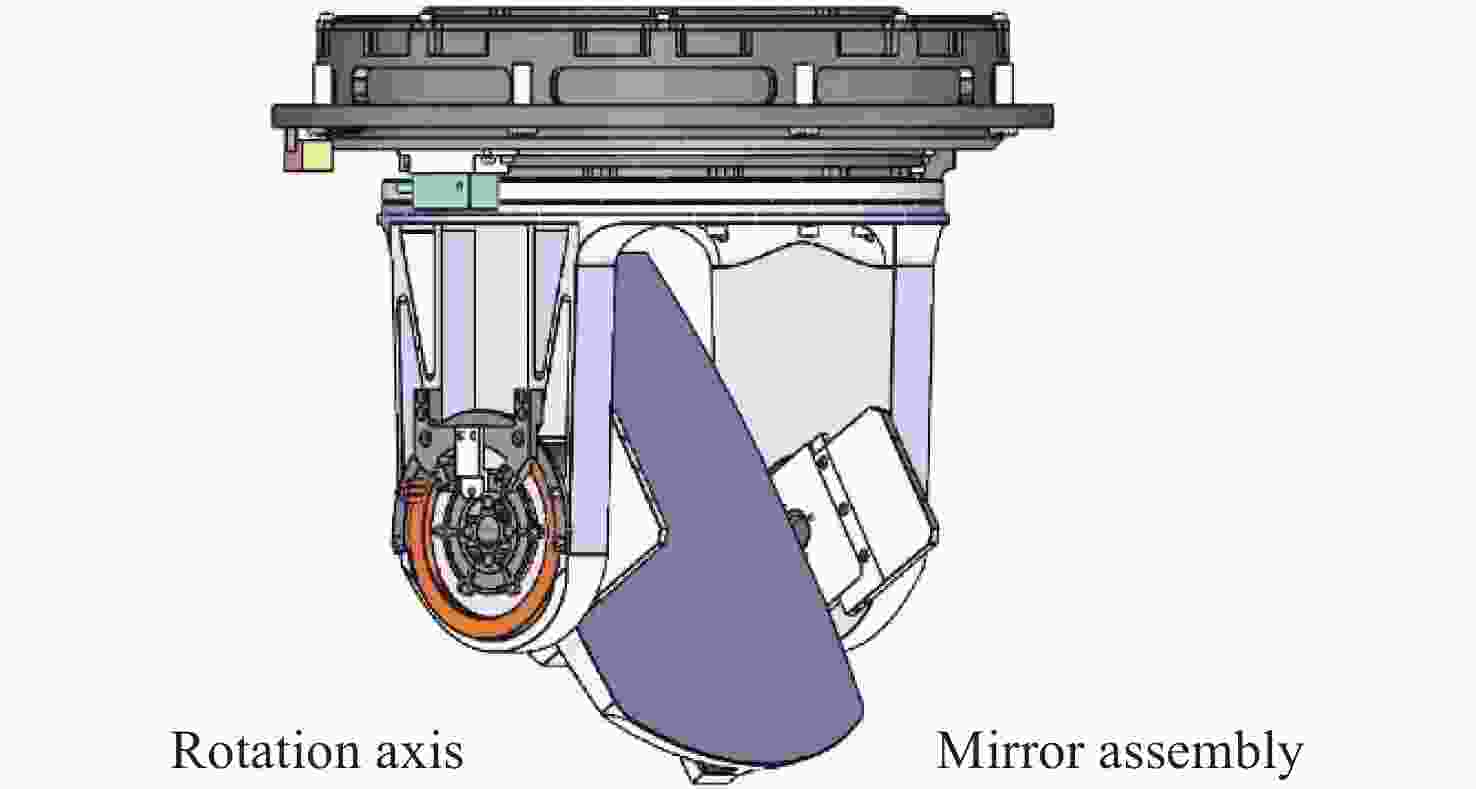
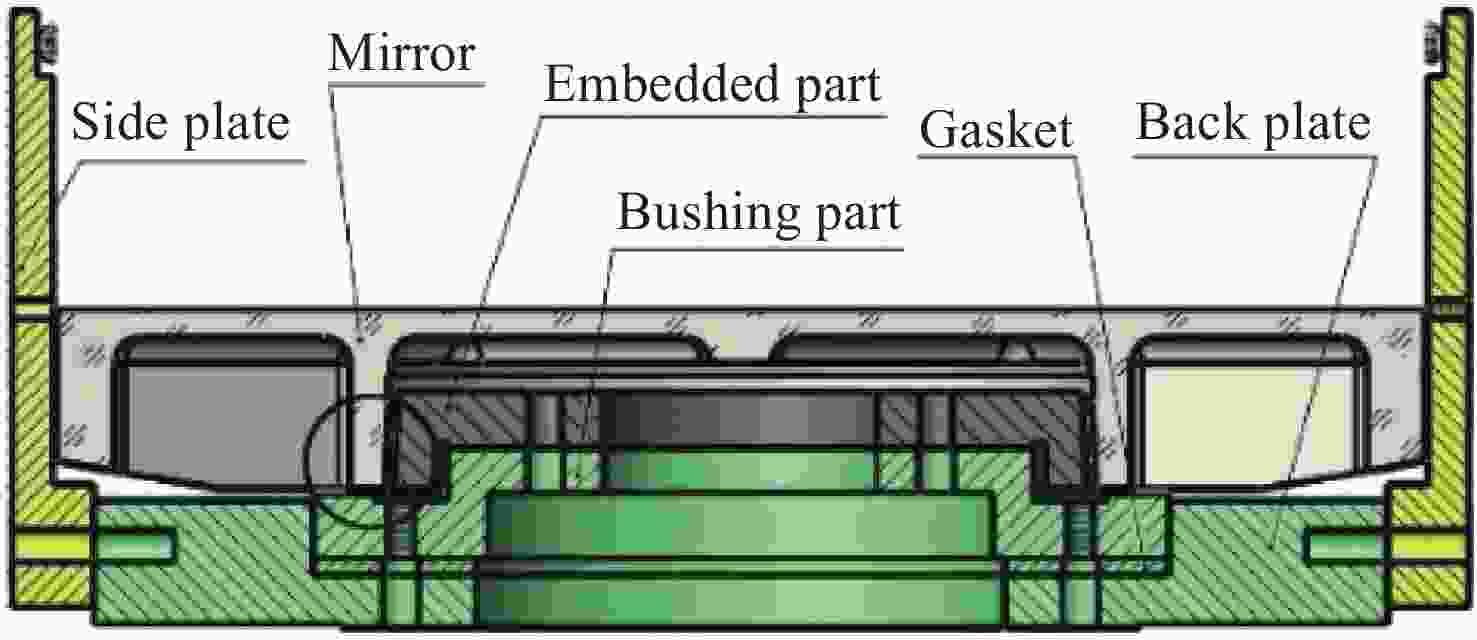
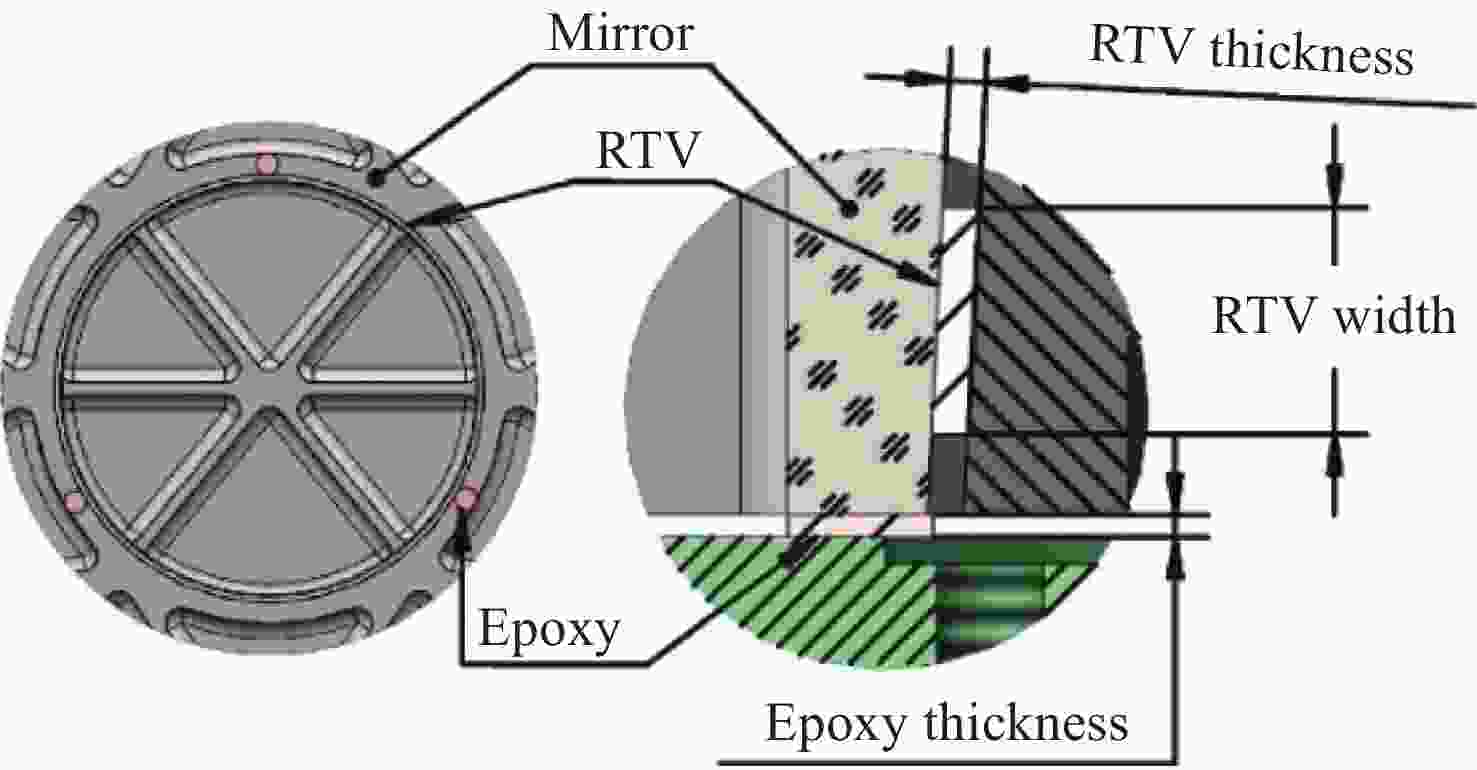
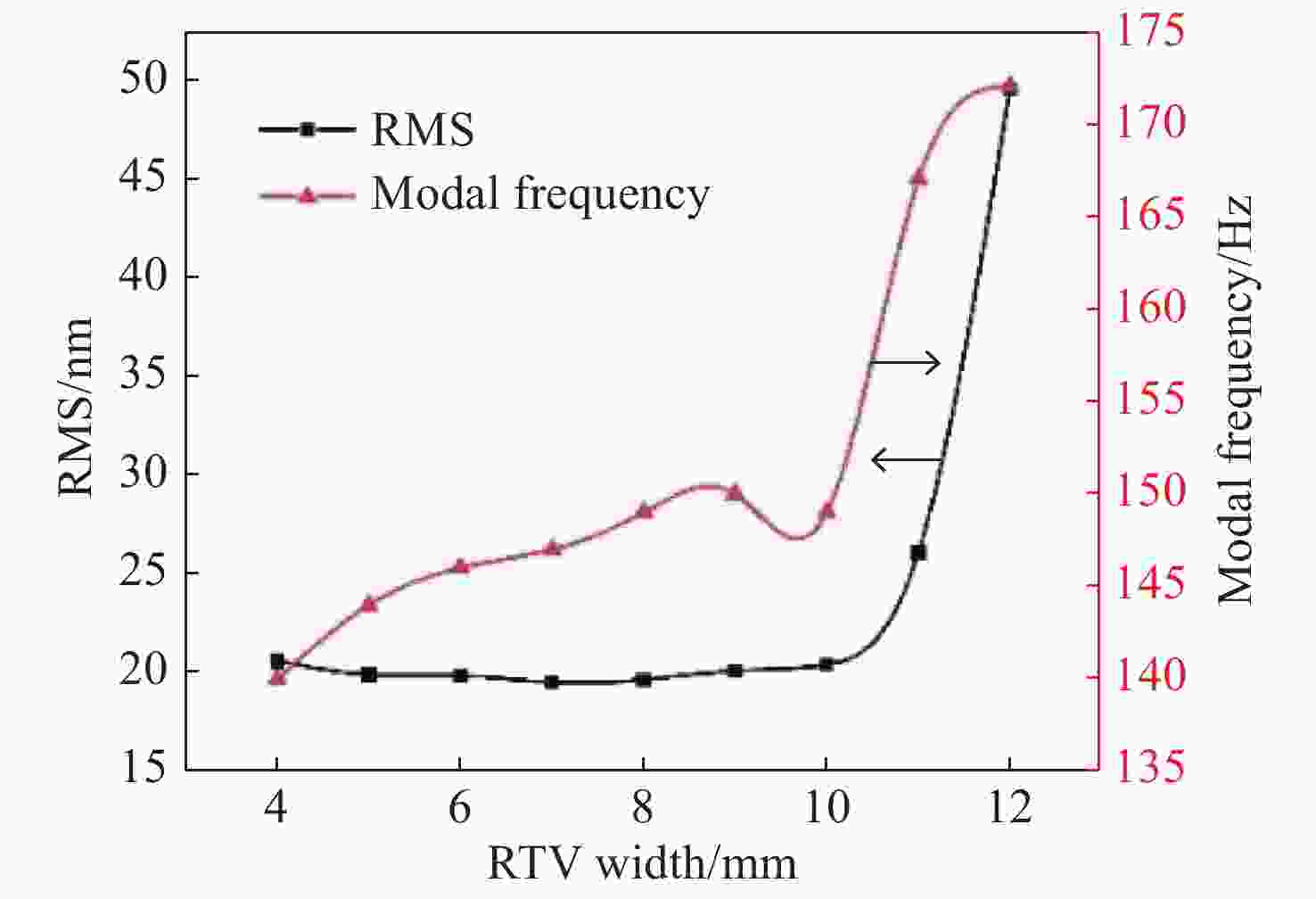
Design of reflector assembly and adhesive layer under airborne wide temperature conditions
-
摘要:
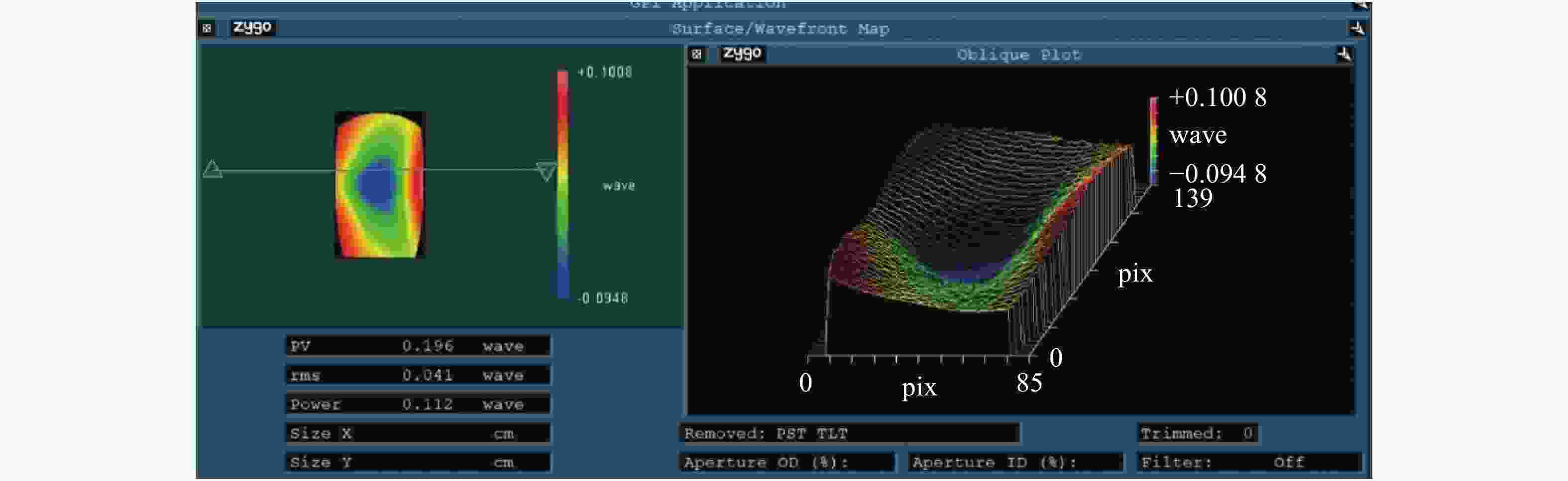
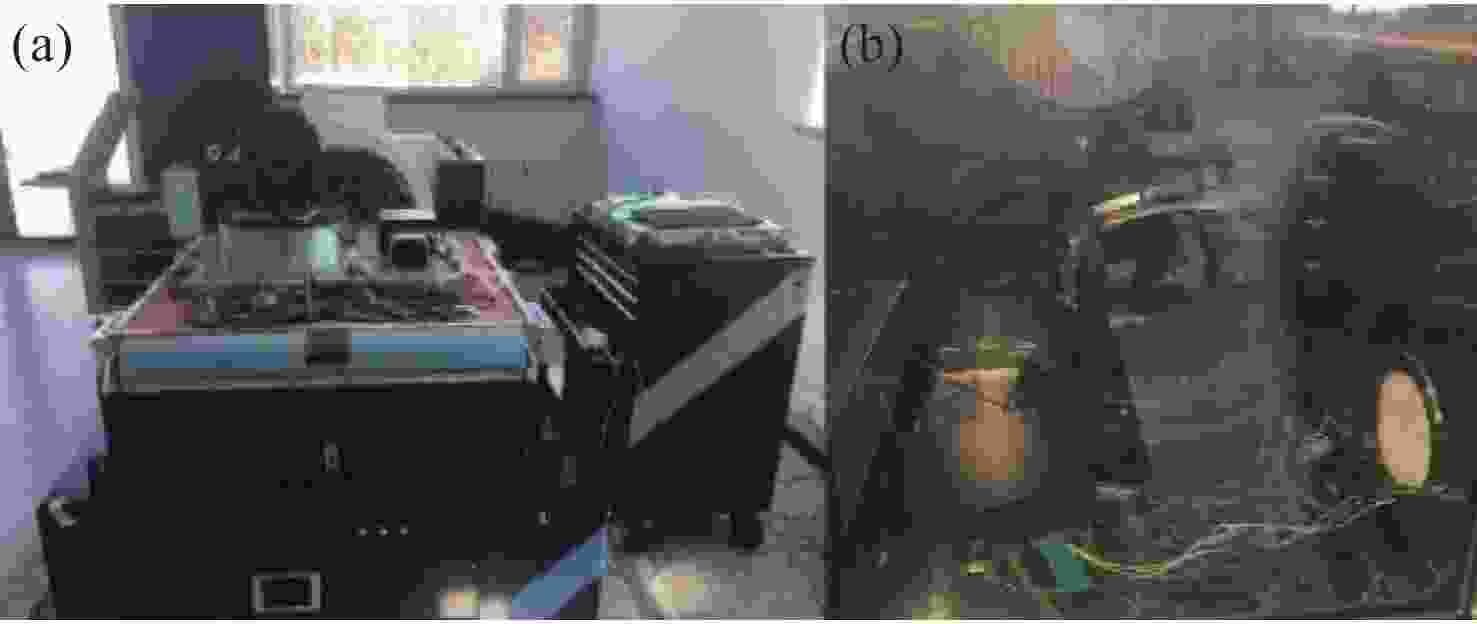
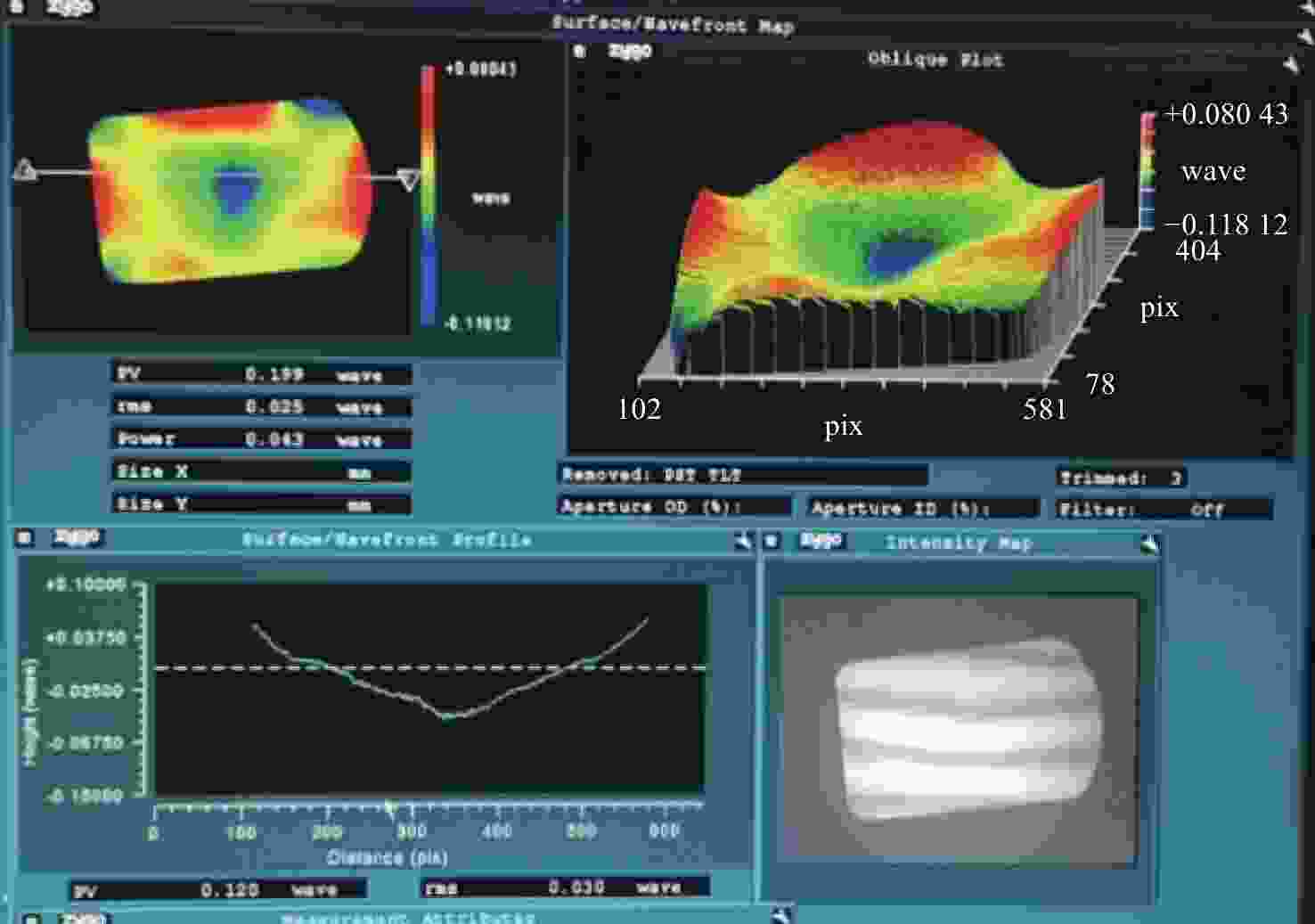
在机载宽温且反射镜镀膜温度较高的条件下,针对传统反射镜镶嵌件粘接工艺导致反射镜粘接失效、铟钢镶嵌件和反射镜线胀系数差异导致宽温下反射镜面型急剧下降的问题,提出了一种反射镜加工镀膜后再粘接镶嵌件的方法,并对其胶层参数进行研究。采用硅橡胶作为主粘接剂粘接反射镜与镶嵌件,利用硅橡胶固化后良好的弹性缓解支撑件热变形对反射镜面型的影响。通过多目标优化选取合适的硅橡胶粘接厚度1.1 mm,硅橡胶宽度7.2 mm,环氧胶厚度0.022 mm。仿真结果显示在重力及温度变化为−40 °C时(初始温度为20 °C),反射镜面型精度RMS值为25.91 nm,镜组模态一阶频率为242 Hz。最终面型检测RMS值为15.8 nm,结构谐振频率为213 Hz。试验结果显示,此方案使反射镜组件适用于大温差条件下工作,其结构和粘接层设计能够满足机载宽温和振动条件下的使用要求。
Abstract:Airborne ambient temperature varies widely and airborne vibration can be strong. Because there is a difference in the thermal expansion coefficients of an Invar inlay and mirror material, a mirror’s higher coating temperature means that the traditional bonding process will lead to bonding failure and the surface precision of the mirror cannot meet system requirements. Therefore, this paper proposes a new method of bonding the mirror after processing and coating, and designs some important parameters for the adhesive layer. RTV is used as the main binder for the mirror and the inlay, and the effect of RTV curing on the structure is alleviated by favorable elasticity. The thickness of RTV is 1.1 mm, its width is 7.2 mm and the thickness of the epoxy adhesive is 0.022 mm. The simulation results show that the RMS of the mirror shape is 25.91 nm and the first-order frequency of the mirror group mode is 242 Hz when the gravity is 1 g and temperature change are −40 °C (the initial temperature is 20 °C). The final surface detection RMS is 15.8 nm and the resonance frequency is 213 Hz. The experimental results show that the design, structure and bonding layer can meet the wide temperature range and vibration requirements.
-
表 1 反射镜组件材料表
Table 1. List of materials for mirror assemblies
Structure Material Density
ρ/(g·cm−3)Young's modulus
E/GPaCTE
α(10−6/K)Thermal conductivity
λ/[W/(m·k)]Specific stiffness
E/ρ(10−6·GNm/g)Thermal distortion ratio
λ/α(106W/m)mirror SiC 3.2 450 2.3 155.00 140 64.58 back plate, side plate,
bushing part, embedded
part, gasket4J32 8.1 150 2.5 145.00 18.5 11 表 2 5种工况下反射镜面型拟合结果
Table 2. Shape fitting results of the mirror under five working conditions
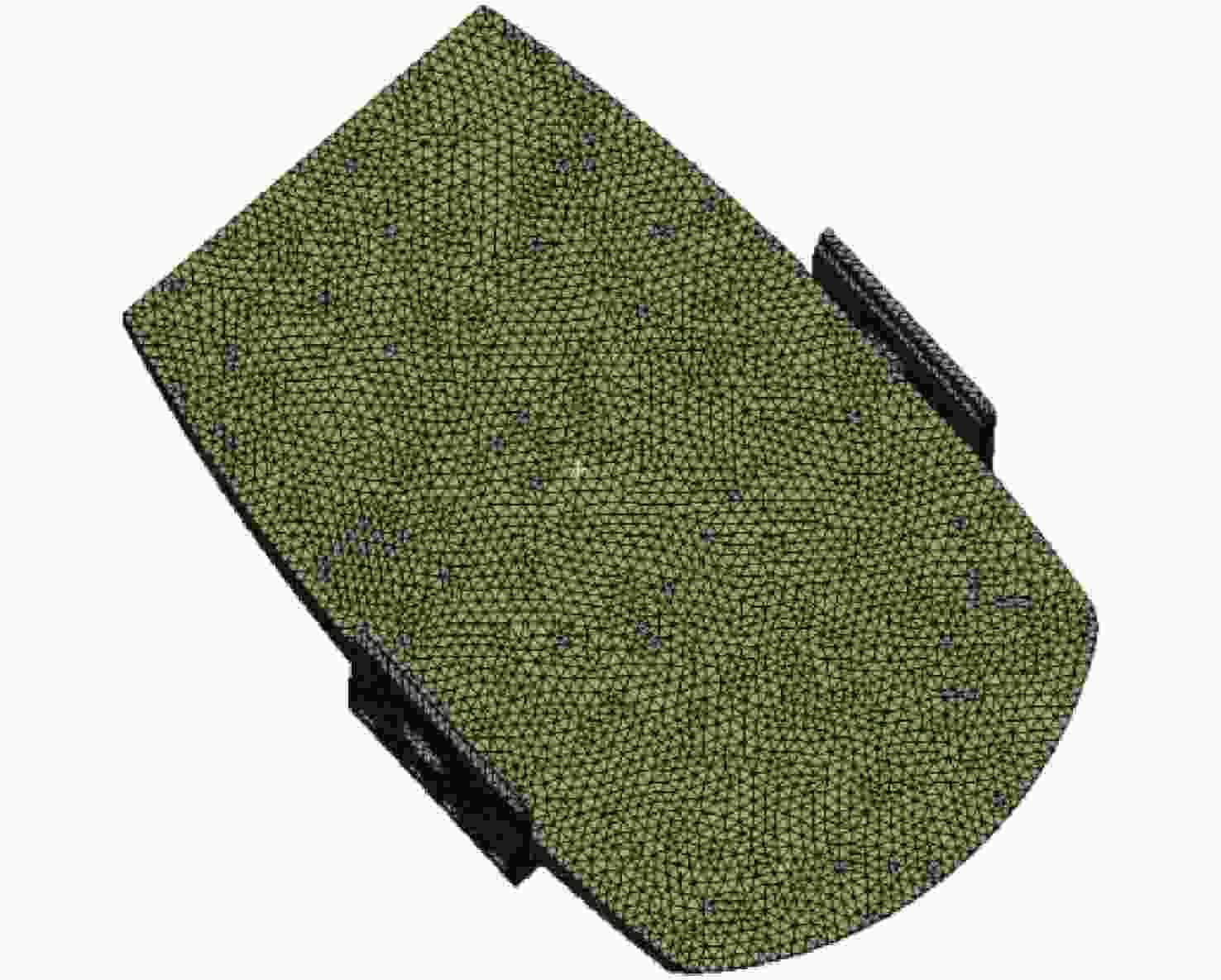
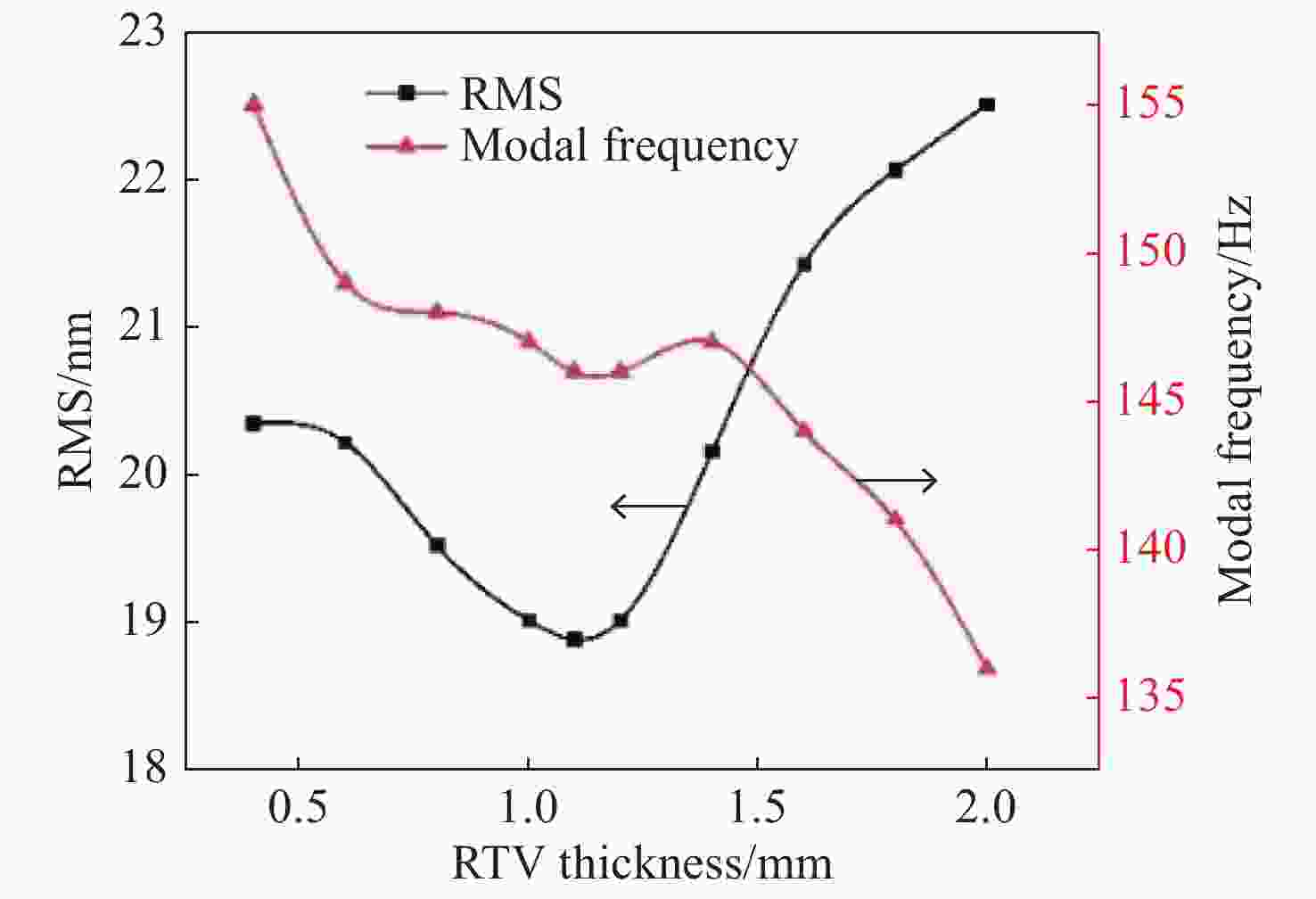
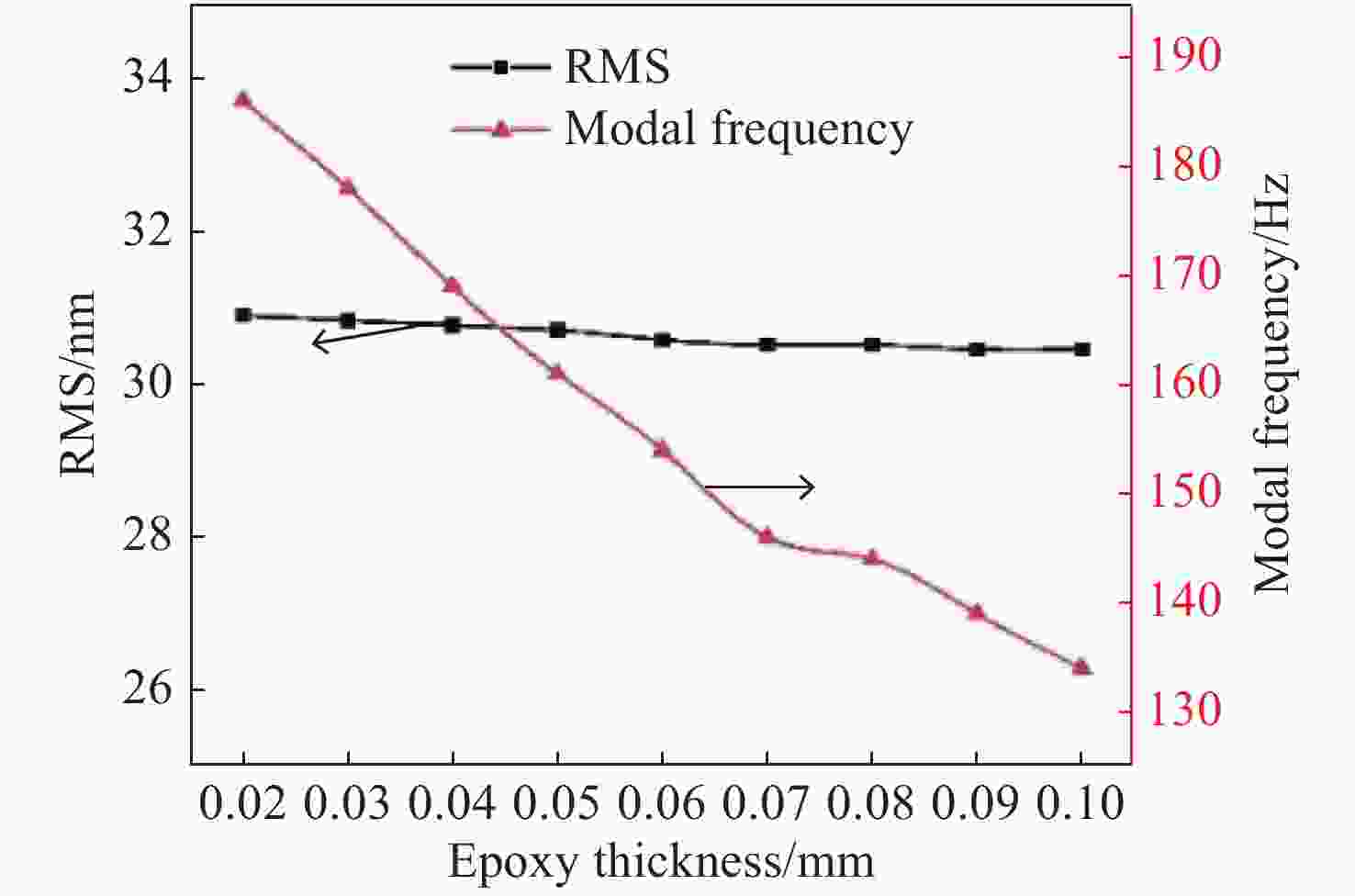
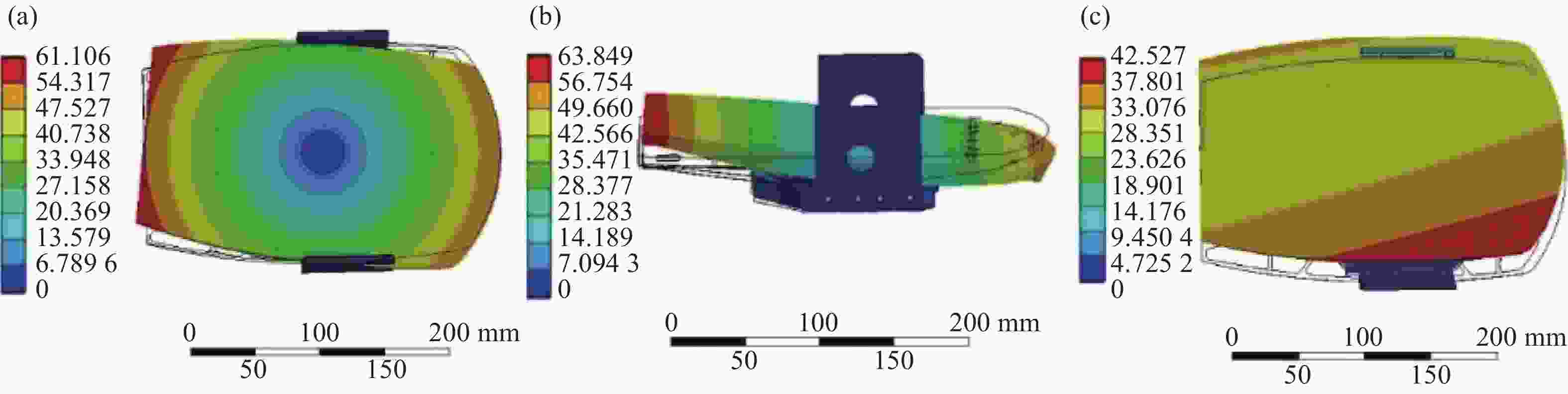
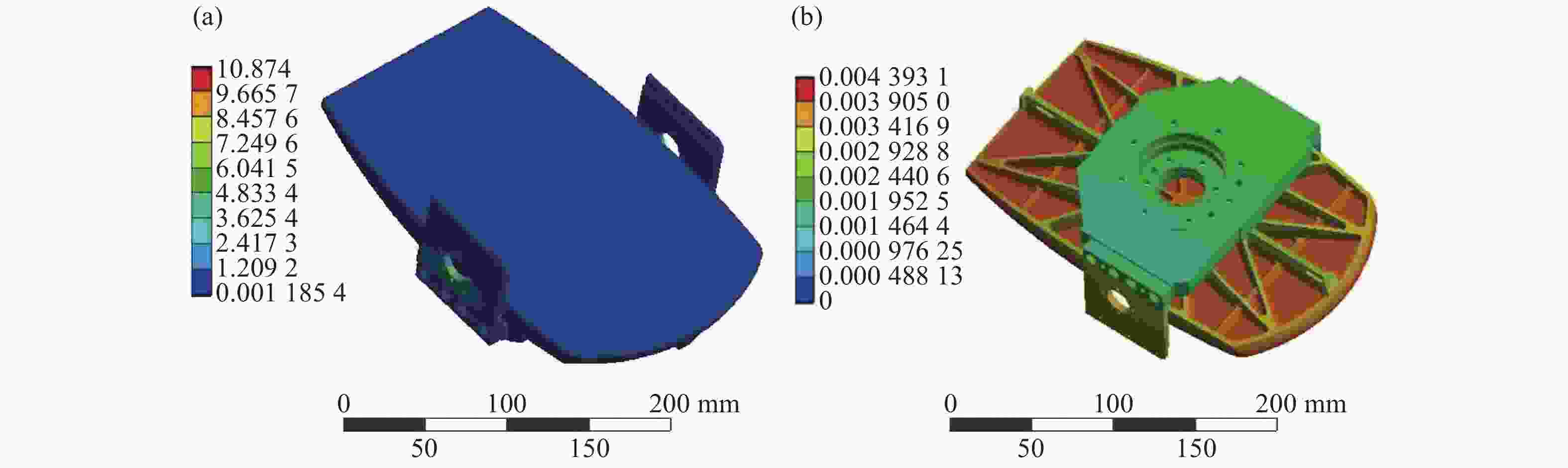
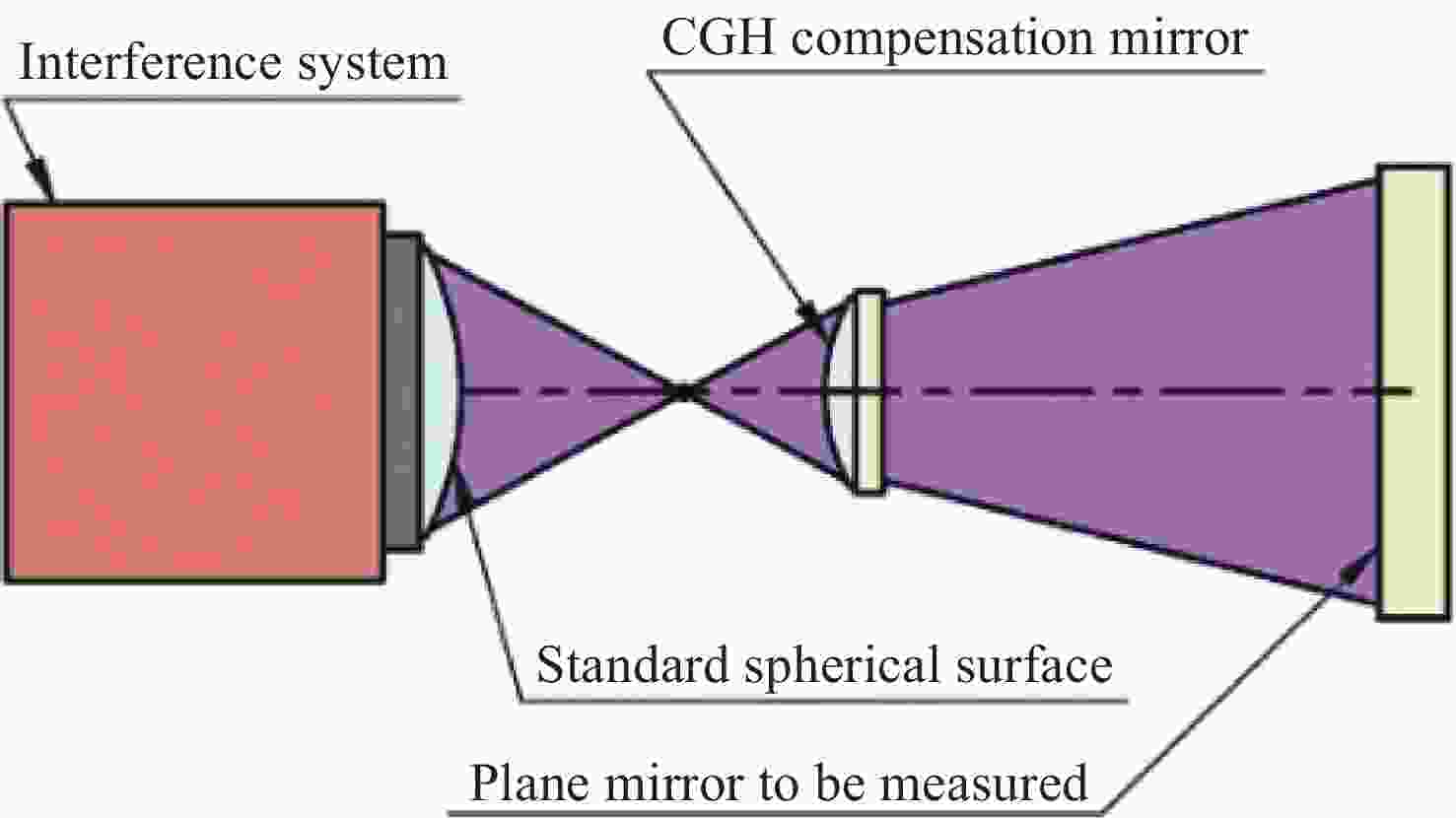
环境温度 20 °C 20 °C 20 °C -40 °C 60 °C 重力方向 X轴 Y轴 Z轴 Z轴 Z轴 PV值/nm 25.91 22.12 55.45 123.87 96.78 RMS值/nm 3.73 3.63 10.25 25.91 17.55 -
[1] 张美君. 航空相机反射镜支撑结构优化设计及环境适应性分析[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2022.ZHANG M J. Optimal design and environmental adaptability analysis for mounting mirror in an aerial camera[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. (in Chinese) [2] KIM H, YANG H S. Design optimization of a 1-m lightweight mirror for a space telescope[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52(9): 091806. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.9.091806 [3] WEINGROD I, CHOU C Y, HOLMES B, et al. Design of bipod flexure mounts for the IRIS spectrometer[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8836: 88360Q. doi: 10.1117/12.2024478 [4] EKINCI M, SELIMOĞLU Ö. Development of a 0.5 m clear aperture cassegrain type collimator telescope[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9912: 991253. [5] 范磊, 张景旭, 赵勇志, 等. 中型主镜的柔性半运动学支撑[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(8):1965-1972. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162408.1965FAN L, ZHANG J X, ZHAO Y ZH, et al. Flexible semi-kinematic support for middling primary mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(8): 1965-1972. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162408.1965 [6] 丁帅. 机载红外小目标探测系统非均匀性校正技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2021.DING SH. Research on non-uniformity correction technology of airborne infrared small target detection system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese) [7] 邵梦旗, 张雷, 李林, 等. 超轻空间相机主支撑背板的优化设计[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(3):0322001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0322001SHAO M Q, ZHANG L, LI L, et al. Optimization design of supporting backplate for ultra-light space camera[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(3): 0322001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0322001 [8] 陈家照, 黄闽翔, 王学仁, 等. 几种典型的橡胶材料本构模型及其适用性[J]. 材料导报,2015,29(S1):118-120,124.CHEN J ZH, HUANG M X, WANG X R, et al. Typical constitutive models of rubber materials and their ranges of application[J]. Materials Review, 2015, 29(S1): 118-120,124. (in Chinese) [9] 庞文武, 陈炳耀, 陈德启, 等. 脱醇型室温硫化硅橡胶的粘接性能研究[J]. 有机硅材料,2022,36(1):57-60. doi: 10.11941/j.issn.1009-4369.2022.01.012PANG W W, CHEN B Y, CHEN D Q, et al. Study on the adhesive properties of dealcoholized RTV silicone rubber[J]. Silicone Material, 2022, 36(1): 57-60. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11941/j.issn.1009-4369.2022.01.012 [10] 杨亮, 李朝辉, 乔克. 某空间反射镜支撑装调技术[J]. 红外与激光工程,2013,42(12):3277-3282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.12.022YANG L, LI ZH H, QIAO K. Support structure and assembling technique of a space mirror[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2013, 42(12): 3277-3282. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2013.12.022 [11] 张琦, 时剑文, 索双富, 等. 基于Mooney-Rivlin模型和Yeoh模型的橡胶材料有限元分析[J]. 合成橡胶工业,2020,43(6):468-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1255.2020.06.006ZHANG Q, SHI J W, SUO SH F, et al. Finite element analysis of rubber materials based on Mooney-Rivlin models and Yeoh models[J]. China Synthetic Rubber Industry, 2020, 43(6): 468-471. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1255.2020.06.006 [12] 韩旭, 吴清文, 董得义, 等. 室温硫化胶层建模在透镜结构分析中的应用[J]. 光学 精密工程,2010,18(1):118-125.HAN X, WU Q W, DONG D Y, et al. Application of RTV adhesive modeling to structure analysis of reflective mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(1): 118-125. (in Chinese) [13] 崔永鹏, 何欣, 张凯. 钛合金和碳纤维的粘接技术[J]. 光学技术,2012,38(1):125-128. doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2012.01.020CUI Y P, HE X, ZHANG K. Technique of cementation between the titanium alloys and carbon fibers[J]. Optical Technique, 2012, 38(1): 125-128. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2012.01.020 [14] 刘波, 丁亚林, 贾继强, 等. 反射镜背部嵌套粘接支撑结构的设计与分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2013,50(9):091201.LIU B, DING Y L, JIA J Q, et al. Design and analysis of back embedded adhesive structure for mirror support[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2013, 50(9): 091201. (in Chinese) [15] 孙冬明, 潘栋, 刘宏旭, 等. 胶层厚度对多点支撑光窗面形的影响[J]. 激光与红外,2021,51(4):480-485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2021.04.013SUN D M, PAN D, LIU H X, et al. Influence of adhesive layer thickness on surface shape of multi-point supported light window[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2021, 51(4): 480-485. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2021.04.013 [16] 付佐红, 董高彬, 程驰青, 等. 天线随机振动分析与设计优化[J]. 雷达与对抗,2022,42(1):33-37. doi: 10.19341/j.cnki.1009-0401.2022.01.009FU Z H, DONG G B, CHENG CH Q, et al. Random vibration analysis and design optimization of an antenna[J]. Radar &ECM, 2022, 42(1): 33-37. (in Chinese) doi: 10.19341/j.cnki.1009-0401.2022.01.009 [17] 段飞飞, 王田宇, 温业堃, 等. 飞行器随机振动试验技术应用研究[J]. 电子产品可靠性与环境试验,2022,40(2):56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5468.2022.02.012DUAN F F, WANG T Y, WEN Y K, et al. Research on the application of random vibration test technology of aircraft[J]. Electronic Product Reliability and Environmental Testing, 2022, 40(2): 56-59. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5468.2022.02.012 [18] 梁子健, 杨甬英, 赵宏洋, 等. 非球面光学元件面型检测技术研究进展与最新应用[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):161-186. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0143LIANG Z J, YANG Y Y, ZHAO H Y, et al. Advances in research and applications of optical aspheric surface metrology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 161-186. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0143 -





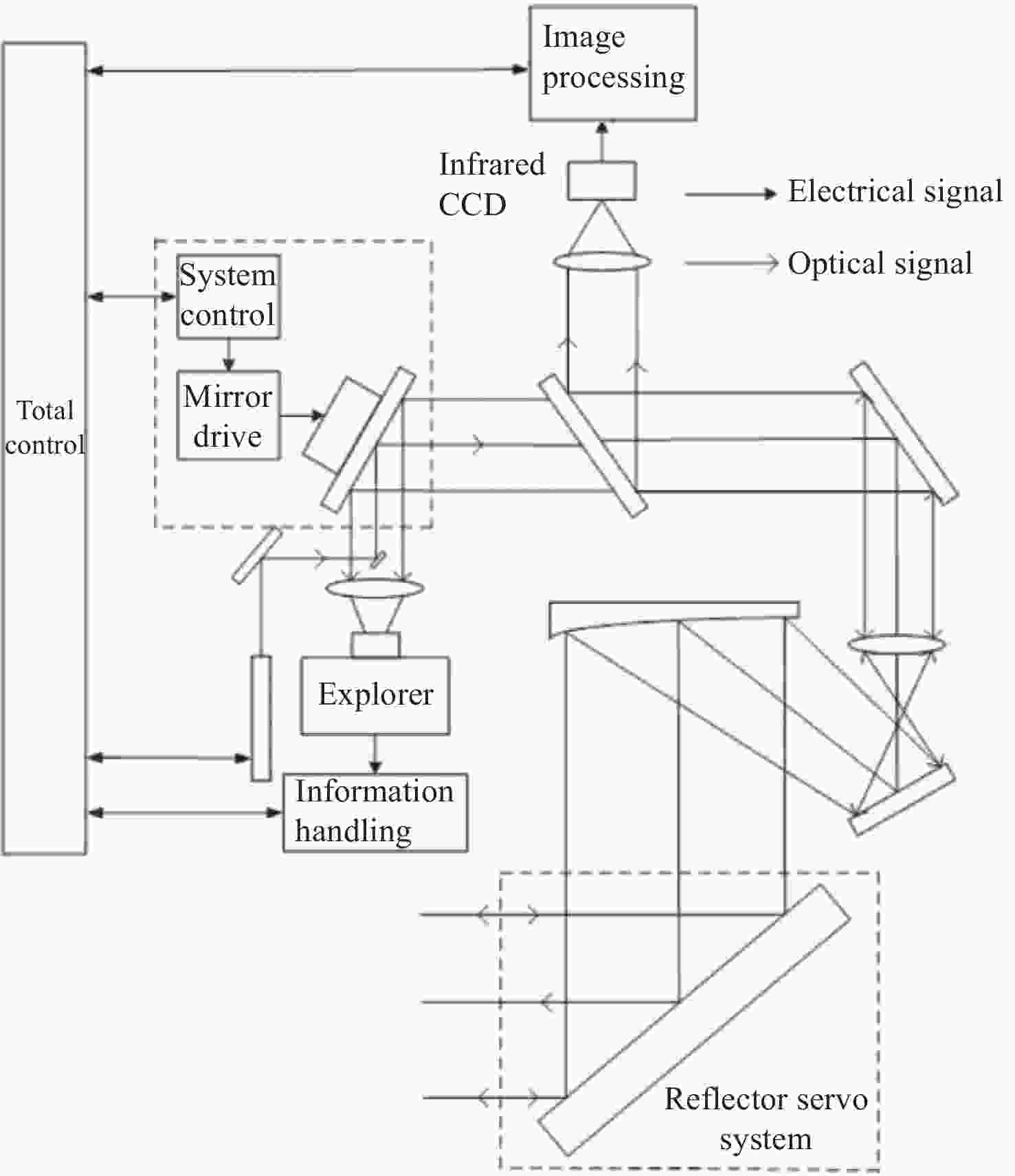
 下载:
下载: