-
摘要:
光学系统性能的有效实现不仅依靠成像质量的设计结果,还受制于光学加工公差、装配公差、环境公差等多种公差的可实现性。具备低误差敏感度特征的光学系统,公差精度要求宽松,可以更好地抵抗误差引起的像质退化,在降低制造成本的同时,有效地提高了光学系统的可实现性,因此降低误差敏感度是光学系统设计应考虑的重要环节。本文分析了光学系统误差敏感度研究现状,总结了典型的光学系统降敏方法,并对这些方法在光学系统设计中的应用进行概述。最后,对光学系统低误差敏感度设计方法的未来发展进行了展望。
Abstract:The effective realization of desired optical system performances depends not only on the design results of imaging quality, but also on the realizability of various tolerances such as optical manufacturing tolerances, assembly tolerances, and environmental tolerances. An optical system with low error sensitivity relaxes tolerance requirements, which can better resist image quality degradation disturbed by errors. While reducing manufacturing costs, it effectively improves the realizability of an optical system, thereby reducing error sensitivity. It is an important link that should be considered in optical system design. This paper analyzes and summarizes the research status of optical system error sensitivity, summarizes typical optical system desensitization methods, and summarizes the application of these methods in optical system design. Finally, potential future development directions for low error sensitivity design methods for optical systems are provided.
-
Key words:
- error sensitivity /
- desensitization design method /
- optical system design
-
图 5 (a)应用非球面的手机相机设计布局图;(b)应用Q-type自由曲面手机相机设计布局图;(c)应用非球面的镜头元件4偏心30 μm后的MTF表现;(d)应用Q-type自由曲面的镜头元件4偏心30 μm后的MTF表现;(e)应用非球面及(f)应用Q-type自由曲面的镜头元件厚度变化10 μm的WFE [17]
Figure 5. (a) Mobile phone camera design layout with Power Series aspheres; (b) mobile phone camera design layout with Q-type aspheres; (c) MTF of Lens with Power Series aspheres element 4 with decenter of 30 μm; (d) MTF of Lens with Q-type aspheres element 4 with decenter of 30 μm; WFE of the lenses with (e) Power Series aspheres and (f) Q-type aspheres with a change in element thickness of 10 µm[17]
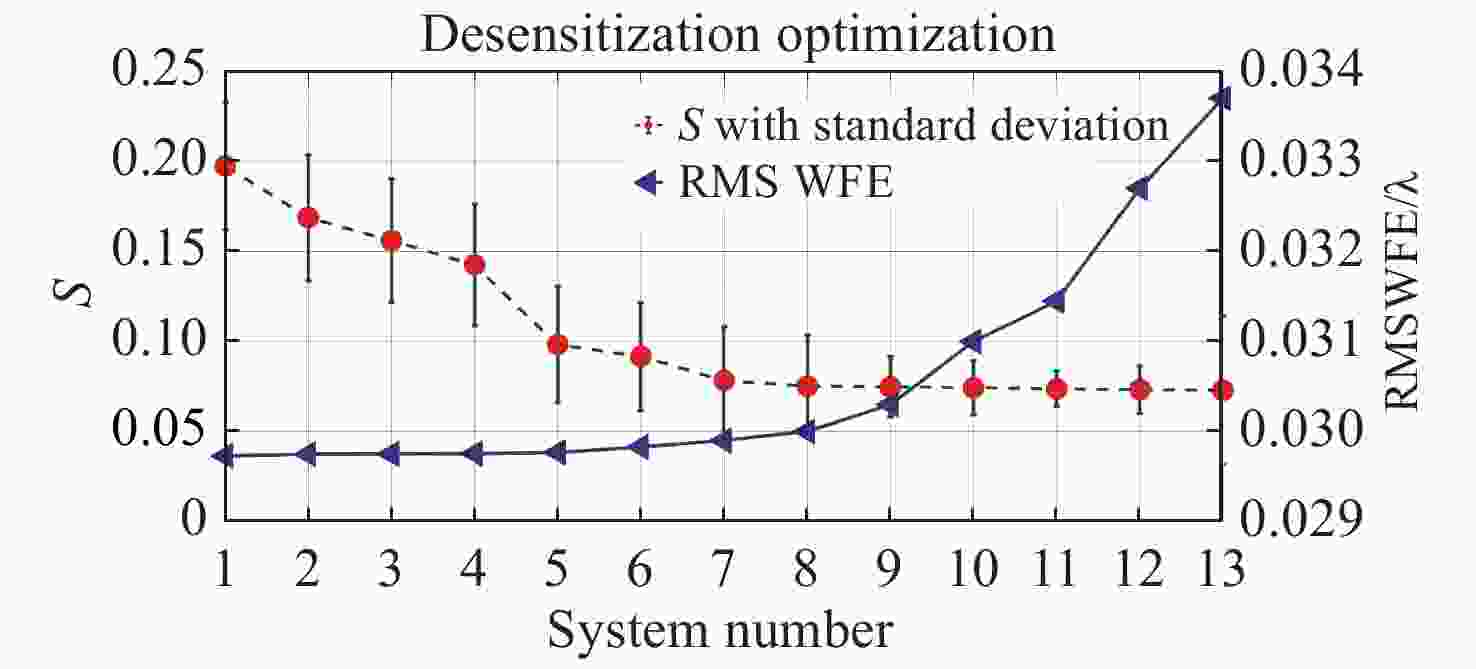
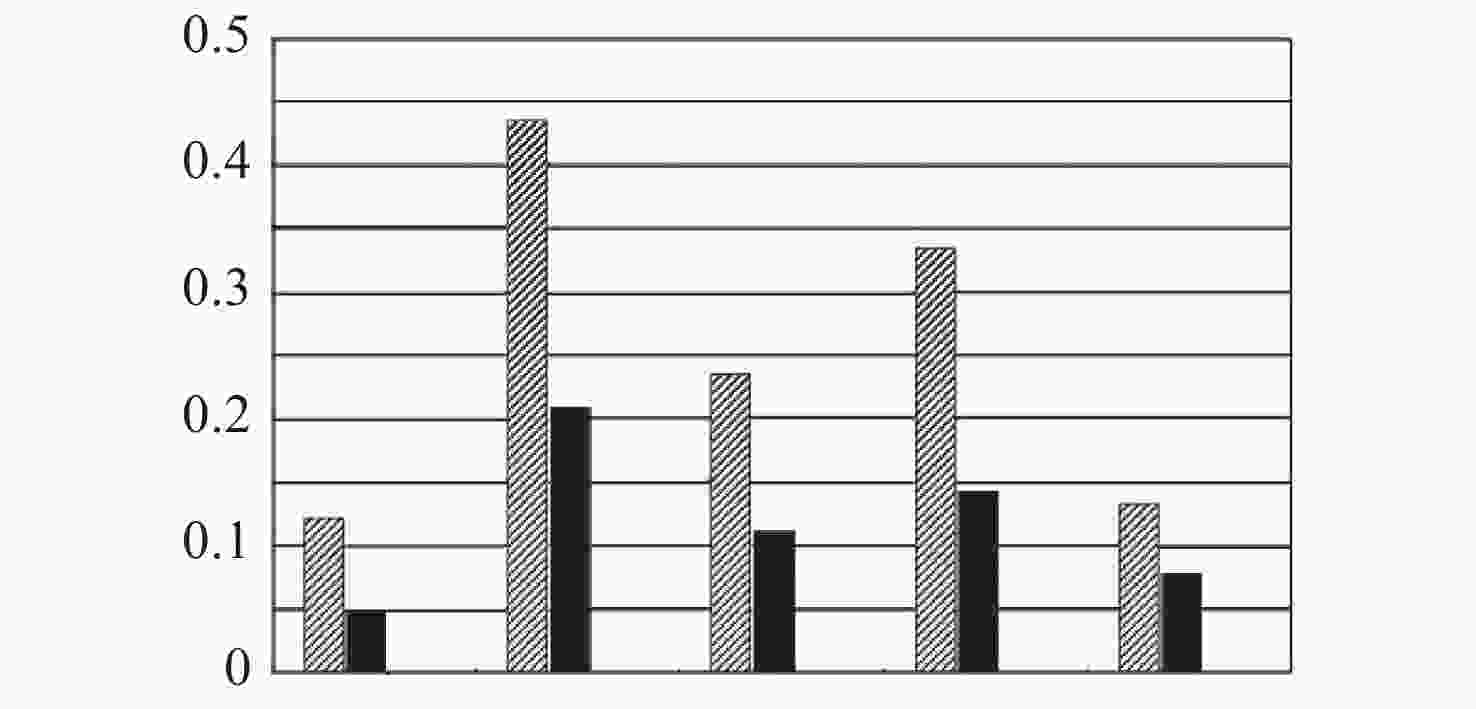
图 9 降敏设计前后变化量对比;(a)S;(b)WFE[25]
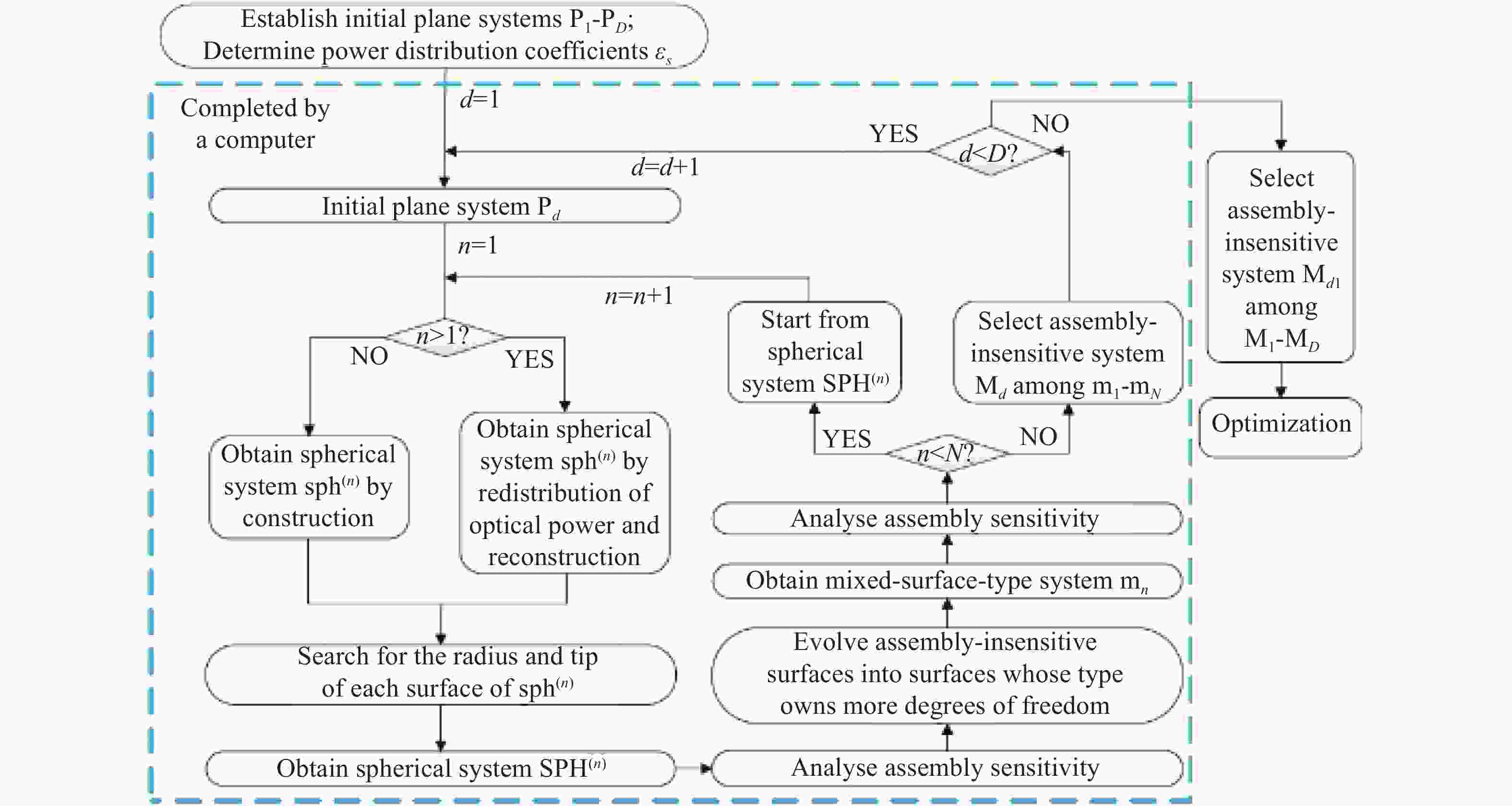
Figure 9. S and ∆RMS WFE before and after desensitization
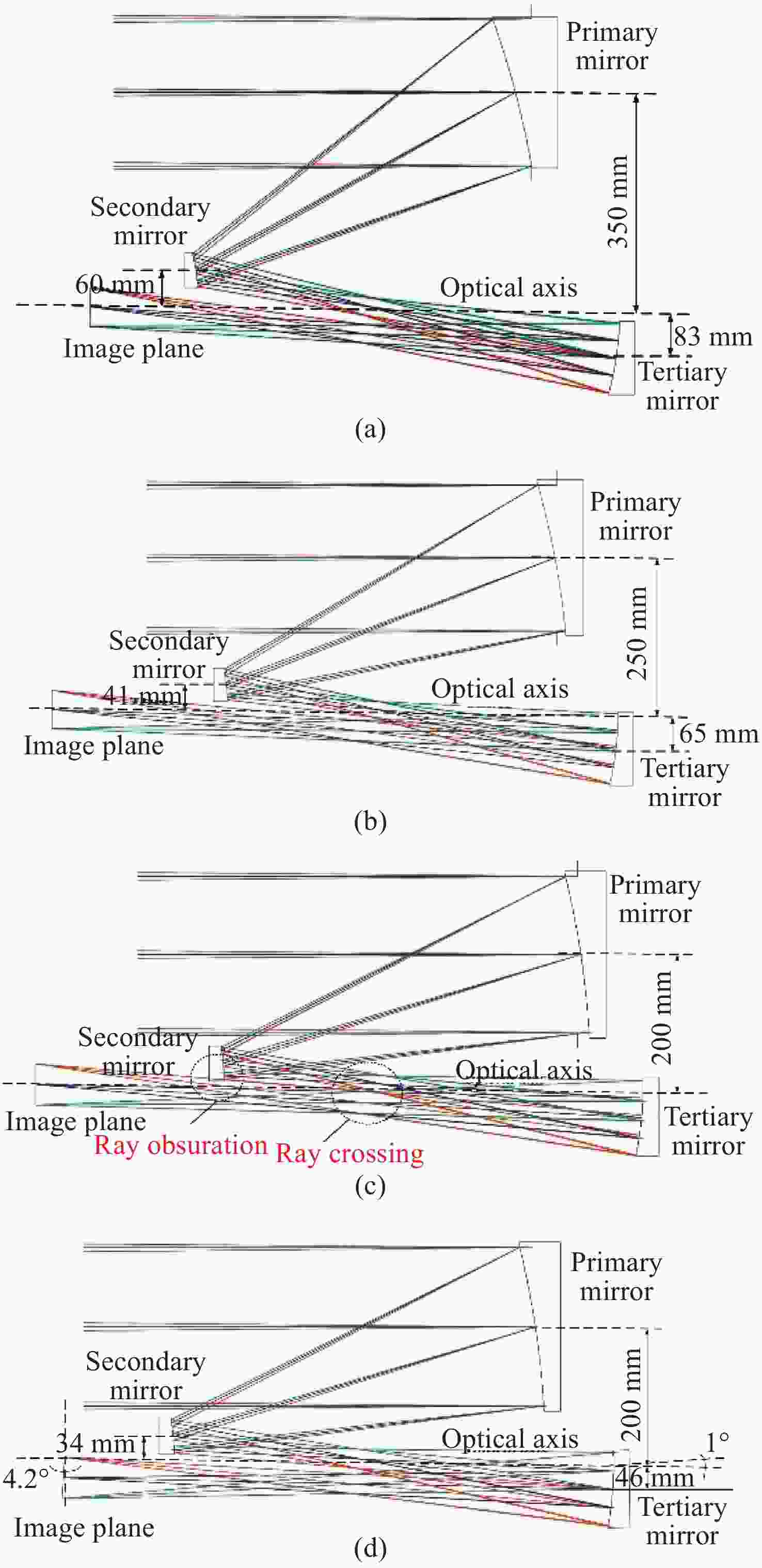
图 11 AOE降敏设计过程中的光学系统:离轴量(a)350 mm;(b)250 mm;(c)200 mm;(d)200 mm,倾斜三镜和像面消除光线遮拦和光线交叉[27]
Figure 11. Optical system in AOE desensitization design process:off-axis magnitude (a) 350 mm; (b) 250 mm; (c) 200 mm; (d) 200 mm, tilt tertiary mirror and image plane to eliminate ray obsuration and ray crossing[27]
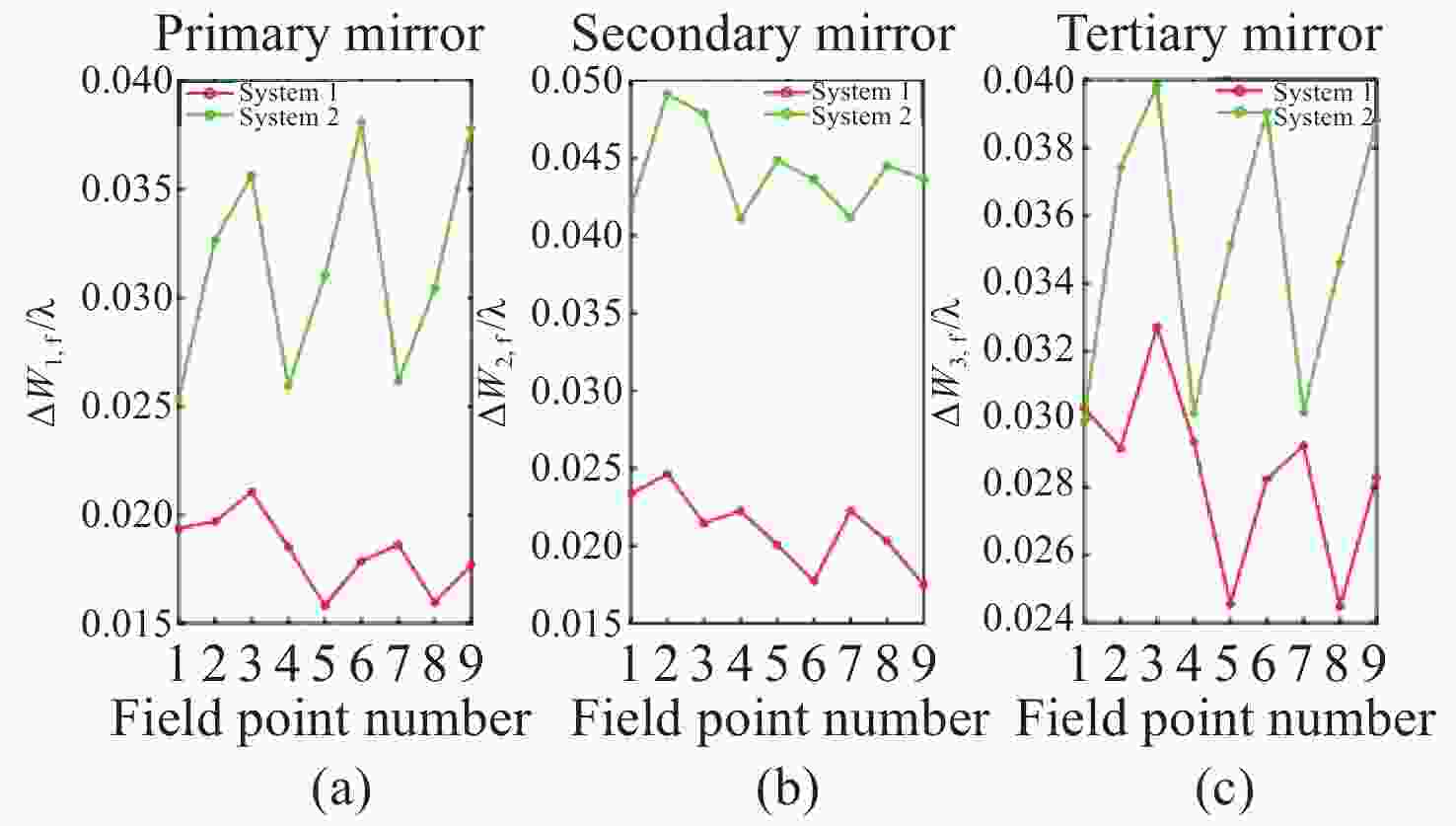
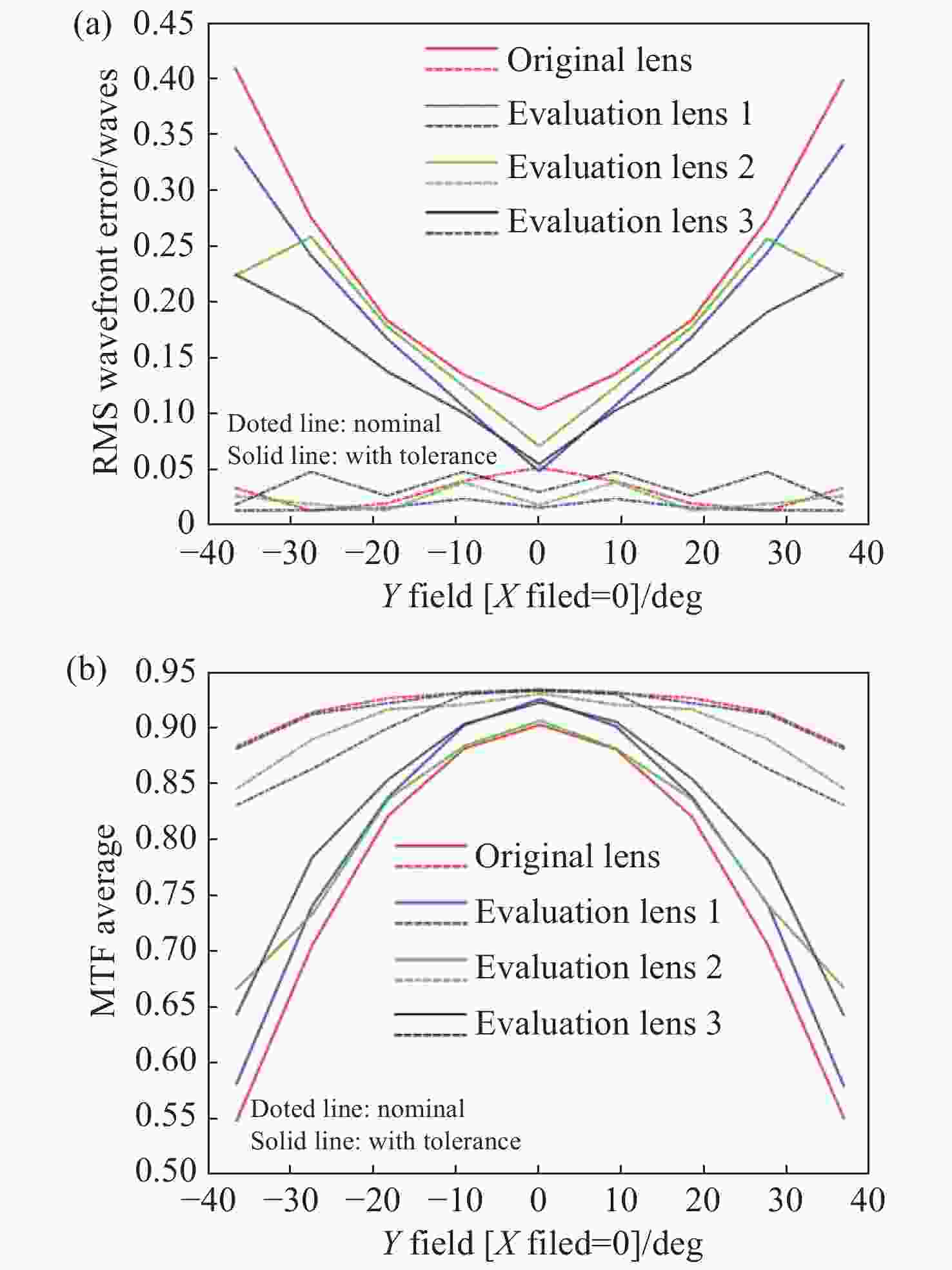
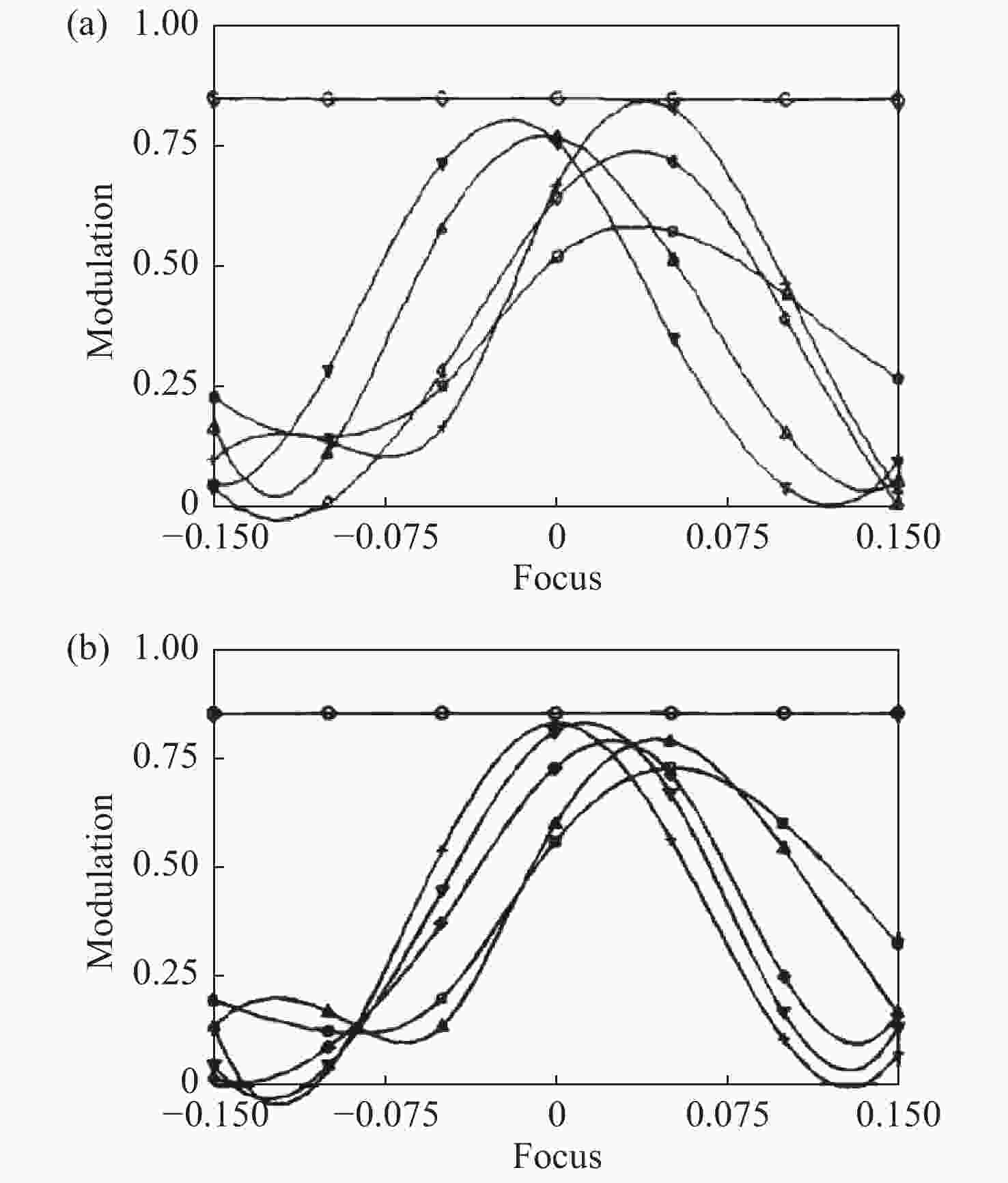
图 17 应用Leticia Carrión-Higueras的三种方法降敏设计前后对比图:(a)降敏设计前后透镜组的波像差;(b)降敏设计前后系统的MTF[1]
Figure 17. Comparison diagrams before and after desensitization design using three methods proposed by Leticia Carrión-Higueras. (a) WFE of lens group before and after desensitization design. (b) MTF of system before and after desensitization design[1]
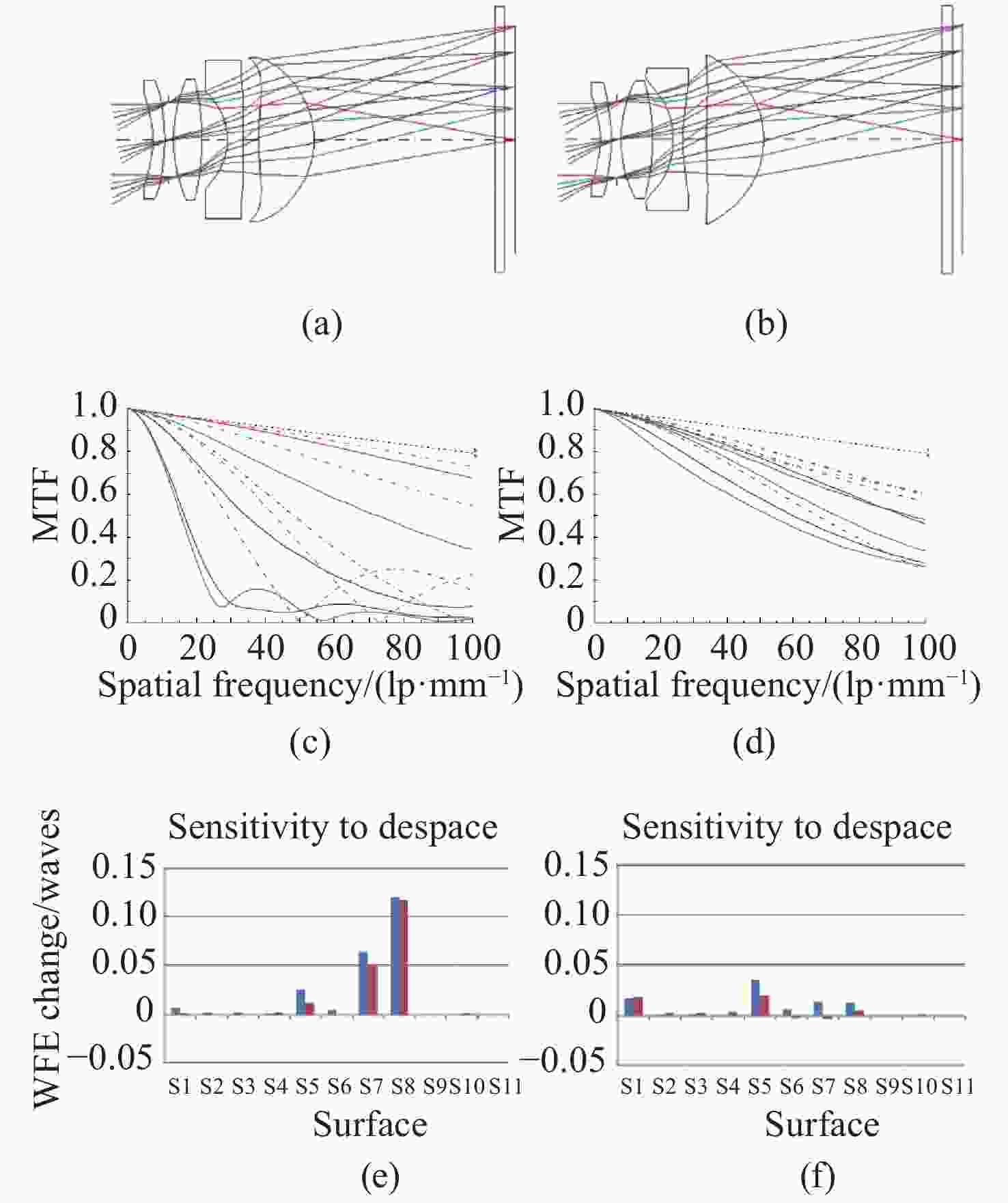
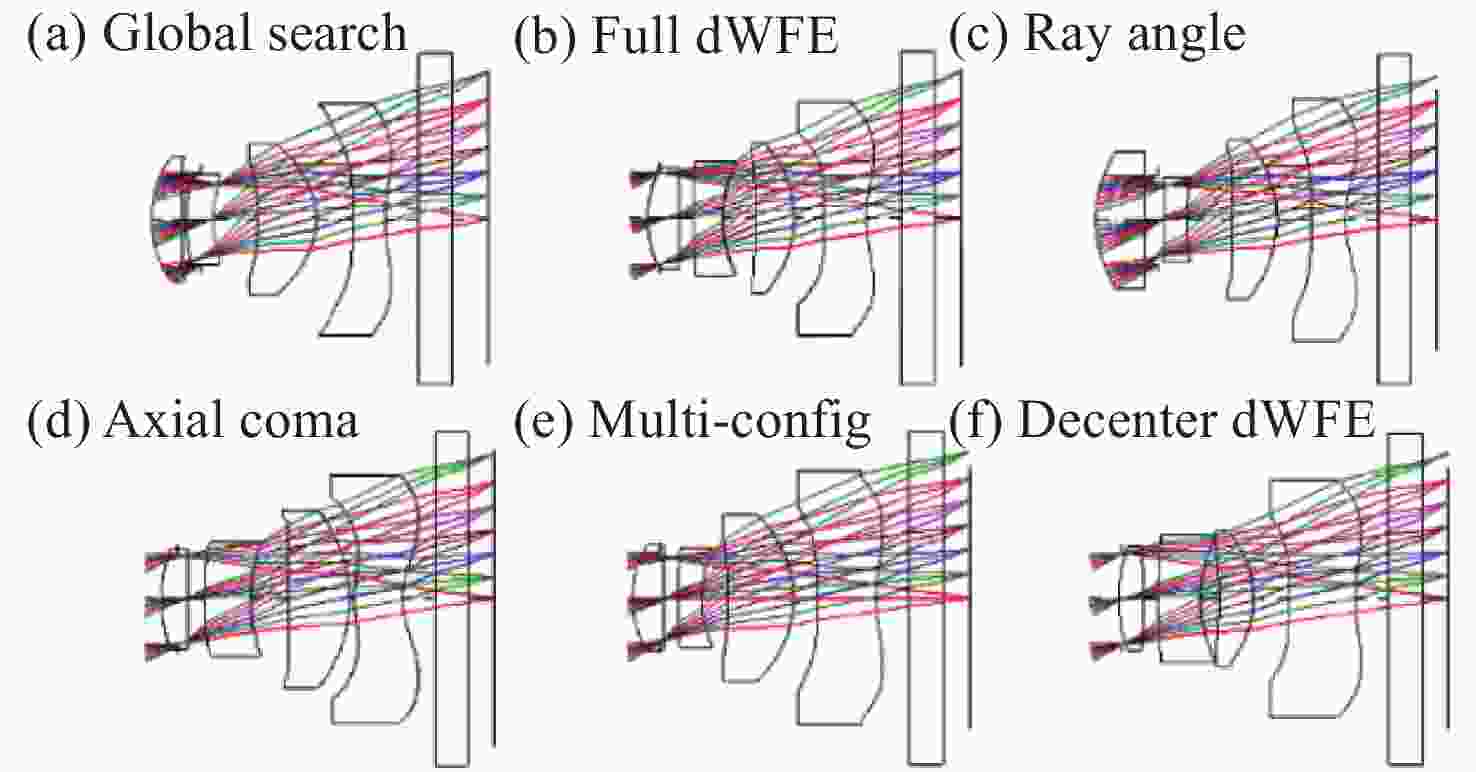
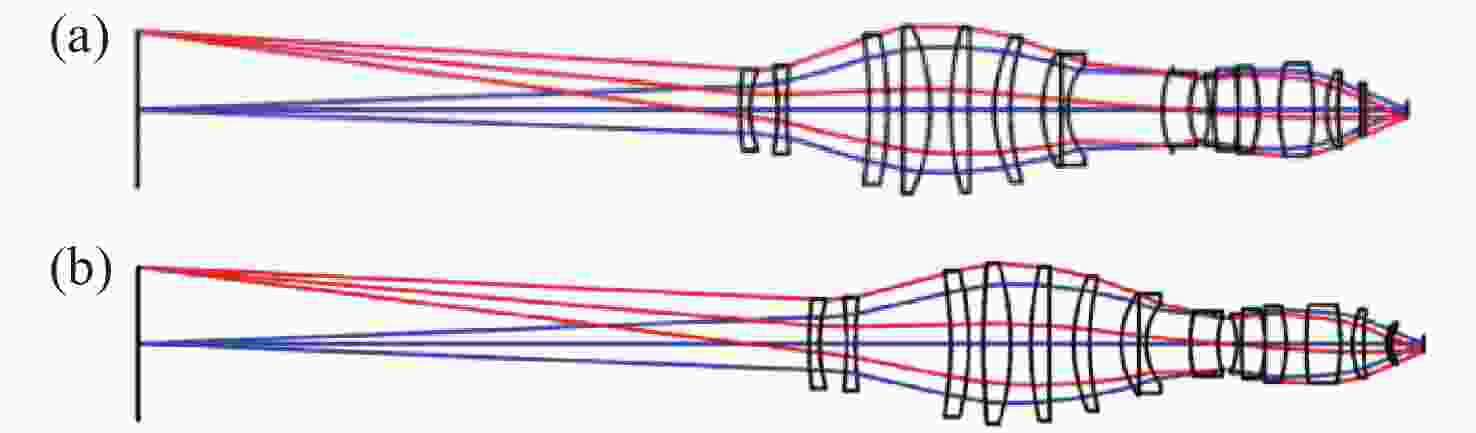
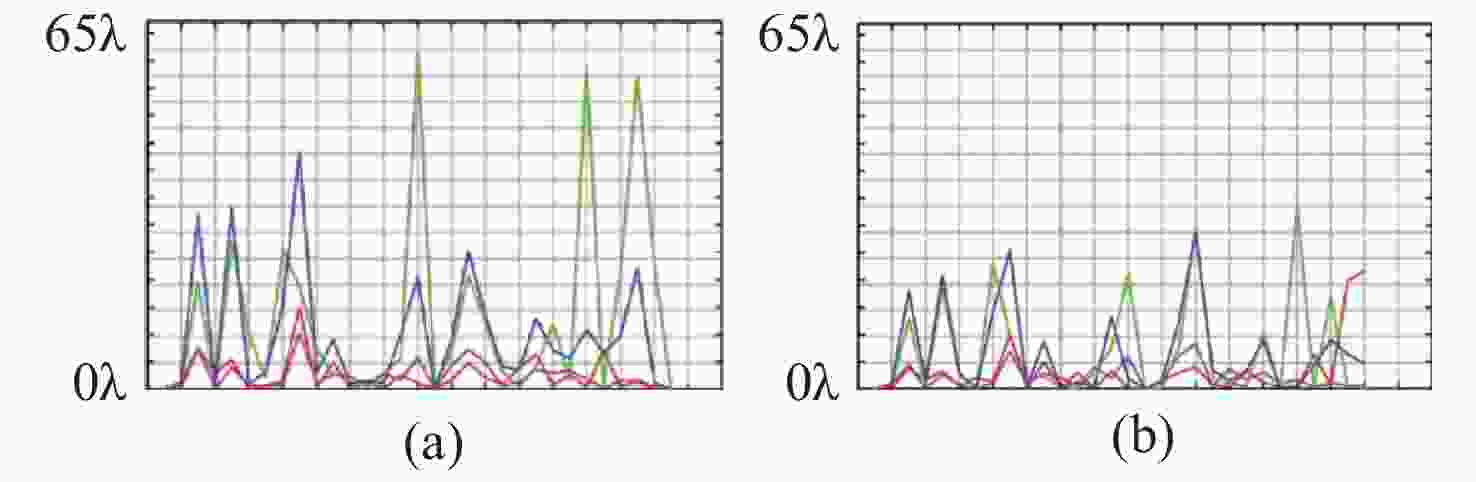
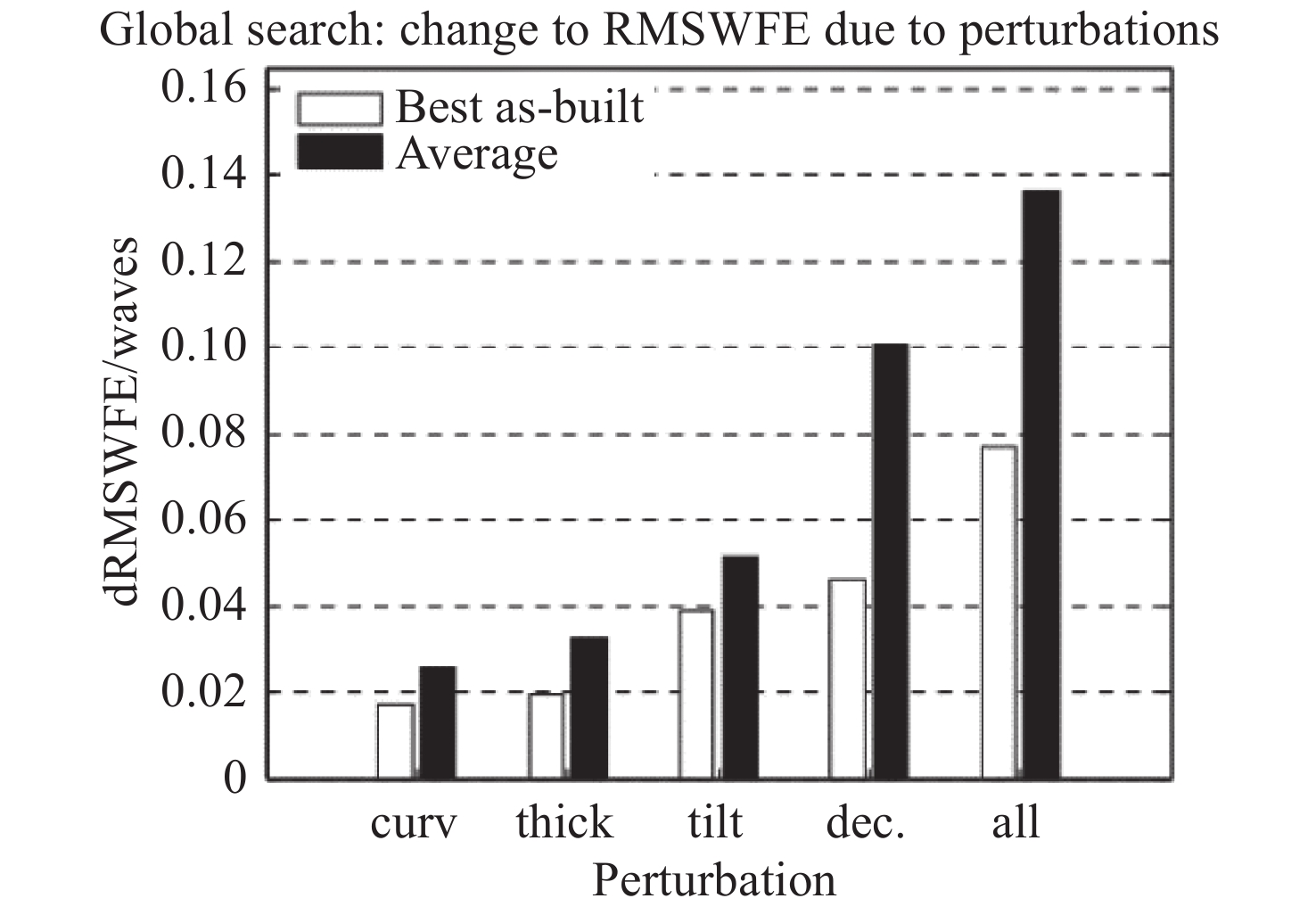
图 21 非球面微型相机镜头降敏设计对比:(a)全局搜索法;(b)全差分波前误差优化法;(c)降低光学入射角;(d)降低倾斜致彗差;(e)多重结构法;(f)降低偏心所致差分波前误差[37]
Figure 21. Comparison using different desensitization design methods for aspheric miniature camera lenses. (a) Global search method. (b) Full differential wavefront error integrated optimization. (c) Reduction of ray angle of incidence. (d) Reduction of tilt-induced axial coma. (e) Zoomed configurations. (f) Reduction of decenter-induced differential wavefront error[37]
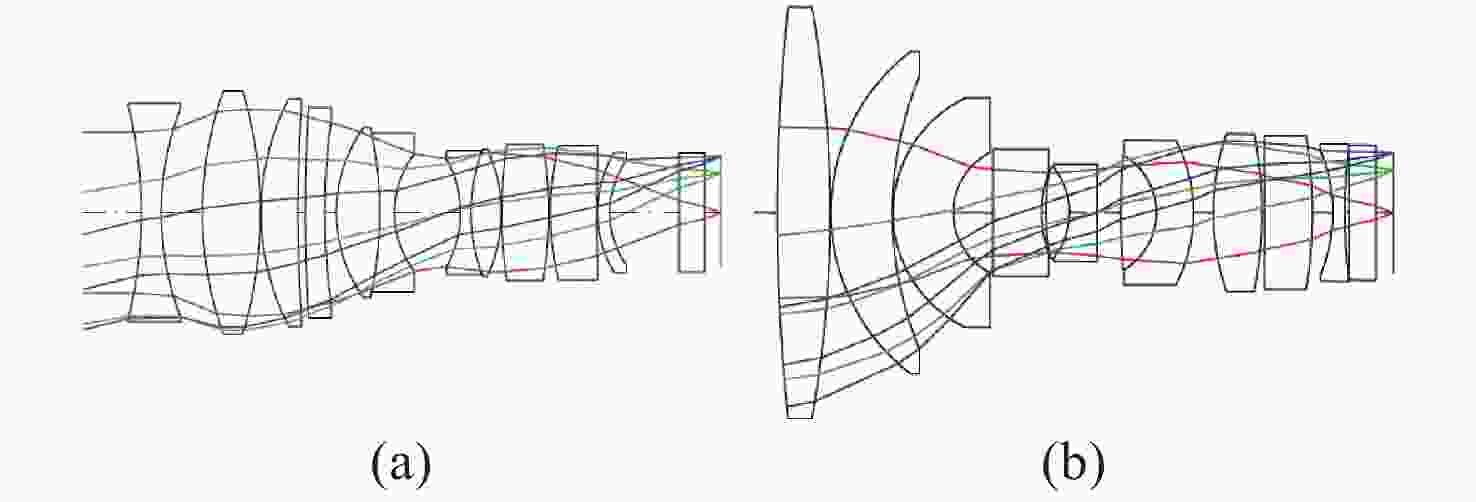
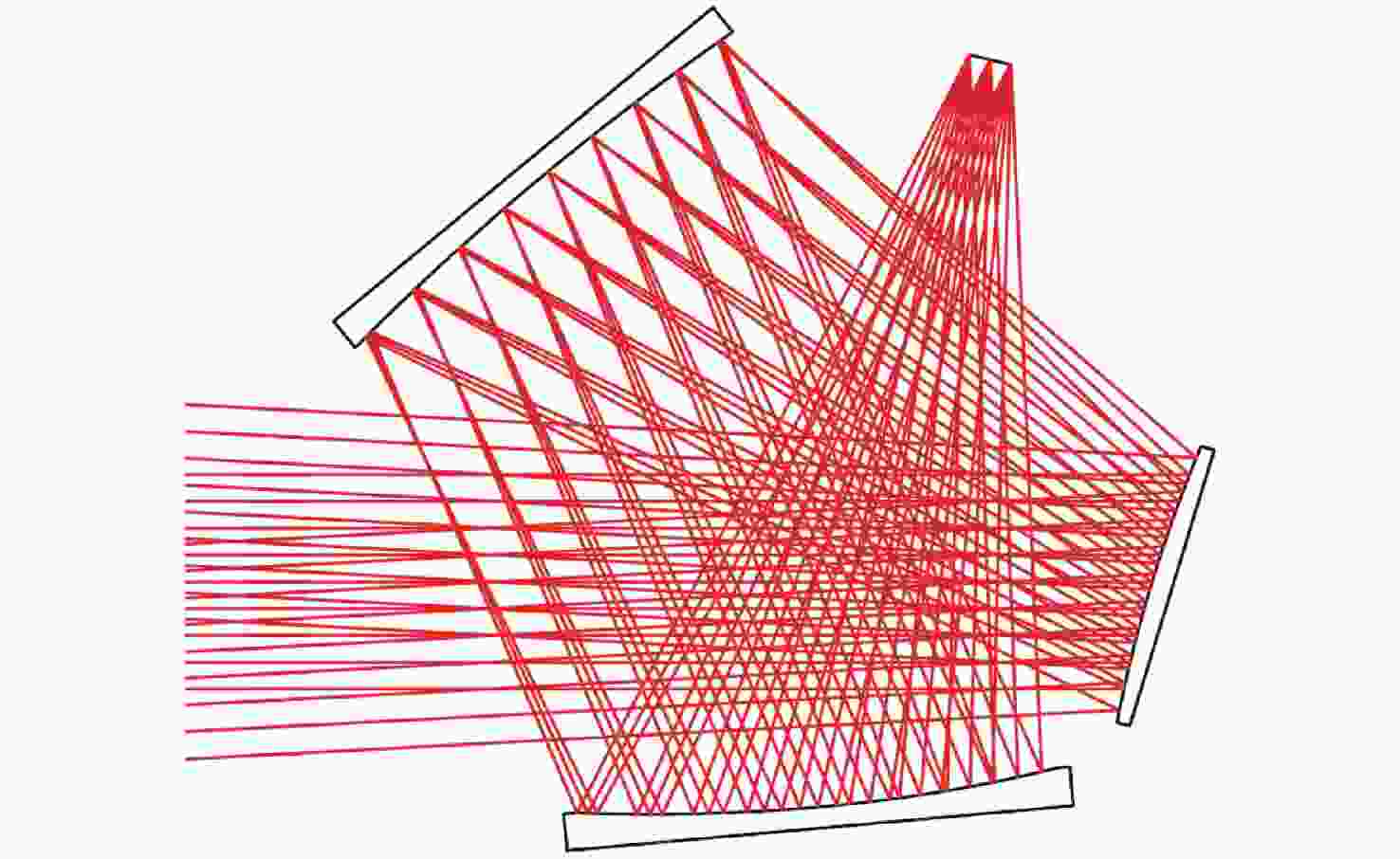
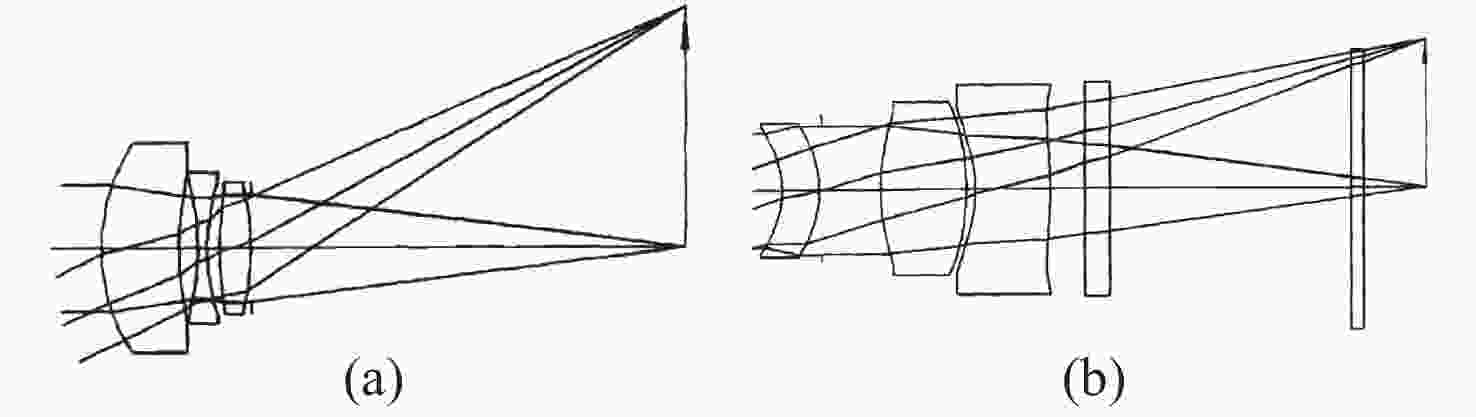
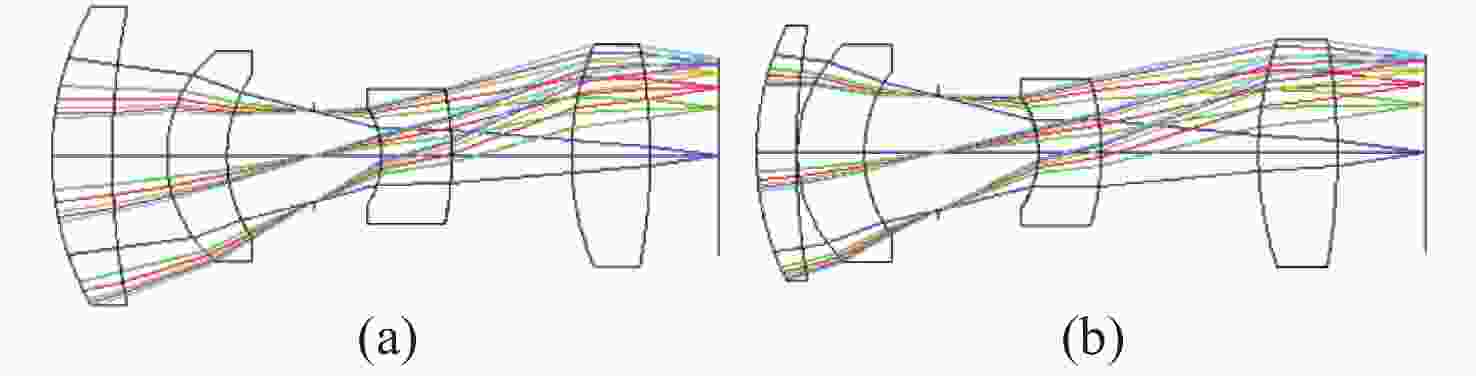
图 29 降敏设计前(a)、后(b)光学系统布局图
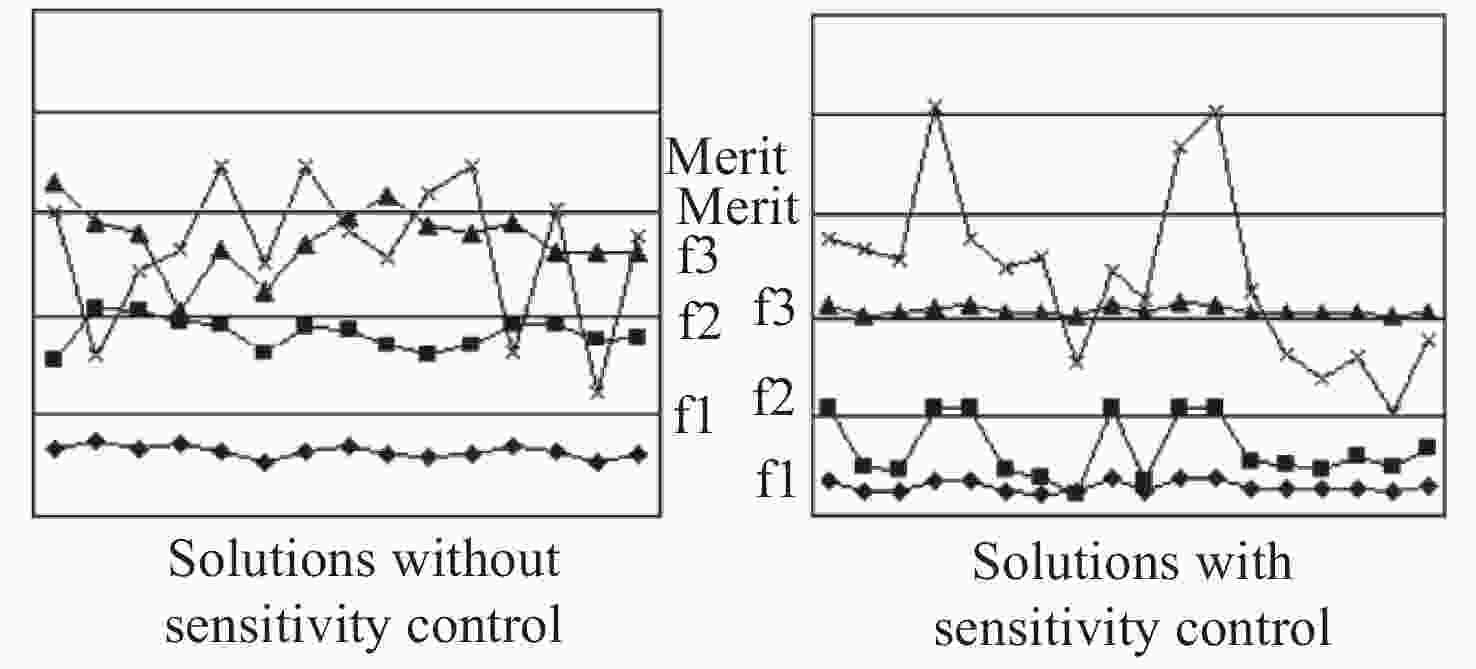
Figure 29. Layout of optical system before (a) and after (b) desensitization design[6]
-
[1] CARRIÓN-HIGUERAS L, CALATAYUD A, SASIAN J M. Improving as-built miniature lenses that use many aspheric surface coefficients with two desensitizing techniques[J]. Optical Engineering, 2021, 60(5): 051208. [2] VAN BELLE G T, MEINEL A B, MEINEL M P. The scaling relationship between telescope cost and aperture size for very large telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5489: 563-570. doi: 10.1117/12.552181 [3] STAHL H P, HENRICHS T. Preliminary multivariable cost model for space telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7731: 773104. doi: 10.1117/12.856214 [4] SHOLL M J, LAMPTON M L, ALDERING G, et al. SNAP telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5487: 1473-1483. doi: 10.1117/12.552081 [5] 孟庆宇. 反射式光学系统误差敏感度理论及降敏设计方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.MENG Q Y. Research on error sensitivity theory and desensitization design method of reflective optical system[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. (in Chinese) [6] SASIAN J. Lens desensitizing: theory and practice[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(3): A62-A67. doi: 10.1364/AO.443758 [7] KUPER T, HARRIS T. A new look at global optimization for optical design[J]. Photonics Spectra, 1992, 1: 151-160. [8] KUPER T. Global optimization finds alternative lens designs[J]. Laser Focus World, 1992, 5: 193-195. [9] FORBES G, JONES A. Global optimization in lens design[J]. Optics and Photonics News, 1992, 3(3): 22. doi: 10.1364/OPN.3.3.000022 [10] JONES A. Global optimization in lens design[D]. Rochester: University of Rochester, 1992. [11] STURLESI D, O'SHEA D. Global view of optical design space[J]. Optical Engineering, 1991, 30(2): 207-218. doi: 10.1117/12.55778 [12] MCGUIRE J P JR. Designing easily manufactured lenses using a global method[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6342: 63420O. doi: 10.1117/12.692254 [13] LIU X Y, GONG T T, JIN G F, et al. Design method for assembly-insensitive freeform reflective optical systems[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(21): 27798-27811. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.027798 [14] FUSE K. Method for designing a refractive or reflective optical system and method for designing a diffraction optical element: US, 6567226[P]. 2003-05-20. [15] ROGERS J R. Using global synthesis to find tolerance-insensitive design forms[C]//International Optical Design Conference, Optica Publishing Group, 2006: TuA4. [16] MA B, THOMPSON K P, SHARMA K, et al. . Applying slope constrained Q-type aspheres to reduce sensitivity of optical systems[C]//Frontiers in Optics 2012, Optica Publishing Group, 2012: FTh3E. 3. [17] MA B, SHARMA K, THOMPSON K P, et al. Mobile device camera design with Q-type polynomials to achieve higher production yield[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(15): 17454-17463. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.017454 [18] THOMPSON K P, SCHIESSER E, ROLLAND J P. Why are freeform telescopes less alignment sensitive than a traditional unobscured TMA?[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9633: 963317. [19] FUERSCHBACH K, DAVIS G E, THOMPSON K P, et al. Assembly of a freeform off-axis optical system employing three φ-polynomial Zernike mirrors[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(10): 2896-2899. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.002896 [20] 李闯, 薛常喜, 杨红芳, 等. 基于Q-type非球面的电子内窥镜物镜光学系统设计[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(6):0622001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0622001LI CH, XUE CH X, YANG H F, et al. Optical system design of electronic endoscope objective with Q-type aspheres[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 0622001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0622001 [21] ISSHIKI M, GARDNER L, GREGORY G G. Automated control of manufacturing sensitivity during optimization[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5249: 343-352. doi: 10.1117/12.514448 [22] ISSHIKI M, SINCLAIR D C, KANEKO S. Lens design: global optimization of both performance and tolerance sensitivity[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6342: 63420N. [23] JEFFS M. Reduced manufacturing sensitivity in multi-element lens systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4832: IMC4. [24] 赵阳, 巩岩, 胡宜宁. 变焦距光学系统降低公差灵敏度的方法[J]. 光电工程,2009,36(7):121-125.ZHAO Y, GONG Y, HU Y N. Method of tolerance sensitivity reduction of zoom optical system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2009, 36(7): 121-125. (in Chinese) [25] QIN Z CH, WANG X D, REN CH M, et al. Design method for a reflective optical system with low tilt error sensitivity[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(26): 43464-43479. doi: 10.1364/OE.447556 [26] DENG Y T, JIN G F, ZHU J. Design method for freeform reflective-imaging systems with low surface-figure-error sensitivity[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(9): 092201. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.092201 [27] MENG Q Y, WANG H Y, WANG W, et al. Desensitization design method of unobscured three-mirror anastigmatic optical systems with an adjustment-optimization-evaluation process[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(6): 1472-1481. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.001472 [28] SASIAN J M, DESCOUR M R. Power distribution and symmetry in lens systems[J]. Optical Engineering, 1998, 37(3): 1001-1004. doi: 10.1117/1.601933 [29] CHENG X M, WANG Y T, HAO Q, et al. Automatic element addition and deletion in lens optimization[J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(7): 1309-1317. doi: 10.1364/AO.42.001309 [30] CHENG X M, WANG Y T, HAO Q. Study on tolerance sensitivity reduction in lens optimization[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5638: 36-42. doi: 10.1117/12.579822 [31] SCADUTO L C N, SASIAN J, STEFANI M A, et al. Two-mirror telescope design with third-order coma insensitive to decenter misalignment[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(6): 6851-6865. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.006851 [32] 孟庆宇, 汪洪源, 王维, 等. 基于光程变化量的反射式光学系统敏感度理论分析与降敏设计方法[J]. 光学精密工程,2021,29(1):72-83. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212901.0072MENG Q Y, WANG H Y, WANG W, et al. Sensitivity theoretical analysis and desensitization design method for reflective optical system based on optical path variation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(1): 72-83. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212901.0072 [33] HASENAUER D. Optical System Tolerancing-A Key to Product Cost Reduction[Z]. Synopsys, Inc. , 2018. [34] SYNOPSYS. CODE V optimization reference manual[S]. Chapter 4 Error Functions, 2017. [35] YABE A. Sensitivity control to surface irregularity[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6342: 634225. doi: 10.1117/12.692246 [36] YABE A. General method of sensitivity control for manufacturing errors[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(27): 5175-5182. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.005175 [37] BATES R. Performance and tolerance sensitivity optimization of highly aspheric miniature camera lenses[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7793: 779302. doi: 10.1117/12.860919 [38] 王之江. 光学设计理论基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1965: 304-314.WANG ZH J. Theoretical Basis of Optical Design[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1965: 304-314. [39] HOPKINS H H, TIZIANI H J. A theoretical and experimental study of lens centring errors and their influence on optical image quality[J]. British Journal of Applied Physics, 1966, 17(1): 33-54. doi: 10.1088/0508-3443/17/1/303 [40] CATALAN G. Design method of an astronomical telescope with reduced sensitivity to misalignment[J]. Applied Optics, 1994, 33(10): 1907-1915. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.001907 [41] BETENSKY E I. Aberration correction and desensitization of an inverse-triplet object lens[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1998, 3482: 264-268. doi: 10.1117/12.322011 [42] WANG L R, SASIAN J M. Merit figures for fast estimating tolerance sensitivity in lens systems[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7652: 76521P. doi: 10.1117/12.868874 [43] 张远健, 唐勇, 王鹏, 等. 光学系统设计中降低公差灵敏度的方法[J]. 光电工程,2011,38(10):127-133.ZHANG Y J, TANG Y, WANG P, et al. Method of tolerance sensitivity reduction of optical system design[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2011, 38(10): 127-133. (in Chinese) [44] 刘智颖, 吕知洋, 高柳絮. 红外显微光学系统的小像差互补设计方法[J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(2):20200153. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200153LIU ZH Y, LV ZH Y, GAO L X. Design method of infrared microscope optical system with lower aberration compensation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(2): 20200153. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200153 [45] ZHANG K, ZHONG X, WANG W, et al. Ultra-low-distortion optical system design based on tolerance sensitivity optimization[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 437: 231-236. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.12.059 [46] DE ALBUQUERQUE B F C, LIAO L Y, MONTES A S, et al. A multi-objective approach in the optimization of optical systems taking into account tolerancing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8131: 813105. doi: 10.1117/12.894980 -






 下载:
下载: