-
摘要:
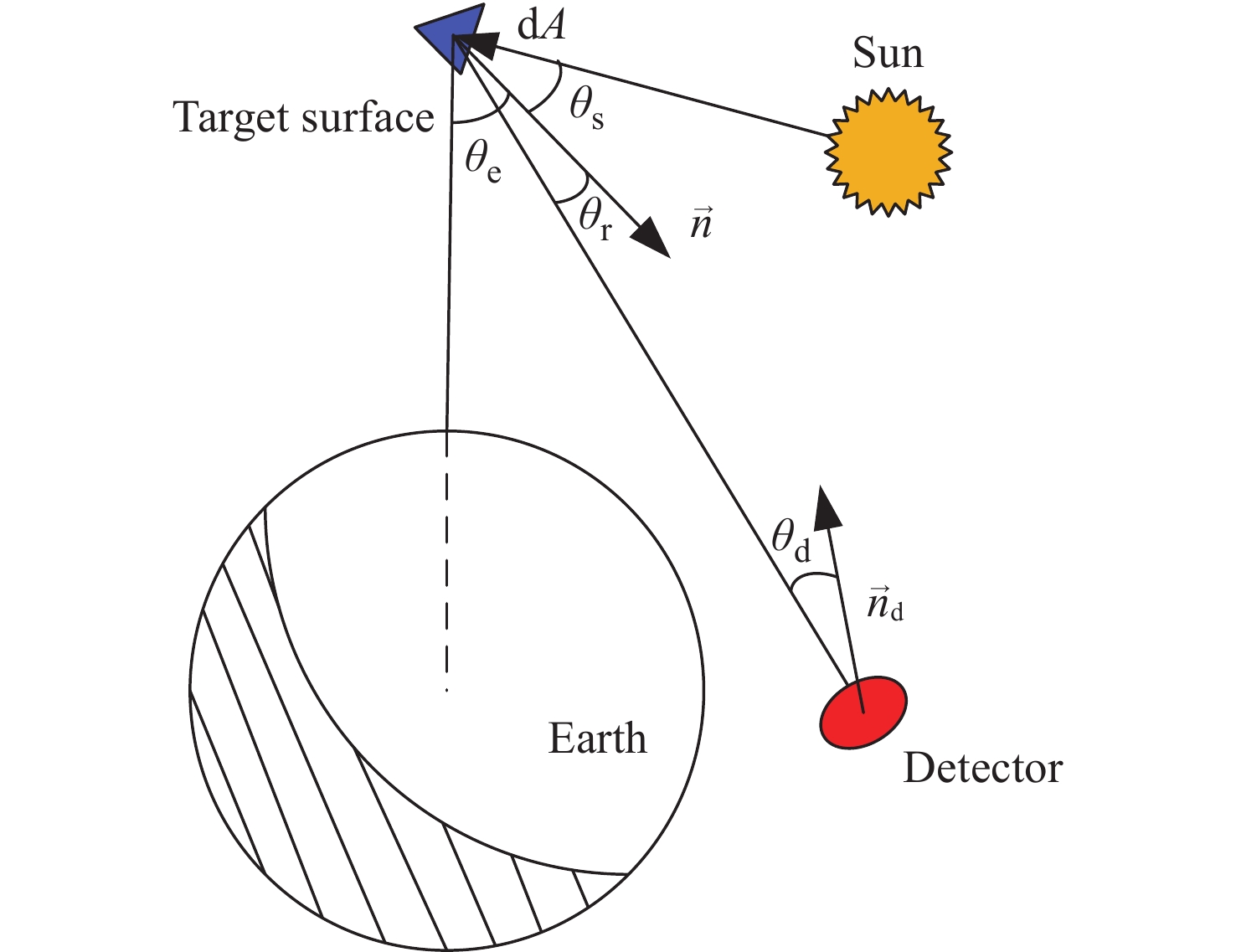
构建空间目标辐射特性对于发展空间态势感知技术具有重要意义。本文针对空间目标红外辐射特性,基于有限元方法,采用非结构四面体网格研制了仿真程序,通过矢量坐标变换,计算得到了目标各表面受到的轨道外热流,并结合表面材料和双向反射分布函数(BRDF)对目标各表面温度和红外辐射特性进行了仿真,并与文献结果进行了对比。进而考虑大气衰减和背景辐射的影响,对地基探测条件下升轨和降轨弧段的目标光谱辐射强度进行了分析。结果显示:对于三轴稳定太阳同步轨道沿飞行方向固定式帆板卫星,各表面在阳照区和地影区内温度变化范围较小;使用8~14 μm长波波段对目标进行观测的效果比3~5 μm中波波段好;辐射强度最大值在770 W/sr左右;地基红外光谱探测受大气影响较大,需要对探测波段进行优选。
Abstract:Constructing the radiation characteristics of space targets is of great significance for the development of space situational awareness technology. In this study, we aim to investigate the infrared radiation characteristics of space targets by developing a simulation program based on the finite element method and unstructured tetrahedral mesh. Through vector coordinate transformation, we calculate the orbit external heat flux received by each surface of the target. By combining the surface material properties and Bidirectional Reflection Distribution Function (BRDF), the temperature and infrared radiation characteristics of each target surface were simulated. Furthermore, we analyze the spectral radiation intensity of the target in the ascending and descending orbital arcs under ground-based detection conditions, taking into account the effects of atmospheric attenuation and background radiation. The results show that, for a three-axis stabilized synchronous orbit satellite with solar panels fixed in the flight direction, the temperature variation range of each surface in the sunlight area and the shadow area is small. The detection effect of the long-wave band of 8~14 μm is better than that of the medium-wave band of 3~5 μm, and the maximum radiation intensity is about 770 W/sr. Ground-based infrared spectrum detection is more affected by the atmosphere, and the detection band must be optimally selected.
-
表 1 轨道参数
Table 1. Orbit parameters
时间 (UTC) 半长轴 / km 偏心率 倾角/(°) 升交点赤经 /(°) 近地点幅角 /(°) 真近点角 /(°) 2000-03-21 04:00:00 7225.578 0.00345 98.757 124.893 102.064 156.019 表 2 表面材料热参数
Table 2. Thermal parameters of surface material
表面 材料 吸收率 发射率 本体 聚酰亚胺 0.23 0.62 太阳帆板 电池片 0.82 0.81 基板 0.88 0.86 表 3 不同位置点处的方位角、俯仰角和距离
Table 3. Azimuth, elevation, and range at different positions
序号 方位角 / (°) 俯仰角 / (°) 距离 / km 升轨弧段 1 165.9 20.0 1886.5 2 266.8 87.4 867.0 3 344.9 20.0 1888.2 降轨弧段 4 40.7 20.0 1870.5 5 97.0 38.1 1270.2 6 153.9 20.0 1860.6 -
[1] 罗秀娟, 刘辉, 张羽, 等. 地球同步轨道暗弱目标地基光学成像技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(4):753-766. doi: 10.3788/co.20191204.0753LUO X J, LIU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Review of ground-based optical imaging techniques for dim GEO objects[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(4): 753-766. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191204.0753 [2] 郑鸿儒, 马岩, 范林东, 等. 高空离轨发动机流场红外辐射特性研究[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):259-266. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0232ZHENG H R, MA Y, FAN L D, et al. Infrared radiation characteristics of high-altitude off-orbit engine plume[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 259-266. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0232 [3] 刘建斌, 吴健. 空间目标的光散射研究[J]. 宇航学报,2006,27(4):802-805.LIU J B, WU J. Light scattering of spatial target[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2006, 27(4): 802-805. (in Chinese) [4] 申文涛, 朱定强, 石良臣, 等. 太阳同步轨道卫星光学特性[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2013,39(1):6-10.SHEN W T, ZHU D Q, SHI L CH, et al. Optical properties of sun synchronous orbit satellite[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(1): 6-10. (in Chinese) [5] 杨帆, 宣益民, 韩玉阁. 基于红外辐射特征的空间目标属性预测[J]. 中国科学:技术科学,2016,46(8):836-843. doi: 10.1360/N092015-00270YANG F, XUAN Y M, HAN Y G. Properties prediction of space objects based on infrared radiative characteristics[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2016, 46(8): 836-843. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N092015-00270 [6] 李文豪, 刘朝晖, 穆猷, 等. 基于辐射散热的空间目标红外特性建模与研究[J]. 红外与激光工程,2017,46(6):0604003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0604003LI W H, LIU ZH H, MU Y, et al. Modeling and research of infrared characteristics of space target based on radiation dissipation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(6): 0604003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.0604003 [7] 谷牧, 任栖锋, 周金梅, 等. 基于地基观测的时序卫星红外光谱建模与分析[J]. 物理学报,2019,68(5):059501. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181933GU M, REN Q F, ZHOU J M, et al. Modeling and analyzing of time-resolved satellite infrared spectrum based on ground-based detector[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(5): 059501. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181933 [8] 孙成明, 袁艳, 吕群波. 天基空间目标光学散射特性建模与验证[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(11):1129001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1129001SUN CH M, YUAN Y, LV Q B. Modeling and verification of space-based optical scattering characteristics of space objects[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(11): 1129001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1129001 [9] SKINNER M, PAYNE T, RUSSELL R, et al. . IR spectrophotometric observations of geosynchronous satellites[C]. Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Hawaii, 2007. [10] SKINNER M A, RUSSELL R W, KELECY T, et al. Observations in the thermal IR and visible of a retired satellite in the graveyard orbit, and comparisons to active satellites in GEO[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2014, 105(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.08.016 [11] 舒锐, 周彦平, 陶坤宇, 等. 空间目标红外辐射特性研究[J]. 光学技术,2006,32(2):196-199.SHU R, ZHOU Y P, TAO K Y, et al. The study of infrared spectrum of space target[J]. Optical Technique, 2006, 32(2): 196-199. (in Chinese) [12] 汪夏, 张雅声, 徐灿, 等. 基于改进Phong模型的天基光学观测GEO目标姿态估计方法[J]. 光子学报,2020,49(1):112004. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204901.0112004WANG X, ZHANG Y SH, XU C, et al. Attitude estimation of GEO objects of space-based optical observation based on the improved Phong model[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(1): 112004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20204901.0112004 [13] 孙成明, 张伟, 王治乐. 双向反射分布函数在空间目标可见光反射特性建模中的应用[J]. 光学技术,2008,34(5):750-753,757.SUN CH M, ZHANG W, WANG ZH L. Application of BRDF for modeling on the visible reflection characteristics of spatial targets[J]. Optical Technique, 2008, 34(5): 750-753,757. (in Chinese) [14] 孟执中. "风云"1号C极轨气象卫星的进展(下)[J]. 中国航天,2001(9):18-22.MENG ZH ZH. The development of FY-1C meteorological satellite (Part 2)[J]. Aerospace China, 2001(9): 18-22. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: