-
摘要:
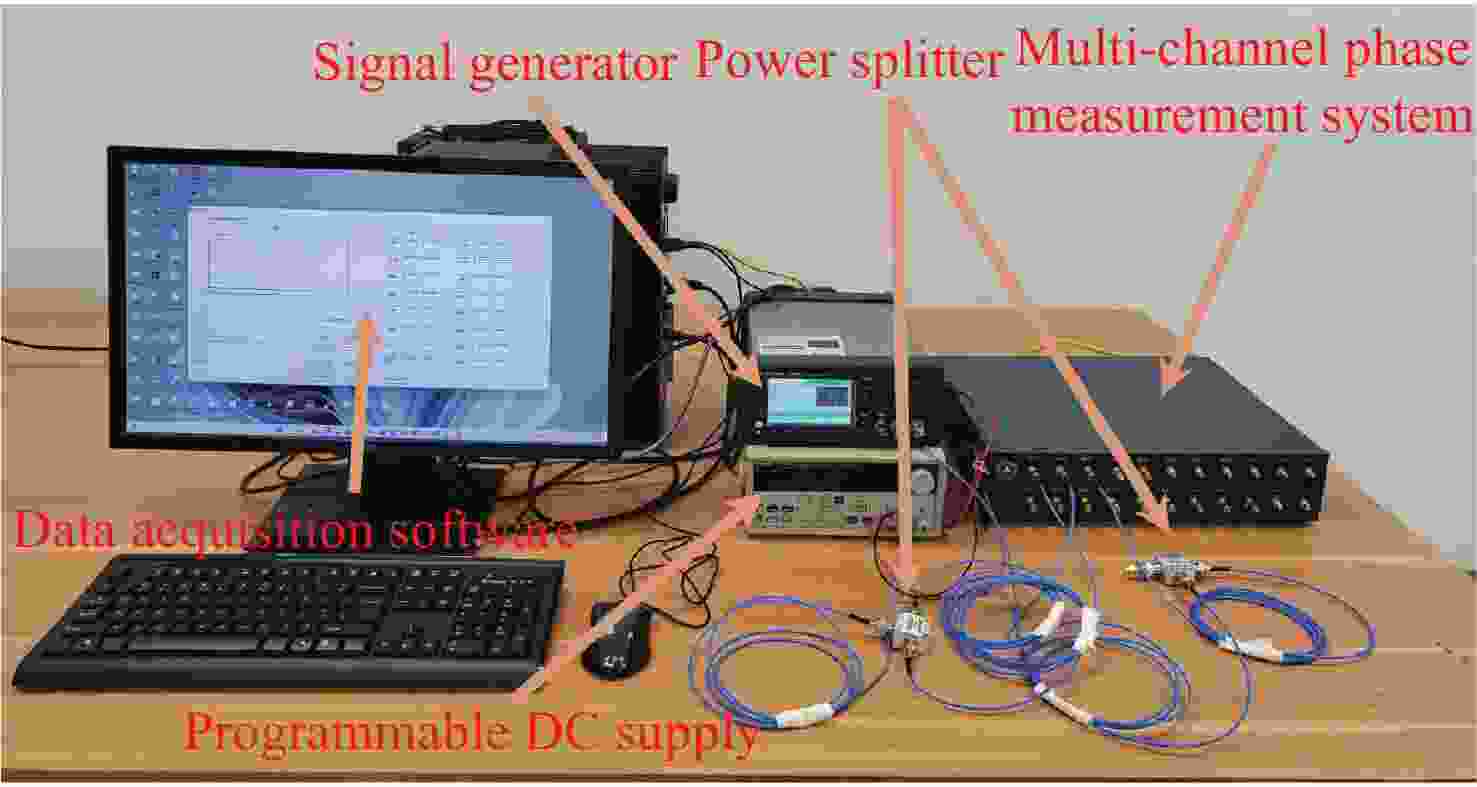
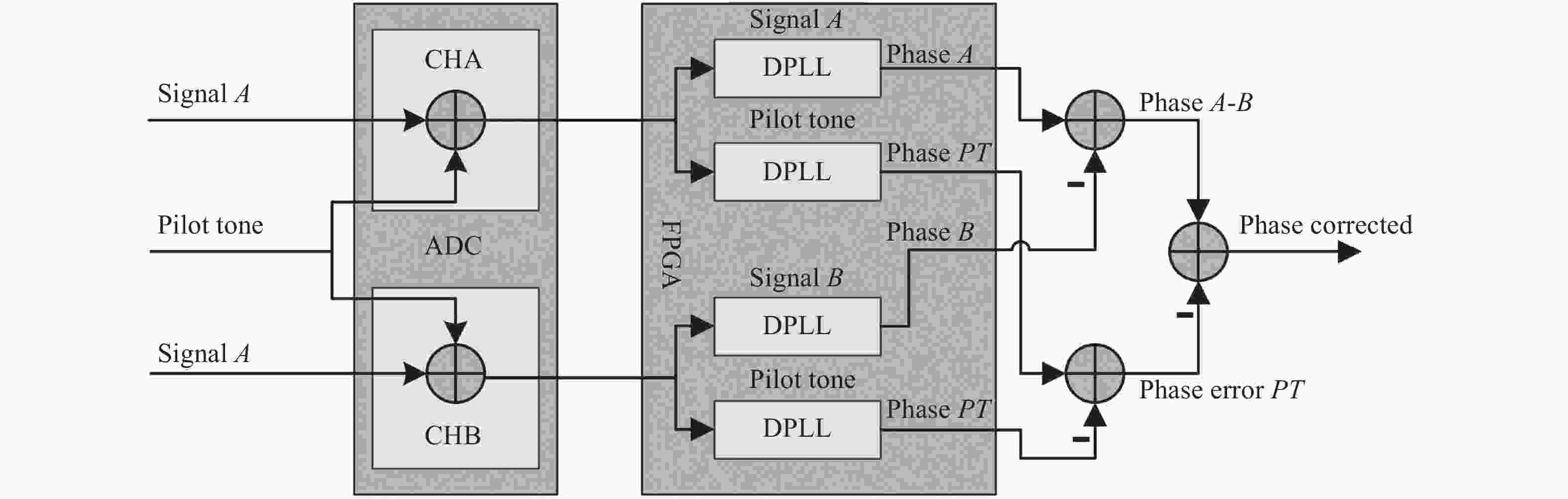
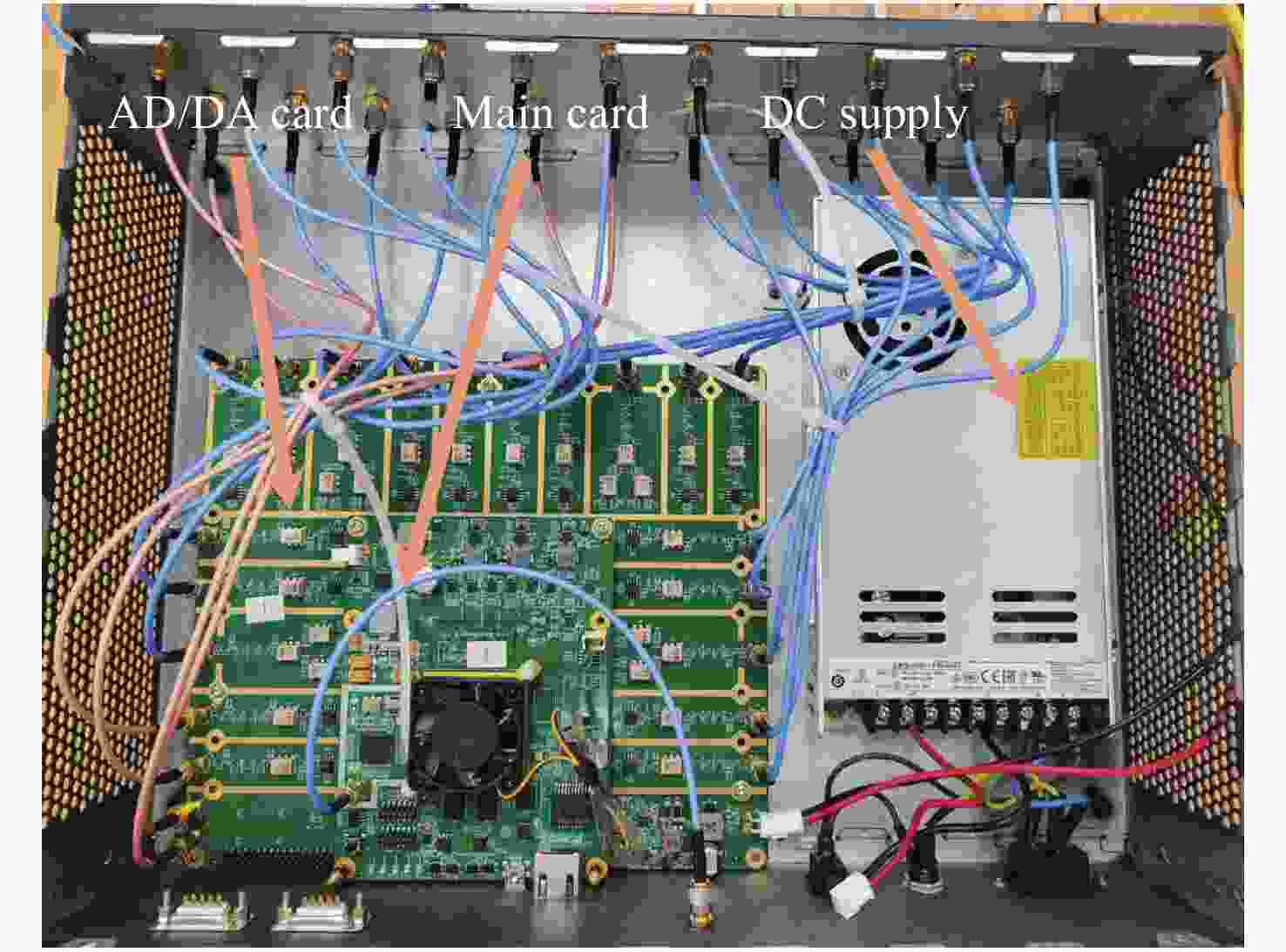
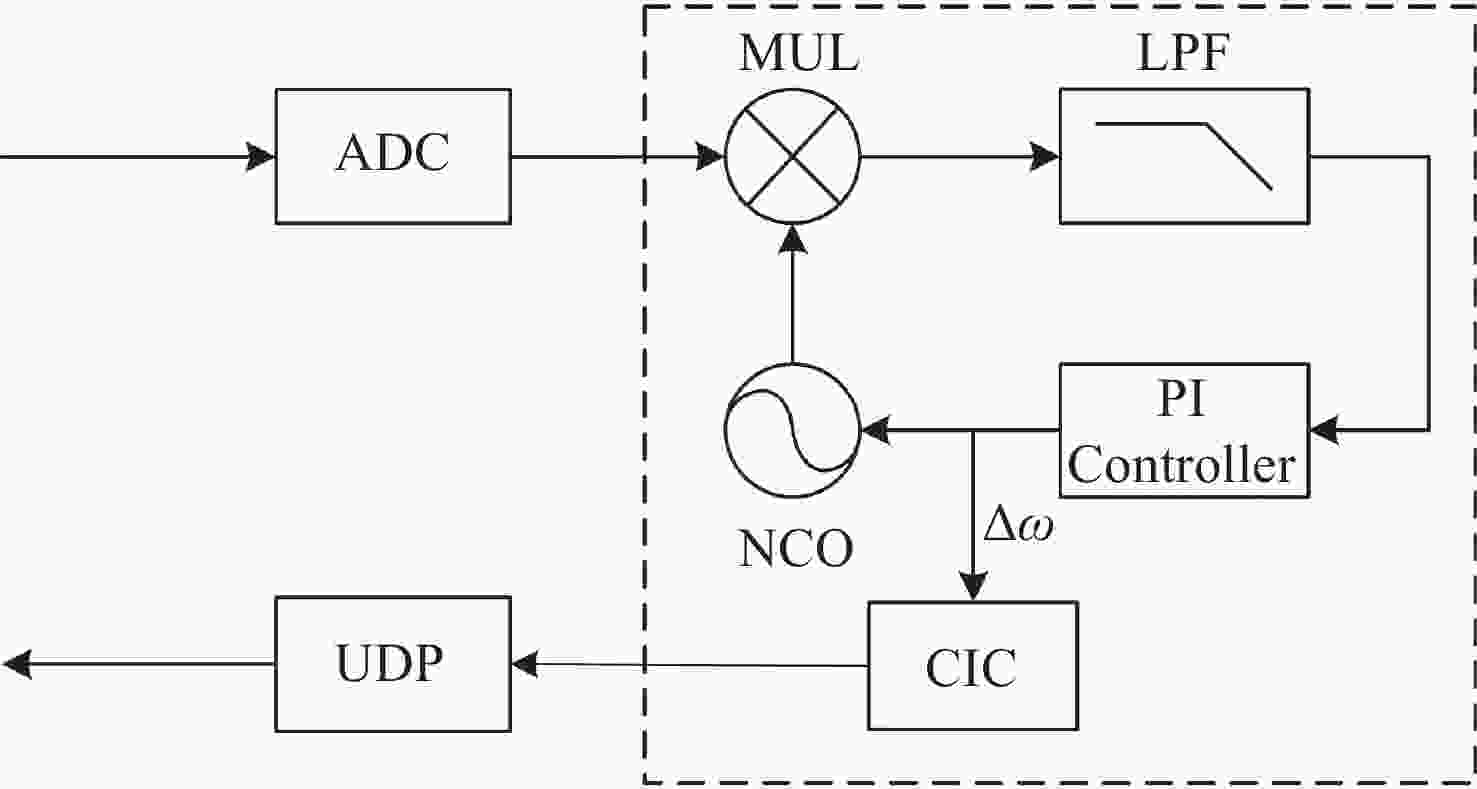
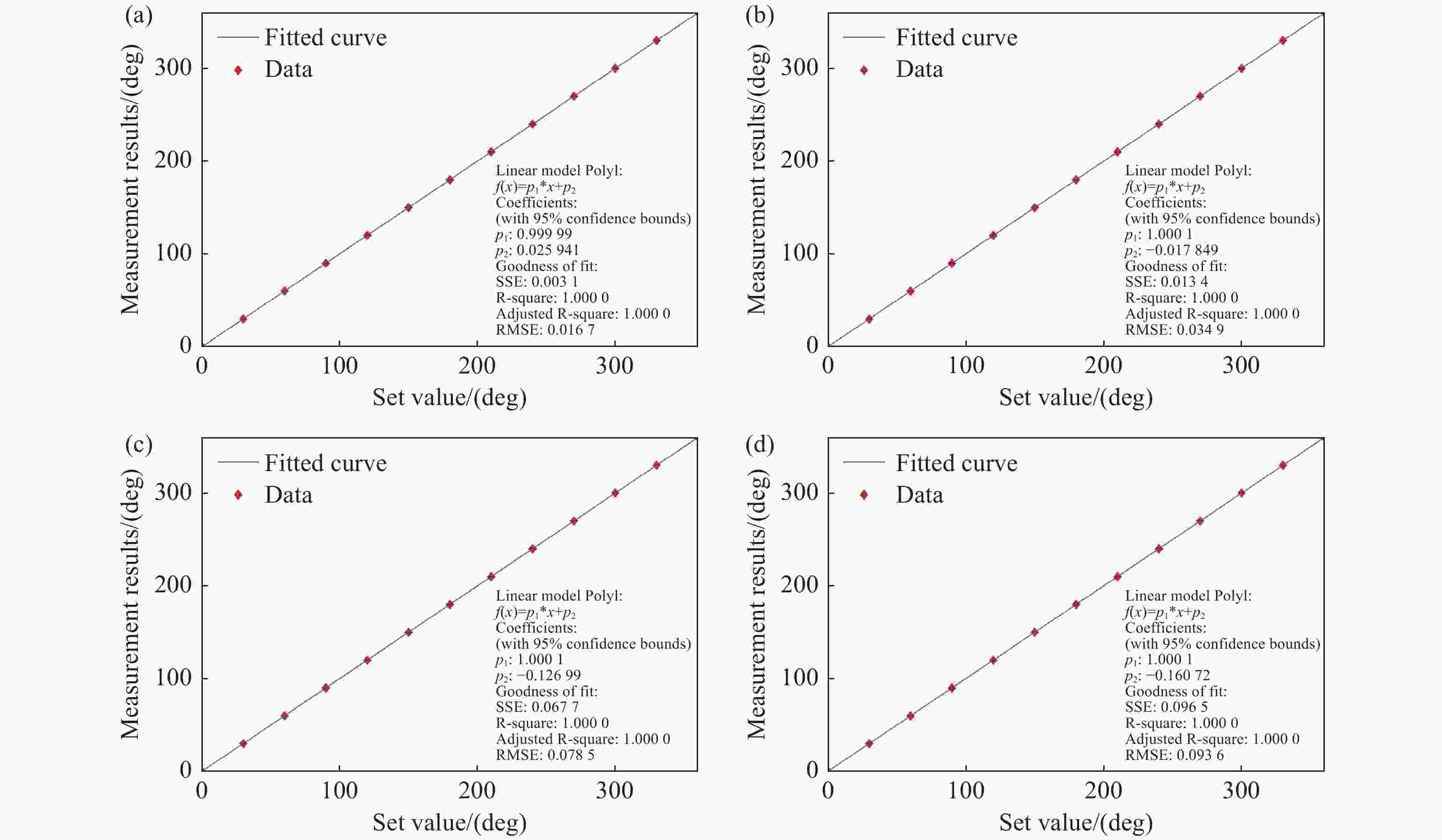
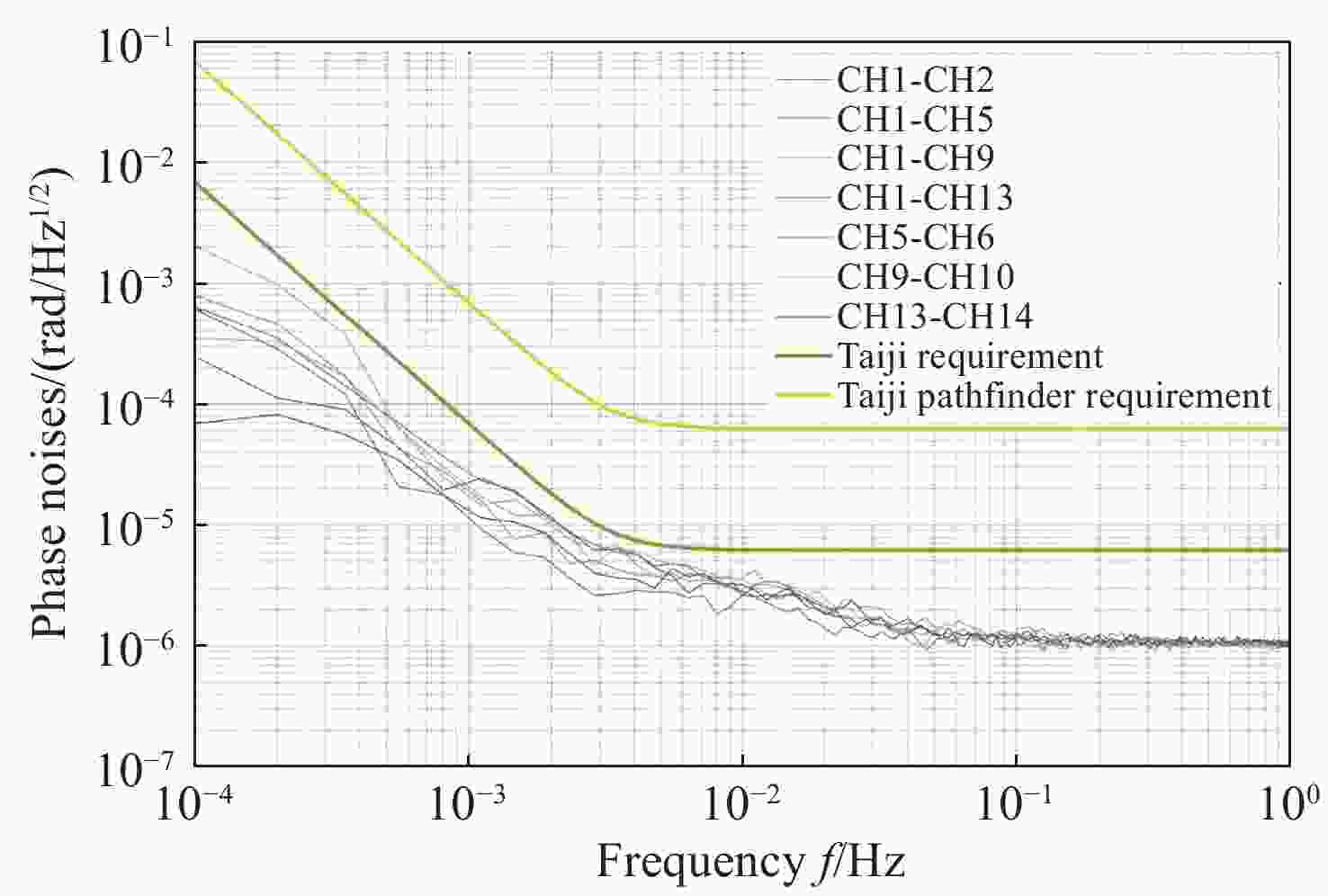
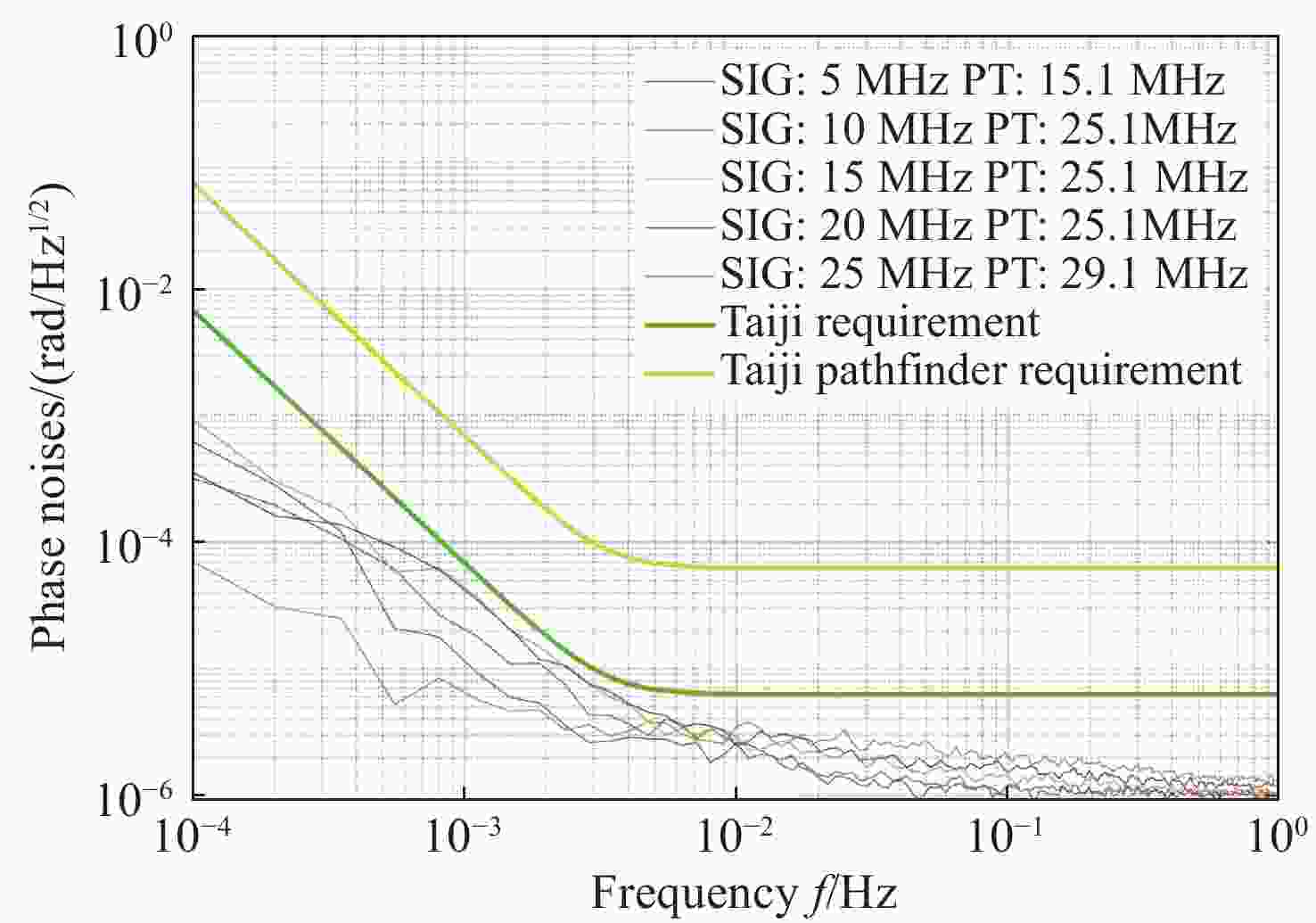
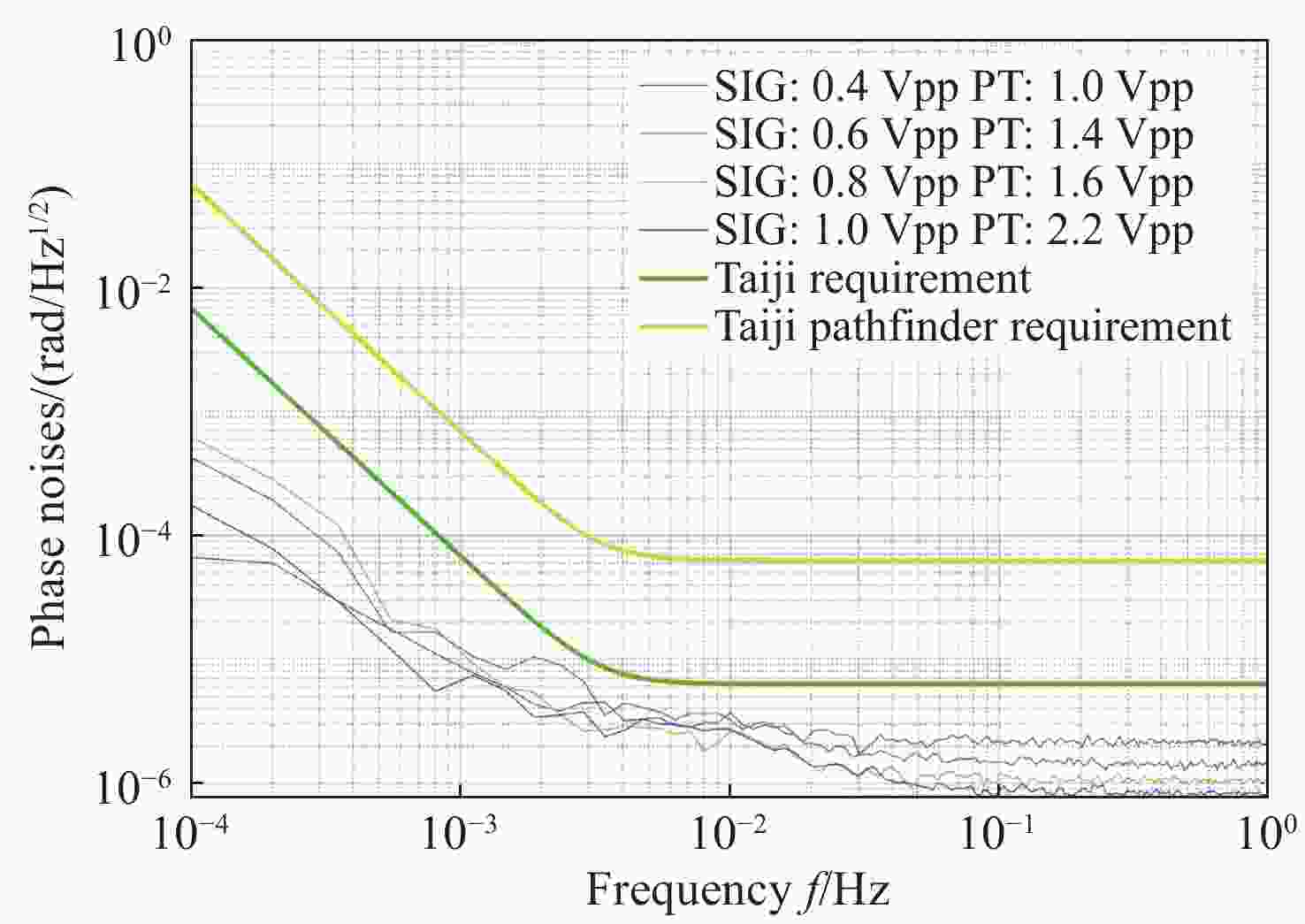
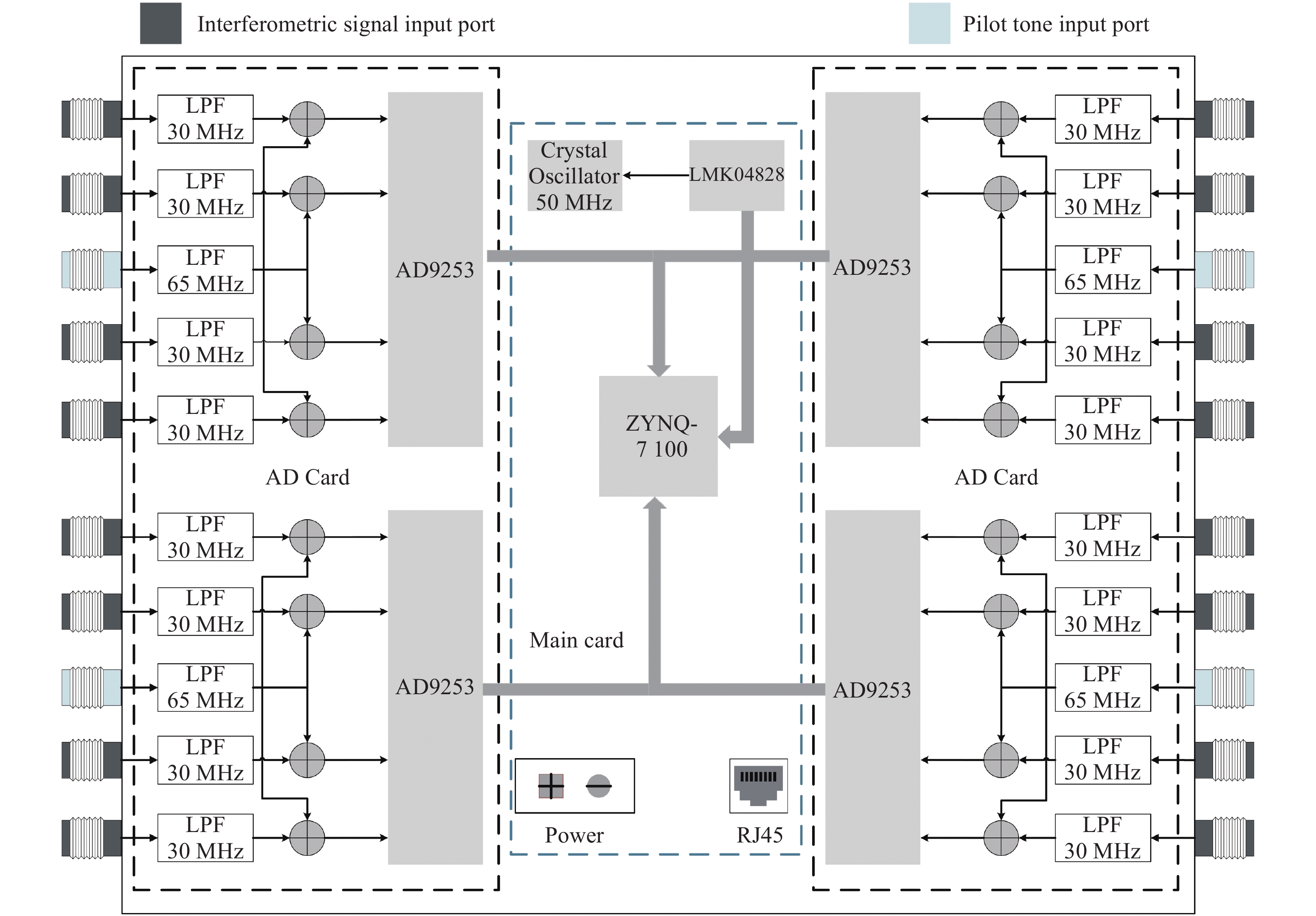
空间引力波探测激光干涉系统由多路干涉仪组成,涉及到多组干涉信号的相位采集和读出,多通道相位测量系统是空间激光干涉的关键核心技术之一。本文从太极计划及其地基激光干涉实验需求入手,设计、搭建并测试了多通道相位测量系统。首先,给出多通道相位测量系统的软硬件设计,包括硬件架构设计、数字锁相环测相算法、软件架构设计等。其次,对多通道相位计进行时域功能测试,包括相位准确度和线性度。测试结果表明多通道相位测量系统在不同工况下的动静态相位线性度和准确度良好。最终,对多通道相位计进行不同通道、不同频率、不同幅值下的频域噪声测试。测试结果还表明本文设计的多通道相位计,在0.1 mHz~1 Hz频段内,相位噪声水平均优于
$ 2{\text{π}}{\text{µ}} {\rm{rad}}/\sqrt{{\rm{Hz}}} $ ;不同通道之间具有很好的一致性,由通道差异或ADC芯片差异引入的相位噪声在目标频段内可以忽略不计;对于频率在5−25 MHz之间的任意干涉信号,相位计在目标频段内均满足需求。因此,该多通道相位测量系统满足空间引力波探测及地基干涉实验的需求。Abstract:In the space gravitational wave detection Taiji mission, a heterodyne laser interferometer is used to detect gravitational wave signals in the middle and low frequency bands. In the Taiji mission, the laser interferometry system is composed of multi-channel interferometers, which involves the phase acquisition and readout of multiple sets of the interference signals. Therefore, the multi-channel phase measurement system is one of the key core technologies of the space laser interferometry. In this paper, a multi-channel phase measurement system is proposed, designed and tested based on the requirements of the Taiji mission and its ground-based laser interferometry experiments. First, the hardware and software design of the multi-channel phase measurement system is given, including hardware architecture design, phase measurement algorithm based on digital phase-locked loop and its implementation on FPGA, software architecture design, etc. Second, a time-domain functional tests of the multi-channel phasemeter are performed, which includes the phase accuracy and linearity. The results show that the dynamic and static phase linearity and accuracy of the multi-channel phase measurement system under different working conditions are good. Finally, the frequency domain noise tests of different channels at different frequencies and different amplitudes are carried out. The results show that the phase noise level of the multi-channel phase meter designed in this paper is better than
$ 2{\text{π}} {\text{µ}} {\rm{rad}}/\sqrt{{\rm{Hz}}} $ in the frequency band of 0.1 mHz−1 Hz. There is good consistency between different channels, and the phase noise introduced by channel differences or ADC chip differences is negligible in the target frequency band. For any interference signal with a frequency between 5−25 MHz, the phasemeter can meet the requirements within the target frequency band. Therefore, the multi-channel phase measurement system meets the requirements of space gravitational wave detection and ground-based interference experiments. At the same time, the research results of this paper also provide an experimental basis for expanding the phase measurement system with more channels in the future.-
Key words:
- phasemeter /
- space interferometer /
- Taiji program
-
表 1 动态测试下拟合曲线斜率
Table 1. The slope of the fitting curve under the dynamic test
0.01Hz 0.02Hz 0.04Hz 0.08Hz 5 MHz 0.010001 0.020002 0.040002 0.080003 15 MHz 0.010001 0.020004 0.040009 0.080012 25 MHz 0.009999 0.020012 0.039980 0.080045 -
[1] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Sensor noise in LISA pathfinder: in-flight performance of the optical test mass readout[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 126(13): 131103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.131103 [2] LUO Z R, GUO Z K, JIN G, et al. A brief analysis to Taiji: science and technology[J]. Results in Physics, 2020, 16: 102918. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102918 [3] HU W R, WU Y L. The Taiji Program in Space for gravitational wave physics and the nature of gravity[J]. National Science Review, 2017, 4(5): 685-686. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx116 [4] LUO J, BAI Y ZH, CAI L, et al. The first round result from the TianQin-1 satellite[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2020, 37(18): 185013. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/aba66a [5] LUO J, CHEN L SH, DUAN H Z, et al. TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2016, 33(3): 035010. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/3/035010 [6] 罗子人, 张敏, 靳刚. 激光干涉引力波空间阵列核心问题的综合讨论[J]. 科学通报,2019,64(24):2468-2474. doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0055LUO Z R, ZHANG M, JIN G. Overall discussion on the key problems of a space-borne laser interferometer gravitational wave antenna[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(24): 2468-2474. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0055 [7] 黄双林, 龚雪飞, 徐鹏, 等. 空间引力波探测——天文学的一个新窗口[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学,2017,47(1):010404.HUANG SH L, GONG X F, XU P, et al. Gravitational wave detection in space—a new window in astronomy[J]. Scientia China Physics,Mechanics &Astronomy, 2017, 47(1): 010404. (in Chinese) [8] 刘河山, 高瑞弘, 罗子人, 等. 空间引力波探测中的绝对距离测量及通信技术[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):486-492. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486LIU H SH, GAO R H, LUO Z R, et al. Laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 486-492. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486 [9] 邓汝杰, 张艺斌, 刘河山, 等. 太极计划中的星间激光测距地面电子学验证[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(4):765-776. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0041DENG R J, ZHANG Y B, LIU H SH, et al. Ground electronics verification of inter-satellites laser ranging in the taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(4): 765-776. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0041 [10] 高瑞弘, 刘河山, 罗子人, 等. 太极计划激光指向调控方案介绍[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):425-431. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0425GAO R H, LIU H SH, LUO Z R, et al. Introduction of laser pointing scheme in the Taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 425-431. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0425 [11] 赵梦阳, 高瑞弘, 张强涛, 罗子人. 太极计划激光链路构建地面模拟控制系统研究[J]. 中国激光,2023,50(17):1706003.ZHAO M Y, GAO R H, ZHANG Q T, et al. Research on simulated laser link construction control system of Taiji program[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(17): 1706003. (in Chinese) [12] The Taiji Scientific Collaboration. China's first step towards probing the expanding universe and the nature of gravity using a space borne gravitational wave antenna[J]. Communications Physics, 2021, 4(1): 34. doi: 10.1038/s42005-021-00529-z [13] LIU H SH, YU T, LUO Z R. A low-noise analog frontend design for the Taiji phasemeter prototype[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(5): 054501. doi: 10.1063/5.0042249 [14] ZHANG J F, YANG ZH, MA X SH, et al. Inter-spacecraft offset frequency setting strategy in the Taiji program[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 61(3): 837-843. doi: 10.1364/AO.442583 [15] LIU H SH, LUO Z R, JIN G. The development of phasemeter for Taiji space gravitational wave detection[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology, 2018, 30(6): 775-781. doi: 10.1007/s12217-018-9625-6 [16] 韩爽. 空间引力波探测相位计测试系统设计与实现[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2022.HAN SH. Design and implementation of phasemeter test system for space gravitational wave detection[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2022. (in Chinese) [17] SCHWARZE T S, FERNÁNDEZ BARRANCO G, PENKERT D, et al. Picometer-stable hexagonal optical bench to verify LISA phase extraction linearity and precision[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122(8): 081104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.081104 [18] WISSEL L, WITTCHEN A, SCHWARZE T S, et al. Relative-intensity-noise coupling in heterodyne interferometers[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2022, 17(2): 024025. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.17.024025 [19] GERBERDING O, SHEARD B, BYKOV I, et al. Phasemeter core for intersatellite laser heterodyne interferometry: modelling, simulations and experiments[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2013, 30(23): 235029. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/30/23/235029 [20] Xilinx Inc. PetaLinux tools documentation: reference guide (UG1144)[DB/OL]. (2022-10-19). https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug1144-petalinux-tools-reference-guide/Overview. [21] HEWITSON M, ARMANO M, BENEDETTI M, et al. Data analysis for the LISA Technology Package[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2009, 26(9): 094003. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/26/9/094003 -







 下载:
下载: