-
摘要:
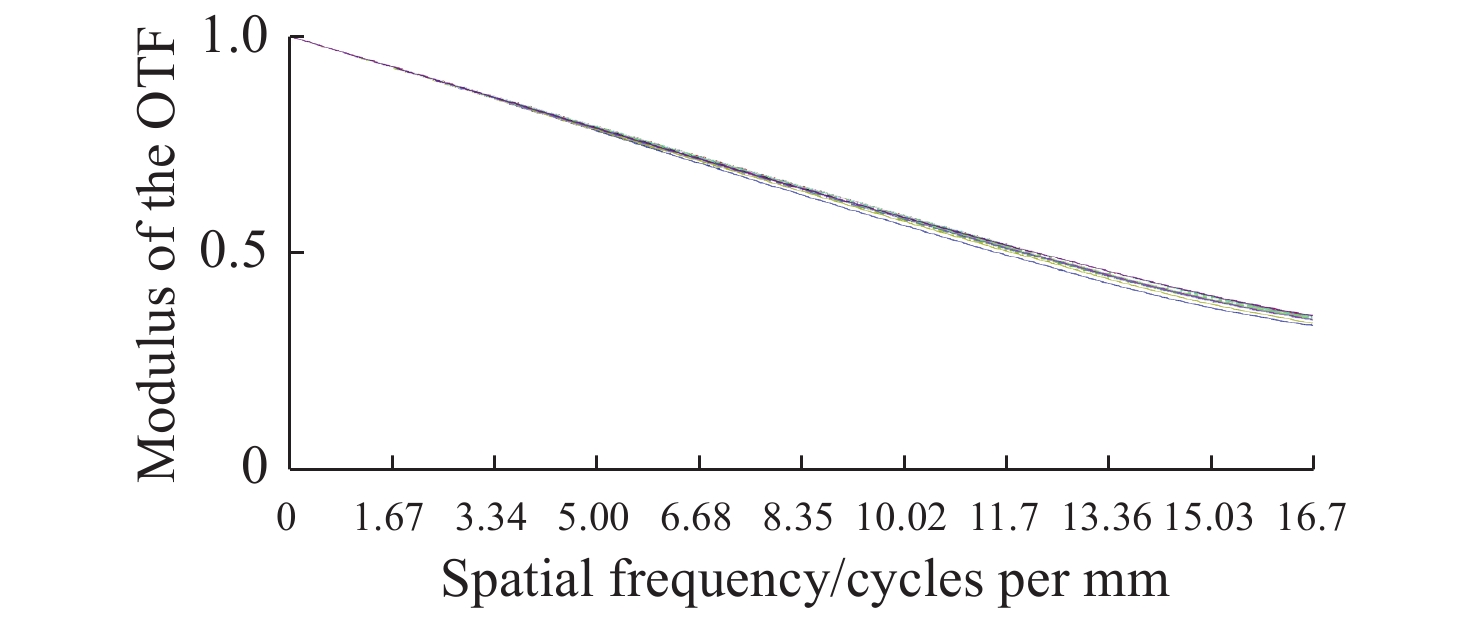
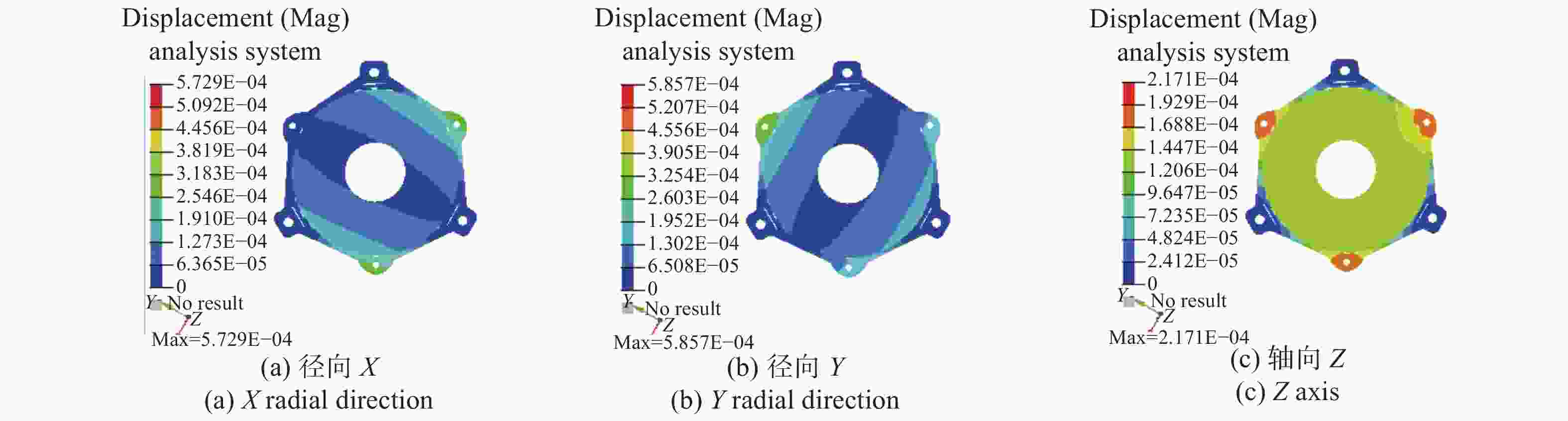
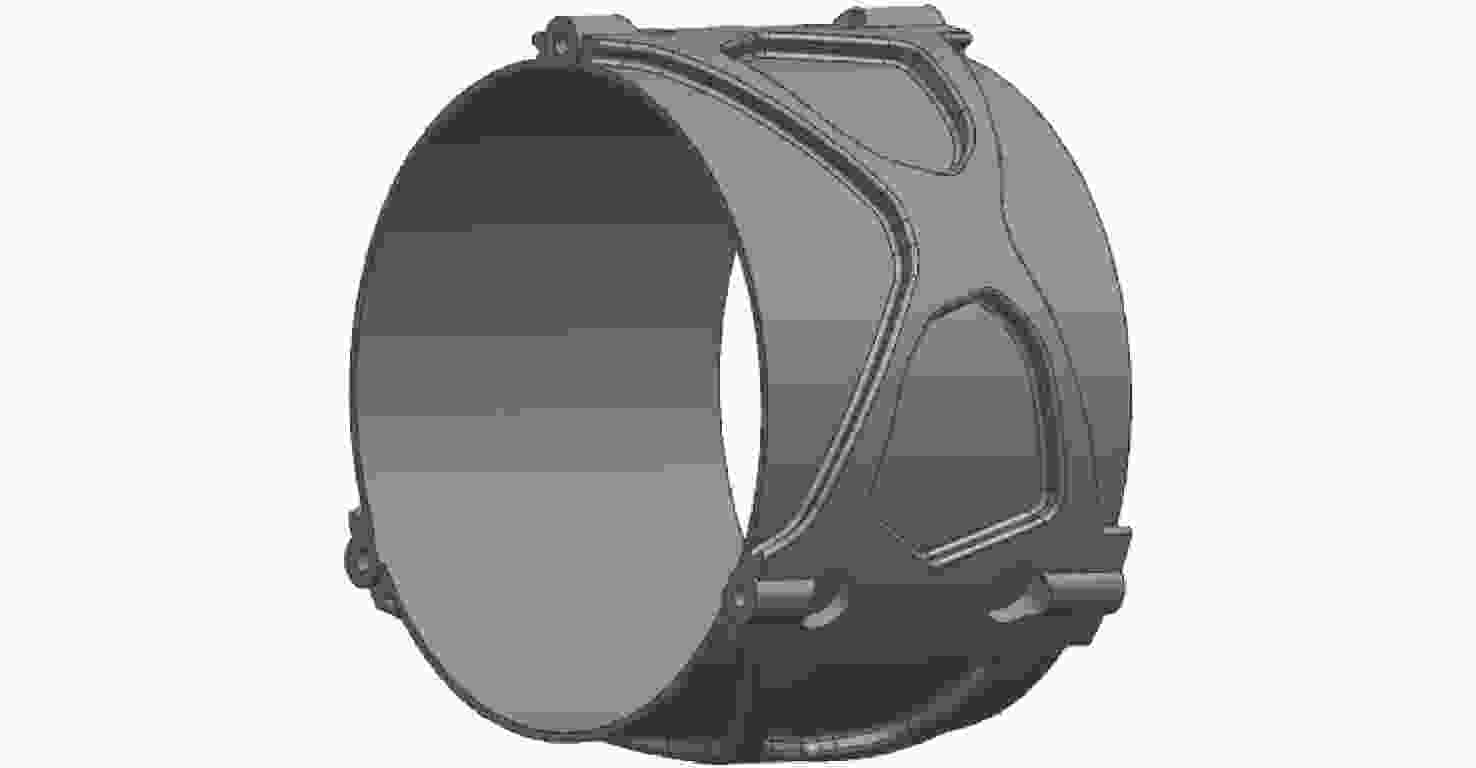
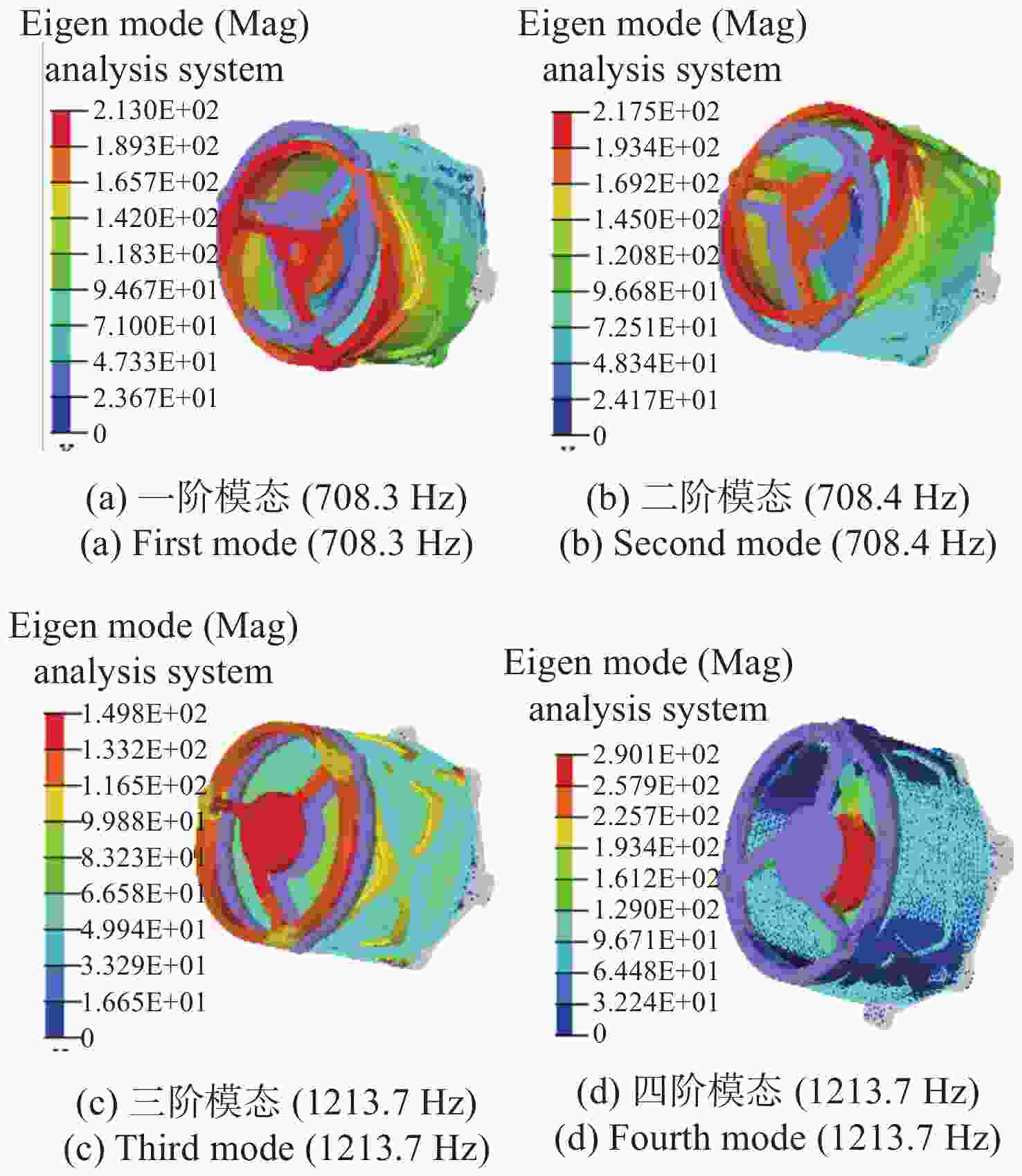
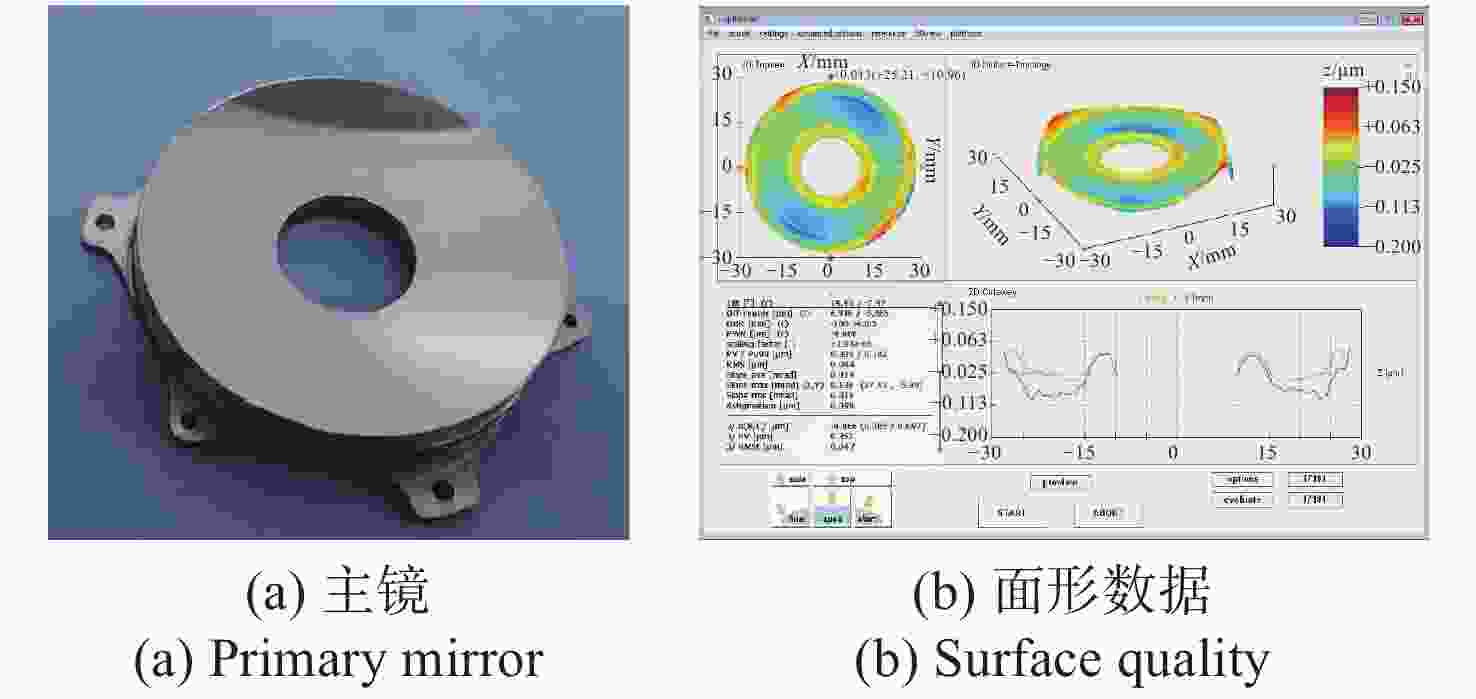
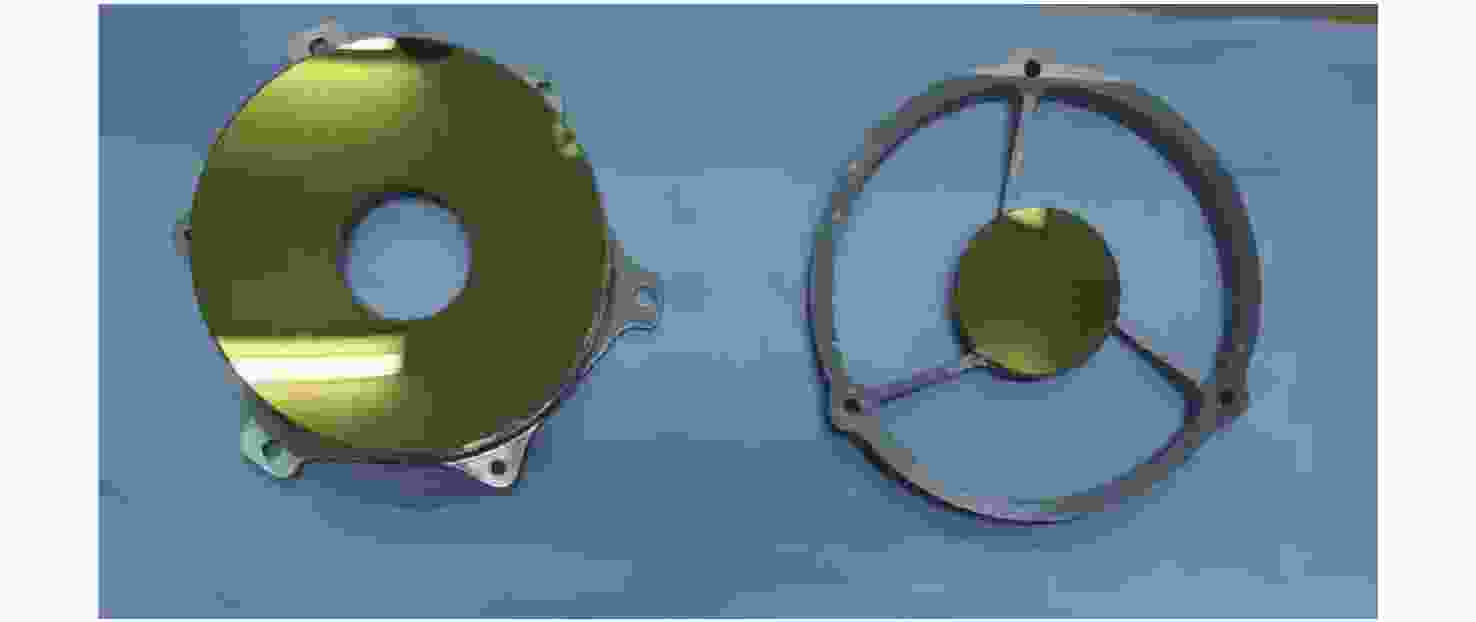
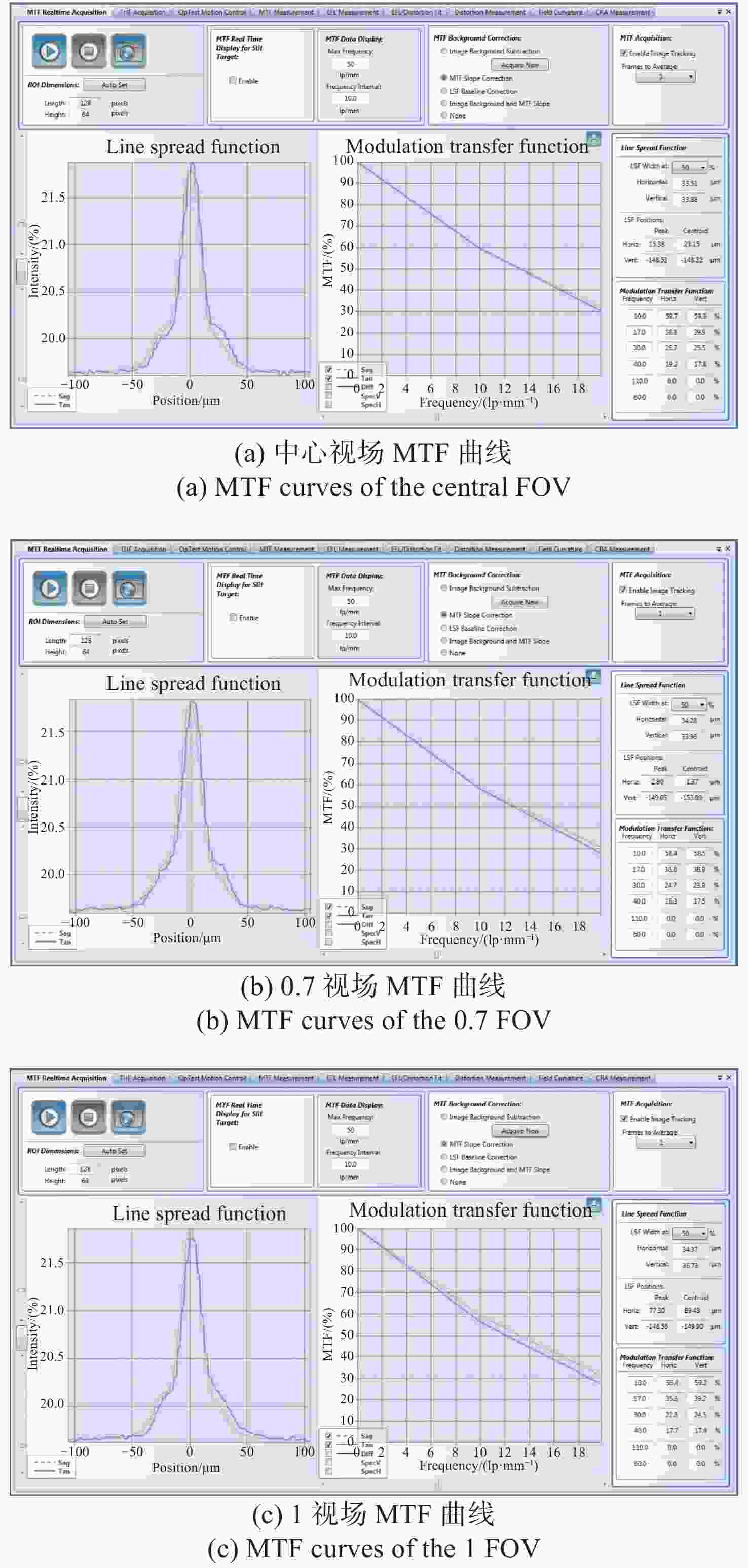
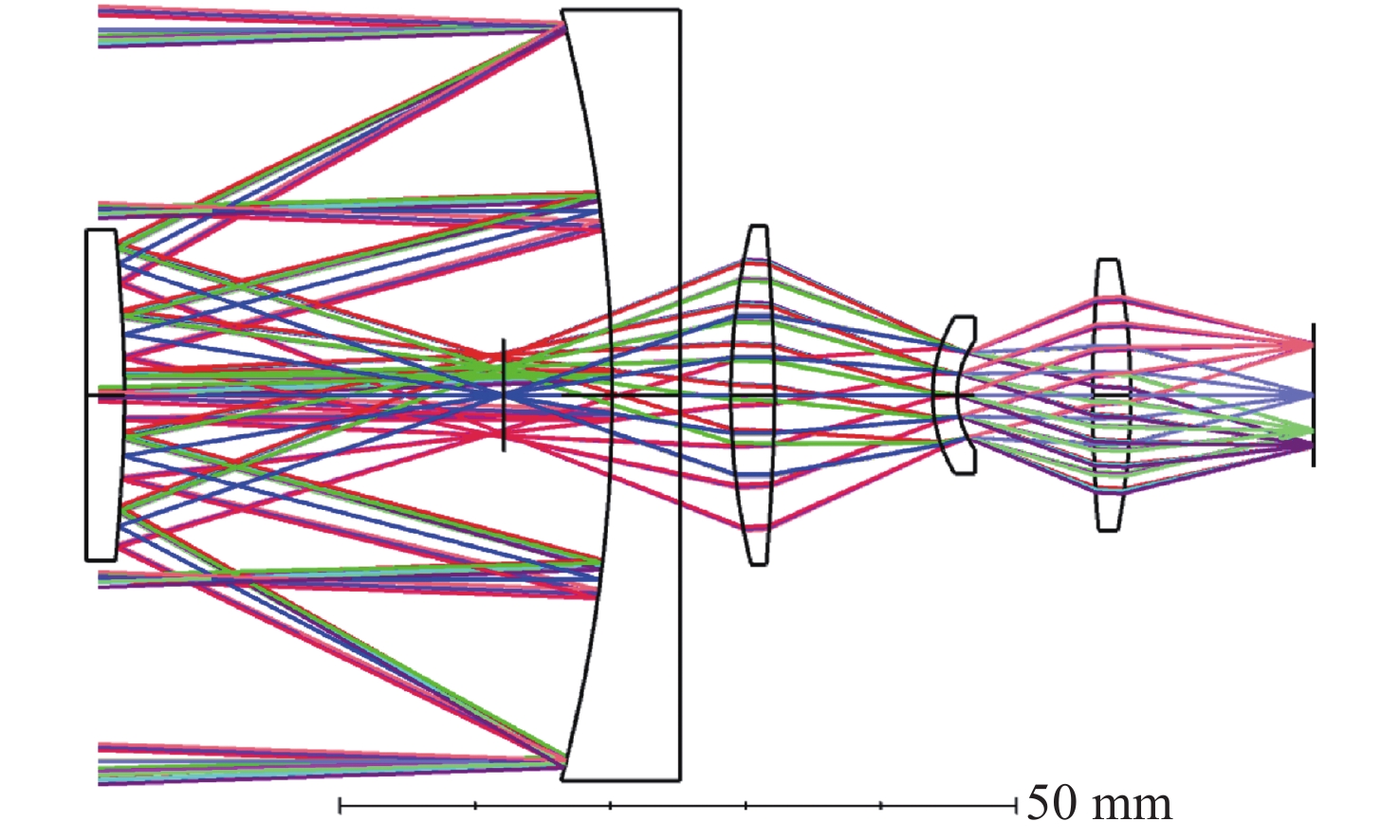
为了实现用于深空低冷目标探测的长波红外折反射式光学系统的进一步轻小型、低辐射和大视场,对局部制冷光学系统、拓扑优化金属基反射镜设计、增材制造、金属基光学加工与表面改性等进行研究。首先,设计完成了紧凑型局部制冷折反射式光学系统,口径为55 mm,焦距为110 mm,视场达到4°×4°;其次,利用拓扑优化理论,设计完成了主镜组件、次镜组件和连接筒,三阶和四阶模态达到1213.7 Hz;接着,采用增材制造、单点金刚石车削、表面改性、表面镀金等手段完成前组光学元件的研制,利用定心装配工艺完成光机装调;最后,对光机装调后的系统性能进行了测试。测试结果表明:光学系统全视场范围内调制传递函数均达到衍射极限,重量仅为96.04 g。金属基增材制造方法可以作为提升光学系统性能的有效手段。
Abstract:In order to realize the target of light and small, low radiation and large field of view of the long-wave infrared catadioptric optical system for deep-space low-temperature target detection, the local cooling optical system, topology optimization, metal-based mirror design, additive manufacturing, Single Point Diamond Turning (SPDT) for metal mirrors and surface modification are studied. First of all, a compact catadioptric optical system with partially cooled is designed, in which the aperture is 55 millimeters, the focal length is 110 millimeters and the field of view is 4 degrees by 4 degrees. Secondly, the primary mirror assembly, the secondary mirror assembly and the connecting baffle are designed using the topology optimization theory, and the third order mode and fourth order mode reach 1213.7 Hz. Then, the front group optical mirrors assembly are developed by means of additive manufacturing, SPDT, surface modification and surface gold plating. We complete the optical mechanical assembly using the centering assembly method. Finally, the performance of the system after optical mechanical centering is tested. The test results show that the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) curves of the optical system reach the diffraction limit in the whole field of views, and the weight is only 96.04 grams. Additive manufacturing method can be used as an effective means to improve the performance of optical systems.
-
表 1 光学系统设计指标
Table 1. Design index of the optical system
参数 指标要求 波段/μm 8~10 相对孔径 1∶2 焦距/mm 110 视场/(°) 4×4 冷光阑效率 100% 主次镜组件重量 不大于100 g 表 2 长波红外探测器指标
Table 2. Index of the long-wave infrared detector
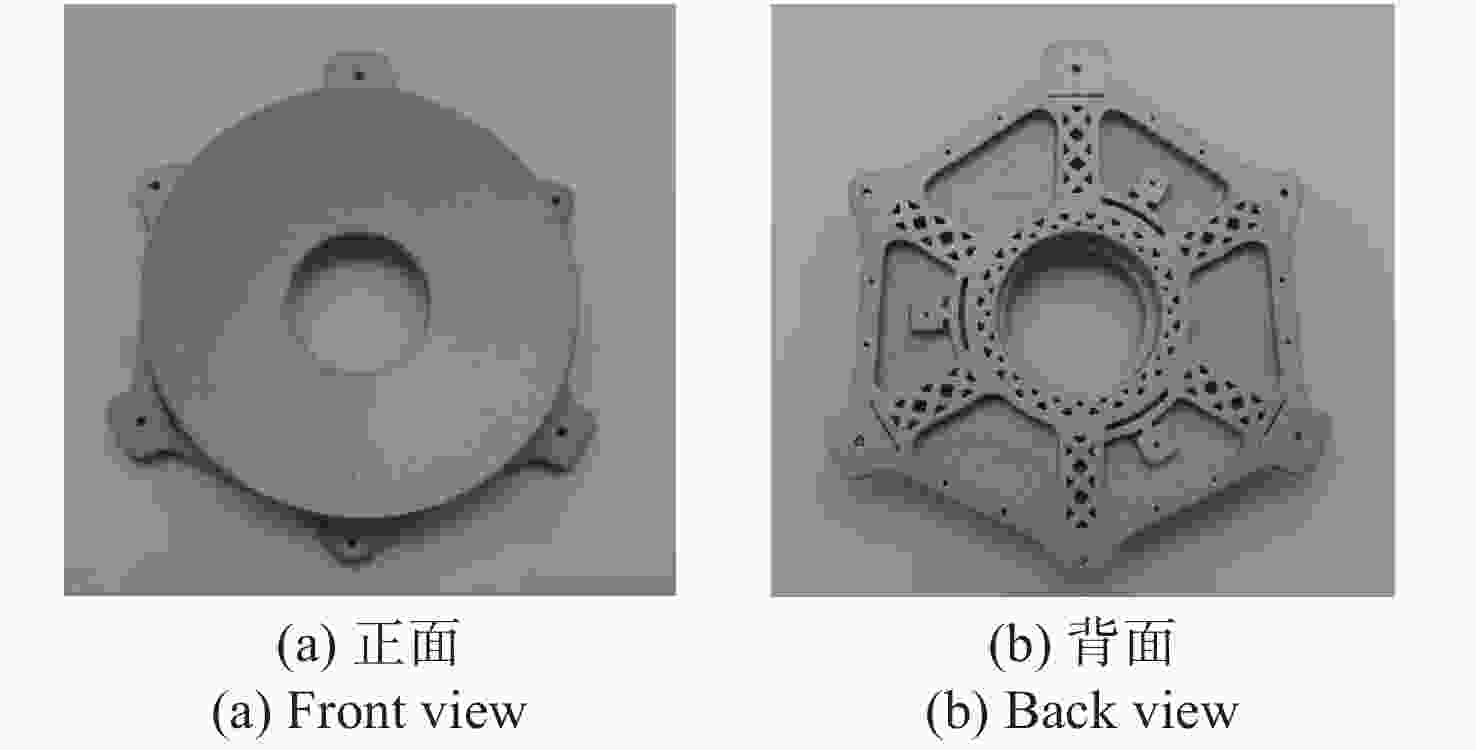
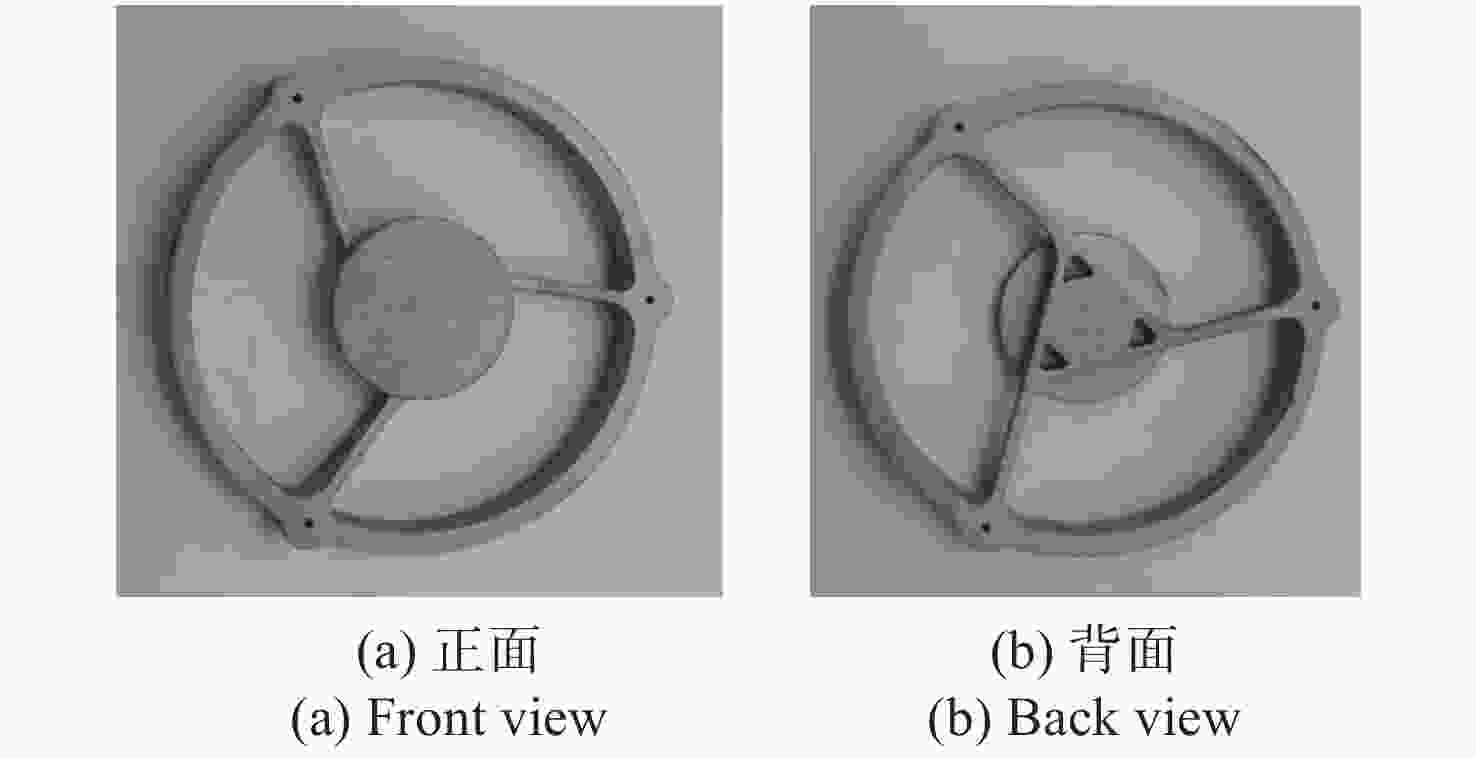
参数 指标数据 阵列尺寸 256×256 像元间距 30 μm×30 μm F数 2 表 3 主、次镜组件、遮光筒和螺钉的重量估算
Table 3. Weight estimation of primary and secondary mirror assemblies, shadding baffle and screws
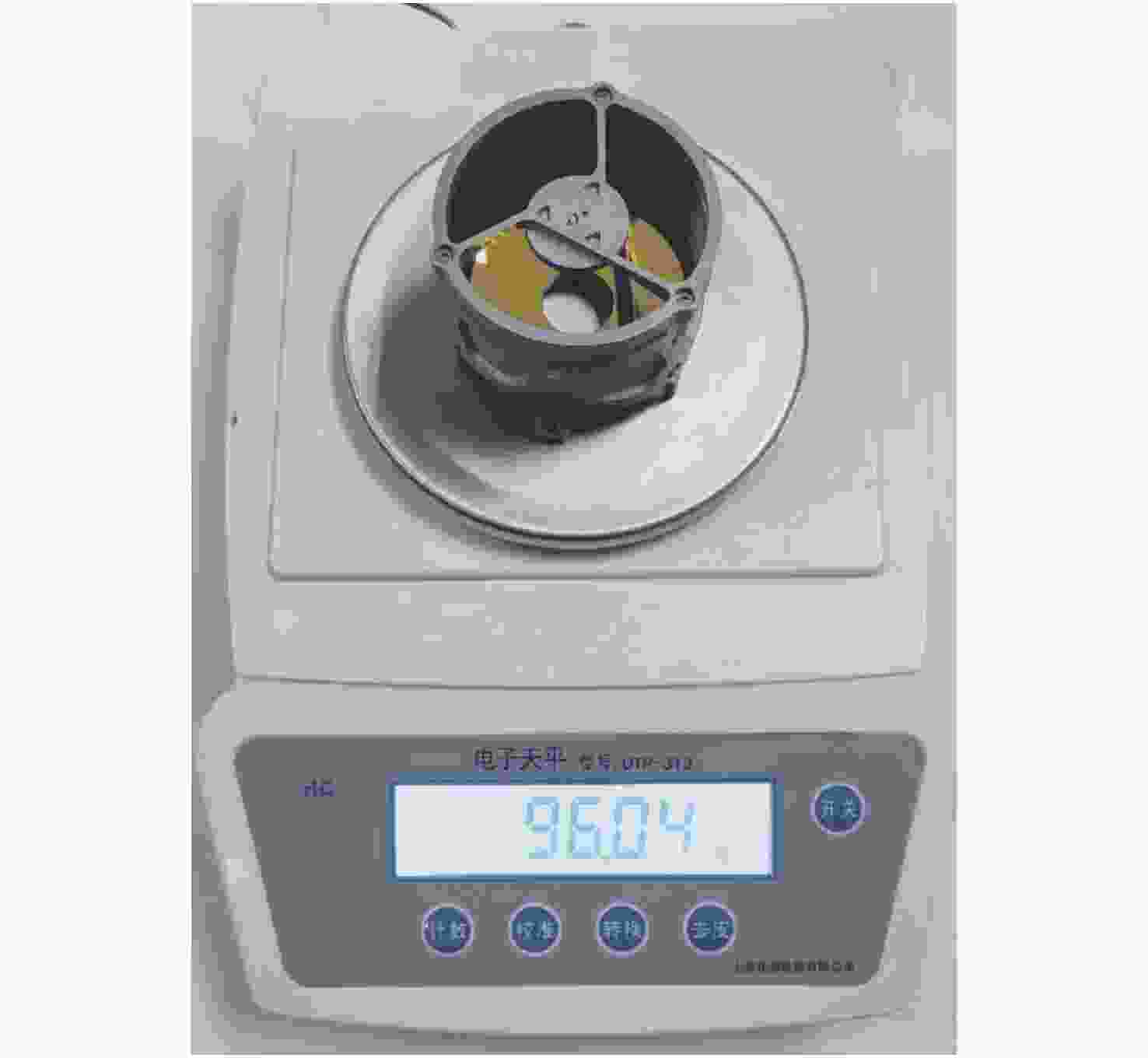
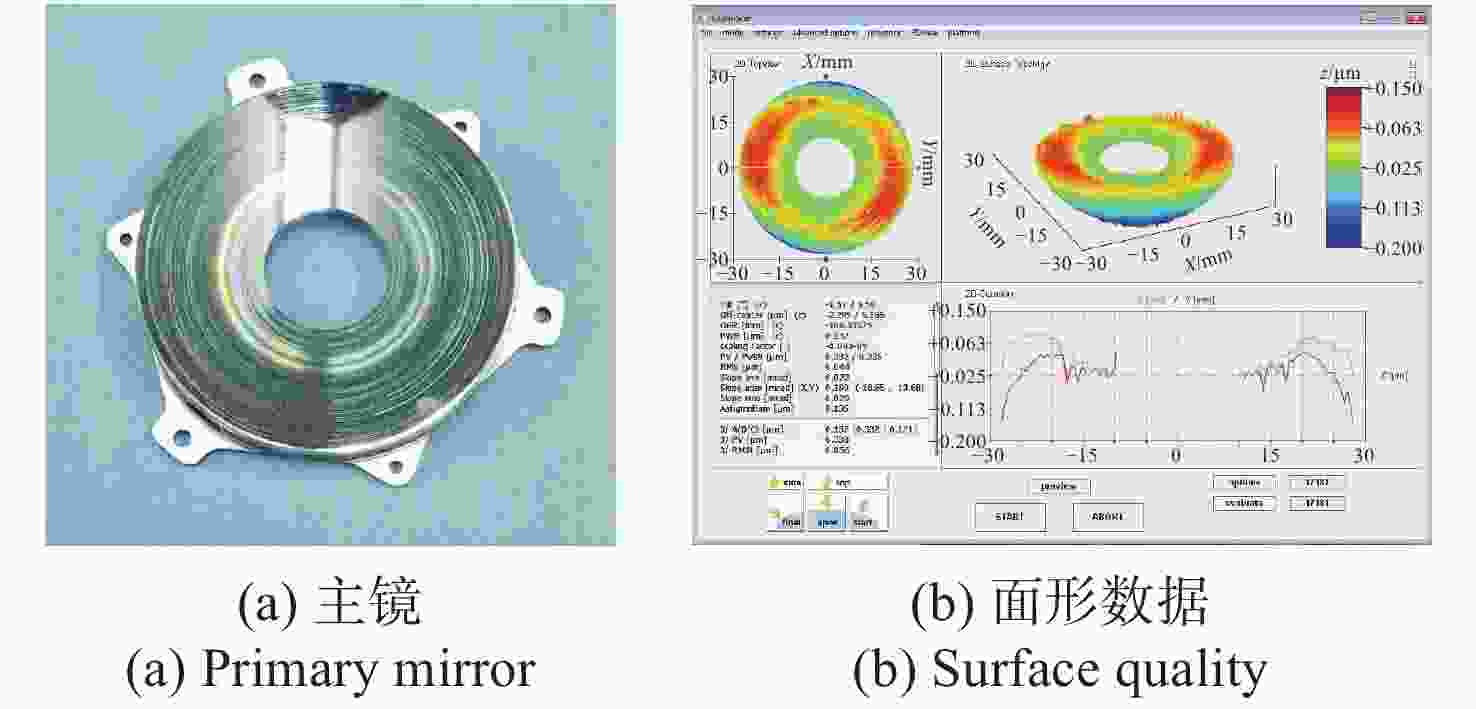
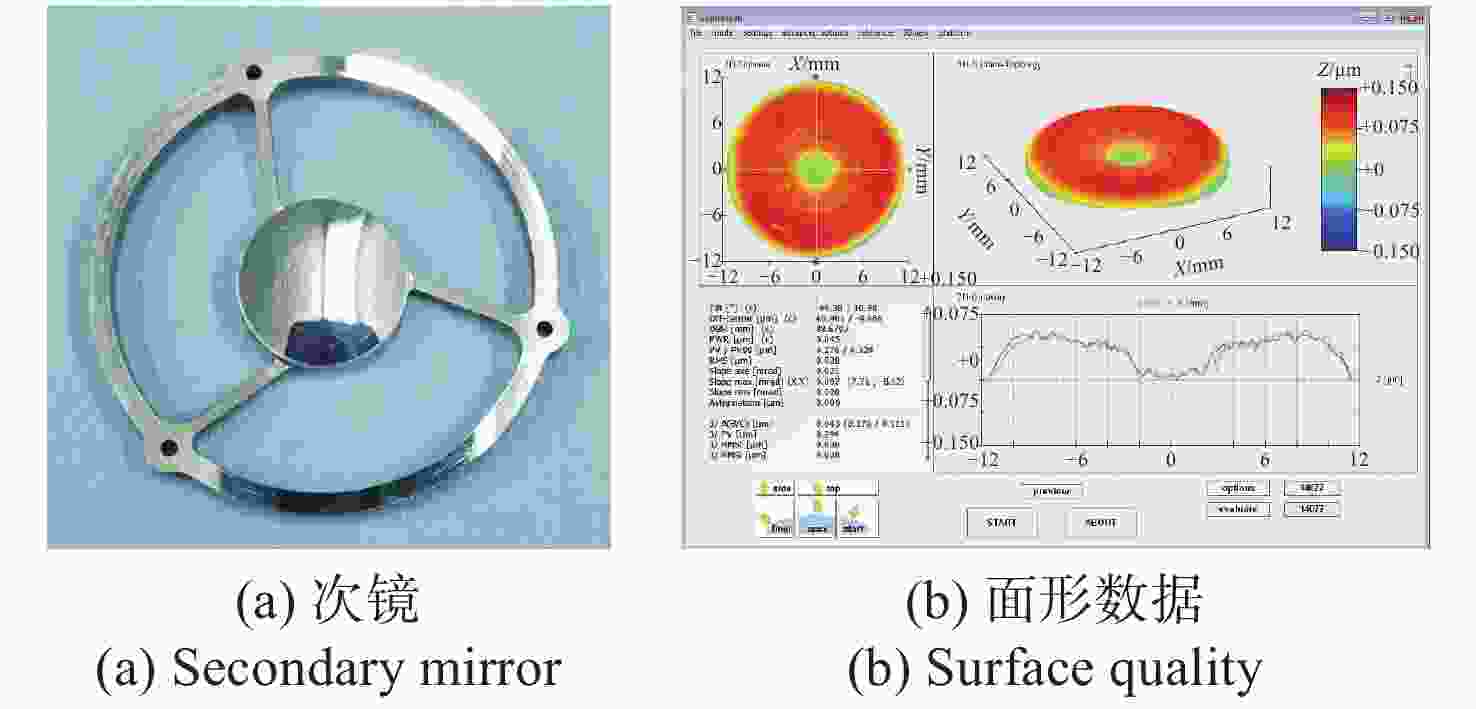
名称 重量g 主镜组件 40.6 次镜组件 16.8 遮光筒 32.2 螺钉 1.50 合计 91.1 表 4 各部件的实测重量
Table 4. Weight test results of each assembly
名称 实测质量(g) 主镜组件 44.64 次镜组件 16.8 遮光筒 33.07 螺钉 1.53 合计 96.04 -
[1] 甄政, 王英瑞, 欧文, 等. 一种新型红外多波段低背景探测技术[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(5):20190361. doi: 10.3788/irla.19_2019-0361ZHEN ZH, WANG Y R, OU W, et al. A novel technology on infrared multi-band low-background detection[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(5): 20190361. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/irla.19_2019-0361 [2] 范晋祥, 侯文涛. 防空反导精确寻的末制导技术的发展与思考[J]. 空天防御,2020,3(3):31-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2020.03.005FAN J X, HOU W T. Development and thinking of precision homing terminal guidance technology for air and missile defense[J]. Air &Space Defense, 2020, 3(3): 31-37. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4641.2020.03.005 [3] VUKOBRATOVICH D, SCHAEFER J P. Large stable aluminum optics for aerospace applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8125: 81250T. doi: 10.1117/12.892039 [4] MOEGGENBORG K, VINCER T, LESIAK S, et al. Super-polished aluminum mirrors through the application of chemical mechanical polishing techniques[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6288: 62880L. doi: 10.1117/12.681043 [5] XIE Y J, MAO X L, LI J P, et al. Optical design and fabrication of an all-aluminum unobscured two-mirror freeform imaging telescope[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(3): 833-840. doi: 10.1364/AO.379324 [6] 谭淞年, 丁亚林, 许永森, 等. 增材制造金属反射镜的发展综述[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(1):75-86. doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0075TAN S N, DING Y L, XU Y S, et al. Development of additively manufacturing metal mirrors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(1): 75-86. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0075 [7] ZHANG K, QU H M, GUAN H J, et al. Design and fabrication technology of metal mirrors based on additive manufacturing: a review[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(22): 10630. doi: 10.3390/app112210630 [8] WOODARD K S, MYRICK B H. Progress on high-performance rapid prototype aluminum mirrors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10181: 101810T. [9] WOODARD K S, COMSTOCK L E, WAMBOLDT L, et al. Optimum selection of high performance mirror substrates for diamond finishing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9822: 98220C. [10] SCHEIDING S, GEBHARDT A, DAMM C, et al. . Method for manufacturing a mirror comprising at least one cavity and optical mirror: USA, 20140247512[P]. 2014-09-04. [11] HILPERT E, HARTUNG J, RISSE S, et al. Precision manufacturing of a lightweight mirror body made by selective laser melting[J]. Precision Engineering, 2018, 53: 310-317. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2018.04.013 [12] HILPERT E, HARTUNG J, VON LUKOWICZ H, et al. Design, additive manufacturing, processing, and characterization of metal mirror made of aluminum silicon alloy for space applications[J]. Optical Engineering, 2019, 58(9): 092613. [13] ATKINS C, FELDMAN C, BROOKS D, et al. Topological design of lightweight additively manufactured mirrors for space[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10706: 107060I. -






 下载:
下载: