-
摘要:
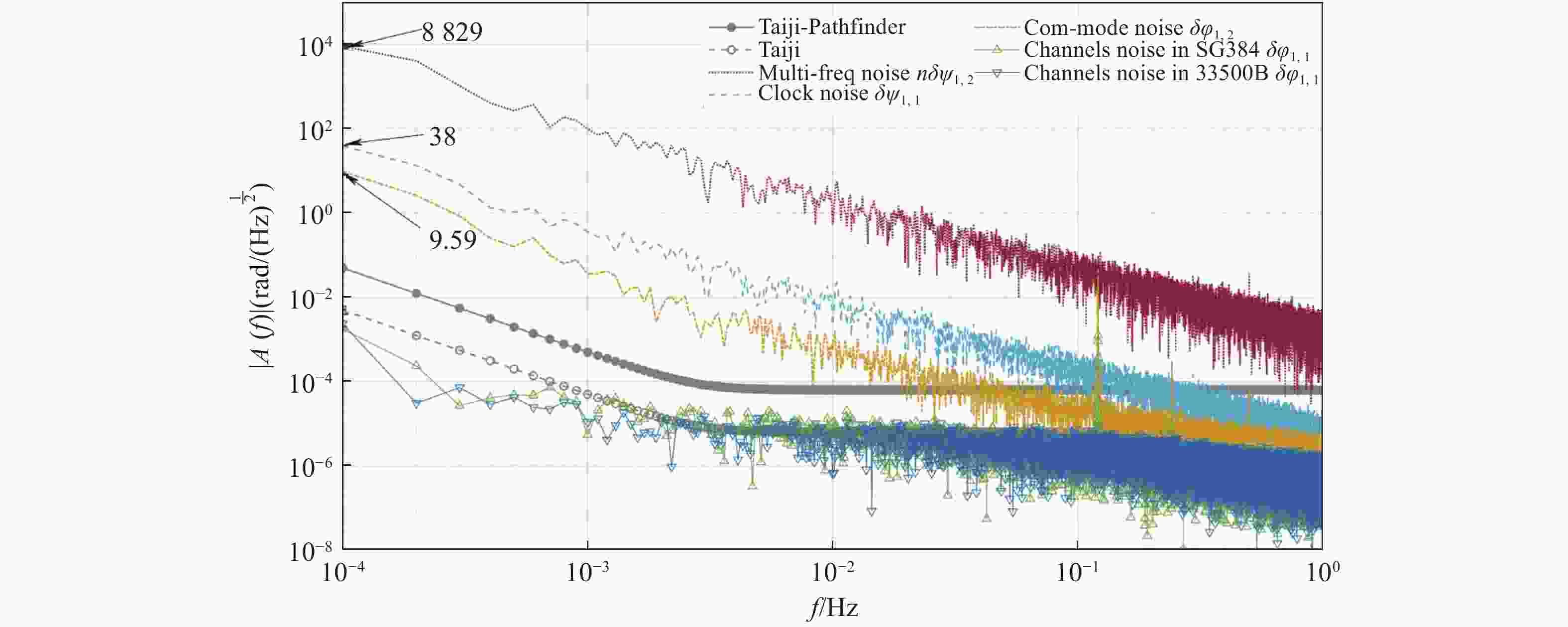
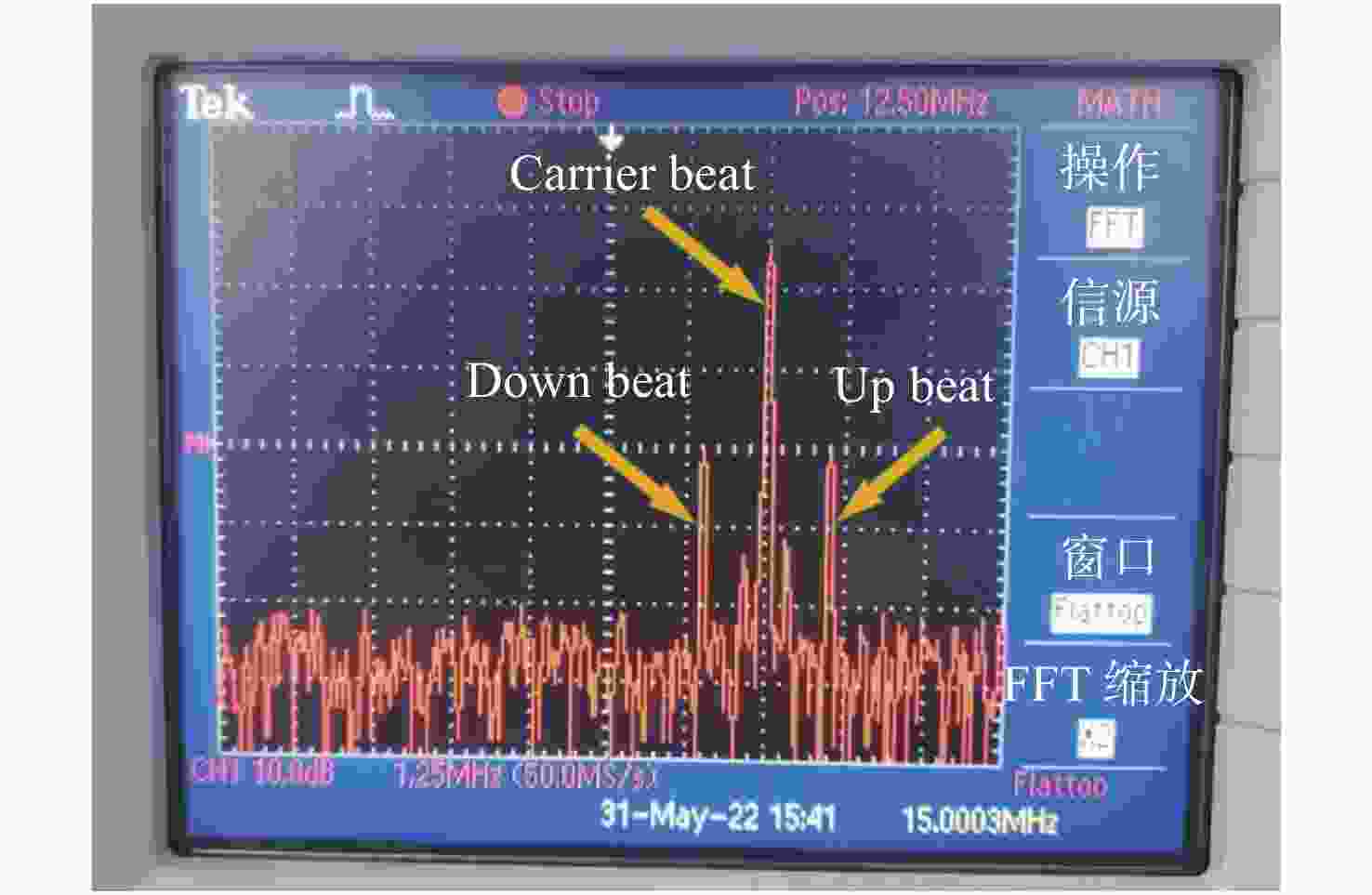
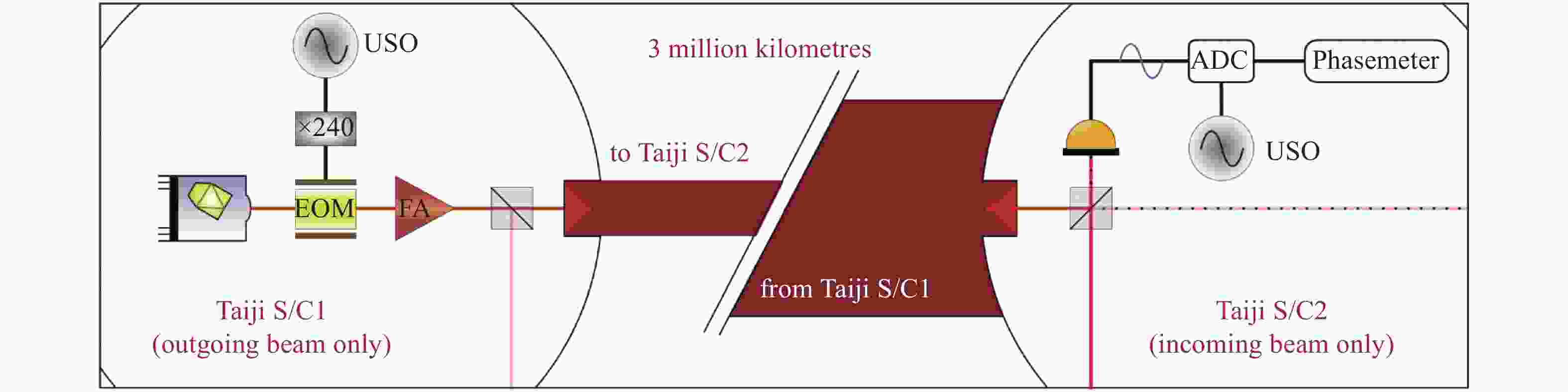
太极计划是中国科学院提出的空间引力波探测任务,其利用激光差分干涉的方法探测卫星间由引力波引起的pm级位移波动。为消除卫星间因时钟不同步而产生的测量误差,拟采用边带倍频时钟噪声传递方法进行星间时钟噪声测量与消除。本文讨论太极计划星间时钟噪声传递的需求、原理、方法,并设计实验进行原理验证。通过搭建电子学实验测试两个系统时钟噪声的极限值,确定实验相关参数,进一步通过光学实验验证边带倍频传递方案的原理。实验结果表明,本文提出的时钟噪声消除方案及相关参数合理可行,满足太极计划的应用需求。在0.05 Hz~1 Hz频段,星间时钟噪声的抑制效果优于2π×10−5 rad/Hz1/2,满足太极探路者的噪声需求。本文研究为未来太极计划的时钟噪声传递方案与参数设计奠定实验和理论基础。
Abstract:The Taiji program is a space gravitational wave detection mission proposed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, which uses laser differential interference to detect pm-level displacement fluctuations caused by gravitational waves between satellites. In order to eliminate the phase measurement error caused by the desynchronization of the clocks in satellites, the Taiji program intends to use the sideband multiplication transfer scheme to measure and eliminate inter-satellite clock noise. We discuss the requirements, principles, and methods of inter-satellite clock noise transmission of the Taiji program, and design experiments for the principle verification. By building an electronics experiment system, the limit value of the clock noise of the two systems was tested, the relevant parameters of the experiment were determined, and the principle of the sideband multiplication transfer scheme was verified by further optical experiments. The experimental results show that the clock noise cancellation scheme and related parameters proposed in this paper are reasonable and feasible, and are suitable for the needs of the Taiji program. Moreover, in the 0.05 Hz−1 Hz frequency band, the suppression effect of inter-satellite clock noise is better than 2π×10−5 rad/Hz1/2, which meets the noise requirements of the Taiji pathfinder and lays an experimental and theoretical foundation for the design of a clock noise transmission scheme and parameters of the Taiji program in the future.
-
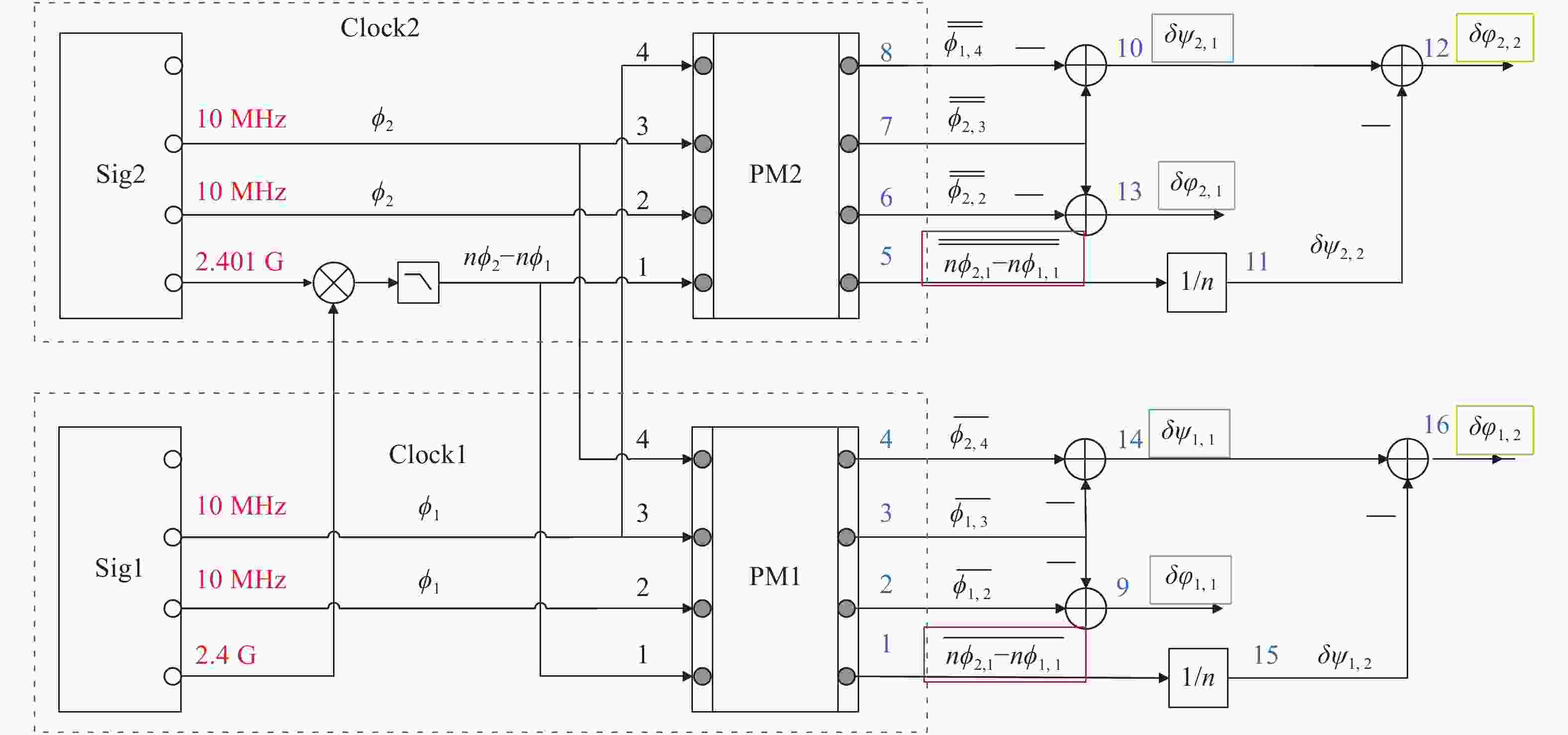
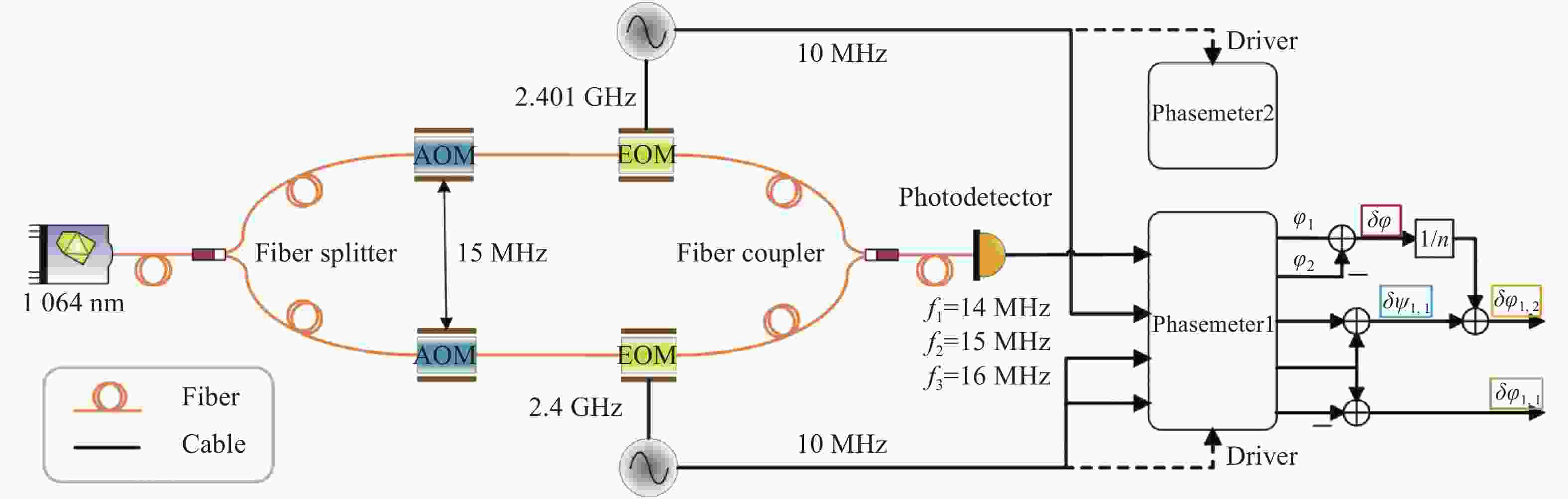
图 3 电子学实验原理框图。
$ \overline {{\phi _{i,j}}} $ 表示相位计PM1的j通道对信号i的读出,$ \overline{\overline {{\phi _{i,j}}}} $ 表示相位计PM2的j通道对信号i的读出(i=1, 2; j=1, 2, 3, 4)Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the electronic experiment.
$ \overline {{\phi _{i,j}}} $ represents the readout of signal i by the j channel of the phasemeter PM1,$ \overline{\overline {{\phi _{i,j}}}} $ represents the readout of signal i by the j channel of the phasemeter PM2 (i=1, 2; j=1, 2, 3, 4) -
[1] ABBOTT B P, ABBOTT R, ABBOTT T D, et al. Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(6): 061102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.061102 [2] GAIR J R, VALLISNERI M, LARSON S L, et al. Testing general relativity with low-frequency, space-based gravitational-wave detectors[J]. Living Reviews in Relativity, 2013, 16(1): 7. doi: 10.12942/lrr-2013-7 [3] 罗子人, 白姗, 边星, 等. 空间激光干涉引力波探测[J]. 力学进展,2013,43(4):415-447.LUO Z R, BAI SH, BIAN X, et al. Gravitational wave detection by space laser interferometry[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2013, 43(4): 415-447. (in Chinese) [4] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Sensor noise in LISA pathfinder: in-flight performance of the optical test mass readout[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 126(13): 131103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.131103 [5] ARMANO M, AUDLEY H, BAIRD J, et al. Sensor noise in LISA Pathfinder: an extensive in-flight review of the angular and longitudinal interferometric measurement system[J]. Physical Review D, 2022, 106(8): 082001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.106.082001 [6] HU W R, WU Y L. The Taiji Program in Space for gravitational wave physics and the nature of gravity[J]. National Science Review, 2017, 4(5): 685-686. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx116 [7] THE TAIJI SCIENTIFIC COLLABORATION. China’s first step towards probing the expanding universe and the nature of gravity using a space borne gravitational wave antenna[J]. Communications Physics, 2021, 4(1): 34. doi: 10.1038/s42005-021-00529-z [8] LUO J, CHEN L SH, DUAN H Z, et al. TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2016, 33(3): 035010. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/33/3/035010 [9] LUO J, BAI Y ZH, CAI L, et al. The first round result from the TianQin-1 satellite[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2020, 37(18): 185013. doi: 10.1088/1361-6382/aba66a [10] 刘河山, 高瑞弘, 罗子人, 等. 空间引力波探测中的绝对距离测量及通信技术[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):486-492. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486LIU H SH, GAO R H, LUO Z R, et al. Laser ranging and data communication for space gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 486-492. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0486 [11] 邓汝杰, 张艺斌, 刘河山, 等. 太极计划中的星间激光测距地面电子学验证[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(4): 765-776.DENG R J, ZHANG Y B, LIU H SH, et al.. Ground electronics verification of inter-satellites laser ranging in the Taiji program[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(4): 765-776. (in Chinese) [12] 李建聪, 林宏安, 罗佳雄, 等. 空间引力波探测望远镜光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(4):761-769. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0018LI J C, LIN H A, LUO J X, et al. Optical design of space gravitational wave detection telescope[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(4): 761-769. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0018 [13] 罗子人, 张敏, 靳刚, 等. 中国空间引力波探测"太极计划"及"太极1号"在轨测试[J]. 深空探测学报,2020,7(1):3-10.LUO Z R, ZHANG M, JIN G, et al. Introduction of Chinese space-borne gravitational wave detection program "Taiji" and "Taiji-1" satellite mission[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2020, 7(1): 3-10. (in Chinese) [14] BARKE S. Inter-spacecraft frequency distribution for future gravitational wave observatories[D] Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2015. [15] BARKE S, TRÖBS M, SHEARD B, et al. EOM sideband phase characteristics for the spaceborne gravitational wave detector LISA[J]. Applied Physics B, 2009, 98(1): 33-39. [16] HELLINGS R W. Elimination of clock jitter noise in spaceborne laser interferometers[J]. Physical Review D, 2001, 64(2): 022002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.64.022002 [17] OTTO M, HEINZEL G, DANZMANN K. TDI and clock noise removal for the split interferometry configuration of LISA[J]. Classical and Quantum Gravity, 2012, 29(20): 205003. doi: 10.1088/0264-9381/29/20/205003 [18] TINTO M, DHURANDHAR S V. Time-delay interferometry[J]. Living Reviews in Relativity, 2020, 24(1): 1. [19] 王登峰, 姚鑫, 焦仲科, 等. 面向天基引力波探测的时间延迟干涉技术[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(2):275-288. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0098WANG D F, YAO X, JIAO ZH K, et al. Time-delay interferometry for space-based gravitational wave detection[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 275-288. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0098 [20] YAMAMOTO K, VORNDAMME C, HARTWIG O, et al. Experimental verification of intersatellite clock synchronization at LISA performance levels[J]. Physical Review D, 2022, 105(4): 042009. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevD.105.042009 [21] LIU H SH, YU T, LUO Z R. A low-noise analog frontend design for the Taiji phasemeter prototype[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(5): 054501. doi: 10.1063/5.0042249 -





 下载:
下载: