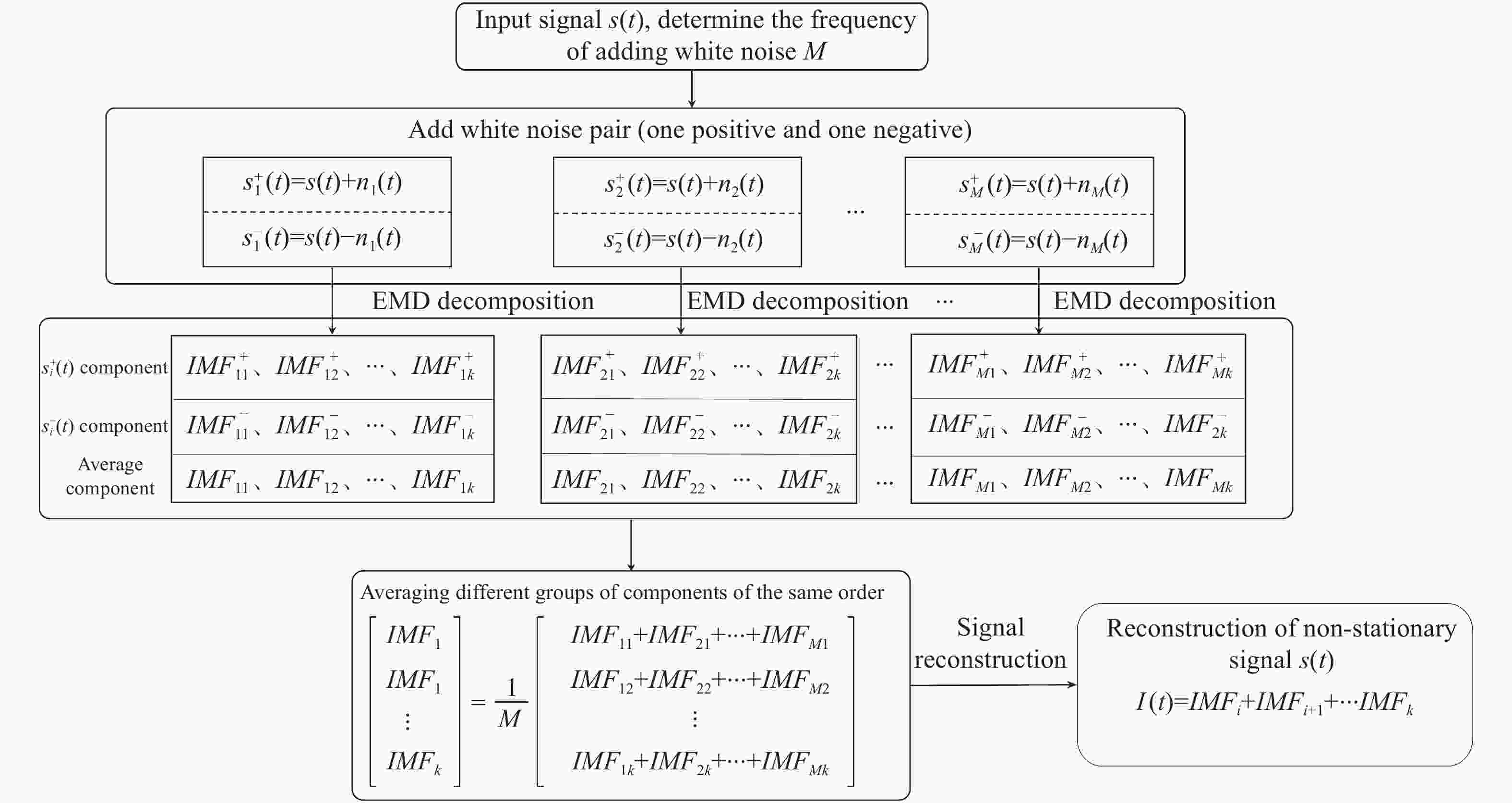
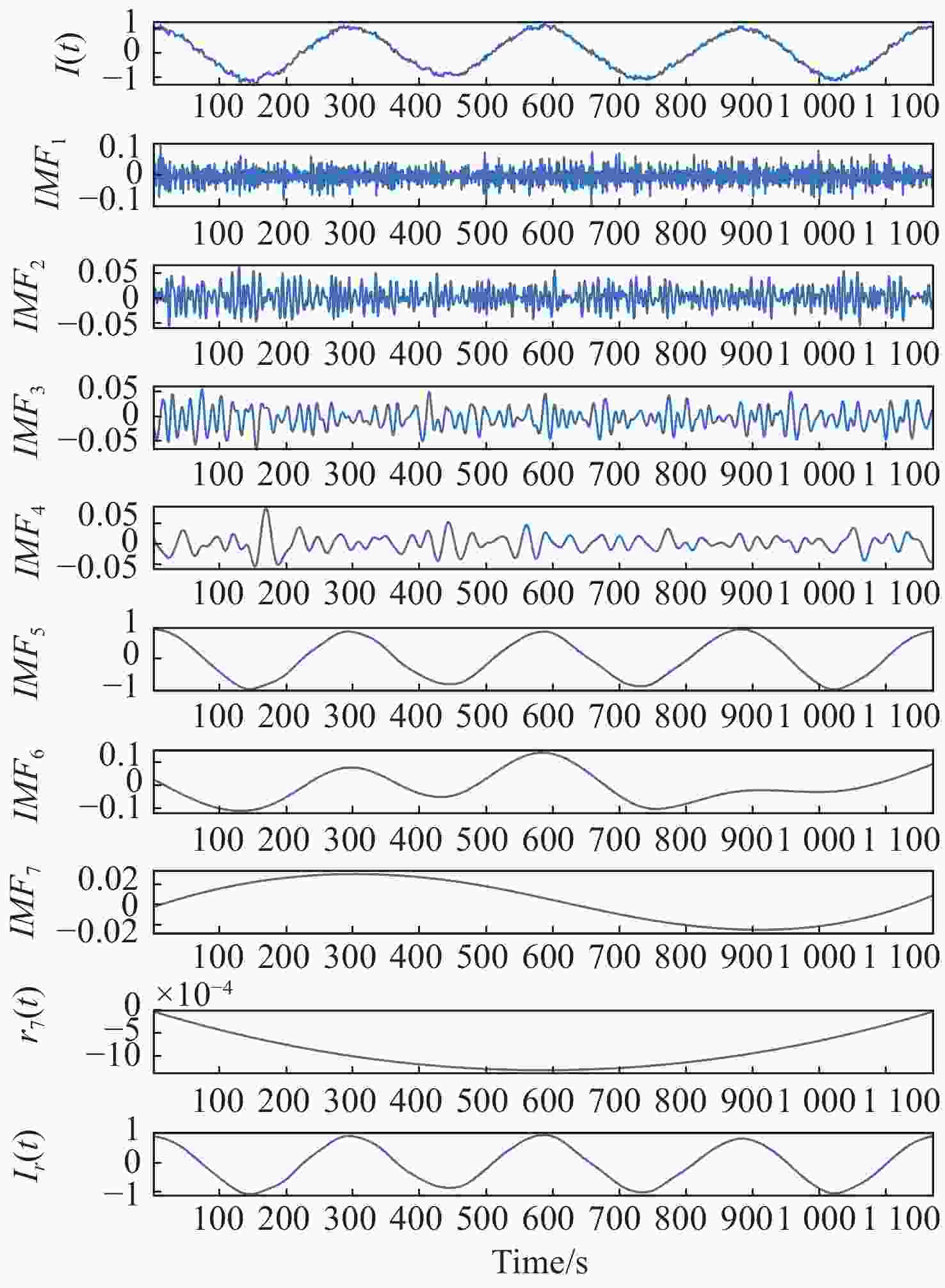
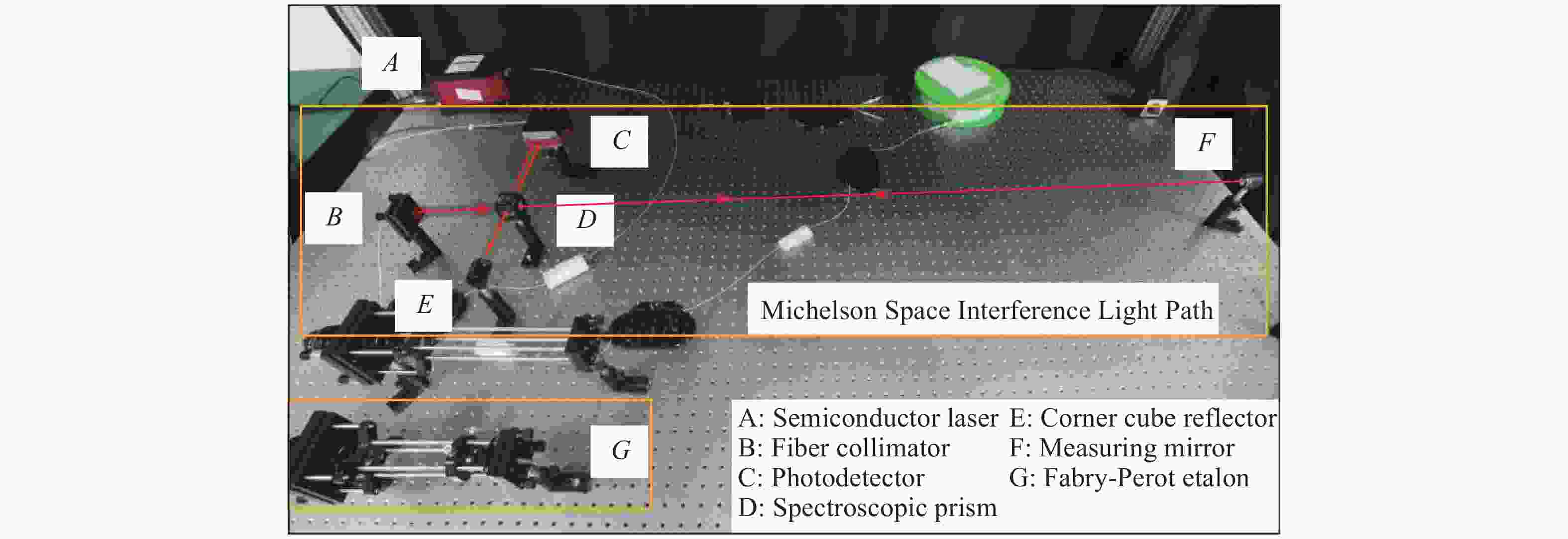
Phase-extracting method of optical frequency scanning interference signals based on the CEEMD-HT algorithm
doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0173
-
摘要:
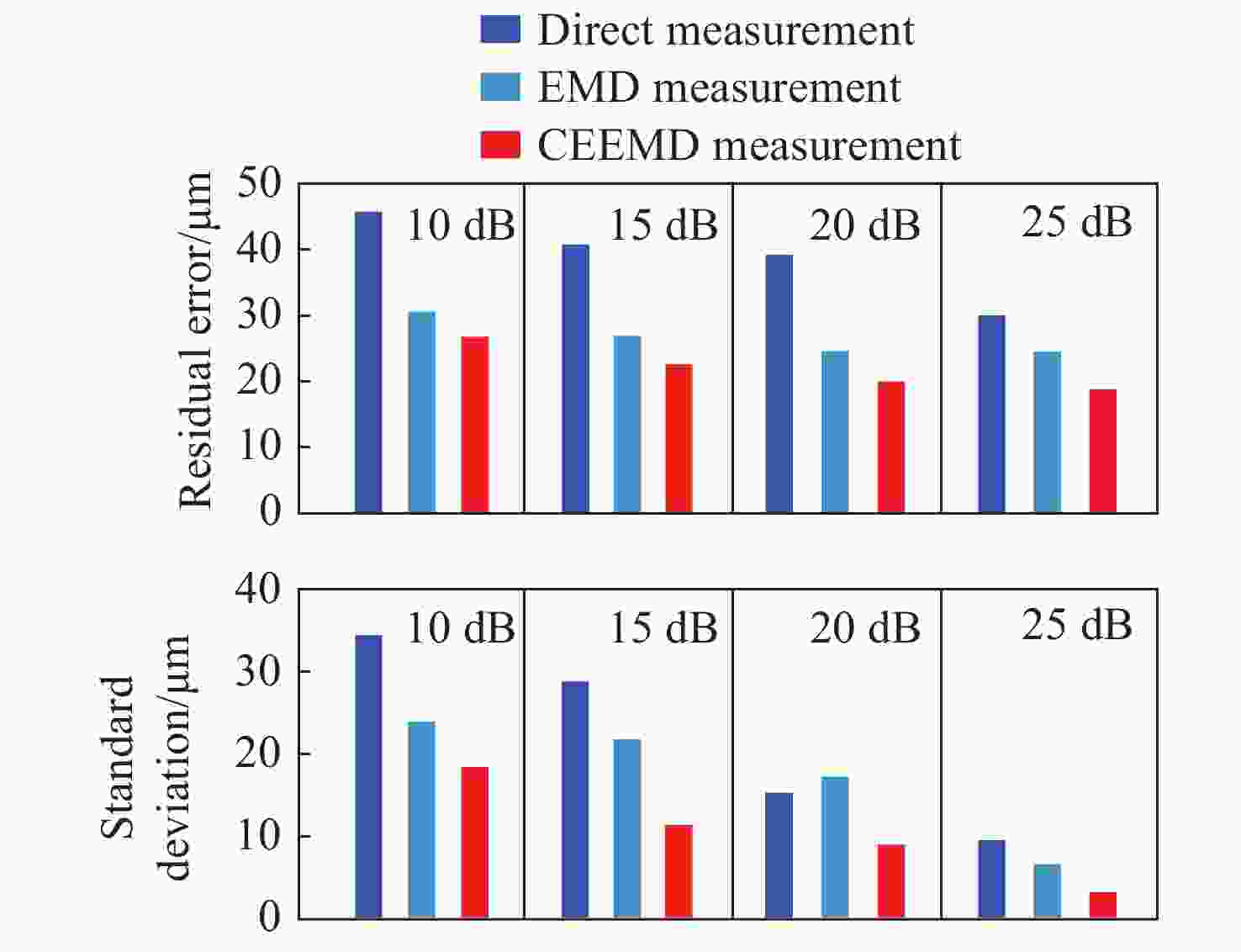
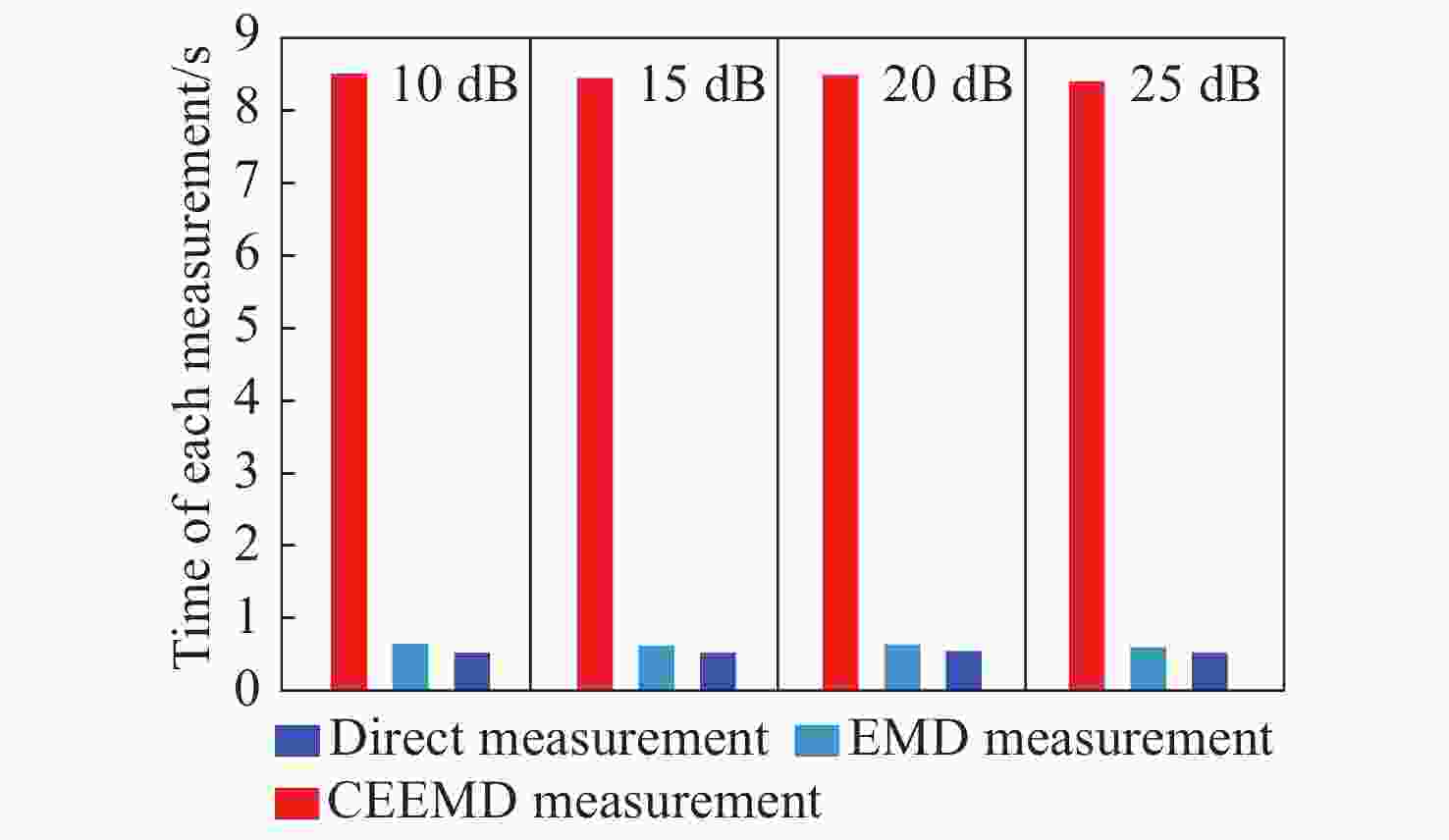
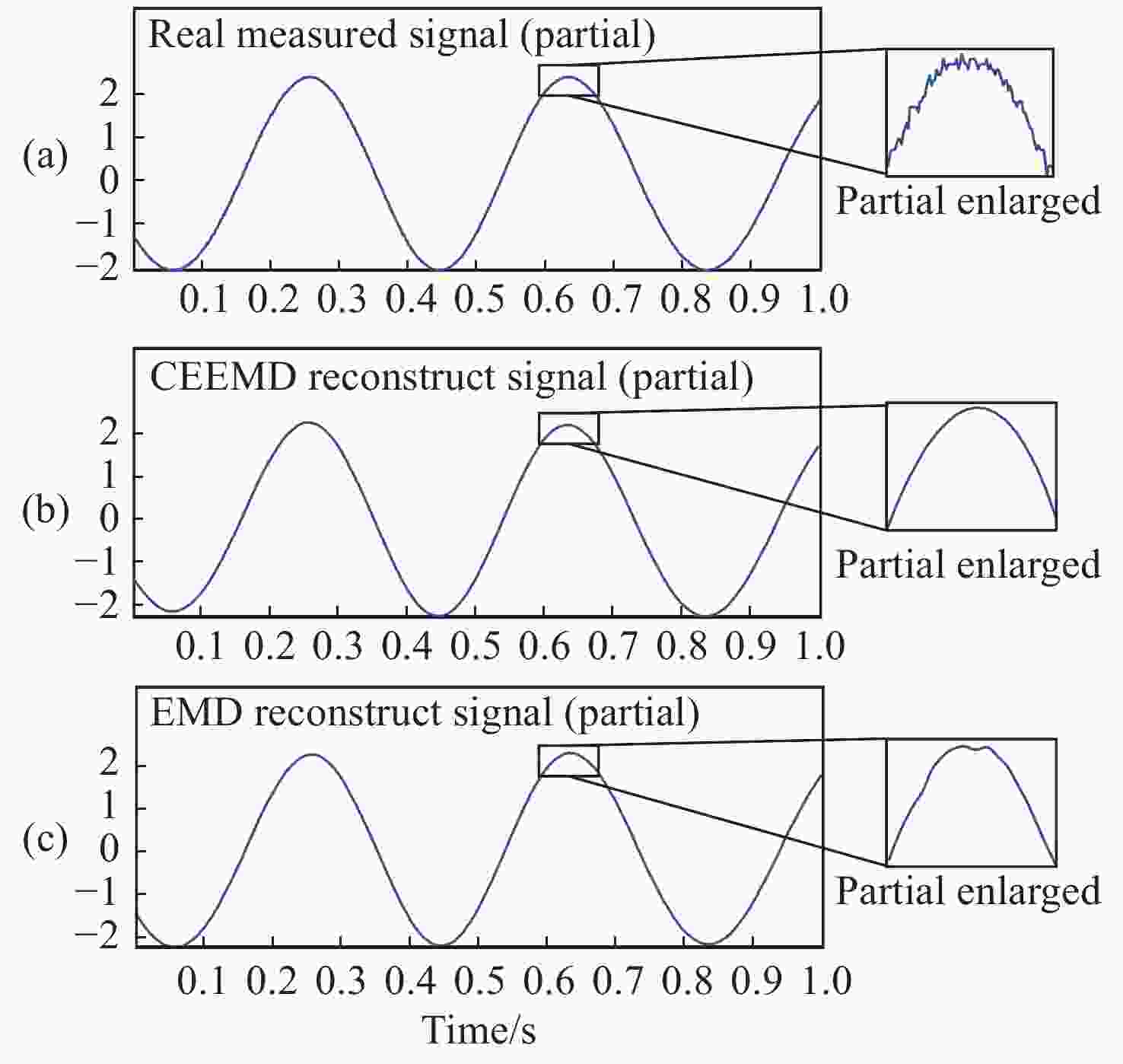
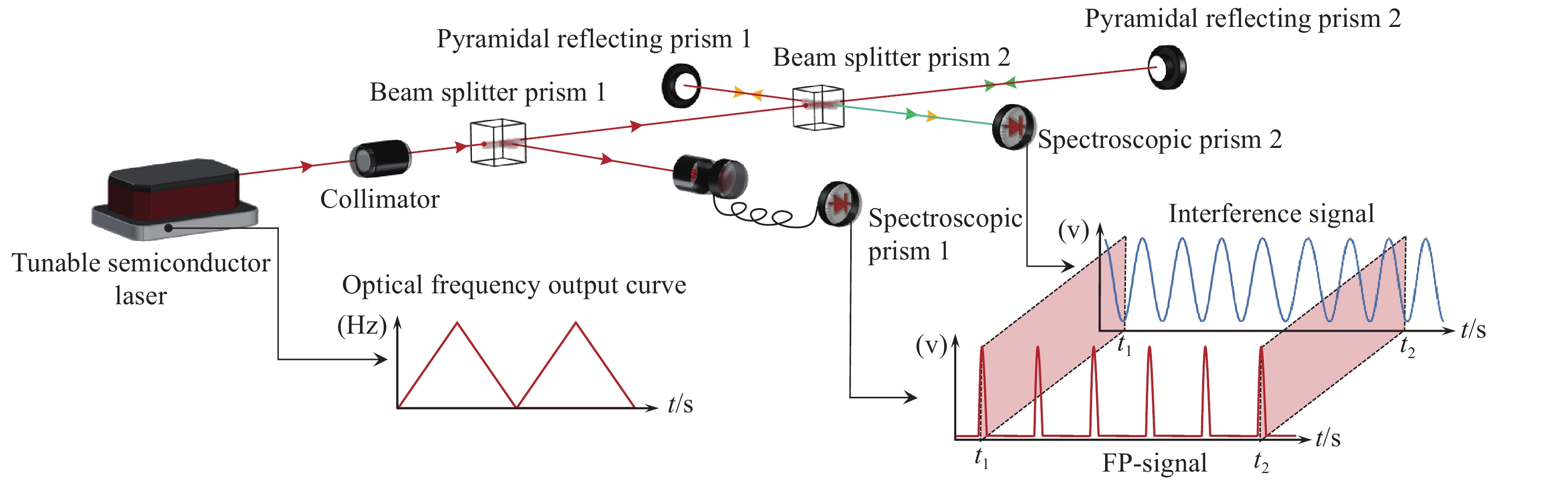
光频扫描非线性会影响光频扫描干涉(FSI)信号的相位提取精度,进而降低扫频干涉测距精度。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于互补集合经验模态分解结合希尔伯特变换(CEEMD-HT)算法的干涉信号相位提取方法。在CEEMD-HT算法进行理论推导和仿真分析的基础上,通过仿真验证了该算法对非平稳扫频干涉信号相位求解的有效性。进一步采用FSI实验系统中的真实输出光频率作为仿真条件进行了仿真实验,仿真结果表明CEEMD-HT算法对干涉信号相位的求解精度以及FSI测距精度都有显著的改善。最后,通过FSI测距系统的测距实验对所提出的干涉信号相位提取方法进行验证。结果表明:在2 m自由空间测量范围内,基于CEEMD-HT算法的重复测距精度为2.79 μm,相较于EMD-HT和直接测量法分别提高了5.19倍和8.28倍。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem that the optical frequency scanning nonlinearity affects the phase extracting accuracy of the optical Frequency Scanning Interferometry (FSI) signal, and thus reduces the FSI ranging accuracy, a phase-extracting method based on the Complementary Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Hilbert Transform (CEEMD-HT) algorithm is proposed in this paper. Based on theoretical derivation and simulation analysis of the CEEMD-HT algorithm, the effectiveness of the algorithm in solving the phase of the non-stationary interference signal in scanning-frequency is verified by simulation. Further simulation experiments were implemented by using the real output optical frequency obtained with FSI ranging system as the simulation conditions. The simulation results showed that the CEEMD-HT algorithm significantly improved the phase extracting accuracy of the interference signal and the FSI ranging accuracy. Finally, the proposed interference signal phase-extracting method was verified via the experiment of the FSI ranging system. The results showed that the ranging repeatability of the measurement system based on the CEEMD-HT algorithm was 2.79 μm in the free space measurement range of 2 m. Compared with EMD-HT and direct measurement methods, the ranging repeatability was improved by 5.19 times and 8.28 times, respectively.
-
表 1 Simulation parameters of the scanning nonlinearity
Table 1. Simulation parameters of the scanning nonlinearity
Parameters Parameter name Value/unit a Interference signal amplitude 1 V ${\upsilon _0}$ ECDL initial optical frequency 0 Hz $\Delta \upsilon $ Optical frequency scanning range 2 THz L Measured distance 10 m n Air refractive index 1 c Velocity of light 3×108 m/s t Scan cycle 5 s SNR Signal to noise ratio of
interference signal25, 20, 15, 10 dB S Interference signal sampling frequency 10 MHz -
[1] LU CH, LIU G D, LIU B G, et al. Absolute distance measurement system with micron-grade measurement uncertainty and 24 m range using frequency scanning interferometry with compensation of environmental vibration[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(26): 30215-30224. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.030215 [2] SHI G, ZHANG F M, QU X H, et al. High-resolution frequency-modulated continuous-wave laser ranging for precision distance metrology applications[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(12): 122402. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.12.122402 [3] SHI G, WANG W, ZHANG F M. Precision improvement of frequency-modulated continuous-wave laser ranging system with two auxiliary interferometers[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 411: 152-157. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.11.062 [4] WANG ZH Y, LIU ZH G, DENG ZH W, et al. Phase extraction of non-stationary interference signal in frequency scanning interferometry using complex shifted Morlet wavelets[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 420: 26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.03.032 [5] CHENG X R, LIU J CH, JIA L H, et al. Precision and repeatability improvement in frequency-modulated continuous-wave velocity measurement based on the splitting of beat frequency signals[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(18): 28582-28596. doi: 10.1364/OE.433637 [6] DALE J, HUGHES B, LANCASTER A J, et al. Multi-channel absolute distance measurement system with sub ppm-accuracy and 20 m range using frequency scanning interferometry and gas absorption cells[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(20): 24869-24893. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.024869 [7] LIU G D, XU X K, LIU B G, et al. Dispersion compensation method based on focus definition evaluation functions for high-resolution laser frequency scanning interference measurement[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 386: 57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.10.052 [8] XU X K, LONG K, XU J X, et al. The method of dispersion cancellation based on the forward and reverse tuning of a laser frequency-modulated continuous wave system[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2021, 40(2): 243-247. [9] WANG D F, YAO X, JIAO ZH K, et al. Time-delay interferometry for space-based gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 275-288. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0098 [10] GONG H, LIU ZH G, ZHOU Y L, et al. Mode-hopping suppression of external cavity diode laser by mode matching[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(4): 694-701. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.000694 [11] DENG ZH W, LIU ZH G, LI B, et al. Precision improvement in frequency-scanning interferometry based on suppressing nonlinear optical frequency sweeping[J]. Optical Review, 2015, 22(5): 724-730. doi: 10.1007/s10043-015-0134-1 [12] GONG H, LIU ZH G, ZHOU Y L, et al. Extending the mode-hop-free tuning range of an external-cavity diode laser by synchronous tuning with mode matching[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(33): 7878-7884. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.007878 [13] YÜKSEL K, WUILPART M, MÉGRET P. Analysis and suppression of nonlinear frequency modulation in an optical frequency-domain reflectometer[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(7): 5845-5851. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.005845 [14] AHN T J, LEE J Y, KIM D Y. Suppression of nonlinear frequency sweep in an optical frequency-domain reflectometer by use of Hilbert transformation[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(35): 7630-7634. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.007630 [15] ROOS P A, REIBEL R R, BERG T, et al. Ultrabroadband optical chirp linearization for precision metrology applications[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(23): 3692-3694. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.003692 [16] DENG W, LIU ZH G, DENG ZH W, et al. Extraction of interference phase in frequency-scanning interferometry based on empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert transform[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(9): 2299-2305. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.002299 [17] BEDROSIAN E. A product theorem for Hilbert transforms[R]. Santa Monica: RAND Corporation, 1962. [18] RILLING G, FLANDRIN P, GONÇALVES P. On empirical mode decomposition and its algorithms[C]. Proceedings of IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing NSIP-03, IEEE, 2003: 8-11. [19] WU ZH H, HUANG N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [20] YEH J R, SHIEH J S, HUANG N E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 2(2): 135-156. doi: 10.1142/S1793536910000422 -






 下载:
下载: