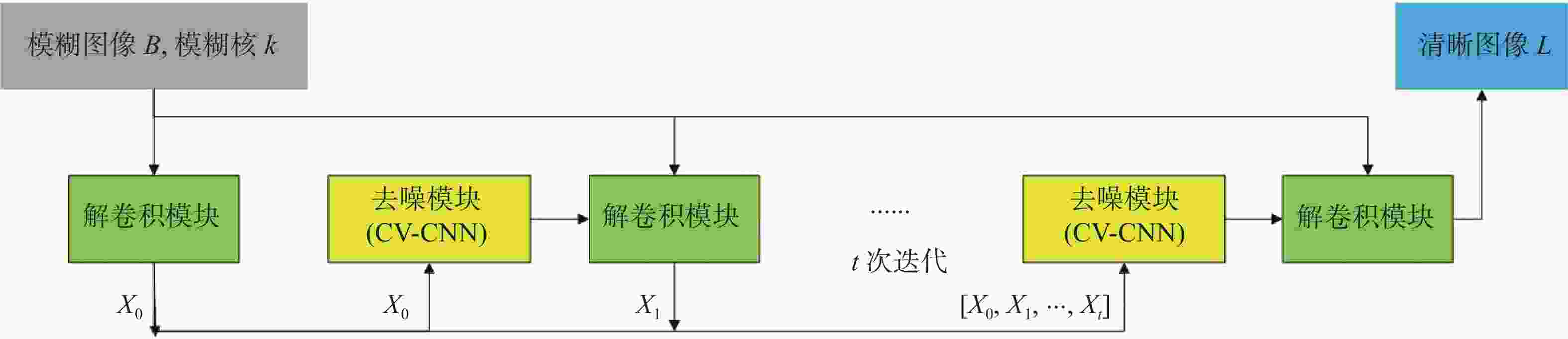
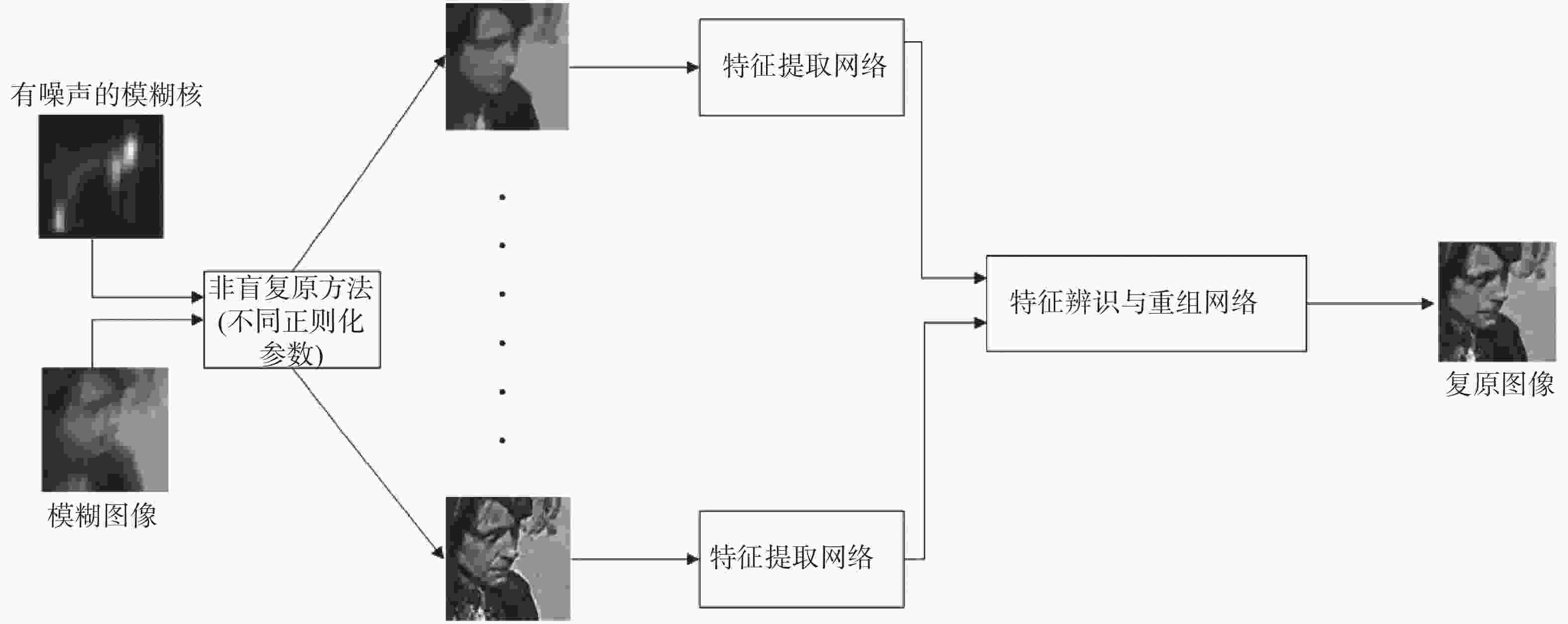
-
摘要:
非盲图像复原在数学上是一种典型的病态问题,也是计算机视觉领域的重要研究内容之一,其目标是在点扩散函数已知的情况下,由模糊图像估计出清晰图像,其研究重点是在改善图像清晰度和抑制噪声之间做出适当的折衷。 近50年来,非盲图像复原取得了长足的发展,从早期的维纳滤波到当前的深度学习,学者们提出了数以百计的非盲图像复原算法,并应用在各个领域。本文首先介绍非盲图像复原的基本概念和研究意义,然后依据算法的属性对非盲图像复原算法进行分类概括,从总体上将其分为传统方法和深度学习方法,又进一步将传统方法细分为直接法和迭代法,并依据不同算法的模型特征,分析不同类别中主要算法的优缺点,同时结合多种典型实验,比较分析了一些代表性算法的复原性能,最后展望了非盲图像复原算法的发展趋势,归纳了重点研究方向。
Abstract:Non-blind image restoration is one of the most improtant research topics in the field of computer vision. It is also a typical ill-posed problem in mathematics. Its goal is to estimate a clear image from a blurred image when the point spread function is known. Its research focuses on how to make an appropriate compromise between improving clarity and suppressing noise. In the past 50 years, non-blind image restoration has made great progress. From the Wiener filtering to deep learning based methods, scholars have proposed hundreds of non-blind image restoration algorithms and applied them in various academic fields. This paper first introduces the basic concept and research significance of non-blind image restoration, then classifies and summarizes the main non-blind image restoration algorithms according to the algorithm attributes, which are generally divided into traditional methods and deep learning based methods. The traditional methods are divided into the direct method and iterative method, then are analyzed for their advantages and disadvantages. The performance of representative restoration algorithms is compared in a varity of typical experiments. Finally, the development trend and important research directions of non-blind image restoration algorithms are proposed.
-
Key words:
- non blind image restoration /
- image priors /
- direct method /
- iterative scheme /
- deep learning
-
表 1 实验设置
Table 1. Experimental settings
序号 点扩散函数 噪声水平 图像 1 9 × 9 boxcar BSNR = 40 dB Cameraman 2 $k(x,y) = 1/({x^2} + {y^2}),x,y = - 7,\cdots,7$ $ {\sigma ^2} = 2 $ Cameraman 3 $k(x,y) = 1/({x^2} + {y^2}),x,y = - 7,\cdots,7$ $ {\sigma ^2} = 8 $ Cameraman 4 $k = {[1,4,6,4,1]^{\rm{T}}}[1,4,6,4,1]/256$ $ {\sigma ^2} = 49 $ Lena 5 Gaussian型点扩散函数,方差为1.6 $ {\sigma ^2} = 2 $ Barbara 6 Gaussian型点扩散函数,方差为0.4 $ {\sigma ^2} = 64 $ House 表 2 8种直接法输出ISNR的对比
Table 2. Comparison of ISNR output by eight methods
表 3 迭代法实验设置
Table 3. Experimental setup for iterative methods
序号 点扩散函数 噪声水平 1 $ k(x,y) = 1/({x^2} + {y^2}),x,y = - 7,\cdots,7 $ ${\sigma ^2} = 2$ 2 $ k(x,y) = 1/({x^2} + {y^2}),x,y = - 7,\cdots,7 $ ${\sigma ^2} = 8 $ 3 9 × 9 boxcar BSNR = 40 dB 4 $ k = {[1,4,6,4,1]^{\rm{T} } }[1,4,6,4,1]/256 $ ${\sigma ^2} = 49 $ 5 Gaussian型点扩散函数,方差为1.6 ${\sigma ^2} = 2 $ 6 Gaussian型点扩散函数,方差为0.4 ${\sigma ^2} = 64 $ 表 4 迭代法实验对比 ISNR
Table 4. Experimental comparison of ISNR
(单位:dB) 实验序号 1 2 3 4 5 6 方法 Cameraman BM3DDEB[31] 8.19 6.40 8.34 3.34 3.73 4.70 L0-Abs[62] 7.70 5.55 9.10 2.93 3.49 1.77 CGMK[36] 7.80 5.49 9.15 2.80 3.54 3.33 TVMM[34] 7.41 5.17 8.54 2.57 3.36 1.30 GFD[33] 8.38 6.52 9.73 3.57 4.02 - NCSR[70] 8.78 6.69 10.33 3.78 4.60 4.50 GSR[71] 8.39 6.39 10.08 3.33 3.94 4.76 IDDBM3D[73] 8.85 7.12 10.45 3.98 4.31 4.89 LRD[76] 8.90 7.05 10.70 3.99 4.62 4.62 House BM3DDEB[31] 9.32 8.14 10.85 5.13 4.56 7.21 L0-Abs[62] 8.40 7.12 11.06 4.55 4.80 2.15 CGMK[36] 8.31 6.97 10.75 4.48 4.97 4.59 TVMM[34] 7.98 6.57 10.39 4.12 4.54 2.44 GFD[33] 9.39 7.75 12.02 5.21 5.39 NCSR[70] 9.96 8.48 13.12 5.81 5.67 6.94 GSR[71] 10.02 8.56 13.44 6.00 5.95 7.18 IDDBM3D[73] 9.95 8.55 12.89 5.79 5.74 7.13 LRD[76] 10.09 8.67 13.49 6.03 6.22 6.74 Lena BM3DDEB[31] 7.95 6.53 7.97 4.81 4.37 6.40 L0-Abs[62] 6.66 5.71 7.79 4.09 4.22 1.93 CGMK[36] 6.76 5.37 7.86 3.49 3.93 4.46 TVMM[34] 6.36 4.98 7.47 3.52 3.61 2.79 GFD[33] 8.12 6.65 8.97 4.77 4.95 - NCSR[70] 8.03 6.54 9.25 4.93 4.86 6.19 GSR[71] 8.24 6.76 9.43 5.17 4.96 6.57 IDDBM3D[73] 7.97 6.61 8.91 4.97 4.85 6.34 LRD[76] 8.25 6.78 9.31 5.13 5.08 6.13 Barbara BM3DDEB[31] 7.80 3.94 5.86 1.90 1.28 5.80 L0-Abs[62] 3.51 1.53 3.98 0.73 0.81 1.17 CGMK[36] 2.45 1.34 3.55 0.44 0.81 0.38 TVMM[34] 3.10 1.33 3.49 0.41 0.75 0.59 NCSR 7.76 3.64 5.92 2.06 1.43 5.50 GSR[71] 8.98 4.80 7.15 2.19 1.58 6.20 IDDBM3D[73] 7.64 3.96 6.05 1.88 1.16 5.45 LRD[76] 8.31 5.17 6.95 2.34 1.70 5.37 表 5 深度学习方法的实验对比
Table 5. Experimental comparison of deep learning of different methods
Levin[106] Sun[107] Martin[108] σ 1% 3% 5% 1% 5% 1% 5% EPLL[82] 34.06 29.09 26.54 32.48 26.78 29.81 24.66 0.9310 0.8460 0.7785 0.8815 0.6975 0.8383 0.6276 CSF[84] 31.09 28.01 26.32 31.52 26.62 29.00 24.93 0.9024 0.8013 0.7427 0.8622 0.6735 0.8230 0.6428 MLP[89] 32.08 27.00 25.38 31.47 24.65 28.47 24.01 0.8884 0.7016 0.6330 0.8535 0.5198 0.7977 0.5619 LDT[109] 31.53 28.39 26.70 30.52 26.71 28.20 24.90 0.8977 0.8052 0.7468 0.8399 0.6694 0.7922 0.6358 FCN[94] 33.22 29.49 27.72 32.36 27.67 29.51 25.45 0.9267 0.8599 0.8142 0.8853 0.7340 0.8339 0.6771 IRCNN[93] 34.33 30.04 28.51 33.57 27.64 30.63 25.65 0.9210 0.8156 0.7762 0.8977 0.6884 0.8645 0.6640 FDN[87] 34.05 29.77 27.94 32.63 27.75 29.93 25.93 0.9335 0.8583 0.8139 0.8887 0.7319 0.8555 0.6943 FNBD[88] 34.81 30.63 27.93 31.22 27.63 30.92 25.49 0.9398 0.8658 0.7759 0.8860 0.7010 0.8799 0.6589 RGDN[92] 33.96 29.71 27.45 31.25 26.93 29.51 25.33 0.9395 0.8662 0.7889 0.8869 0.7161 0.8616 0.6688 VEM[99] 34.31 30.50 28.52 32.73 29.41 − − 0.9382 0.8798 0.8348 0.8952 0.8055 − − DWDN[101] 36.90 32.77 30.77 34.05 − 31.74 − 0.9614 0.9179 0.8857 0.9225 − 0.8938 − CV-CNN[97] 35.44 30.85 28.80 33.10 29.54 − − 0.9467 0.8829 0.8381 0.9022 0.8094 − − SVMAP[110] − − − 34.51 29.20 31.89 27.25 − − − 0.9273 0.7940 0.8973 0.7550 -
[1] STARCK J L, PANTIN E, MURTAGH F. Deconvolution in astronomy: a review[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2002, 114(800): 1051-1069. doi: 10.1086/342606 [2] JAIN A K. Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing[M]. Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall, 1989: 1420-1424. [3] 沈峘, 李舜酩, 毛建国, 等. 数字图像复原技术综述[J]. 中国图像图形学报,2009,14(9):1764-1775.SHEN H, LI SH M, MAO J G, et al. Digital image restoration techniques: a review[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2009, 14(9): 1764-1775. (in Chinese) [4] 闫敬文, 彭鸿, 刘蕾, 等. 基于L0正则化模糊核估计的遥感图像复原[J]. 光学 精密工程,2014,22(9):2572-2579. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20142209.2572YAN J W, PENG H, LIU L, et al. Remote sensing image restoration based on zero-norm regularized kernel estimation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2014, 22(9): 2572-2579. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20142209.2572 [5] 李东升, 陈春晓, 王章立, 等. 基于全局方差和噪声估计的维纳滤波图像的复原方法[J]. 生物医学工程研究,2017,36(4):331-335. doi: 10.19529/j.cnki.1672-6278.2017.04.11LI D SH, CHEN CH X, WANG ZH L, et al. Wiener filter image restoration based on global variance and noise estimation[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research, 2017, 36(4): 331-335. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19529/j.cnki.1672-6278.2017.04.11 [6] 朱非甲, 金鹏. 面向工业检测的图像快速去直线运动模糊方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2018,50(9):123-129. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201704118ZHU F J, JIN P. Fast moving line motion de-blurring for image detection of industrial inspection[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(9): 123-129. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201704118 [7] 陈灏. 光学稀疏孔径成像系统图像恢复算法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.CHEN H. Image restoration algorithm for optical sparse aperture systems[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. (in Chinese) [8] 杨航. 图像反卷积算法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012: 3-7.YANG H. The study on image deconvolution algorithm[D]. Changsha: Jilin University, 2012: 3-7. (in Chinese) [9] HANSEN P C. Rank-Deficient and Discrete Ill-Posed Problems: Numerical Aspects of Linear Inversion[M]. Philadelphia: SIAM, 1997. [10] FAN J Q, KOO J. Wavelet deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2002, 48(3): 734-747. doi: 10.1109/18.986021 [11] JOHNSTONE I M, KERKYACHARIAN G, PICARD D, et al. Wavelet deconvolution in a periodic setting[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B, 2004, 66(3): 547-573. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2004.02056.x [12] PENSKY M, VIDAKOVIC B. Adaptive wavelet estimator for nonparametric density deconvolution[J]. Annals of Statistics, 1999, 27(6): 2033-2053. [13] DONOHO D L. Nonlinear solution of linear inverse problems by wavelet–vaguelette decomposition[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 1995, 2(2): 101-126. doi: 10.1006/acha.1995.1008 [14] KALIFA J, MALLAT S, ROUGE B. Deconvolution by thresholding in mirror wavelet bases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2003, 12(4): 446-457. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.810592 [15] NEELAMANI R, CHOI H, BARANIUK R. ForWaRD: Fourier-wavelet regularized deconvolution for Ill-conditioned systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(2): 418-433. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2003.821103 [16] CANDÈS E, DEMANET L, DONOHO D L, et al. Fast discrete curvelet transforms[J]. Multiscale Modeling &Simulation, 2006, 5(3): 861-899. [17] DO M N, VETTERLI M. The contourlet transform: an efficient directional multiresolution image representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(12): 2091-2106. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.859376 [18] EASLEY G R, LABATE D, LIM W Q. Sparse directional image representations using the discrete shearlet transform[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2008, 25(1): 25-46. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2007.09.003 [19] DEMANET L, YING L X. Wave atoms and sparsity of oscillatory patterns[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2007, 23(3): 368-387. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2007.03.003 [20] NEELAMANI R N, DEFFENBAUGH M, BARANIUK R G. Texas two-step: a framework for optimal multi-input single-output deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(11): 2752-2765. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.906251 [21] PATEL V M, EASLEY G R, HEALY D M. Shearlet-based deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(12): 2673-2685. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2029594 [22] YANG H, ZHANG ZH B. Fusion of wave atom-based wiener shrinkage filter and joint non-local means filter for texture-preserving image deconvolution[J]. Optical Engineering, 2012, 51(6): 067009. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.51.6.067009 [23] PORTILLA J, SIMONCELLI E. Image restoration using Gaussian scale mixtures in the wavelet domain[C]. Proceedings 2003 International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2003: Ⅱ-965. [24] GUERRERO-COLON J A, MANCERA L, PORTILLA J. Image restoration using space-variant Gaussian scale mixtures in overcomplete pyramids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(1): 27-41. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.911473 [25] XUE F, LUISIER F, BLU T. Multi-wiener SURE-LET deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(5): 1954-1968. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2240004 [26] KATKOVNIK V, EGIAZARIAN K O, ASTOLA J. A spatially adaptive nonparametric regression image deblurring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(10): 1469-1478. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.851705 [27] FOI A, DABOV K, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Shape-adaptive DCT for denoising and image reconstruction[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6064: 203-214. [28] BUADES A, COLL B, MOREL J. Nonlocal image and movie denoising[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 76(2): 123-139. doi: 10.1007/s11263-007-0052-1 [29] CHEN F, HUANG X J, CHEN W F. Texture-preserving image deblurring[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(12): 1018-1021. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2010.2078807 [30] DABOV K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions On Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080-2095. [31] DABOVE K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image restoration by sparse 3D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 6812: 681207. doi: 10.1117/12.766355 [32] BANHAM M R, KATSAGGELOS A K. Spatially adaptive wavelet-based multiscale image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1996, 5(4): 619-634. doi: 10.1109/83.491338 [33] YANG H, ZHANG ZH B, GUAN Y J. An adaptive parameter estimation for guided filter based image deconvolution[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 138: 16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.03.006 [34] WANG Y L, YANG J F, YIN W T, et al. A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2008, 1(3): 248-272. doi: 10.1137/080724265 [35] CHO S, WANG J, LEE S. Handling outliers in non-blind image deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2011: 495-502. [36] CHANTAS G, GALATSANOS N P, MOLINA R, et al. Variational Bayesian image restoration with a product of spatially weighted total variation image priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(2): 351-362. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2033398 [37] WEN Y W, NG M K, CHING W K. Iterative algorithms based on decoupling of deblurring and denoising for image restoration[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2008, 30(5): 2655-2674. doi: 10.1137/070683374 [38] TAKEDA H, FARSIU S, MILANFAR P. Deblurring using regularized locally adaptive kernel regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(4): 550-563. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.918028 [39] LUCY L B. An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions[J]. Astronomical Journal, 1974, 79: 745. doi: 10.1086/111605 [40] WHYTE O, SIVIC J, ZISSERMAN A. Deblurring shaken and partially saturated images[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, IEEE, 2011: 745-752. [41] RUDIN L I, OSHER S, FATEMI E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[J]. Physica D:Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 60(1-4): 259-268. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F [42] BECK A, TEBOULLE M. Fast gradient-based algorithms for constrained total variation image denoising and deblurring problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(11): 2419-2434. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2028250 [43] CHAN T F, GOLUB G H, MULET P. A nonlinear primal-dual method for total variation-based image restoration[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1999, 20(6): 1964-1977. doi: 10.1137/S1064827596299767 [44] CHEN D Q, ZHANG H, CHENG L ZH. A fast fixed point algorithm for total variation deblurring and segmentation[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2012, 43(3): 167-179. doi: 10.1007/s10851-011-0298-7 [45] SHI F, CHENG J, WANG L, et al. LRTV: MR image super-resolution with low-rank and total variation regularizations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(12): 2459-2466. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2437894 [46] RUDIN L I, OSHER S. Total variation based image restoration with free local constraints[C]. Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 1994: 31-35. [47] 童蓓蕾. 基于变分法的图像复原算法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018.TONG B L. Research of image restoration algorithm based on variational method[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018. (in Chinese) [48] OSHER S, BURGER M, GOLDFARB D, et al. An iterative regularization method for total variation-based image restoration[J]. SIAM Journal on Multiscale Model &Simulation, 2005, 4(2): 460-489. [49] GOLDSTEIN T, OSHER S. The split Bregman method for L1-regularized problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 323-343. doi: 10.1137/080725891 [50] BIOUCAS-DIAS J M, FIGUEIREDO M A T. A new TwIST: two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(12): 2992-3004. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.909319 [51] MICHAILOVICH O V. An iterative shrinkage approach to total-variation image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(5): 1281-1299. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2090532 [52] VONESCH C, UNSER M. A fast thresholded landweber algorithm for wavelet-regularized multidimensional deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(4): 539-549. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.917103 [53] NG M K, WEISS P, YUAN X M. Solving constrained total-variation image restoration and reconstruction problems via alternating direction methods[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2010, 32(5): 2710-2736. doi: 10.1137/090774823 [54] OLIVEIRA J P, BIOUCAS-DIAS J M, FIGUEIREDO M A T. Adaptive total variation image deblurring: a majorization-minimization approach[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 89(9): 1683-1693. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.03.018 [55] KRISHNAN D, FERGUS R. Fast image deconvolution using hyper-Laplacian priors[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates Inc. , 2009: 1033-1041. [56] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289-1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [57] PAN J SH, HU ZH, SU ZH X, et al. L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior for deblurring text images and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 342-355. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2551244 [58] VONESCH C, UNSER M. A fast iterative thresholding algorithm for wavelet-regularized deconvolution[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6701: 67010D. [59] FIGUEIREDO M A T, NOWAK R D. An EM algorithm for wavelet-based image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2003, 12(8): 906-916. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.814255 [60] DONG B, ZHANG Y. An efficient algorithm for ℓ0 minimization in wavelet frame based image restoration[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2013, 54(2): 350-368. [61] CAI J F, DONG B, SHEN Z W. Image restoration: a wavelet frame based model for piecewise smooth functions and beyond[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2016, 41(1): 94-138. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2015.06.009 [62] PORTILLA J. Image restoration through l0 analysis-based sparse optimization in tight frames[C]. Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2009: 3909-3912. [63] CAI J F, OSHER S, SHEN Z W. Split Bregman methods and frame based image restoration[J]. Multiscale Modeling &Simulation, 2010, 8(2): 337-369. [64] STARCK J L, NGUYEN M K, MURTAGH F. Wavelets and curvelets for image deconvolution: a combined approach[J]. Signal Processing, 2003, 83(10): 2279-2283. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(03)00150-6 [65] LV X G, SONG Y ZH, LI F. An efficient nonconvex regularization for wavelet frame and total variation based image restoration[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2015, 290: 553-566. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2015.06.006 [66] ELAD M, AHARON M. Image denoising via sparse and redundant representations over learned dictionaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(12): 3736-3745. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.881969 [67] AHARON M, ELAD M, BRUCKSTEIN A. K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311-4322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199 [68] YANG H, ZHU M, WU X T, et al. Dictionary learning approach for image deconvolution with variance estimation[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(25): 5677-5684. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.005677 [69] DONG W SH, ZHANG L, SHI G M. Centralized sparse representation for image restoration[C]. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2011: 1259-1266. [70] DONG W SH, ZHANG L, SHI G M, et al. Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(4): 1620-1630. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2235847 [71] ZHANG J, ZHAO D B, GAO W. Group-based sparse representation for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3336-3351. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2323127 [72] KHERADMAND A, MILANFAR P. A general framework for regularized, similarity-based image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(12): 5136-5151. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2362059 [73] DANIELYAN A, KATKOVNIK V, EGIAZARIAN K O. BM3D frames and variational image deblurring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1715-1728. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2176954 [74] DONG W SH, SHI G M, LI X. Nonlocal image restoration with bilateral variance estimation: a low-rank approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(2): 700-711. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2221729 [75] GU SH H, ZHANG L, ZUO W M, et al. . Weighted nuclear norm minimization with application to image denoising[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2014: 2862-2869. [76] YANG H, HU G SH, WANG Y Q, et al. Low-rank approach for image nonblind deconvolution with variance estimation[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2015, 24(6): 063013. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.24.6.063013 [77] TOMASI C, MANDUCHI R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images[C]. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 1998: 839-846. [78] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(6): 1397-1409. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213 [79] YANG H, ZHANG ZH B, ZHU M, et al. Edge-preserving image deconvolution with nonlocal domain transform[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2013, 54: 128-136. [80] SUN L B, CHO S, WANG J, et al. . Good image priors for non-blind deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2014: 231-246. [81] SCHMIDT U, ROTHER C, NOWOZIN S, et al. . Discriminative non-blind deblurring[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2013: 604-611. [82] ZORAN D, WEISS Y. From learning models of natural image patches to whole image restoration[C]. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2011: 479-486. [83] ROTH S, BLACK M J. Fields of experts: a framework for learning image priors[C]. Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Computer Society IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2005: 860-867. [84] SCHMIDT U, ROTH S. Shrinkage fields for effective image restoration[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2014: 2774-2781. [85] CHEN Y J, YU W, POCK T. On learning optimized reaction diffusion processes for effective image restoration[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2015: 5261-5269. [86] REN W Q, ZHANG J W, MA L, et al. . Deep non-blind deconvolution via generalized low-rank approximation[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates Inc. , 2018: 295-305. [87] KRUSE J, ROTHER C, SCHMIDT U. Learning to push the limits of efficient FFT-based image deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2017: 4596-4604. [88] SON H, LEE S. Fast non-blind deconvolution via regularized residual networks with long/short skip-connections[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, IEEE, 2017: 1-10. [89] SCHULER C J, BURGER H C, HARMELING S, et al. . A machine learning approach for non-blind image deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2013: 1067-1074. [90] XU L, REN J S J, LIU C, et al. . Deep convolutional neural network for image deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, MIT Press, 2014: 1790-1798. [91] EBOLI T, SUN J, PONCE J. End-to-end interpretable learning of non-blind image deblurring[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2020: 314-331. [92] GONG D, ZHANG ZH, SHI Q F, et al. Learning deep gradient descent optimization for image deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(12): 5468-5482. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2968289 [93] ZHANG K, ZUO W M, GU SH H, et al. . Learning deep CNN denoiser prior for image restoration[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017: 2808-2817. [94] ZHANG J W, PAN J SH, LAI W SH, et al. . Learning fully convolutional networks for iterative non-blind deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017: 6969-6977. [95] DONG W SH, WANG P Y, YIN W T, et al. Denoising prior driven deep neural network for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(10): 2305-2318. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2873610 [96] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Springer, 2015: 234-241. [97] QUAN Y H, LIN P K, XU Y, et al. . Nonblind image deblurring via deep learning in complex field[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021: 1-14 (2021-04-14). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9404870/. [98] CHEN L, ZHANG J W, PAN J SH, et al. . Learning a non-blind deblurring network for night blurry images[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2021: 10537-10545. [99] NAN Y S, QUAN Y H, JI H. Variational-EM-based deep learning for noise-blind image deblurring[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 3623-3632. [100] JIN M G, ROTH S, FAVARO P. Noise-blind image deblurring[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017: 3834-3842. [101] DONG J X, ROTH S, SCHIELE B. DWDN: deep wiener deconvolution network for non-blind image deblurring[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021 (2021-12-28). https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9664009/. [102] LEMPITSKY V, VEDALDI A, ULYANOV D. Deep image prior[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 9446-9454. [103] WANG ZH X, WANG Z P, LI Q Q, et al. . Image deconvolution with deep image and kernel priors[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, IEEE, 2019: 980-989. [104] ZUKERMAN J, TIRER T, GIRYES R. BP-DIP: a backprojection based deep image prior[C]. Proceedings of the 28th European Signal Processing Conference, IEEE, 2021: 675-679. [105] BIGDELI S A, JIN M G, FAVARO P, et al. . Deep mean-shift priors for image restoration[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Curran Associates Inc. , 2017: 763-772. [106] LEVIN A, WEISS Y, DURAND F. Understanding and evaluating blind deconvolution algorithms[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2009: 1964-1971. [107] SUN L B, CHO S, WANG J, et al. . Edge-based blur kernel estimation using patch priors[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, IEEE, 2013: 1-8. [108] MARTIN D, FOWLKES C, TAL D, et al. . A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics[C]. Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2001: 416-423. [109] DONG J X, PAN J SH, SUN D Q, et al. . Learning data terms for non-blind deblurring[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2018: 777–792. [110] DONG J X, ROTH S, SCHIELE B. Learning spatially-variant MAP models for non-blind image deblurring[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2021: 4884-4893. [111] REN D W, ZUO W M, ZHANG D, et al. Simultaneous fidelity and regularization learning for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(1): 284-299. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2926357 [112] WANG ZH, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [113] REN D W, ZUO W M, ZHANG D, et al. Partial deconvolution with inaccurate blur kernel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 511-524. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2764261 [114] JI H, WANG K. Robust image deblurring with an inaccurate blur kernel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(4): 1624-1634. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2171699 [115] VASU S, MALIGIREDDY V R, RAJAGOPALAN A N. Non-blind deblurring: handling kernel uncertainty with CNNs[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 3272-3281. [116] NAN Y S, JI H. Deep learning for handling kernel/model uncertainty in image deconvolution[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 2385-2394. [117] WHYTE O, SIVIC J, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Non-uniform deblurring for shaken images[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2012, 98(2): 168-186. doi: 10.1007/s11263-011-0502-7 [118] TAI Y W, TAN P, BROWN M S. Richardson-Lucy deblurring for scenes under a projective motion path[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(8): 1603-1618. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.222 [119] HIRSCH M, SCHULER C J, HARMELING S, et al. . Fast removal of non-uniform camera shake[C]. Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2011: 463-470. [120] SUN J, CAO W F, XU Z B, et al. . Learning a convolutional neural network for non-uniform motion blur removal[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2015: 769-777. [121] KUPYN O, BUDZAN V, MYKHAILYCH M, et al. . DeblurGAN: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 8183-8192. [122] PAN J SH, SUN D Q, PFISTER H, et al. . Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2016: 1628-1636. [123] CHEN L, FANG F M, WANG T T, et al. . Blind image deblurring with local maximum gradient prior[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 1742-1750. -






 下载:
下载: