Non-uniform illumination correction algorithm for cytoendoscopy images based on illumination model
-
摘要:
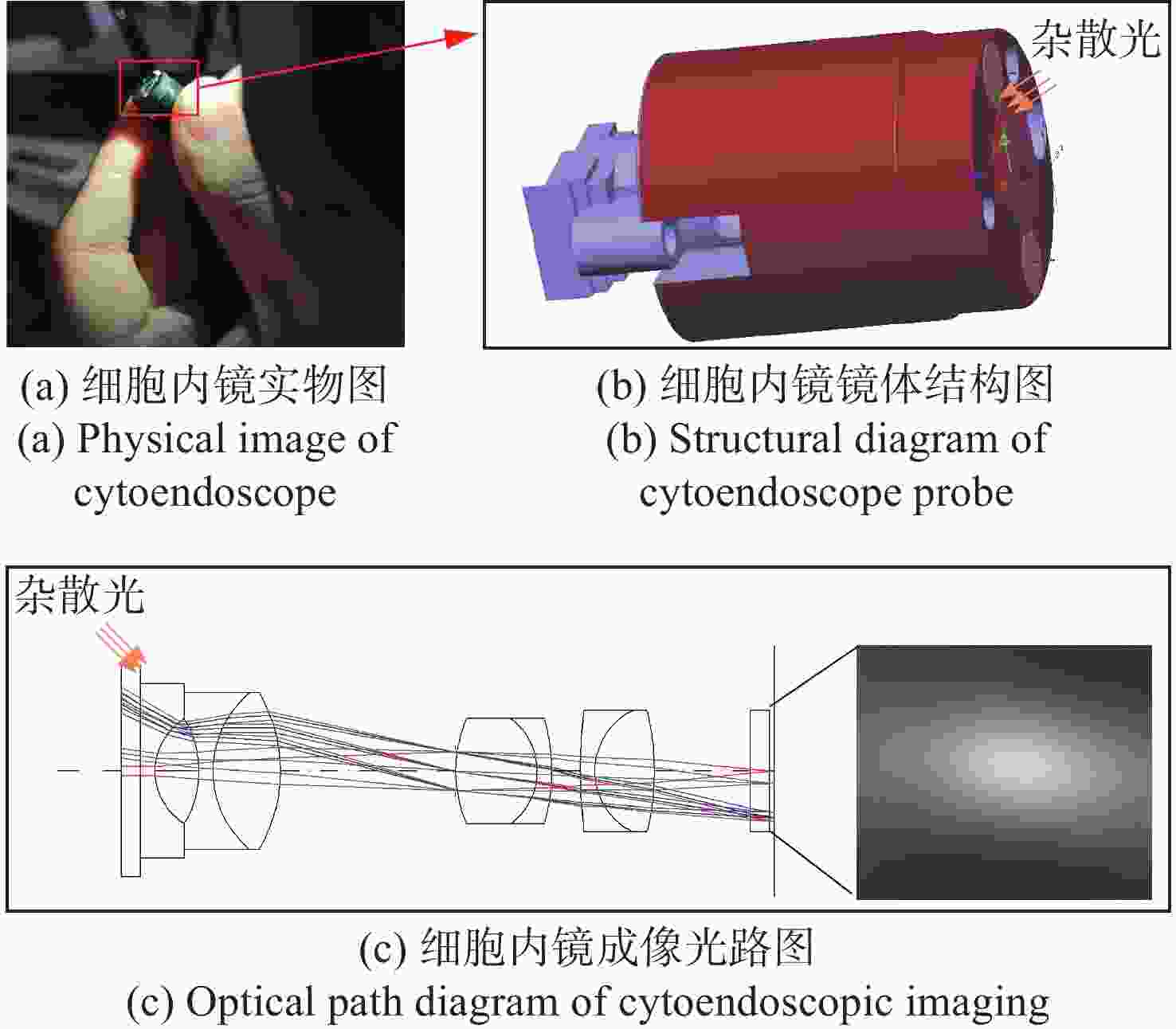
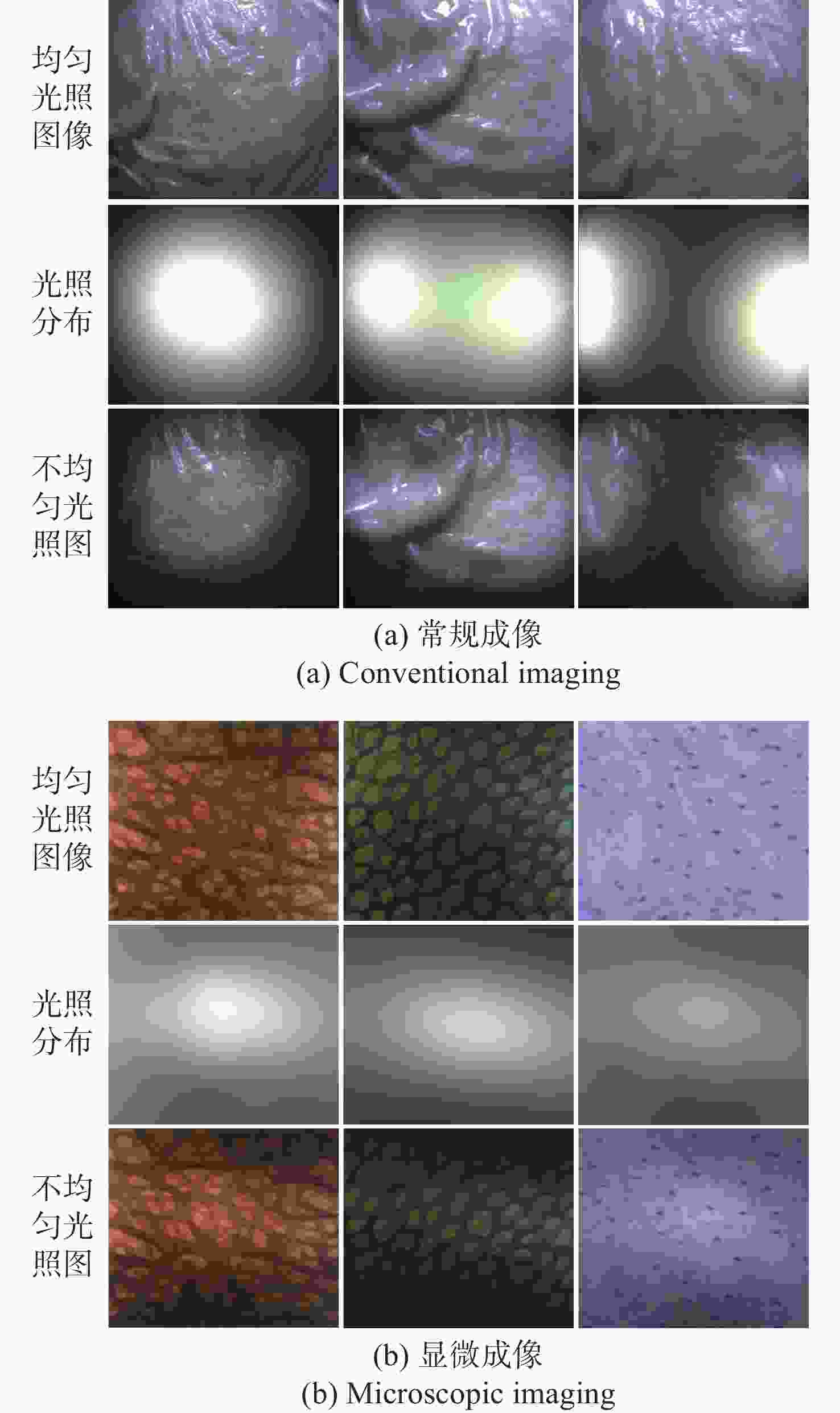
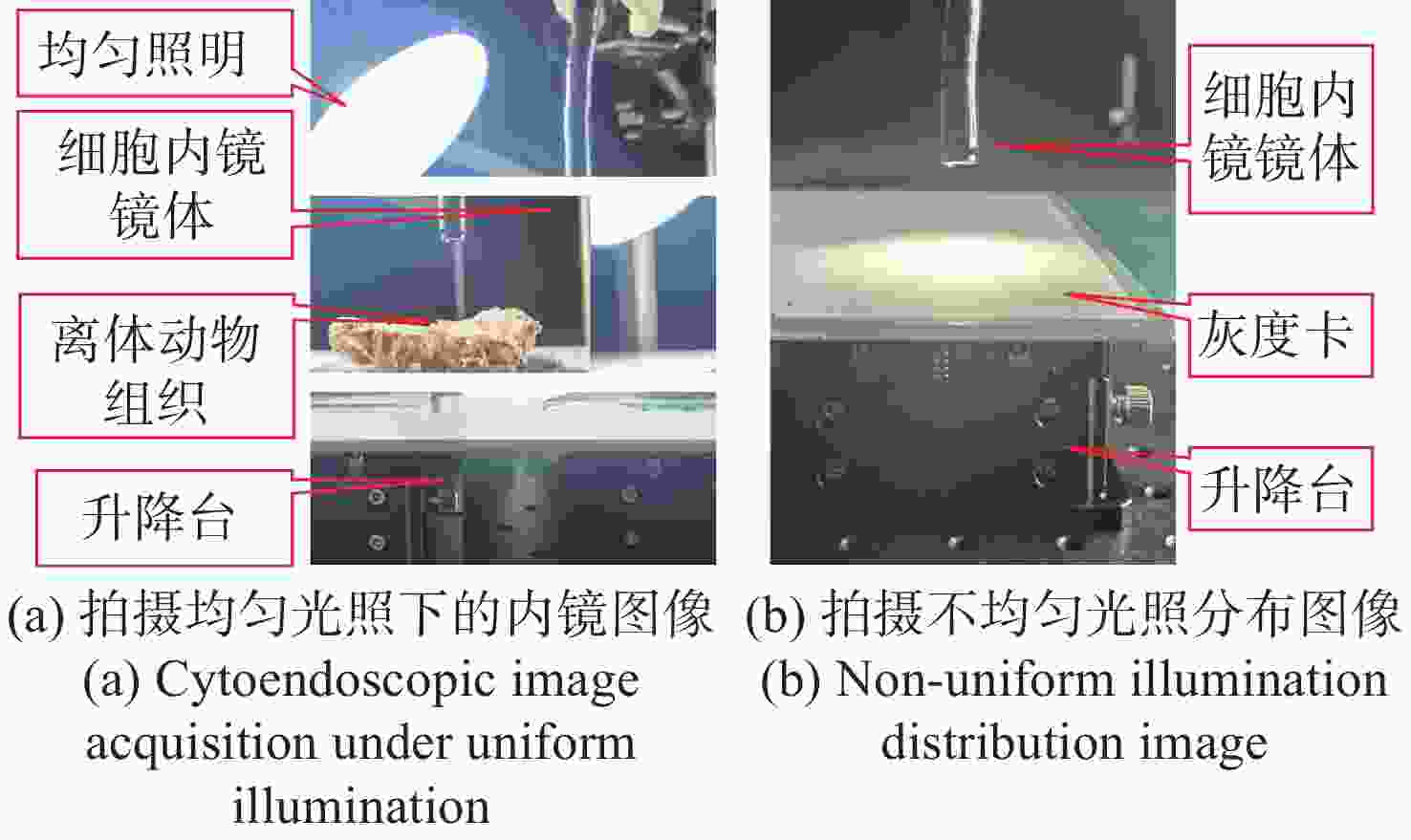
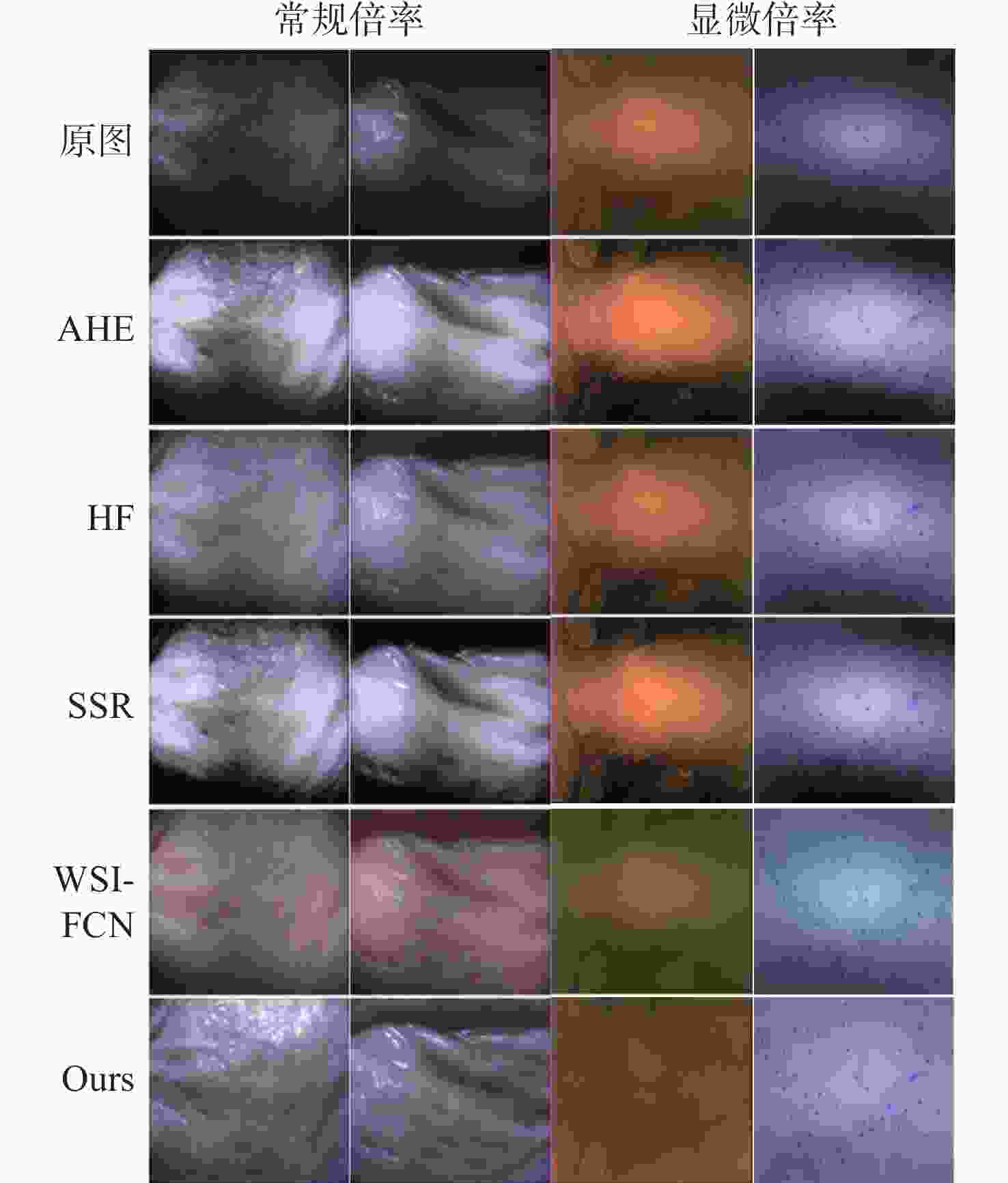
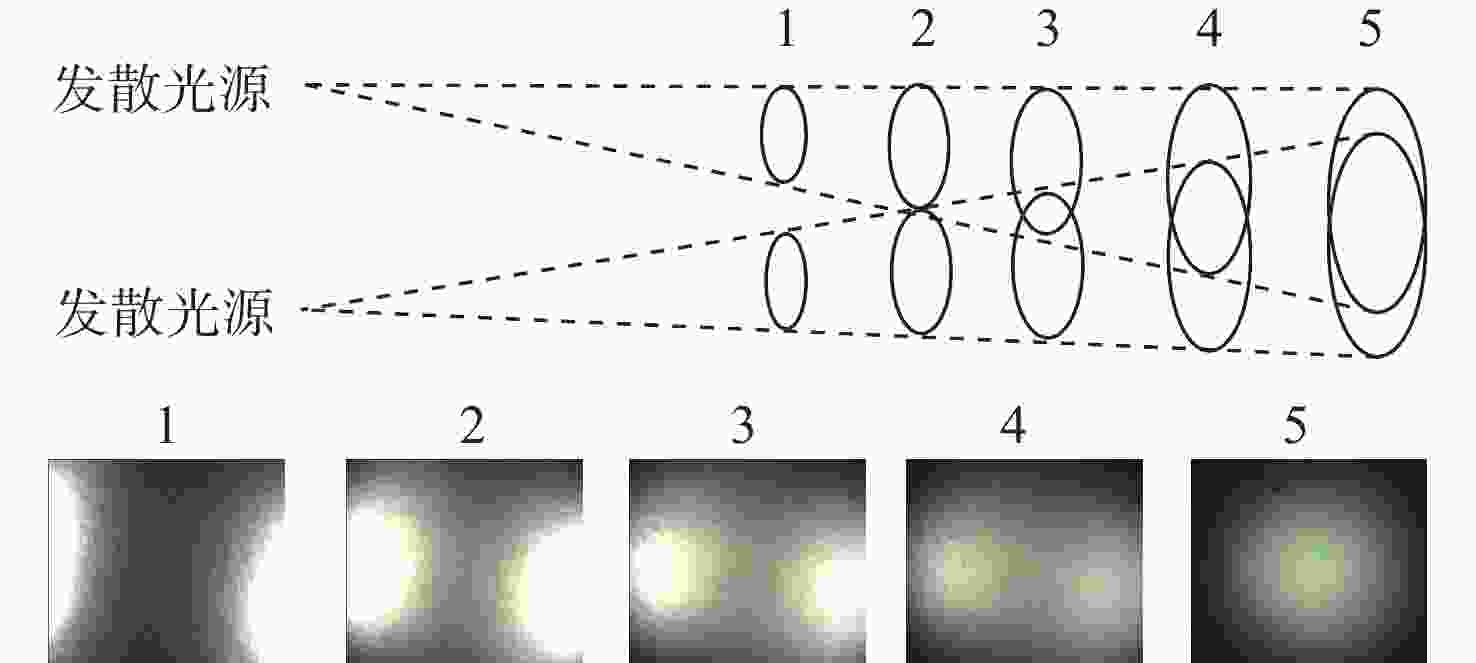
细胞内镜需实现最大倍率约500倍的连续放大成像,受光纤照明及杂散光的影响,其图像存在不均匀光照,且光照分布会随放大倍率的变化而变化。这会影响医生对病灶的观察及判断。为此,本文提出一种基于细胞内镜光照模型的图像不均匀光照校正算法。根据图像信息由光照分量和反射分量组成这一基础,该算法通过卷积神经网络学习图像的光照分量,并基于二维Gamma函数实现不均匀光照校正。实验表明,经本文方法进行不均匀光照校正后,图像的光照分量平均梯度和离散熵分别为0.22和7.89,优于自适应直方图均衡化、同态滤波和单尺度Retinex等传统方法以及基于深度学习的WSI-FCN算法。
Abstract:Cytoendoscopy requires continuous amplification with a maximum magnification rate of about 500 times. Due to optical fiber illumination and stray light, the image has non-uniform illumination that changes with the magnification rate, which affects the observation and judgement of lesions by doctors. Therefore, we propose an image non-uniform illumination correction algorithm based on the illumination model of cytoendoscopy. According to the principle that image information is composed of illumination and reflection components, the algorithm obtains the illumination component of the image through a convolutional neural network, and realizes non-uniform illumination correction based on the two-dimensional Gamma function. Experiments show that the average gradient of the illumination channel and the discrete entropy of the image are 0.22 and 7.89, respectively, after the non-uniform illumination correction by the proposed method, which is superior to the traditional methods such as adaptive histogram equalization, homophobic filtering, single-scale Retinex and the WSI-FCN algorithm based on deep learning.
-
表 1 不同方法的定量结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of quantitative results for different correction methods
AGIC DE AHE 0.40 5.58 HF 0.26 7.68 SSR 0.34 7.54 WSI-FCN 0.29 7.23 Ours 0.22 7.89 表 2 不同方法的速度对比
Table 2. Speed comparison of different correction methods
耗时(GPU)/ms 耗时(CPU)/ms AHE / 5260 HF / 120 SSR / 1340 WSI-FCN 185 1190 Ours 6 50 -
[1] GOETZ M, MALEK N P, KIESSLICH R. Microscopic imaging in endoscopy: endomicroscopy and endocytoscopy[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2014, 11(1): 11-18. [2] 霍嘉燚, 李冕豪, 王子川, 等. 全景内窥成像技术及应用[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):44-60. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0074HUO J Y, LI M H, WANG Z CH, et al. Panoramic endoscopic imaging technology and it’s applications[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 44-60. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0074 [3] 王子川, 张伟, 郭飞, 等. 跨尺度光学内窥成像技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(6):1287-1301. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0078WANG Z CH, ZHANG W, GUO F, et al. Trans-scale optical endoscopy imaging technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1287-1301. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0078 [4] 张伟, 牛春阳, 游兴海, 等. 高倍率大视场细胞内镜成像系统研究[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(17):1717001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1717001ZHANG W, NIU CH Y, YOU X H, et al. Endocytoscopic imaging system with high magnification and large field of view[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(17): 1717001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.1717001 [5] PIZER S M, AMBURN E P, AUSTIN J D, et al. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1987, 39(3): 355-368. doi: 10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X [6] XIE X D, LAM K M. Face recognition under varying illumination based on a 2D face shape model[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2005, 38(2): 221-230. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(04)00275-4 [7] LEE P H, WU S W, HUNG Y P. Illumination compensation using oriented local histogram equalization and its application to face recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(9): 4280-4289. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2202670 [8] FAN CH N, ZHANG F Y. Homomorphic filtering based illumination normalization method for face recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2011, 32(10): 1468-1479. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2011.03.023 [9] AL SOBBAHI R, TEKLI J. Low-light homomorphic filtering network for integrating image enhancement and classification[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2022, 100: 116527. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2021.116527 [10] LAND E H, MCCANN J J. Lightness and Retinex theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1971, 61(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.61.000001 [11] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, WOODELL G A. Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(3): 451-462. doi: 10.1109/83.557356 [12] ZHANG SH, WANG T, DONG J Y, et al. Underwater image enhancement via extended multi-scale Retinex[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 245: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.029 [13] ZHOU J CH, YAO J, ZHANG W SH, et al. Multi-scale Retinex-based adaptive gray-scale transformation method for underwater image enhancement[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(2): 1811-1831. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11327-8 [14] MEI X F, XIE F Y, JIANG ZH G. Uneven illumination removal based on fully convolutional network for dermoscopy images[C]. 2016 13th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing (ICCWAMTIP), IEEE, 2016: 243-247. [15] WANG J H, WANG X, ZHANG P, et al. Correction of uneven illumination in color microscopic image based on fully convolutional network[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(18): 28503-28520. doi: 10.1364/OE.433064 -





 下载:
下载: