-
摘要:
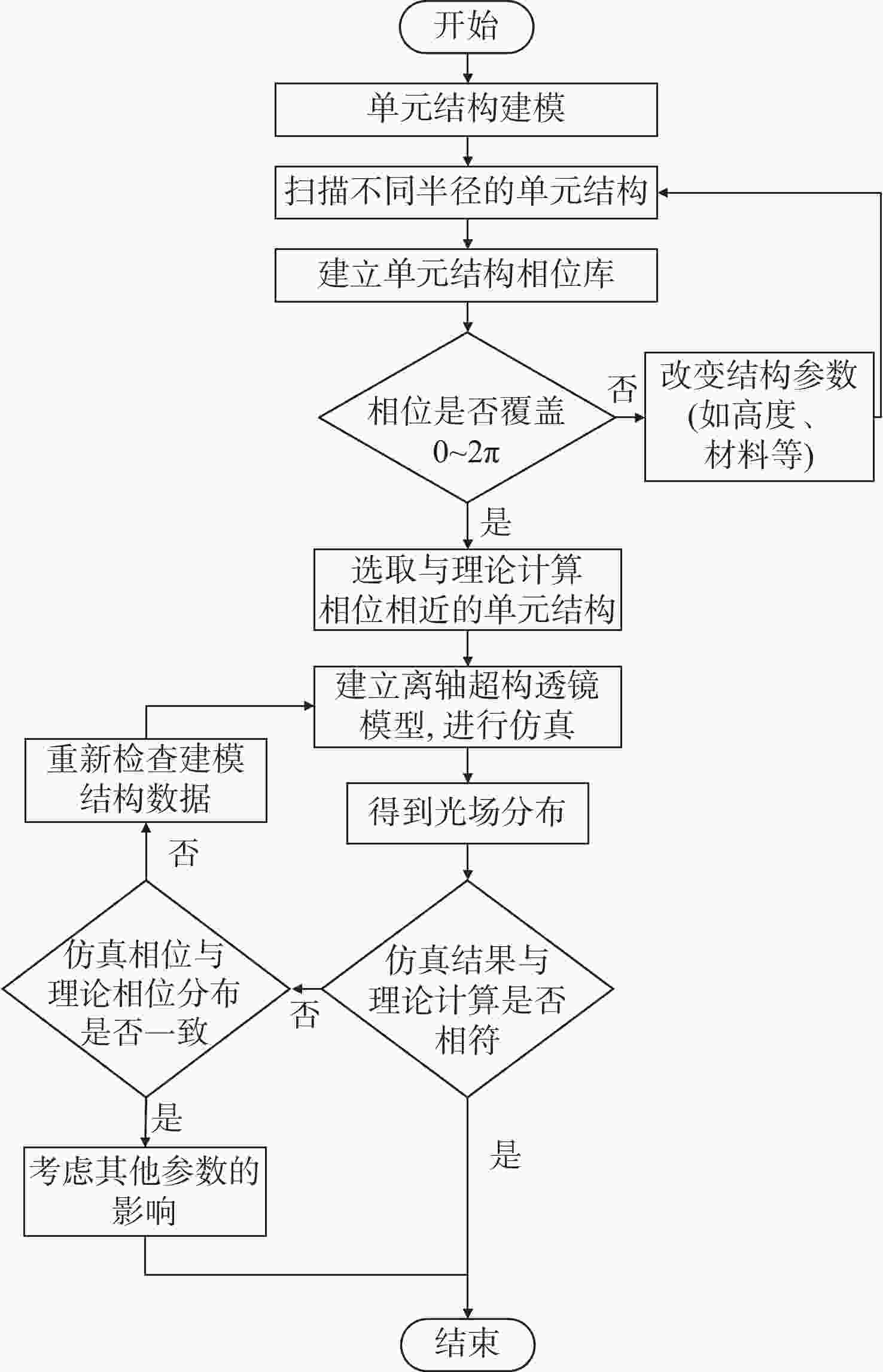
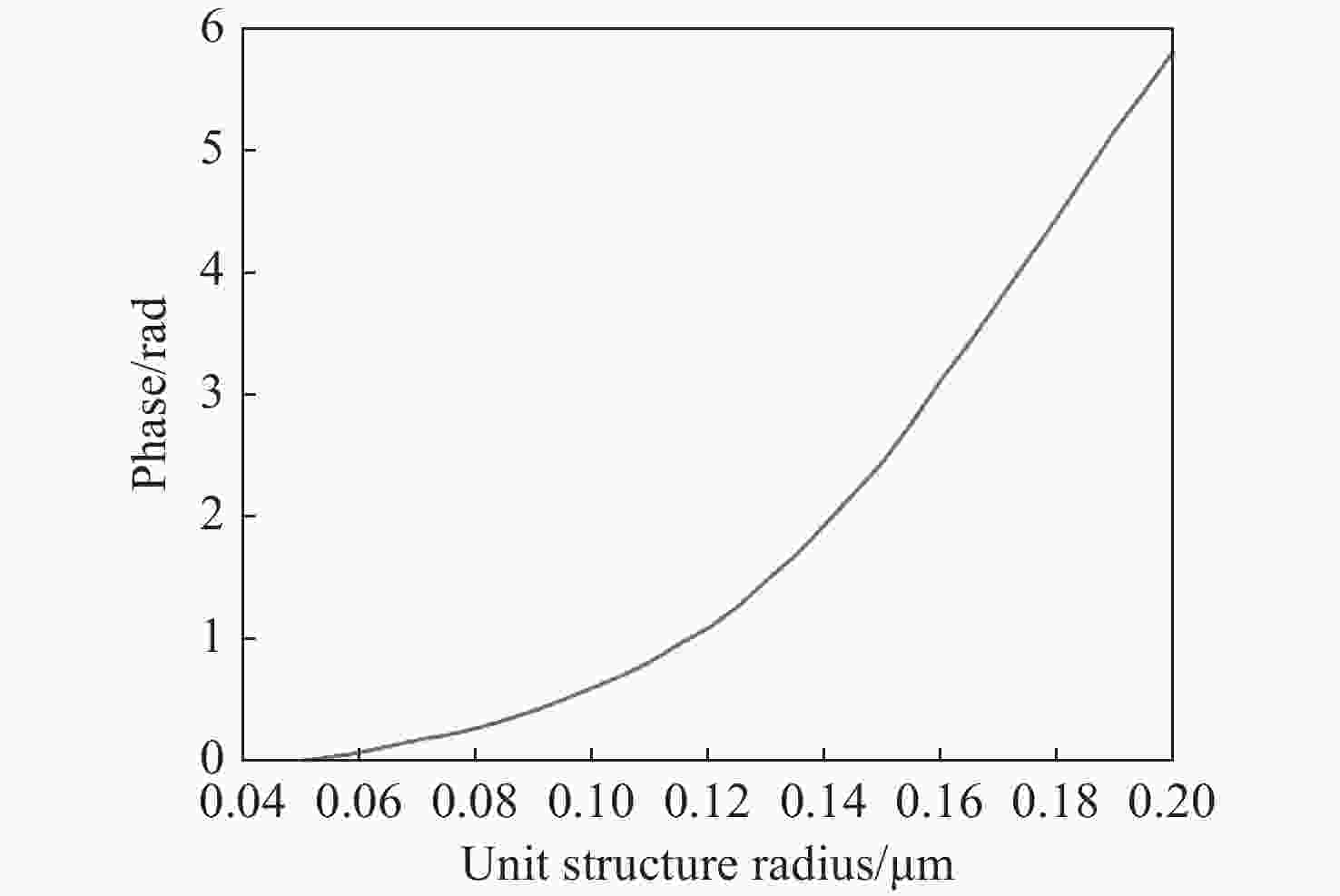
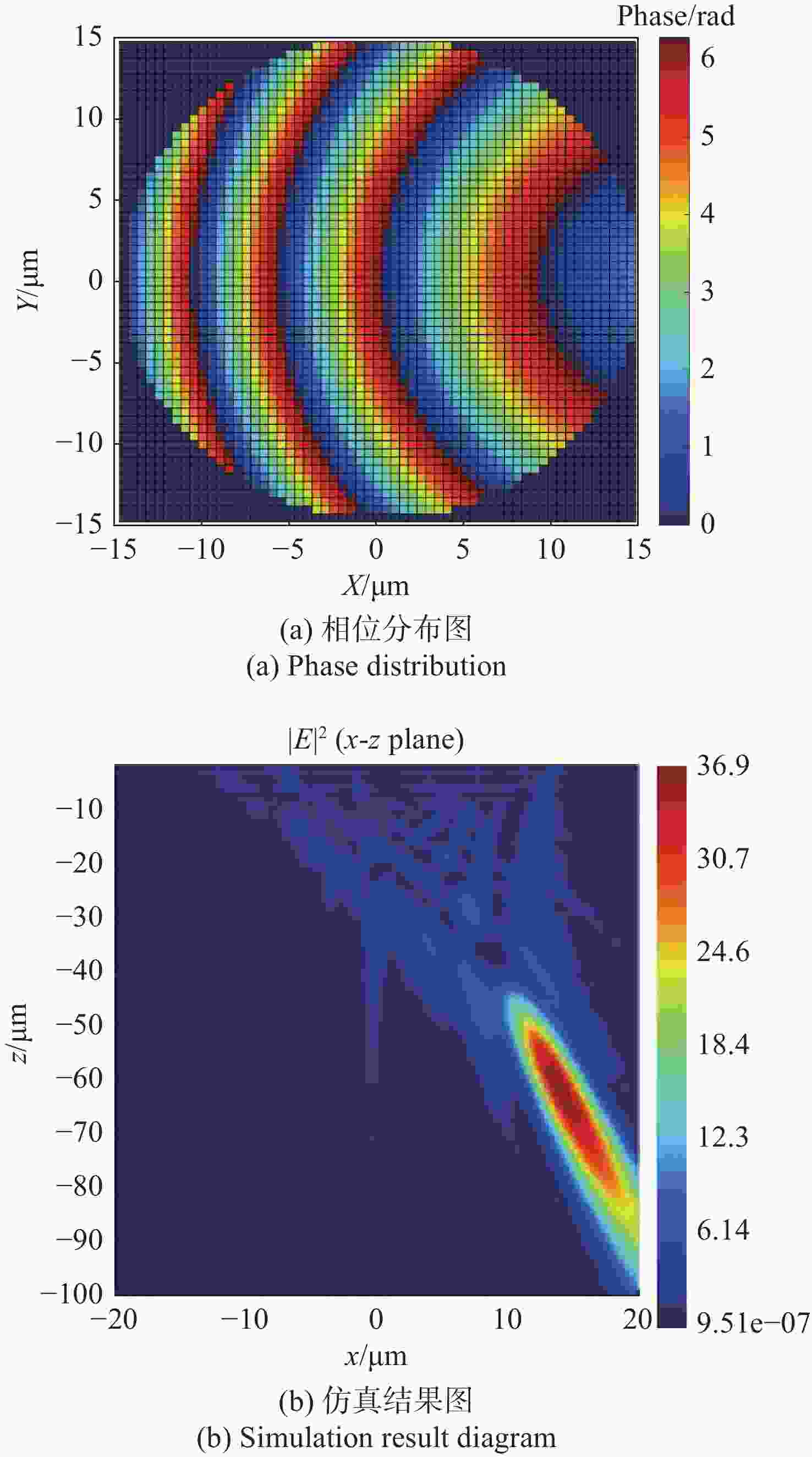
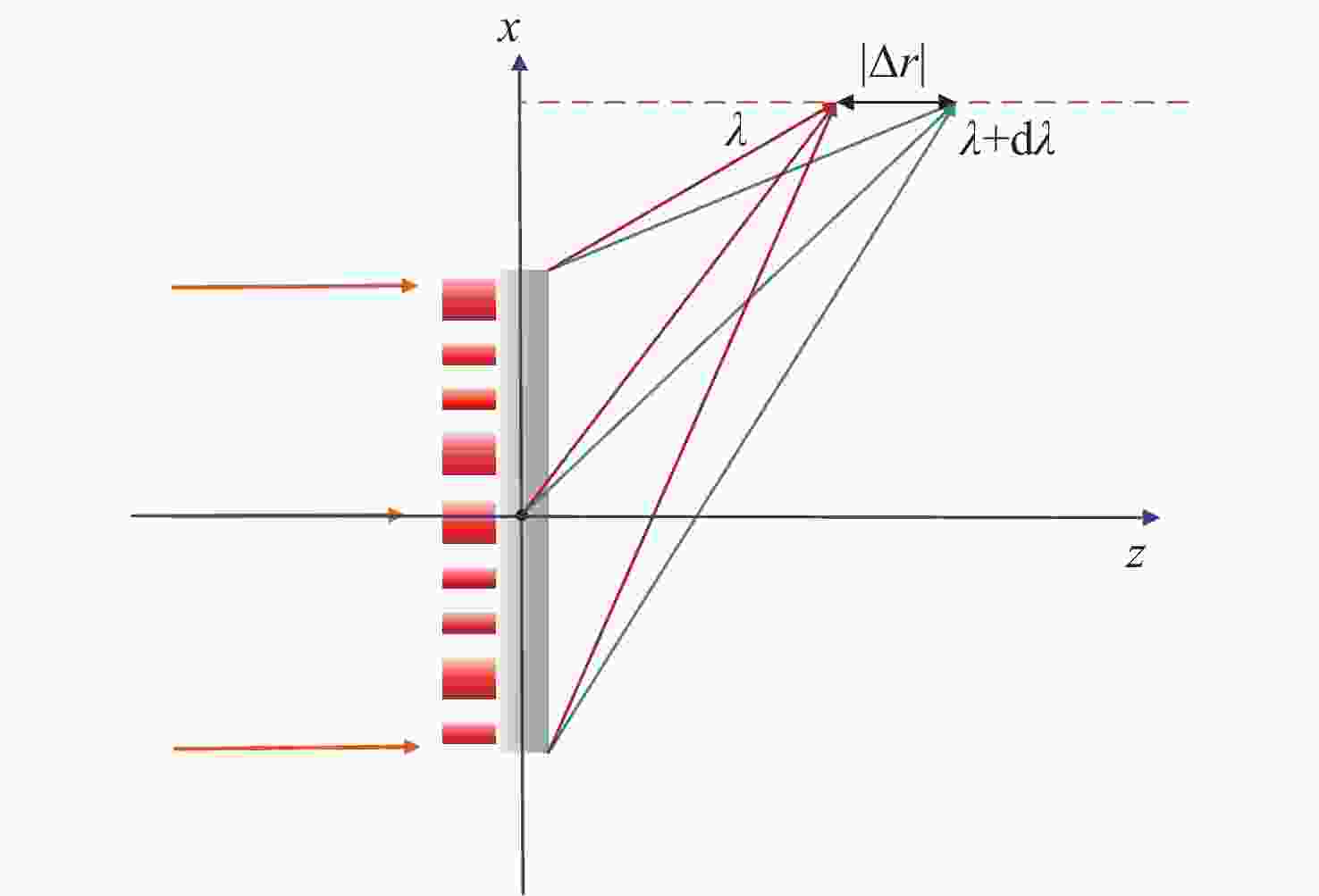
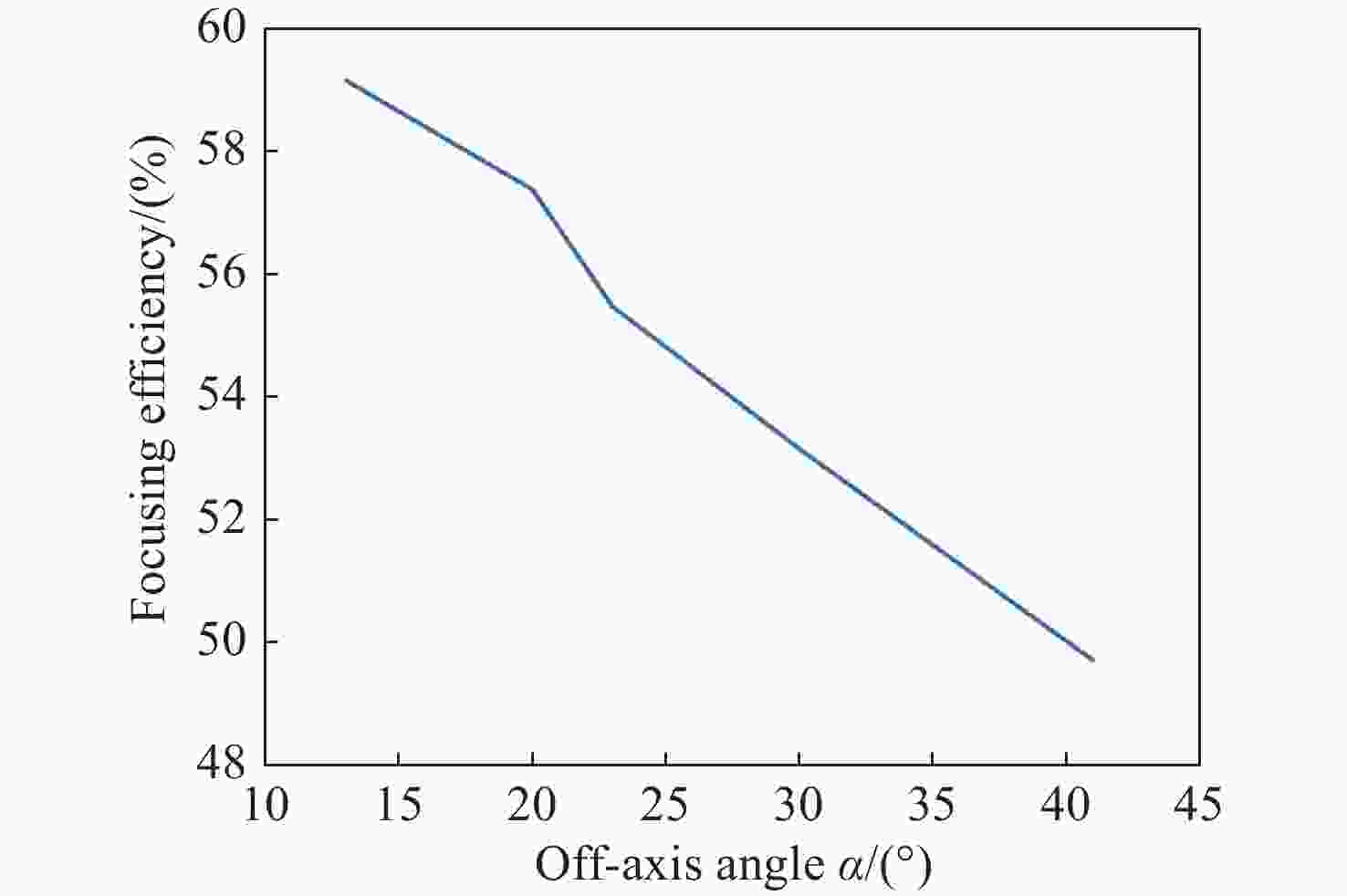
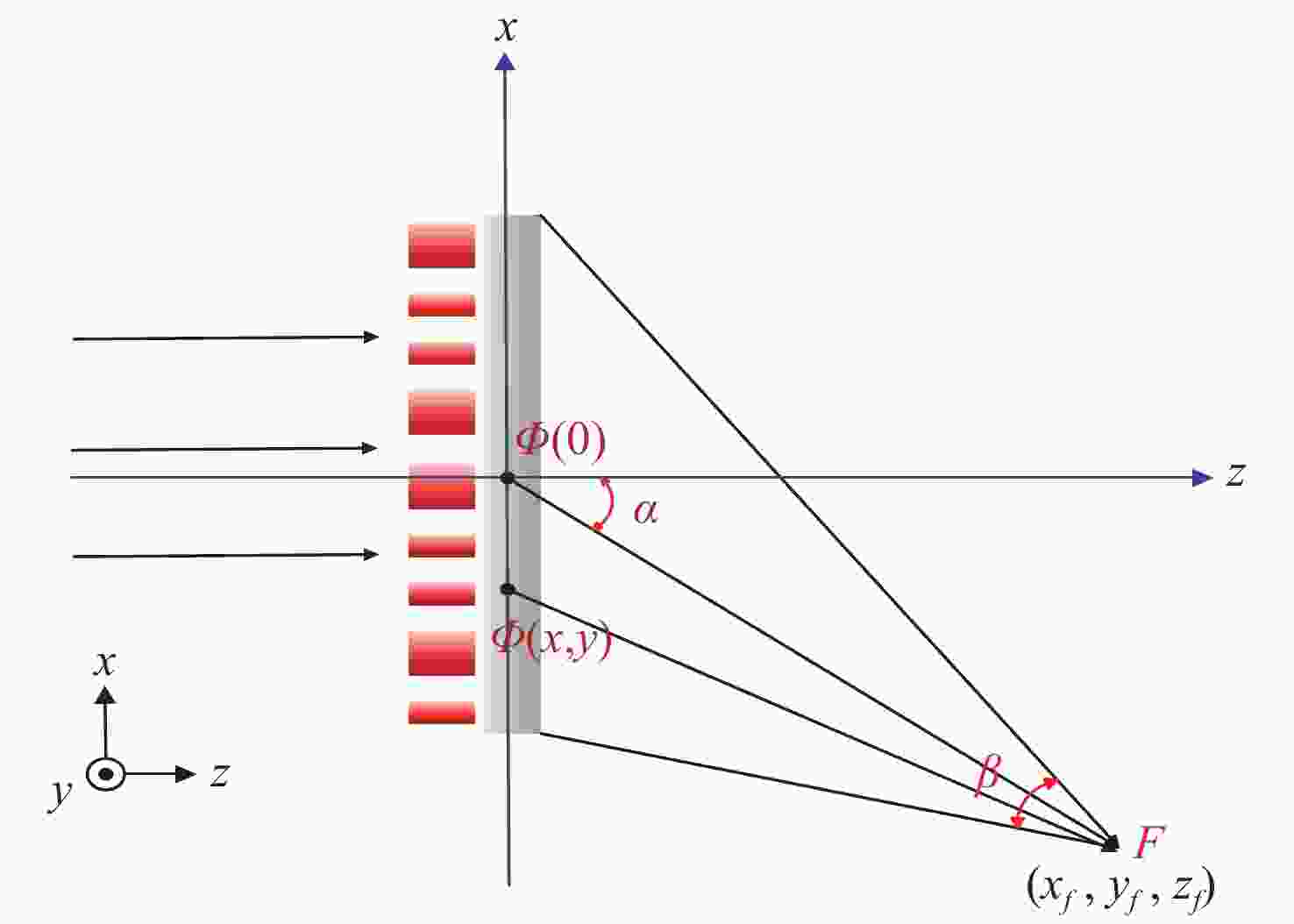
本文提出了一种离轴超构透镜的设计方法,并分析了不同数值孔径、离轴角度等参数对于离轴超构透镜的光谱分辨率、聚焦效率以及仿真结果的影响。利用Lumerical软件分别仿真了参数为
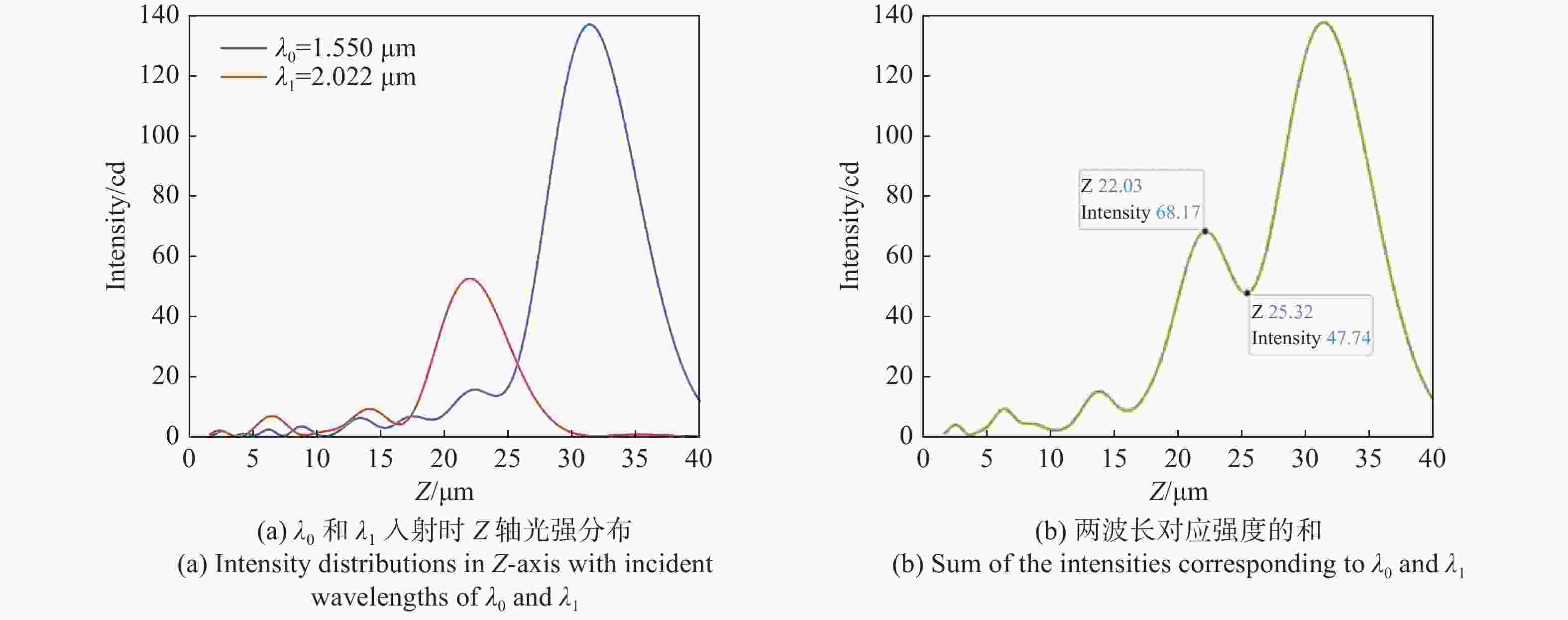
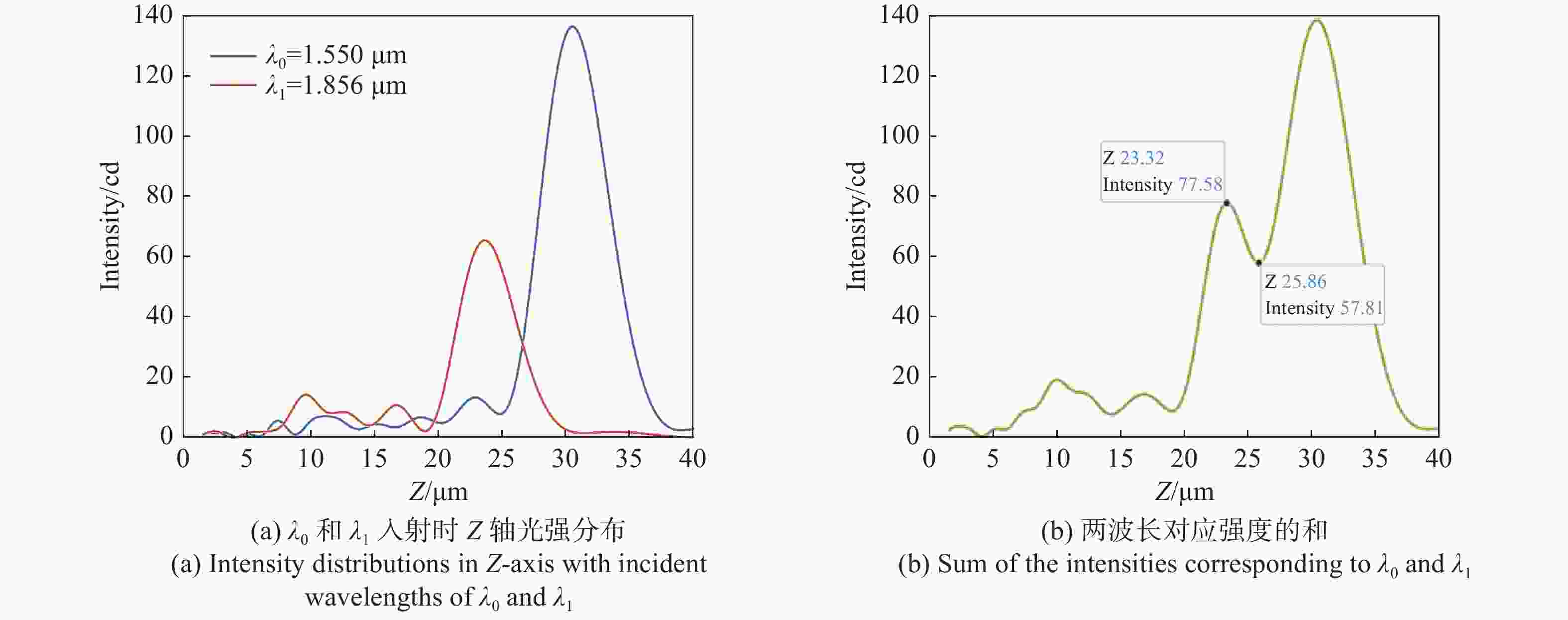
NA =0.408、α =13°;NA =0.180、α =13°及NA =0.408α =20°等多个离轴超构透镜。仿真结果表明:离轴角度与光谱分辨率大小成正相关,离轴角度越大,光谱分辨能力越强,但聚焦效率越低;数值孔径越小,相位分布的覆盖范围越小,会导致仿真聚焦位置与理论值偏差变大。设计者需要根据需求合理平衡数值孔径、离轴角度等参数,最终实现理想效果。本文得出的结论对离轴超构透镜的理论分析和实际应用中的参数设计具有重要参考价值。Abstract:We propose a design method for off-axis meta-lens and analyze the effects of numerical aperture, off-axis angle, and incident wavelength on the simulation deviation, resolution and focusing efficiency of off-axis meta-lenses. Several off-axis meta-lenses with parameters
NA =0.408α =13°,NA =0.180α =13°,NA =0.408α =20° were simulated by Lumerical, respectively. The simulation results indicate that the off-axis angle is directly proportional to the spectral resolution. As the angle increases, the spectral resolution becomes better, but the focusing efficiency decreases. A smaller numerical aperture result in a smaller coverage of the phase distribution, leading to a larger deviation between the simulation and theory. Designers need to reasonably balance parameters such as numerical aperture and off-axis angle according to the requirements to finally achieve the desired effect. This study has an important reference value for theoretical analysis and parameter design of off-axis meta-lens in practical application.-
Key words:
- meta-lens /
- off-axis meta-lens /
- simulation analysis
-
表 1 离轴超构透镜设计参数
Table 1. Designed parameters of off-axis meta-lens
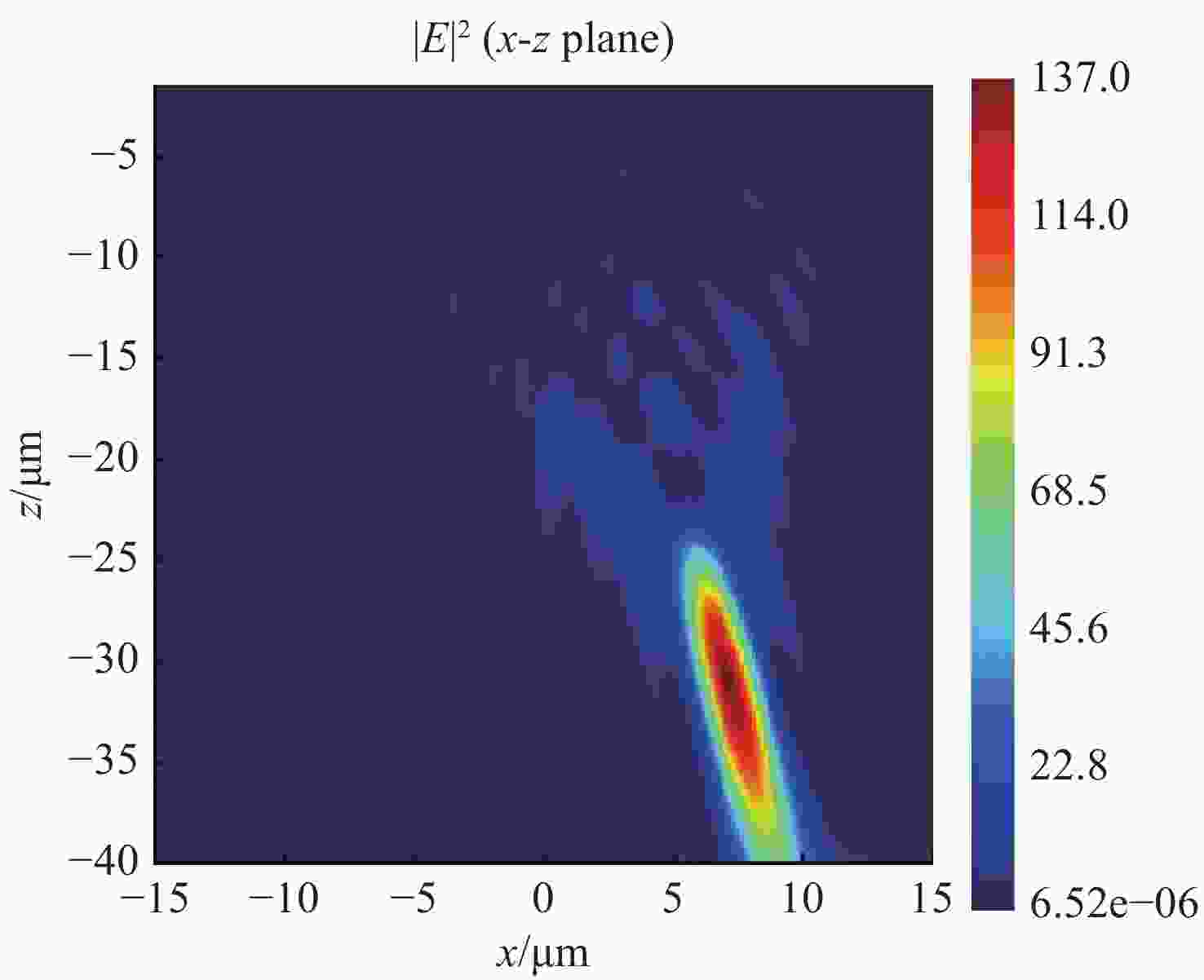
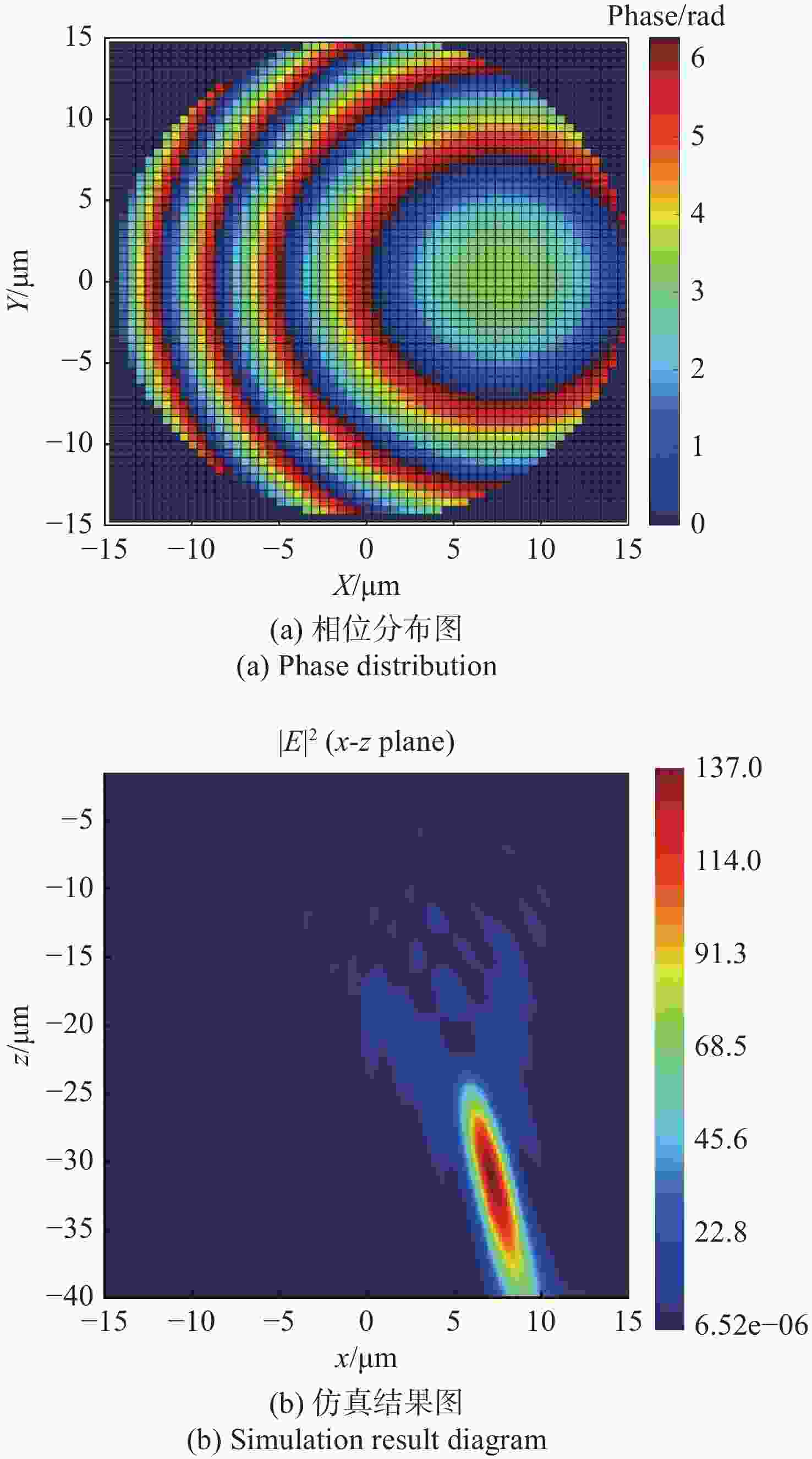
参数 数值 设计波长/μm 1.550 焦距/μm 32.986 离轴角度/(°) 13 数值孔径 0.408 表 2 不同NA(不同焦距f)的离轴超构透镜理论计算与仿真聚焦位置对比
Table 2. Comparison of the focusing positions of off-axis meta-lens with different NA and different focal lengths obtained by theoretical calculation and simulation
(Unit: μm) NA 理论聚焦位置x-z 仿真聚焦位置x-z 相对偏差δx-δz 0.408 (7.420, 32.141) (7.100, 31.200) (0.320, 0.941) 0.180 (17.996, 77.950) (14, 62) (3.996, 15.950) 表 3 不同NA(不同离轴角度d)的离轴超构透镜理论计算与仿真聚焦位置对比
Table 3. Comparison of the focusing positions of off-axis meta-lens with different NA and different off-axis angles obtained by theoretical calculation and simulation
(Unit: μm) NA 理论聚焦位置x-z 仿真聚焦位置x-z 相对偏差δx-δz 0.388 (14.975,29.391) (14.322,28.416) (0.653,0.975) 0.371 (18.446,27.347) (17.638,26.300) (0.808,1.047) 表 4 离轴角度α=13°时不同工作波长对应的聚焦效率
Table 4. Focusing efficiencies at different working wavelength at the off-axis angle α=13°
工作波长 λ(μm) 聚焦效率 1.550 59.14% 2.022 29.32% 2.800 18.42% 3.000 17.65% -
[1] 徐碧洁, 陈向宁, 赵峰, 等. 近红外波长超透镜的设计与仿真[J]. 激光与红外,2021,51(11):1466-1471.XU B J, CHEN X N, ZHAO F, et al. Near-infrared wavelength metalens design and simulation[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2021, 51(11): 1466-1471. (in Chinese) [2] 刘逸天, 陈琦凯, 唐志远, 等. 超表面透镜的像差分析和成像技术研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(4):831-850. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0014LIU Y T, CHEN Q K, TANG ZH Y, et al. Research progress of aberration analysis and imaging technology based on metalens[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 831-850. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0014 [3] WANG Y J, CHEN Q M, YANG W H, et al. High-efficiency broadband achromatic metalens for near-IR biological imaging window[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 5560. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25797-9 [4] LIN P, LIN Y SH, LIN J, et al. Stretchable metalens with tunable focal length and achromatic characteristics[J]. Results in Physics, 2021, 31: 105005. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.105005 [5] SHAN D ZH, XU N X, GAO J S, et al. Design of the all-silicon long-wavelength infrared achromatic metalens based on deep silicon etching[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(8): 13616-13629. doi: 10.1364/OE.449870 [6] 林若雨, 吴一凡, 付博妍, 等. 超构透镜的色差调控应用[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(4):764-781. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0096LIN R Y, WU Y F, FU B Y, et al. Application of chromatic aberration control of metalens[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 764-781. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0096 [7] LI M M, LI SH SH, CHIN L K, et al. Dual-layer achromatic metalens design with an effective abbe number[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(18): 26041-26055. doi: 10.1364/OE.402478 [8] SHAN D ZH, GAO J S, XU N X, et al. Bandpass filter integrated metalens based on electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(13): 2282. doi: 10.3390/nano12132282 [9] ZUO R ZH, LIU W W, CHENG H, et al. Breaking the diffraction limit with radially polarized light based on dielectric metalenses[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(21): 1800795. doi: 10.1002/adom.201800795 [10] LI Y Y, CAO L Y, WEN ZH Q, et al. Broadband quarter-wave birefringent meta-mirrors for generating sub-diffraction vector fields[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(1): 110-113. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.000110 [11] LI R ZH, GUO ZH Y, WEI W, et al. Arbitrary focusing lens by holographic metasurface[J]. Photonics Research, 2015, 3(5): 252-255. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.3.000252 [12] SAJEDIAN I, LEE H, RHO J. Double-deep Q-learning to increase the efficiency of metasurface holograms[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 10899. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47154-z [13] 付娆, 李子乐, 郑国兴. 超构表面的振幅调控及其功能器件研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(4):886-899. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0017FU R, LI Z L, ZHENG G X. Research development of amplitude-modulated metasurfaces and their functional devices[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 886-899. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0017 [14] AVAYU O, ALMEIDA E, PRIOR Y, et al. Composite functional metasurfaces for multispectral achromatic optics[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 14992. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14992 [15] JIN J J, PU M B, WANG Y Q, et al. Multi-channel vortex beam generation by simultaneous amplitude and phase modulation with two-dimensional metamaterial[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2017, 2(2): 1600201. doi: 10.1002/admt.201600201 [16] WEI Q SH, HUANG L L, LI X W, et al. Broadband multiplane holography based on plasmonic metasurface[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2017, 5(18): 1700434. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700434 [17] CHENG H, WEI X Y, YU P, et al. Integrating polarization conversion and nearly perfect absorption with multifunctional metasurfaces[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(17): 171903. doi: 10.1063/1.4982240 [18] BAI W, YANG P, WANG SH, et al. Actively tunable metalens array based on patterned phase change materials[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(22): 4927. doi: 10.3390/app9224927 [19] YU P, LI J X, ZHANG SH, et al. Dynamic Janus metasurfaces in the visible spectral region[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(7): 4584-4589. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01848 [20] SHE A, ZHANG SH Y, SHIAN S, et al. Adaptive metalenses with simultaneous electrical control of focal length, astigmatism, and shift[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(2): eaap9957. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aap9957 [21] KHORASANINEJAD M, CHEN W T, OH J, et al. Super-dispersive off-axis meta-lenses for compact high resolution spectroscopy[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(6): 3732-3737. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01097 [22] ZHU A Y, CHEN W T, KHORASANINEJAD M, et al. Ultra-compact visible chiral spectrometer with meta-lenses[J]. APL Photonics, 2017, 2(3): 036103. doi: 10.1063/1.4974259 [23] ZHOU Y, CHEN R, MA Y G. Design of optical wavelength demultiplexer based on off-axis meta-lens[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(22): 4716-4719. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.004716 [24] ZHOU Y, CHEN R, MA Y G. Characteristic analysis of compact spectrometer based on off-axis meta-lens[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(3): 321. doi: 10.3390/app8030321 [25] ZHU A Y, CHEN W T, SISLER J, et al. Compact aberration‐corrected spectrometers in the visible using dispersion‐tailored metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2019, 7(14): 1801144. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801144 [26] 罗先刚. 亚波长电磁学: 上册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 208-214.LUO X G. Sub-Wavelength Electromagnetics:Vol. 1[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 208-214. (in Chinese) [27] XIAO S Y, ZHAO F, WANG D Y, et al. Inverse design of a near-infrared metalens with an extended depth of focus based on double-process genetic algorithm optimization[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(5): 8668-8681. doi: 10.1364/OE.484471 [28] 丁继飞, 刘文兵, 李含辉, 等. 大焦深离轴超透镜的设计与制作[J]. 物理学报,2021,70(19):197802. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20202235DING J F, LIU W B, LI H H, et al. Design and fabrication of off-axis meta-lens with large focal depth[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(19): 197802. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20202235 [29] BANERJI S, MEEM M, MAJUMDER A, et al. Imaging with flat optics: metalenses or diffractive lenses?[J]. Optica, 2019, 6(6): 805-810. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.6.000805 -





 下载:
下载: