Assembling and test method for main focus survey telescope based on curvature sensing
-
摘要:
通过对望远镜进行曲率波前感知,以更好地实现主焦巡天望远镜的集成检测。首先,利用傅立叶光学理论分析了主焦巡天望远镜曲率传感过程以及多环节动态稳定性传递基本原理。其次,对主焦巡天望远镜集成检测中的静态校正与动面形测量过程进行误差分析。然后,分析了调节过程中的自由度锁定。最后,通过实验实现了集成检测过程的原理贯通。所获得的波前探测残差优于0.08
λ (λ =633 nm)。空间分辨率为0.1 m,时间分辨率为0.2 Hz。本方法可有效提升主焦点大口径大视场望远镜的成像质量,利用曲率传感非干涉、高鲁棒的特点,降低了集成检测过程对外界环境稳定性的需求,为未来更加精细的时域天文学观测提供助力。Abstract:The integrated detection of the main focus telescope is realized by sensing the curvature wavefront of the telescope. First of all, the curvature sensing process of the main focus telescope and the basic principle of dynamic stability transfer in multiple links are analyzed using Fourier optics theory. Secondly, the error analysis of static correction and dynamic surface shape measurement in the integrated detection of the main focus telescope is carried out. After that, the degree of freedom locking in the adjustment process is analyzed. Finally, the principle of the integrated detection process is realized through experiments. The obtained wavefront detection residual is better than 0.08
λ (λ =633 nm). The spatial resolution is 10/m−1, and the temporal resolution is 0.2 Hz. This method can effectively improve the imaging quality of main focus telescope with the large-aperture large-field, and reduce the demand for the stability of the external environment in the integrated detection process by using the non-interference and high robustness characteristics of the curvature sensor, so as to provide assistance for the more detailed time-domain astronomical observation in the future.-
Key words:
- curvature sensing /
- wavefront aberration /
- main focus telescope /
- integrated detection
-
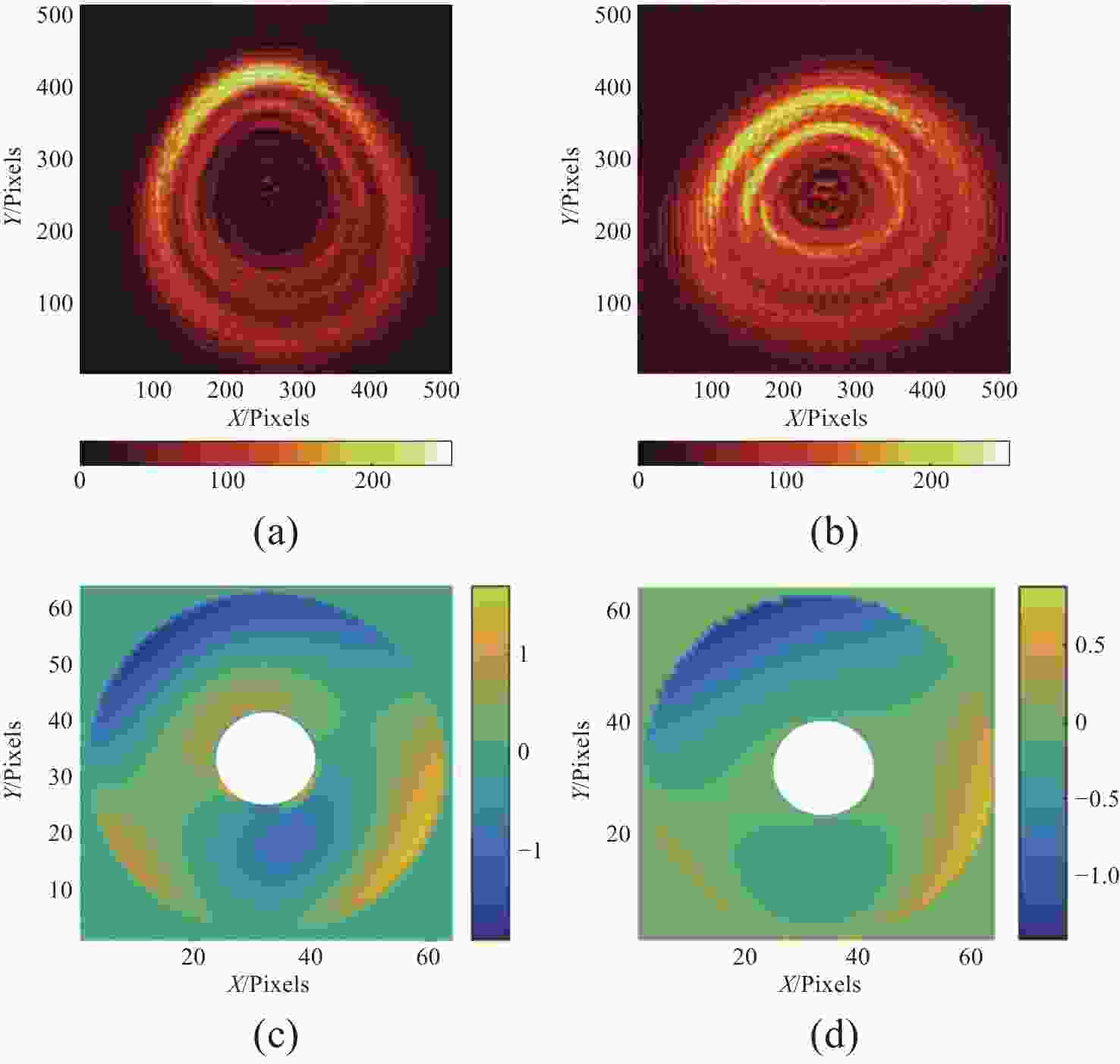
图 4 1-μm抖动影响下的波前感知情况。(a)焦前光强分布;(b)焦后光强分布;(c)重建波前;(d)多色重建波前与单色原始波前结果对比
Figure 4. Wavefront perception under the influence of 1-μm Jitter. (a) Pre-focal light intensity distribution; (b) light intensity distribution of extra focus; (c) reconstructed wavefront; (d) comparison of reconstructed wavefront and original wavefront
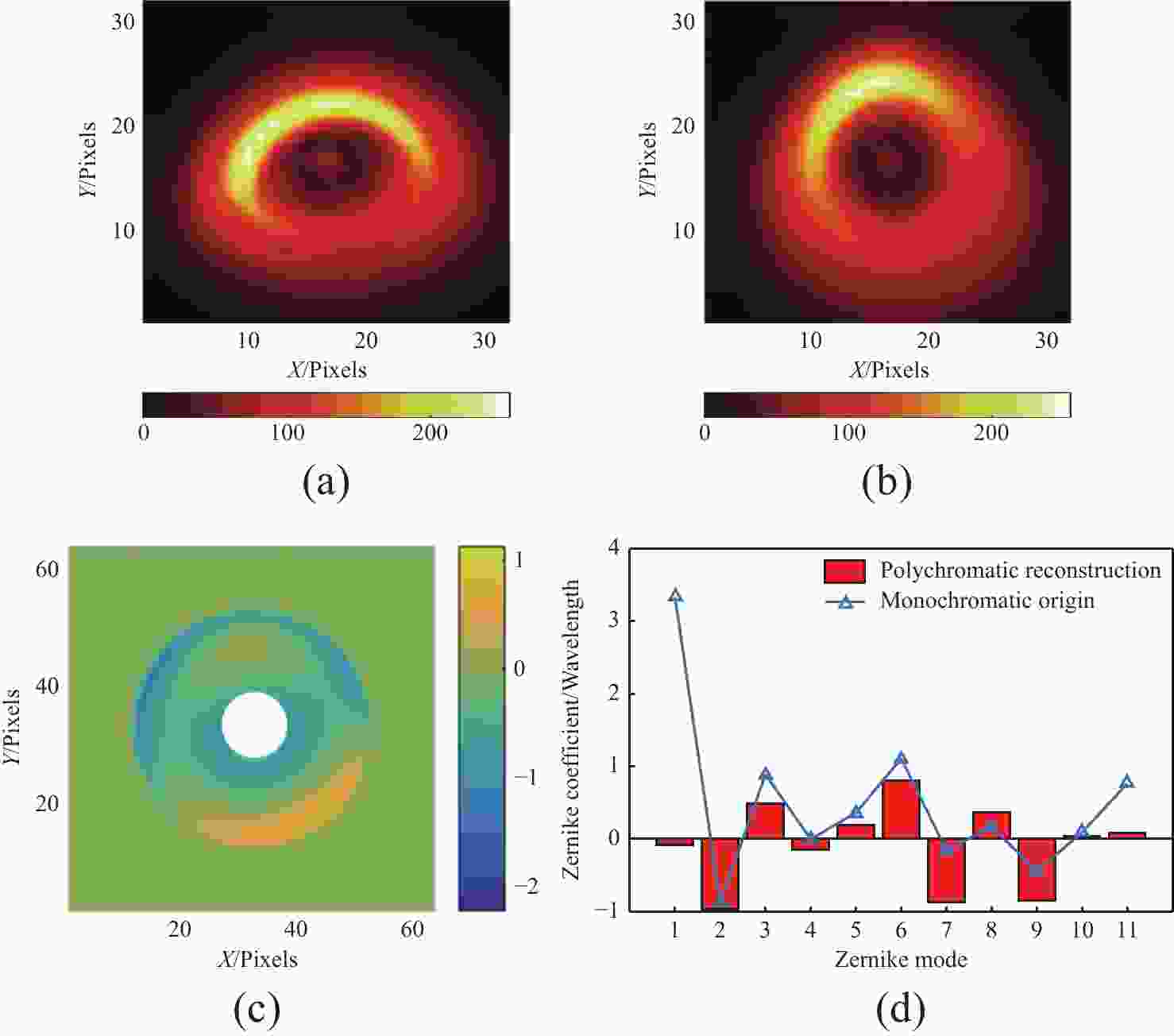
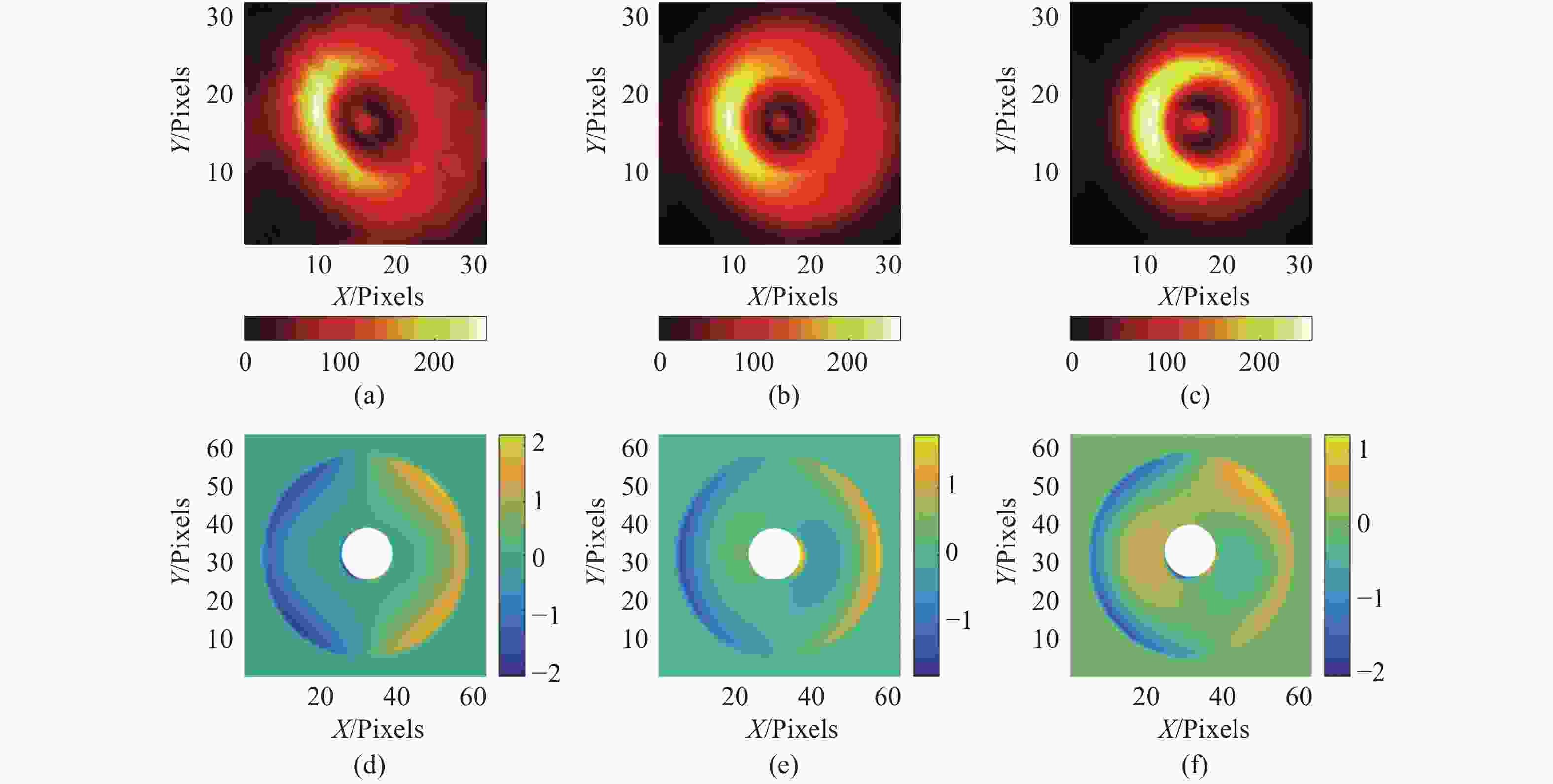
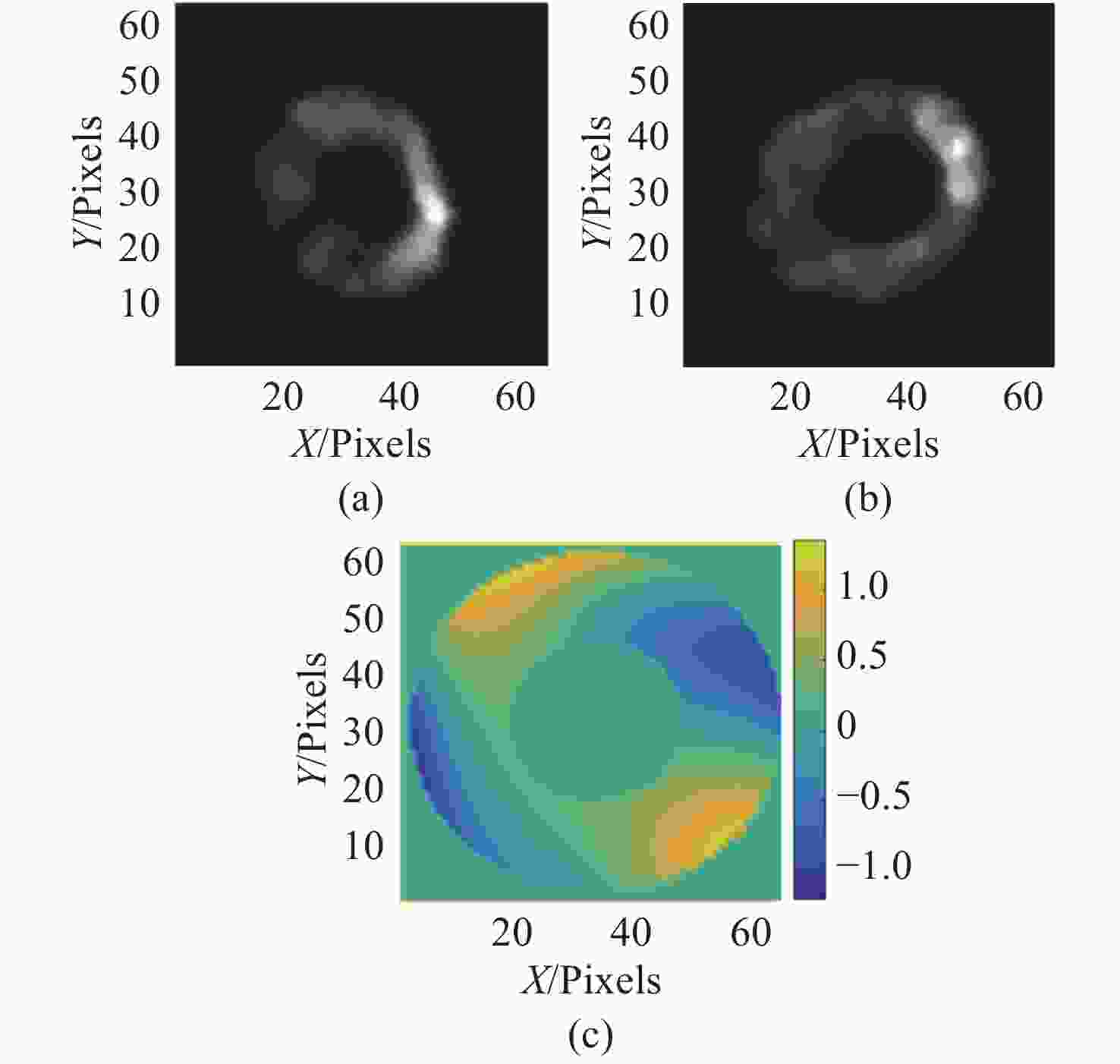
图 5 绕偏置点旋转下的离焦星点像与系统波前。(a) 第一次修正离焦星点像;(b)第二次修正离焦星点像;(c)第三次修正离焦星点像;(d) 第一次修正系统波前;(e)第二次修正系统波前;(f)第三次修正系统波前
Figure 5. The defocus donut and system wavefront under rotation around the offset point. (a) First corrected defocus donut; (b) second corrected defocus donut; (c) third corrected defocus donut; (d) first corrected system wavefront; (e) second corrected system wavefront; (f) third corrected system wavefront
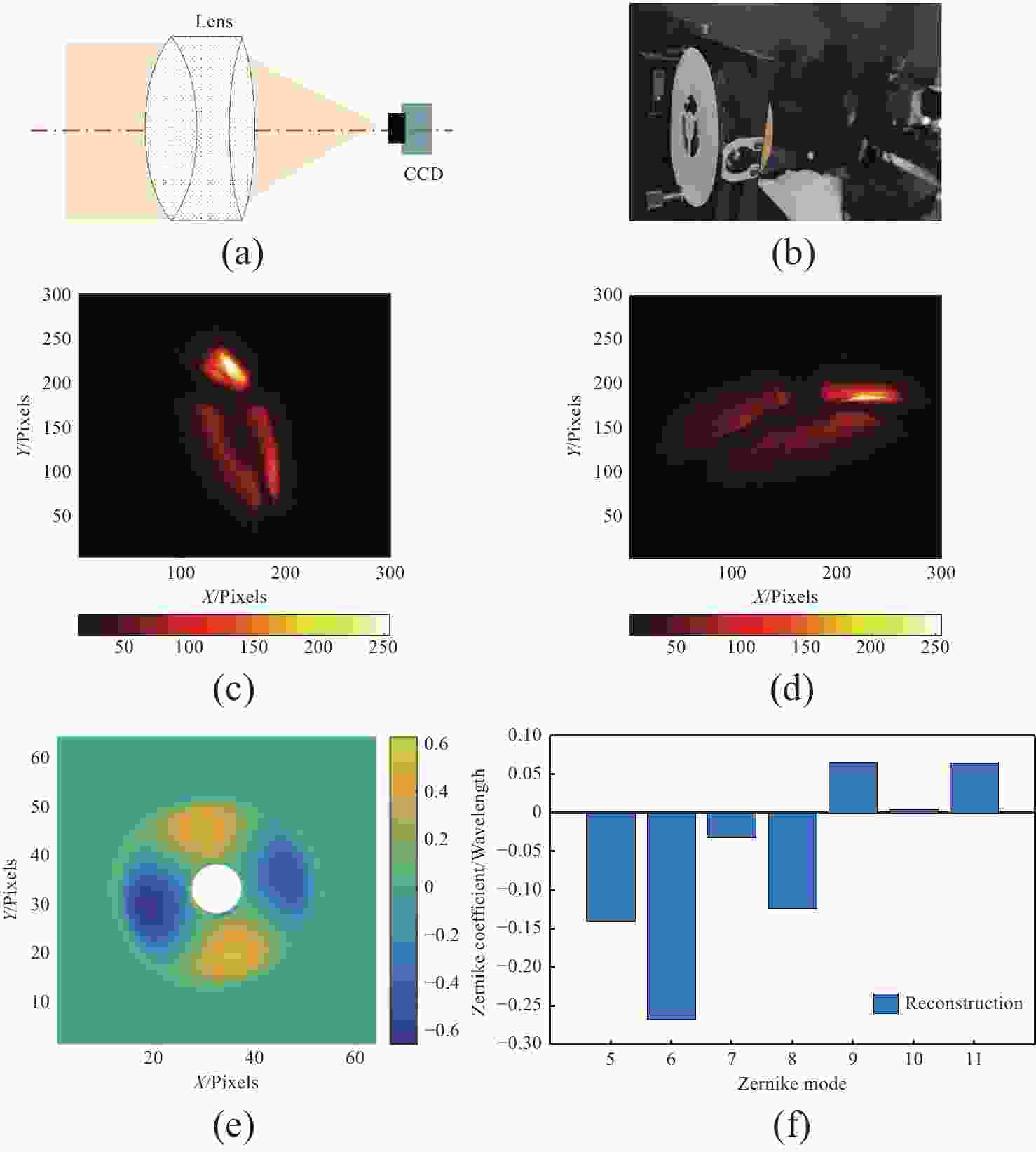
图 6 利用单个透镜的验证平台与验证结果。(a)光路原理图;(b)实验现场图;(c)焦前光强分布;(d)焦后光强分布;(e)波前解算结果;(f)低阶像差估计
Figure 6. Verification platform using single lens and its verification results. (a) Schematic diagram of optical path; (b) experimental set up diagram; (c) inter focus intensity distribution; (d) extra focus intensity distribution; (e) wavefront solution results; (f) low order aberration estimation
-
[1] 姜晰文, 赵金宇, 吕天宇, 等. 大口径主焦点式光学系统的设计与装调[J]. 光学精密工程,2022,30(23):2987-2994.JIANG X W,ZHAO J Y,LV T Y,et al. Design and alignment of large-aperture prime focus optical system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(23): 2987-2994. (in Chinese) [2] FLAUGHER B, BEBEK C. The dark energy spectroscopic instrument (DESI)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9147: 91470S. [3] GREGGIO L, REJKUBA M, GONZALEZ O A, et al. A panoramic VISTA of the stellar halo of NGC 253[J]. Astronomy &Astrophysics, 2014, 562: A73. [4] FLAUGHER B, DIEHL H T, HONSCHEID K, et al. The dark energy camera[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 2015, 150(5): 150. doi: 10.1088/0004-6256/150/5/150 [5] 安其昌, 吴小霞, 张景旭, 等. 大口径主动光学巡天望远镜大动态范围曲率传感[J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(10):20210224. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210224AN Q CH, WU X X, ZHANG J X, et al. Large dynamic range curvature sensing for large-aperture active-optics survey telescope[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(10): 20210224. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210224 [6] SCHOBER C, BEISSWANGER R, GRONLE A, et al. Tilted wave Fizeau interferometer for flexible and robust asphere and freeform testing[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2022, 3: 48. [7] 安其昌, 姜晰文, 李洪文, 等. 基于差分传递函数法的大口径平面镜检测[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):992-999.AN Q CH, JIANG X W, LI H W, et al. Detection of large aperture flat mirror based on the differential optics transfer function method[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 992-999. (in Chinese) [8] GENG Z CH, TONG ZH, JIANG X Q. Review of geometric error measurement and compensation techniques of ultra-precision machine tools[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2021, 2(2): 211-227. doi: 10.37188/lam.2021.014 [9] FRATZ M, SEYLER T, BERTZ A, et al. Digital holography in production: an overview[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2021, 2(3): 283-295. [10] 朱沁雨, 陈梅蕊, 陆焕钧, 等. 微透镜阵列衍射效应对夏克一哈特曼波前探测器的影响分析[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):94-102.ZHU Q Y, CHEN M R, LU H J, et al. Analysis of influence of diffraction effect of microlens array on Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 94-102. (in Chinese) [11] TYSON J A, WITTMAN D M, HENNAWI J F, et al. LSST: a complementary probe of dark energy[J]. Nuclear Physics B - Proceedings Supplements, 2003, 124: 21-29. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5632(03)02073-5 [12] VOSTEEN A, DRAAISMA F, VAN WERKHOVEN W, et al. Wavefront sensor for the GAIA mission[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 10565: 105650L. [13] HARTLIEB S, RINGKOWSKI M, HAIST T, et al. Multi-positional image-based vibration measurement by holographic image replication[J]. Light:Advanced Manufacturing, 2021, 2(4): 425-433. [14] TRAUGER J, STAPELFELDT K, TRAUB W, et al. ACCESS: a NASA mission concept study of an actively corrected coronagraph for exoplanet system studies[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7010: 701029. doi: 10.1117/12.789119 -





 下载:
下载: