Fusion of infrared and visible light images based on visual saliency weighting and maximum gradient singular value
-
摘要:
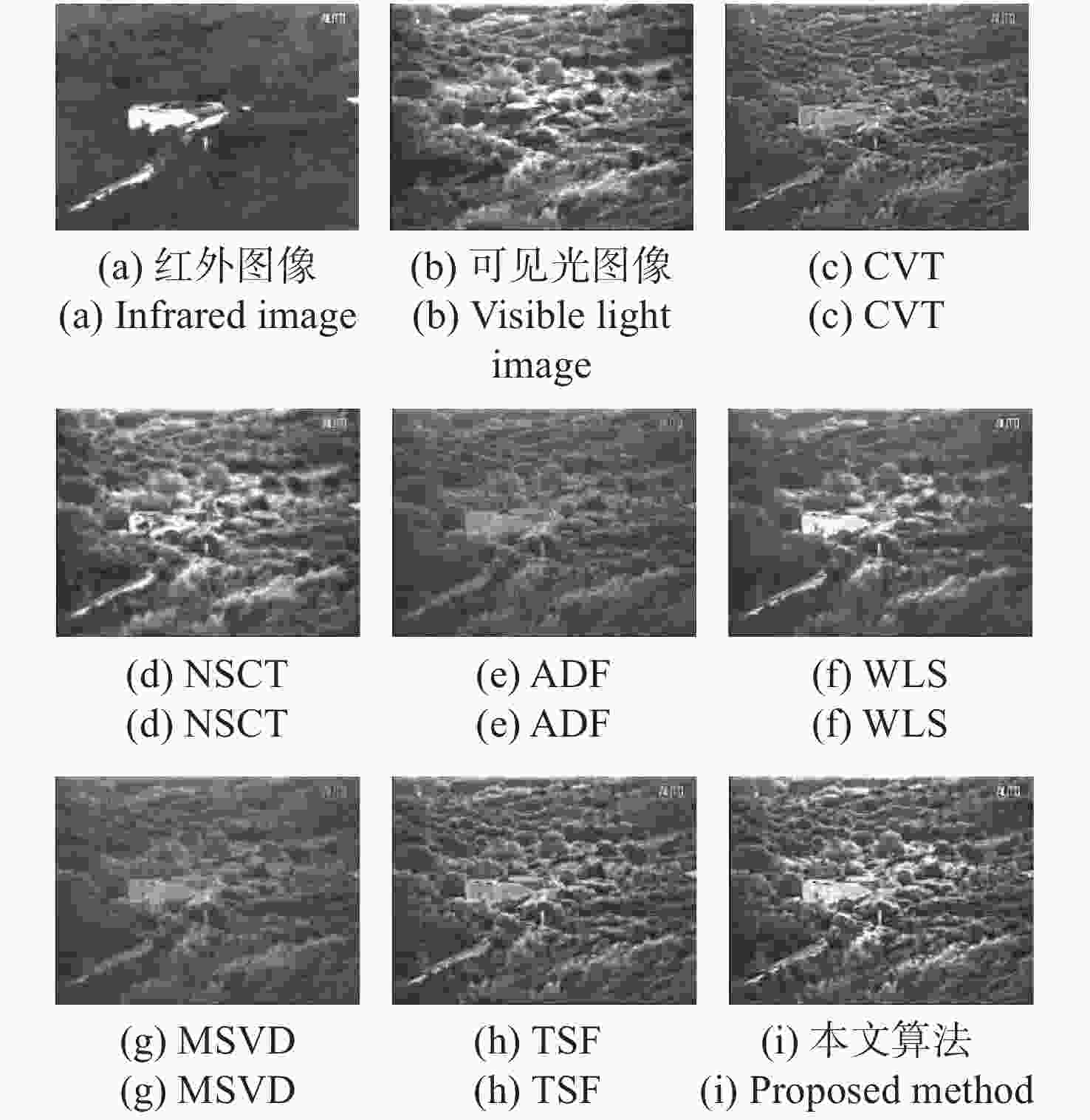
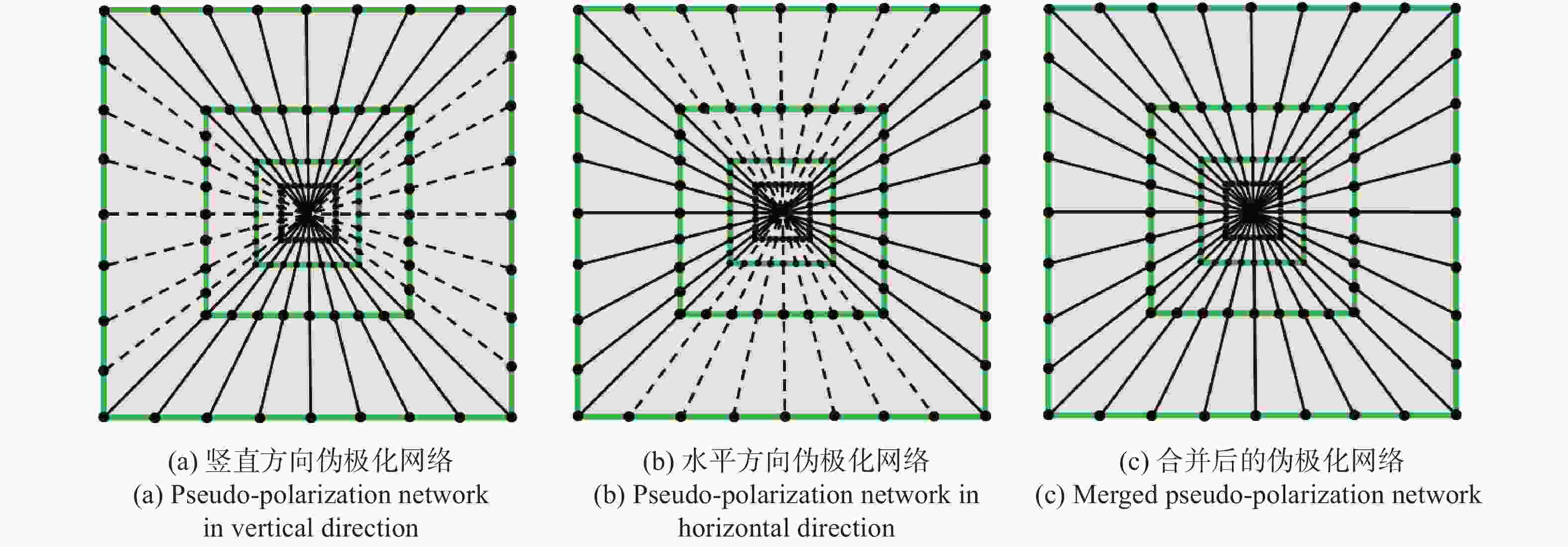
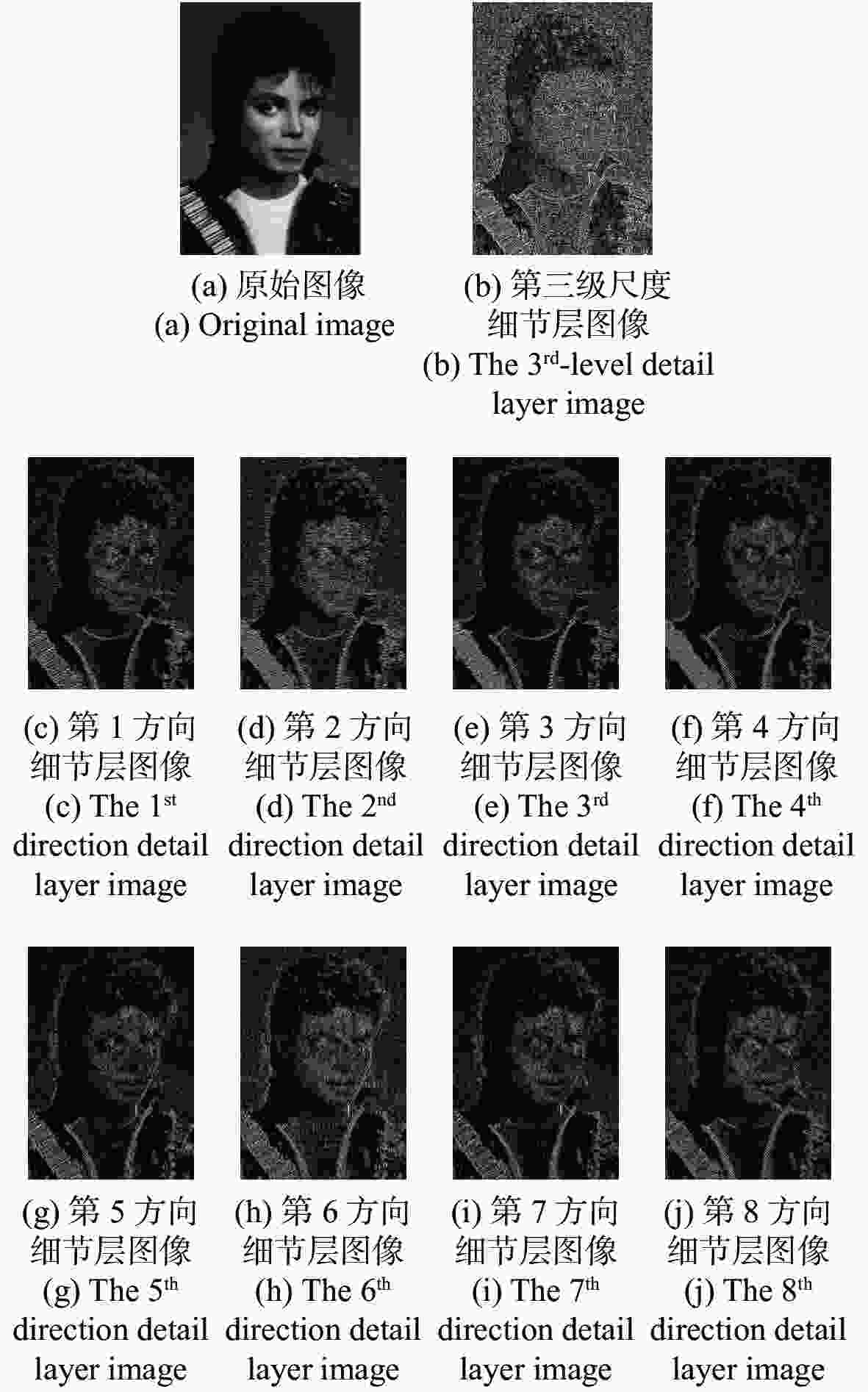
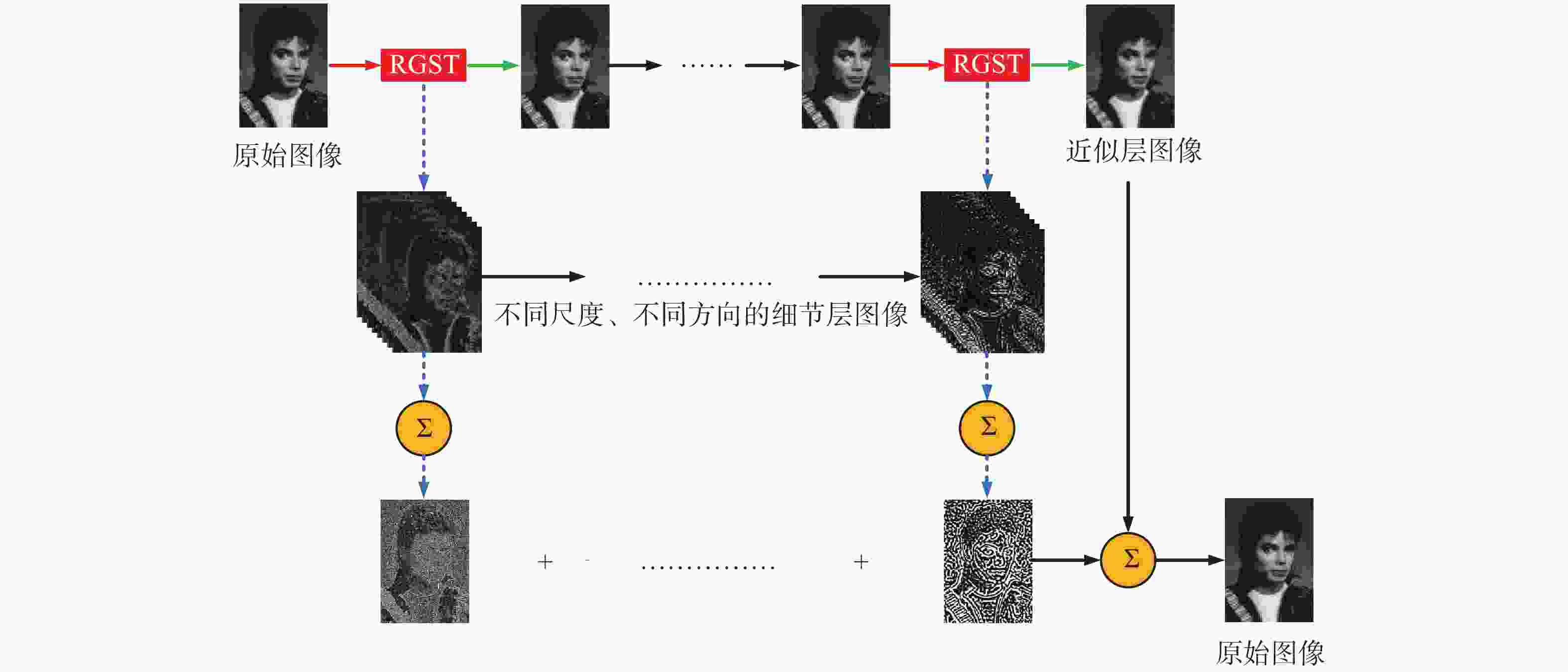
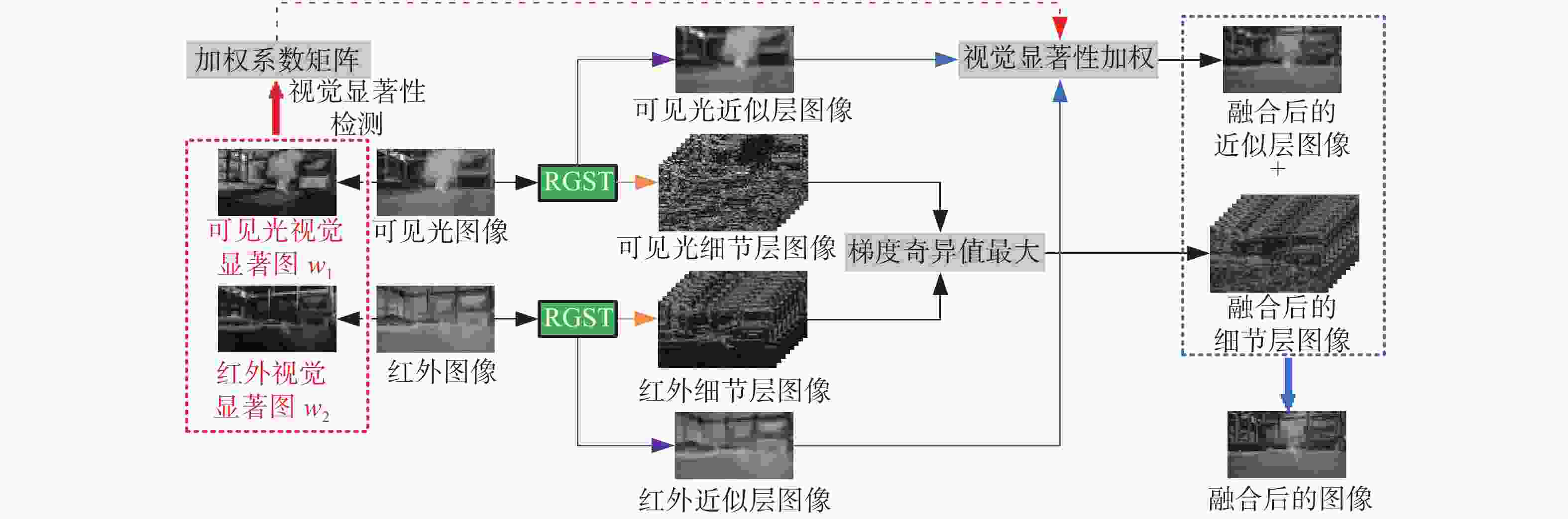
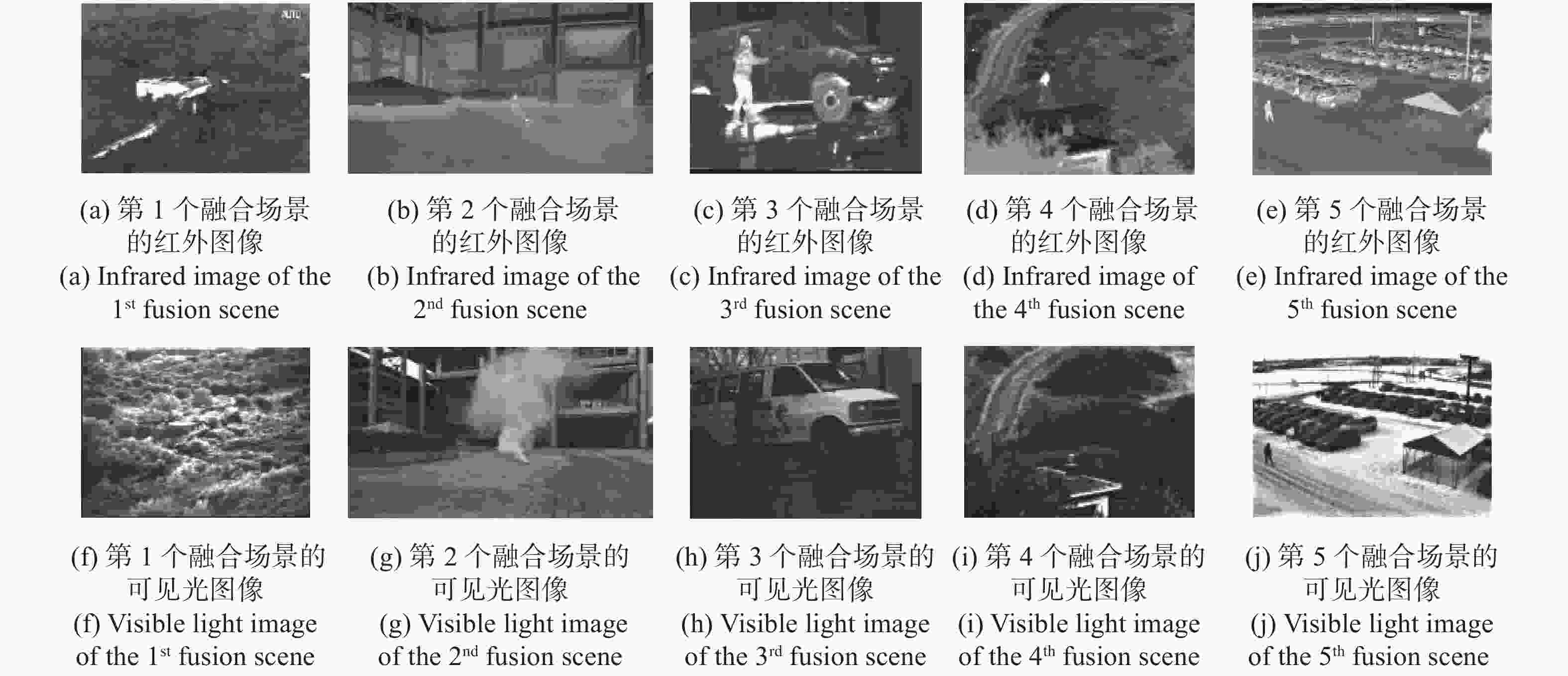
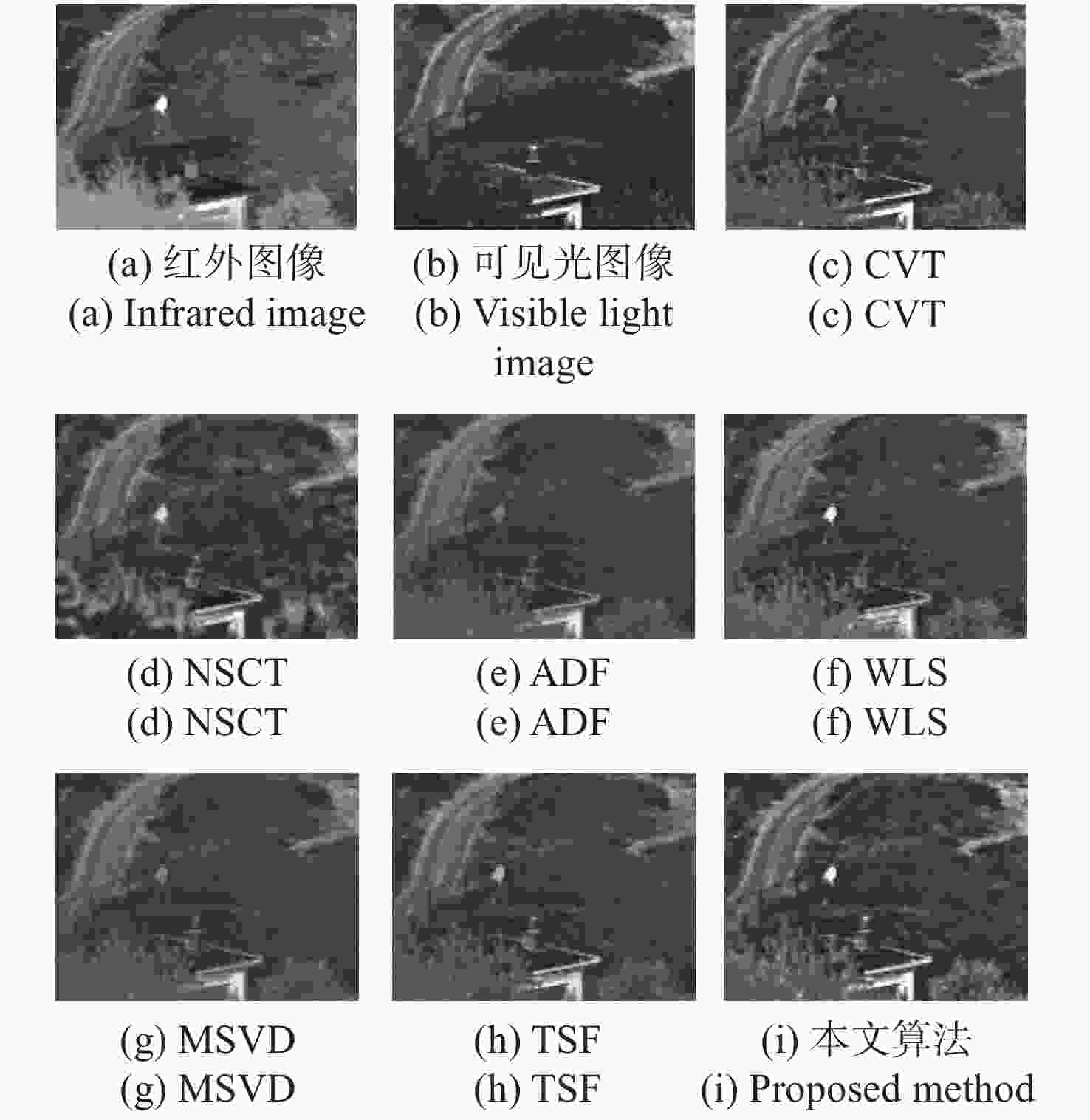
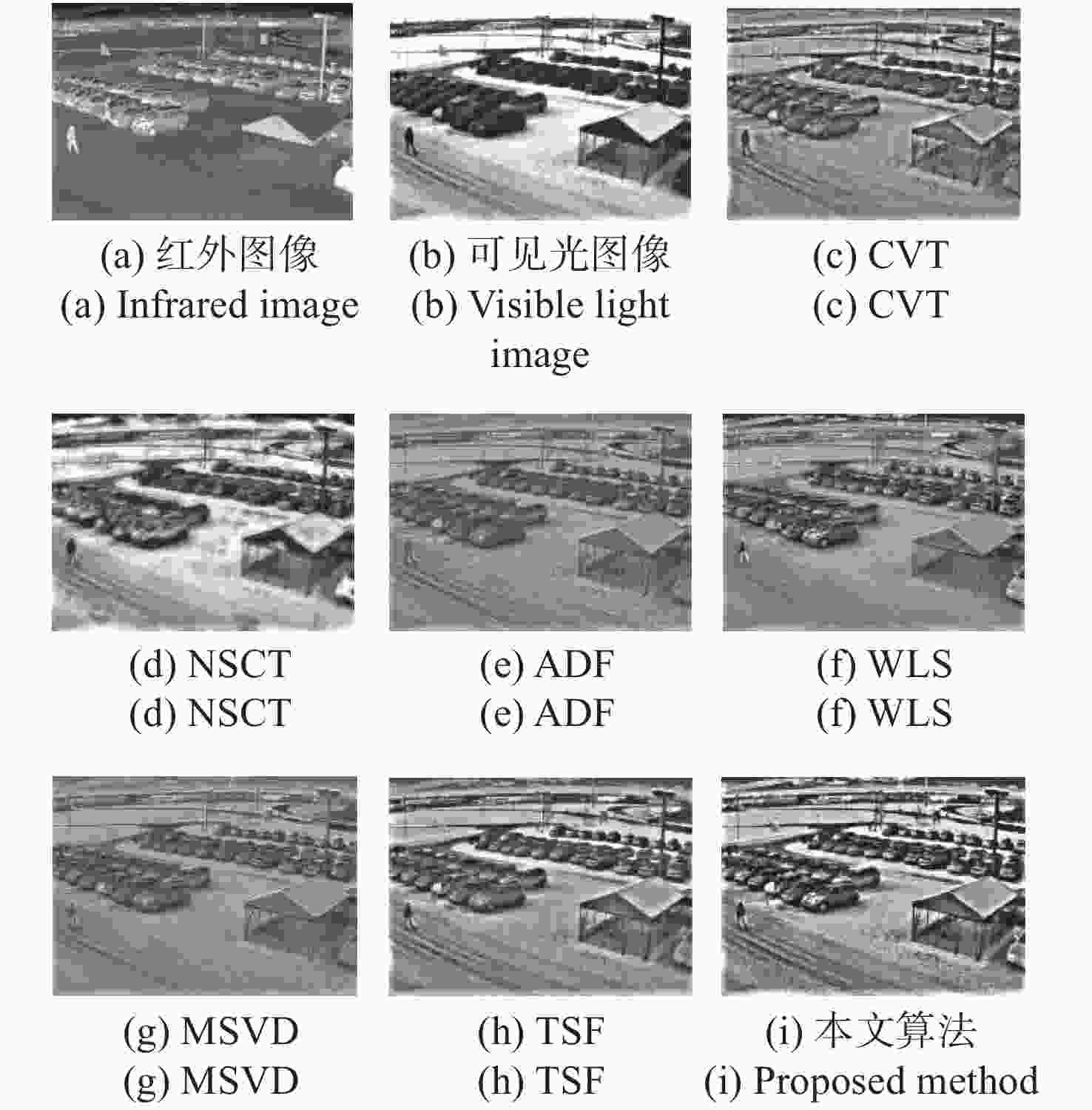
为了综合利用红外与可见光图像的光谱显著性信息,同时提高融合图像的视觉对比度,本文提出了一种基于视觉显著性加权与梯度奇异值最大的红外与可见光图像融合方法。首先,该全新算法通过滚动引导剪切波变换作为多尺度分析工具,来获取图像的近似层分量与多方向细节层分量。其次,针对反映图像主体能量特征的近似层分量,采用视觉显著性加权融合作为其融合规则,该方法利用显著性加权系数矩阵指导图像内的光谱显著性信息有效融合,提高了融合图像的视觉观察度。此外,采用基于梯度奇异值最大原则来指导细节层分量的融合,该方法可以极大程度地将隐藏在两种源图像内的梯度特征还原到融合图像中,使融合图像具有更加清晰的边缘细节。为了验证本文算法的有效性,进行了5组独立的融合实验,最终的实验结果表明,本文算法融合图像的对比度更高,边缘细节更加丰富,并且相较于其它现有典型方法,AVG、IE、QE、SF、SD、SCD等客观参数指标分别提高了16.4%、3.9%、11.8%、17.1%、21.4%、10.1%,因此具有更加优良的视觉效果。
Abstract:In order to effectively integrate the spectral saliency information of infrared and visible light images and improve the visual contrast of the fused images, a fusion method of infrared and visible light images based on weighted visual saliency and maximum gradient singular value is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the new algorithm uses the rolling guidance shearlet transform as a multi-scale analysis tool to obtain the approximate layer components and multi-directional detail layer components of the image. Secondly, for the approximate layer components that reflect the energy characteristics of the image subject, visual saliency weighted fusion is used as its fusion rule. This method uses the saliency weighted coefficient matrix to guide the effective fusion of spectral saliency information in the image, and improves the visual observation of the fused image. In addition, the principle of maximum gradient singular value is used to guide the fusion of detail layer components. This method can restore the gradient features hidden in the two source images to the fused image to a great extent, so that the fused image has clearer edge details. In order to verify the effectiveness of this algorithm, we have adopted five groups of independent fusion experiments. The final experimental results show that this algorithm has higher contrast and richer edge details. Compared with the existing typical methods, the objective parameters such as AVG, IE, QE, SF, SD and SCD are improved by 16.4%, 3.9%, 11.8%, 17.1%, 21.4% and 10.1%, respectively, so it has better visual effect.
-
表 1 第1组图像融合实验的客观评价指标
Table 1. Objective evaluation indicators for the first group of image fusion experiments
第1组
融合实验评价指标 AVG IE QE SF SD SCD t CVT 10.59 7.10 0.58 18.88 35.67 1.54 3.93 NSCT 6.42 7.51 0.45 11.41 47.22 1.59 109.8 ADF 10.22 6.91 0.53 17.64 30.76 1.51 2.07 WLS 11.14 7.14 0.398 20.38 41.19 1.74 4.18 MSVD 9.36 6.84 0.37 16.63 29.26 1.52 0.76 TSF 9.61 7.27 0.56 17.76 40.58 1.68 0.13 本文方法 11.44 7.42 0.62 20.65 47.66 1.78 8.82 表 2 第2组图像融合实验的客观评价指标
Table 2. Objective evaluation indicators for the second group of image fusion experiments
第2组
融合实验评价指标 AVG IE QE SF SD SCD t CVT 8.76 7.05 0.58 21.67 33.65 1.51 1.81 NSCT 5.73 7.17 0.42 12.15 37.88 1.20 65.1 ADF 7.55 6.83 0.50 17.18 28.28 1.50 1.25 WLS 8.88 7.06 0.46 20.88 33.54 1.65 2.36 MSVD 7.84 6.83 0.46 19.75 28.42 1.54 0.35 TSF 7.68 7.11 0.55 19.40 35.16 1.58 0.13 本文方法 9.44 7.26 0.62 22.95 40.11 1.65 4.64 表 3 第3组图像融合实验的客观评价指标
Table 3. Objective evaluation indicators for the third group of image fusion experiments
第3组
融合实验评价指标 AVG IE QE SF SD SCD t CVT 4.98 6.91 0.59 14.80 34.32 1.60 2.22 NSCT 4.13 7.37 0.54 9.78 50.49 1.62 91.1 ADF 3.03 6.62 0.41 8.88 28.99 1.52 1.42 WLS 5.11 7.10 0.55 15.47 47.80 1.81 3.16 MSVD 3.95 6.65 0.46 11.99 29.52 1.53 0.45 TSF 4.918 7.08 0.63 14.93 39.02 1.70 0.14 本文方法 5.75 7.15 0.65 16.39 48.65 1.82 7.51 表 4 第4组图像融合实验的客观评价指标
Table 4. Objective evaluation indicators for the fourth group of image fusion experiments
第4组
融合实验评价指标 AVG IE QE SF SD SCD t CVT 9.18 6.91 0.39 17.27 33.98 1.48 1.34 NSCT 6.06 7.18 0.31 11.15 38.07 1.21 29.46 ADF 5.37 6.62 0.34 10.10 27.90 1.46 0.90 WLS 9.82 6.96 0.39 17.99 34.19 1.58 1.29 MSVD 7.94 6.66 0.32 14.57 28.34 1.45 0.18 TSF 8.13 7.04 0.43 16.82 37.05 1.63 0.11 本文方法 9.84 7.15 0.43 18.42 39.04 1.68 2.44 表 5 第5组图像融合实验的客观评价指标
Table 5. Objective evaluation indicators for the fifth group of image fusion experiments
第5组
融合实验评价指标 AVG IE QE SF SD SCD t CVT 12.25 7.54 0.50 24.83 46.91 1.75 2.25 NSCT 9.75 7.81 0.43 18.79 55.87 1.64 53.80 ADF 9.19 6.97 0.42 17.96 32.86 1.74 1.33 WLS 12.53 7.35 0.38 24.62 43.74 1.87 2.64 MSVD 10.66 6.99 0.43 22.59 33.35 1.78 0.32 TSF 12,00 7.68 0.53 25.74 52.17 1.84 0.15 本文方法 14.31 7.76 0.57 28.76 57.92 1.89 3.42 -
[1] 陈清江, 张彦博, 柴昱洲, 等. 有限离散剪切波域的红外可见光图像融合[J]. 中国光学,2016,9(5):523-531. doi: 10.3788/co.20160905.0523CHEN Q J, ZHANG Y B, CHAI Y ZH, et al. Fusion of infrared and visible images based on finite discrete shearlet domain[J]. Chinese Optics, 2016, 9(5): 523-531. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20160905.0523 [2] 王成, 张艳超. 像素级自适应融合的夜间图像增强[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(9):888-896. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0888WANG CH, ZHANG Y CH. Night image enhancement based on pixel level adaptive image fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(9): 888-896. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0888 [3] 陈广秋, 高印寒, 才华, 等. 局部化NSST与PCNN相结合的图像融合[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(4):701-712. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153004.0701CHEN G Q, GAO Y H, CAI H, et al. Image fusion algorithm based on local NSST and PCNN[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Display, 2015, 30(4): 701-712. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153004.0701 [4] 陈广秋, 陈昱存, 李佳悦, 等. 基于DNST和卷积稀疏表示的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版),2021,51(3):996-1010.CHEN G Q, CHEN Y C, LI J Y, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on discrete nonseparable shearlet transform and convolutional sparse representation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition) , 2021, 51(3): 996-1010. (in Chinese) [5] PRAKASH O, PARK C M, KHARE A, et al. Multiscale fusion of multimodal medical images using lifting scheme based biorthogonal wavelet transform[J]. Optik, 2019, 182: 995-1014. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.12.028 [6] TAO T W, LIU M X, HOU Y K, et al. Latent low-rank representation with sparse consistency constraint for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Optik, 2022, 261: 169102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.169102 [7] LIU Y Y, HE K J, XU D, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visibility enhancement and hybrid multiscale decomposition[J]. Optik, 2022, 258: 168914. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168914 [8] ANOOP SURAJ A, FRANCIS M, KAVYA T S, et al. Discrete wavelet transform based image fusion and de-noising in FPGA[J]. Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology, 2014, 1(1): 72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jesit.2014.03.006 [9] DONOHO D L, DUNCAN M R. Digital curvelet transform: strategy, implementation, and experiments[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2000, 4056: 12-30. doi: 10.1117/12.381679 [10] CUNHA A L D, ZHOU J, DO M N. The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: theory, design, and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(10): 3089-3101. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.877507 [11] GUO K H, LABATE D. Optimally sparse multidimensional representation using shearlets[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 2007, 39(1): 298-318. doi: 10.1137/060649781 [12] KONG W W, MIAO Q G, LEI Y, et al. Guided filter random walk and improved spiking cortical model based image fusion method in NSST domain[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 488: 509-527. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.11.060 [13] 陈广秋, 梁小伟, 段锦, 等. 多级方向引导滤波器及其在多传感器图像融合中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版),2019,57(1):129-138. doi: 10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2017447CHEN G Q, LIANG X W, DUAN J, et al. Multistage directional guided filter and its application in multi-sensor image fusion[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Science Edition) , 2019, 57(1): 129-138. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2017447 [14] ZHANG Q, SHEN X Y, XU L, et al.. Rolling guidance filter[C]. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2014: 815-830. [15] 程博阳. 基于滚动引导剪切波变换的红外与可见光图像融合研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020.CHENG B Y. Research on fusion of infrared and visible light image based on rolling guidance shearlet transform[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. [16] GUO ZH Y, YU X T, DU Q L. Infrared and visible image fusion based on saliency and fast guided filtering[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2022, 123: 104178. [17] LI W SH, LI R Y, FU J, et al. MSENet: a multi-scale enhanced network based on unique features guidance for medical image fusion[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 74: 103534. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103534 [18] CHAO ZH, DUAN X G, JIA SH F, et al. Medical image fusion via discrete stationary wavelet transform and an enhanced radial basis function neural network[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 118: 108542. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108542 [19] GUO Y N, LI X, GAO A, et al.. A scale-aware pansharpening method with rolling guidance filter[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IEEE, 2017: 5121-5124. [20] 刘博, 韩广良, 罗惠元. 基于多尺度细节的孪生卷积神经网络图像融合算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2021,36(9):1283-1293. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0339LIU B, HAN G L, LUO H Y. Image fusion algorithm based on multi-scale detail Siamese convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(9): 1283-1293. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2020-0339 [21] XIANG I B, YU Z, FU G Z. Quadtree-based multi-focus image fusion using a weighted focus-measure[J]. Inform. Fusion, 2015, 22: 105-118. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102852 [22] JOSE J, GAUTAM N, TIWARI M, et al. An image quality enhancement scheme employing adolescent identity search algorithm in the NSST domain for multimodal medical image fusion[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 66: 102480. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102480 [23] ACHANTA R, HEMAMI S, ESTRADA F, et al. . Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2009: 1597-1604. [24] CHENG B Y, JIN L X, LI G N. Adaptive fusion framework of infrared and visual image using saliency detection and improved dual-channel PCNN in the LNSST domain[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2018, 79: 30-43. [25] CHENG B Y, JIN L X, LI G N. Infrared and visual image fusion using LNSST and an adaptive dual-channel PCNN with triple-linking strength[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 310: 135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.028 [26] 陈广秋, 高印寒, 段锦, 等. 基于奇异值分解的PCNN红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(1):126-136. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153001.0126CHEN G Q, GAO Y H, DUAN J, et al. Fusion algorithm of infrared and visible images based on singular value decomposition and PCNN[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(1): 126-136. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153001.0126 [27] NENCINI F, GARZELLI A, BARONTI S, et al. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform[J]. Information Fusion, 2007, 8(2): 143-156. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2006.02.001 [28] LIU Y, LIU SH P, WANG Z F. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation[J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 24: 147-164. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2014.09.004 [29] BAVIRISETTI D P, DHULI R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and karhunen-loeve transform[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(1): 203-209. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2478655 [30] JIN L M, ZHI Q Z, BO W. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2017, 82: 8-17. [31] NAIDU V P S. Image fusion technique using multi-resolution singular value decomposition[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2011, 61(5): 479-484. doi: 10.14429/dsj.61.705 [32] BAVIRISETTI D P, DHULI R. Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2016, 76: 52-64. [33] D. P. B, R. D Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2016, 76: 52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.04.010 [34] LIN Y C, CAO D X, ZHOU X C. Adaptive infrared and visible image fusion method by using rolling guidance filter and saliency detection[J]. Optik, 2022, 262: 169218. [35] ZHE L, YU Q S, VICTOR S. MRI and PET image fusion using the nonparametric density model and the theory of variable-weight[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2019, 175: 73-82. [36] BAI X ZH, ZHANG Y, ZHOU F G, et al. Quadtree-based multi-focus image fusion using a weighted focus-measure[J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 22: 105-118. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2014.05.003 [37] FARID M S, MAHMOOD A, AL-MAADEED S A. Multi-focus image fusion using Content Adaptive Blurring[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 45: 96-112. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.01.009 [38] YIN M, DUAN P H, LIU W, et al. A novel infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on shift-invariant dual-tree complex shearlet transform and sparse representation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 226: 182-191. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.11.051 [39] KONG X Y, LIU L, QIAN Y SH, et al. . Infrared and visible image fusion using structure-transferring fusion method[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2019, 98: 161-173. ASLANTAS V, BENDES E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: the sum of the correlations of differences[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12): 1890-1896. [40] ASLANTAS V, BENDES E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: the sum of the correlations of differences[J]. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12): 1890-1896. -






 下载:
下载: