-
摘要:
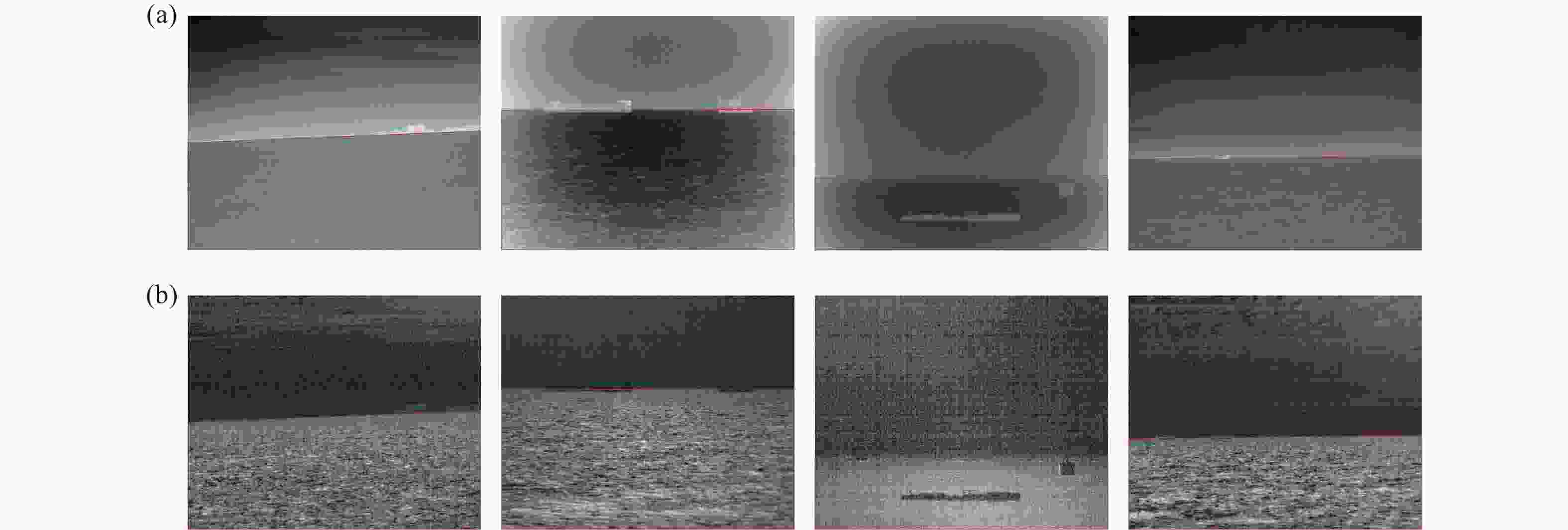
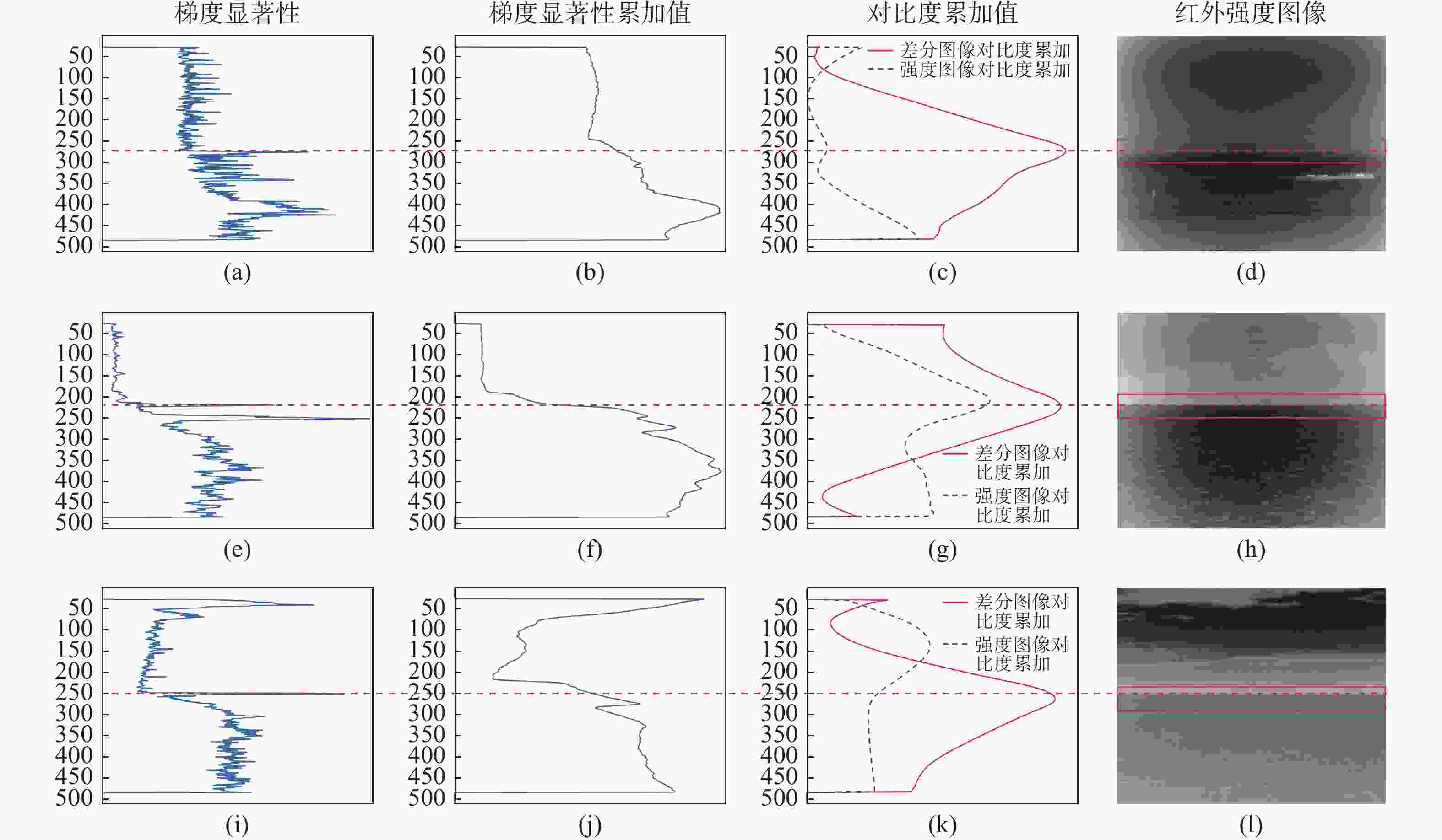
针对低对比度红外图像中海天线检测困难,且易受云层、条状波浪和海杂波等干扰因素影响的问题,提出了一种采用偏振差分图像进行海天线检测的方法。首先,利用偏振差分方法增强海面区域的局部对比度和海天线的信噪比;其次,对偏振差分图像采用大尺度的局部对比度累加方法确定海天线区域;最后,在海天线区域中采用梯度显著性及多项式拟合方法完成小尺度的海天线精确检测。该方法将偏振度、偏振角等多维信息融入海天线检测,并采用了大尺度与小尺度相结合的检测方法,能够有效克服云层、条状波浪和海杂波等因素的干扰。实验结果表明该算法的海天线检测准确率为98.5%,平均耗时16 ms,能够实现快速、准确的海天线检测,具有较强的场景适用性。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of sea-sky-line detection in low-contrast infrared images being difficult and easily affected by interference factors such as clouds, strip waves and sea clutter, we propose a method of using polarization difference images for sea-sky-line detection. Firstly, Polarization Difference Imaging (PDI) is used to enhance the local contrast of the sea surface area and the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of the sea-sky-line. A large-scale local contrast accumulation method of the polarization difference images is then used to determine the sea-sky-line area. Finally, the accurate detection of a small-scale sea-sky-line is completed by combining the gradient significance and polynomial fitting in the sea-sky-line area. Overall, the methodology integrates multi-dimensional information such as the Degree of Linear Polarization (DOLP) and the Angle of Polarization (AOP) for sea-sky-line detection, and combines large-scale and small-scale detection, which can effectively overcome interference of factors such as clouds, strip waves and sea clutter. The experimental results show that the accuracy of this algorithm for sea-sky-line detection is 98.5%, and the average time consumed is 16 ms. The experimental results indicate that the proposed algorithm can realize fast and accurate sea-sky-line detection so it has wide applicability in different scenes.
-
Key words:
- polarization difference /
- sea-sky-line detection /
- low contrast /
- gradient saliency /
- infrared imaging
-
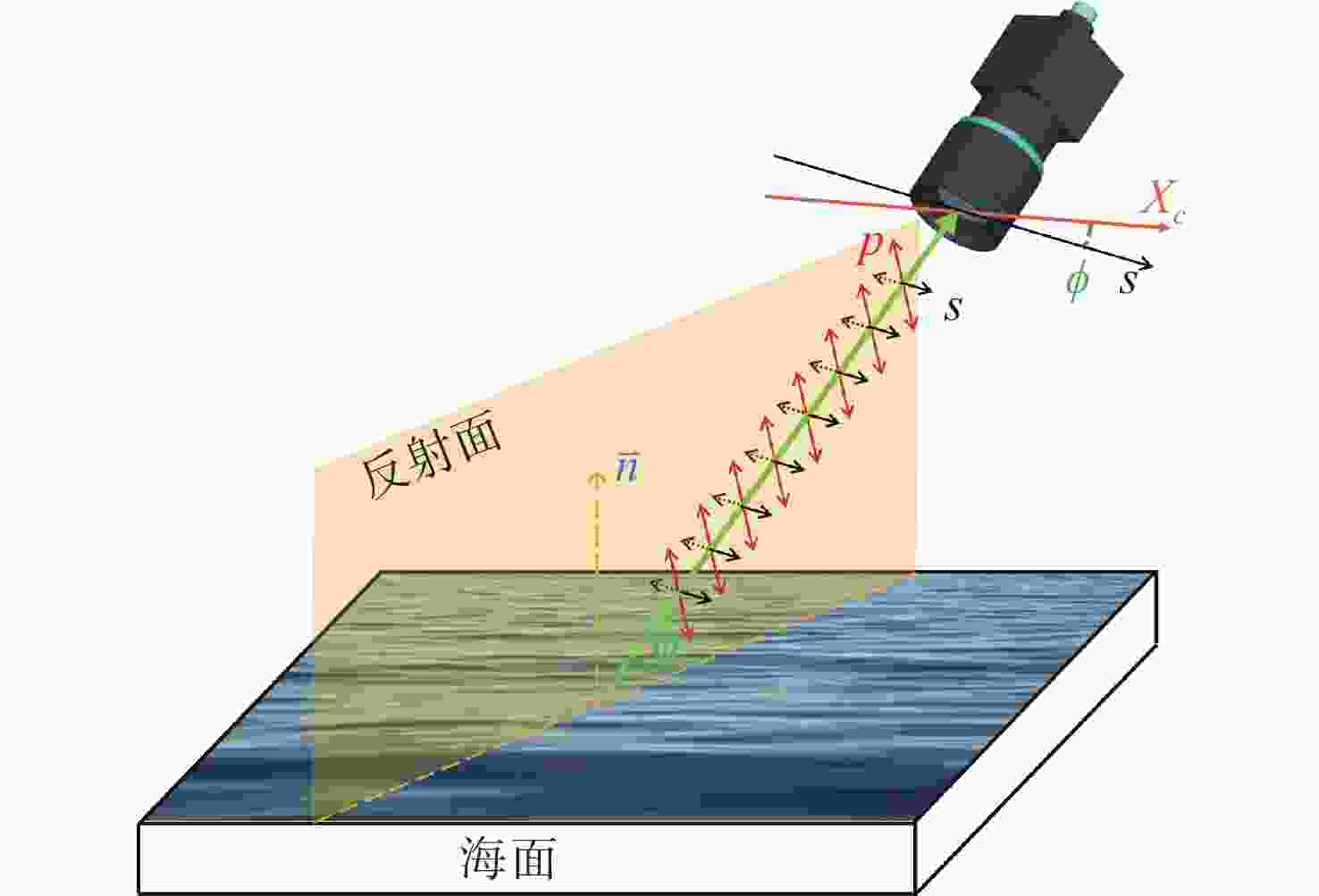
图 2 海面长波红外辐射偏振成像原理(图中
$\phi $ 为滚动角,$\varphi $ 为俯仰角,$s,p$ 分别表示$s$ 偏振和$p$ 偏振,${X_c}$ 为相机水平轴)Figure 2. Polarization imaging principle of sea surface radiation in long wave infrared band (
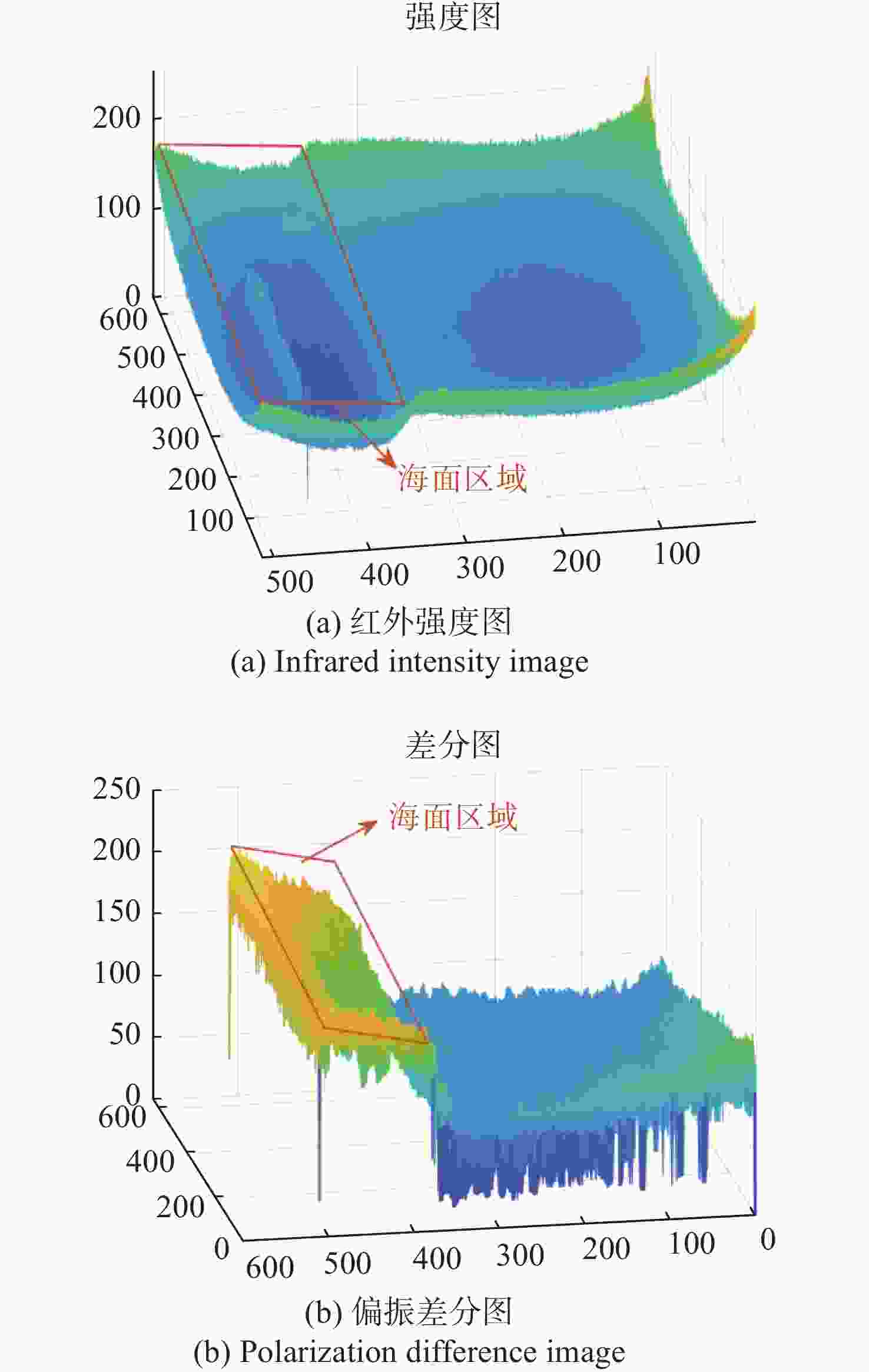
$\phi $ and$\varphi $ are the roll angle and pitch angle respectively;$s$ and$p$ are represent the s-polarized and p-polarized components respectively;${X_c}$ represents the horizontal axis of the camera)表 1 红外强度图像与偏振差分图像的LC和SNR
Table 1. The LCs and SNRs of infrared intensity image and polarization difference image
评价指标 图像类型 场景1 场景2 场景3 场景4 LC 强度图像 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.04 差分图像 0.33 0.32 0.28 0.29 SNR 强度图像 0.49 0.72 0.27 0.38 差分图像 1.03 1.46 0.96 0.95 表 2 不同方法性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison results by different methods
指标 霍夫变换 梯度方法+
多项式拟合累加方法+
多项式拟合本文方法 准确率(%) 36.9 87.7 95.4 98.5(128组) 平均耗时(ms) 91 102 112 16 -
[1] 冯天伟, 刘金清, 肖金超, 等. 海天线检测方法研究综述[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(16):160002.FENG T W, LIU J Q, XIAO J CH, et al. Sea-sky line detection methods: an overview[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(16): 160002. (in Chinese) [2] 韩嘉隆, 毛征, 王宁, 等. 基于二维OTSU的海天分界线提取算法[J]. 国外电子测量技术,2016,35(8):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2016.08.015HAN J L, MAO ZH, WANG N, et al. Algorithm for sea-sky-line extraction based on two-dimension OTSU[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2016, 35(8): 67-70. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2016.08.015 [3] 张志祥, 王秋萍, 朱旭芳, 等. 基于场景划分的海天线检测方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(8):61-66.ZHANG ZH X, WANG Q P, ZHU X F, et al. Sea-sky line detection method based on scene division[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2020, 48(8): 61-66. (in Chinese) [4] 戴永寿, 刘博文, 李立刚, 等. 基于局部Otsu分割与Hough变换的海天线检测[J]. 光电工程,2018,45(7):180039.DAI Y SH, LIU B W, LI L G, et al. Sea-sky-line detection based on local Otsu segmentation and Hough transform[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(7): 180039. (in Chinese) [5] KONG X Y, LIU L, QIAN Y SH, et al. Automatic detection of sea-sky horizon line and small targets in maritime infrared imagery[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2016, 76: 185-199. [6] 徐良玉, 马录坤, 谢燮, 等. 基于结构森林边缘检测和Hough变换的海天线检测[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版),2017,23(1):47-55.XU L Y, MA L K, XIE X, et al. Sea-sky line detection based on structured forests edge detection and Hough transform[J]. Journal of Shanghai University (Natural Science), 2017, 23(1): 47-55. (in Chinese) [7] 曾文静, 万磊, 张铁栋, 等. 基于海面可见光图像的海界线快速检测[J]. 光学学报,2012,32(1):0111001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.0111001ZENG W J, WAN L, ZHANG T D, et al. Fast detection of sea line based on the visible characteristics of marine images[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(1): 0111001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.0111001 [8] 王博, 苏玉民, 万磊, 等. 基于梯度显著性的水面无人艇的海天线检测方法[J]. 光学学报,2016,36(5):0511002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0511002WANG B, SU Y M, WAN L, et al. Sea sky line detection method of unmanned surface vehicle based on gradient saliency[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(5): 0511002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0511002 [9] WANG B, SU Y M, WAN L. A sea-sky line detection method for unmanned surface vehicles based on gradient saliency[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(4): 543. doi: 10.3390/s16040543 [10] 董宇星, 刘伟宁. 基于灰度特性的海天背景小目标检测[J]. 中国光学与应用光学,2010,3(3):252-256.DONG Y X, LIU W N. Detection of sea-sky line in complicated background based on grey characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics, 2010, 3(3): 252-256. (in Chinese) [11] 刘士建, 吴滢跃, 蔡能斌. 低SNR海天线提取算法[J]. 红外与激光工程,2013,42(12):3491-3495. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.12.059LIU SH J, WU Y Y, CAI N B. Novel low-SNR sea-sky-line extraction algorithm[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(12): 3491-3495. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.12.059 [12] 李林丰, 田甜, 沙漠洲, 等. 基于局部熵滤波和梯度累积的海天线检测方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(11):47-52.LI L F, TIAN T, SHA M ZH, et al. Sea-sky line detection method based on local entropy filtering and gradient accumulation[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2021, 49(11): 47-52. (in Chinese) [13] 林昌. 大雾下海上图像的目标分离与智能辨识研究[D]. 厦门: 集美大学, 2021.LIN CH. Research on target separation and intelligent recognition of maritime images under fog[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2021. (in Chinese) [14] 宫剑, 吕俊伟, 刘亮, 等. 红外偏振图像的舰船目标检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(2):586-594.GONG J, LÜ J W, LIU L, et al. Ship target detection based on infrared polarization image[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(2): 586-594. (in Chinese) [15] 宫剑, 吕俊伟, 刘亮, 等. 红外偏振舰船目标自适应尺度局部对比度检测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(1):223-233. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0223GONG J, LV J W, LIU L, et al. Adaptive scale local contrast detection for infrared polarization ship targets[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(1): 223-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0223 [16] 赵如雪. 基于偏振差分成像的浑浊介质中目标检测方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2020.ZHAO R X. Research on target detection method in turbid media based on polarization difference imaging[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [17] 张玉鑫. 基于全偏振信息探测的海空背景图像去雾关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020.ZHANG Y X. Research on key technologies of haze removal of sea-sky background image based on full polarization information detection[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2020. (in Chinese) [18] 汪杰君, 梁磊, 李树, 等. 水下目标偏振差分成像模型修正与实现[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(11):1111003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1111003WANG J J, LIANG L, LI SH, et al. Correction and implementation of polarization-difference imaging model for underwater target[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(11): 1111003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1111003 [19] 韩裕生, 周浦城, 乔延利, 等. 基于最小互信息的自适应偏振差分成像方法[J]. 红外与激光工程,2011,40(3):487-491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2011.03.022HAN Y SH, ZHOU P CH, QIAO Y L, et al. Adaptive polarization difference imaging approach based on minimum mutual information[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2011, 40(3): 487-491. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2011.03.022 [20] 宿德志, 刘亮, 吴世永, 等. 辐射耦合效应对目标红外偏振特性的影响[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(2): 318-328.SU D ZH, LIU L, WU SH Y, et al. . Influence of radiation coupling effect on polarization characteristics of targets[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 318-328. (in Chinese) [21] 柳祎, 史浩东, 姜会林, 等. 粗糙目标表面红外偏振特性研究[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(3):459-471. doi: 10.3788/CO.2019-0123LIU Y, SHI H D, JIANG H L, et al. Infrared polarization properties of targets with rough surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(3): 459-471. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.2019-0123 [22] LIU H ZH, SHI Z L, FENG B. An infrared DoLP computational model considering surrounding irradiance[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2019, 106: 103043. [23] 王琪, 梁静秋, 梁中翥, 等. 分孔径红外偏振成像仪光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(1):92-99. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181101.0092WANG Q, LIANG J Q, LIANG ZH ZH, et al. Design of decentered aperture-divided optical system of infrared polarization imager[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(1): 92-99. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20181101.0092 [24] 张景华. 基于红外偏振信息的海面杂波抑制及舰船目标识别技术[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2018.ZHANG J H. Research on sea clutter suppression and ship target detection based on infrared polarization information[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018. (in Chinese) [25] 张景华, 张焱, 石志广. 基于长波红外的海面场景偏振特性分析与建模[J]. 红外与毫米波学报,2018,37(5):586-594. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.05.011ZHANG J H, ZHANG Y, SHI ZH G. Study and modeling of infrared polarization characteristics based on sea scene in long wave band[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2018, 37(5): 586-594. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2018.05.011 [26] ZHANG J H, ZHANG Y, SHI ZH G. Long-wave infrared polarization feature extraction and image fusion based on the orthogonality difference method[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2018, 27(2): 023021. [27] COOK R L, TORRANCE K E. A reflectance model for computer graphics[J]. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1981, 15(3): 307-316. doi: 10.1145/965161.806819 [28] 仇荣超, 吕俊伟, 宫剑, 等. 前视红外图像中海岸线与海天线的通用检测方法研究[J]. 兵工学报,2019,40(6):1171-1178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.06.007QIU R CH, LÜ J W, GONG J, et al. Research on general detection method of coastline and sea-sky line in FLIR Image[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(6): 1171-1178. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.06.007 [29] 杨章含, 曾培峰. 基于MSER的弹孔识别算法的研究[J]. 信息技术与网络安全,2019,38(3):24-29.YANG ZH H, ZENG P F. A research on bullet holes recognition algorithm based on MSER[J]. Information Technology and Network Security, 2019, 38(3): 24-29. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: