Research progress of miniature head-mounted single photon fluorescence microscopic imaging technique
-
摘要:
微型头戴式单光子荧光显微成像技术是近些年出现的用于神经科学研究的一种突破性方法,可以对自由移动活体动物的神经活动进行实时成像,提供了一种前所未有的方式来访问神经信号,增强了对大脑如何工作的理解。在脑科学研究需求的推动下,目前已经出现了许多种类型的微型头戴式单光子荧光显微镜,如高分辨率成像、无线记录、三维成像、双区域成像和双色成像等。为了更加全面地了解和认识这种新兴的光学神经成像技术,本文按成像视场进行分类,对目前报道的不同类型微型头戴式单光子荧光显微镜所具有的特点进行了介绍,重点讨论了其所采用的光学系统方案和光学性能参数,分析对比了不同方案的优缺点,以及未来的改进方向,以便为脑科学研究人员的实际应用提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 微型单光子荧光显微镜 /
- 神经信号 /
- 脑科学 /
- 光学系统
Abstract:Miniature head-mounted single-photon fluorescence microscopy is a breakthrough approach for neuroscience research that has emerged in recent years. It can image the neural activity of freely moving vivo animals in real time, providing an unprecedented way to access neural signals and rapidly enhancing the understanding of how the brain works. Driven by the needs of brain science research, there have been many types of miniature head-mounted single-photon fluorescence microscopes, such as high-resolution imaging, wireless recording, 3D imaging, two-region imaging and two-color imaging. In order to have a more comprehensive understanding of this new optical neuroimaging technology, we classify its technologies according to the imaging field of view, introduce the characteristics of different types of micro-head-mounted single-photon fluorescence microscopes reported so far, and focus on the optical system scheme and optical performance parameters used. The advantages and disadvantages of different schemes are analyzed and compared and the future direction of development is described to provide reference for the practical application of brain science researchers.
-
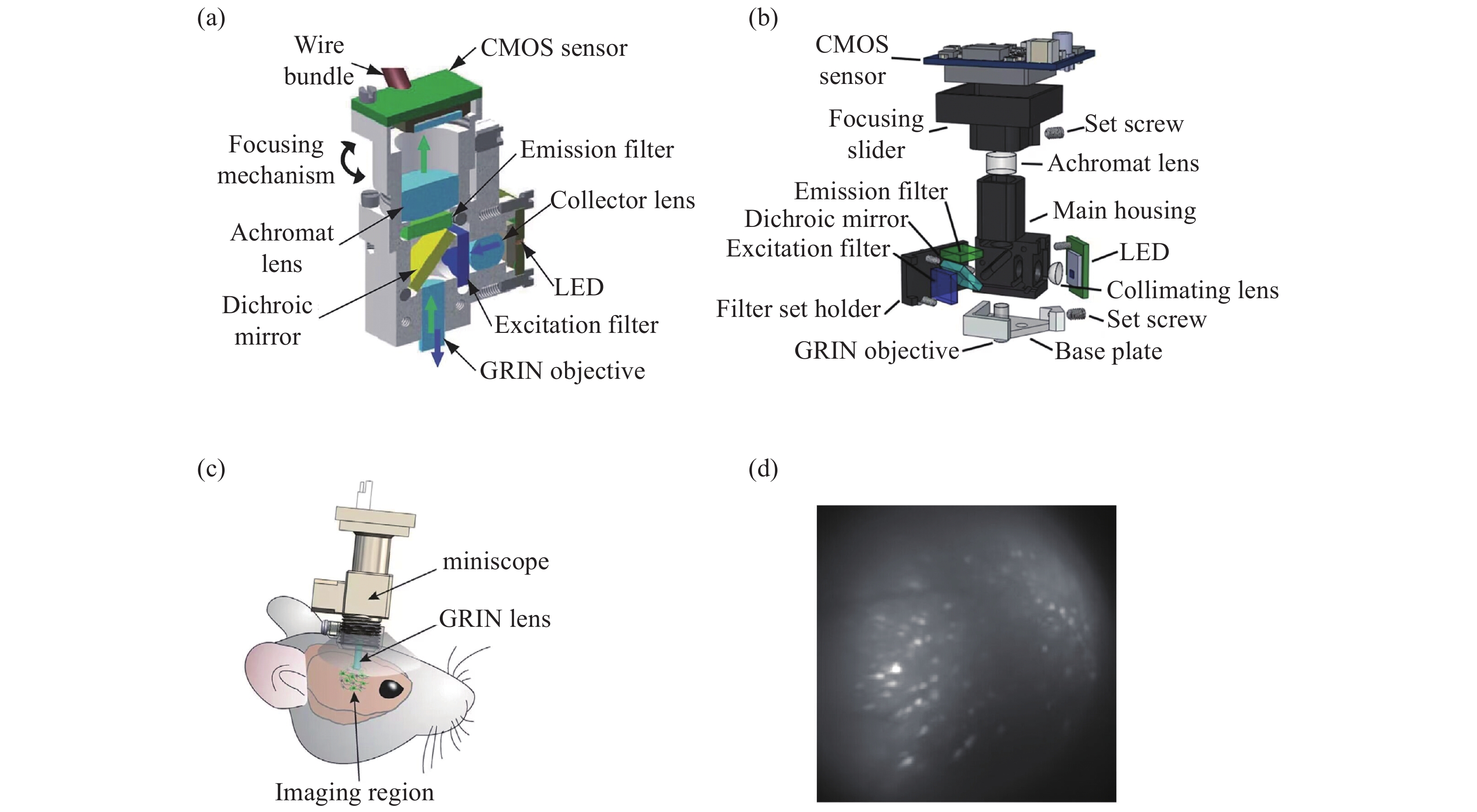
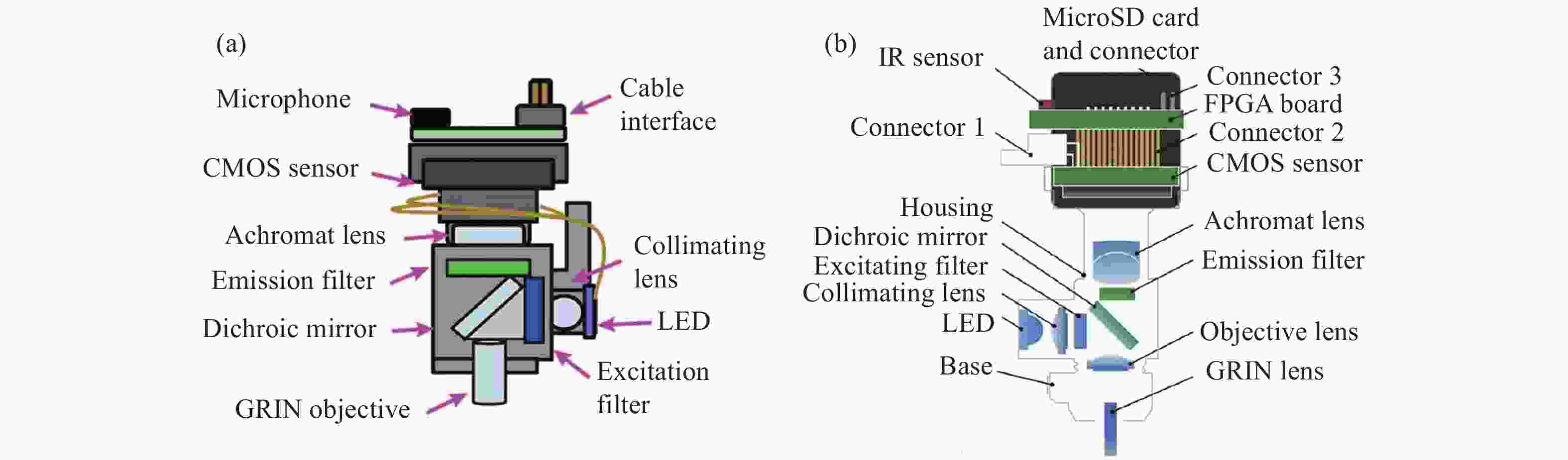
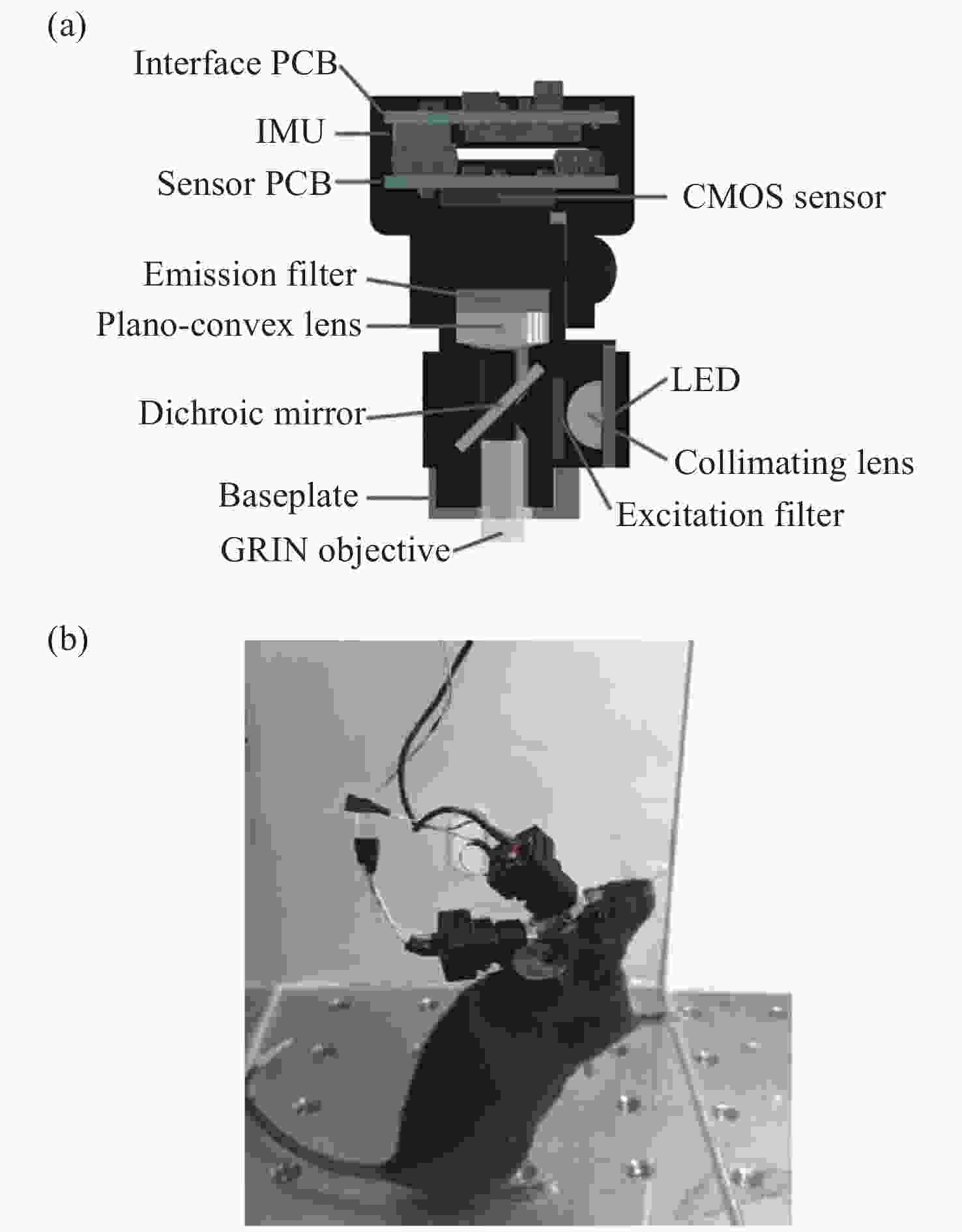
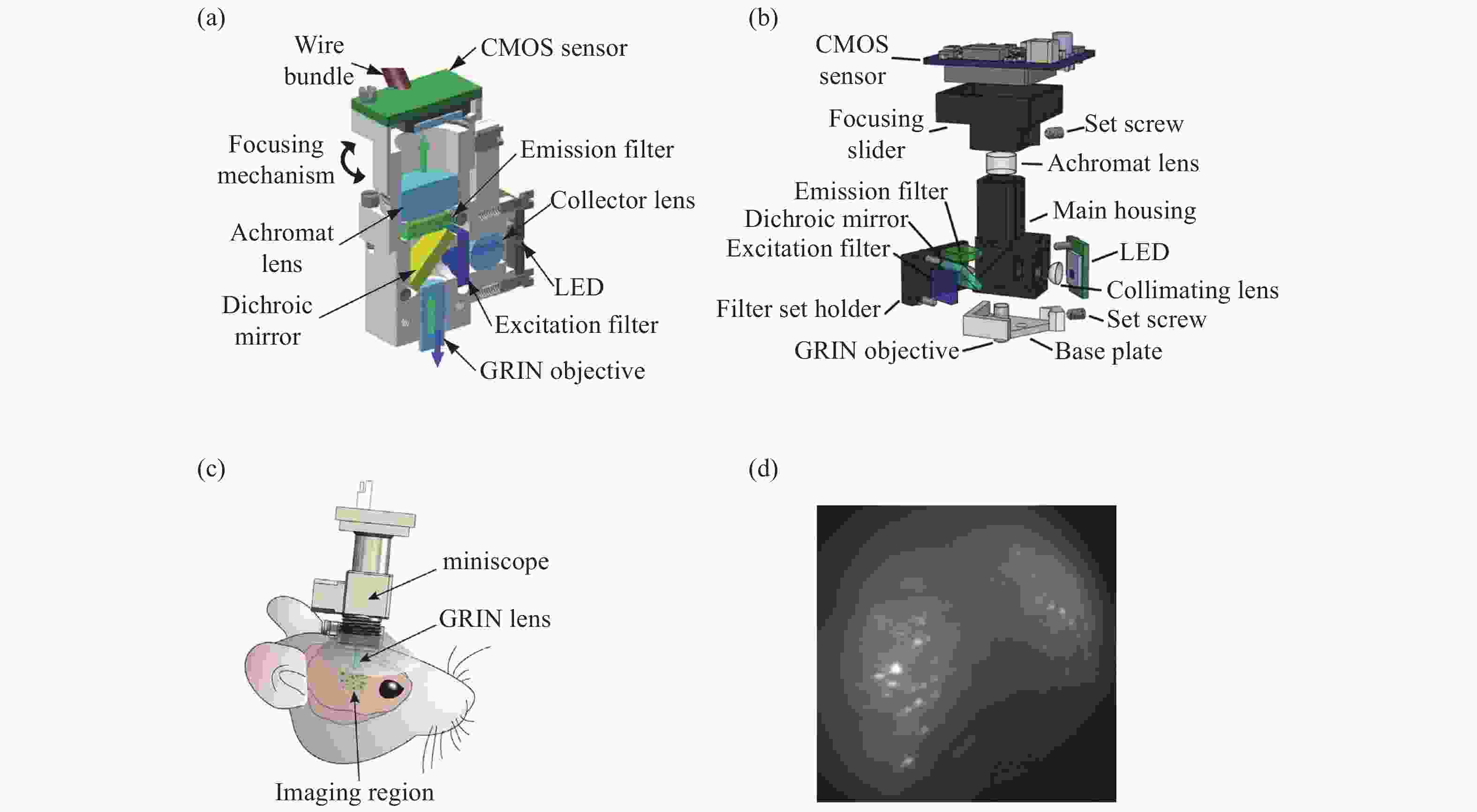
图 1 具有基本成像功能的系统。(a)Ghosh等人的集成显微镜的横截面图[10];(b)MiniScope V3的分解图; (c)戴着微型显微镜的小鼠示意图[14];(d)小鼠大脑中神经元活动的荧光图像[14]
Figure 1. A system with a basic imaging function. (a) Cross sectional view of integrated microscope proposed by Ghosh et al; (b) exploded view of the MiniScope V3; (c) a schematic of a mouse wearing a miniature microscope; (d) fluorescent images of neural activity in a mouse brain
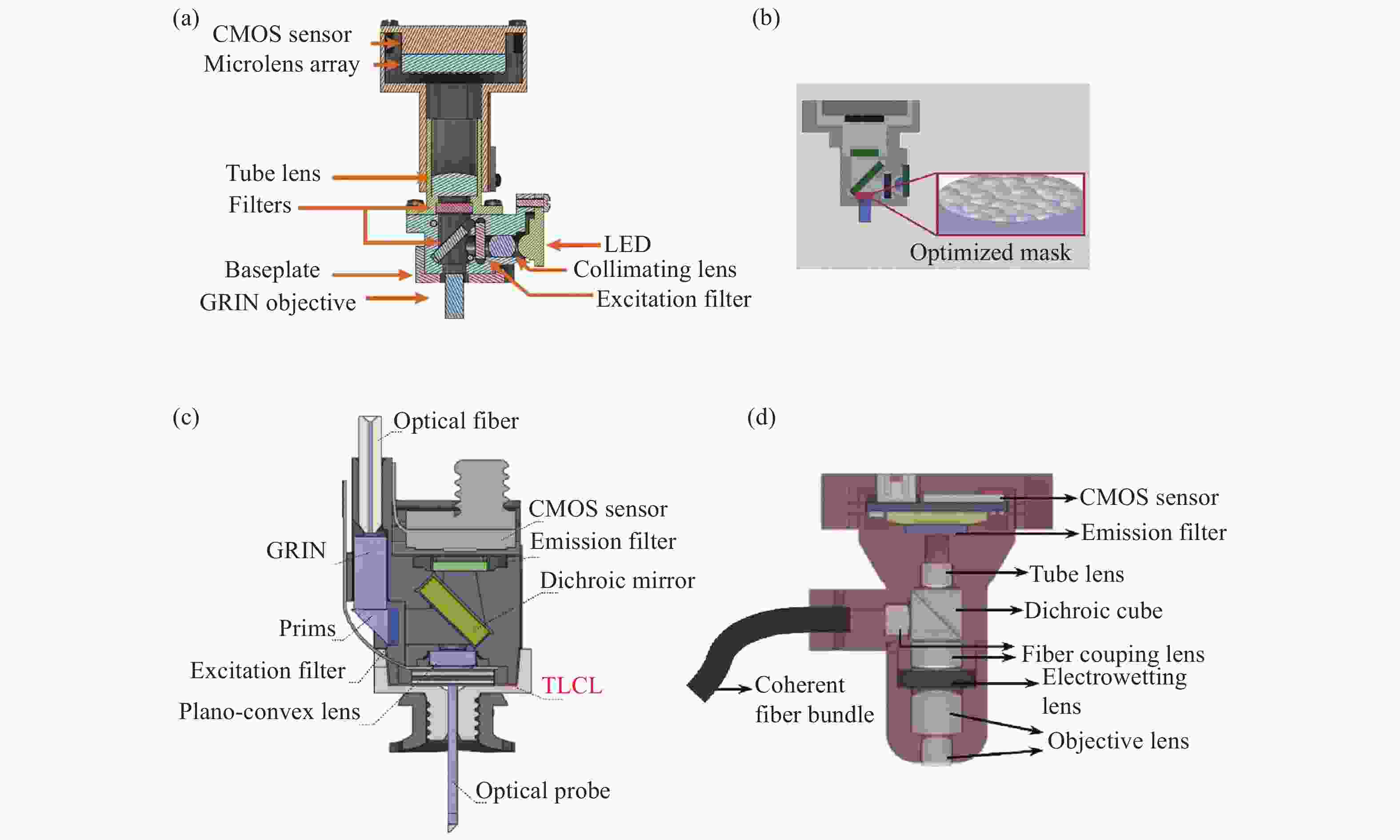
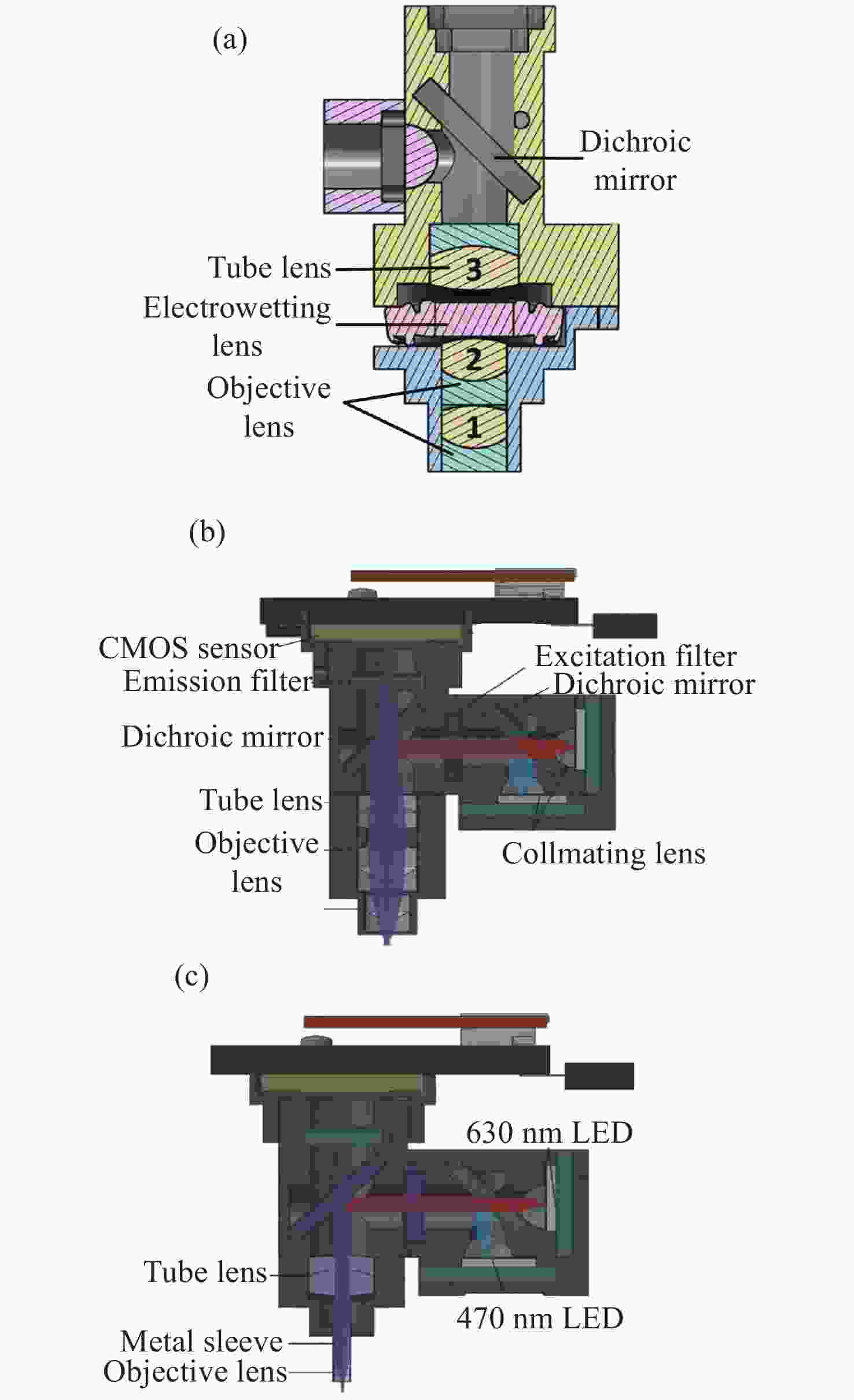
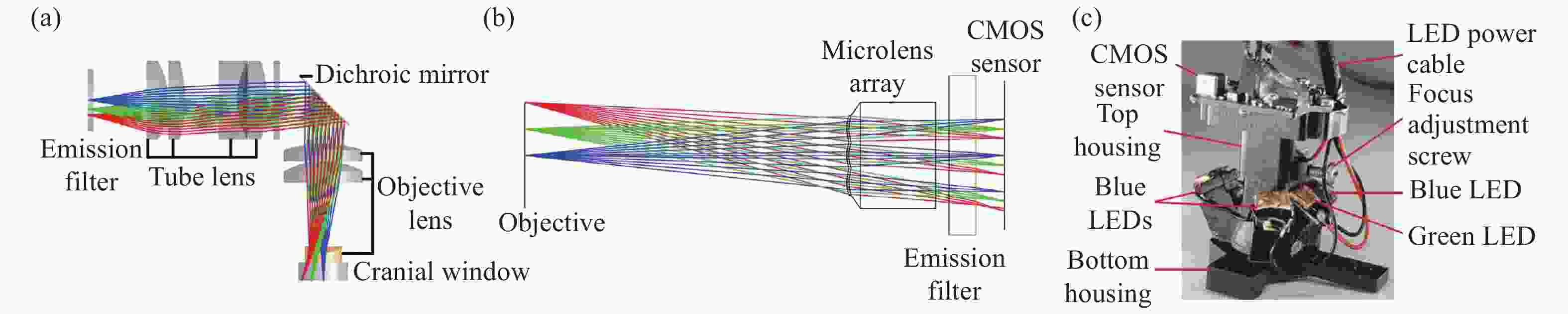
图 3 具有三维成像功能的系统。(a)MiniLFM的横截面图[24];(b)Miniscope3D的横截面图[27];(c)Bagramyan等人的显微镜横截面图[28];(d)SIMscope3D的横截面图[29]
Figure 3. A system with 3D imaging functionality. (a) Cross sectional view of MiniLFM; (b) cross sectional view of Miniscope3D; (c) microscope cross section by Bagramyan et al; (d) cross sectional view of SIMscope3D
表 1 具有基本成像功能的微型荧光显微镜的光学系统和光学性能参数
Table 1. Optical system and optical performance parameters of the miniature fluorescence microscope with basic imaging functionality
系统参数 Ghosh 等人 MiniScope V3 miniscope CHEndoscope Bagramyan 等人 物镜 梯度折射率透镜 梯度折射率透镜 非球面透镜 梯度折射率透镜 梯度折射率透镜 管镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 平凸透镜 视场 600 μm×800 μm 750 μm×450 μm 1100 μm×1100 μm ~500 μm ~105 μm 分辨率 2.5 μm 1.0 μm/pix 单细胞分辨率 单细胞分辨率 1.0 μm 图像传感器 MT9V021
(5.6 μm/pix)MT9V032
(6.0 μm/pix)MT9V022
(6.0 μm/pix)MT9P031
(2.2 μm/pix)OV7251
(3.0 μm/pix)成像速度 36 Hz 60 Hz 10 Hz 20 Hz 50 Hz 表 2 具有无线功能的微型荧光显微镜的光学系统和光学性能参数
Table 2. Optical system and optical performance parameters of a miniature fluorescence microscope with wireless function
系统参数 FinchScope Wire-free MiniScope miniscope wScope 物镜 梯度折射率透镜 梯度折射率透镜 非球面透镜 梯度折射率透镜 管镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 视场 800 μm×600 μm — 500 μm×500 μm 700 μm×450 μm 分辨率 单细胞分辨率 1 μm/pix 单细胞分辨率 1.8 μm 图像传感器 OV7960(6.00 μm/pix) EV76C454(5.80 μm/pix) MT9V022(6.00 μm/pix) OV7690 (1.75 μm/pix) 成像速度 30 Hz 10 Hz 10 Hz 25 Hz 表 3 具有三维成像功能的微型荧光显微镜的光学系统和光学性能参数
Table 3. Optical system and optical performance parameters of the miniature fluorescence microscope with 3D imaging functionality
系统参数 MiniLFM Miniscope3D Bagramyan等人 OMKAR 等人 物镜 梯度折射率透镜 梯度折射率透镜 梯度折射率透镜 两片双胶合透镜 管镜 双胶合透镜 相位掩模板 平凸透镜 双胶合透镜 视场 700 μm×600 μm×360 μm 900 μm×700 μm×390 μm 横向 150 μm
轴向 98 μm横向207 μm
轴向220 μm三维成像元件 微透镜阵列 相位掩模板 可调谐液晶透镜 电湿润透镜 横向分辨率 6.0 μm 2.8 μm 1.4 μm 1.0 μm/pix 轴向分辨率 30.0 μm 15.0 μm 15.0 μm 18.0 μm 图像传感器 MT9V032 (6.0 μm/pix) MT9V032 (6.0 μm/pix) OV7251 (3.0 μm/pix) MT9P031 (2.2 μm/pix) 成像速度 16 Hz 40 Hz 50 Hz — 表 4 具有双区域成像功能的微型荧光显微镜的光学系统和光学性能参数
Table 4. Optical system and optical performance parameters of a miniature fluorescence microscope with dual region imaging functionality
系统参数 Gonzalez 等人 NINscope 物镜 梯度折射率透镜 梯度折射率透镜 管镜 双胶合透镜 平凸透镜 视场 600 μm×479 μm 786 μm×502 μm 分辨率 0.83 μm/pix 单细胞分辨率 图像传感器 OV7690 (6 μm/pix) PYTHON480 (4.8 μm/pix) 成像速度 — 30 Hz 表 5 具有双色成像功能的微型荧光显微镜的光学系统和光学性能参数
Table 5. Optical system and optical performance parameters of a miniature fluorescence microscope with two-color imaging functionality
系统参数 MiniScope V4 DCFIMM-SBI DCFIMM-DBI 物镜 两片双胶合透镜 两片双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 管镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 双胶合透镜 视场 ~1.00 mm2 1.10 mm×1.10 mm 0.77 mm×0.77 mm 分辨率 单细胞分辨率 3.47 μm 3.47 μm 图像传感器 PYTHON480
(4.8 μm/pix)EV76C454
(5.8 μm/pix)EV76C454
(5.8 μm/pix)成像速度 120 Hz 20 Hz 20 Hz 表 6 小视场微型单光子荧光显微镜的光学系统组成和光学性能参数
Table 6. Optical system composition and optical performance parameters of miniature single photon fluorescence microscope with a small field
表 7 大视场微型荧光显微镜的光学系统和光学性能参数
Table 7. Optical system and optical performance parameters of a large field miniature fluorescence microscope
cScope CM2 mScope 物镜 多片球面透镜 微透镜阵列 双凸透镜 管镜 多片球面透镜 视场 7.8 mm×4.0 mm 7.3 mm×8.1 mm×
2.5 mm8.0 mm×10.0 mm 横向分辨率 14.0 μm 7 μm 39.4~55.7 μm 图像传感器 MT9V032
(6 µm/pix)MT9P031
(2.2 µm/pix)MT9V032
(6 µm/pix)成像速度 60Hz — — -
[1] CHEN SH Y, WANG Z CH, ZHANG D, et al. Miniature fluorescence microscopy for imaging brain activity in freely-behaving animals[J]. Neuroscience Bulletin, 2020, 36(10): 1182-1190. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00561-z [2] GRIENBERGER C, KONNERTH A. Imaging calcium in neurons[J]. Neuron, 2012, 73(5): 862-885. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.011 [3] 王义强, 林方睿, 胡睿, 等. 大视场光学显微成像技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(6):1194-1210.WANG Y Q, LIN F R, HU R, et al. Large field-of-view optical microscopic imaging technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1194-1210. (in Chinese) [4] 陈帅, 任林, 周镇乔, 等. 在体跨尺度双光子显微成像技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(6):1167-1181.CHEN SH, REN L, ZHOU ZH Q, et al. In-vivo across-scales two-photon microscopic imaging technique[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1167-1181. (in Chinese) [5] 王鹏, 周瑶, 赵宇轩, 等. 用于多尺度高分辨率三维成像的双环光片荧光显微技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(6):1321-1331.WANG P, ZHOU Y, ZHAO Y X, et al. Double-ring-modulated light sheet fluorescence microscopic technique for multi-scale high-resolution 3D imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1321-1331. (in Chinese) [6] YU H, SENARATHNA J, TYLER B M, et al. Miniaturized optical neuroimaging in unrestrained animals[J]. NeuroImage, 2015, 113: 397-406. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.070 [7] AHARONI D, KHAKH B S, SILVA A J, et al. All the light that we can see: a new era in miniaturized microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(1): 11-13. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0266-x [8] ZONG W J, WU R L, LI M L, et al. Fast high-resolution miniature two-photon microscopy for brain imaging in freely behaving mice[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(7): 713-719. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4305 [9] GHOSH K K, BURNS L D, COCKER E D, et al. Miniaturized integration of a fluorescence microscope[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(10): 871-878. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1694 [10] CAI D J, AHARONI D, SHUMAN T, et al. A shared neural ensemble links distinct contextual memories encoded close in time[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7605): 115-118. doi: 10.1038/nature17955 [11] CAMPOS P, WALKER J J, MOLLARD P. Diving into the brain: deep-brain imaging techniques in conscious animals[J]. Journal of Endocrinology, 2020, 246(2): R33-R50. doi: 10.1530/JOE-20-0028 [12] BARBERA G, LIANG B, ZHANG L F, et al. Spatially compact neural clusters in the dorsal striatum encode locomotion relevant information[J]. Neuron, 2016, 92(1): 202-213. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.08.037 [13] ZHANG L F, LIANG B, BARBERA G, et al. Miniscope GRIN lens system for calcium imaging of neuronal activity from deep brain structures in behaving animals[J]. Current Protocols in Neuroscience, 2019, 86(1): e56. doi: 10.1002/cpns.56 [14] LIANG B, ZHANG L F, BARBERA G, et al. Distinct and dynamic ON and OFF neural ensembles in the prefrontal cortex code social exploration[J]. Neuron, 2018, 100(3): 700-714.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.08.043 [15] JACOB A D, RAMSARAN A I, MOCLE A J, et al. A compact head-mounted endoscope for in vivo calcium imaging in freely behaving mice[J]. Current Protocols in Neuroscience, 2018, 84(1): e51. doi: 10.1002/cpns.51 [16] BAGRAMYAN A. Lightweight 1-photon miniscope for imaging in freely behaving animals at subcellular resolution[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(15): 909-912. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3004283 [17] LIBERTI III W A, MARKOWITZ J E, PERKINS L N, et al. Unstable neurons underlie a stable learned behavior[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2016, 19(12): 1665-1671. doi: 10.1038/nn.4405 [18] COHEN Y, SHEN J, SEMU D, et al. Hidden neural states underlie canary song syntax[J]. Nature, 2020, 582(7813): 539-544. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2397-3 [19] LIBERTI III W A, PERKINS L N, LEMAN D P, et al. An open source, wireless capable miniature microscope system[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2017, 14(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aa6806 [20] Alvarado J S, Goffinet J, Michael V, et al. Neural dynamics underlying birdsong practice and performance[J]. Nature, 2021, 599(7886): 635-639. [21] SHUMAN T, AHARONI D, CAI D J, et al. Breakdown of spatial coding and interneuron synchronization in epileptic mice[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2020, 23(2): 229-238. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0559-0 [22] BARBERA G, LIANG B, ZHANG L F, et al. A wireless miniScope for deep brain imaging in freely moving mice[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2019, 323: 56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.05.008 [23] WANG Y ZH, MA ZH T, LI W ZH, et al.. Cable-free brain imaging with miniature wireless microscopes[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2023, 28(2): 026503. [24] SKOCEK O, NÖBAUER T, WEILGUNY L, et al. High-speed volumetric imaging of neuronal activity in freely moving rodents[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(6): 429-432. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0008-0 [25] PREVEDEL R, YOON Y G, HOFFMANN M, et al. Simultaneous whole-animal 3D imaging of neuronal activity using light-field microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(7): 727-730. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2964 [26] NÖBAUER T, SKOCEK O, PERNÍA-ANDRADE A J, et al. Video rate volumetric Ca2+ imaging across cortex using seeded iterative demixing (SID) microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2017, 14(8): 811-818. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4341 [27] YANNY K, ANTIPA N, LIBERTI W, et al. Miniscope3D: optimized single-shot miniature 3D fluorescence microscopy[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2020, 9: 171. [28] BAGRAMYAN A, TABOURIN L, RASTQAR A, et al. Focus-tunable microscope for imaging small neuronal processes in freely moving animals[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(7): 1300-1309. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.418154 [29] SUPEKAR O D, SIAS A, HANSEN S R, et al. Miniature structured illumination microscope for in vivo 3D imaging of brain structures with optical sectioning[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2022, 13(4): 2530-2541. doi: 10.1364/BOE.449533 [30] GONZALEZ W G, ZHANG H W, HARUTYUNYAN A, et al. Persistence of neuronal representations through time and damage in the hippocampus[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6455): 821-825. doi: 10.1126/science.aav9199 [31] DE GROOT A, VAN DEN BOOM B J G, VAN GENDEREN R M, et al. NINscope, a versatile miniscope for multi-region circuit investigations[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e49987. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49987 [32] Silva A J. Miniaturized two-photon microscope: seeing clearer and deeper into the brain[J]. Light,science &applications, 2017, 6(8): e17104. [33] WIRTSHAFTER H S, DISTERHOFT J F. In vivo multi-day calcium imaging of CA1 hippocampus in freely moving rats reveals a high preponderance of place cells with consistent place fields[J]. Journal of Neuroscience, 2022, 42(22): 4538-4554. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1750-21.2022 [34] AHARONI D, HOOGLAND T M. Circuit investigations with open-source miniaturized microscopes: past, present and future[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2019, 13: 141. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00141 [35] 蓝凯秋, 杨西斌, 徐宝腾, 等. 双色荧光成像在体微型显微镜[J]. 光子学报,2022,51(6):0618001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225106.0618001LAN K Q, YANG X B, XU B T, et al. In vivo, dual-color fluorescent imaging miniature microscope[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(6): 0618001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225106.0618001 [36] SCOTT B B, THIBERGE S Y, GUO C Y, et al. Imaging cortical dynamics in GCaMP transgenic rats with a head-mounted widefield macroscope[J]. Neuron, 2018, 100(5): 1045-1058.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.050 [37] XUE Y J, DAVISON I G, BOAS D A, et al. Single-shot 3D wide-field fluorescence imaging with a Computational Miniature Mesoscope[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(43): eabb7508. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb7508 [38] STERN A, JAVIDI B. Three-dimensional image sensing, visualization, and processing using integral imaging[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2006, 94(3): 591-607. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2006.870696 [39] 邓慧, 吕国皎, 杨梅, 等. 基于掩膜板阵列的消串扰集成成像3D显示方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2022,37(5):592-597. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0027DENG H, LYU G J, YANG M, et al. Crosstalk-free integral imaging 3D display method based on a mask array[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2022, 37(5): 592-597. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0027 [40] CONG L, WANG Z G, CHAI Y M, et al. Rapid whole brain imaging of neural activity in freely behaving larval zebrafish (Danio rerio)[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e28158. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28158 [41] 徐斌, 于迅博, 高鑫, 等. 一种视点均匀分布的桌面式光场显示系统[J]. 液晶与显示,2022,37(5):573-580. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0041XU B, YU X B, GAO X, et al. Tabletop light field display system with uniform distribution of viewpoints[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2022, 37(5): 573-580. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0041 [42] 于迅博, 李涵宇, 高鑫, 等. 基于预处理卷积神经网络提升3D光场显示视觉分辨率的方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2022,37(5):549-554. doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0044YU X B, LI H Y, GAO X, et al. 3D light field display with improved visual resolution based on pre-processing convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2022, 37(5): 549-554. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CJLCD.2022-0044 [43] TANIDA J, KUMAGAI T, YAMADA K, et al. Thin observation module by bound optics (TOMBO): concept and experimental verification[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(11): 1806-1813. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.001806 [44] MCCALL B, OLSEN R J, NELLES N J, et al. Evaluation of a miniature microscope objective designed for fluorescence array microscopy detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. Archives of Pathology &Laboratory Medicine, 2014, 138(3): 379-389. [45] ANTIPA N, KUO G, HECKEL R, et al. DiffuserCam: lensless single-exposure 3D imaging[J]. Optica, 2018, 5(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.000001 [46] RYNES M L, SURINACH D A, LINN S, et al. Miniaturized head-mounted microscope for whole-cortex mesoscale imaging in freely behaving mice[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(4): 417-425. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01104-8 [47] WU J M, GUO Y D, DENG CH, et al. An integrated imaging sensor for aberration-corrected 3D photography[J]. Nature, 2022, 612(7938): 62-71. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05306-8 -





 下载:
下载: