-
摘要:
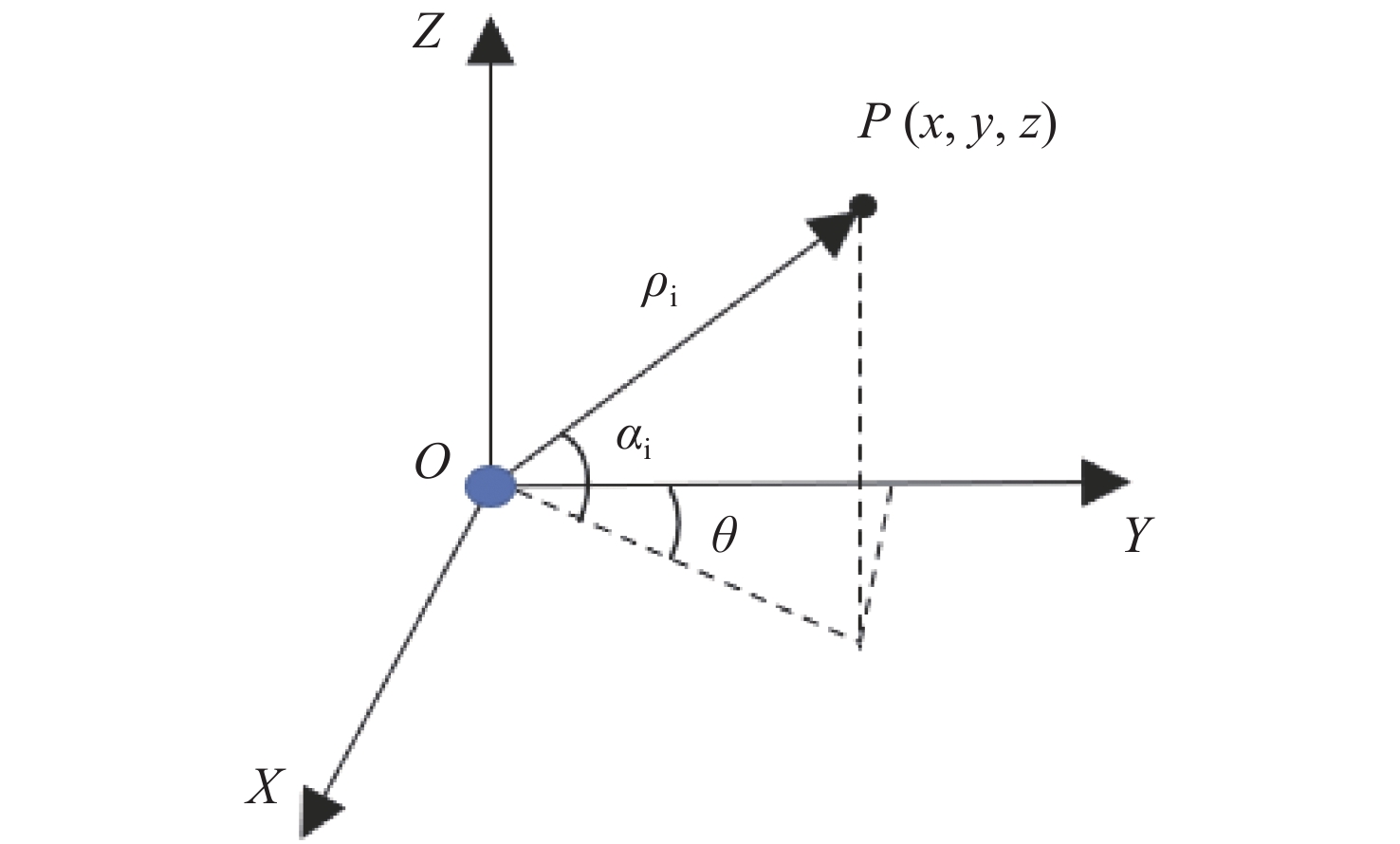
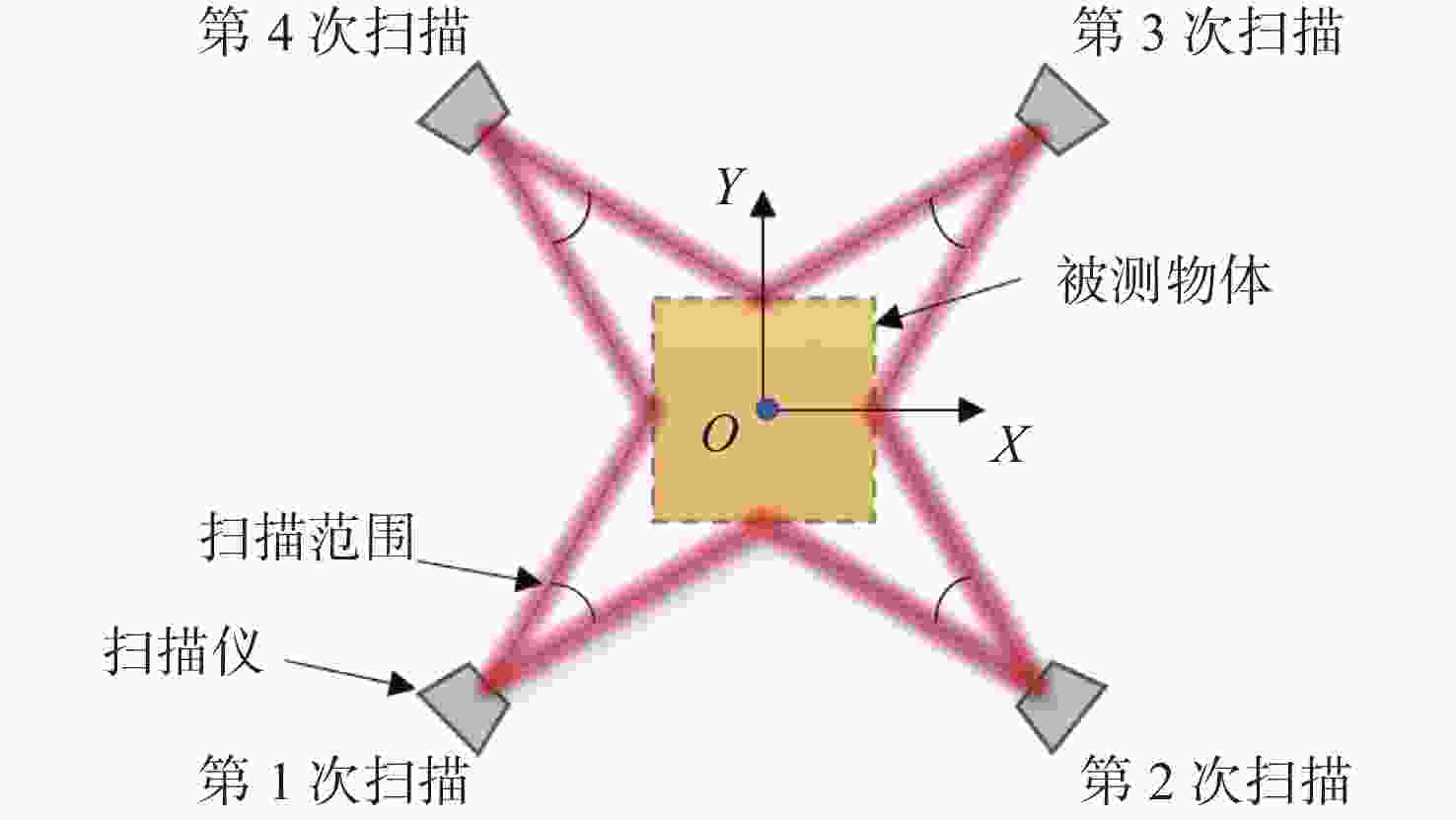
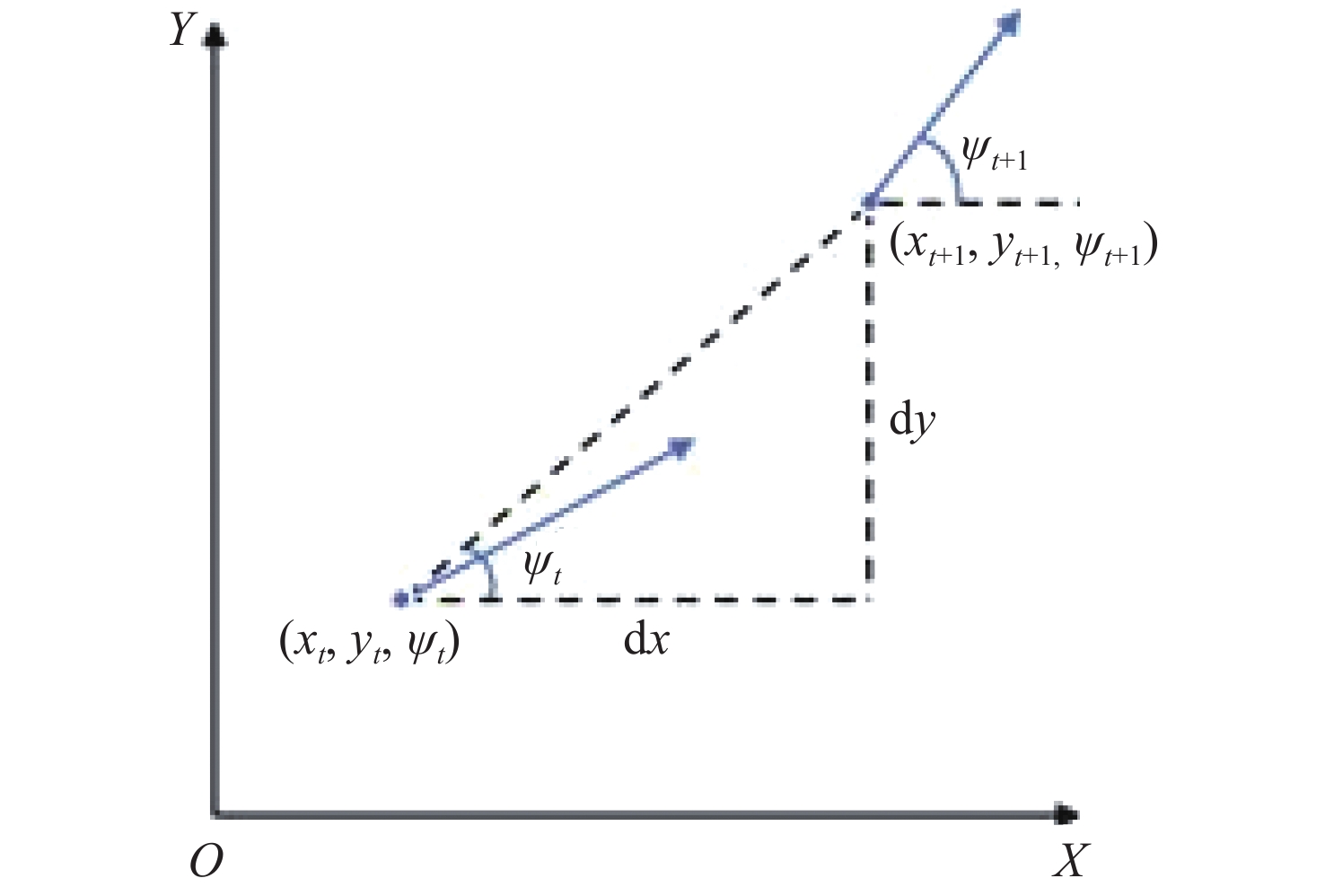
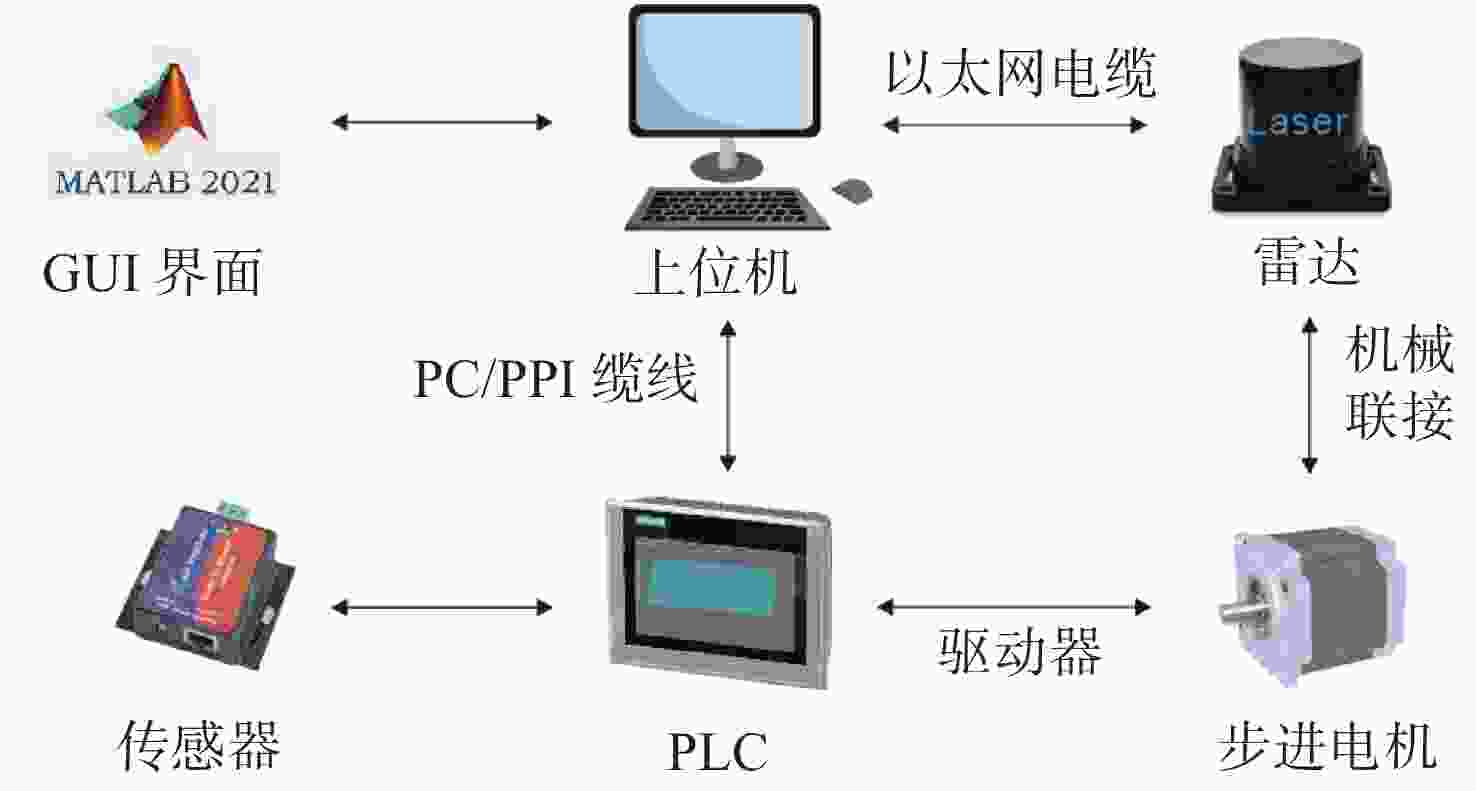
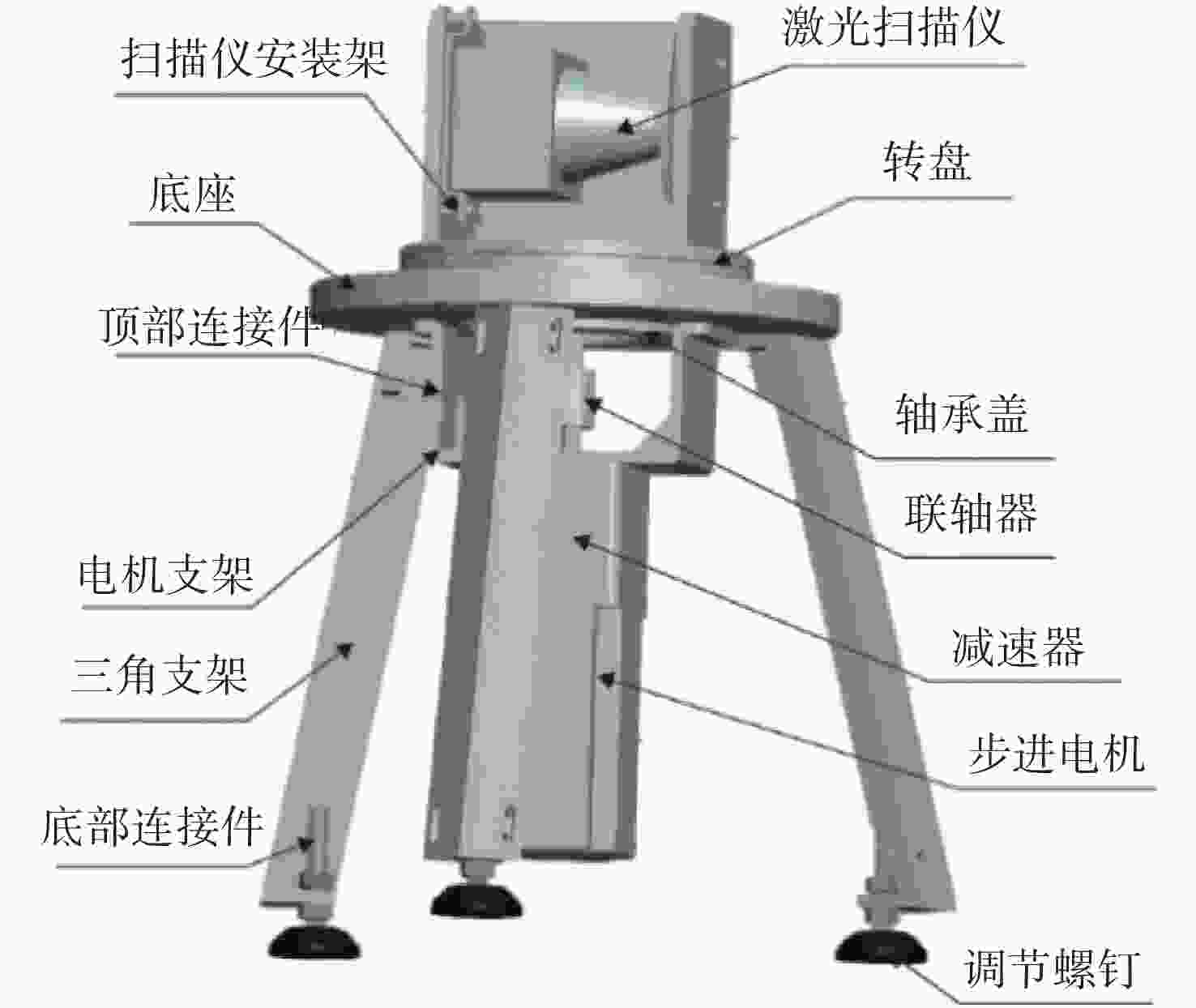
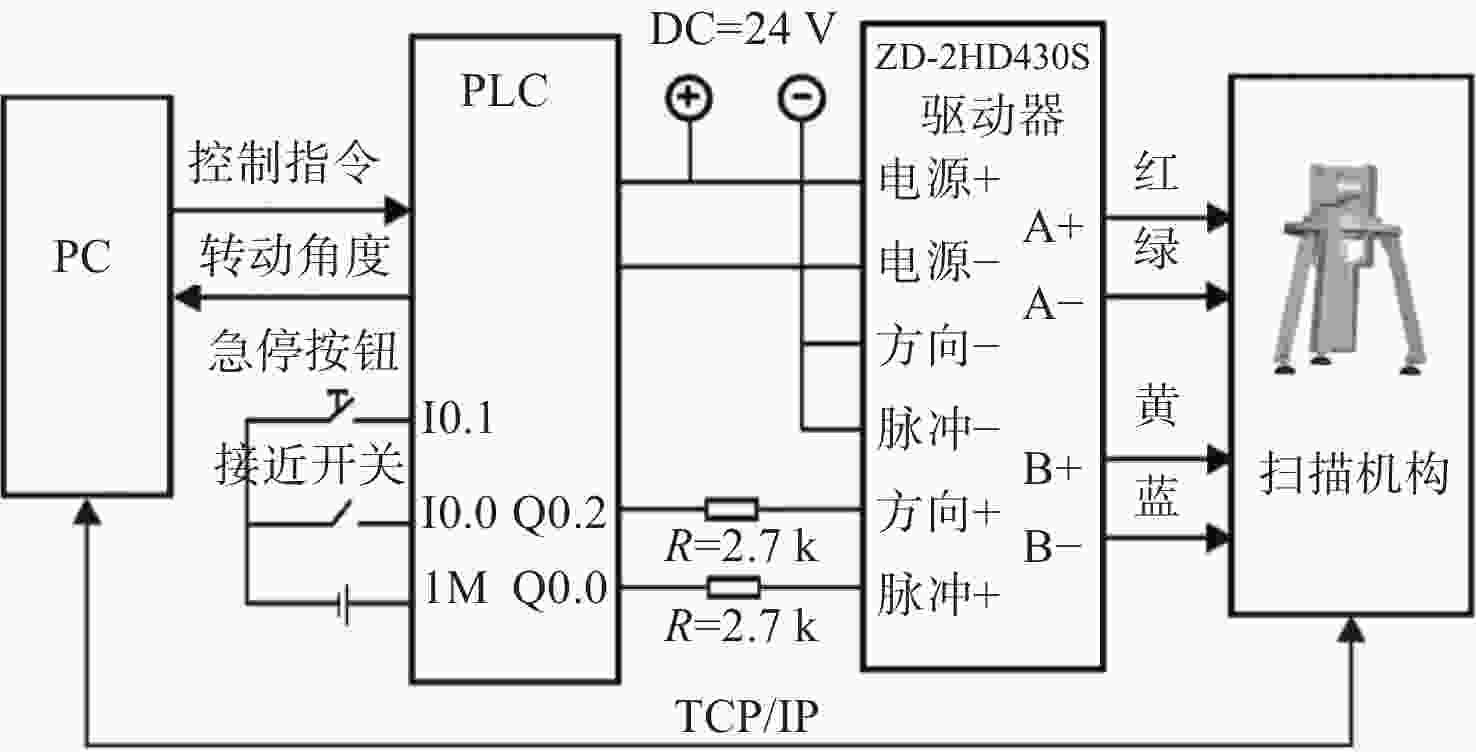
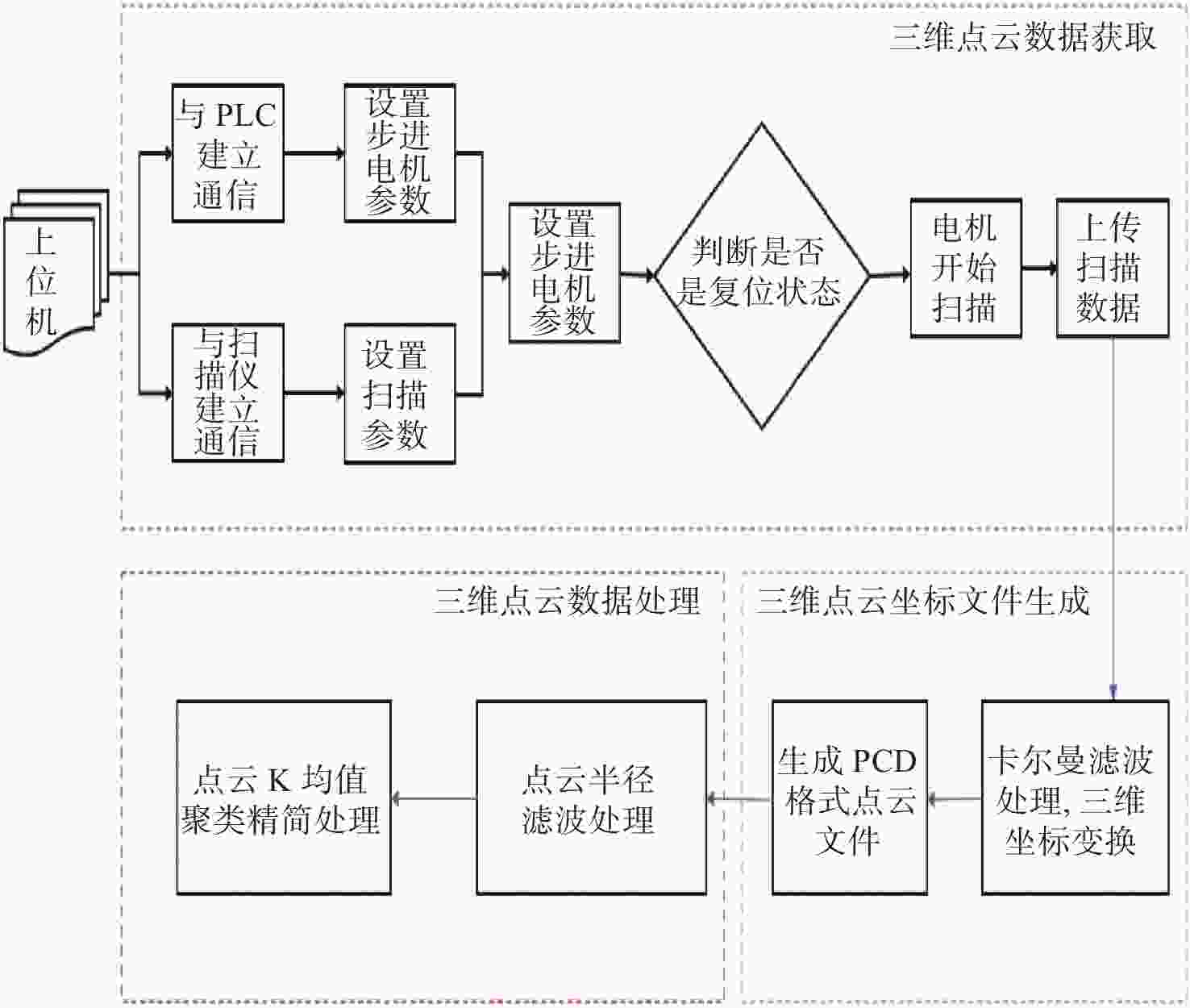
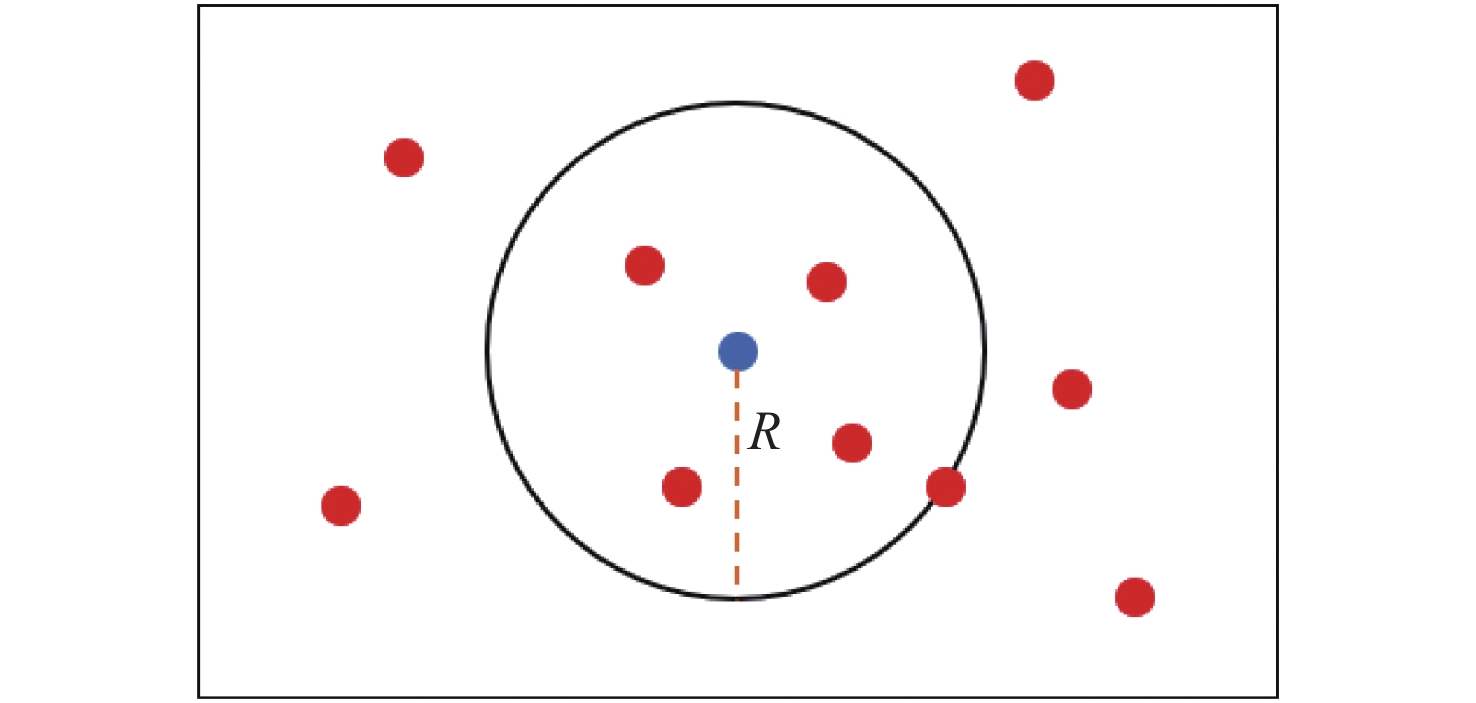
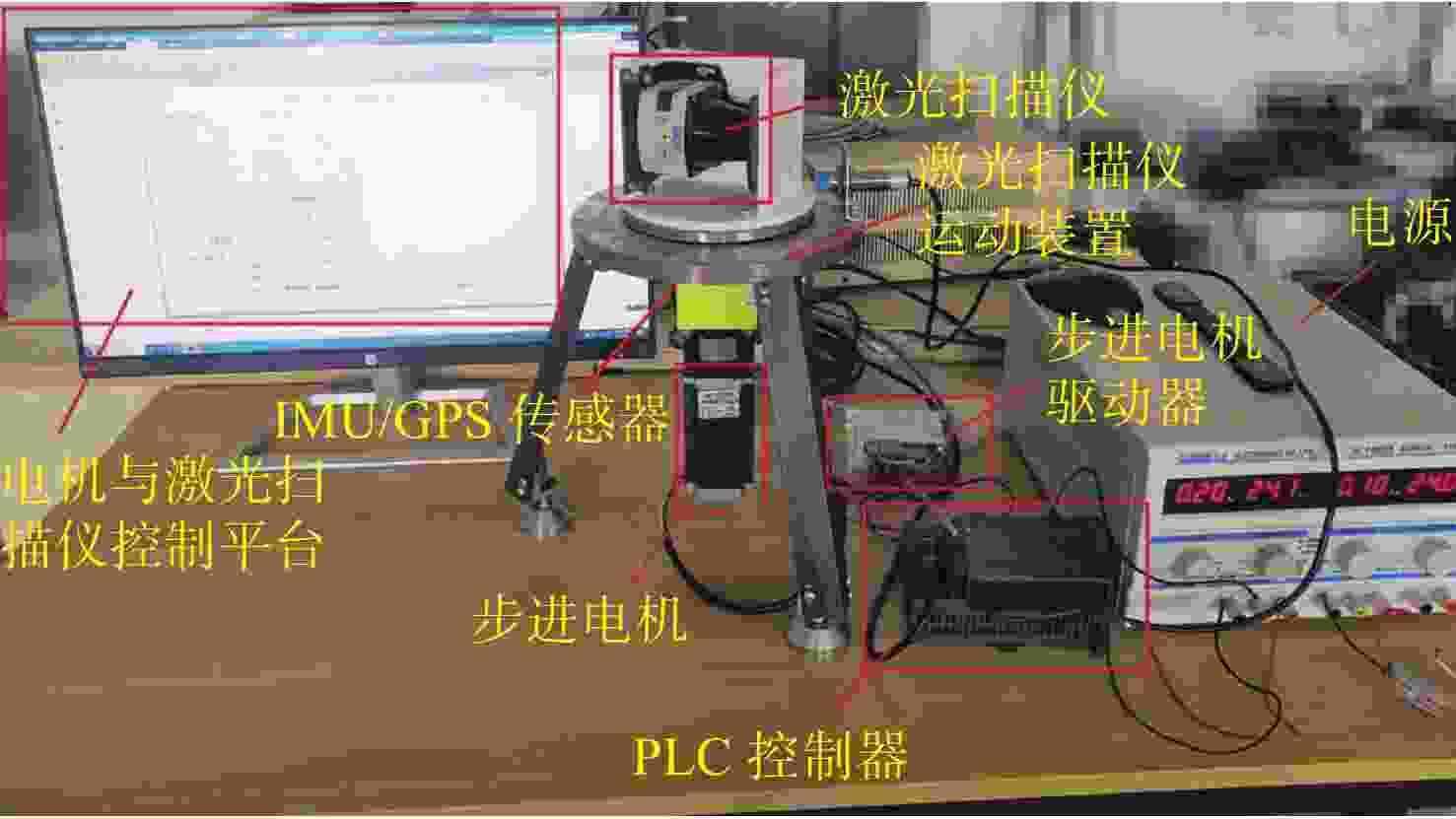
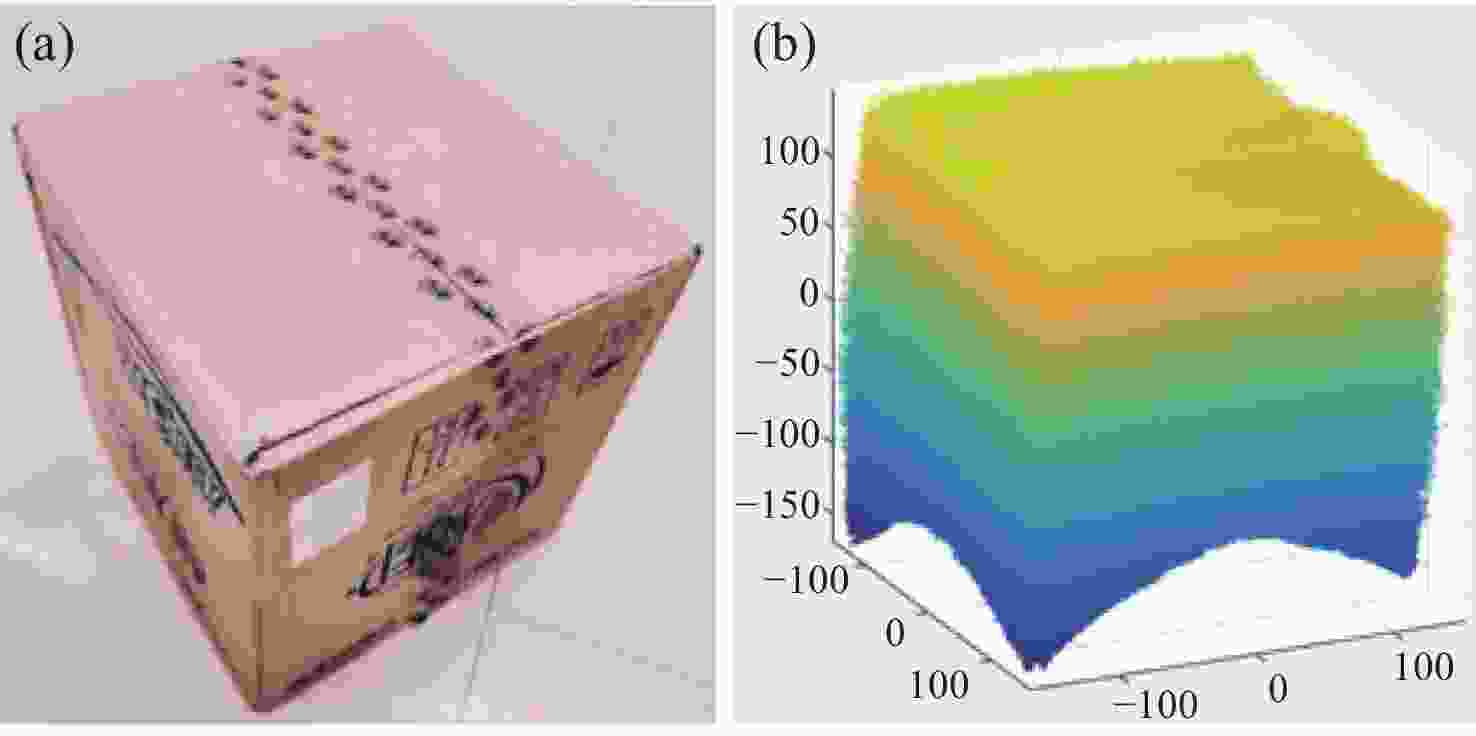
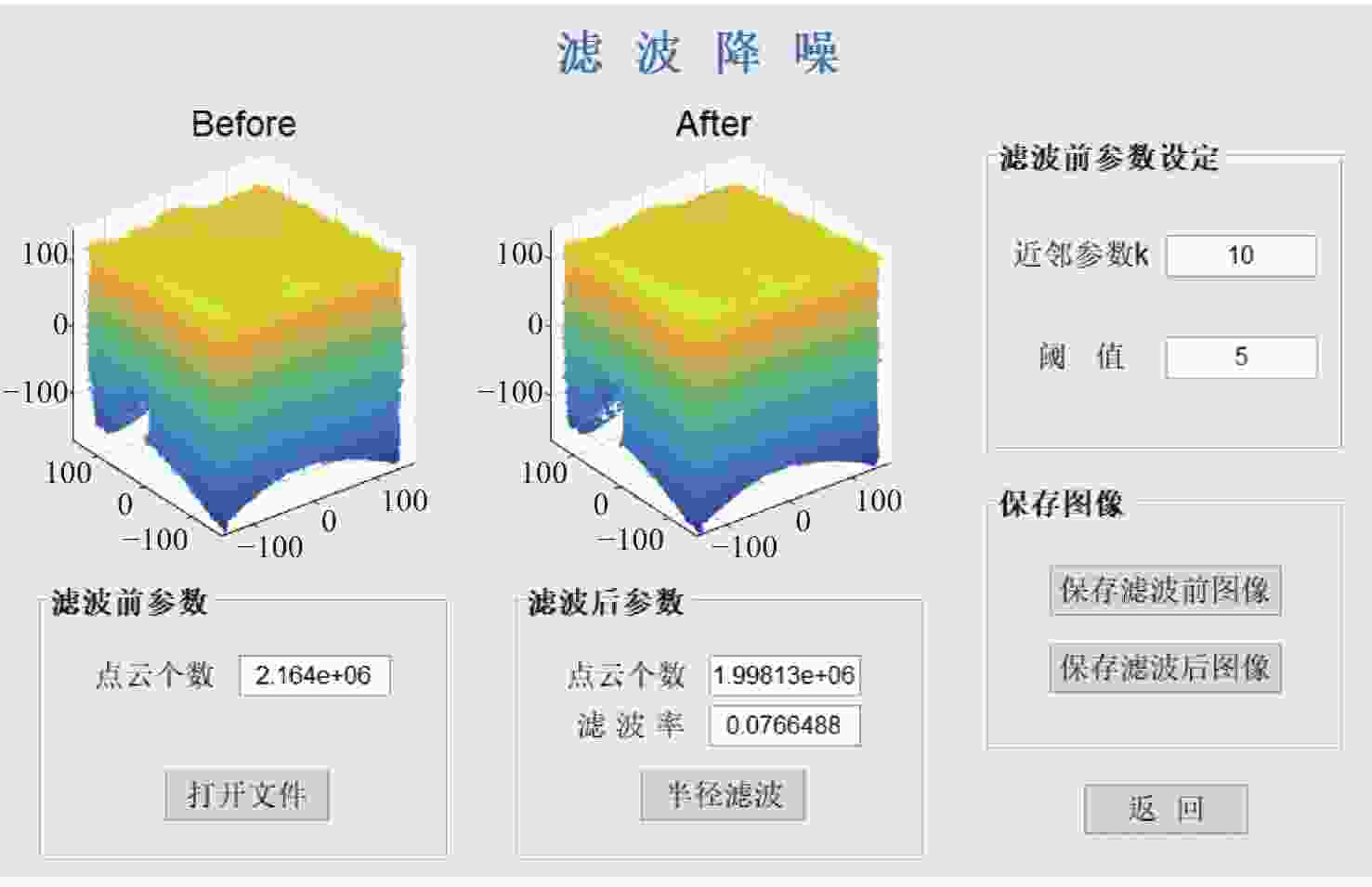
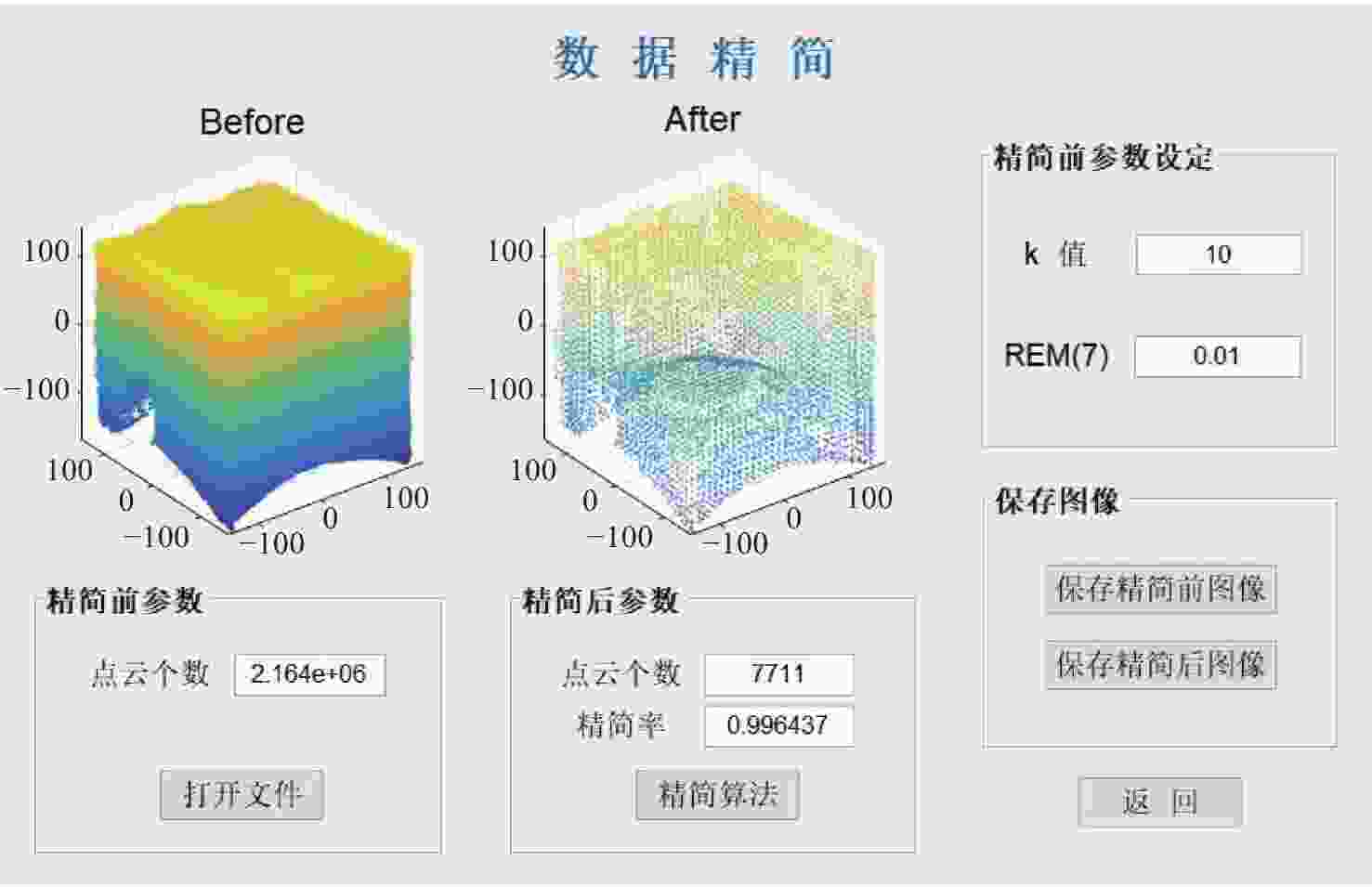
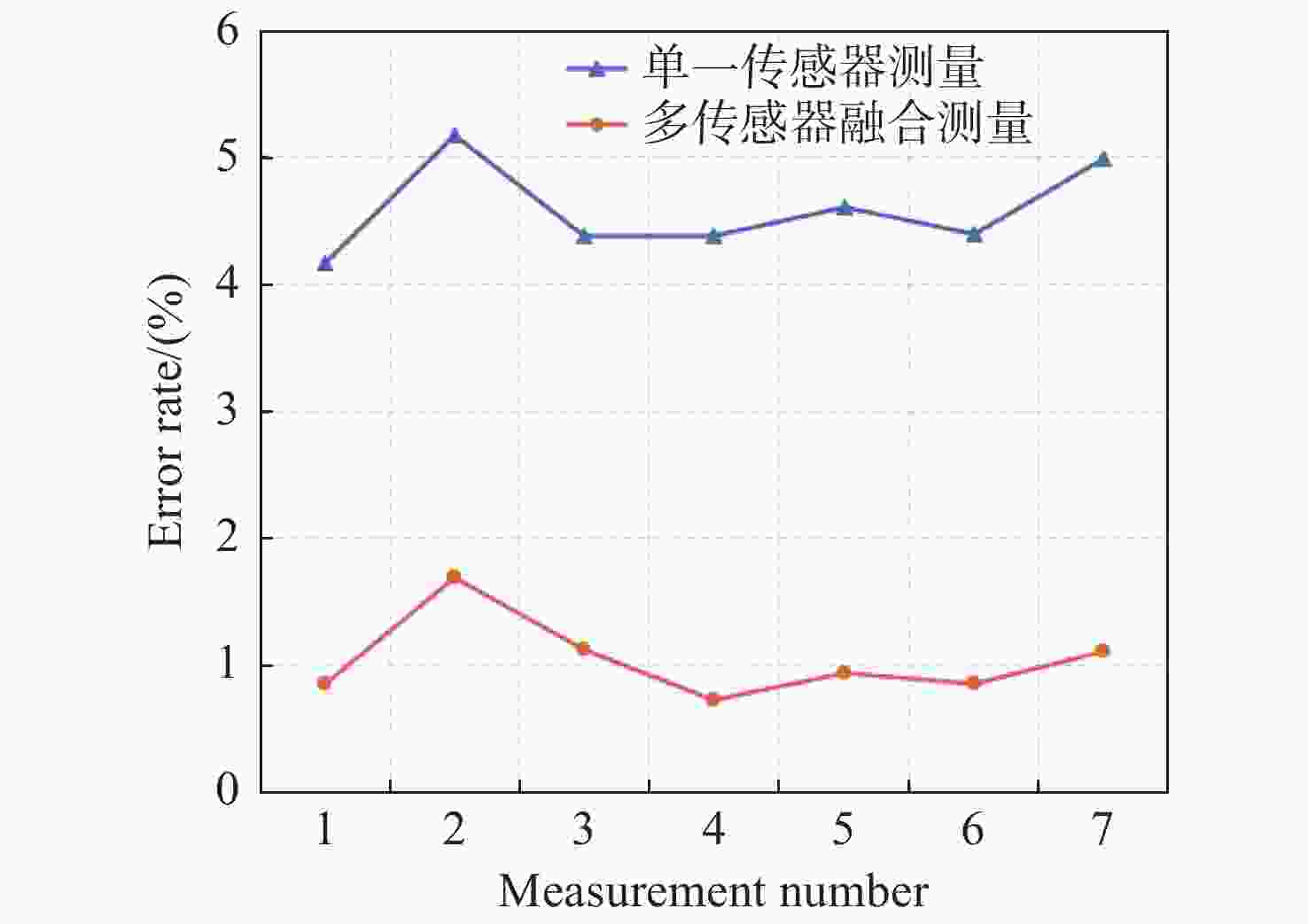
三维重建技术是机器视觉中最热门的研究方向之一,在无人驾驶和数字化加工与生产等领域得到了广泛的应用。传统的三维重建方法包括深度相机和多线激光扫描仪,但是通过深度相机获得的点云存在着信息不完整和不精确的问题,而多线激光扫描仪成本高,阻碍了该项技术的应用和研究。为解决上述问题,提出了一种基于转动式二维激光扫描仪的三维重建方法。首先,用步进电机带动二维激光扫描仪旋转运动来获取三维点云数据。然后,用多传感器融合的方法对激光扫描仪的位置进行标定,采用坐标系变换完成点云数据的匹配。最后,对采集得到的点云数据进行了滤波和精简处理。实验结果表明:相较于深度相机/IMU数据融合的重建方法,平均误差降低了0.93 mm,为4.24 mm;精度达到了毫米级别,误差率也控制在了2%以内;整套设备的成本相较于多线激光扫描仪大大降低。本文方法基本满足保留物体的外形特征、高精度和成本低的要求。
Abstract:3D reconstruction technology is one of the most popular research directions in machine vision, and has been widely used in the fields of unmanned driving and digital processing and production. Traditional 3D reconstruction methods include depth cameras and multi-line laser scanners, but the point clouds obtained by depth cameras have incomplete and inaccurate information, and the high cost of multi-line laser scanners hinders their application and research. To solve these problems, a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on a rotating two-dimensional laser scanner was proposed. First, a stepper motor was used to rotate a 2D laser scanner to obtain 3D point cloud data. Then, the position of the laser scanner was calibrated by multi-sensor fusion, and the point cloud data was matched by transforming the coordinate system. Finally, the collected point cloud data were filtered and simplified. The experimental results show that compared with depth camera/IMU data fusion, the reconstruction method’s average error of the proposed method is reduced by 0.93 mm, and it is 4.24 mm, the accuracy has reached the millimeter level, and the error rate is also controlled within 2%. The cost of the whole set of equipment is also greatly reduced compared to the multi-line laser scanner. It basically meets the requirements of high precision and low cost and retaining the shape characteristics of the object.
-
表 1 根据V′对点云进行分类
Table 1. Categorizion of the point cloud according to V′
分类类别 V′的取值区间 1 [0,0.003) 2 [0.003,0.004) 3 [0.004,0.008) 4 [0.008,0.016) 5 [0.016,0.032) 6 [0.032,0.064) 7 [0.064,1] 表 2 实验测量结果
Table 2. Experimental measurement results
测量次数 实际距离(mm) 误差修正前(mm) 误差修正后(mm) 1 374 389.6 377.2 2 377 396.5 383.4 3 452 471.8 457.1 4 397 414.4 399.9 5 445 465.5 449.2 6 421 439.5 424.6 7 385 404.2 389.3 表 3 实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental results
测量次数 实际距离
(mm)本文方法
(mm)深度相机的重建方法
(mm)1 374 377.2 379.5 2 377 383.4 383.1 3 452 457.1 447.3 4 397 399.9 402.6 5 445 449.2 440.5 6 421 424.6 417.4 7 385 389.3 391.2 -
[1] 姚程, 马彩文. 基于平面补丁的自适应八叉树三维图像重建[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(9):1113-1122. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223009.1113YAO CH, MA C W. Adaptive octree 3D image reconstruction based on plane patch[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(9): 1113-1122. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223009.1113 [2] PULITI M, MONTAGGIOLI G, SABATO A. Automated subsurface defects' detection using point cloud reconstruction from infrared images[J]. Automation in Construction, 2021, 129: 103829. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103829 [3] 赵杰, 陈小梅, 侯玮旻, 等. 基于城市遥感卫星影像对的立体匹配[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(7):830-839. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223007.0830ZHAO J, CHEN X M, HOU W M, et al. Stereo matching based on urban satellite remote sensing image pair[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(7): 830-839. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223007.0830 [4] 孙艺洋, 许金凯, 于占江, 等. 微细铣刀位姿同轴全息重建方法[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):355-363. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0089SUN Y Y, XU J K, YU ZH J, et al. Coaxial holographic reconstruction method of micro-milling tool pose[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 355-363. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0089 [5] SHUANG Y C, WANG Z Z. Active stereo vision three-dimensional reconstruction by RGB dot pattern projection and ray intersection[J]. Measurement, 2021, 167: 108195. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108195 [6] WANG C W, PENG C C. 3D face point cloud reconstruction and recognition using depth sensor[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(8): 2587. doi: 10.3390/s21082587 [7] WANG B Y, WANG Q, CHENG J C P, et al. Vision-assisted BIM reconstruction from 3D LiDAR point clouds for MEP scenes[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 133: 103997. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103997 [8] 蔡军, 赵原, 李宇豪, 等. 一种三维激光扫描系统的设计及参数标定[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2018,44(10):2208-2216. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0029CAI J, ZHAO Y, LI Y H, et al. A 3D laser scanning system design and parameter calibration[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(10): 2208-2216. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0029 [9] 钱超杰, 杨明, 戚明旭, 等. 基于摆动单线激光雷达的大场景稠密点云地图创建系统[J]. 机器人,2019,41(4):464-472,492. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.180543QIAN CH J, YANG M, QI M X, et al. Swinging single-layer LiDAR based dense point cloud map reconstruction system for large-scale scenes[J]. Robot, 2019, 41(4): 464-472,492. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.180543 [10] 王锐, 常锴, 符国浩, 等. 单线激光雷达与GNSS/INS的空间重构[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(4):851-858.WANG R, CHANG K, FU G H, et al. Space reconstruction using single-line LIDAR and GNSS/INS fused data[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(4): 851-858. (in Chinese) [11] LU H J, XU SH G, CAO SH. SGTBN: generating dense depth maps from single-line LiDAR[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(17): 19091-19100. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3088308 [12] WEN W S, PFEIFER T, BAI X W, et al. Factor graph optimization for GNSS/INS integration: a comparison with the extended Kalman filter[J]. Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2021, 68(2): 315-331. doi: 10.1002/navi.421 [13] NING X J, LI F, TIAN G, et al. An efficient outlier removal method for scattered point cloud data[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(8): e0201280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201280 [14] 袁小翠, 吴禄慎, 陈华伟. 特征保持点云数据精简[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(9):2666-2676. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152309.2666YUAN X C, WU L SH, CHEN H W. Feature preserving point cloud simplification[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(9): 2666-2676. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152309.2666 [15] TIAN Y, XU H, GUAN F, et al. Projection and integration of connected-infrastructure LiDAR sensing data in a global coordinate[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2021, 144: 107421. [16] WELCH G F. Kalman filter[J]. Computer Vision:A Reference Guide, 2020: 1-3. [17] NAGUI N, ATTALLAH O, ZAGHLOUL M S, et al. Improved GPS/IMU loosely coupled integration scheme using two kalman filter-based cascaded stages[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2021, 46(2): 1345-1367. doi: 10.1007/s13369-020-05144-8 -





 下载:
下载: