-
摘要:
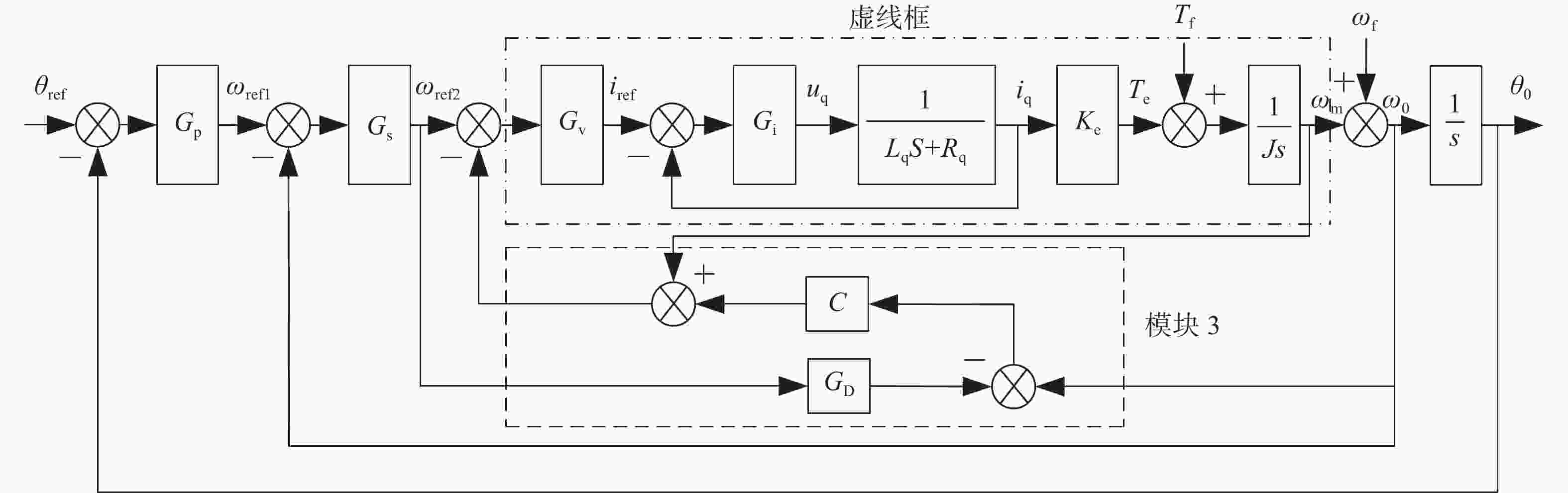
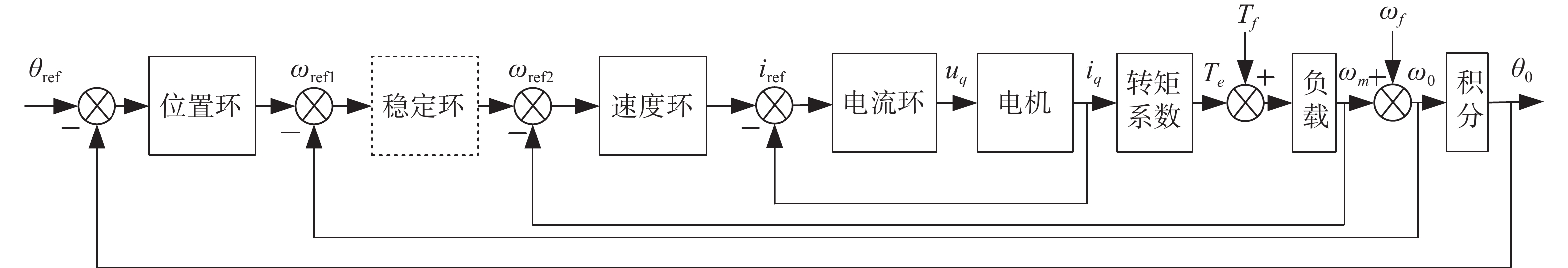
本文设计了一种可以使光电伺服平台对目标对象进行高精度、稳定追踪的基于双速度环的扰动观测器,可以消除光电平台内部摩擦力矩、外部载体扰动以及传感器噪声的影响,提升系统的动态响应性能。首先,根据直流电机工作原理与负载模型,建立双速度环的数学控制模型。接着,通过分析多类型传感器的速度信号频谱和响应性能,选择噪声和延时较小的圆光栅代替传统测速设备,作为速度控制内环;同时选择光纤陀螺作为速度外环的反馈设备。然后,基于陀螺速度信号设计扰动观测器,对内速度环中的扰动补偿残差和外部载体扰动信号进行观测,并进行前馈信号补偿。实验结果表明,双速度环观测器的控制方法可以将系统调节时间降至原来的45%,在不同幅值(0.25°~2°)和频率(0.25 Hz~2 Hz)的正弦扰动信号下,该方法均能显著提高系统的扰动抑制能力,并将系统隔离度由原来的20.9 dB提升至30 dB。本文所提出的基于双速度环扰动观测器的控制方法满足光电跟踪平台快速响应、跟踪稳定、抗干扰能力强等要求。
Abstract:To achieve high-precision and stable tracking performance, a novel disturbance observer for the photoelectric platform based on dual velocity loops is designed. This method aims to minimize the impact of internal friction torque, external carrier disturbances and sensor noise, thereby enhancing the dynamic response performance of the system. Firstly, the mathematical model of double speed-loop is established. By analyzing the signal spectrum and response performance of various sensors, we have chosen the circular grating sensor with low noise and short delay to replace the traditional measuring machine for closing the inner speed loop. Moreover, the Fiber Optic Gyro (FOG) is utilized for the feedback device of the outer speed loop. Then, a disturbance observer is designed based on the gyro speed signal to observe the disturbance compensation residual in the inner speed loop and the outer carrier disturbance signal, while the feed-forward compensation is performed. The experimental results demonstrate that the double speed loop observer control method can reduce the system regulation time to 45% of the original. When subjected to sinusoidal disturbance signals with varying amplitudes (0.25° to 2°) and frequencies (0.25 Hz to 2 Hz), this method effectively improves the system's ability to suppress disturbances and increases the isolation degree from the initial 20.9 dB to 30 dB. The disturbance observer with double speed loops meets the system requirements of rapid response, stable tracking, high precision and strong anti-disturbance ability of the photoelectric tracking platform.
-
-
[1] 朱孟真, 陈霞, 刘旭, 等. 战术激光武器反无人机发展现状和关键技术分析[J]. 红外与激光工程,2021,50(7):20200230. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200230ZHU M ZH, CHEN X, LIU X, et al. Situation and key technology of tactical laser anti-UAV[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(7): 20200230. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200230 [2] 禹化龙, 伍尚慧. 美军定向能武器反无人机技术进展[J]. 国防科技,2019,40(6):42-47.YU H L, WU SH H. Progress and development trend analysis on US directed energy weapons against unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. National Defense Technology, 2019, 40(6): 42-47. (in Chinese) [3] 高博, 张乃千, 范旭. 反无人机电子战发展[J]. 国防科技,2019,40(1):35-39.GAO B, ZHANG N Q, FAN X. Analysis on the development and application of anti-UAV electronic warfare[J]. National Defense Technology, 2019, 40(1): 35-39. (in Chinese) [4] 李磊. 基于视频的空中目标检测技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2019.LI L. Research on video based airborne target detection technology[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese) [5] 薛猛, 周学文, 孔维亮. 反无人机系统研究现状及关键技术分析[J]. 飞航导弹,2021(5):52-56,60.XUE M, ZHOU X W, KONG W L. Research status and key technology analysis of anti UAV system[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2021(5): 52-56,60. (in Chinese) [6] 李朝龙, 李明辉, 陈玉华. 激光武器在陆军全域作战中的运用[J]. 激光与红外,2020,50(5):515-520.LI CH L, LI M H, CHEN Y H. The application of laser weapon in the army's whole area operation[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2020, 50(5): 515-520. (in Chinese) [7] 姚杰. 基于双目视觉的无人机目标追踪系统研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.YAO J. Target tracking system for UAV based on stereo vision[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. (in Chinese) [8] 张棋. 基于FPGA的运动目标检测与跟踪系统设计[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2018.ZHANG Q. Moving object detection and tracking system design based on FPGA[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2018. (in Chinese) [9] 周新力, 李醒飞. 光电跟踪系统积分反步自抗扰控制策略[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版),2021,54(4):379-387.ZHOU X L, LI X F. Integral backstepping active disturbance rejection control strategy for the electro-optical targeting system[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2021, 54(4): 379-387. (in Chinese) [10] 贾桐, 李秀智, 张祥银. 车载惯性稳定平台的神经网络滑模控制[J]. 控制理论与应用,2021,38(1):13-22.JIA T, LI X ZH, ZHANG X L. Neural network sliding mode control for vehicle inertially stabilized platform[J]. Control Theory &Applications, 2021, 38(1): 13-22. (in Chinese) [11] 邢泽智, 王秀和, 赵文良. 基于不同极弧系数组合分段倾斜磁极的表贴式永磁同步电机齿槽转矩削弱措施研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2021,41(16):5737-5747.XING Z ZH, WANG X H, ZHAO W L. Research on reduction methods of cogging torque based on segmented skewing magnetic poles with different combinations of pole-arc coefficients in surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motors[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(16): 5737-5747. (in Chinese) [12] 刘盟. 光电吊舱伺服控制系统的设计与开发[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2020.LIU M. Design and development of servo control system for photoelectric pod[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2020. (in Chinese) [13] 崔慧敏. 基于智能差分算法的摩擦力补偿方法研究[J]. 遥测遥控,2022,43(5):61-67.CUI H M. Research on friction compensation method based on intelligent differential algorithm[J]. Journal of Telemetry,Tracking and Command, 2022, 43(5): 61-67. (in Chinese) [14] 李林, 宣明, 贾宏光, 等. 光电稳定平台隔振系统的设计与优化[J]. 计算机仿真,2017,34(3):77-81.LI L, XUAN M, JIA H G, et al. Design and optimization of vibration isolation system for photoelectric stabilized platform[J]. Computer Simulation, 2017, 34(3): 77-81. (in Chinese) [15] 邓超. 运动平台预测跟踪技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 2018.DENG CH. Research on prediction tracking control on moving bed[D]. Changchun: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese) [16] 王中石, 田大鹏, 石磊, 等. 考虑安装基座影响的光电平台等价捷联惯性稳定控制[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(6):1344-1352. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1344WANG ZH SH, TIAN D P, SHI L, et al. Equivalent strapdown inertial stability control of photoelectric platform considering the effect of mounting base[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(6): 1344-1352. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1344 [17] 潘帅, 杨奕, 陈丹丹, 等. 基于干扰补偿的稳定平台控制系统设计[J]. 机械设计与制造,2018(1):22-25.PAN SH, YANG Y, CHEN D D, et al. The design of inertial stabilization platform based on disturbance compensation[J]. Machinery Design &Manufacture, 2018(1): 22-25. (in Chinese) [18] 任彦, 王义敏, 牛志强, 等. 高阶终端滑模控制在稳定平台中的应用[J]. 控制工程,2021,28(3):553-558.REN Y, WANG Y M, NIU ZH Q, et al. Application of high-order terminal sliding mode control in stable platform[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2021, 28(3): 553-558. (in Chinese) [19] 夏先齐, 张葆, 李贤涛, 等. 基于扩张状态观测器的永磁同步电机低速滑模控制[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(12):2628-2638. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2628XIA X Q, ZHANG B, LI X T, et al. Low speed sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on extended state observer[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(12): 2628-2638. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2628 -






 下载:
下载: