [14] XU M, LIU Y T, YUAN Y, et al. Variable-focus liquid lens based on electrically responsive fluid[J]. Optics Letters, 2022, 47(3): 509-512. doi: 10.1364/OL.447182 [15] WANG Y ZH, LI P CH, GUPTA U, et al. . Tunable soft lens of large focal length change[J/OL]. Soft Robotics, 2021(2021-08-12).https://doi.org/10.1089/soro.2021.0036. [16] PUSENKOVA A, SOVA O, GALSTIAN T. Electrically variable liquid crystal lens with spiral electrode[J]. Optics Communications, 2022, 508: 127783. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127783 [17] 张伟, 牛春阳, 游兴海, 等. 高倍率大视场细胞内镜成像系统研究[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(17):1717001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1717001ZHANG W, NIU CH Y, YOU X H, et al. Endocytoscopic imaging system with high magnification and large field of view[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(17): 1717001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1717001 [18] KUMAGAI Y, KAWADA K, YAMAZAKI S, et al. Current status and limitations of the newly developed endocytoscope GIF-Y0002 with reference to its diagnostic performance for common esophageal lesions[J]. Journal of Digestive Diseases, 2012, 13(8): 393-400. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2012.00612.x [19] KUMAGAI Y, TAKUBO K, KAWADA K, et al. A newly developed continuous zoom-focus endocytoscope[J]. Endoscopy, 2016, 49(2): 176-180. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-119267 [20] 马场智之. 内窥镜用物镜及内窥镜: 日本, 113721355A[P]. 2021-11-30.TOMAYUKI B. Objective lens for an endoscope and endoscope: JI, 113721355A[P]. 2021-11-30. (in Chinese) [21] 那须幸子. 内窥镜用变倍光学系统及内窥镜: 中国, 111630429A[P]. 2020-09-04.SACHIKO N. Variable power optical system for endoscope and endoscope: CN, 111630429A[P]. 2020-09-04. (in Chinese) [22] ZOU Y CH, CHAU F S, ZHOU G Y. Ultra-compact optical zoom endoscope using solid tunable lenses[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(17): 20675-20688. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.020675 [23] 郭鑫, 张薇, 速晋辉, 等. 可调焦胶囊内窥镜光学系统设计[J]. 光子学报,2015,44(5):0522004. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154405.0522004GUO X, ZHANG W, SU J H, et al. Design of a focus-tunable capsule endoscope system[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(5): 0522004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154405.0522004 [24] 邵晓鹏, 刘飞, 李伟, 等. 计算成像技术及应用最新进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(2):020001.SHAO X P, LIU F, LI W, et al. Latest progress in computational imaging technology and application[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(2): 020001. (in Chinese) [25] WU J M, LU ZH, JIANG D, et al. Iterative tomography with digital adaptive optics permits hour-long intravital observation of 3D subcellular dynamics at millisecond scale[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(12): 3318-3332.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.029 [26] SCHARF E, DREMEL J, KUSCHMIERZ R, et al. Video-rate lensless endoscope with self-calibration using wavefront shaping[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(13): 3629-3632. doi: 10.1364/OL.394873 [27] WANG J W, ZHAO Y. Lensless multispectral camera based on a coded aperture array[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(22): 7757. doi: 10.3390/s21227757 [28] MIRIROSTAMI S, KATKOVNIK V Y, EGUIAZARIAN K O. Extended DoF and achromatic inverse imaging for lens and lensless MPM camera based on wiener filtering of defocused OTFs[J]. Optical Engineering, 2021, 60(5): 051204. [29] BERGEN T, WITTENBERG T. Stitching and surface reconstruction from endoscopic image sequences: a review of applications and methods[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2016, 20(1): 304-321. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2384134 [30] 王霞, 赵家碧, 孙晶, 等. 偏振图像融合技术综述[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2021,42(6):9-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2021.06.002WANG X, ZAO J B, SUN J, et al. Review of polarization image fusion technology[J]. Spacecraft Recovery &Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(6): 9-21. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2021.06.002 [31] AZAM M A, KHAN K B, SALAHUDDIN S, et al. A review on multimodal medical image fusion: compendious analysis of medical modalities, multimodal databases, fusion techniques and quality metrics[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2022, 144: 105253. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105253 [32] 张丽霞, 曾广平, 宣兆成. 多源图像融合方法的研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与科学,2022,44(2):321-334. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2022.02.018ZHANG L X, ZENG G P, XUAN ZH CH. A survey of fusion methods for multi-source image[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2022, 44(2): 321-334. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2022.02.018 [33] TANG Y B, KORTUM A, PARRA S G, et al. In vivo imaging of cervical precancer using a low-cost and easy-to-use confocal microendoscope[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11(1): 269-280. doi: 10.1364/BOE.381064 [34] CORDOVA R, KIEKENS K, BURRELL S, et al. Sub-millimeter endoscope demonstrates feasibility of in vivo reflectance imaging, fluorescence imaging, and cell collection in the fallopian tubes[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2021, 26(7): 076001. [35] SI P, HONKALA A, DE LA ZERDA A, et al. Optical microscopy and coherence tomography of cancer in living subjects[J]. Trends in Cancer, 2020, 6(3): 205-222. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.008 [36] LI H M, LI Y, MENG Y L, et al. . Research on the resonance frequency reduction of the single fiber scanner[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 18th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks (ICOCN), IEEE, 2019: 1-3. [37] WU T, ZHANG L, WANG J M, et al. Miniaturized precalibration-based Lissajous scanning fiber probe for high speed endoscopic optical coherence tomography[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(8): 2470-2473. doi: 10.1364/OL.389364 [38] PIYAWATTANAMETHA W, COCKER E D, BURNS L D, et al. In vivo brain imaging using a portable 2.9 g two-photon microscope based on a microelectromechanical systems scanning mirror[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(15): 2309-2311. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.002309 [39] SEO Y H, PARK H C, JEONG K H. Electrothermal MEMS fiber scanner with lissajous patterns for endomicroscopic applications[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 29th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), IEEE, 2016: 367-370. [40] GIATAGANAS P, HUGHES M, PAYNE C J, et al. Intraoperative robotic-assisted large-area high-speed microscopic imaging and intervention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 66(1): 208-216. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2837058 [41] 刘磊, 吴威, 张冰, 等. 高分辨率光栅精密定位系统研究[J]. 红外,2020,41(5):35-39.LIU L, WU W, ZHANG B, et al. Research on high resolution grating precision positioning system[J]. Infrared, 2020, 41(5): 35-39. (in Chinese) [42] KAUR M, LANE P M, MENON C. Endoscopic optical imaging technologies and devices for medical purposes: state of the art[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(19): 6865-6865. doi: 10.3390/app10196865 [43] 吴彤, 霍文麒, 黄蕴智, 等. 用于内窥光学相干层析成像的小型化预标定Lissajous扫描光纤探头[J]. 物理学报,2021,70(15):150701. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210151WU T, HUO W L, HUANG Y ZH, et al. A miniaturized pre-calibration based Lissajous scanning fiber probe for endoscopic optical coherence tomography[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(15): 150701. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210151 [44] KAUR M, LANE P M, MENON C. Scanning and actuation techniques for cantilever-based fiber optic endoscopic scanners——a review[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(1): 251. doi: 10.3390/s21010251 [45] TSAI T H, LEE H C, AHSEN O O, et al. Ultrahigh speed endoscopic optical coherence tomography for gastroenterology[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2014, 5(12): 4387-4404. doi: 10.1364/BOE.5.004387 [46] ZHANG J, NGUYEN T, POTSAID B, et al. Multi-MHz MEMS-VCSEL swept-source optical coherence tomography for endoscopic structural and angiographic imaging with miniaturized brushless motor probes[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2021, 12(4): 2384-2403. doi: 10.1364/BOE.420394 [47] LÓPEZ-MARÍN A, SPRINGELING G, BEURSKENS R, et al. Motorized capsule for shadow-free OCT imaging and synchronous beam control[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(15): 3641-3644. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.003641 [48] TANISAKA Y, RYOZAWA S, NONAKA K, et al. Diagnosis of biliary strictures using probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy under the direct view of peroral cholangioscopy: results of a prospective study (with video)[J]. Gastroenterology Research and Practice, 2020, 2020: 6342439. [49] BAHLMANN J, MADRAHIMOV N, DANIEL F, et al. Establishment of a guided, in vivo, multi-channel, abdominal, tissue imaging approach[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 9224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65950-w [50] VASILEV I V, MAMENKO I S, MAKAROVA A V, et al. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in COVID-19[J]. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 2021, 89(4): 456-459. doi: 10.5603/ARM.a2021.0067 [51] 张朋涛, 杨西斌, 周伟, 等. 双模切换显微内窥镜成像系统设计及应用[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(6):1335-1344. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192706.1335ZHANG P T, YANG X B, ZHOU W, et al. Design and applied research of dual-mode switching endomicroscopic imaging system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(6): 1335-1344. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192706.1335 [52] FRIDMAN M, SHEMESH D, ABOOKASIS D. Dual-camera endoscopic imaging probe combining simultaneous illumination of white-light and laser sources for near real-time monitoring of tissue features[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2022, 154: 107018. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.107018 [53] LI W J, FAN J F, LI SH W, et al. Homography-based robust pose compensation and fusion imaging for augmented reality based endoscopic navigation system[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 138: 104864. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104864 [54] ABDALBARI A, HUANG X SH, REN J. Endoscopy-MR image fusion for image guided procedures[J]. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2013, 2013: 472971. [55] WARTAK A, KELADA A K, ALARCON P A L, et al. Dual-modality optical coherence tomography and fluorescence tethered capsule endomicroscopy[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2021, 12(7): 4308-4323. doi: 10.1364/BOE.422453 [56] GIATAGANAS P, HUGHES M, YANG G ZH. Force adaptive robotically assisted endomicroscopy for intraoperative tumour identification[J]. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2015, 10(6): 825-832. [57] ZHANG L, YE M L, GIATAGANAS P, et al. From macro to micro: autonomous multiscale image fusion for robotic surgery[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2017, 24(2): 63-72. -





 下载:
下载: