-
摘要:
车载红外图像的目标检测是自动驾驶进行道路环境感知的重要方式。针对现有车载红外图像目标检测算法中内存利用率低、计算复杂和检测精度低的问题,提出了一种改进YOLOv5s的轻量型目标检测算法。首先,将C3Ghost和Ghost模块引入YOLOv5s检测网络,以降低网络复杂度。其次,引进αIoU损失函数,以提升目标的定位精度和训练效率。然后,降低网络结构下采样率,并利用KMeans聚类算法优化先验框大小,以提高小目标检测能力。最后,分别在主干网络和颈部引入坐标注意力(Coordinate Attention,CA)和空间深度卷积模块进一步优化模型,提升模型特征的提取能力。实验结果表明,相对于原YOLOv5s算法,改进算法的模型大小压缩78.1%,参数量和每秒千兆浮点运算数分别减少84.5%和40.5%,平均检测精度和检测速度分别提升4.2%和10.9%。
Abstract:Vehicle infrared image target detection is an important way of road environment perception for autonomous driving. However, existing vehicle infrared image target detection algorithms have defects, such as low memory utilization, complex calculation and low detection accuracy. In order to solve the above problems, an improved YOLOv5s lightweight target detection algorithm is proposed. Firstly, the C3Ghost and Ghost modules are introduced into the YOLOv5s detection network to reduce network complexity. Secondly, the αIoU loss function is introduced to improve the positioning accuracy of the target and the networks training efficiency. Then, the subsampling rate of the network structure is reduced and the KMeans clustering algorithm is used to optimize the prior anchor size to improve the ability to detect of small targets. Finally, coordinate attention and spatial depth convolution modules are respectively introduced into the Backbone and Neck to further optimize the model and improve the feature extraction of the model. The experimental results show that compared with the original YOLOv5s algorithm, the improved algorithm can compress the model size by 78.1%, reduce the number of parameters and Giga Floating-point Operations Per Second by 84.5% and 40.5% respectively, and improve the mean average precision and detection speed by 4.2% and 10.9%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- autonomous driving /
- target detection /
- infrared image /
- lightweight /
- YOLOv5s
-
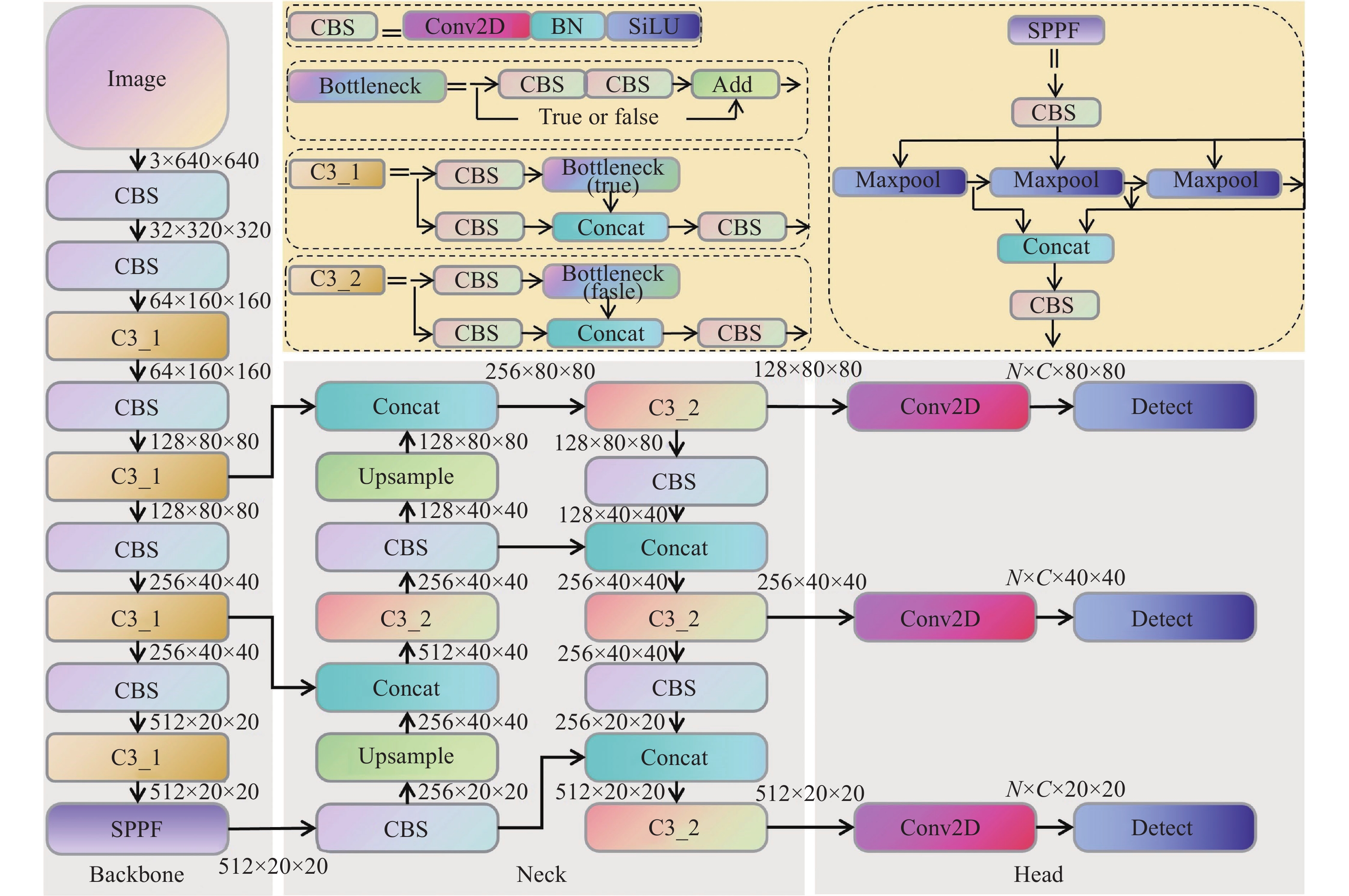
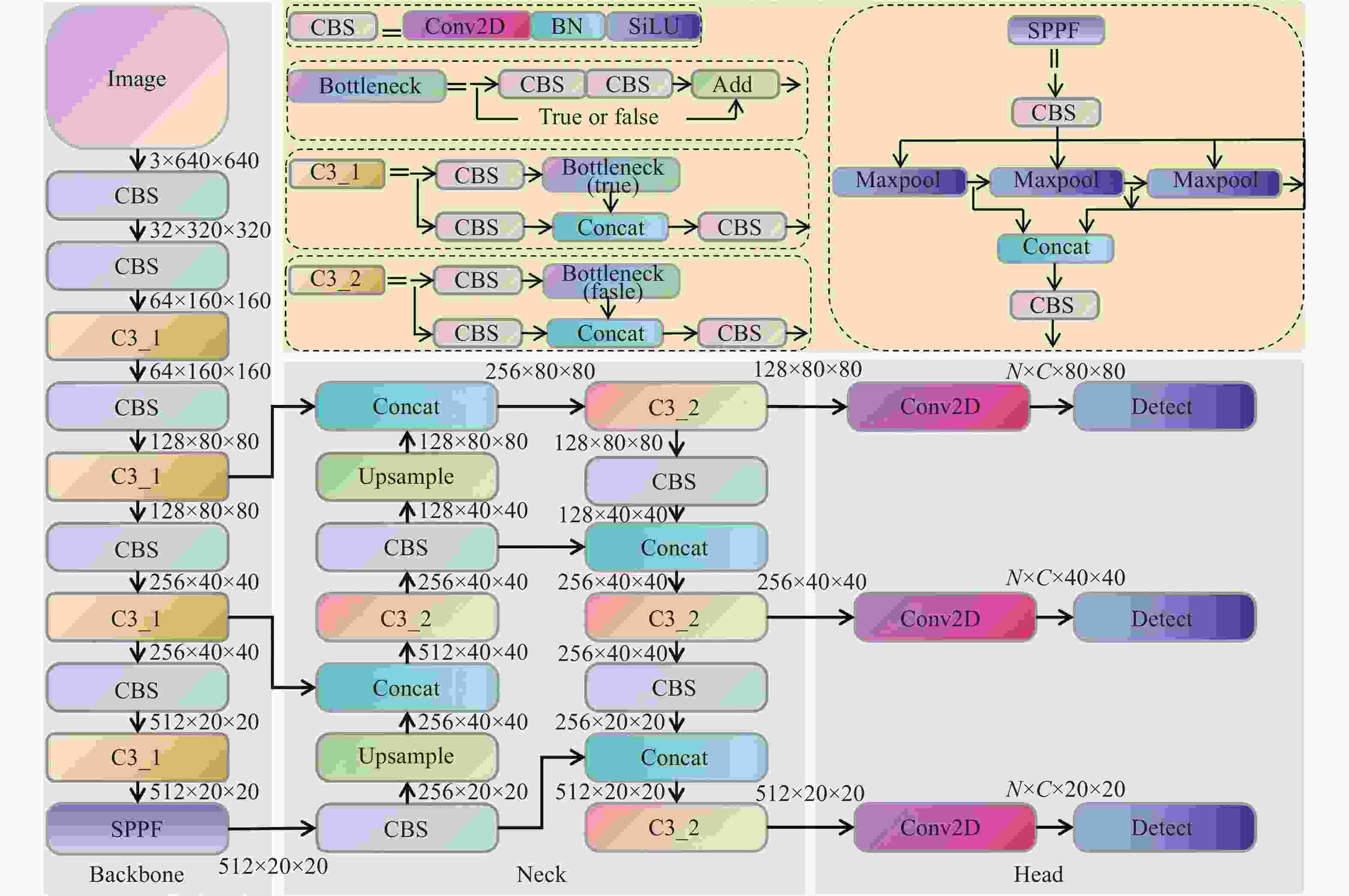
表 1 优化后先验框大小
Table 1. Optimized prior anchor size
特征图尺度 160×160 80×80 40×40 感受野大小 小 中 大 [6,8] [14,37] [35,94] 先验框 [7,19] [31,26] [96,68] [15,13] [50,37] [154,145] 表 2 YOLOv5s和YOLOv5s-G轻量化性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of lightweight for YOLOv5s and YOLOv5s-G
Model t/hours Size/MB Params/M GFLOPs P(%) R(%) mAP(%) FPS YOLOv5s 48.77 13.70 7.02 15.8 87.1 69.8 80.8 119 YOLOv5s-G 30.25 7.46 3.68 8.0 86.1 66.3 77.5 137 表 3 不同损失函数性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of different loss functions
Model t/hours P(%) R(%) mAP(%) FPS YOLOv5s-G 30.25 86.1 66.3 77.5 137 YOLOv5s-G-EIoU 24.31 84.5 68.7 78.9 141 YOLOv5s-G-SIoU 24.62 85.8 67.2 77.8 139 YOLOv5s-G-αIoU 23.50 85.9 69.3 79.8 147 表 4 多尺度融合性能对比
Table 4. Performance comparison of multi-scale fusion
Model t/hours Size/MB Params/M GFLOPs P(%) R(%) mAP(%) FPS YOLOv5s-G-αIoU 23.50 7.46 3.68 8.0 85.9 69.3 79.8 147 YOLOv5s-G1-αIoU 26.89 8.60 3.75 9.6 86.0 73.6 83.6 125 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU 24.56 2.73 0.95 7.2 84.5 72.8 82.9 154 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-KMeans 25.62 2.73 0.95 7.2 85.5 72.4 83 154 表 5 不同注意力机制性能对比
Table 5. Performance comparison of different attention mechanisms
Model t/hours Size/MB Params/M GFLOPs P(%) R(%) mAP(%) FPS YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-KMeans 25.62 2.73 0.95 7.2 85.5 72.4 83 154 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-KMeans-SE 30.95 2.75 0.96 7.2 86.0 73.5 84.1 149 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-KMeans-ECA 26.06 2.73 0.95 7.2 85.5 73.8 84.2 145 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-KMeans-CBAM 28.21 2.76 0.96 7.3 85.7 73.4 84 135 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-KMeans-CA 28.62 2.76 0.96 7.3 86.6 73.6 84.3 139 表 6 空间深度卷积效果
Table 6. SPD-Conv effect
Model t/hours Size/MB Params/M GFLOPs P(%) R(%) mAP(%) FPS YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-Kmeans-CA 28.62 2.76 0.96 7.3 86.6 73.6 84.3 139 YOLOv5s-G2-αIoU-Kmeans-CA-SPD 30.28 3.0 1.09 9.4 87.4 74.6 85.0 132 表 7 与其他先进算法对比
Table 7. Comparison with other advanced algorithms
Model Size/MB Params/M GFLOPs P(%) R(%) mAP(%) FPS SSD 186.0 23.70 115.7 68.9 55.7 63.2 88 EfficientDet 302.0 39.40 107.5 72.8 58.4 67.8 52 YOLOv4+GhostNet 150.3 39.30 25.6 81.1 66.9 77.7 112 YOLOv5-MobileNetV3 7.9 4.0 9.3 83.7 67.5 76.9 128 YOLOv3-tiny 16.6 8.67 12.9 79.3 54.9 62.9 175 YOLOv4-tiny 12.9 6.27 16.2 78.9 57.3 67.2 149 YOLOv5n 3.7 1.76 5.1 83.6 66.1 76.6 164 YOLOv6-N 9.3 4.30 11.1 84.8 71.5 80.3 208 YOLOv7-tiny 12.3 6.02 13.2 84.2 74.7 83.6 143 YOLOv5s 13.7 7.02 15.8 87.1 69.8 80.8 119 proposed in this paper 3.0 1.09 9.4 87.4 74.6 85.0 132 -
[1] MUHAMMAD K, ULLAH A, LLORET J, et al. Deep learning for safe autonomous driving: current challenges and future directions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(7): 4316-4336. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3032227 [2] TAKUMI K, WATANABE K, HA Q SH, et al. . Multispectral object detection for autonomous vehicles[C]. Proceedings of the on Thematic Workshops of ACM Multimedia 2017, ACM, 2017: 35-43. [3] CHOI Y, KIM N, HWANG S, et al. KAIST multi-spectral day/night data set for autonomous and assisted driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 934-948. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2791533 [4] LIU Q, ZHUANG J J, MA J. Robust and fast pedestrian detection method for far-infrared automotive driving assistance systems[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2013, 60: 288-299. [5] 任凤雷, 周海波, 杨璐, 等. 基于双注意力机制的车道线检测[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):645-653.REN F L, ZHOU H B, YANG L, et al. Lane detection based on dual attention mechanism[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 645-653. (in Chinese) [6] WANG H, CAI Y F, CHEN X B, et al. Night-time vehicle sensing in far infrared image with deep learning[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2016, 2016: 3403451. [7] GALARZA-BRAVO M A, FLORES-CALERO M J. Pedestrian detection at night based on faster R-CNN and far infrared images[C]. Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Springer, 2018: 335-345. [8] CHEN Y F, XIE H, SHIN H. Multi‐layer fusion techniques using a CNN for multispectral pedestrian detection[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2018, 12(8): 1179-1187. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2018.5315 [9] 王驰, 于明坤, 杨辰烨, 等. 抛撒地雷的夜视智能探测方法研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(5):1202-1211. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0214WANG CH, YU M K, YANG CH Y, et al. Night vision intelligent detection method of scatterable landmines[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(5): 1202-1211. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0214 [10] GONG J, ZHAO J H, LI F, et al. . Vehicle detection in thermal images with an improved yolov3-tiny[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power, Intelligent Computing and Systems, IEEE, 2020: 253-256. [11] SUN M Y, ZHANG H CH, HUANG Z L, et al. Road infrared target detection with I‐YOLO[J]. IET Image Processing, 2022, 16(1): 92-101. doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12331 [12] 吴海滨, 魏喜盈, 刘美红, 等. 结合空洞卷积和迁移学习改进YOLOv4的X光安检危险品检测[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1417-1425. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0078WU H B, WEI X Y, LIU M H, et al. Improved YOLOv4 for dangerous goods detection in X-ray inspection combined with atrous convolution and transfer learning[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1417-1425. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0078 [13] 张印辉, 庄宏, 何自芬, 等. 氨气泄漏混洗自注意力轻量化红外检测[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):607-619.ZHANG Y H, ZHUANG H, HE Z F, et al. Lightweight infrared detection of ammonia leakage using shuffle and self-attention[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 607-619. (in Chinese) [14] JIANG X H, CAI W, YANG ZH Y, et al. IEPet: a lightweight multiscale infrared environmental perception network[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2021, 2078: 012063. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2078/1/012063 [15] WU ZH L, WANG X, CHEN CH. Research on lightweight infrared pedestrian detection model algorithm for embedded Platform[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 2021: 1549772. [16] XIN X L, PAN F, WANG J CH, et al. . SwinT-YOLOv5s: improved YOLOv5s for vehicle-mounted infrared target detection[C]. Proceedings of the 41st Chinese Control Conference (CCC), IEEE, 2022: 7326-7331. [17] ZHAI SH P, SHANG D R, WANG SH H, et al. DF-SSD: an improved SSD object detection algorithm based on DenseNet and feature fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24344-24357. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971026 [18] DAI X R, YUAN X, WEI X Y. TIRNet: object detection in thermal infrared images for autonomous driving[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(3): 1244-1261. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-01882-2 [19] 2022. FREE FLIR Thermal Dataset for Algorithm Training. [Online]. Available: https://www.flir.com/oem/adas/adas-dataset-form. [20] CAO M L, FU H, ZHU J Y, et al. Lightweight tea bud recognition network integrating GhostNet and YOLOv5[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2022, 19(12): 12897-12914. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022602 [21] HE J B, ERFANI S M, MA X J, et al.. Alpha-IoU: a family of power intersection over union losses for bounding box regression[C]. Proceedings of the 34th Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021. [22] ZHA M F, QIAN W B, YI W L, et al. A lightweight YOLOv4-Based forestry pest detection method using coordinate attention and feature fusion[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23(12): 1587. doi: 10.3390/e23121587 [23] SUNKARA R, LUO T. No more strided convolutions or pooling: a new CNN building block for low-resolution images and small objects[C]. Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Springer, 2022: 443-459. -





 下载:
下载: