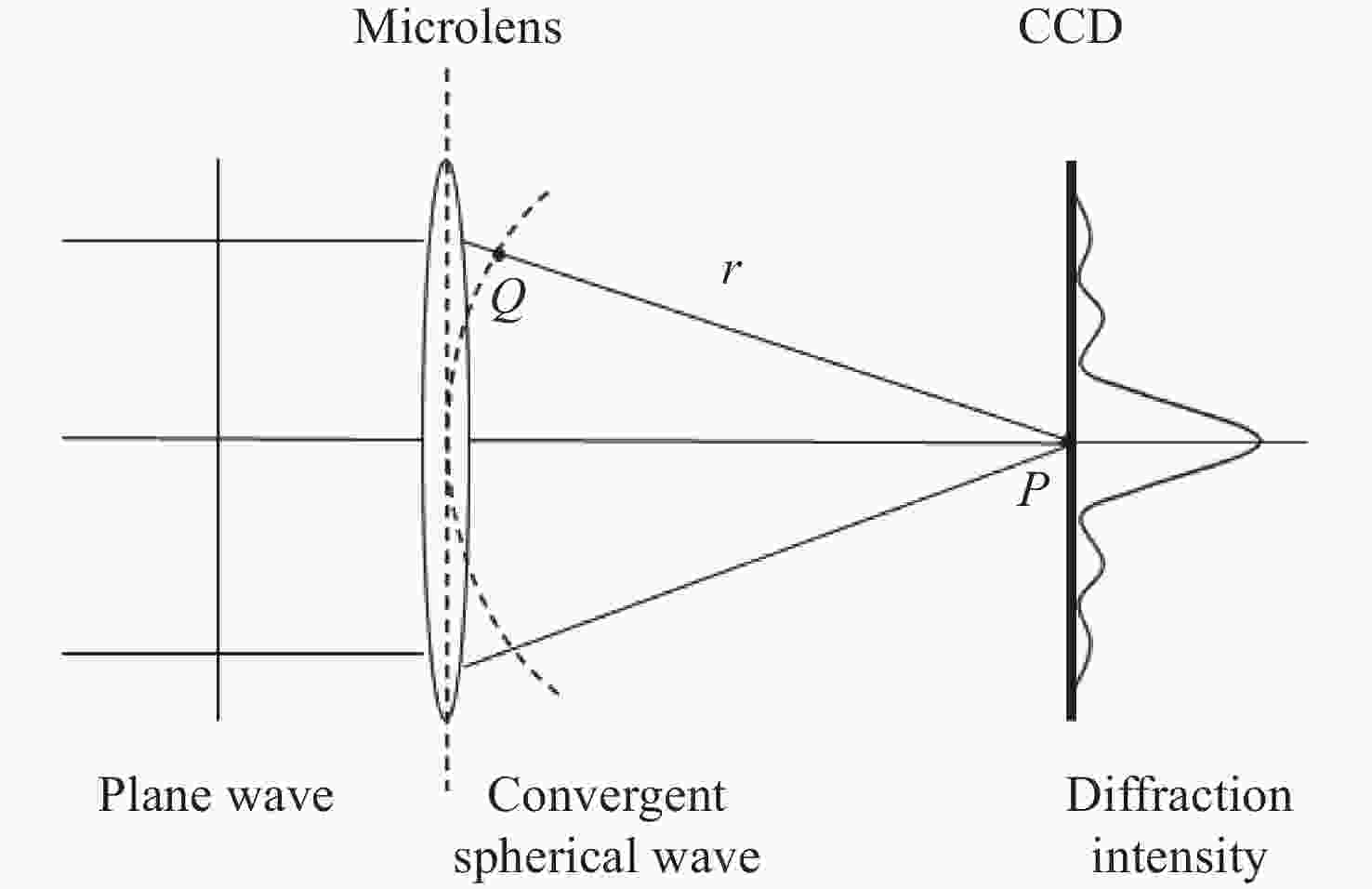
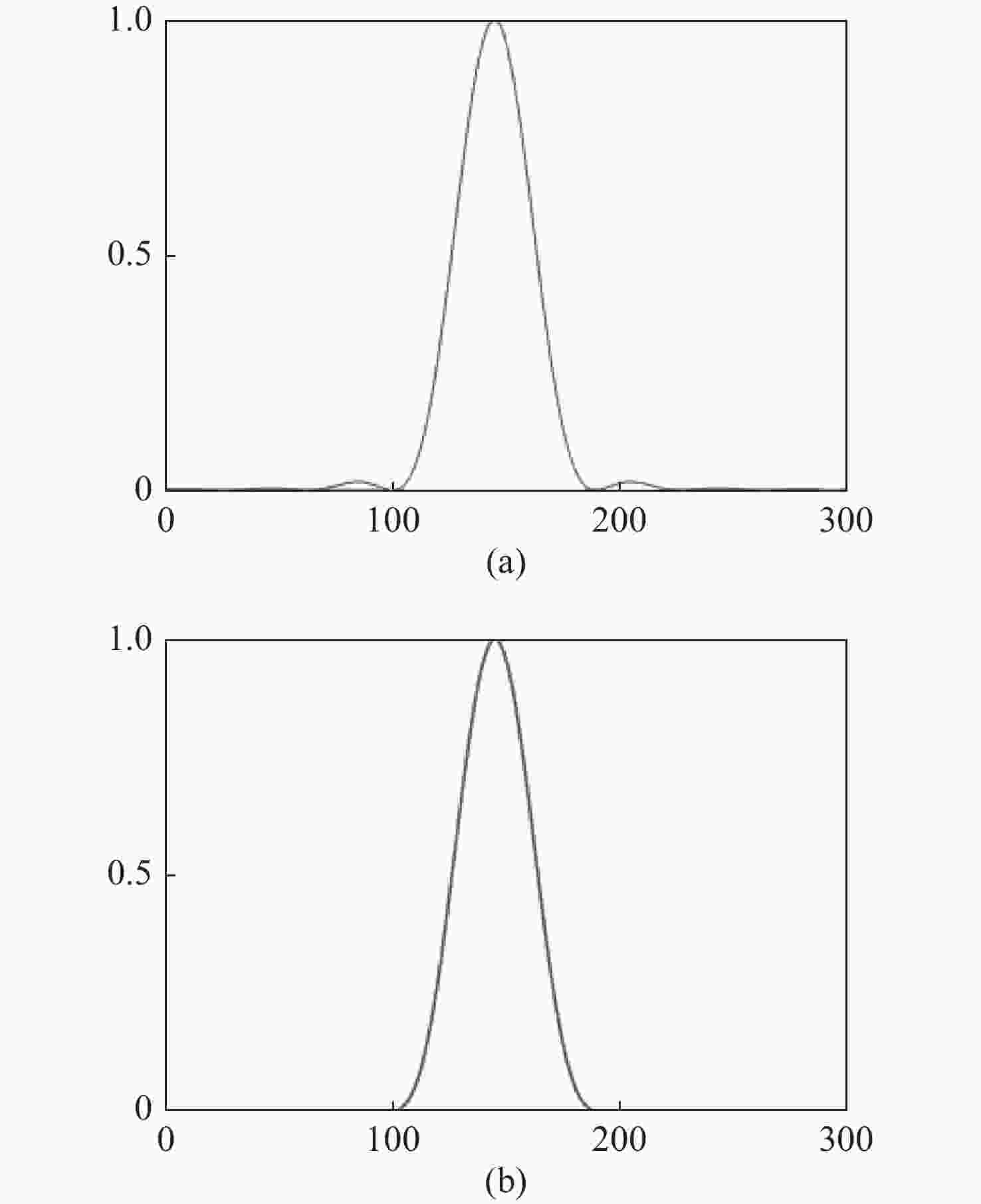
Analysis of influence of diffraction effect of microlens array on Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor
-
摘要:
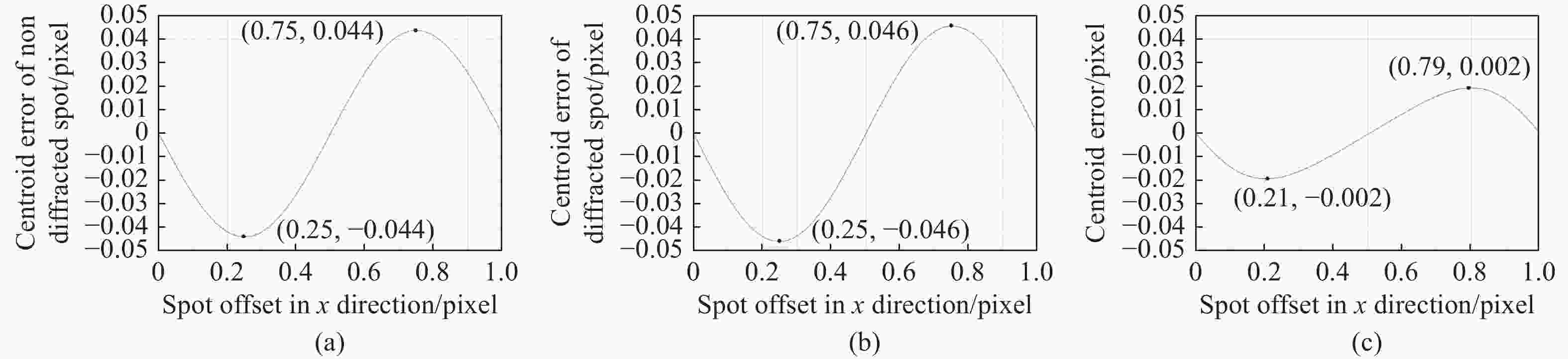
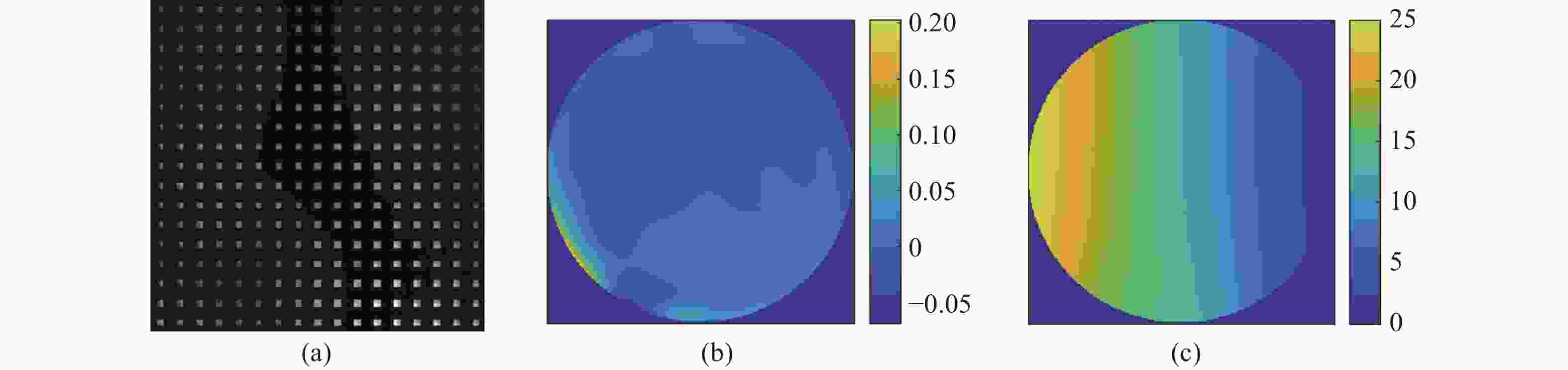
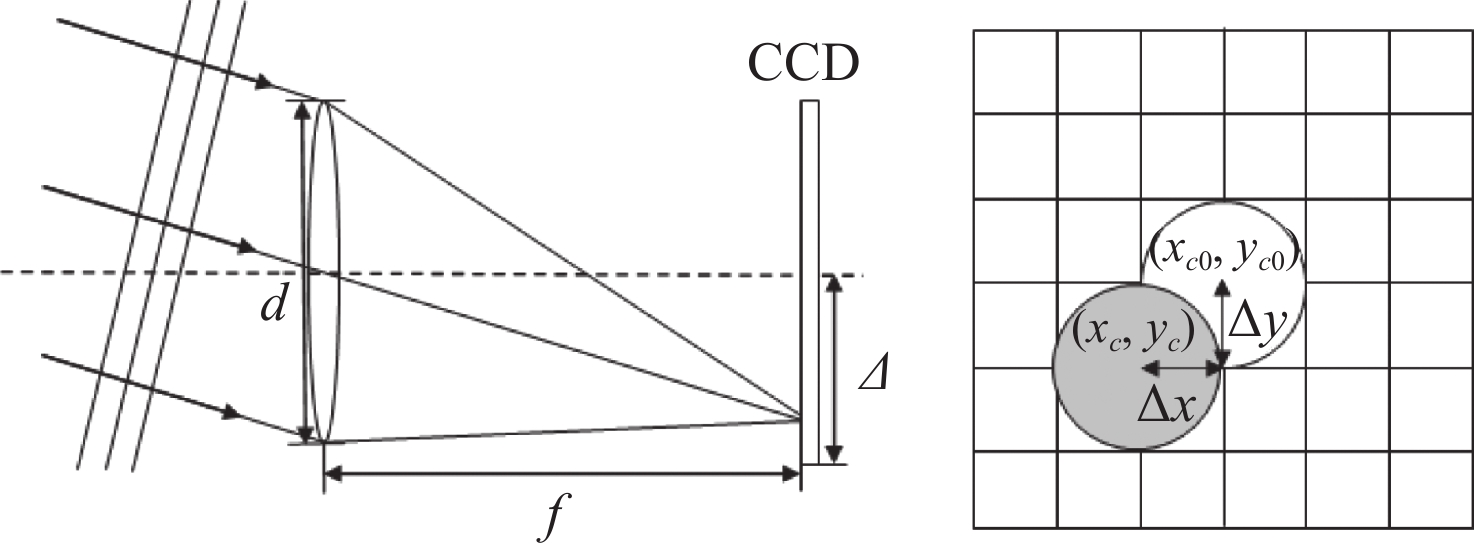
微透镜阵列的衍射效应会影响夏克—哈特曼波前探测器的探测精度。本文根据惠更斯-菲涅耳衍射理论建立二维微透镜阵列衍射模型,模拟分析使用理想平行光入射微透镜阵列时在焦平面产生的二维衍射光斑阵列。然后,通过计算衍射光斑偏移一个像素的过程中质心的误差,确定最大质心计算误差。接着,利用模式法进行波前重构,获得波前探测误差。仿真结果显示:在偏移0.21和0.79个像素,即波面偏转0.03°和0.13°时,衍射导致的波前误差最大为0.125
λ 。最后,实验验证了该误差计算方法的有效性。该研究结果可为夏克一哈特曼波前探测器的设计提供理论依据。Abstract:The diffraction effect of microlens array will affect the detection accuracy of Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor. Based on Huygens-Fresnel diffraction theory, a two-dimensional microlens array diffraction model is established to simulate and analyze the two-dimensional diffraction spot array generated in the focal plane when the ideal parallel light is incident on the microlens array. First, the maximum centroid calculation error is determined by calculating the centroid error in the process of diffraction spot shifting by one pixel. Then the wavefront is reconstructed by using the modal method to obtain the wavefront detection error. The simulation results show that the maximum wavefront error caused by diffraction is 0.125
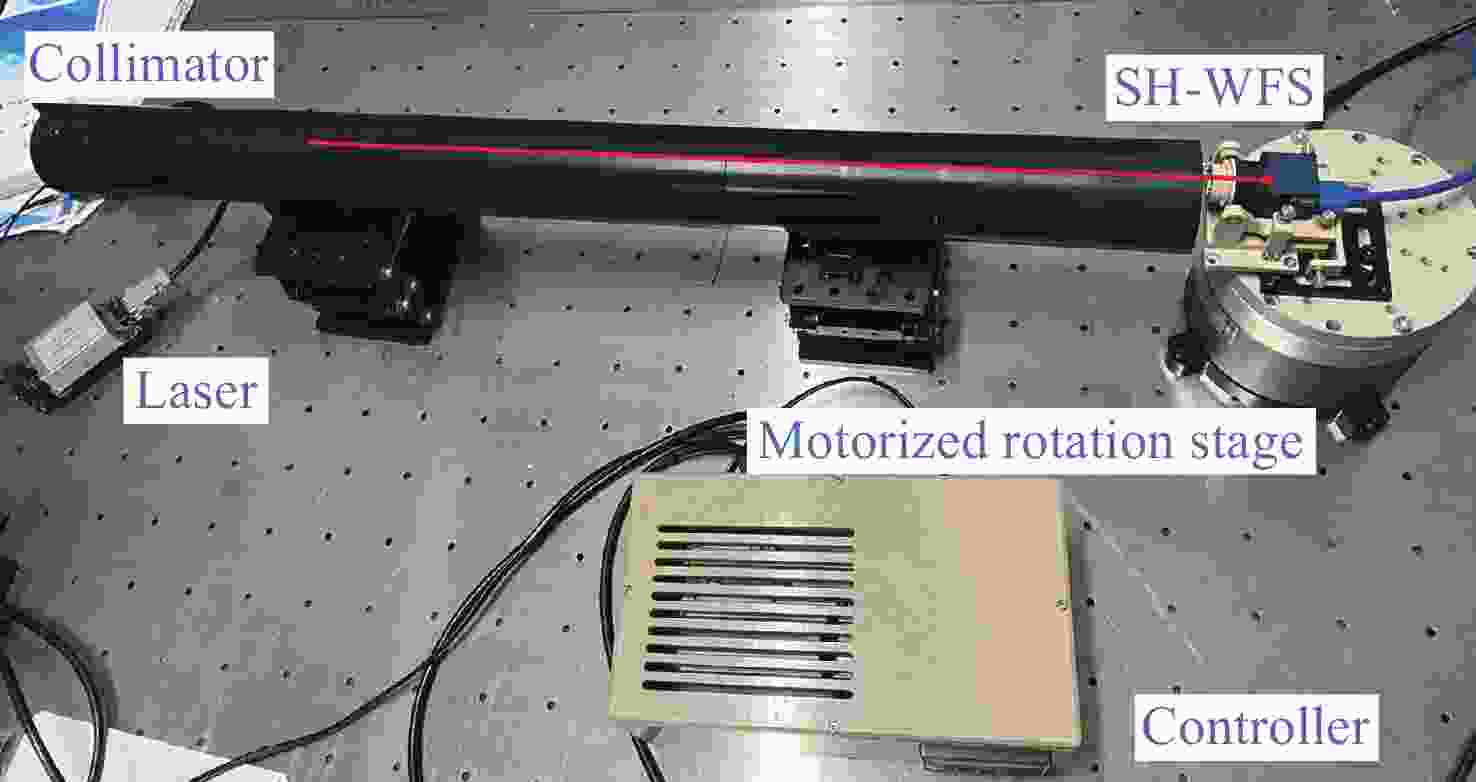
λ at 0.21 and 0.79 pixels offset, that is, when the wavefront deflection is 0.03° and 0.13°. Finally, an experiment is performed to verify the effectiveness of the error calculation method. This work provides a theoretical basis for the design of shack-Hartmann wavefront detector. -
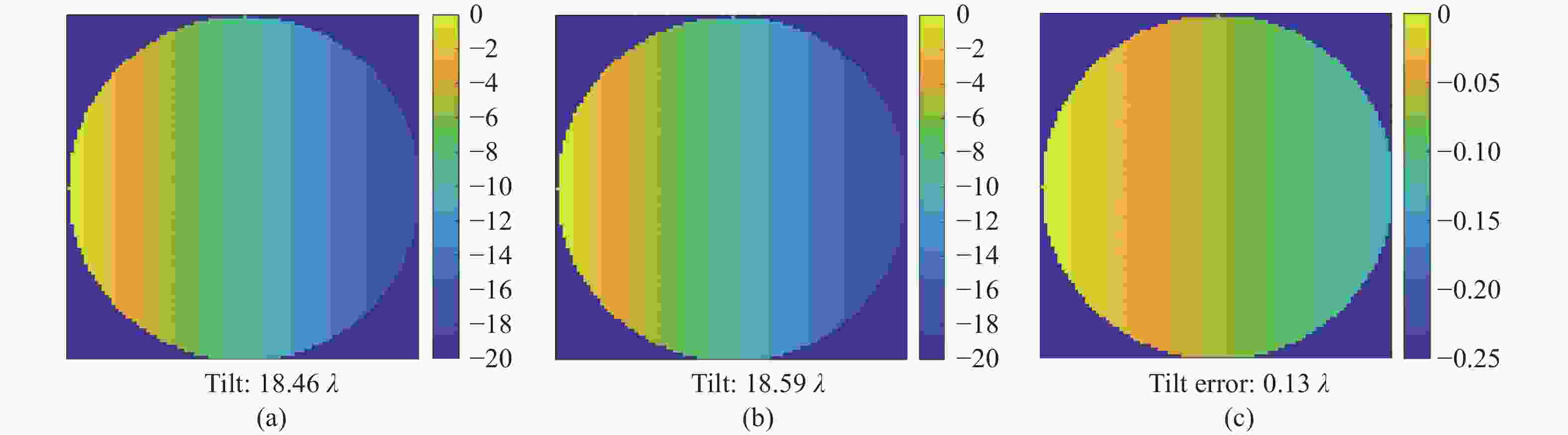
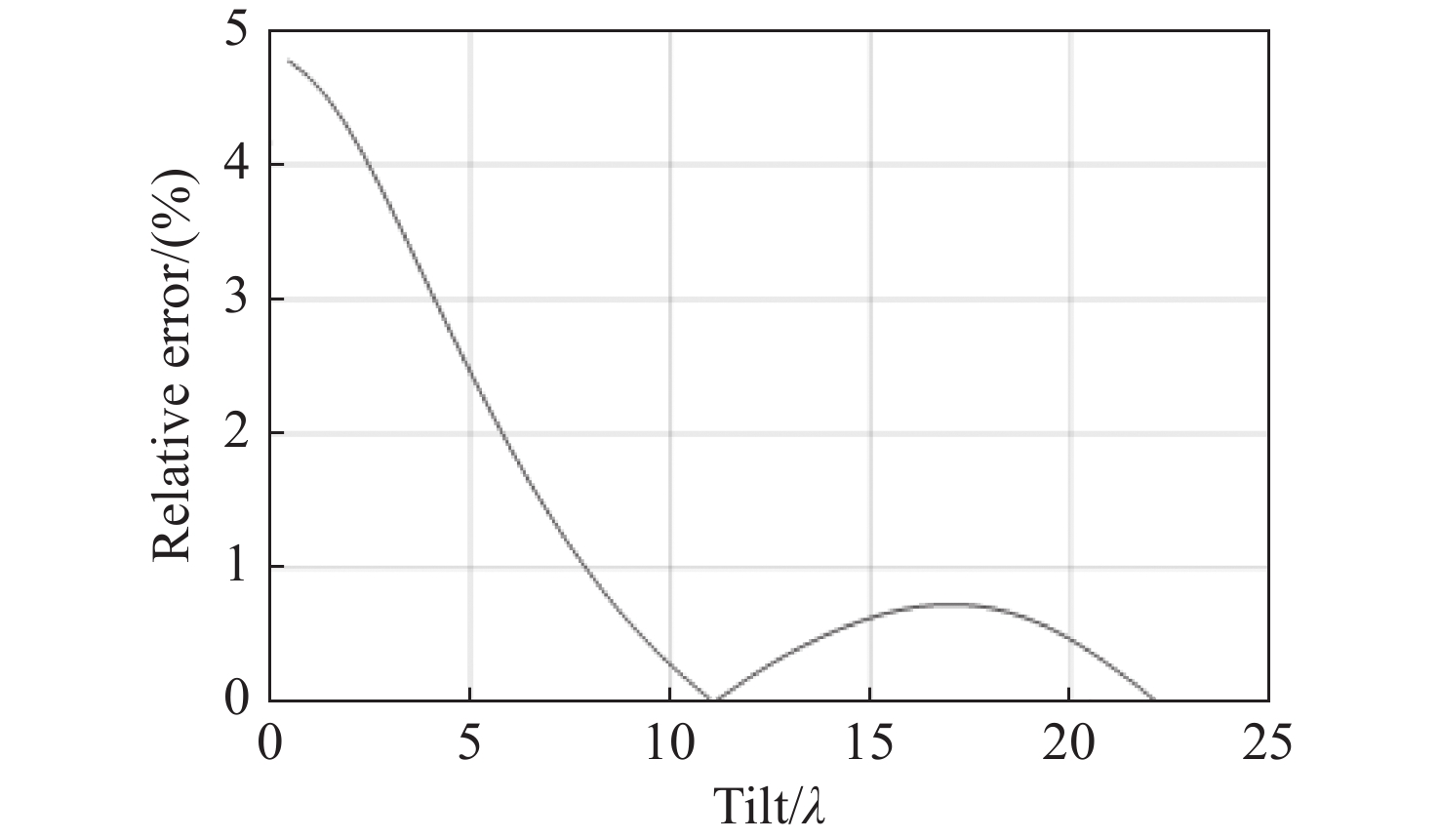
图 8 (a) 无衍射的光斑偏移1个像素过程中的波前倾斜误差;(b) 有衍射的光斑偏移1个像素过程中的波前倾斜误差;(c)衍射效应造成的波前倾斜误差
Figure 8. (a)Wavefront tilt error in the process of diffraction free spot shifting by 1 pixel; (b) wavefront tilt error in the process of diffraction spot shifting by 1 pixel; (c) wavefront tilt error caused by diffraction effect
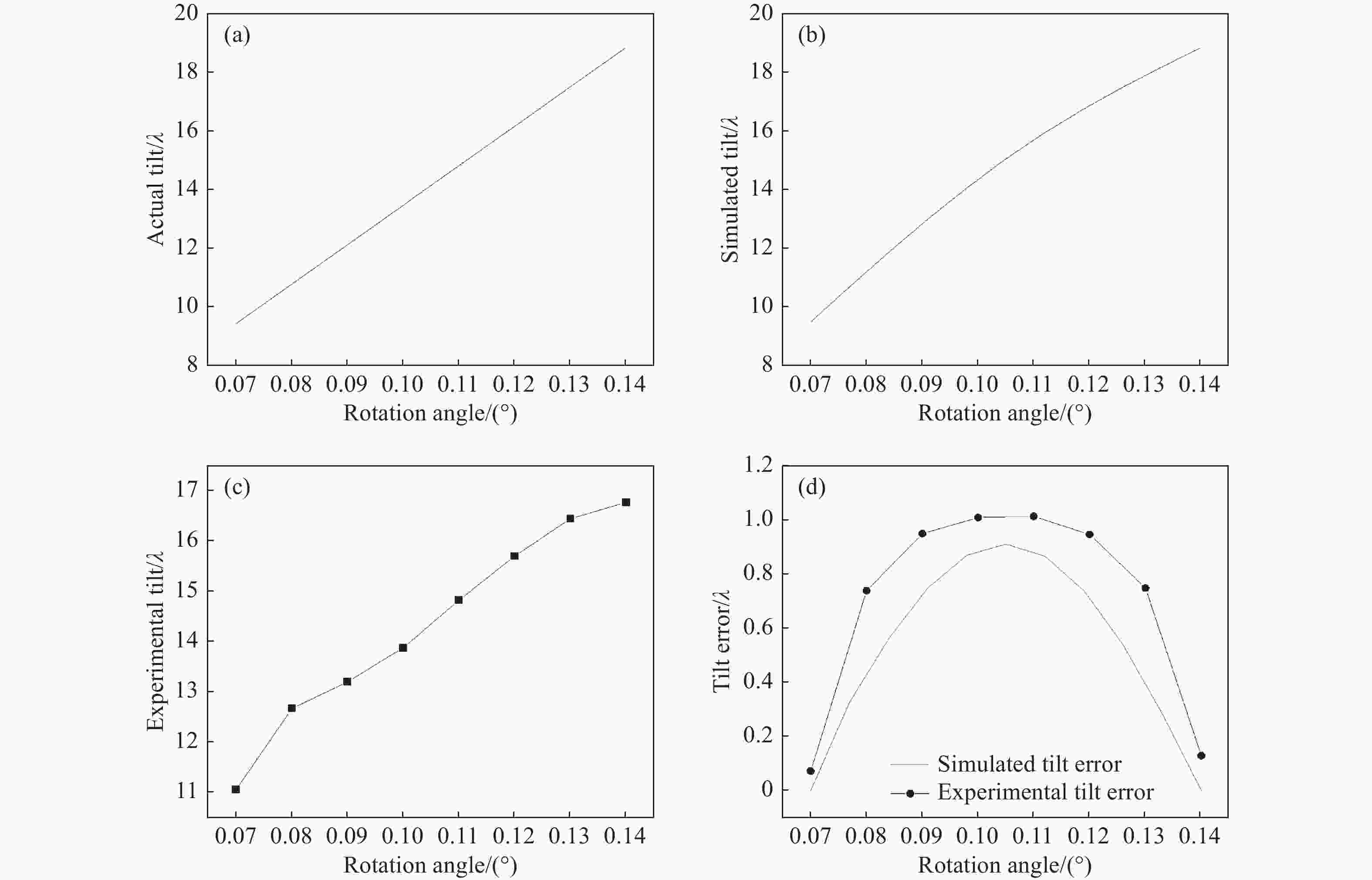
图 12 (a) 实际波前倾斜量与旋转角度的关系曲线;(b) 仿真波前倾斜量与旋转角度关系曲线;(c) 实验波前倾斜量与旋转角度关系曲线;(d) 波前倾斜误差曲线
Figure 12. (a) Relation curve between actual wavefront tilt and rotation angle; (b) relationship curve between simulated wavefront tilt and rotation angle; (c) relation curve between experimental wavefront tilt and rotation angle; (d) wavefront tilt error curve
-
[1] 姜文汉, 鲜浩, 杨泽平, 等. 哈特曼波前传感器的应用[J]. 量子电子学报,1998,15(2):228-235.JIANG W H, XIAN H, YANG Z P, et al. Applications of shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1998, 15(2): 228-235. (in Chinese) [2] ZAVALOVA V Y, KUDRYASHOV A V. Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor for laser beam analyses[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002, 4493: 277-284. doi: 10.1117/12.454723 [3] 程少园, 曹召良, 胡立发, 等. 用夏克-哈特曼探测器测量人眼波前像差[J]. 光学 精密工程,2010,18(5):1060-1067.CHENG SH Y, CAO ZH L, HU L F, et al. Measurement of wavefront aberrations of human eyes with Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(5): 1060-1067. (in Chinese) [4] OGANE H, AKIYAMA M, OYA S, et al. Atmospheric turbulence profiling with multi-aperture scintillation of a Shack–Hartmann sensor[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2021, 503(4): 5778-5788. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stab105 [5] XU L, WANG J, YAO K, et al. Application of the Gaussian modeling algorithm to a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor for daylight adaptive optics[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(17): 4196-4199. doi: 10.1364/OL.434941 [6] 苏鹏程, 陈宇, 张家铭, 等. 基于六边形紧密拼接结构的仿生复眼系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(4):20200338. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200338SU P CH, CHEN Y, ZHANG J M, et al. Design of bionic compound eye system based on hexagonal closely spliced structure[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(4): 20200338. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200338 [7] 程利群, 景文博, 王晓曼. 夏克-哈特曼波前传感器光斑质心探测方法比较与分析[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,37(3):23-26.CHENG L Q, JING W B, WANG X M. Comparison and analysis of shack-Hartmann wave-front sensor spot centroid detection methods[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2014, 37(3): 23-26. (in Chinese) [8] PRIETO P M, VARGAS-MARTÍN F, GOELZ S, et al. Analysis of the performance of the Hartmann–Shack sensor in the human eye[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2000, 17(8): 1388-1398. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.17.001388 [9] 李晶, 巩岩, 呼新荣, 等. 哈特曼-夏克波前传感器的高精度质心探测方法[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(3):0316002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0316002LI J, GONG Y, HU X R, et al. A high-precision centroid detecting method for Hartmann-shack wavefront sensor[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(3): 0316002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0316002 [10] 师亚萍, 刘缠牢. 提高夏克-哈特曼波前传感器光斑质心的定位精度[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(8):081201.SHI Y P, LIU CH L. Positioning accuracy improvement of spot centroid for shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(8): 081201. (in Chinese) [11] 李旭旭, 李新阳, 王彩霞. 哈特曼传感器子孔径光斑的局部自适应阈值分割方法[J]. 光电工程,2018,45(10):170699.LI X X, LI X Y, WANG C X. Local adaptive threshold segmentation method for subapture spots of shack-Hartmann sensor[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(10): 170699. (in Chinese) [12] BAIK S H, PARK S K, KIM C J, et al. A center detection algorithm for shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2007, 39(2): 262-267. [13] RUFFIEUX P, SCHARF T, HERZIG H P, et al. On the chromatic aberration of microlenses[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(11): 4687-4694. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.004687 [14] 韩妍娜, 胡新奇, 董冰. 一种扩大夏克-哈特曼波前传感器动态范围的迭代外推法[J]. 光学学报,2020,40(16):1611004. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.1611004HAN Y N, HU X Q, DONG B. Iterative extrapolation method to expand dynamic range of shack-Hartmann wavefront sensors[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(16): 1611004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.1611004 [15] WANG K, XU K F. A review on wavefront reconstruction methods[C]. 2021 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Aided Education, Association for Computing Machinery, 2021: 1528-1531. [16] PRIMOT J. Theoretical description of Shack–Hartmann wave-front sensor[J]. Optics Communications, 2003, 222(1-6): 81-92. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(03)01565-7 [17] 刘逸天, 陈琦凯, 唐志远, 等. 超表面透镜的像差分析和成像技术研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(4):831-850. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0014LIU Y T, CHEN Q K, TANG ZH Y, et al. Research progress of aberration analysis and imaging technology based on metalens[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 831-850. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0014 [18] 夏明亮. 高精度人眼像差哈特曼探测器的研制[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院(长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2011.XIA M L. The development of high precision Hartmann wavefront detector for eye aberration[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2011. (in Chinese) [19] JOHNSON T P, SASIAN J. Zernike monomials in wide field of view optical designs[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(22): G146-G153. doi: 10.1364/AO.392305 [20] LAKSHMINARAYANAN V, FLECK A. Zernike polynomials: a guide[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2011, 58(7): 545-561. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2011.554896 [21] 李建聪, 林宏安, 罗佳雄, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(4):761-769. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0018LI J C, LIN H A, LUO J X, et al. Optical design of space gravitational wave detection telescope[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(4): 761-769. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0018 -






 下载:
下载: