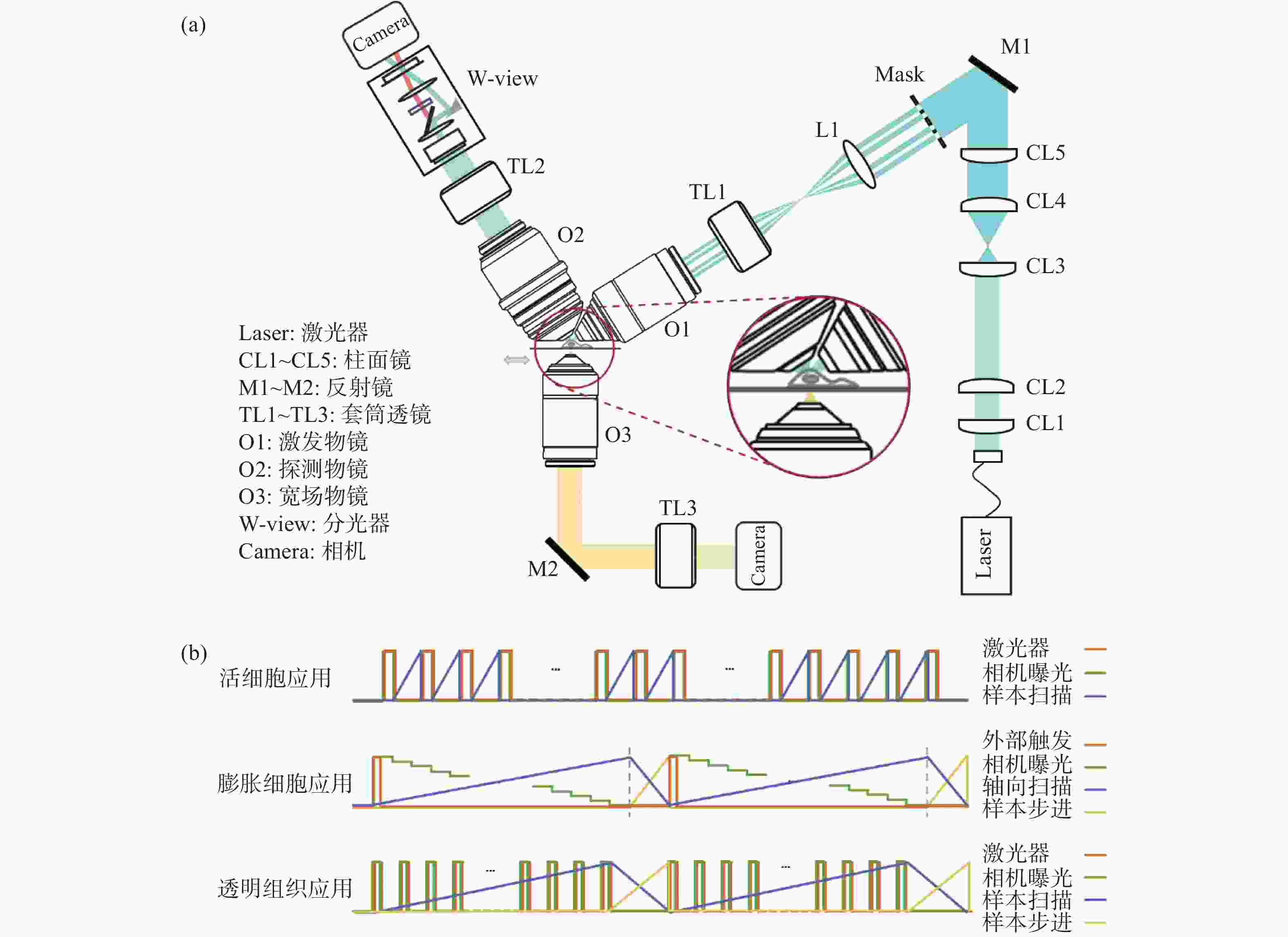
Double-ring-modulated light sheet fluorescence microscopic technique for multi-scale high-resolution 3D imaging
-
摘要:
本文提出了一种无衍射光片荧光显微成像技术,可以方便地对从微米到厘米各种尺寸的多种生物样本进行多尺度三维荧光成像。提出一种双环调控方法以解决传统贝塞尔光片旁瓣过重的问题,该方法能够可调节地产生0.4~5 μm之间不同厚度类型的无衍射光片,同时其旁瓣占比被压低到30%以下。基于这种新的调控手段设计搭建了一套多尺度光片荧光显微成像系统。该系统展示出适用性极强的多尺度成像能力,例如:活细胞双色三维动态成像、膨胀细胞三维超分辨成像以及介观尺度下全器官的高通量三维成像。证明该多尺度成像模式能够显著提升光片荧光显微镜的成像效率,由此可以推进细胞生物学、组织病理学、神经科学等多种生物医学相关研究的发展。
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a non-diffraction Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy (LSFM) technique, which readily enables multi-scale 3D fluorescence imaging of diverse biological samples with size ranging from microns to centimeters. To solve the problem of heavy sidelobes in conventional non-diffraction Bessel LSFM, we invent a double-ring-modulated approach which can generate non-diffraction light sheets with ~0.4 to ~5 µm tunable thickness and the ratio of the sidelobe was reduced to less than 30%. Then we built a multi-scale LSFM system based on this novel approach. The system showed versatile multi-scale imaging abilities, such as dual-color 3D dynamic imaging of single live cell, 3D super-resolution imaging of expansion cells and high-throughput 3D mapping of entire meso-scale organs. Therefore, we demonstrate that this multi-scale imaging modality can substantially improve the efficiency of LSFM for advancing various biomedical studies, such as cell biology, tissue pathology, and neuroscience.
-
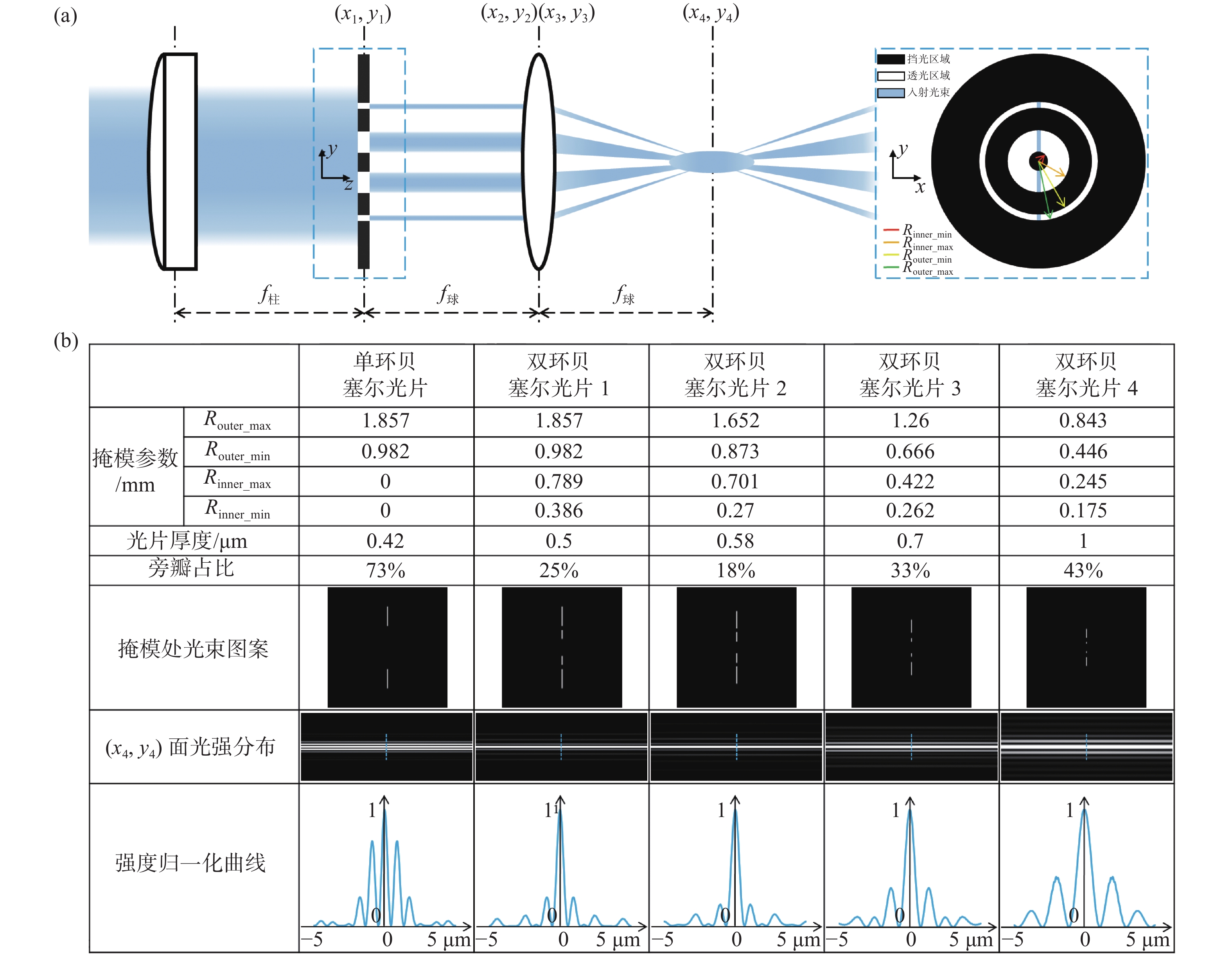
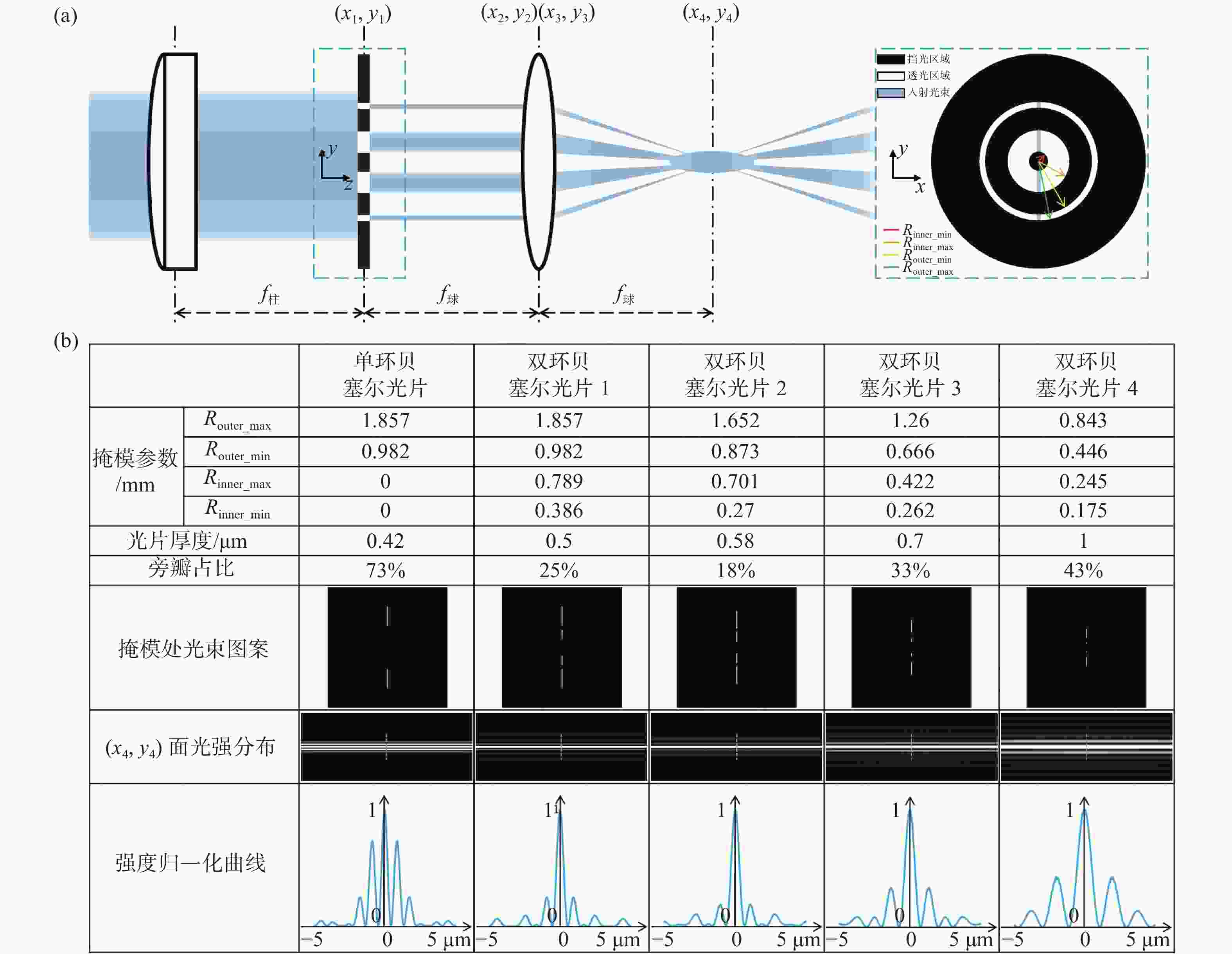
图 1 光束整形原理和光片性能表征。(a)双环掩模调控生成低旁瓣贝塞尔光片;(b)不同尺度类型光片性能表征及对比
Figure 1. Principle of double-ring beam reshaping and its comparative performance. (a) Lowsidelobe Bessel light sheet obtained by the modulation of a double-ring mask; (b) characterization and comparison of performance of our multi-scale low sidelobe light sheet
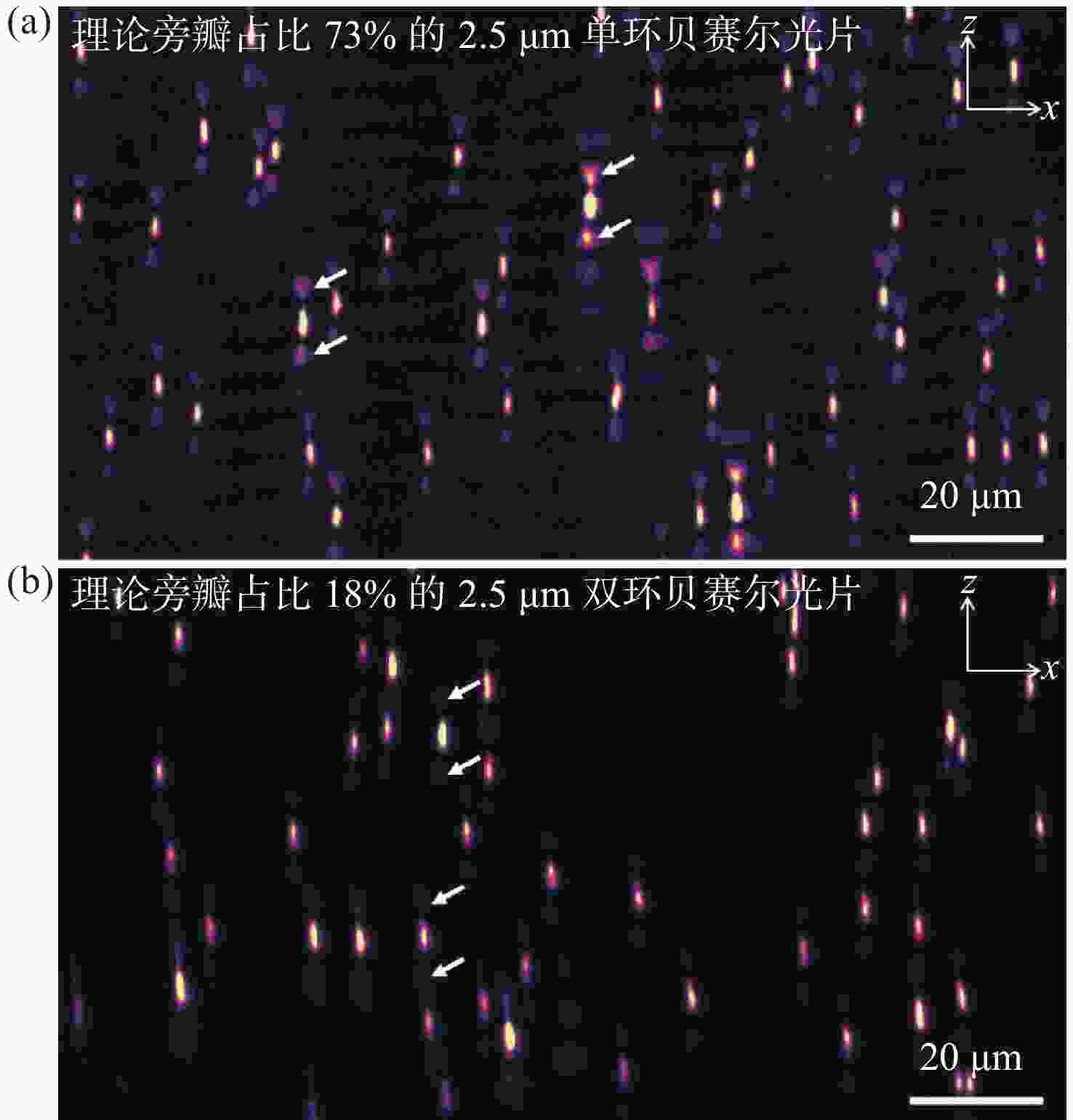
图 3 单环贝塞尔光片与双环贝塞尔光片成像性能对比。(a)使用旁瓣占比73%的2.5 μm单环贝塞尔光片获得的点扩散函数x-z面最大强度投影;(b)使用旁瓣占比18%的2.5 μm双环贝塞尔光片获得的点扩散函数x-z面最大强度投影
Figure 3. Comparison of imaging results between single-ring Bessel light sheet and DR-SPIM. (a) x-z plane max intensity projection of point spread function by 2.5 μm single-ring Bessel light sheet with 73% side lobes; (b) x-z plane max intensity projection of point spread function by 2.5 μm DR-SPIM with 18% side lobes
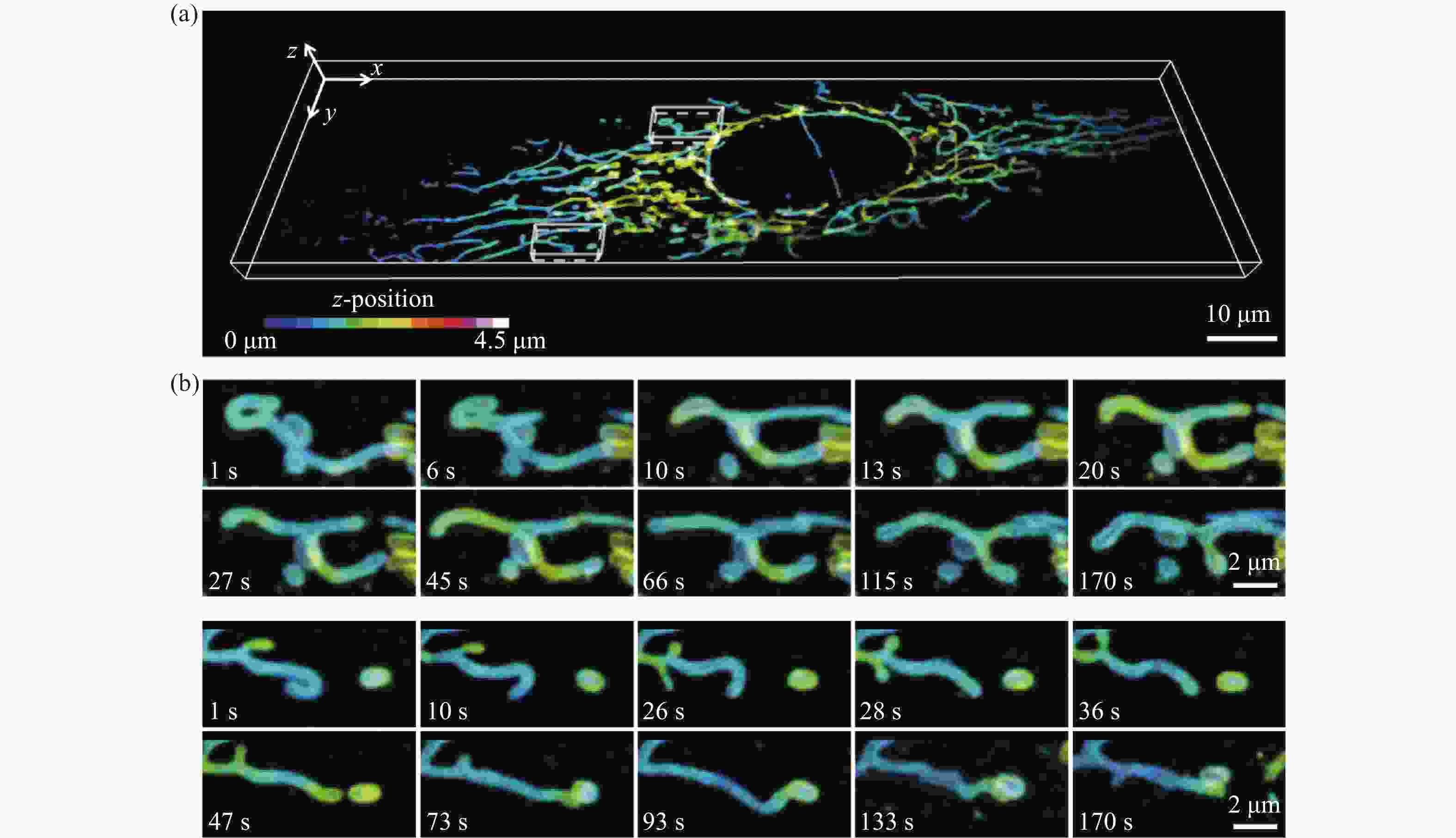
图 4 U2OS细胞中线粒体外膜的分布及其运动变化。(a)整个细胞中线粒体外膜的三维分布图,比例尺:10 μm;(b)局部线粒体外膜的运动变化过程,比例尺:2 μm
Figure 4. 3D dynamics of mitochondrial outer membrane in U2OS cell. (a) Three-dimensional distribution of mitochondrial outer membrane in a whole live cell, scale bar: 10 μm; (b) the movement of local mitochondrial outer membrane, scale bar: 2 μm
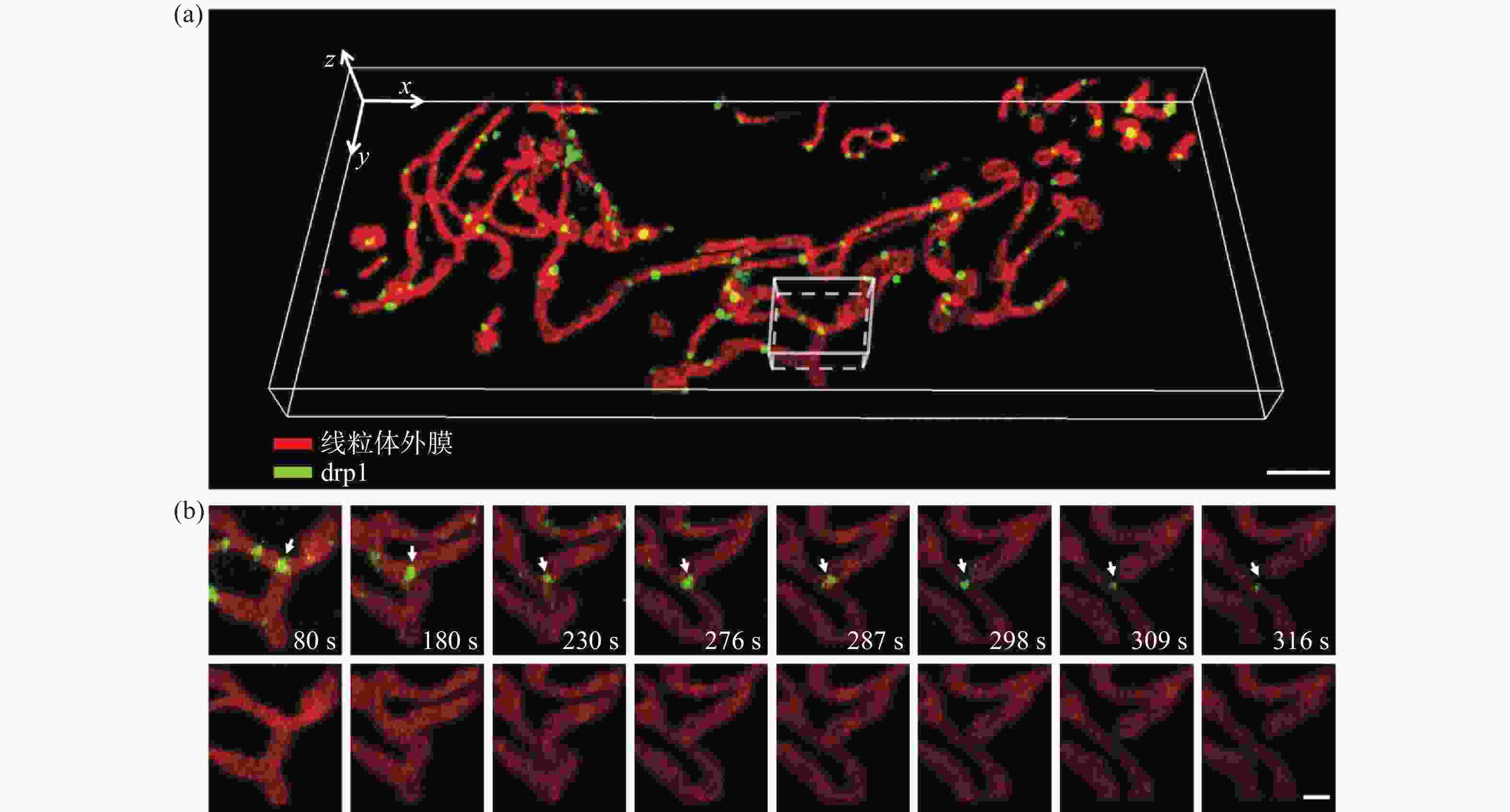
图 5 U2OS细胞中线粒体外膜与Drp1的分布与相互作用。(a)线粒体外膜与Drp1的三维分布图,比例尺:3 μm;(b)感兴趣区域内线粒体外膜与Drp1相互作用过程,比例尺:1 μm
Figure 5. Interactions between mitochondrial outer membrane and Drp1 in U2OS cell. (a) Three-dimensional co-localization of mitochondrial outer membrane and Drp1, scale bar: 3 μm; (b) interactions between mitochondrial outer membrane and Drp1 in a region of interest, scale bar: 1 μm
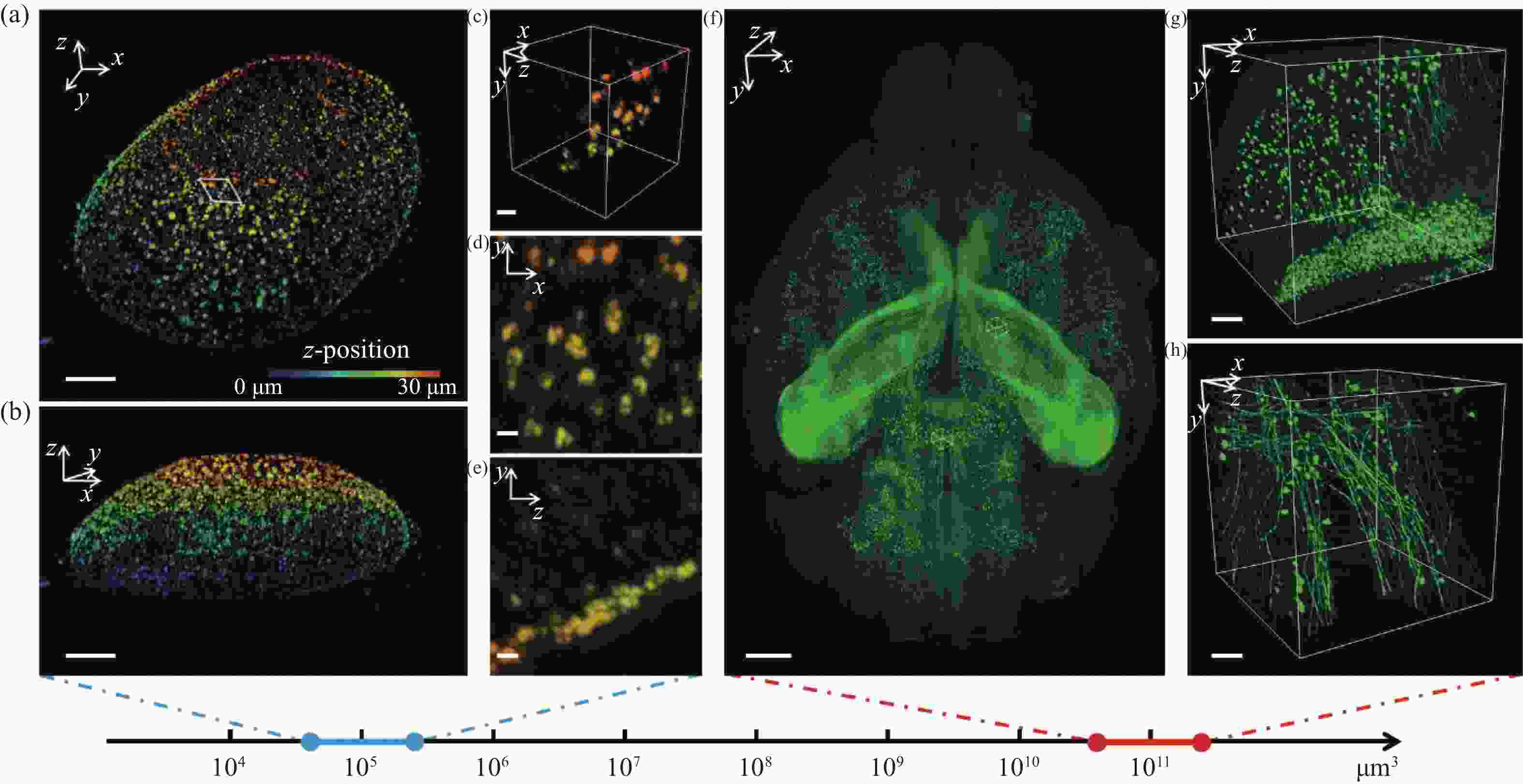
图 6 多尺度成像应用可视化结果。4倍膨胀核孔(a)可视化结果及其(b)轴向视角,比例尺:10 μm;(c)区域三维可视化,比例尺:2 μm;(d)区域x-y面和(e)区域y-z面最大强度投影,比例尺:1 μm;(f)鼠脑全脑可视化结果,比例尺:1 mm;(g)位于皮层和(h)位于丘脑的感兴趣区域三维可视化结果,比例尺:100 μm
Figure 6. 3D visualization of multi-scale imaging results. (a) 3D visualization and (b) axial 3D view of an expanded nuclear hole (expansion factor: 4), scale bar: 10 μm; (c) 3D visualization of a selected small region, scale bar: 2 μm; max intensity projection of the (d) x-y plane and (e) y-z plane of the region, scale bar: 1 μm; (f) 3D visualization of a whole mouse brain, scale bar: 1 mm; 3D visualization of a region of interest in (g) cortex and (h) thalamus, scale bar: 100 μm
表 1 不同应用场景下所用的掩模参数与物镜型号
Table 1. Mask parameters and objectives in different application scenarios
应用场景 线粒体外膜的高
速、低光毒性成像线粒体外膜与
Drp1相互作用的
双色成像4倍膨胀核孔
三维体成像透明化鼠脑
三维体成像单环贝塞尔光片与双环贝塞尔
光片成像性能对比光片类型 500 nm 双环贝塞尔光片 3.5 μm 双环
贝塞尔光片2.5 μm 单环
贝塞尔光片2.5 μm 双环
贝塞尔光片掩模参数
/mmRouter_max 1.857 1.652 1.95 2.395 Router_min 0.982 0.873 1.03 1.266 Rinner_max 0.789 0.701 0 1.016 Rinner_min 0.386 0.27 0 0.392 照明物镜 28.6 × SO Microscope Objective, 0.66 NA,
3.74mm Water, Special OpticsXLFLUOR4X/340, Olympus 探测物镜 LUMFLN60XW,Olympus UMPLFLN10XW, Olympus UMPLFLN20XW,Olympus -
[1] LICHTMAN J W, CONCHELLO J A. Fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2005, 2(12): 910-919. doi: 10.1038/nmeth817 [2] CHOQUET D, SAINLOS M, SIBARITA J B. Advanced imaging and labelling methods to decipher brain cell organization and function[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2021, 22(4): 237-255. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00441-z [3] STELZER E H K, STROBL F, CHANG B J, et al. Light sheet fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2021, 1(1): 73. doi: 10.1038/s43586-021-00069-4 [4] HUISKEN J, SWOGER J, DEL BENE F, et al. Optical sectioning deep inside live embryos by selective plane illumination microscopy[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5686): 1007-1009. doi: 10.1126/science.1100035 [5] KELLER P J, SCHMIDT A D, WITTBRODT J, et al. Reconstruction of zebrafish early embryonic development by scanned light sheet microscopy[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5904): 1065-1069. doi: 10.1126/science.1162493 [6] DEAN K M, ROUDOT P, WELF E S, et al. Deconvolution-free subcellular imaging with axially swept light sheet microscopy[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2015, 108(12): 2807-2815. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.05.013 [7] FAHRBACH F O, GURCHENKOV V, ALESSANDRI K, et al. Self-reconstructing sectioned Bessel beams offer submicron optical sectioning for large fields of view in light-sheet microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(9): 11425-11440. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.011425 [8] LIU Y CH, KE Y G, ZHOU J X, et al. Generation of perfect vortex and vector beams based on Pancharatnam-Berry phase elements[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 44096. doi: 10.1038/srep44096 [9] ZHAO T, LAU S C, WANG Y, et al. Multicolor 4D fluorescence microscopy using ultrathin bessel light sheets[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 26159. doi: 10.1038/srep26159 [10] CAO B, COELHO S, LI J R, et al. Volumetric interferometric lattice light-sheet imaging[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(11): 1385-1393. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01042-y [11] CHANG B J, KITTISOPIKUL M, DEAN K M, et al. Universal light-sheet generation with field synthesis[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(3): 235-238. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0327-9 [12] DUNSBY C. Optically sectioned imaging by oblique plane microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(25): 20306-20316. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.020306 [13] YANG B, LANGE M, MILLETT-SIKKING A, et al. DaXi—high-resolution, large imaging volume and multi-view single-objective light-sheet microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(4): 461-469. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01417-2 [14] POWER R M, HUISKEN J. A guide to light-sheet fluorescence microscopy for multiscale imaging[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(4): 360-373. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4224 [15] MORI S. Side lobe suppression of a Bessel beam for high aspect ratio laser processing[J]. Precision Engineering, 2015, 39: 79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.07.008 [16] 郁道银, 谈恒英. 工程光学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015.YU D Y, TAN H Y. Engineering Optics[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015. (in Chinese) [17] ZHAO Y X, ZHANG M, ZHANG W T, et al. Isotropic super-resolution light-sheet microscopy of dynamic intracellular structures at subsecond timescales[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(3): 359-369. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01395-5 [18] SCHERMELLEH L, FERRAND A, HUSER T, et al. Super-resolution microscopy demystified[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2019, 21(1): 72-84. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0251-8 [19] WU Y C, HAN X F, SU Y J, et al. Multiview confocal super-resolution microscopy[J]. Nature, 2021, 600(7888): 279-284. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04110-0 [20] VALLI J, GARCIA-BURGOS A, ROONEY L M, et al. Seeing beyond the limit: a guide to choosing the right super-resolution microscopy technique[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2021, 297(1): 100791. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100791 [21] ZHAO W S, ZHAO SH Q, LI L J, et al. Sparse deconvolution improves the resolution of live-cell super-resolution fluorescence microscopy[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(4): 606-617. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01092-2 [22] HUANG X SH, FAN J CH, LI L J, et al. Fast, long-term, super-resolution imaging with Hessian structured illumination microscopy[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(5): 451-459. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4115 [23] QIAO CH, LI D, GUO Y T, et al. Evaluation and development of deep neural networks for image super-resolution in optical microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(2): 194-202. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-01048-5 [24] ZHELUDEV N I, YUAN G H. Optical superoscillation technologies beyond the diffraction limit[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2022, 4(1): 16-32. doi: 10.1038/s42254-021-00382-7 [25] BODÉN A, PENNACCHIETTI F, COCEANO G, et al. Volumetric live cell imaging with three-dimensional parallelized RESOLFT microscopy[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(5): 609-618. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-00779-2 [26] SUN D E, FAN X Q, SHI Y J, et al. Click-ExM enables expansion microscopy for all biomolecules[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(1): 107-113. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-01005-2 [27] GAO R X, YU C C, GAO L Y, et al. A highly homogeneous polymer composed of tetrahedron-like monomers for high-isotropy expansion microscopy[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(6): 698-707. doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00875-7 [28] THEVATHASAN J V, KAHNWALD M, CIEŚLIŃSKI K, et al. Nuclear pores as versatile reference standards for quantitative superresolution microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(10): 1045-1053. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0574-9 [29] JING D, ZHANG SH W, LUO W J, et al. Tissue clearing of both hard and soft tissue organs with the pegasos method[J]. Cell Research, 2018, 28(8): 803-818. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0049-z [30] ZHU J T, LIU X M, DENG Y T, et al. Tissue optical clearing for 3D visualization of vascular networks: a review[J]. Vascular Pharmacology, 2021, 141: 106905. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2021.106905 [31] SUN Q T, LI X N, REN M, et al. A whole-brain map of long-range inputs to GABAergic interneurons in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2019, 22(8): 1357-1370. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0429-9 [32] FANG CH Y, YU T T, CHU T T, et al. Minutes-timescale 3D isotropic imaging of entire organs at subcellular resolution by content-aware compressed-sensing light-sheet microscopy[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 107. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20329-3 [33] XU F, SHEN Y, DING L F, et al. High-throughput mapping of a whole rhesus monkey brain at micrometer resolution[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(12): 1521-1528. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-00986-5 -





 下载:
下载: