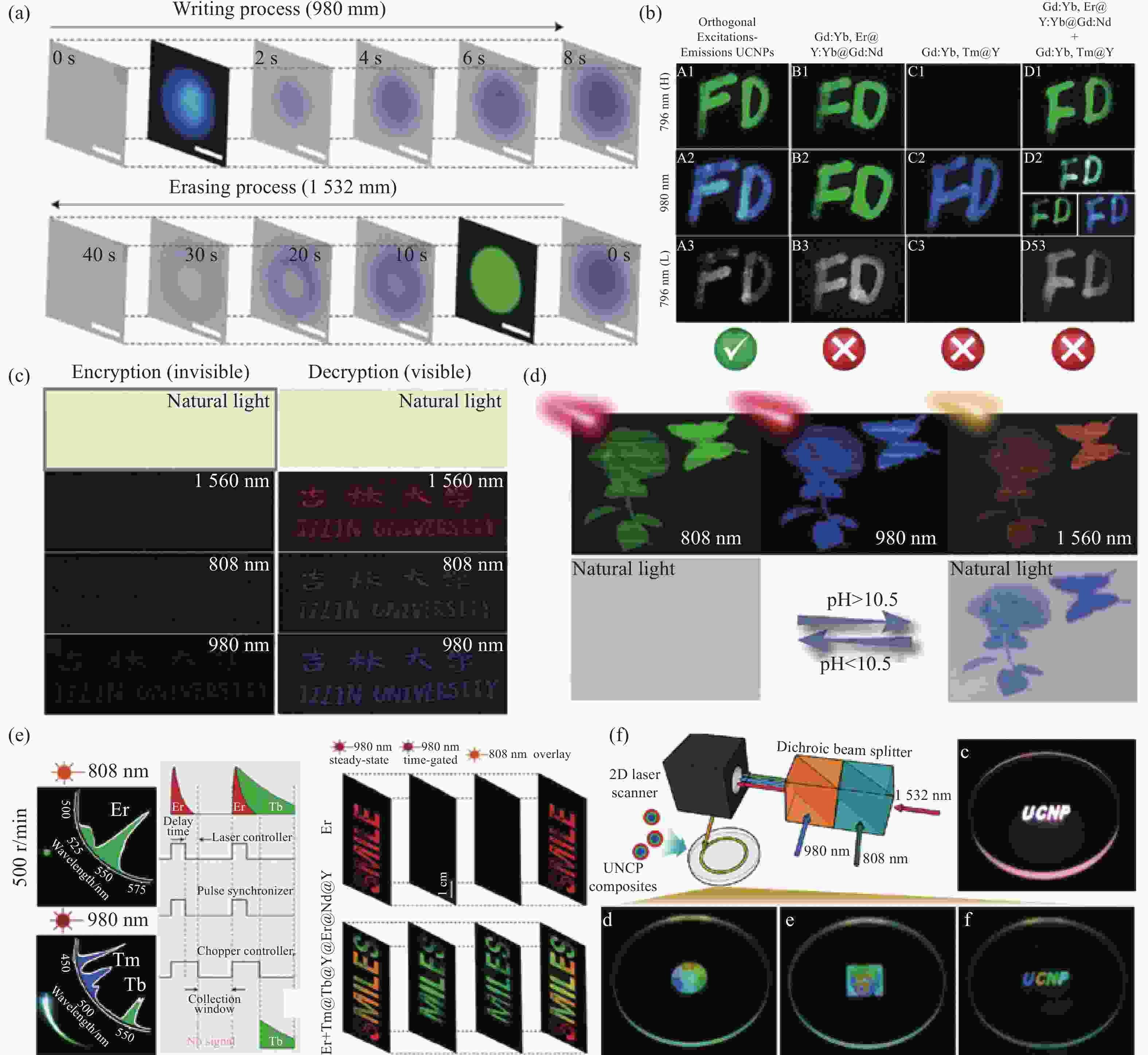
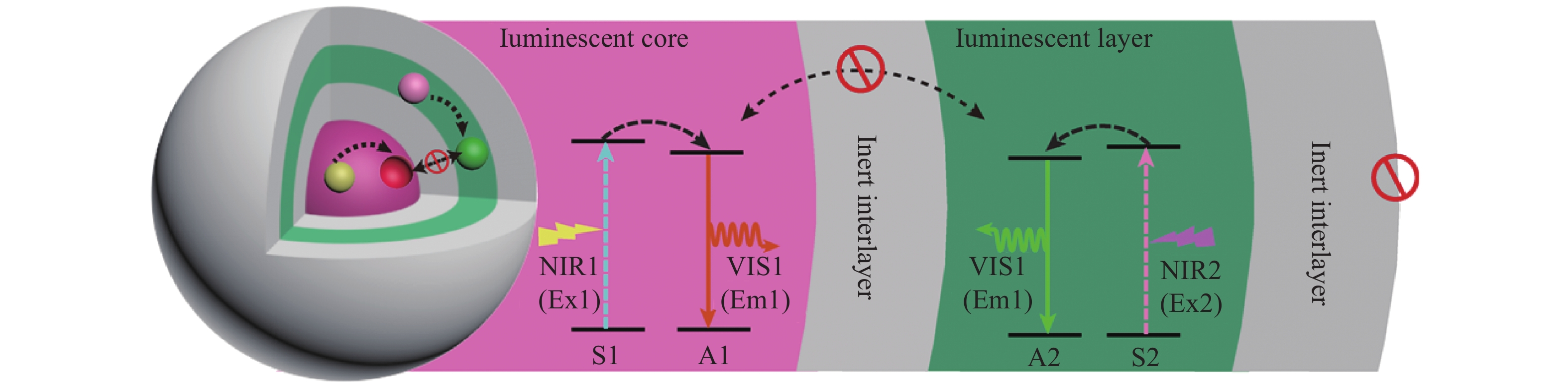
Design, preparation and application of orthogonal excitation-emission upconversion nanomaterials
-
摘要:
稀土掺杂的上转换发光纳米材料在信息安全、生物医学、光纤通信、显示和能源等众多领域有着巨大的应用潜力,受到了相关各领域研究人员的广泛关注。特别是近年来发展起来的具有正交激发发射特性的上转换发光纳米颗粒,其可在不同的激发条件下产生动态变化的光色输出,因而具备一系列新的特性与功能,大大地扩展了应用范围。本文综述稀土离子正交上转换发光的发展历程,系统论述了基于核壳结构的正交激发发射体系的设计原理和构建方法,介绍了其在信息存储、安全防伪、显示、传感、生物成像及治疗等领域的最新研究进展,并探讨了未来相关研究中可能面临的机遇和挑战。
Abstract:Rare earth-doped upconversion luminescence nanomaterials have received considerable attention from researchers due to their great potential for applications in many fields such as information security, biomedicine, optical fiber communication, digital displays, and energy. The recently-developed upconversion luminescence nanoparticles with orthogonal excitation-emission properties have attracted especially strong research interest because their distinct luminescence outputs can be dynamically modulated by switching the excitation conditions. The orthogonal luminescence properties further endow such nanocrystals with a set of new features and functionalities, which largely expands their potential applications. This review summarizes the progress in the development of orthogonal upconversion luminescence of rare earth ions, and provides a systematic discussion on design principles and construction strategies of orthogonal excitation-emission systems based on core-shell structures, as well as introduces their recent advances in various fields of applications including data storage, security anti-counterfeiting, digital displays, sensing, bioimaging and therapy. Furthermore, the prospective opportunities and challenges in the future research of orthogonal luminescence systems are also provided.
-
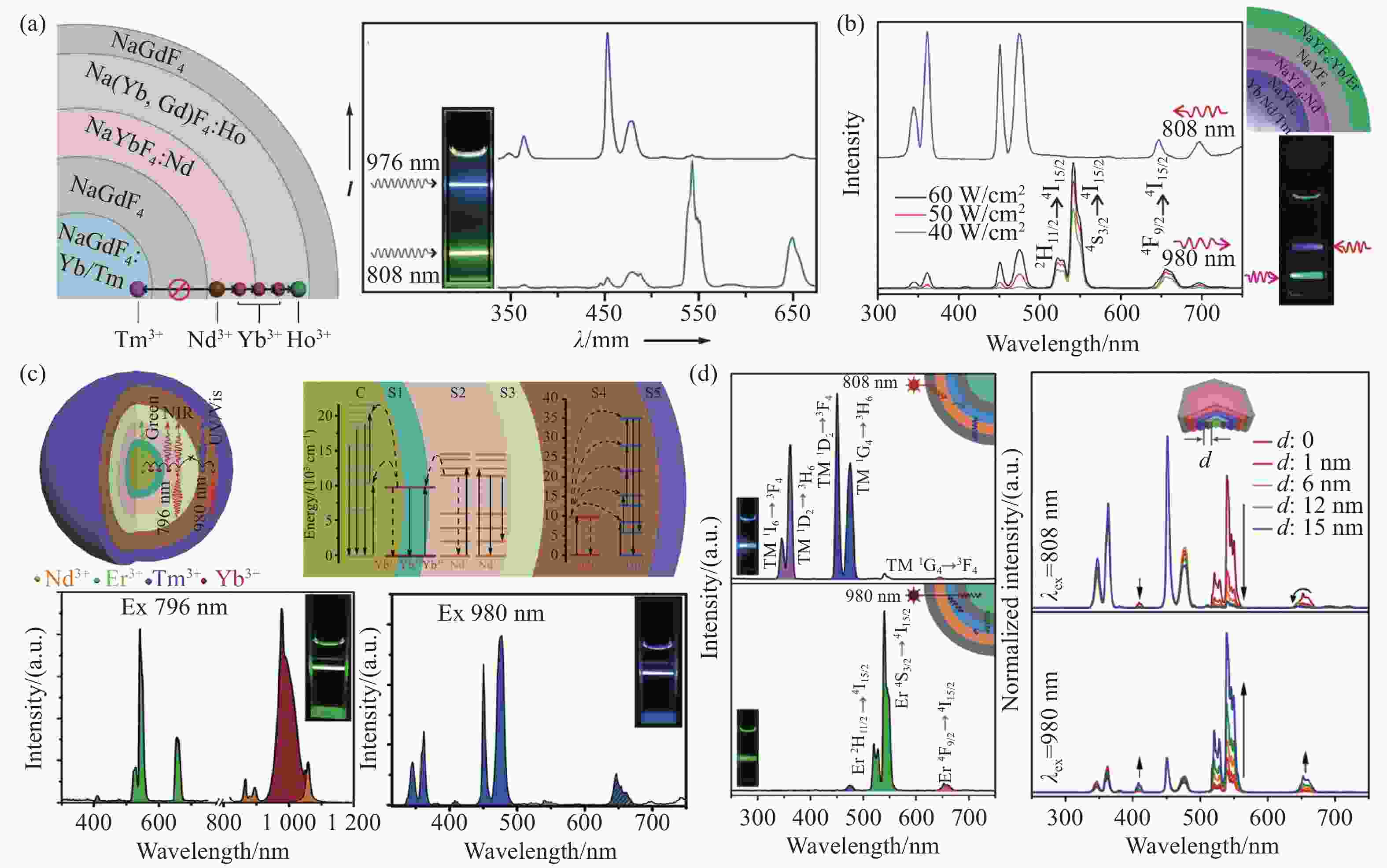
图 2 基于正交双色上转换发光的二元正交激发发射体系。(a)具有蓝-绿双色正交发光的四层核壳纳米结构NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaGdF4@NaYbF4:Nd@Na(Yb,Gd)F4:Ho@NaGdF4示意图和在980/808 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[41];(b) 蓝-绿双色正交发光的NaYF4: Nd/Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Nd@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb /Er三层核壳结构示意图和在980/808 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[33];(c)具有不依赖于激发功率密度的高色纯度蓝-绿双色正交发射的NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4:Yb@NaGdF4:Yb,Nd@NaYF4@NaGdF4: Yb,Tm@NaYF4五层核壳结构示意图和在980/796 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[42];(d)具有不同中间NaYF4纳米壳层厚度的NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb,Tm@NaYbF4:Nd@NaYF4四层核壳结构在808/980 nm二元激发下的发射光谱[43]。(a)转载自文献[41],版权所有(2013)威立出版集团; (b)转载自文献[33],版权所有(2014)威立出版集团; (c)转载自文献[42],版权所有(2016)威立出版集团; (d)转载自文献[43],版权所有(2017)美国化学学会
Figure 2. Binary orthogonal excitation-emission systems for orthogonal dual-color upconversion luminescence. (a) Schematic illustration of core/quadruple-shell NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaGdF4@NaYbF4:Nd@Na(Yb,Gd)F4:Ho@NaGdF4 with blue-green dual-color orthogonal luminescence and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 980/808 nm binary excitations[41]; (b) schematic illustration of core/triple-shell NaYF4:Nd/Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Nd@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Er with blue-green dual-color orthogonal luminescence and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 980/808 nm binary excitations[33]; (c) schematic illustration of core/quintuple-shell NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4:Yb@NaGdF4:Yb,Nd@NaYF4@NaGdF4:Yb,Tm@NaYF4 with excitation power density-independent blue-green high-pure dual-color orthogonal luminescence and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 980/796 nm binary excitations[42]; (d) emission spectra of core/quadruple-shell NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb, Tm@NaYbF4:Nd@NaYF4 with varied thickness of an NaYF4 interlayer under 808/980 nm binary excitations[43]. (a) Reproduced with permission ref. [41]. Copyright 2013, Wiley-VCH; (b) reproduced with permission ref. [33]. copyright 2014, Wiley-VCH; (c) reproduced with permission ref. [42]. copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH; (d) reproduced with permission ref. [43]. copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
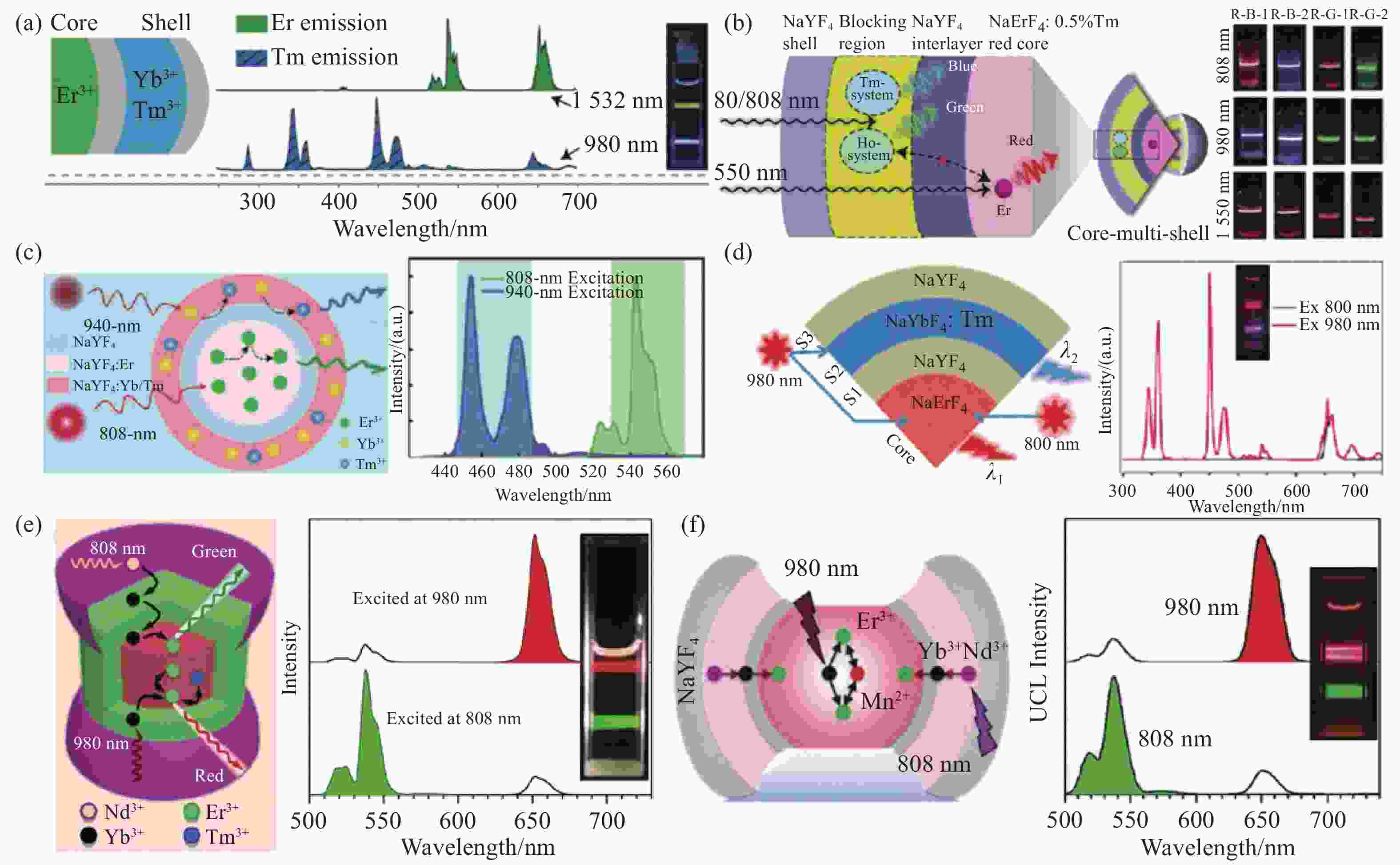
图 3 正交双色发射的二元正交激发发射体系。(a)基于敏化剂Er3+的绿-蓝双色正交发射NaYF4:Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4三层核壳纳米结构示意图和在1532/980 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[44];(b)基于NaErF4:Tm红光发射核的多层核壳纳米结构示意图和在1550 nm和980/808 nm二元激发下的发光照片[20];(c) 基于Er3+自敏化的蓝-绿双色正交发射NaYF4:Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Tm双层核壳纳米结构示意图和在808/940 nm二元激发下的发射光谱[45];(d) 基于NaErF4红光发射核的红-蓝双色正交发射NaErF4@NaYF4@NaYbF4:Tm@NaYF4三层核壳纳米结构示意图和在800/980 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[46];(e)基于单发光层的红-绿双色正交发射NaErF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb双层核壳纳米结构示意图和在980/808 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[47];(f) 基于单发光层的二元正交激发发射体系(NaYF4:Yb/Er/Mn@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb)示意图和在980/808 nm二元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[49]。(a)转载自文献[44],版权所有(2018)威立出版集团; (b)转载自文献[20],版权所有(2019)威立出版集团; (c)转载自文献[45],版权所有(2018)皇家化学学会; (d)转载自文献[46],版权所有(2018)美国化学学会; (e)转载自文献[47],版权所有(2019)自然出版集团; (f)转载自文献[49],版权所有(2020)威立出版集团
Figure 3. Binary orthogonal excitation-emission systems with orthogonal dual-color emissions. (a) Schematic illustration of Er3+ sensitizer-based core/triple-shell NaYF4:Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4 with green-blue dual-color orthogonal emissions and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 1532/980 nm binary excitations[44]; (b) schematic illustration of red-emitting NaErF4:Tm core-based multilayer core-shell nanostructures and their corresponding photographs under 1550 nm and 980/808 nm binary excitations[20]; (c) schematic illustration of self-sensitization of Er3+-based core/double-shell NaYF4:Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Tm with blue-green dual-color orthogonal emissions and its corresponding emission spectra under 808/940 nm binary excitations[45]; (d) schematic illustration of red-emitting NaErF4 core-based core/triple-shell NaErF4@NaYF4@NaYbF4:Tm@NaYF4 with red-blue dual-color orthogonal emissions and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 808/980 nm binary excitations[46]; (e) schematic illustration of a single-emissive layer-based core/double-shell NaErF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb with red-green dual-color orthogonal emissions and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 980/808 nm binary excitations[47]; (f) schematic illustration of a single-emissive layer-based binary orthogonal excitation-emission systems (NaYF4:Yb/Er/Mn@NaYF4:Yb@NaNdF4:Yb) and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 980/808 nm binary excitations[49]. (a) Reproduced with permission ref. [44]. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH; (b) reproduced with permission ref. [20]. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH; (c) reproduced with permission ref. [45]. Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry; (d) reproduced with permission ref. [46]. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (e) reproduced with permission ref. [47]. Copyright 2019, Nature Publishing Group; (f) reproduced with permission ref. [49]. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH
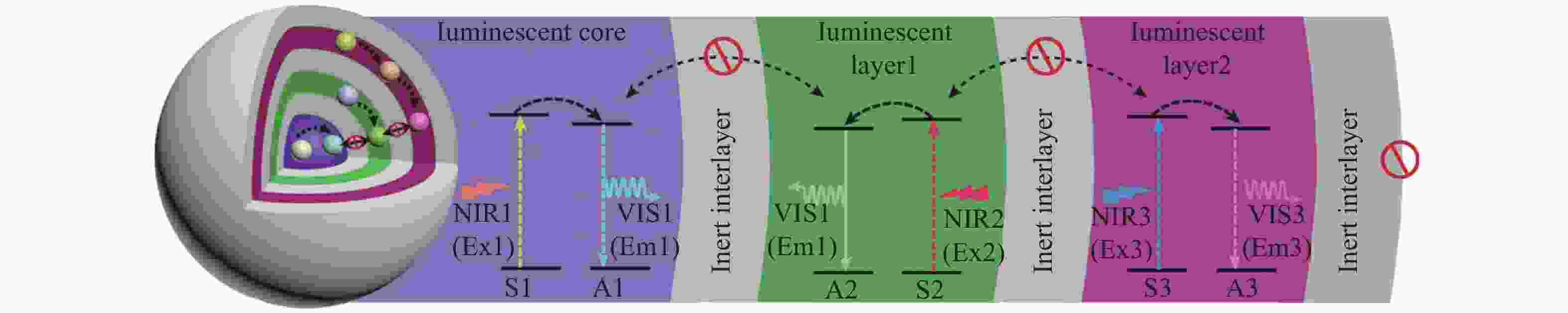
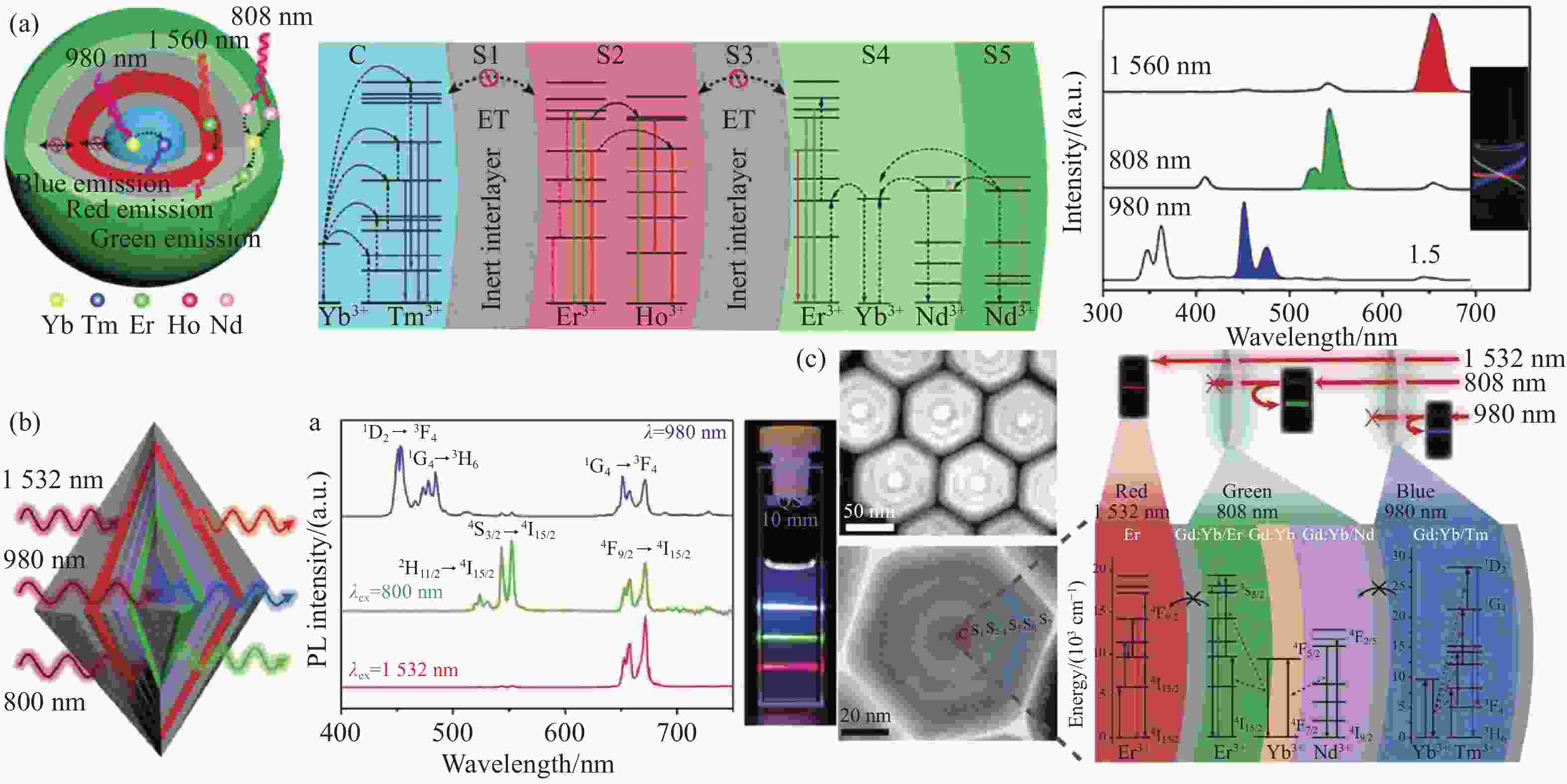
图 5 基于正交三基色上转换发光的三元正交激发发射体系。(a)具有不依赖于激发功率密度的高色纯度红-绿-蓝三基色正交发光的NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4@NaYF4:Er/Ho@NaYF4@NaYF4:Nd/Yb/Er@NaYF4:Nd五层核壳纳米结构示意图和在1560/808/980 nm三元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[52];(b) 具有不依赖于激发功率密度的正交三基色发光的LiYbF4:Tm@LiGdF4@LiGdF4:Yb/Er@LiYF4:Nd/Yb@LiGdF4@LiErF4:Tm@LiGdF4六层核壳纳米结构示意图和在1532/980/800 nm三元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[59];(c)具有不依赖于激发功率密度的正交三基色发光的NaErF4@NaYF4@NaGdF4:Yb/Er@NaGdF4:Yb@NaGdF4:Nd/Yb@NaYF4@NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4七层核壳纳米结构示意图和在1532/808/980 nm三元激发下的发射光谱及对应的发光照片[60]。 (a)转载自文献[52],版权所有(2021)美国化学学会; (b)转载自文献[59],版权所有(2021)美国化学学会; (c)转载自文献[60],版权所有(2021)自然出版集团
Figure 5. Ternary orthogonal excitation-emission systems for orthogonal three-primary-color upconversion luminescence. (a) Schematic illustration of core/quintuple-shell NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4@NaYF4:Er/Ho@NaYF4@NaYF4:Nd/Yb/Er@NaYF4:Nd with excitation power density-independent red-green-blue high-pure three-primary-color orthogonal emissions and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 1560/808/980 nm ternary excitations[52]; (b) schematic illustration of core/sextuple-shell LiYbF4:Tm@LiGdF4@LiGdF4:Yb/Er@LiYF4:Nd/Yb@LiGdF4@LiErF4:Tm@LiGdF4 with excitation power density-independent orthogonal three-primary-color luminescence and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 1532/980/800 nm ternary excitations[59]; (c) transmission electron microscopy image and schematic illustration of core/septuple-shell NaErF4@NaYF4@NaGdF4:Yb/Er@NaGdF4:Yb@NaGdF4:Nd/Yb@NaYF4@NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4 with excitation power density-independent orthogonal three-primary-color luminescence and its corresponding emission spectra and photographs under 1532/808/980 nm ternary excitations[60]. (a) Reproduced with permission ref. [52]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (b) reproduced with permission ref. [59]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (c) reproduced with permission ref. [60]. Copyright 2021, Nature Publishing Group.
图 7 正交激发发射体系在光学存储、安全防伪及显示领域的应用。(a)二元正交激发发射体系用于近红外光驱动下的光学数据存储[44];(b)二元正交激发发射体系用于多级防伪[42];(c)三元正交激发发射体系用于信息的加密与解密[52];(d)三元正交激发发射体系用于高级防伪[58];(e)二元正交激发发射体系用于多维度防伪[43];(f)三元正交激发发射体系用于二维彩色显示[59]。(a)转载自文献[44],版权所有(2018)威立出版集团; (b)转载自文献[42],版权所有(2016)威立出版集团; (c)转载自文献[52],版权所有(2021)美国化学学会;(d)转载自文献[58],版权所有(2022)美国化学学会;(e)转载自文献[43],版权所有(2017)美国化学学会;(f)转载自文献[59],版权所有(2021)美国化学学会
Figure 7. Typically applications of orthogonal excitation-emission systems in the fields of optical storage, security anticounterfeiting and displays. (a) Binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for NIR-guided optical data storage[44]; (b) binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for multi-level anti-counterfeiting[42]; (c) ternary orthogonal excitation-emission system for information encryption and decryption[52]; (d) ternary orthogonal excitation-emission system for advanced anti-counterfeiting[58]; (e) binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for multi-dimensional anti-counterfeiting[43]; (f) ternary orthogonal excitation-emission system for 2D color display[59]. (a) Reproduced with permission ref. [44]. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH; (b) reproduced with permission ref. [42]. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH; (c) reproduced with permission ref. [52]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (d) reproduced with permission ref. [58]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society; (e) reproduced with permission ref. [43]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (f) reproduced with permission ref. [59]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society
图 8 正交激发发射体系在传感及生物医学领域的应用。(a)二元正交激发发射体系用于对指纹内残留物TNT的检测[49];(b)二元正交激发发射体系用于对黄曲霉毒素B1的检测[48];(c)二元正交激发发射体系用于超分辨成像[45];(d) 二元正交激发发射体系用于成像引导的光动力/化疗联合治疗[42]。(a)转载自文献[49],版权所有(2020)威立出版集团; (b)转载自文献[48],版权所有(2021)美国化学学会; (c)转载自文献[45],版权所有(2021)皇家化学学会;(d)转载自文献[42],版权所有(2016)威立出版集团
Figure 8. Typically applications of orthogonal excitation-emission systems in the fields of sensing and biomedicine. (a) Binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for the detection of TNT residues in the fingerprint[49]; (b) binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for the detection of aflatoxin B1[48]; (c) binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for super-resolution image[45]; (d) binary orthogonal excitation-emission system for imaging-guided combined photodynamic therapy/ chemotherapy[42]. (a) Reproduced with permission ref. [49]. Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH; (b) reproduced with permission ref. [48]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (c) reproduced with permission ref. [45]. Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry; (d) reproduced with permission ref. [42]. Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH.
表 1 正交激发发射体系类型及研究进展与应用前景汇总
Table 1. Summary of system types, research progress and application prospects for orthogonal excitation-emission
Core-shell nanomaterials with orthogonal excitations-emissions Orthogonal excitation type Sensitizer-Activator Luminescence color@
Excitation wavelengthApplication fields Reference/
PublicationYearNaErF4:Tm@NaYF4@
NaYF4:Yb/Ho@NaYF4Binary Er3+-Tm3+/
Yb3+-Ho3+Red@808/1550 nm
Green@980 nm— [20]
2019NaErF4:Tm@NaYF4@
NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4Binary Er3+-Tm3+/
Yb3+-Tm3+Red@808/1550 nm
Blue@980 nm— [20]
2019NaYF4:Nd/Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Nd@
NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/ErBinary Nd3+-Yb3+-Tm3+/
Yb3+-Er3+UV/blue@808 nm
Green@980 nmPhoto-switching [33]
2014NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaGdF4@NaYbF4:Nd@Na(Yb,Gd)F4:Ho@NaGdF4 Binary Yb3+-Tm3+/
Nd3+-Yb3+-Ho3+UV/blue@980 nm
Green@808 nm— [41]
2013NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4:Yb@
NaGdF4:Yb,Nd@NaYF4@
NaGdF4:Yb,Tm@NaYF4Binary Nd3+-Yb3+-Er3+/
Yb3+-Tm3+Green@796 nm
UV/blue@980 nmanticounterfeiting/PDT/CT [42]
2016NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4@ NaYF4:Yb,Tm@NaYbF4:Nd@NaYF4 Binary Yb3+-Er3+/
Nd3+-Yb3+-Tm3+Green@980 nm
UV/blue@808 nmFingerprint imaging [43]
2017NaYF4:Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4 Binary Er3+/
Yb3+-Tm3+Green@1532 nm
UV/blue@980 nmOptical data storage [44]
2018NaYF4:Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Tm Binary Er3+/
Yb3+-Tm3+Green@808 nm
Blue@980 nmSuper-resolution image [45]
2018NaErF4@NaYF4@NaYbF4:Tm @NaYF4 Binary Er3+/
Yb3+-Tm3+Red@800 nm
Blue@980 nmImaging-guided PDT [46]
2018NaErF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Yb@
NaNdF4:YbBinary Er3+-Tm3+/
Nd3+-Yb3+-Er3+Red@980 nm
Green@808 nmPhotoactivation/detection [47,48]
2019/2021NaYF4:Yb/Er/Mn@NaYF4:Yb@
NaNdF4:YbBinary Yb3+-Er3+-Mn2+/Nd3+-Yb3+-Er3+ Red@980 nm
Green@808 nmLatent fingerprint
sensing[49]
2020NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb,Tm@NaYbF4:Nd@NaYF4 Binary Yb3+-Er3+/ Nd3+-Yb3+-Tm3+ Green@980 nm
UV/blue@808 nmTumor cell recognition/PDT [50]
2020NaErF4:Yb/Tm@NaYbF4 Binary Er3+-Tm3+/
Yb3+-Er3+Green@808 nm
Red@980 nmInformation
security[51]
2021NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4@NaYF4:Er/Ho@NaYF4@NaYF4:Nd/Yb/Er@
NaYF4:NdTernary Yb3+-Tm3+/
Er3+-Ho3+/ Nd3+-Yb3+-Er3+UV/blue@980 nm Red@1560 nm Green@808 nm Information
Security/ anticounterfeiting[52-54,55-58]
2021/2022LiYbF4:Tm@LiGdF4@LiGdF4:Yb/Er@LiYF4:Nd/Yb@LiGdF4@
LiErF4:Tm@LiGdF4Ternary Yb3+-Tm3+/
Nd3+-Yb3+-Er3+/ Er3+-Tm3+UV/blue@980 nm Green@808 nm Red@1532 nm 2D full-color display [59]
2021NaErF4@NaYF4@NaGdF4:Yb/Er@
NaGdF4:Yb@NaGdF4:Nd/Yb@
NaYF4@ NaGdF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4Ternary Er3+/ Nd3+-Yb3+-Er3+/ Yb3+-Tm3+ Red@1532 nm
Green@808 nm
Blue@980 nmNeuronal
population[60]
2021NaYF4:Yb/Tm@NaYF4:Yb/Nd@
NaLuF4@NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaLuF4@
NaErF4:Tm@NaLuF4Ternary Nd3+-Yb3+-Tm3+/ Yb3+-Er3+/ Er3+-Tm3+ Blue@808 nm
Green@980 nm
Red@1532 nmMultiplexed
detection[61]
2022NaErF4:Tm@NaYF4@NaYF4:Yb/Ho@NaYF4:Nd/Yb@NaYF4@
NaYbF4:Tm@ NaYF4:YbTernary Er3+-Tm3+/ Nd3+-Yb3+-Ho3+/ Yb3+-Tm3+ Red@1550 nm
Green@808 nm
UV/blue@980 nmFlexible display/ anticounterfeiting [62]
2022 -
[1] WANG F, LIU X G. Recent advances in the chemistry of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanocrystals[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(4): 976-989. doi: 10.1039/b809132n [2] LIU X G, Yan CH H, CAPOBIANCO J A. Photon upconversion nanomaterials[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1299-1301. doi: 10.1039/C5CS90009C [3] ZHOU B, SHI B Y, JIN D Y, et al. Controlling upconversion nanocrystals for emerging applications[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(11): 924-936. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.251 [4] AUZEL F. Upconversion and anti-Stokes processes with f and d Ions in solids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(1): 139-174. doi: 10.1021/cr020357g [5] BLOEMBERGEN N. Solid State Infrared Quantum Counters[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1959, 2(3): 84-85. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.2.84 [6] AUZEL F. Compteur quantique par transfert d'energie entre deux ions de terres rares dans un tungstate mixte et dans un verre[J]. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences de Paris, 1966, 262: 1016-1019. [7] WANG M, ABBINENI G, CLEVENGER A, et al. Upconversion nanoparticles: synthesis, surface modification and biological applications[J]. Nanomedicine:Nanotechnology,Biology and Medicine, 2011, 7(6): 710-729. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2011.02.013 [8] HAASE M, SCHÄFER H. Upconverting Nanoparticles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(26): 5808-5829. doi: 10.1002/anie.201005159 [9] LIU S B, YAN L, HUANG J SH, et al. Controlling upconversion in emerging multilayer core–shell nanostructures: from fundamentals to frontier applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(5): 1729-1765. doi: 10.1039/D1CS00753J [10] YAN CH L, ZHAO H G, PEREPICHKA D F, et al. Lanthanide ion doped upconverting nanoparticles: synthesis, structure and properties[J]. Small, 2016, 12(29): 3888-3907. doi: 10.1002/smll.201601565 [11] ZHU X H, ZHANG J, LIU J L, et al. Recent progress of rare-earth doped upconversion nanoparticles: synthesis, optimization, and applications[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(22): 1901358. doi: 10.1002/advs.201901358 [12] ZHENG K ZH, LOH K Y, WANG Y, et al. Recent advances in upconversion nanocrystals: expanding the kaleidoscopic toolbox for emerging applications[J]. Nano Today, 2019, 29: 100797. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2019.100797 [13] QIN W P, Sin C, Liu ZH Y, et al. Theory on cooperative quantum transitions of three identical lanthanide ions[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2015, 32(2): 303-308. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.32.000303 [14] QIN W P, LIU ZH Y, SIN C N, et al. Multi-ion cooperative processes in Yb3+ clusters[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2014, 3(8): e193-e193. [15] TU L P, LIU X M, WU F, et al. Excitation energy migration dynamics in upconversion nanomaterials[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1331-1345. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00168K [16] DONG H, SUN L D, YAN CH H. Energy transfer in lanthanide upconversion studies for extended optical applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1608-1634. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00188E [17] DENG R R, QIN F, CHEN R F, et al. Temporal full-colour tuning through non-steady-state upconversion[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(3): 237-242. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.317 [18] LI ZH Q, ZHANG Y, JIANG SH. Multicolor core/shell-structured upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(24): 4765-4769. doi: 10.1002/adma.200801056 [19] WANG F, LIU X G. Multicolor tuning of lanthanide-doped nanoparticles by single wavelength excitation[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2014, 47(4): 1378-1385. doi: 10.1021/ar5000067 [20] WU M, YAN L, WANG T, et al. Controlling red color–based multicolor upconversion through selective photon blocking[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(25): 1804160. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201804160 [21] LI L L, ZHANG R B, YIN L L, et al. Biomimetic surface engineering of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles as versatile bioprobes[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2012, 124(25): 6225-6229. doi: 10.1002/ange.201109156 [22] WÜRTH C, FISCHER S, GRAUEL B, et al. Quantum yields, surface quenching, and passivation efficiency for ultrasmall core/shell upconverting nanoparticles[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(14): 4922-4928. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b01458 [23] REN W, WEN SH H, TAWFIK S A, et al. Anisotropic functionalization of upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(18): 4352-4358. doi: 10.1039/C8SC01023D [24] FAN Y, LIU L, ZHANG F. Exploiting lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles with core/shell structures[J]. Nano Today, 2019, 25: 68-84. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2019.02.009 [25] CHEN X, PENG D F, JU Q, et al. Photon upconversion in core–shell nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1318-1330. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00151F [26] YAO W J, TIAN Q Y, WU W. Tunable emissions of upconversion fluorescence for security applications[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2019, 7(6): 1801171. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801171 [27] TANG Y N, DI W H, ZHAI X S, et al. NIR-responsive photocatalytic activity and mechanism of NaYF4:Yb, Tm@TiO2 core–shell nanoparticles[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(3): 405-412. doi: 10.1021/cs300808r [28] CHEN G Y, ÅGREN H, OHULCHANSKYY T Y, et al. Light upconverting core–shell nanostructures: nanophotonic control for emerging applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1680-1713. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00170B [29] GAI SH L, YANG P P, LI CH X, et al. Synthesis of magnetic, up-conversion luminescent, and mesoporous core-shell-structured nanocomposites as drug carriers[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(7): 1166-1172. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200902274 [30] ZHOU L, FAN Y, WANG R, et al. High-capacity upconversion wavelength and lifetime binary encoding for multiplexed biodetection[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(39): 12824-12829. doi: 10.1002/anie.201808209 [31] ZHOU B, YAN L, HUANG J SH, et al. NIR II-responsive photon upconversion through energy migration in an ytterbium sublattice[J]. Nature Photonics, 2020, 14(12): 760-766. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-00714-6 [32] ZHANG ZH, ZHANG Y. Orthogonal emissive upconversion nanoparticles: material design and applications[J]. Small, 2021, 17(11): 2004552. doi: 10.1002/smll.202004552 [33] LAI J P, ZHANG Y X, PASQUALE N, et al. An upconversion nanoparticle with orthogonal emissions using dual NIR excitations for controlled two-way photoswitching[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(52): 14419-14423. doi: 10.1002/anie.201408219 [34] LIU L, YAN D, XU L, et al. Intense and color-tunable upconversion through 980 and 1530 nm excitations[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2020, 224: 117306. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117306 [35] QUINTANILLA M, REN F Q, MA D L, et al. Light management in upconverting nanoparticles: ultrasmall core/shell architectures to tune the emission color[J]. ACS Photonics, 2014, 1(8): 662-669. doi: 10.1021/ph500208q [36] LIU S B, YAN L, LI Q Q, et al. Tri-channel photon emission of lanthanides in lithium-sublattice core-shell nanostructures for multiple anti-counterfeiting[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 397: 125451. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125451 [37] WANG F, DENG R R, WANG J, et al. Tuning upconversion through energy migration in core–shell nanoparticles[J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10(12): 968-973. doi: 10.1038/nmat3149 [38] CHEN D Q, LEI L, YANG A P, et al. Ultra-broadband near-infrared excitable upconversion core/shell nanocrystals[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(47): 5898-5900. doi: 10.1039/c2cc32102e [39] XU M, CHEN D Q, HUANG P, et al. A dual-functional upconversion core@shell nanostructure for white-light-emission and temperature sensing[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(27): 6516-6524. doi: 10.1039/C6TC02218A [40] FISCHER S, BRONSTEIN N D, SWABECK J K, et al. Precise tuning of surface quenching for luminescence enhancement in core–shell lanthanide-doped nanocrystals[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(11): 7241-7247. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03683 [41] WEN H L, ZHU H, CHEN X, et al. Upconverting near-infrared light through energy management in core-shell-shell nanoparticles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(50): 13419-13423. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306811 [42] LI X M, GUO ZH ZH, ZHAO T C, et al. Filtration shell mediated power density independent orthogonal excitations-emissions upconversion luminescence[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(7): 2464-2469. doi: 10.1002/anie.201510609 [43] DONG H, SUN L D, FENG W, et al. Versatile spectral and lifetime multiplexing nanoplatform with excitation orthogonalized upconversion luminescence[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(3): 3289-3297. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b00559 [44] ZHENG K ZH, HAN S Y, ZENG X, et al. Rewritable optical memory through high-registry orthogonal upconversion[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(30): 1801726. doi: 10.1002/adma.201801726 [45] HUANG B R, WU Q SH, PENG X Y, et al. One-scan fluorescence emission difference nanoscopy developed with excitation orthogonalized upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(45): 21025-21030. doi: 10.1039/C8NR07017B [46] ZUO J, TU L P, LI Q Q, et al. Near infrared light sensitive ultraviolet–blue nanophotoswitch for imaging-guided “off–on” therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(4): 3217-3225. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07393 [47] MEI Q S, BANSAL A, JAYAKUMAR M K G, et al. Manipulating energy migration within single lanthanide activator for switchable upconversion emissions towards bidirectional photoactivation[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12374-4 [48] GUO X R, YUAN Y, LIU J L, et al. Single-line flow assay platform based on orthogonal emissive upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(5): 3010-3017. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05061 [49] LEI ZH D, LING X, MEI Q S, et al. An excitation navigating energy migration of lanthanide ions in upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(9): 1906225. doi: 10.1002/adma.201906225 [50] DI ZH H, LIU B, ZHAO J, et al. An orthogonally regulatable DNA nanodevice for spatiotemporally controlled biorecognition and tumor treatment[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(25): eaba9381. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba9381 [51] HUANG J SH, YAN L, LIU S B, et al. Dynamic control of orthogonal upconversion in migratory core–shell nanostructure toward information security[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(14): 2009796. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202009796 [52] JIA H, LI D G, ZHANG D, et al. High color-purity red, green, and blue-emissive core–shell upconversion nanoparticles using ternary near-infrared quadrature excitations[J]. ACS Applied Materials &Interfaces, 2021, 13(3): 4402-4409. [53] 秦伟平, 贾恒, 张丹, 等. 具有三元正交激发响应三基色上转换发光性能的五层核壳结构纳米材料: 中国, 202010685751. 7[p]. 2022–05-31.QIN W P, JIA H, ZHANG D, et al. . Core/quintuple-shell nanomaterials with ternary orthogonal excitation-responsive three-primary-color upconversion luminescence property: CN, 202010685751. 7[p]. 2022–05-31. (in Chinese) [54] 秦伟平, 贾恒, 董妍惠, 等. 一种制备正交激发-发射响应的三基色上转换发光材料的方法: 中国, 202010685752. 1[p]. 2022–05-31.QIN W P, JIA H, DONG Y H, et al. . A method for preparing orthogonal excitation-emission-responsive three-primary-color upconversion luminescencet materials: CN, 202010685752. 1[p]. 2022–05-31. (in Chinese) [55] 秦伟平, 贾恒, 崔珈豪, 等. 一种基于δ-MnO2纳米片修饰正交三基色上转换发光纳米晶的加密墨水及其制备方法: 中国, 202010685712. 7[p]. 2021–08-27.QIN W P, JIA H, CUI J H, et al. . An encryption ink based on orthogonal three-primary-color upconversion luminescence nanocrystals modified by δ-MnO2 nanosheets and its preparation method: CN, 202010685712. 7[p]. 2021–08-27. (in Chinese) [56] 秦伟平, 贾恒, 李大光, 等. 一种红绿蓝三基色正交上转换荧光安全墨水的制备方法: 中国, 202010685263. 6[p]. 2021–09-24.QIN W P, JIA H, LI D G, et al. . A preparation method of red, green and blue tri-color orthogonal upconversion fluorescence security ink: CN, 202010685263. 6[p]. 2021–09-24. (in Chinese) [57] 秦伟平, 贾恒, 周敏, 等. 一种具有三基色正交上转换荧光特性的多级防伪材料及应用: 中国, 202010685713. 1[p]. 2021–08-17.QIN W P, JIA H, ZHOU M, et al. . A multi-level anticounterfeiting material with three-primary-color orthogonal upconversion fluorescence property and its application: CN, 202010685713. 1[p]. 2021–08-17. (in Chinese) [58] JIA H, TENG Y Y, LI N, et al. Dual stimuli-responsive inks based on orthogonal upconversion three-primary-color luminescence for advanced anticounterfeiting applications[J]. ACS Materials Letters, 2022, 4(7): 1306-1313. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.2c00328 [59] HONG A R, KYHM J H, KANG G M, et al. Orthogonal R/G/B upconversion luminescence-based full-color tunable upconversion nanophosphors for transparent displays[J]. Nano Letters, 2021, 21(11): 4838-4844. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01510 [60] LIU X, CHEN H M, WANG Y T, et al. Near-infrared manipulation of multiple neuronal populations via trichromatic upconversion[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5662. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25993-7 [61] CHEN T, SHANG Y F, HAO SH W, et al. Reproducible single-droplet multiplexed detection through excitation-encoded tri-mode upconversion solid sensors[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 131242. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131242 [62] HU P, ZHOU SH, WANG Y, et al. Printable, room-temperature self-healing and full-color-tunable emissive composites for transparent panchromatic display and flexible high-level anti-counterfeiting[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133728. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133728 [63] BOYER J C, CARLING C J, GATES B D, et al. Two-way photoswitching using one type of near-infrared light, upconverting nanoparticles, and changing only the light intensity[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(44): 15766-15772. doi: 10.1021/ja107184z [64] SHAO Q Y, ZHANG G T, OUYANG L L, et al. Emission color tuning of core/shell upconversion nanoparticles through modulation of laser power or temperature[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(33): 12132-12141. doi: 10.1039/C7NR03682E [65] WANG Y, ZHENG K ZH, SONG SH Y, et al. Remote manipulation of upconversion luminescence[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(17): 6473-6485. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00124C [66] ZHANG C, YANG L, ZHAO J, et al. White-light emission from an integrated upconversion nanostructure: toward multicolor displays modulated by laser power[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 127(39): 11693-11697. doi: 10.1002/ange.201504518 [67] HU M, MA D D, LIU CH CH, et al. Intense white emission from a single-upconversion nanoparticle and tunable emission colour with laser power[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(29): 6975-6981. doi: 10.1039/C6TC01437B [68] CHEN B, LIU Y, XIAO Y, et al. Amplifying excitation-power sensitivity of photon upconversion in a NaYbF4:Ho nanostructure for direct visualization of electromagnetic hotspots[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(23): 4916-4921. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02210 [69] ZHAO F F, YIN D G, WU CH L, et al. Huge enhancement of upconversion luminescence by dye/Nd3+ sensitization of quenching-shield sandwich structured upconversion nanocrystals under 808 nm excitation[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2017, 46(46): 16180-16189. doi: 10.1039/C7DT03383D [70] XIONG W, LIN SH K, XIE Y P. Growth and spectral properties of Er3+:GdVO4 crystal[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2004, 263(1–4): 353–357. [71] YIN X M, WANG H, TIAN Y, et al. Three primary color emissions from single multilayered nanocrystals[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(20): 9673-9678. doi: 10.1039/C8NR01752B [72] TANG M, ZHU X H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Near-infrared excited orthogonal emissive upconversion nanoparticles for imaging-guided on-demand therapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9): 10405-10418. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b04200 [73] SUO H, Zhu Q, Zhang X, et al. High-security anti-counterfeiting through upconversion luminescence[J]. Materials Today Physics, 2021, 21: 100520. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100520 [74] DOWNING E, HESSELINK L, RALSTON J, et al. A three-color, solid-state, three-dimensional display[J]. Science, 1996, 273(5279): 1185-1189. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5279.1185 -





 下载:
下载: