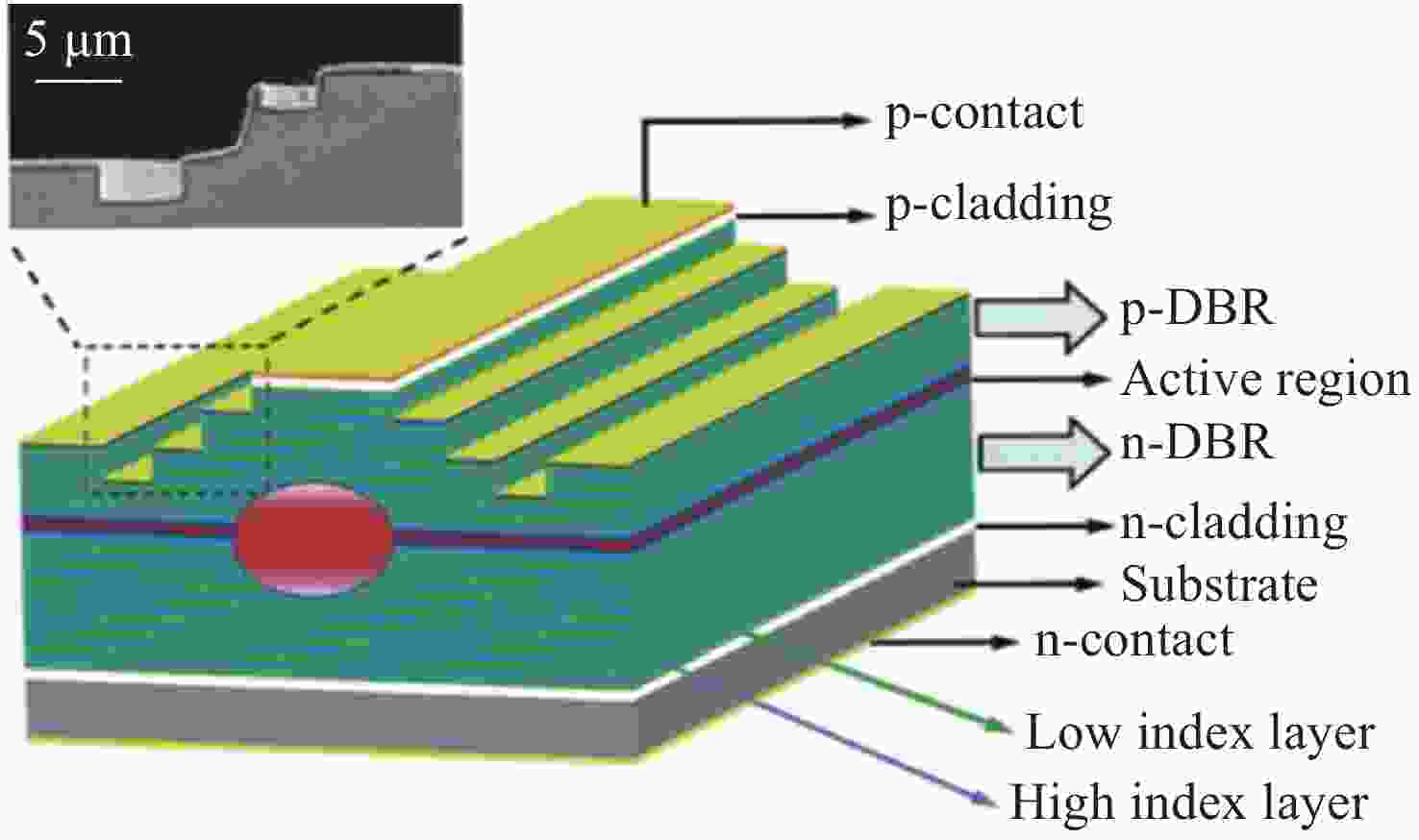
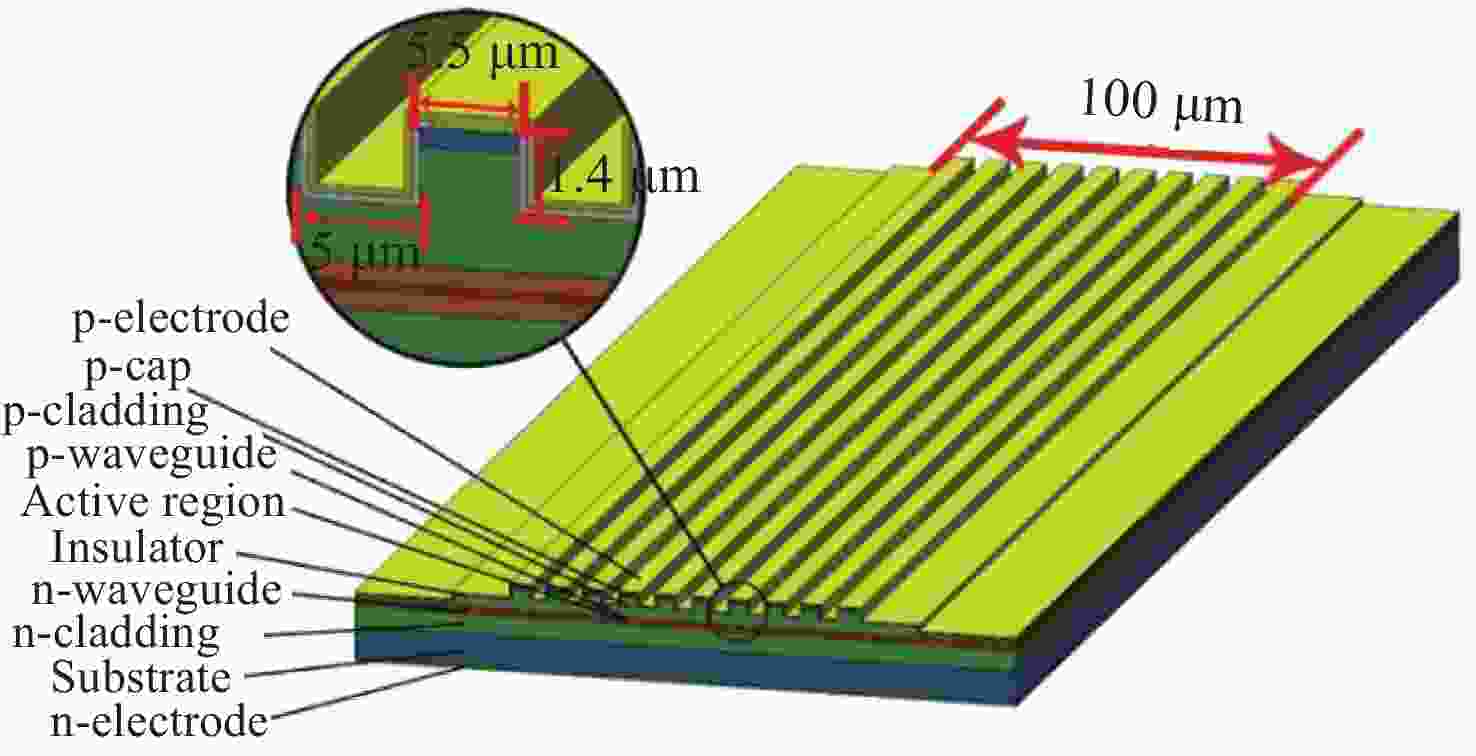
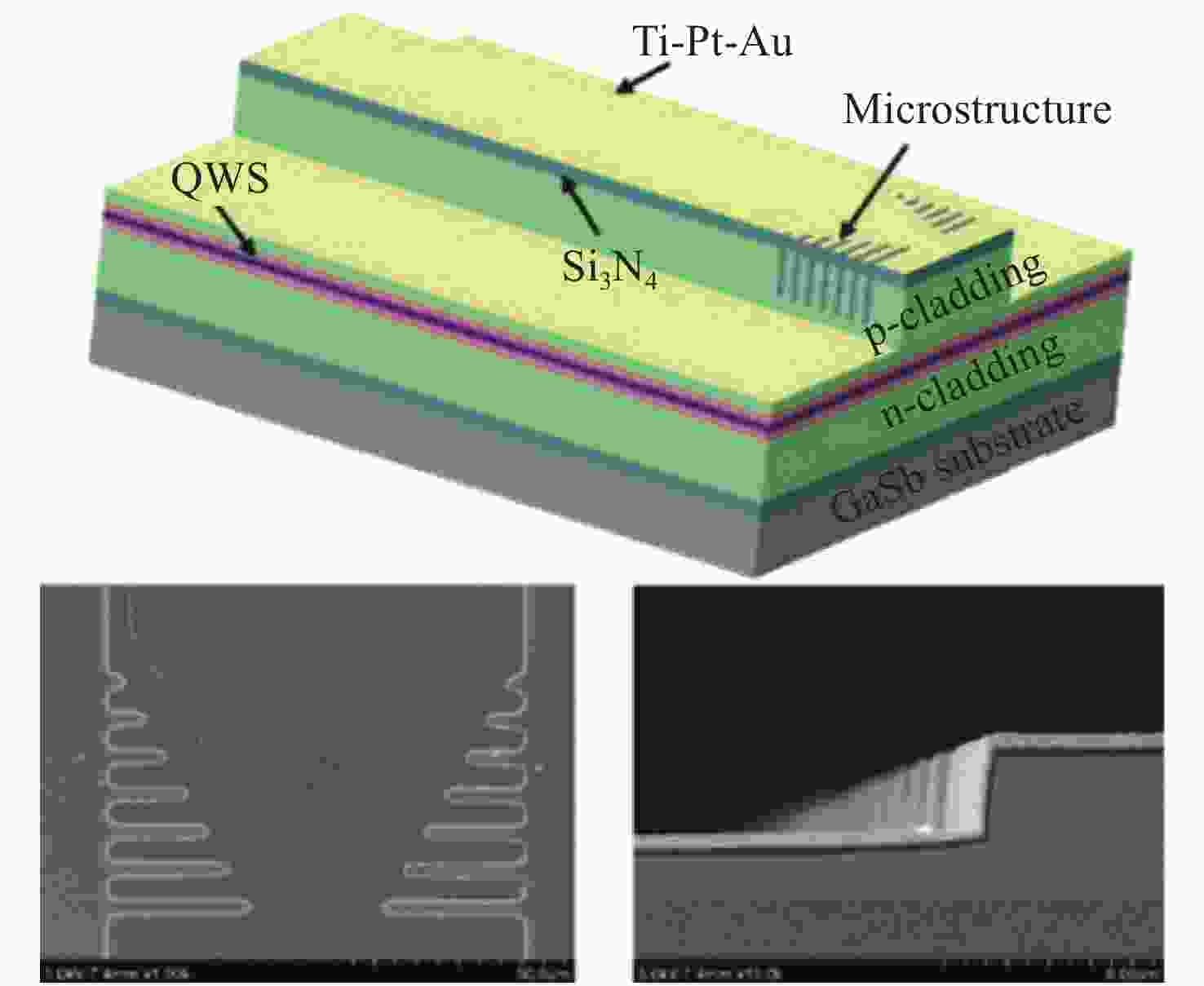
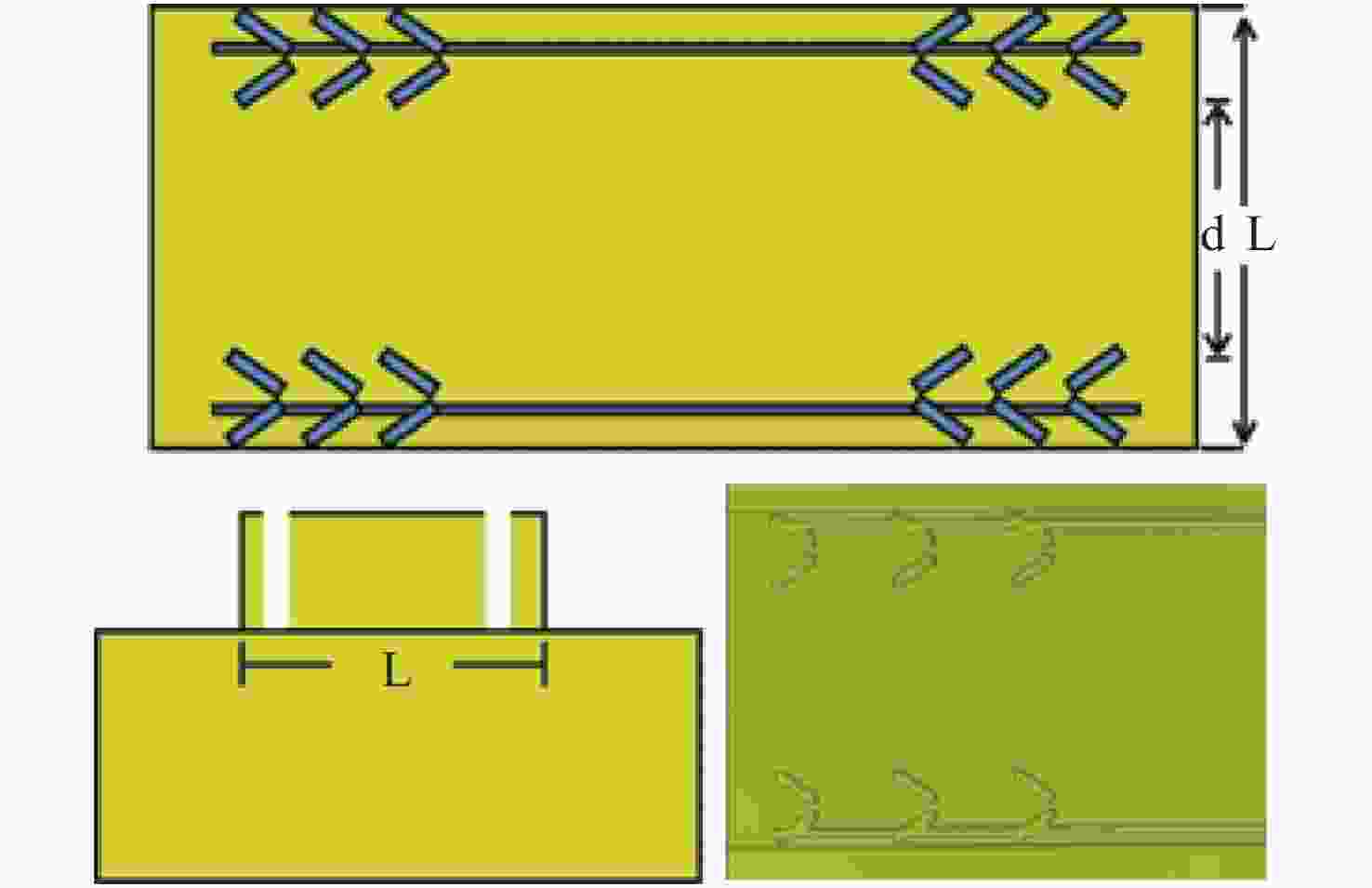
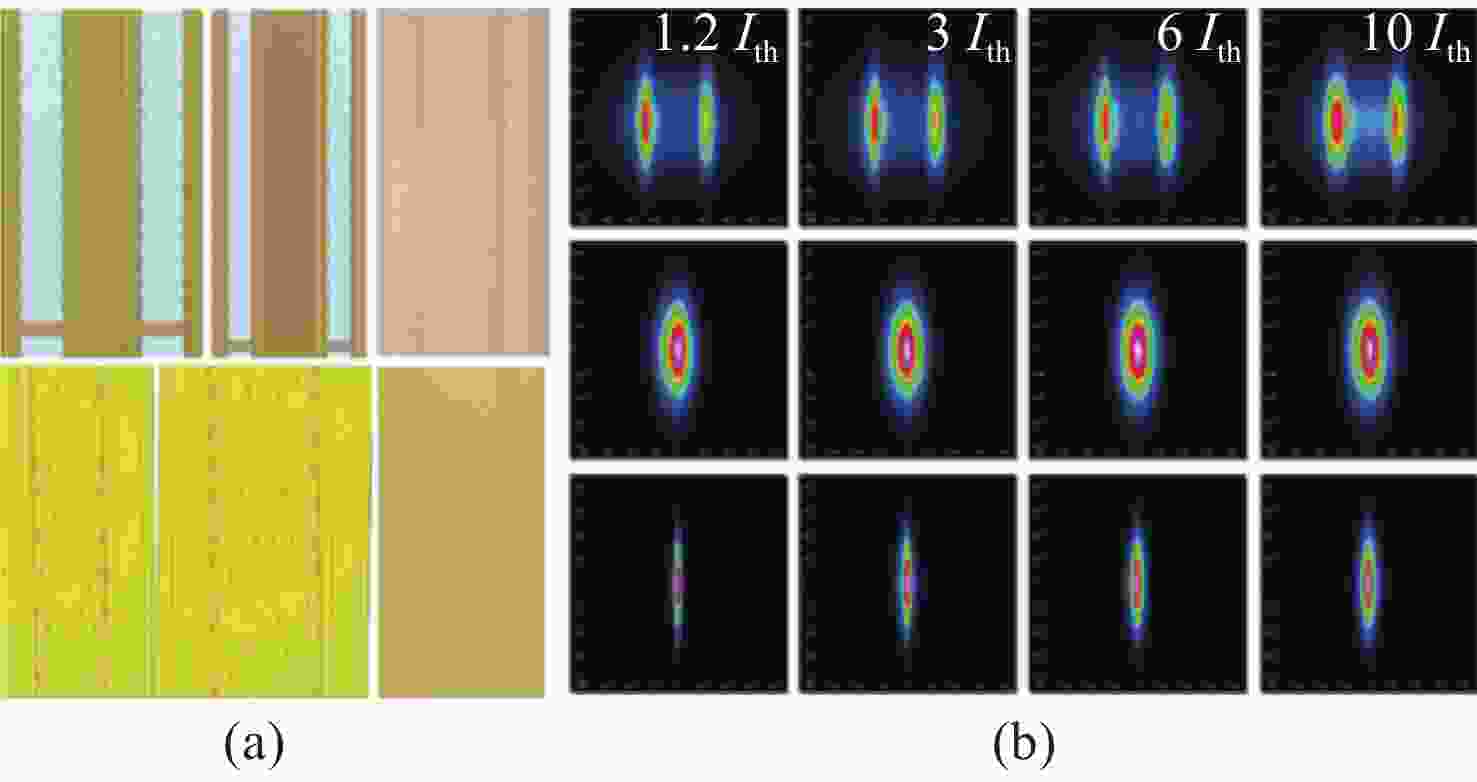
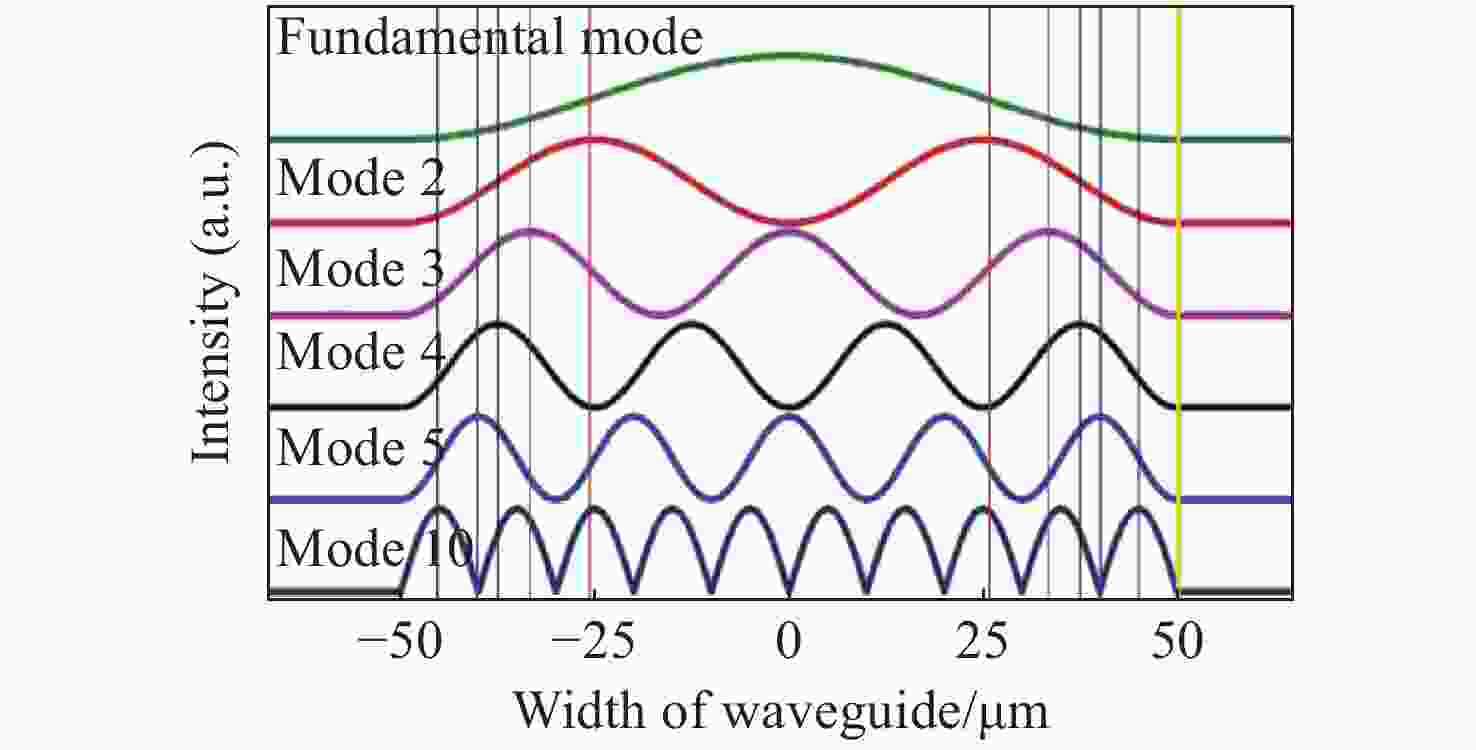
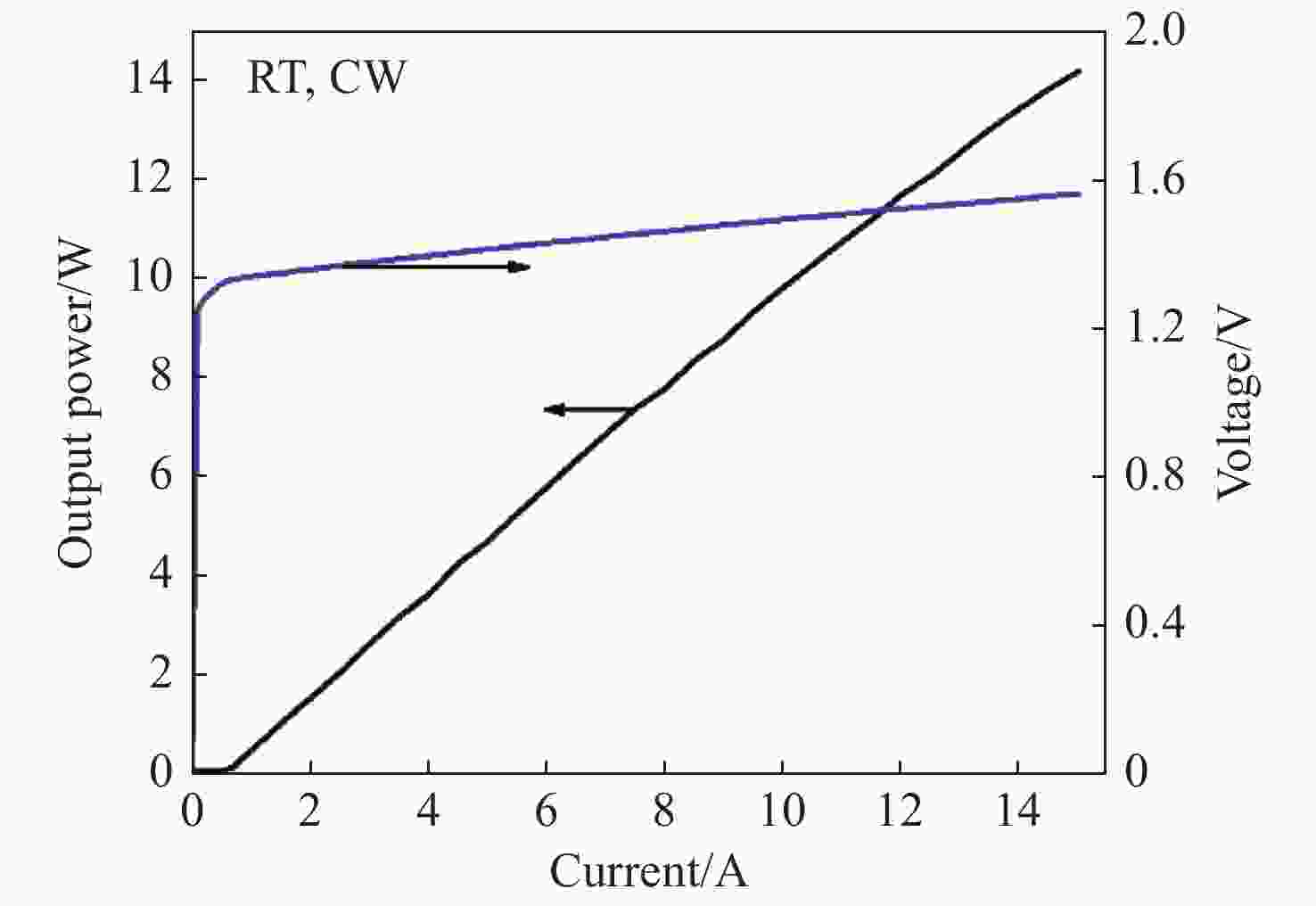
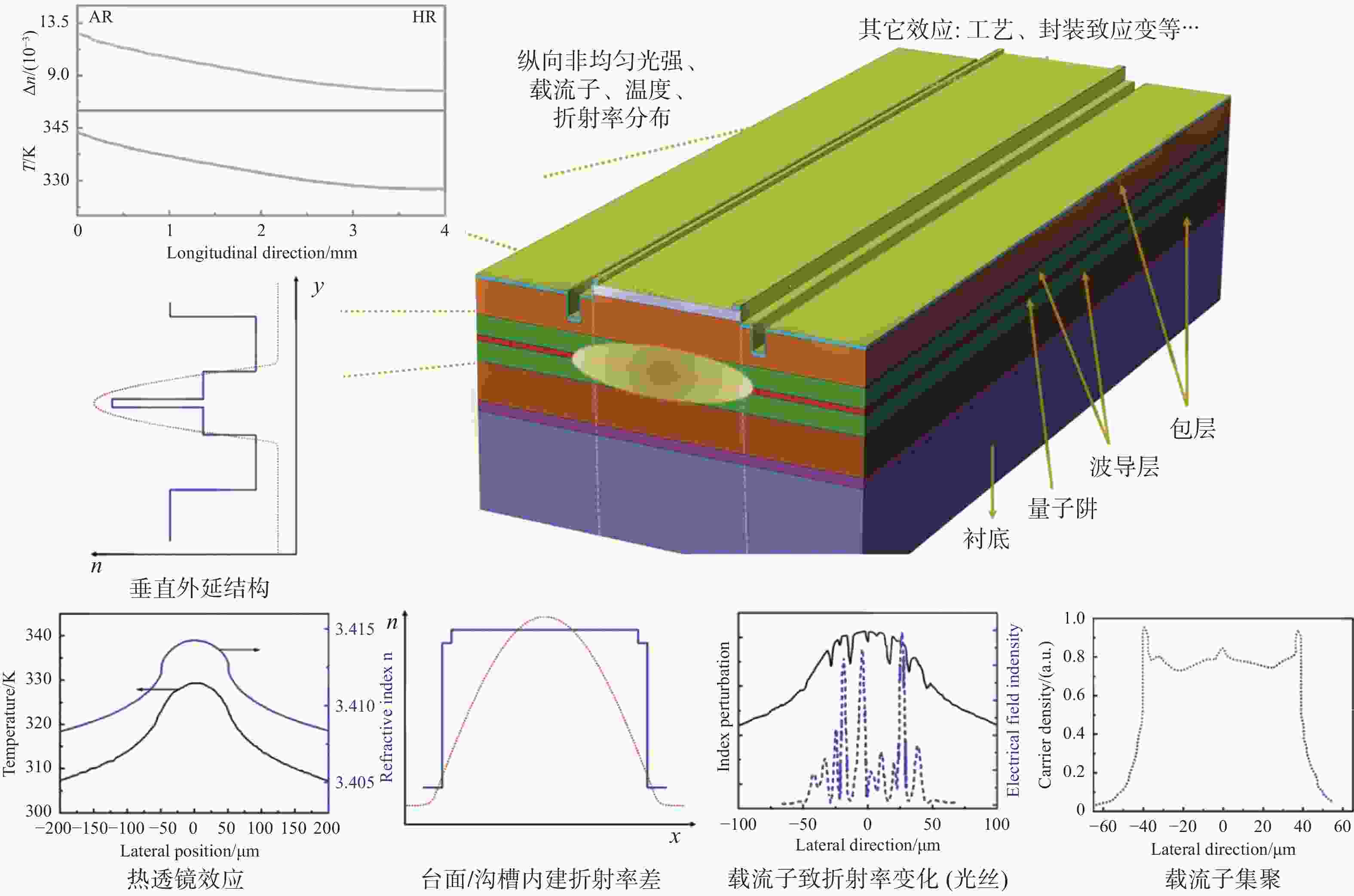
-
摘要:
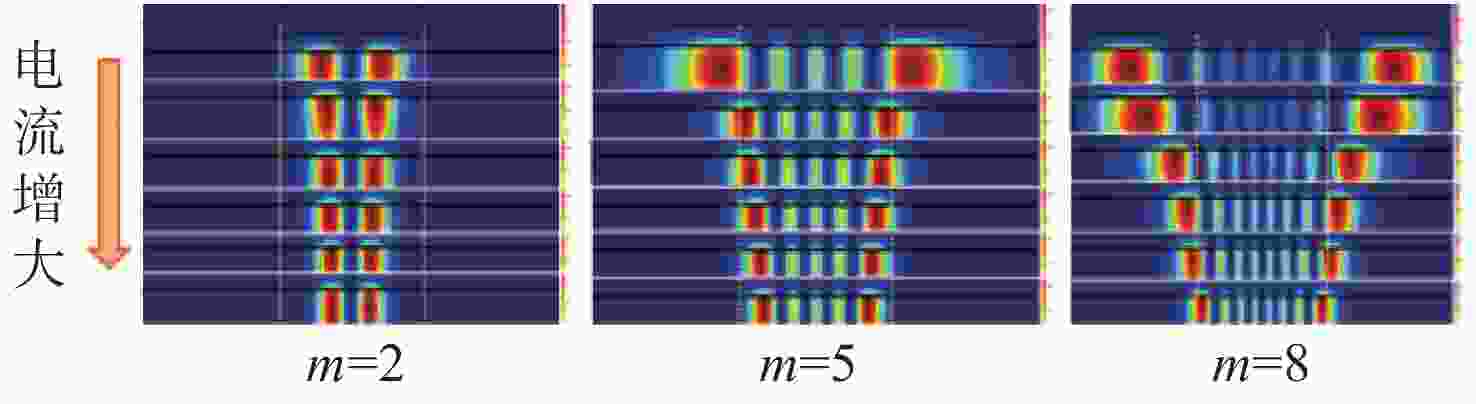
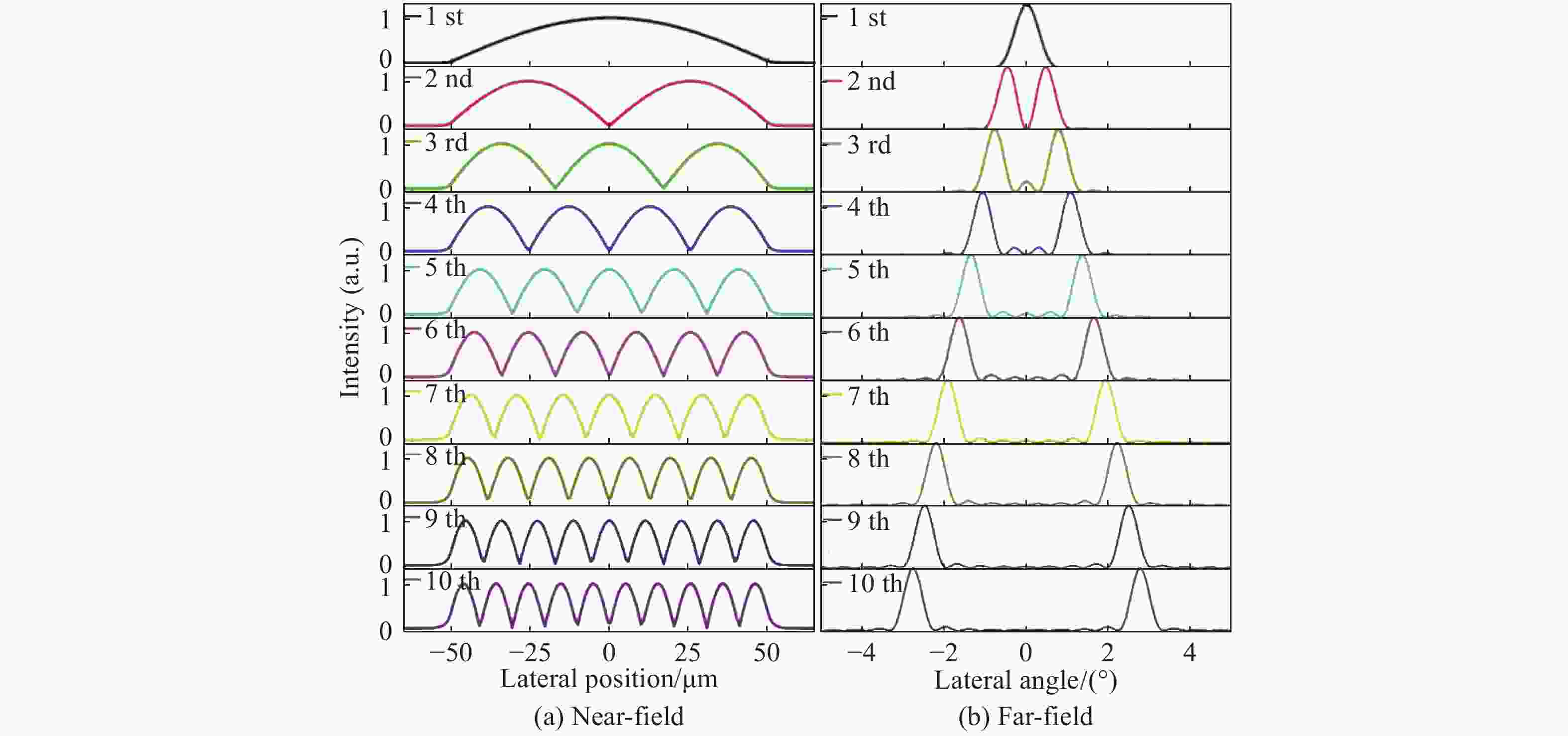
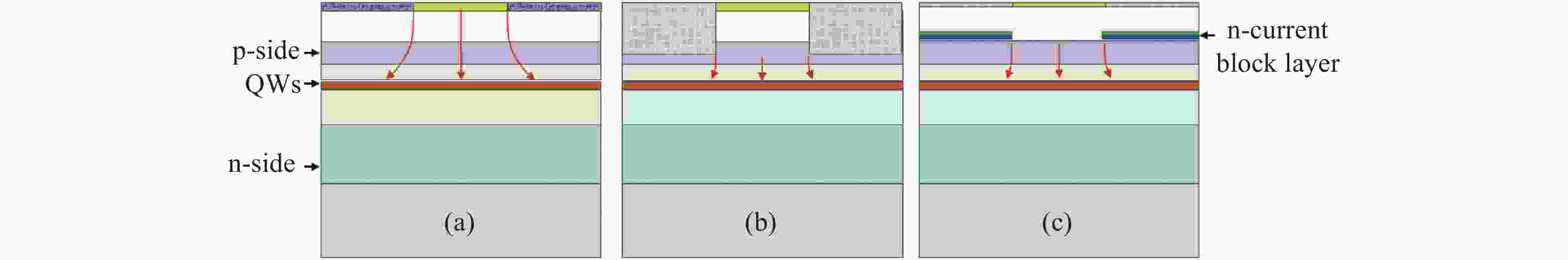
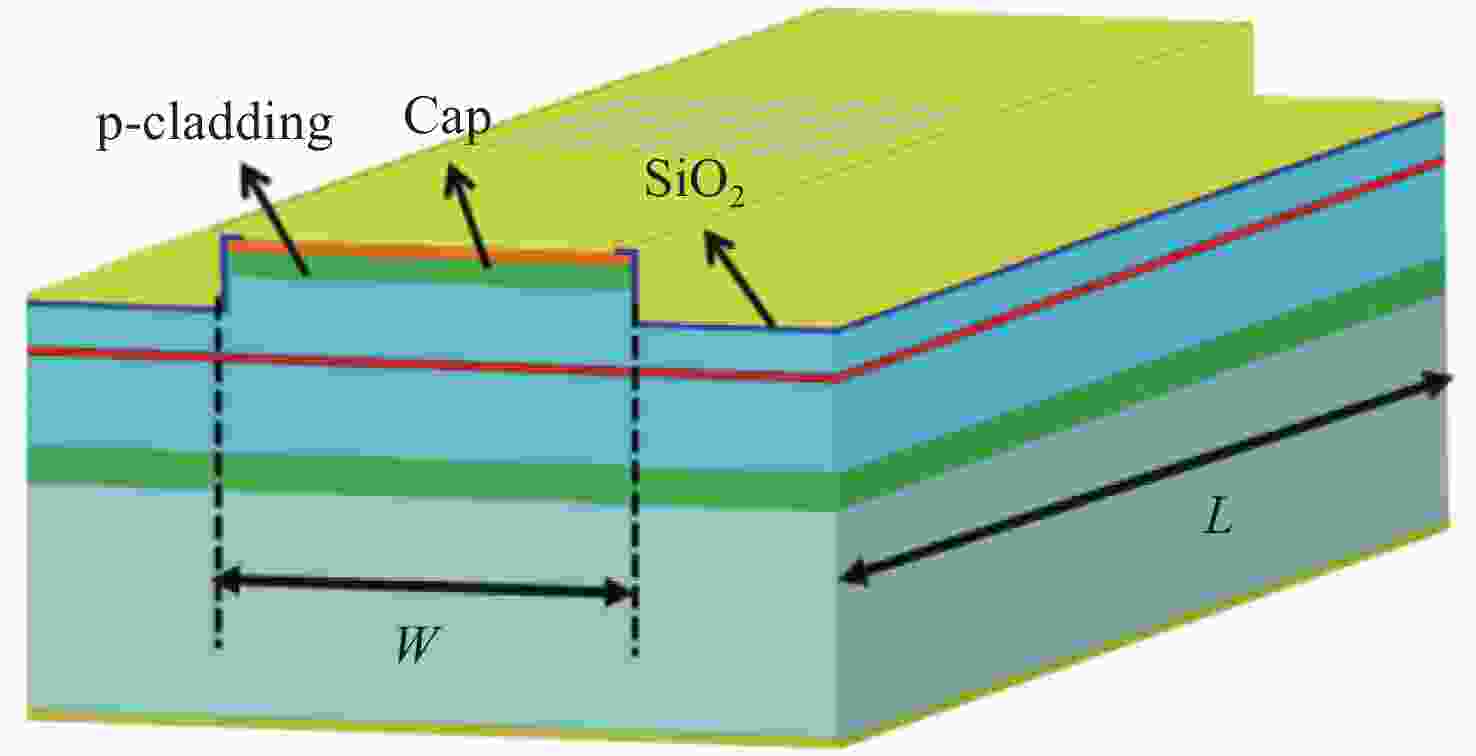
高功率半导体激光器在固体或光纤激光器泵浦、材料加工、激光雷达、空间通讯及国防等领域具有重大需求,但传统器件面临发散角大、光束质量差、亮度低的难题,限制了其直接应用。宽区半导体激光器具有输出功率和转换效率高的优点,但其侧向模式受多种物理效应的影响,高电流下激射模式数很大,导致远场宽度随电流增大迅速展宽,光束质量非常差,成为制约半导体激光亮度提高的关键瓶颈难题。因此,需要对半导体激光器的侧向模式进行控制。本文首先从半导体激光器的侧向模式影响机制出发,分析了其侧向模式特性及光场分布与器件结构的关联关系;接着,介绍了目前主要的侧向模式控制技术,通过抑制高阶模式及侧向远场展宽,实现光束质量的改善及激光亮度的提升。采用先进的侧向模式控制技术,可从芯片层次发展新型的高亮度半导体激光器,有利于拓展半导体激光器应用领域及降低应用成本,具有重要的研究意义。
Abstract:High power diode lasers are widely used for pumping solid-state lasers and fiber lasers, material processing, laser radars, free-space optical communication, security and defense. However, conventional diode lasers suffer from large far-field divergence angles, poor beam quality and low brightness, which restricts their direct applications. Broad-Area diode Lasers (BALs) can achieve high output power and efficiency. However, their lateral mode is usually influenced by many physical mechanisms, leading to a large number of guided lateral modes at high-power operation. It results in a rapid increase of the far-field width and strongly deteriorated beam quality, limiting the improvement of diode lasers′ brightness. Therefore, the lateral modes should be carefully controlled. In this paper, the factors influencing the diode lasers′ lateral modes are reviewed, and the lateral mode characteristics, optical field distribution and their relations with the device construction are analyzed. Then, the current lateral mode control technologies are described in detail. The beam quality and brightness of the output beam can be enhanced via the suppression of high-order lateral modes and the far-field blooming effect. As a result of advanced lateral mode control, novel high-brightness diode lasers can be developed at the chip level, which is beneficial for developing new diode lasers applications and reducing their system cost.
-
Key words:
- diode laser /
- lateral mode /
- beam quality /
- high brightness /
- low divergence angle
-
-
[1] PIETRZAK A, ZORN M, HUELSEWEDE R, et al. Development of highly efficient laser diodes emitting around 1060nm for medical and industrial applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 10900: 109000K. [2] LI Y, IBANEZ-GUZMAN J. Lidar for autonomous driving: the principles, challenges, and trends for automotive lidar and perception systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(4): 50-61. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2973615 [3] STRATEGIES UNLIMITED. The worldwide market for lasers: market review and forecast 2020[R]. Nashville, TN: Endeavor Business Media, 2020. https://store.strategies-u.com/products/the-worldwide-market-for-lasers-market-review-and-forecast-2020.html [4] BAUMANN M, BALCK A, MALCHUS J, et al. 1000 W blue fiber-coupled diode-laser emitting at 450 nm[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 10900: 1090005. [5] SKIDMORE J. Semiconductor lasers for 3-D sensing[J]. Optics and Photonics News, 2019, 30(2): 26-33. doi: 10.1364/OPN.30.2.000026 [6] SCHLEUNING D, DROZ P Y. Lidar sensors for autonomous driving[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11262: 112620D. [7] WENZEL H, CRUMP P, PIETRZAK A, et al. Theoretical and experimental investigations of the limits to the maximum output power of laser diodes[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2010, 12: 085007. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/12/8/085007 [8] YAMAGATA Y, KAIFUCHI Y, NOGAWA R, et al. Highly efficient 9xx-nm band single emitter laser diodes optimized for high output power operation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11262: 1126203. [9] CRUMP P, TRÄNKLE G. A brief history of kilowatt-class diode-laser bars[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11301: 113011D. [10] HUANG R K, CHANN B, BURGESS J, et al. Teradiode’s high brightness semiconductor lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9730: 97300C. [11] ZHU H B, LIN X CH, ZHANG Y W, et al. kW-class fiber-coupled diode laser source based on dense spectral multiplexing of an ultra-narrow channel spacing[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(19): 24723-24733. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.024723 [12] ALBRODT P, JAMAL M T, HANSEN A K, et al. Coherent combining of high brightness tapered amplifiers for efficient non-linear conversion[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(2): 928-937. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.000928 [13] CRUMP P, BÖLDICKE S, SCHULTZ C M, et al. Experimental and theoretical analysis of the dominant lateral waveguiding mechanism in 975 nm high power broad area diode lasers[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2012, 27(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/27/4/045001 [14] WINTERFELDT M, CRUMP P, WENZEL H, et al. Experimental investigation of factors limiting slow axis beam quality in 9xx nm high power broad area diode lasers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 116(6): 063103. doi: 10.1063/1.4892567 [15] CRUMP P, ELATTAR M, MIAH J, et al. Experimental studies into the beam parameter product of GaAs high-power diode lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2022, 28(1): 1501111. [16] ZHOU K, DU W CH, YANG X, et al. Effect of lateral index step on the performance of high-power broad-area 970-nm diode lasers based a large-optical-cavity waveguide structure[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11333: 113330X. [17] RIEPRICH J, WINTERFELDT M, KERNKE R, et al. Chip-carrier thermal barrier and its impact on lateral thermal lens profile and beam parameter product in high power broad area lasers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 123(12): 125703. doi: 10.1063/1.5004503 [18] WINTERFELDT M, CRUMP P, KNIGGE S, et al. High beam quality in broad area lasers via suppression of lateral carrier accumulation[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2015, 27(17): 1809-1812. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2015.2443186 [19] HOLLY C, LIU X H, HEINEMANN S, et al. . Influence of lateral refractive index profiles on the divergence angle of gain-guided broad-area laser diode bars[C]. 2018 IEEE Photonics Conference (IPC), IEEE, 2018: 1-2. [20] RAUCH S, WENZE H, RADZIUNAS M, et al. Impact of longitudinal refractive index change on the near-field width of high-power broad-area diode lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(26): 263504. doi: 10.1063/1.4990531 [21] WINTERFELDT M, RIEPRICH J, KNIGGE S, et al. Assessing the influence of the vertical epitaxial layer design on the lateral beam quality of high-power broad area diode lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9733: 97330O. [22] WANG L J, TONG C ZH, SHU SH L, et al. Loss tailoring of high-power broad-area diode lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(14): 3562-3565. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.003562 [23] CRUMP P, WINTERFELDT M, DECKER J, et al. Novel approaches to increasing the brightness of broad area lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9767: 97671L. [24] BONI A, ARSLAN S, ERBERT G, et al. Epitaxial design progress for high power, efficiency, and brightness in 970 nm broad area lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11668: 1166807. [25] MIAH J, KALOSHA V P, BIMBERG D, et al. Astigmatism-free high-brightness 1060 nm edge-emitting lasers with narrow circular beam profile[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(26): 30514-30522. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.030514 [26] ZHAO SH Y, QI A Y, WANG M J, et al. High-power high-brightness 980 nm lasers with >50% wall-plug efficiency based on asymmetric super large optical cavity[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(3): 3518-3526. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.003518 [27] SMITH G M, DONNELLY J P, MISSAGGIA L J, et al. Slab-coupled optical waveguide lasers and amplifiers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8241: 82410S. doi: 10.1117/12.905028 [28] KOESTER J P, PUTZ A, WENZEL H, et al. Mode competition in broad-ridge-waveguide lasers[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2021, 36(1): 015014. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/abc6e7 [29] DECKER J, WINTERFELDT M, FRICKE J, et al. . Study of lateral brightness in 20 μm to 50 μm wide narrow stripe broad area lasers[C]. 2015 IEEE High Power Diode Lasers and Systems Conference (HPD), IEEE, 2015: 21-22. [30] WILKENS M, WENZEL H, FRICKE J, et al. High-efficiency broad-ridge waveguide lasers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(6): 545-548. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2801621 [31] KNIGGE A, KLEHR A, WENZEL H, et al. Wavelength-stabilized high-pulse-power laser diodes for automotive LiDAR[J]. Physica Status Solidi, 2018, 215(8): 1700439. doi: 10.1002/pssa.201700439 [32] WANG L J, LI ZH, TONG C ZH, et al. Near-diffraction-limited Bragg reflection waveguide lasers[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(34): F15-F21. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.000F15 [33] PASCHKE K, BLUME G, WENZEL H, et al. 635 nm tapered diode lasers with more than 2000 h operation at 500 mW output power[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 12024: 120240A. [34] SUMPF B, THEURER L S, MAIWALD M, et al. 783 nm wavelength stabilized DBR tapered diode lasers with a 7 W output power[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(18): 5418-5423. doi: 10.1364/AO.422688 [35] DITTMAR F, SUMPF B, FRICKE J, et al. High-power 808-nm tapered diode lasers with nearly diffraction-limited beam quality of M2 = 1.9 at P = 4.4 W[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2006, 18(4): 601-603. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2006.870152 [36] DITTMAR F, KLEHR A, SUMPF B, et al. 9-W output power from an 808-nm tapered diode laser in pulse mode operation with nearly diffraction-limited beam quality[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2007, 13(5): 1194-1199. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2007.902838 [37] SUMPF B, HASLER K H, ADAMIEC P, et al. High-brightness quantum well tapered lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2009, 15(3): 1009-1020. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2008.2010952 [38] MÜLLER A, ZINK C, FRICKE J, et al. Efficient, high brightness 1030 nm DBR tapered diode lasers with optimized lateral layout[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2017, 23(6): 1501107. [39] MÜLLER A, ZINK C, FRICKE J, et al. 1030nm DBR tapered diode laser with up to 16 W of optical output power[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10123: 101231B. [40] SUMPF B, HASLER X H, ADAMIEC P, et al. . 12.2 W output power from 1060 nm DBR tapered lasers with narrow spectral line width and nearly diffraction limited beam quality[C]. CLEO/Europe-EQEC 2009-European Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics and the European Quantum Electronics Conference, IEEE, 2009: 1. [41] AHO A T, VIHERIÄLÄ J, KOSKINEN M, et al. High-power 1.5 μm tapered distributed Bragg reflector laser diodes for eye-safe LIDAR[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(19): 1249-1252. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3019845 [42] PFAHLER C, KAUFEL G, KELEMEN M T, et al. GaSb-based tapered diode lasers at 1.93 μm with 1.5-W nearly diffraction-limited power[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2006, 18(6): 758-760. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2006.871679 [43] GÖKDEN B, MANSURIPUR T S, BLANCHARD R, et al. High-brightness tapered quantum cascade lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(5): 053503. doi: 10.1063/1.4791557 [44] SCHWERTFEGER S, WIEDMANN J, SUMPF B, et al. 7.4 W continuous-wave output power of master oscillator power amplifier system at 1083 nm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2006, 42(6): 346-347. doi: 10.1049/el:20060260 [45] WENZEL H, PASCHKE K, BROX O, et al. 10 W continuous-wave monolithically integrated master-oscillator power-amplifier[J]. Electronics Letters, 2007, 43(3): 160-162. doi: 10.1049/el:20073297 [46] ZINK C, MAAßDORF A, FRICKE J, et al. Monolithic master oscillator tilted tapered power amplifier emitting 9.5 W at 1060 nm[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(1): 59-62. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2019.2957063 [47] VU T N, TIEN T Q, SUMPF B, et al. 16.3 W peak-power pulsed all-diode laser based multi-wavelength master-oscillator power-amplifier system at 964 nm[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(18): 8608. [48] WILKENS M, ERBERT G, WENZEL H, et al. Highly efficient high-brightness 970-nm ridge waveguide lasers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(7): 406-409. [49] ZEGHUZI A, CHRISTOPHER H, KLEHR A, et al. High-brightness nanosecond-pulse operation from tapered-ridge-waveguide lasers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2021, 33(3): 151-154. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3047150 [50] HOHIMER J P, HADLEY G R, OWYOUNG A. Mode control in broad-area diode lasers by thermally induced lateral index tailoring[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1988, 52(4): 260-262. doi: 10.1063/1.99487 [51] BAI J G, LEISHER P, ZHANG SH G, et al. Mitigation of thermal lensing effect as a brightness limitation of high-power broad area diode lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 7953: 79531F. doi: 10.1117/12.875849 [52] KIM Y, YANG J T, CHOI W Y. High-power broad-area laser diode performance improvement with a double pedestal structure[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 58(4): 042004. doi: 10.7567/1347-4065/ab0c71 [53] KIM Y, SUNG Y, YANG J T, et al. Numerical analysis of high-power broad-area laser diode with improved heat sinking structure using epitaxial liftoff technique[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10514: 105140C. [54] ZEGHUZI A, RADZIUNAS M, WÜNSCHE H J, et al. Traveling wave analysis of non-thermal far-field blooming in high-power broad-area lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2019, 55(2): 2000207. [55] CASA P D, MARTIN D, MAAßDORF A, et al. High power broad-area lasers with buried implantation for current confinement[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2019, 34(10): 105005. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/ab39b8 [56] ELATTAR M, BROX O, CASA P D, et al. High-brightness broad-area diode lasers with enhanced self-aligned lateral structure[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2020, 35(9): 095011. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/ab9bec [57] LINDSEY C, DERRY P, YARIV A. Fundamental lateral mode oscillation via gain tailoring in broad area semiconductor lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1985, 47(6): 560-562. doi: 10.1063/1.96070 [58] MALĄG A, SOBCZAK G, DĄBROWSKA E, et al. Emitted beam stabilization in junction plane by lateral periodic structure in laser diodes emitting at 980 nm[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10974: 1097404. [59] SHEEM S K, VOJAK B A. Broad-area semiconductor lasers with gain-length variation for lateral mode control: the bow-tie geometry laser[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1988, 63(1): 248-250. doi: 10.1063/1.340453 [60] BO B X, GAO X, WANG L, et al. Rhombus-like stripe BA InGaAs-AlGaAs-GaAs lasers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2004, 16(5): 1248-1249. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2004.826114 [61] WANG T, TONG C ZH, WANG L J, et al. Injection-insensitive lateral divergence in broad-area diode lasers achieved by spatial current modulation[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2016, 9(11): 112102. doi: 10.7567/APEX.9.112102 [62] WANG T, WANG L J, SHU SH L, et al. Suppression of far-field blooming in high-power broad-area diode lasers by optimizing gain distribution[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(7): 071404. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.071404 [63] WANG T, WANG L J, SHU SH L, et al. Beam control of high-power broad-area photonic crystal lasers using ladderlike groove structure[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2017, 10(6): 062701. [64] LU Z F, WANG L J, ZHANG Y, et al. High-power GaSb-based microstripe broad-area lasers[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2018, 11(3): 032702. doi: 10.7567/APEX.11.032702 [65] AHN S, SCHWARZER C, ZEDERBAUER T, et al. High-power, low-lateral divergence broad area quantum cascade lasers with a tilted front facet[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(5): 051101. [66] AHN S, SCHWARZER C, ZEDERBAUER T, et al. Enhanced light output power of quantum cascade lasers from a tilted front facet[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(13): 15869-15877. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.015869 [67] HEYDARI D, BAI Y, BANDYOPADHYAY N, et al. High brightness angled cavity quantum cascade lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(9): 091105. doi: 10.1063/1.4914477 [68] LU Z F, WANG L J, ZHAO ZH D, et al. Broad-area laser diodes with on-chip combined angled cavity[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(8): 081402. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.081402 [69] SCIFRES D R, STREIFER W, BURNHAM R D. Curved stripe GaAs: GaAlAs diode lasers and waveguides[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1978, 32(4): 231-234. doi: 10.1063/1.90001 [70] SWINT R B, YEOH T S, ELARDE V C, et al. Curved waveguides for spatial mode filters in semiconductor lasers[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2004, 16(1): 12-14. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2003.818933 [71] HOU L P, HAJI M, AKBAR J, et al. Narrow linewidth laterally coupled 1.55 μm AlGaInAs/InP distributed feedback lasers integrated with a curved tapered semiconductor optical amplifier[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(21): 4525-4527. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004525 [72] TAWFIEQ M, FRICKE J, MÜLLER A, et al. Characterisation and comparison between different S-bend shaped GaAs Y-branch distributed Bragg reflector lasers emitting at 976 nm[J]. Semiconductor Science and Technology, 2018, 33(11): 115001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aadfbd [73] FRICKE J, MATALLA M, PASCHKE K, et al. Fabricating and testing of Bragg gratings for 1060-nm α-DFB lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4947: 223-231. doi: 10.1117/12.471994 [74] LIU Y, WANG Y F, QU H W, et al. Angled cavity photonic crystal lasers with asymmetrical high-order surface gratings[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2017, 10(3): 032701. doi: 10.7567/APEX.10.032701 [75] ZHAO Y S, ZHU L. Folded cavity angled-grating broad-area lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(20): 24087-24092. [76] LANG R J, MITTELSTEIN M, YARIV A, et al. Unstable resonator semiconductor lasers. Part 1: theory[J]. IEE Proceedings J (Optoelectronics) , 1987, 134(1): 69-75. doi: 10.1049/ip-j.1987.0013 [77] YANG C, PAXTON A H, NEWELL T C, et al. On-chip unstable resonator cavity GaSb-based quantum well lasers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 121(14): 143101. doi: 10.1063/1.4980028 [78] BIELLAK S A, FANNING C G, SUN Y, et al. Reactive-ion-etched diffraction-limited unstable resonator semiconductor lasers[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1997, 33(2): 219-230. doi: 10.1109/3.552262 [79] STRYCKMAN D, ROUSSEAU G, D’AUTEUIL M, et al. Improvement of the lateral-mode discrimination of broad-area diode lasers with a profiled reflectivity output facet[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(30): 5955-5959. [80] PAYUSOV A, SERIN A, MUKHIN I, et al. Lateral mode control in edge-emitting lasers with modified mirrors[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2017, 917(5): 052035. [81] GORDEEV N Y, PAYUSOV A S, MUKHIN I S, et al. Lateral mode discrimination in edge-emitting lasers with spatially modulated facet reflectance[J]. Semiconductors, 2019, 53(2): 200-204. doi: 10.1134/S1063782619020106 [82] RAUCH S, MODAK P, HOLLY C, et al. . Beam quality improvement of broad-area laser diodes by symmetric facet reflectivities[C]. 2018 IEEE International Semiconductor Laser Conference (ISLC), IEEE, 2018: 1-2. [83] MAILHOT S, CHAMPAGNE Y, DOYON B, et al. Lateral mode analysis of a broad-area laser operated with an external cavity[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1994, 2041: 432-443. doi: 10.1117/12.165641 [84] VIJAYAKUMAR D, JENSEN O B, THESTRUP B. 980 nm high brightness external cavity broad area diode laser bar[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(7): 5684-5690. [85] ZHAO Y F, SUN F Y, TONG C ZH, et al. Going beyond the beam quality limit of spectral beam combining of diode lasers in a V-shaped external cavity[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(11): 14058-14065. [86] SUN F Y, SHU SH L, ZHAO Y F, et al. High-brightness diode lasers obtained via off-axis spectral beam combining with selective feedback[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(17): 21813-21818. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.021813 [87] SUN F Y, ZHAO Y F, SHU SH L, et al. High beam quality broad-area diode lasers by spectral beam combining with double filters[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(1): 011401. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.011401 [88] CHOI J M, ZHU L, GREEN W M J, et al. Large-area, semiconductor transverse bragg resonance (TBR) lasers for efficient, high power operation[J]. ICALEO, 2005, 2005: 406. [89] ZHU L, CHOI J M, DEROSE G A, et al. Electrically pumped two-dimensional Bragg grating lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31(12): 1863-1865. [90] ZHU L, CHAK P, POON J K S, et al. Electrically-pumped, broad-area, single-mode photonic crystal lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(10): 5966-5975. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.005966 [91] ZHU Y Y, ZHAO Y S, ZHU L. Two-dimensional photonic crystal Bragg lasers with triangular lattice for monolithic coherent beam combining[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 10610. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10896-9 [92] FAN J A, BELKIN M A, CAPASSO F, et al. Wide-ridge metal-metal terahertz quantum cascade lasers with high-order lateral mode suppression[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(3): 031106. doi: 10.1063/1.2835202 [93] WENZEL H, CRUMP P, FRICKE J, et al. Suppression of higher-order lateral modes in broad-area diode lasers by resonant anti-guiding[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2013, 49(12): 1102-1108. [94] KASPI R, LUONG S, BATE T, et al. Distributed loss method to suppress high order modes in broad area quantum cascade lasers[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(20): 201109. doi: 10.1063/1.5006042 [95] MIAH M J, STROHMAIER S, URBAN G, et al. Beam quality improvement of high-power semiconductor lasers using laterally inhomogeneous waveguides[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 113(22): 221107. doi: 10.1063/1.5054645 [96] ECKSTEIN H C, ZEITNER U D, TÜNNERMANN A, et al. Mode shaping in semiconductor broad area lasers by monolithically integrated phase structures[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(21): 4480-4482. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.004480 [97] RONG J M, XING E B, ZHANG Y, et al. Low lateral divergence 2 μm InGaSb/ AlGaAsSb broad-area quantum well lasers[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(7): 7246-7252. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.007246 [98] XING E B, RONG J M, ZHANG Y, et al. Watt-class low divergence 2 μm GaSb based broad-area quantum well lasers[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2017, 36(3): 280-283. [99] RONG J M, XING E B, WANG L J, et al. Control of lateral divergence in high-power, broad-area photonic crystal lasers[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2016, 9(7): 072104. doi: 10.7567/APEX.9.072104 [100] SU J X, TONG C ZH, WANG L J, et al. Selective loss tailoring of broad-area diode lasers[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 60(2): 020901. [101] SU J X, TONG C ZH, WANG L J, et al. Beam waist shrinkage of high-power broad-area diode lasers by mode tailoring[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(9): 13131-13140. doi: 10.1364/OE.390265 -





 下载:
下载: