-
摘要:
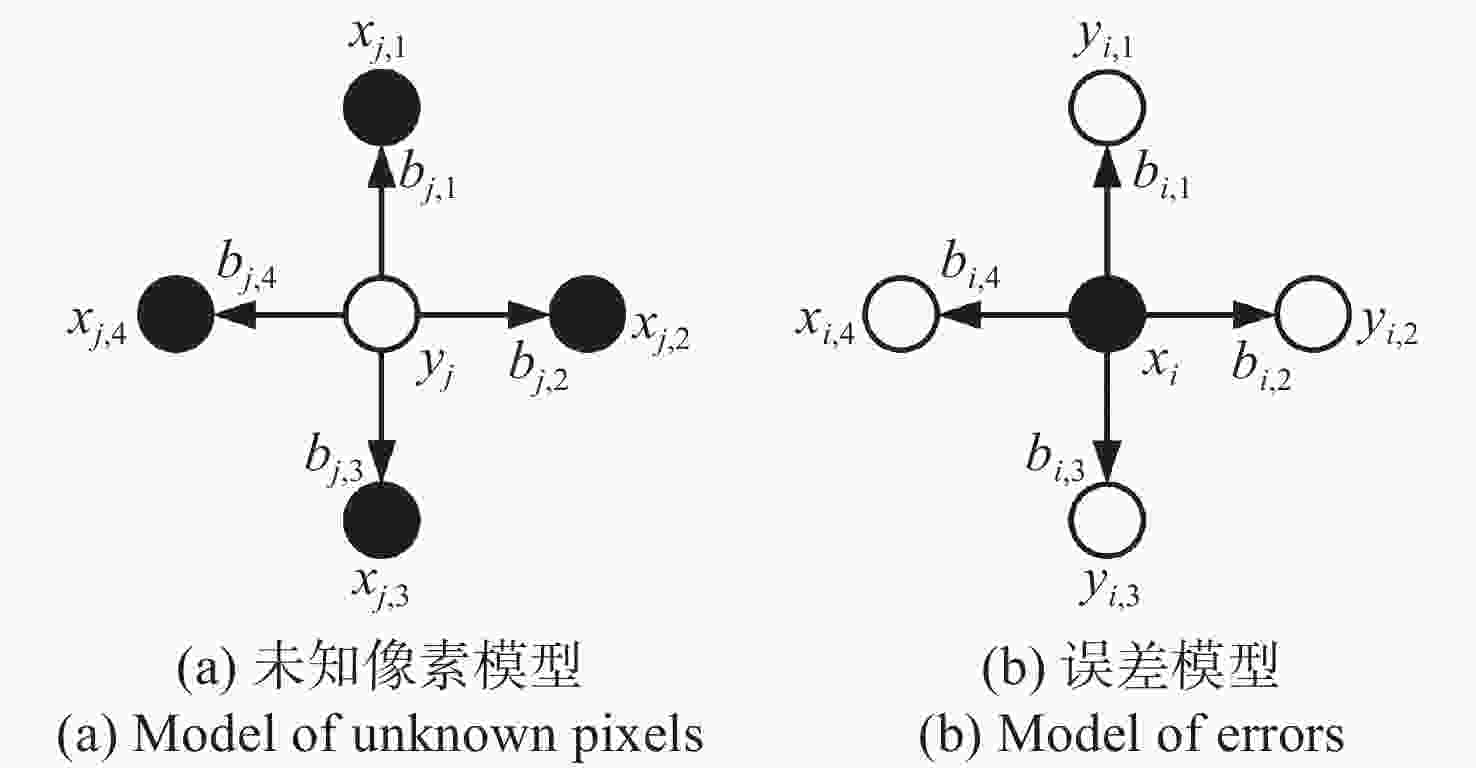
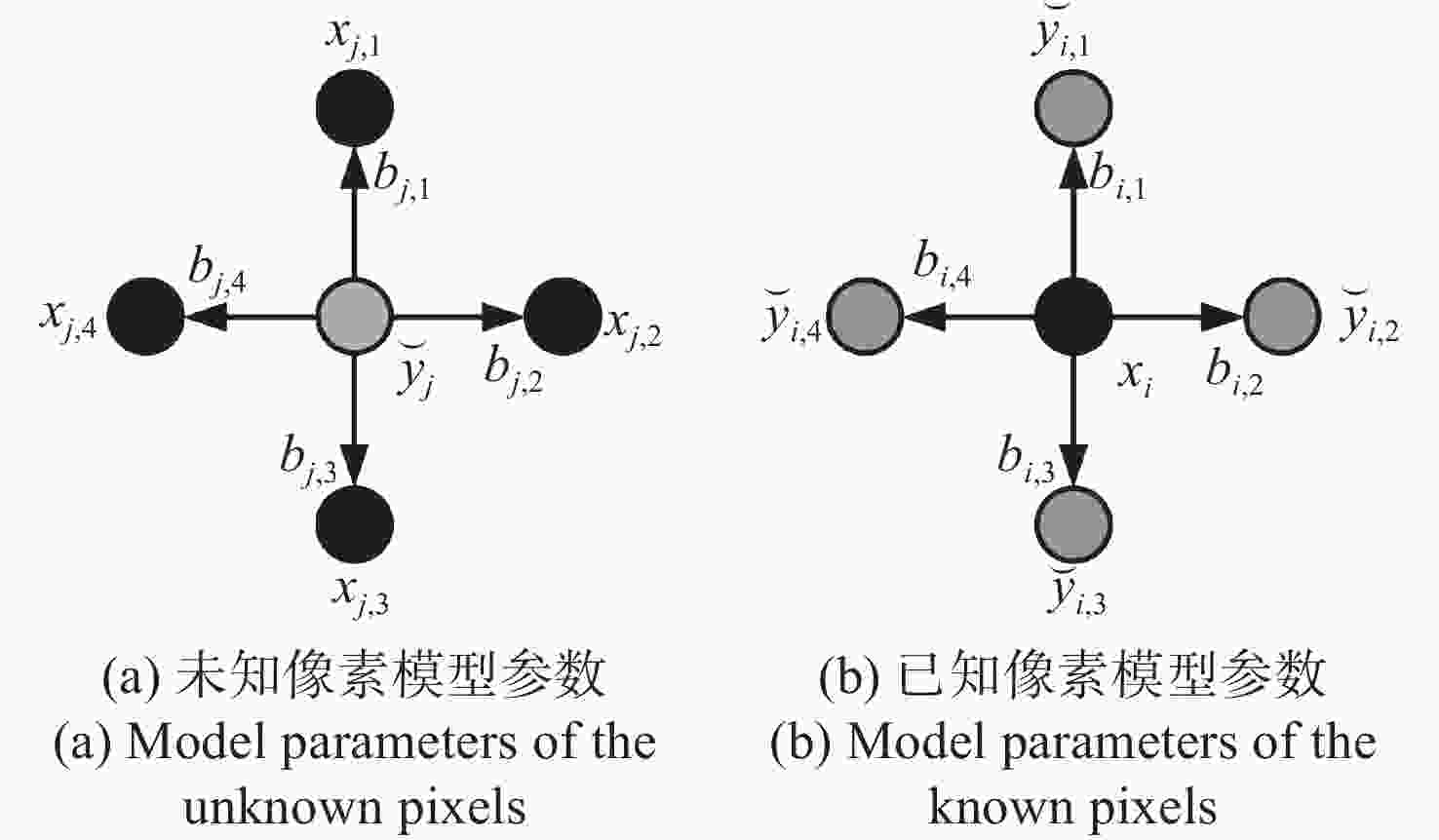
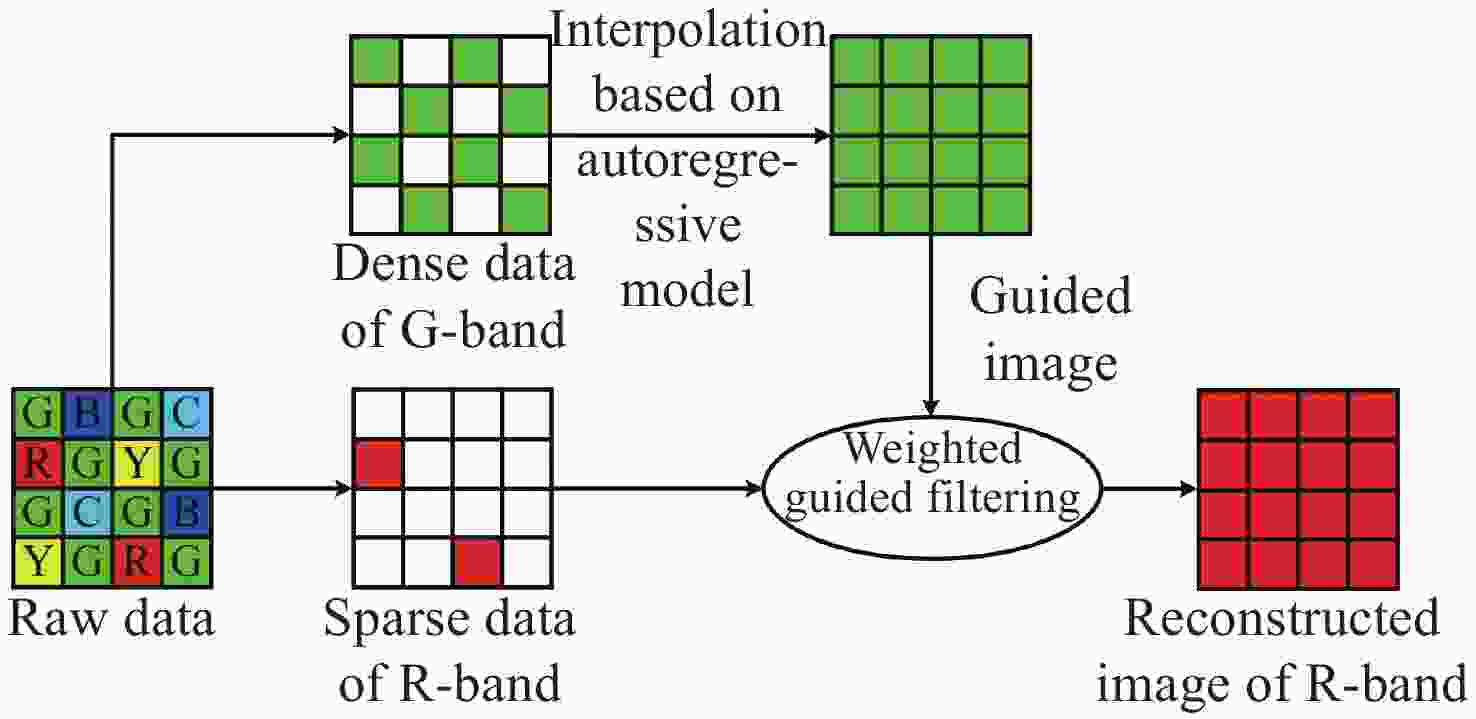
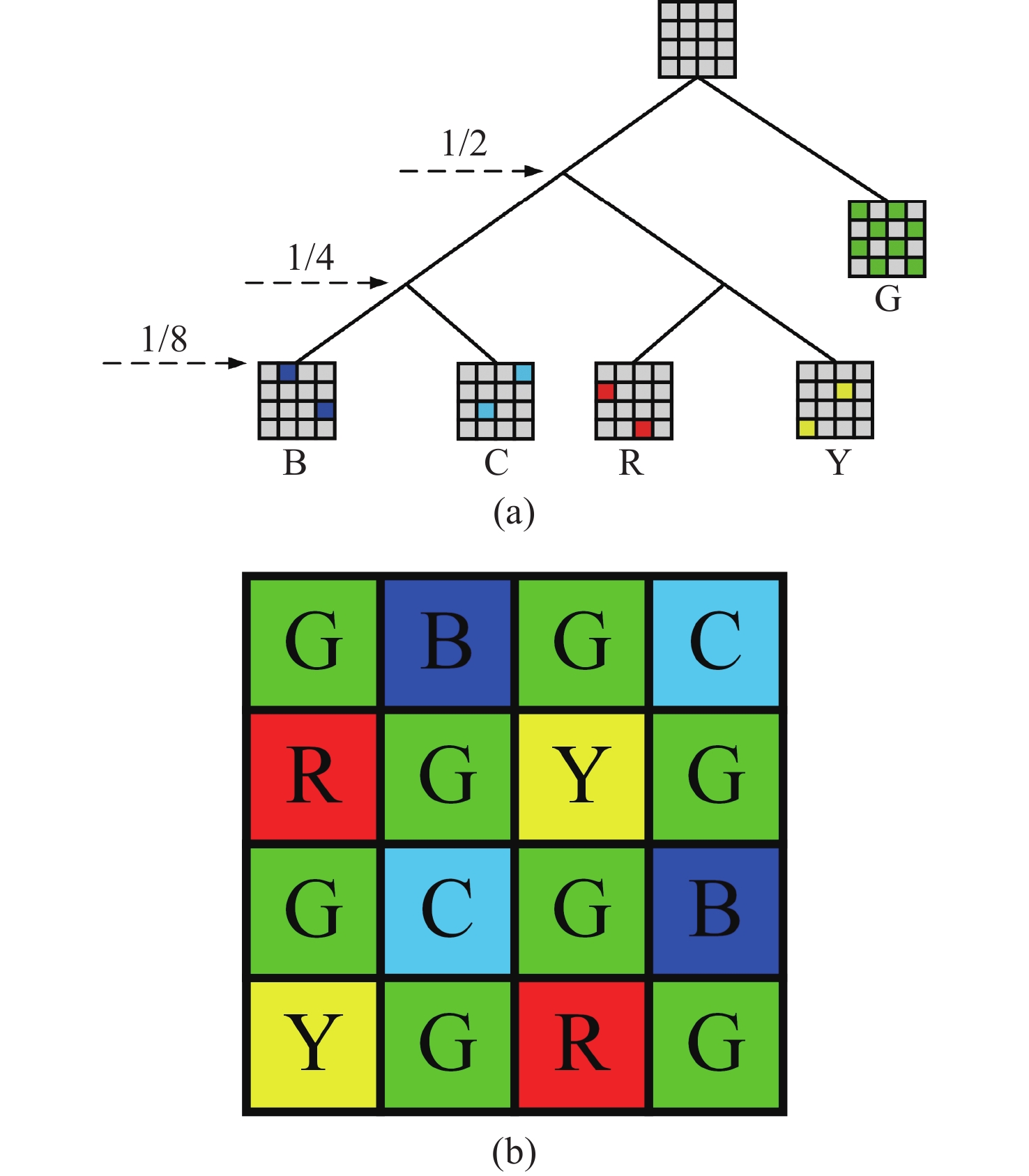
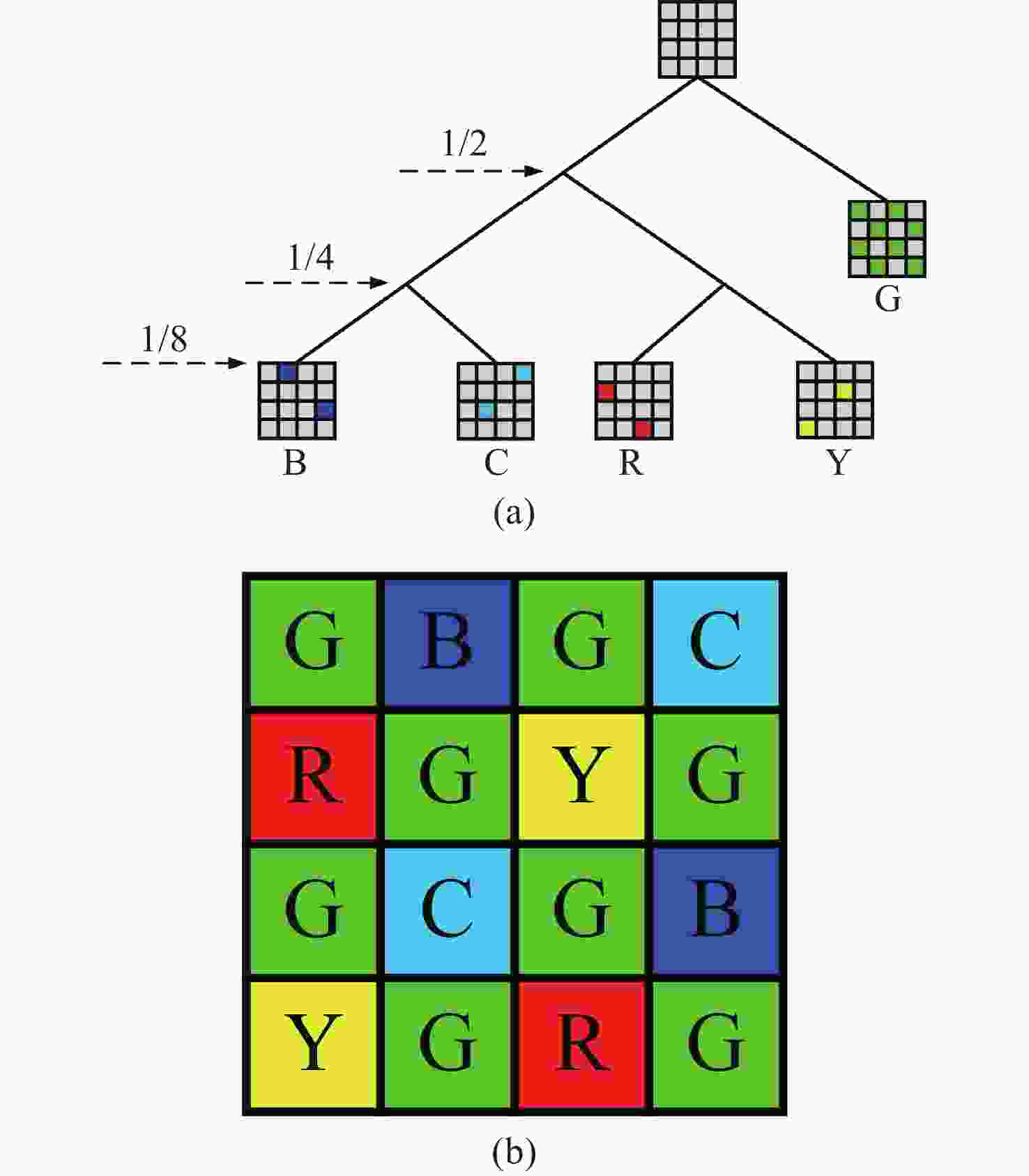
为了更好地保留多光谱去马赛克图像中的高频信息,本文提出了一种基于改进引导滤波器的多光谱图像去马赛克方法。首先,基于自回归模型对相邻像素点间的强相关性进行建模,在每个像素处渐进估计其模型参数,通过最小化局部窗口内的估计误差,得到最优估计值来插值采样密集波段G,并生成高质量的引导图像;然后,引入加窗固有变分系数到惩罚因子中,得到具有边缘感知能力的加权引导滤波器并重建其余稀疏采样波段。最后,使用CAVE数据集和TokyoTech数据集进行仿真。实验结果表明:相较于主流的5波段多光谱图像去马赛克方法,本方法重建图像的峰值信噪比和结构相似度在CAVE数据集和TokyoTech数据集上分别提高了3.40%,2.02%,1.34%,0.30%和6.11%,5.95%,2.28%,1.42%,且更好地保留了原始图像的局部结构和颜色信息,减少了边缘伪影和噪声现象的出现。
Abstract:In order to better preserve high-frequency information in demosaicing multispectral images, we propose a new demosaicing method for multispectral images based on an improved guided filter. Firstly, the strong correlation between adjacent pixels based on the autoregressive model is constructed, gradually estimates the model parameters at each pixel, and the optimal estimation value is obtained by minimizing the estimation error in the local window, interpolates the sampling dense band G, and generates high-quality guide images. The windowed intrinsic variation coefficient is then introduced into the penalty factor to obtain a weighted guide filter with edge sensing ability and to reconstruct the remaining sparse sampling bands. Finally, the CAVE dataset and the TokyoTech dataset are used for simulation. The experimental results show that compared with the mainstream five-band multispectral image demosaicing method, the peak signal-to-noise ratio and structure similarity of the reconstructed image in the CAVE dataset and the TokyoTech dataset are improved by 3.40%, 2.02%, 1.34%, 0.30% and 6.11%, 5.95%, 2.28%, 1.42%, respectively. The local structure and color information of the original image are also better preserved, and the edge artifacts and noise are reduced.
-
表 1 CAVE数据集上3种方法的客观评价指标
Table 1. Objective evaluation metrics of the three methods on the CAVE dataset
CAVE sRGB PSNR/dB sRGB SSIM CIEDE 2000 GF APMID Pro GF APMID Pro GF APMID Pro Balloons 41.62 42.68 43.11 0.9859 0.9916 0.9936 1.18 1.06 0.99 Clay 37.33 37.63 38.69 0.8758 0.8817 0.8852 1.07 0.94 0.89 Beers 41.57 42.18 43.52 0.9816 0.9868 0.9894 1.25 1.28 1.07 Lemons 42.91 42.87 42.91 0.9749 0.9805 0.9822 1.11 1.08 1.03 Peppers 42.14 42.08 42.52 0.9715 0.9801 0.9805 0.89 0.78 0.73 Feathers 35.64 35.94 35.99 0.9413 0.9593 0.9614 2.30 2.10 2.04 Flowers 38.93 41.18 42.50 0.9523 0.9778 0.9824 1.26 0.91 0.83 Paints 36.16 34.88 36.32 0.9696 0.9729 0.9797 2.40 2.43 2.17 Apples 45.24 45.10 45.68 0.9838 0.9875 0.9886 0.77 0.75 0.70 Toys 38.83 41.29 42.77 0.9666 0.9845 0.9891 1.24 0.90 0.80 Avg 40.04 40.58 41.40 0.9603 0.9703 0.9732 1.35 1.22 1.13 表 2 TokyoTech数据集上3种方法的客观评价指标
Table 2. Objective evaluation metrics of the three methods on the TokyoTech dataset
TokyoTech sRGB PSNR/dB sRGB SSIM CIEDE 2000 GF APMID Pro GF APMID Pro GF APMID Pro Butterfly 37.53 38.95 40.44 0.9596 0.9678 0.9810 1.60 1.42 1.17 Butterfly3 38.42 42.94 41.99 0.9487 0.9777 0.9793 1.37 0.91 0.84 Butterfly4 40.63 40.73 42.37 0.9691 0.9590 0.9827 1.12 1.23 0.87 CD 32.20 32.78 32.87 0.9450 0.9580 0.9629 1.97 1.72 1.65 Character 37.74 37.45 38.14 0.9673 0.9736 0.9835 1.83 1.94 1.73 Cloth 34.18 35.00 35.87 0.9321 0.9481 0.9573 3.34 3.22 2.75 Color 39.22 38.62 41.36 0.9782 0.9630 0.9895 1.74 2.00 1.47 Colorchart 42.83 44.79 47.80 0.9819 0.9847 0.9941 0.92 0.77 0.55 Fan2 32.68 33.29 34.09 0.9257 0.9426 0.9629 2.63 2.34 2.04 Party 32.79 33.45 35.78 0.9366 0.9509 0.9693 2.06 1.66 1.36 Avg 36.82 37.80 39.07 0.9544 0.9625 0.9762 1.86 1.72 1.44 表 3 不同方法在两种数据集上的运行时间
Table 3. Running times of different methods on the two datasets
(s) 数据集 GF APMID Pro CAVE 1.49 0.71 1.33 TokyoTech 1.36 0.56 1.29 -
[1] ORTEGA S, HALICEK M, FABELO H, et al. Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging in digital and computational pathology: a systematic review[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2020, 11(6): 3195-3233. doi: 10.1364/BOE.386338 [2] 王成, 刘宾, 周楚, 等. 窄带LED照明的多光谱显微成像系统研究[J]. 中国激光,2020,47(12):1207006. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.1207006WANG CH, LIU B, ZHOU CH, et al. Multispectral microimaging system with narrowband LED illumination[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(12): 1207006. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.1207006 [3] 唐凌宇, 葛明锋, 董文飞. 全自动推扫式高光谱显微成像系统设计与研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1486-1494. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0040TANG L Y, GE M F, DONG W F. Design and research of fully automatic push-broom hyperspectral microscopic imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1486-1494. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0040 [4] SU W H, SUN D W. Multispectral imaging for plant food quality analysis and visualization[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2018, 17(1): 220-239. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12317 [5] CHAMBINO L L, SILVA J S, BERNARDINO A. Multispectral facial recognition: a review[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 207871-207883. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3037451 [6] WU F, JING X Y, FENG Y J, et al. Spectrum-aware discriminative deep feature learning for multi-spectral face recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 111: 107632. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107632 [7] 李云辉. 压缩光谱成像系统中物理实现架构研究综述[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):929-945. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0104LI Y H. Review of physical implementation architecture in compressive spectral imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 929-945. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0104 [8] 杨鹰, 孔玲君, 刘真. 基于压缩感知的多光谱图像去马赛克算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2017,32(1):56-61. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20173201.0056YANG Y, KONG L J, LIU ZH. Multi-spectral demosaicking method based on compressive sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2017, 32(1): 56-61. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20173201.0056 [9] HABTEGEBRIAL T A, REIS G, STRICKER D. Deep convolutional networks for snapshot hypercpectral demosaicking[C]. 2019 10th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), IEEE, 2019: 1-5. [10] FENG K, ZHAO Y Q, CHAN J C W, et al. Mosaic convolution-attention network for demosaicing multispectral filter array images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2021, 7: 864-878. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2021.3102052 [11] 肖树林, 胡长虹, 高路尧, 等. 像元映射变分辨率光谱成像重构[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):1045-1054.XIAO SH L, HU CH H, GAO L Y, et al. Pixel mapping variable-resolution spectral imaging reconstruction[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 1045-1054. (in Chinese) [12] MIAO L D, QI H R. The design and evaluation of a generic method for generating mosaicked multispectral filter arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(9): 2780-2791. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.877315 [13] MIAO L D, QI H R, RAMANATH R, et al. Binary tree-based generic demosaicking algorithm for multispectral filter arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(11): 3550-3558. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.877476 [14] GUPTA M, RAM M. Weighted bilinear interpolation based generic multispectral image demosaicking method[J]. Journal of Graphic Era University, 2019, 7(2): 108-118. [15] GUPTA M, RATHI V, GOYAL P. Adaptive and progressive multispectral image demosaicking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022, 8: 69-80. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2022.3140554 [16] 孙帮勇, 袁年曾, 胡炳樑. 一种八谱段滤光片成像系统设计[J]. 光子学报,2020,49(5):0511001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204905.0511001SUN B Y, YUAN N Z, HU B L. Design of an eight-band filter imaging system[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(5): 0511001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204905.0511001 [17] RATHI V, GOYAL P. Generic multispectral Demosaicking based on directional interpolation[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 64715-64728. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3182493 [18] MONNO Y, TANAKA M, OKUTOMI M. Multispectral demosaicking using guided filter[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8299: 82990O. doi: 10.1117/12.906168 [19] 任杰, 刘家瑛, 白蔚, 等. 基于隐式分段自回归模型的图像插值算法[J]. 软件学报,2012,23(5):1248-1259. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2012.04049REN J, LIU J Y, BAI W, et al. Image interpolation algorithm based on implicit piecewise autoregressive model[J]. Journal of Software, 2012, 23(5): 1248-1259. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2012.04049 [20] ZHANG X J, WU X L. Image interpolation by adaptive 2-D autoregressive modeling and soft-decision estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(6): 887-896. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.924279 [21] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(6): 1397-1409. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213 [22] LI ZH G, ZHENG J H, ZHU Z J, et al. Weighted guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1): 120-129. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2371234 [23] XU L, YAN Q, XIA Y, et al. Structure extraction from texture via relative total variation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(6): 139. [24] 路陆, 姜鑫, 杨锦程, 等. 基于自适应引导滤波的红外图像细节增强[J]. 液晶与显示,2022,37(9):1182-1189. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0024LU L, JIANG X, YANG J CH, et al. Adaptive guided filtering based infrared image detail enhancement[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2022, 37(9): 1182-1189. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0024 [25] YASUMA F, MITSUNAGA T, ISO D, et al. Generalized assorted pixel camera: Postcapture control of resolution, dynamic range, and spectrum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(9): 2241-2253. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2046811 [26] MONNO Y, KIKUCHI S, TANAKA M, et al. A practical one-shot multispectral imaging system using a single image sensor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(10): 3048-3059. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2436342 [27] PARK J I, LEE M H, GROSSBERG M D, et al. . Multispectral imaging using multiplexed illumination[C]. 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2007: 1-8. [28] SARA U, AKTER M, UDDIN M S. Image quality assessment through FSIM, SSIM, MSE and PSNR—a comparative study[J]. Journal of Computer and Communications, 2019, 7(3): 8-18. doi: 10.4236/jcc.2019.73002 [29] SHARMA G, WU W CH, DALAL E N. The CIEDE2000 color-difference formula: Implementation notes, supplementary test data, and mathematical observations[J]. Color Research &Application, 2005, 30(1): 21-30. [30] 贾停停, 王慧琴, 王可, 等. 相位相关性增强的自适应低重叠率多光谱图像快速拼接算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2022,37(4):483-493. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2021-0294JIA T T, WANG H Q, WANG K, et al. Adaptive low overlap multispectral image fast mosaic algorithm based on phase correlation enhancement[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2022, 37(4): 483-493. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2021-0294 -





 下载:
下载: