-
摘要:
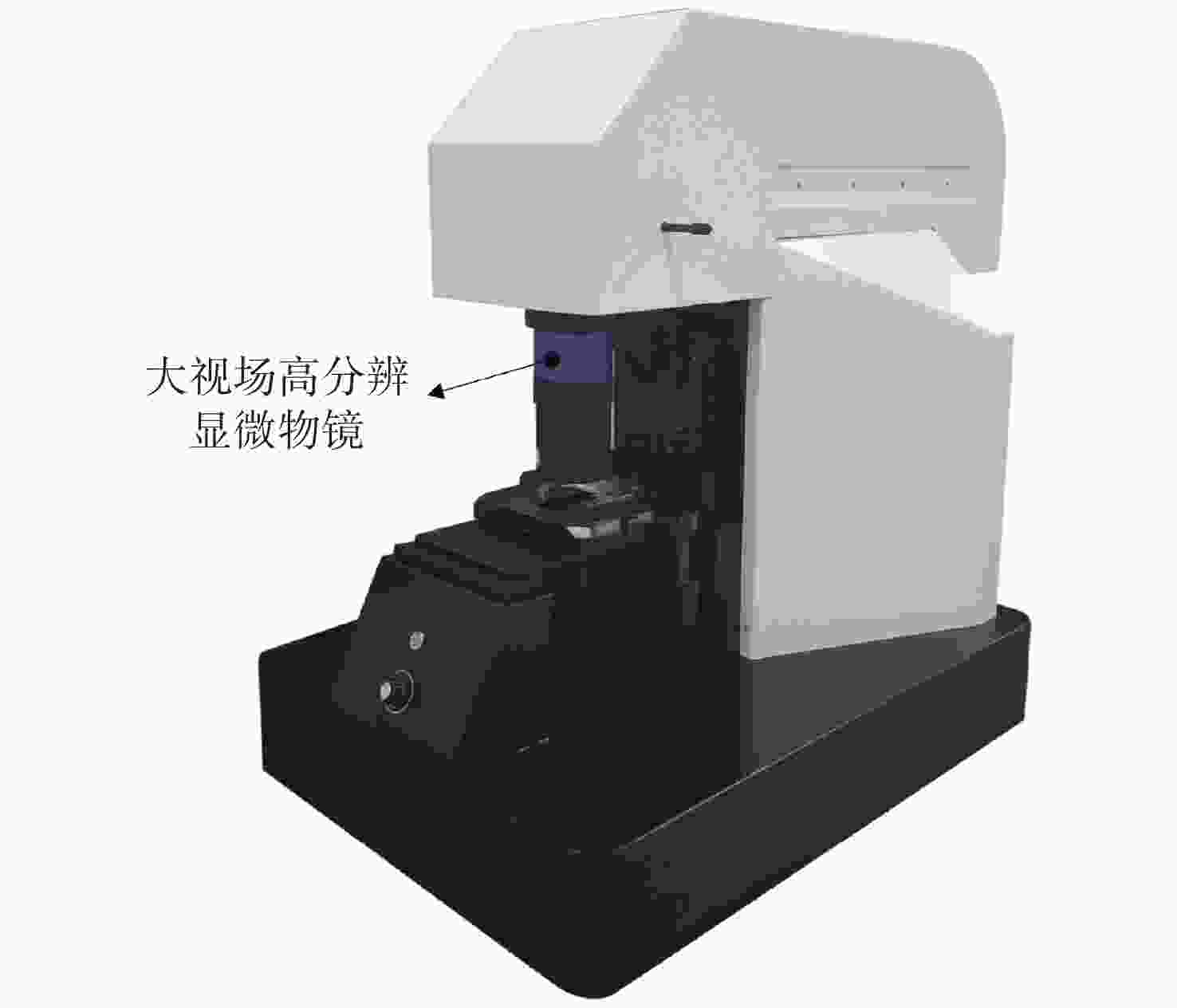
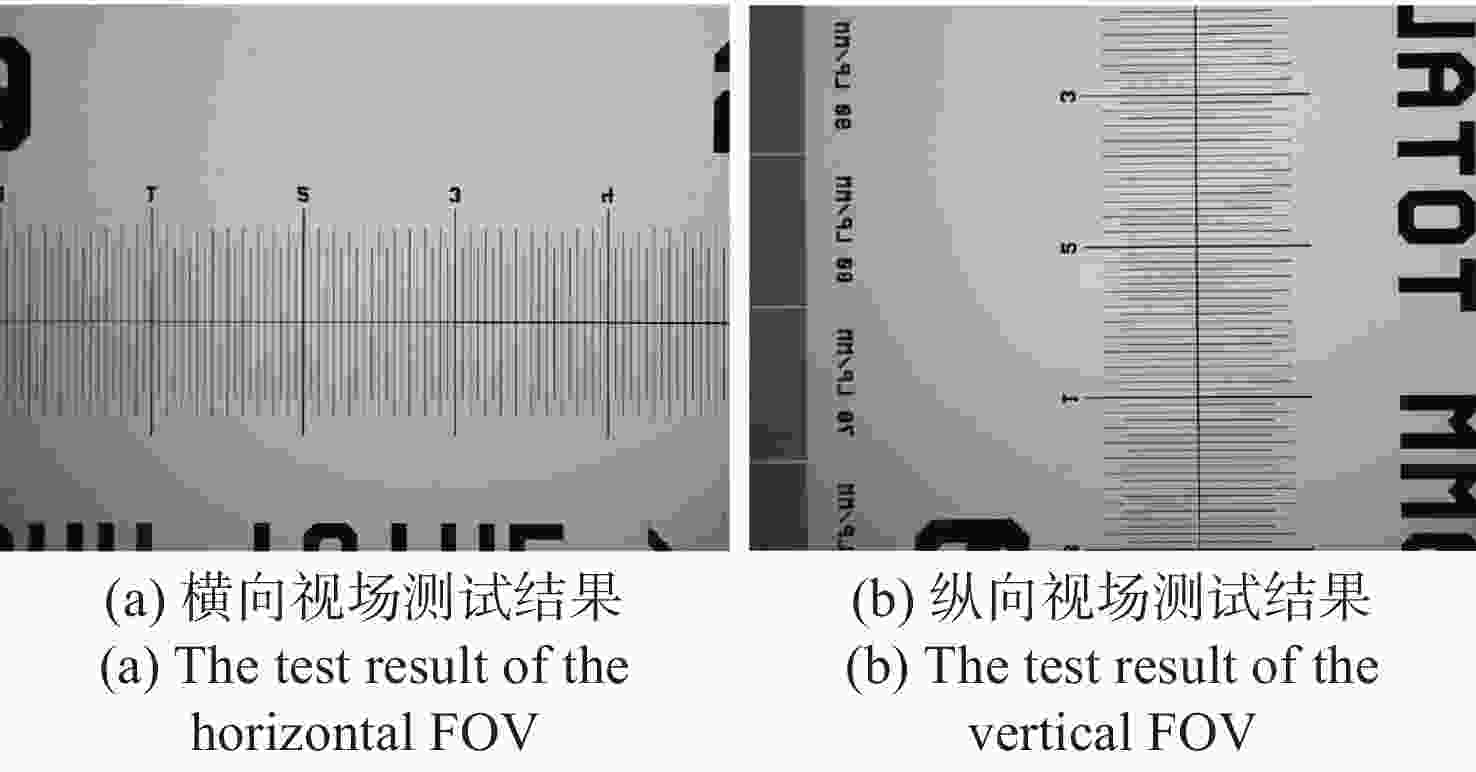
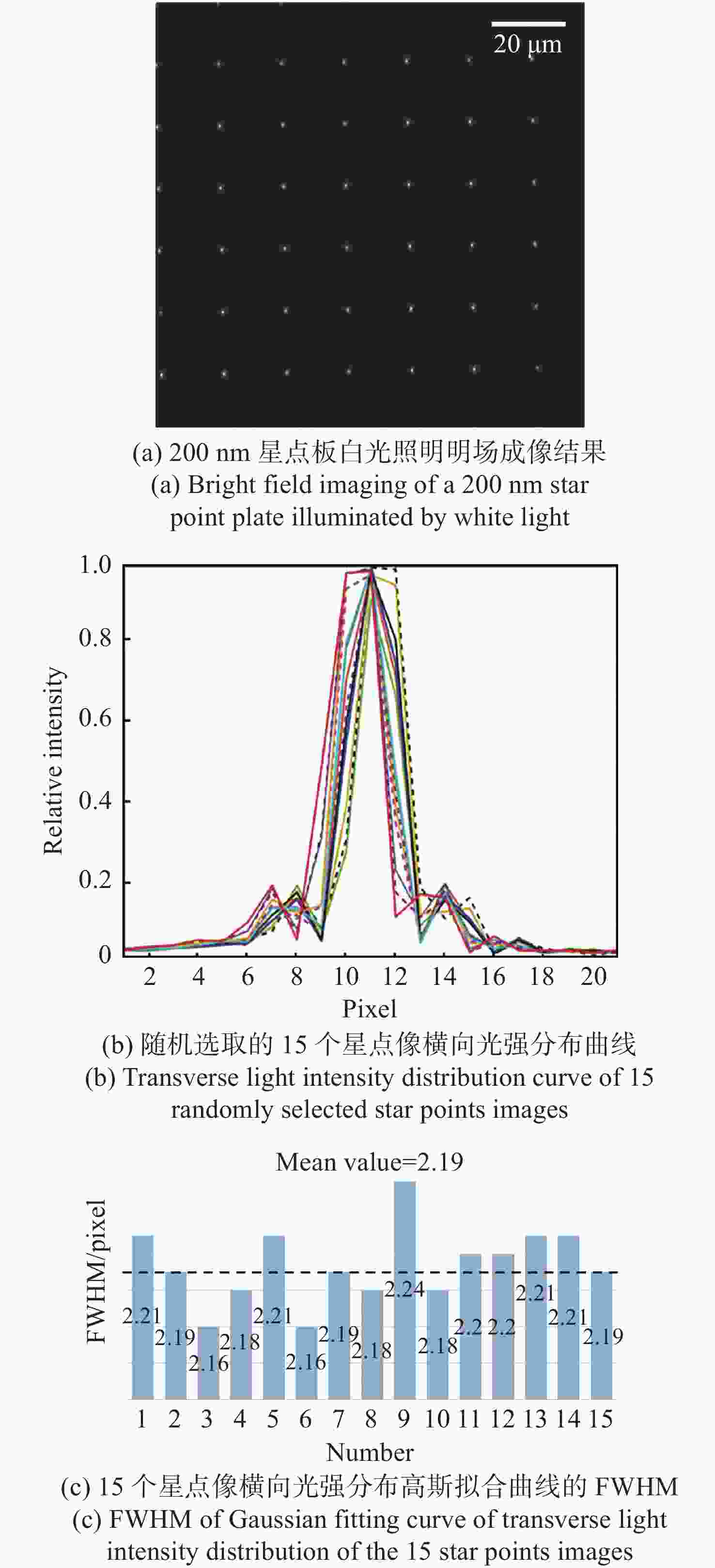
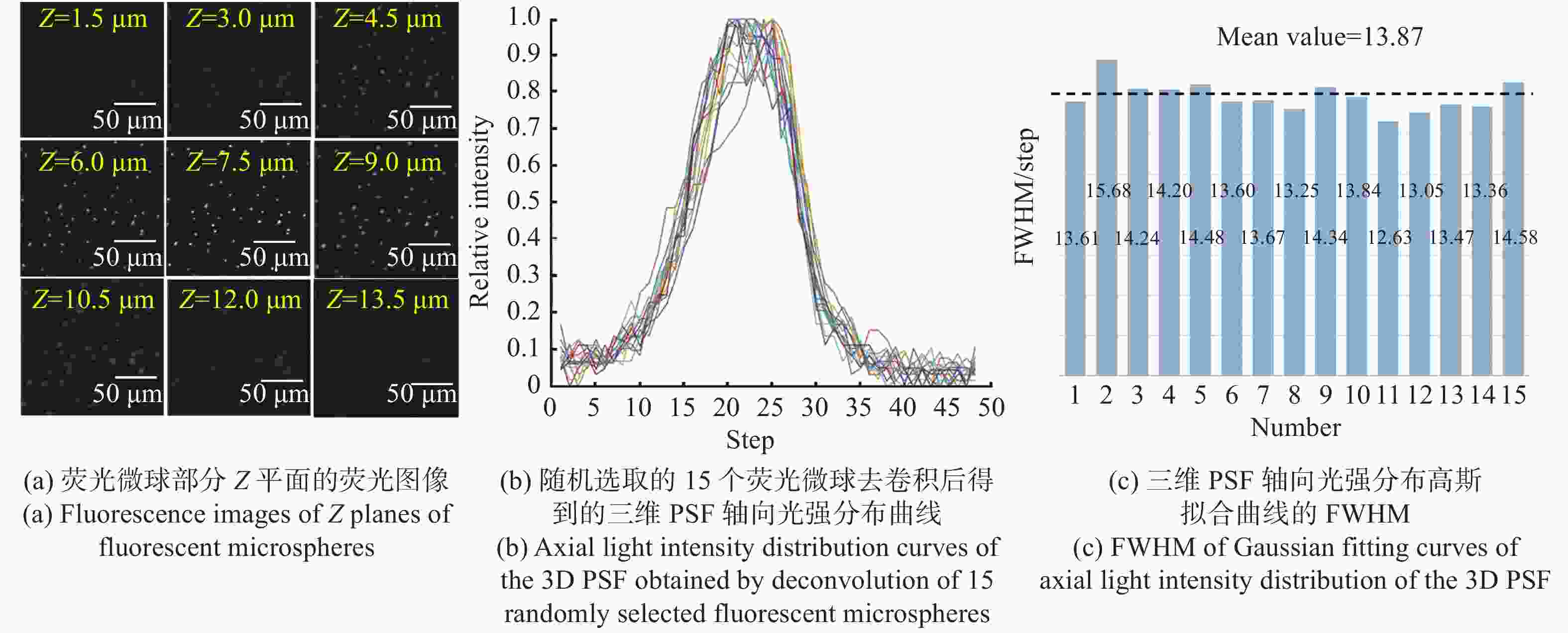
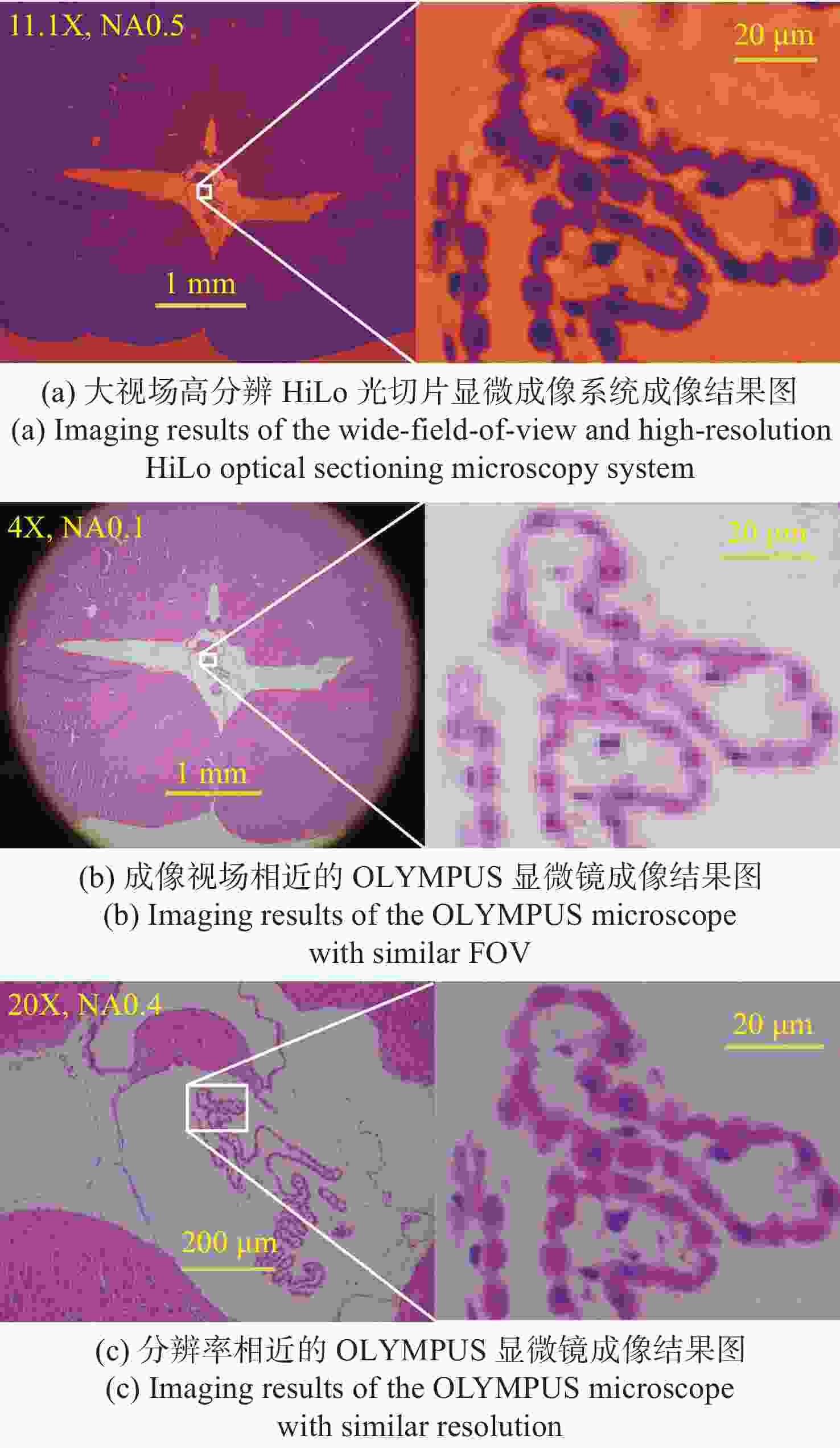
现代生物学和生物医学领域迫切需要研制兼顾大视场、高分辨率的显微成像技术和仪器以对生物样品实现跨尺度观测,满足重大科学问题的研究需求。受限于系统的空间带宽积,传统商业显微镜无法满足这一需求,且现有高空间带宽积显微成像系统存在体积庞大、实施成本高昂等问题。本文基于HiLo光切片技术和自主设计的大视场高分辨显微物镜,研发了具有高空间带宽积特点的大视场高分辨HiLo光切片显微成像系统,测试了系统的成像视场和分辨率。应用该系统对小鼠脑切片开展了白光照明明场成像实验,并与OLYMPUS商业显微镜成像结果做了对比;对小麦种子荧光切片开展了光切片成像和宽场荧光成像对比实验。实验结果表明, 大视场高分辨HiLo光切片显微成像系统的成像视场达到4.8 mm×3.6 mm (对角视场为6.0 mm),横向分辨率达到0.74 μm,轴向分辨率达到4.16 μm。大视场高分辨HiLo光切片显微成像系统兼有大视场和高分辨率成像的优势和快速光切片成像的能力,能够对大体积生物样本开展快速三维成像,将为胚胎发育、脑成像、数字病理诊断等研究提供有力的技术支撑。
Abstract:The fields of modern biology and biomedicine urgently need wide-field-of-view (FOV), high-resolution microscopic technology and instruments for trans-scale observation of biological samples to meet the requirement of major scientific for research. Limited by the spatial bandwidth product, traditional commercial microscopes cannot meet this demand. Besides, the existing high spatial bandwidth product microscopy systems have problems such as bulky volume and high implementation costs. In this paper, based on the HiLo optical sectioning technology and the self-designed wide-field-of-view and high-resolution objective, a wide-field-of-view and high-resolution HiLo optical sectioning microscopy system was developed. The FOV and imaging resolution of this system were tested. Brightfield imaging experiments were carried out on mouse brain slices by this system and the results were compared with that of OLYMPUS commercial microscope. At the same time, wide-field fluorescence imaging comparison experiments were carried out on wheat seed fluorescent slices. The experiment results show that the FOV of this system reaches 4.8 mm×3.6 mm (the diagonal FOV is 6.0 mm), the lateral resolution reaches 0.74 μm, and the axial resolution reaches 4.16 μm. The comparative experiment proved that this system has the advantages of wide FOV, high resolution and the ability of fast optical sectioning imaging simultaneously. This system can carry out rapid 3D imaging of large-volume biological samples, which will provide strong technical support for researches such as embryonic development, brain imaging, and digital pathology diagnosis.
-
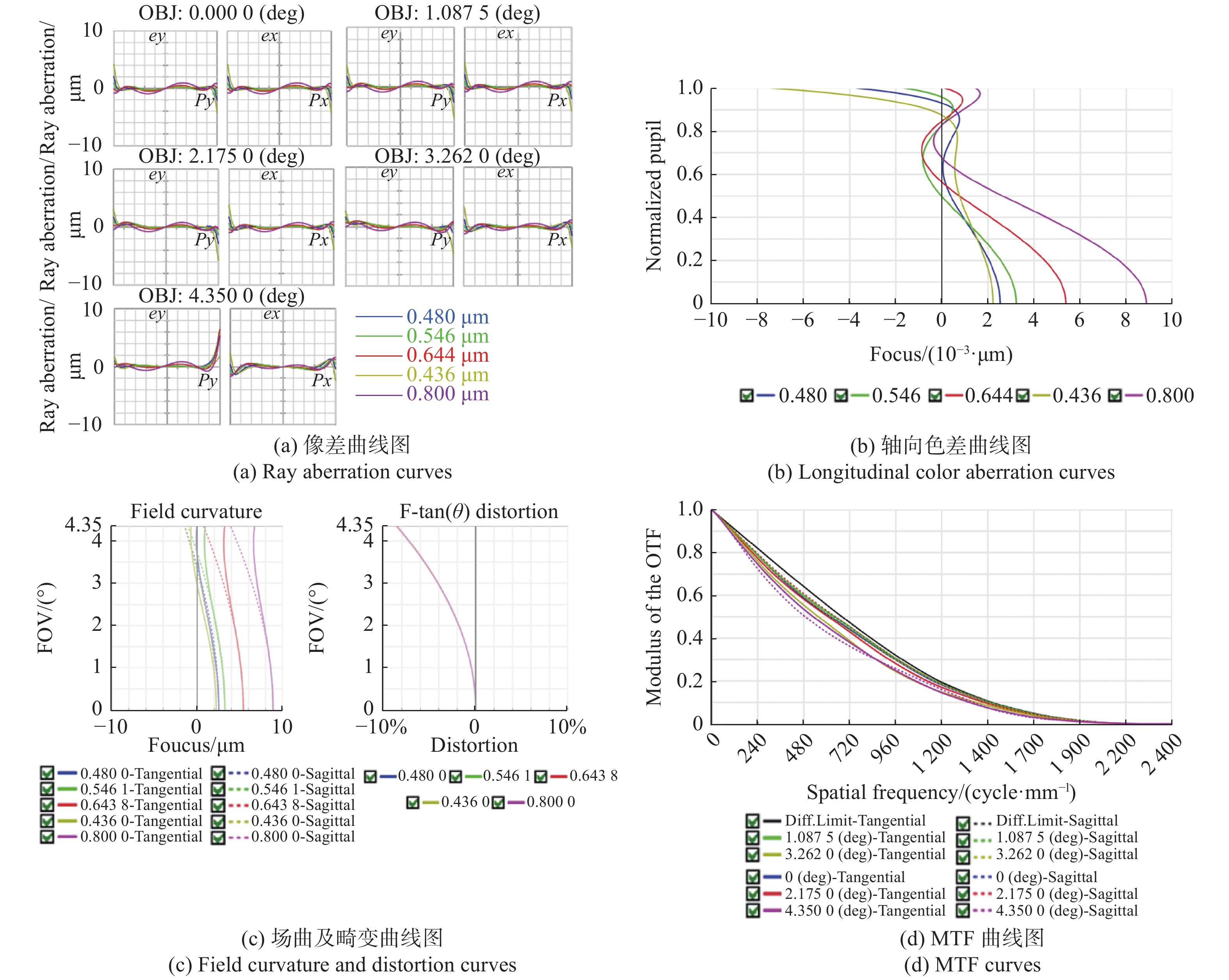
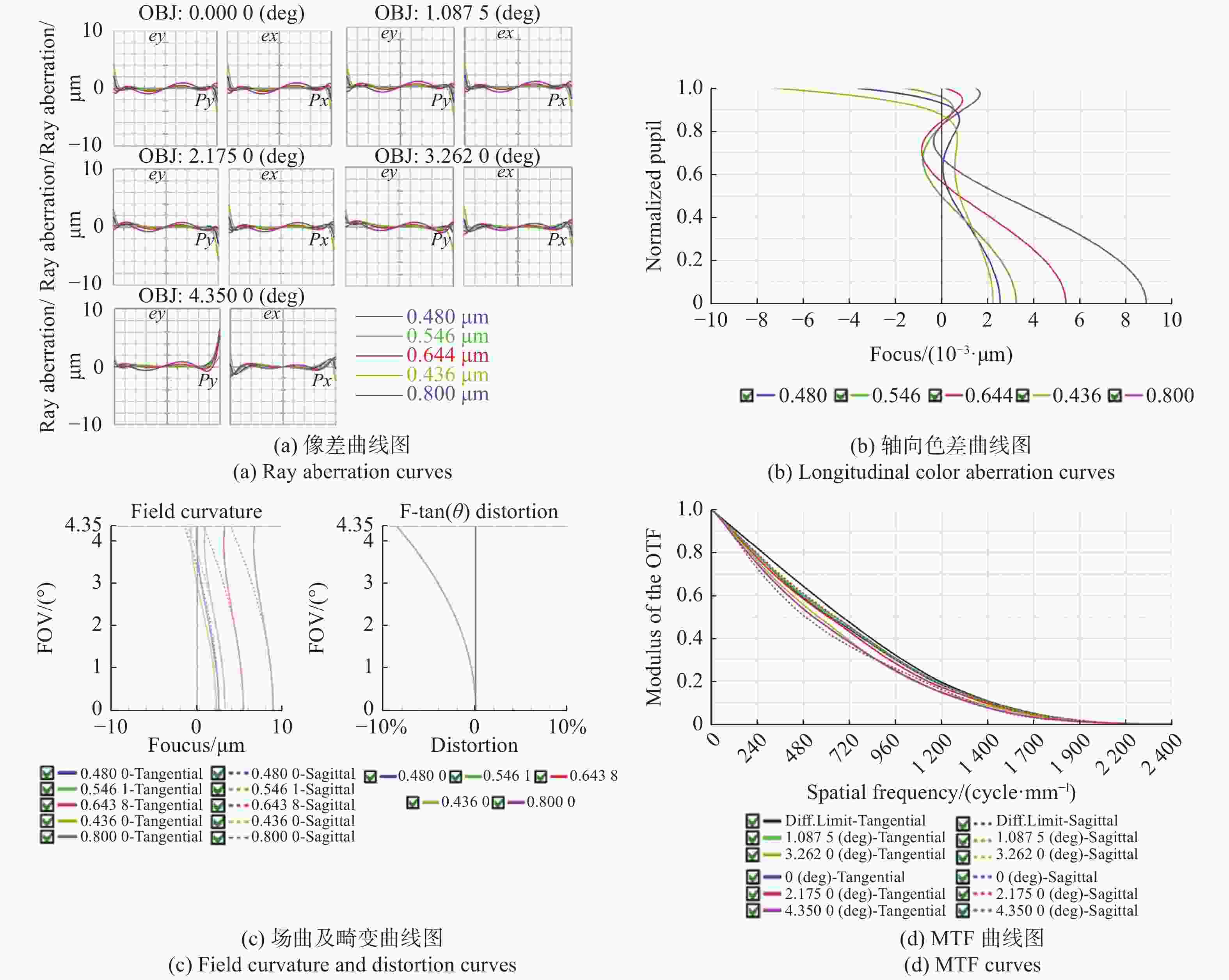
表 1 大视场高分辨显微物镜设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of the wide-field-of-view and high-resolution objective
参数 指标 物方视场(Field of View, FOV) Φ6.0 mm 数值孔径(Numerical Aperture, NA) 0.5 工作距(Working Distance, WD) 2 mm 焦距(Focus, F) 40 mm 工作波段(Working Waveband) 436 ~ 800 nm 浸没介质(Immersion Medium) 空气 表 2 系统参数
Table 2. Parameters of the system
参数 指标 照明光源 白光、488 nm/561 nm激光 成像视场 4.8 mm×3.6 mm(对角6.0 mm) 分辨率 横向0.74 μm,轴向4.16 μm 放大倍率 11.1 × 系统空间带宽积 151 M 工作模式 明场成像、宽场荧光成像、HiLo光切片成像 外形尺寸 565 mm(宽)×890 mm(长)×830 mm(高) -
[1] 骆清铭. 脑空间信息学——连接脑科学与类脑人工智能的桥梁[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2017,47(10):1015-1024. doi: 10.1360/N052017-00094LUO Q M. Brainsmatics—bridging the brain science and brain-inspired artificial intelligence[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2017, 47(10): 1015-1024. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N052017-00094 [2] QU L, LI Y, XIE P, et al. Cross-modal coherent registration of whole mouse brains[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(1): 111-118. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01334-w [3] YU W, KANG L, TSANG V T C, et al.. Three-dimensional multicolor subcellular imaging by fast serial sectioning tomography for centimeter-scale specimens[J]. Biorxiv, 2021,doi: 10.1101/2021.11.11.468237. [4] BERTELS S, JAGGY M, RICHTER B, et al. Geometrically defined environments direct cell division rate and subcellular YAP localization in single mouse embryonic stem cells[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 9269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88336-y [5] WU J M, LU ZH, JIANG D, et al. Iterative tomography with digital adaptive optics permits hour-long intravital observation of 3D subcellular dynamics at millisecond scale[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(12): 3318-3332.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.029 [6] HUGONNET H, KIM Y W, LEE M, et al. Multiscale label-free volumetric holographic histopathology of thick-tissue slides with subcellular resolution[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2021, 3(2): 026004. [7] LI A N, GONG H, ZHANG B, et al. Micro-optical sectioning tomography to obtain a high-resolution atlas of the mouse brain[J]. Science, 2010, 330(6009): 1404-1408. doi: 10.1126/science.1191776 [8] ZHANG Y, KANG L, YU W T, et al. Three-dimensional label-free histological imaging of whole organs by microtomy-assisted autofluorescence tomography[J]. iScience, 2022, 25(1): 103721. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103721 [9] TSAI P S, MATEO C, FIELD J J, et al. Ultra-large field-of-view two-photon microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(11): 13833-13847. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.013833 [10] ZHONG Q Y, JIANG CH Y, ZHANG D J, et al. High-throughput optical sectioning via line-scanning imaging with digital structured modulation[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(3): 504-507. doi: 10.1364/OL.412323 [11] ZHENG G A, HORSTMEYER R, YANG CH H. Wide-field, high-resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopy[J]. Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(9): 739-745. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.187 [12] ZHENG G A, SHEN CH, JIANG SH W, et al. Concept, implementations and applications of Fourier ptychography[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3(3): 207-223. doi: 10.1038/s42254-021-00280-y [13] FAN J T, SUO J L, WU J M, et al. Video-rate imaging of biological dynamics at centimetre scale and micrometre resolution[J]. Nature Photonics, 2019, 13(11): 809-816. doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0474-7 [14] MCCONNELL G, TRÄGÅRDH J, AMOR R, et al. A novel optical microscope for imaging large embryos and tissue volumes with sub-cellular resolution throughout[J]. Elife, 2016, 5: e18659. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18659 [15] MCCONNELL G, AMOS W B. Application of the mesolens for subcellular resolution imaging of intact larval and whole adult Drosophila[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2018, 270(2): 252-258. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12693 [16] SOFRONIEW N J, FLICKINGER D, KING J, et al. A large field of view two-photon mesoscope with subcellular resolution for in vivo imaging[J]. Elife, 2016, 5: e14472. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14472 [17] YU CH H, STIRMAN J N, YU Y Y, et al. Diesel2p mesoscope with dual independent scan engines for flexible capture of dynamics in distributed neural circuitry[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 6639. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26736-4 [18] 张小宇. 基于深度学习的显微光学层析[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2020.ZHANG X Y. Deep learning-based optical sectioning microscopy[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [19] YANG M K, ZHOU ZH Q, ZHANG J X, et al. MATRIEX imaging: multiarea two-photon real-time in vivo explorer[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2019, 8: 109. [20] STELZER E H K, STROBL F, CHANG B J, et al. Light sheet fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2021, 1(1): 73. doi: 10.1038/s43586-021-00069-4 [21] PRIYADARSHI A, DULLO F T, WOLFSON D L, et al. A transparent waveguide chip for versatile total internal reflection fluorescence-based microscopy and nanoscopy[J]. Communications Materials, 2021, 2(1): 85. doi: 10.1038/s43246-021-00192-5 [22] NWANESHIUDU A, KUSCHAL C, SAKAMOTO F H, et al. Introduction to confocal microscopy[J]. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 2012, 132(12): 1-5. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.429 [23] XU L Y, ZHANG Y W, LANG S, et al. Structured illumination microscopy based on asymmetric three-beam interference[J]. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences, 2021, 14(2): 2050027. doi: 10.1142/S1793545820500273 [24] 尹君, 王少飞, 张俊杰, 等. 基于动态散斑照明的宽场荧光显微技术理论研究[J]. 物理学报,2021,70(23):238701. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20211022YIN J, WANG SH F, ZHANG J J, et al. Theoretical study of wide-field fluorescence microscopy based on dynamic speckle illumination[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(23): 238701. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20211022 [25] LIM D, CHU K K, MERTZ J. Wide-field fluorescence sectioning with hybrid speckle and uniform-illumination microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(16): 1819-1821. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.001819 [26] LIM D, FORD T N, CHU K K, et al. Optically sectioned in vivo imaging with speckle illumination HiLo microscopy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2011, 16(1): 016014. doi: 10.1117/1.3528656 -





 下载:
下载: