Propagation properties of one-dimensional array vortex beams in a marine atmosphere
-
摘要:
相较于单涡旋光束,涡旋阵列光束能够扩充信息的传输容量,研究其传输特性对其光通信应用具有重要意义。本文选取阶数为
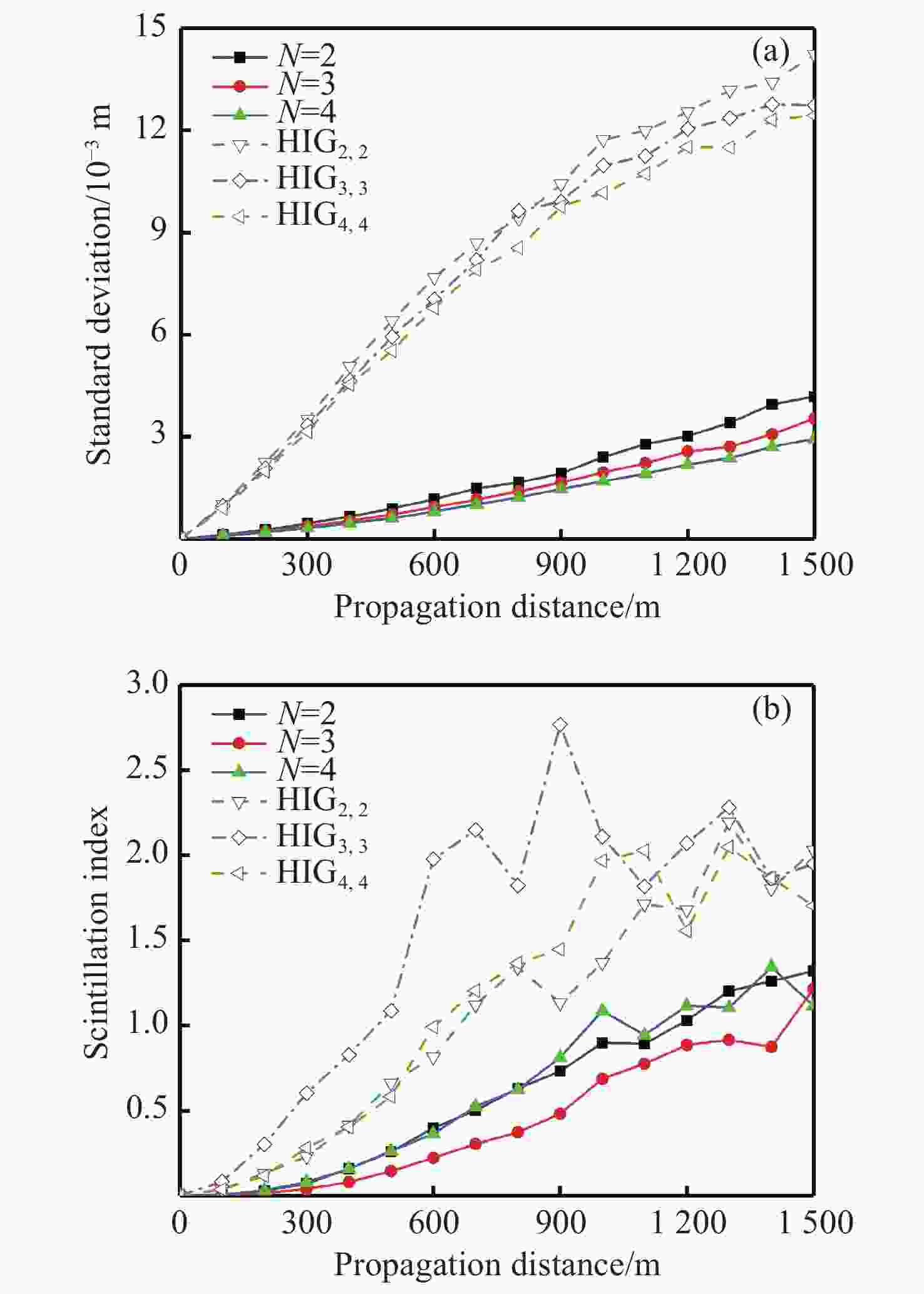
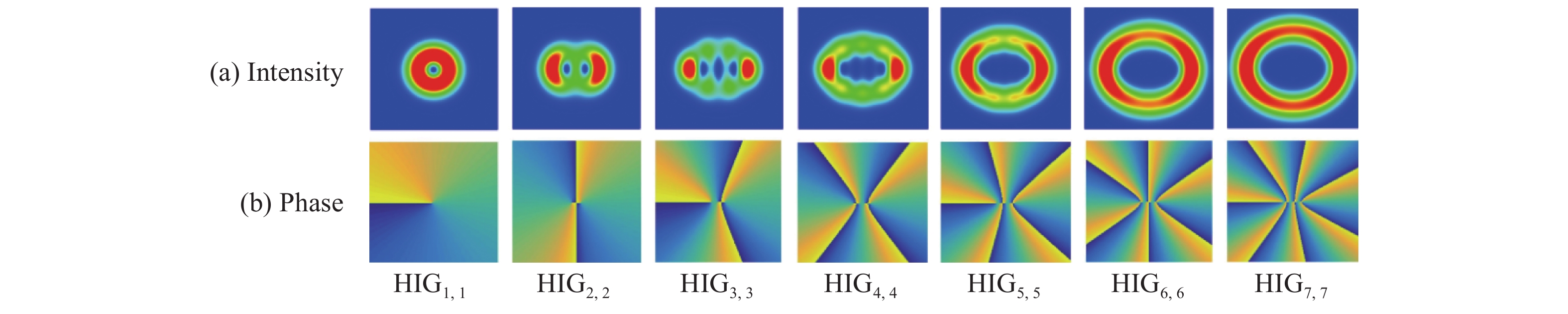
n 的螺旋因斯-高斯(HIGn ,n )模式,采用海上大气折射率变换的功率谱,模拟海面大气湍流。基于相位屏法研究了一维阵列涡旋光束在海面大气湍流中光强、相位、闪烁因子和质心漂移的变化情况。结果表明:(1)HIGn ,n 模式的闪烁因子和质心漂移标准差随湍流强度以及大气湍流内尺度的增加而增加;(2)n 为奇数的HIGn ,n 模式的闪烁因子随着阶数的增大而减小,且高于n 为偶数的HIGn ,n 模式;(3)阶数n >1的HIGn ,n 模式比LG0,1模式具有更好的稳定性;(4)阶数越高,HIGn ,n 模式的质心漂移标准差越小。其次,选取线性阵列涡旋光束(LAVBs)进行对比,研究得出虽然LAVBs比HIG光束具有更好的传输性能,但由于HIG光束具有独特的结构,故可适用于不同的应用场景。最后,分析了椭圆参量和椭圆环数对HIG模式传输的影响,结果表明适当地增大椭圆参量或椭圆环数有助于提高HIG模式的抗湍流能力。本文研究结果对涡旋光束的海上应用具有指导意义。Abstract:Compared to a single vortex beam, vortex array beams can increase the information transmission capacity. Therefore, studying the propagation properties of vortex array beams is significant for their optical communication applications. In this paper, we select the helical Ince-Gaussian (HIG
n ,n ) modes of ordern and simulate the marine atmosphere turbulence using the power spectrum of the refractive index fluctuations in the marine atmosphere. The changes in intensity, phase, scintillation index and spot centroid wander of a one-dimensional array vortex beam in marine atmospheric turbulence have been investigated systematically by using the phase screen method. We find that (1) an increase in either the turbulence intensity or atmospheric turbulence inner scale enhances both the scintillation index and spot centroid wander standard deviation for HIGn ,n modes; (2) the scintillation index of HIGn ,n mode with oddn decreases with increasing mode order, and is higher than that of HIGn ,n mode for evenn ; (3) the HIGn ,n mode with ordern >1 has better stability than the LG0,1 mode; and (4) the higher the mode order, the smaller the standard deviation of spot centroid wander of HIGn ,n mode. In addition, we perform comparative study on the propagation performance of the linear array vortex beams (LAVBs) and HIG beams. Our study indicates that although LAVBs have better propagation performance than HIG beams, the unique structures of HIG beams can be applied to various application scenarios. Finally, the effects of both the ellipticity parameter and elliptic ring number on the propagation of the HIG modes are explored and analyzed. The results show that increasing either the ellipticity parameter or elliptic ring number is beneficial to improving the anti-turbulence ability of the HIG modes. These results offer significant guidance for the offshore vortex beams application.-
Key words:
- atmospheric optics /
- helical ince-gaussian mode /
- array vortex beam /
- scintillation index /
- turbulence
-
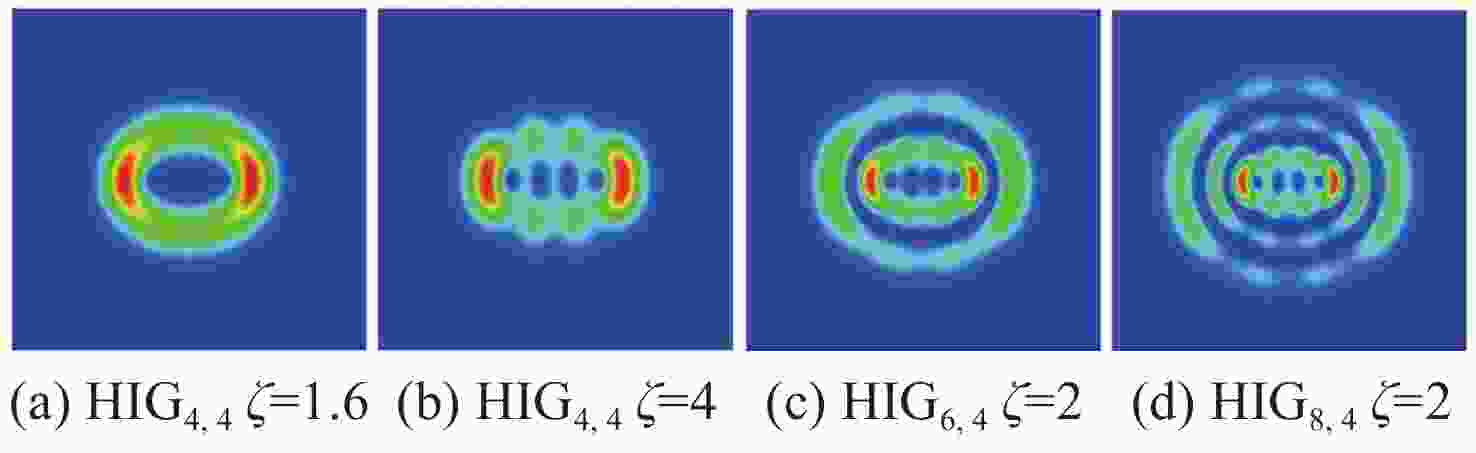
图 9 椭圆参数对HIG光束传输的影响。(a)HIG4,4光束的闪烁因子随椭圆参量的变化;(b)HIG4,4光束的质心漂移标准差随椭圆参量的变化;(c)不同椭圆环数的HIG光束的闪烁因子;(d)不同椭圆环数的HIG光束的质心漂移标准差
Figure 9. Influence of ellipticity parameters on HIG beam transmission. (a) Scintillation index and (b) standard deviation of spot centroid wander of HIG4,4 beams as a function of ellipticity parameter; (c) scintillation index and (d) standard deviation of spot centroid wander of HIG beams with different elliptic ring numbers
-
[1] BAI Y H, LV H R, FU X, et al. Vortex beam: generation and detection of orbital angular momentum [Invited][J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2022, 20(1): 012601. doi: 10.3788/COL202220.012601 [2] WANG J, YANG J Y, FAZAL I M, et al. Terabit free-space data transmission employing orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Nature Photonics, 2012, 6(7): 488-496. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.138 [3] PADGETT M, BOWMAN R. Tweezers with a twist[J]. Nature Photonics, 2011, 5(6): 343-348. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2011.81 [4] WESTPHAL V, RIZZOLI S O, LAUTERBACH M A, et al. Video-rate far-field optical nanoscopy dissects synaptic vesicle movement[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5873): 246-249. doi: 10.1126/science.1154228 [5] NICOLAS A, VEISSIER L, GINER L, et al. A quantum memory for orbital angular momentum photonic qubits[J]. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(3): 234-238. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.355 [6] KOLMOGOROV A N. Equations of turbulent motion in an incompressible fluid[J]. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1941, 30(4): 299-303. [7] 王飞, 余佳益, 刘显龙, 等. 部分相干光束经过湍流大气传输研究进展[J]. 物理学报,2018,67(18):184203. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180877WANG F, YU J Y, LIU X L, et al. Research progress of partially coherent beams propagation in turbulent atmosphere[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(18): 184203. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20180877 [8] WANG SH L, CHENG M J, YANG X H, et al. Self-focusing effect analysis of a perfect optical vortex beam in atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(13): 20861-20871. doi: 10.1364/OE.492275 [9] 王红星, 吴晓军, 宋博. 海上大气湍流中光束漂移模型分析[J]. 中国激光,2016,43(2):0213001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0213001WANG H X, WU X J, SONG B. Modeling and analysis of beam wander in maritime atmospheric turbulence[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(2): 0213001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0213001 [10] ZHUANG Y, YANG Q X, WU P F, et al. Vortex beam array generated by a volume compound fork grating in lithium niobite[J]. Results in Physics, 2021, 24: 104083. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104083 [11] FAN H H, ZHANG H, CAI C Y, et al. Flower-shaped optical vortex array[J]. Annalen der Physik, 2021, 533(4): 2000575. doi: 10.1002/andp.202000575 [12] YUAN J P, ZHANG H F, WU CH H, et al. Creation and control of vortex-beam arrays in atomic vapor[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(5): 2200667. [13] 吴武明, 宁禹, 任亚杰, 等. 阵列光束在湍流大气中传输的光强闪烁研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2012,49(7):070008.WU W M, NING Y, REN Y J, et al. Research progress of scintillations for laser array beams in atmospheric turbulence[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2012, 49(7): 070008. (in Chinese). [14] 骆传凯, 卢芳, 苗志芳, 等. 径向阵列涡旋光束在大气中的传输与扩展[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(6):0601004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0601004LUO CH K, LU F, MIAO ZH F, et al. Propagation and spreading of radial vortex beam array in atmosphere[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 0601004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0601004 [15] 牛超君, 卢芳, 韩香娥. 相位屏法模拟高斯阵列光束海洋湍流传输特性[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(6):0601004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0601004NIU CH J, LU F, HAN X E. Propagation properties of Gaussian array beams transmitted in oceanic turbulence simulated by phase screen method[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(6): 0601004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0601004 [16] LUO CH K, LU F, HAN X E. Propagation and evolution of rectangular vortex beam array through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Optik, 2020, 218: 164913. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164913 [17] 陈盼盼, 屈军, 周正仙, 等. 阵列光束在各向异性湍流大气传输时的光束漂移[J]. 量子电子学报,2019,36(3):270-277.CHEN P P, QU J, ZHOU ZH X, et al. Beam wander of array beams propagating through anisotropic turbulent atmosphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2019, 36(3): 270-277. (in Chinese). [18] MA X L, LIU D J, WANG Y CH, et al. Propagation of rectangular multi-Gaussian Schell-model array beams through free space and non-Kolmogorov turbulence[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(2): 450. doi: 10.3390/app10020450 [19] 凡顺利. 大气中阵列合成光束稳态热晕的数值模拟[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018.FAN SH L. Numerical simulation of steady-state thermal blooming of array composite beams in atmosphere[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2018. (in Chinese). [20] 张明明, 白胜闯, 董俊. Ince-Gaussian模式激光的研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2016,53(2):020002.ZHANG M M, BAI SH CH, DONG J. Advances in Ince-Gaussian modes laser[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2016, 53(2): 020002. (in Chinese). [21] WOERDEMANN M, ALPMANN C, DENZ C. Optical assembly of microparticles into highly ordered structures using Ince-Gaussian beams[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(11): 111101. doi: 10.1063/1.3561770 [22] ROBERTSON E, PIRES D G, DAI K J, et al. Constant-envelope modulation of Ince-Gaussian beams for high bandwidth underwater wireless optical communications[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2023, 41(16): 5209-5216. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3252466 [23] YU Y, CHEN Y, WANG CH Y, et al. Optical storage of Ince-Gaussian modes in warm atomic vapor[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(5): 1021-1024. doi: 10.1364/OL.414762 [24] GONZÁLEZ-DOMÍNGUEZ M A, PICENO-MARTÍNEZ A E, ROSALES-ZÁRATE L E C. Nonlocality and quantum correlations in Ince-Gauss structured light modes[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2023, 40(4): 881-890. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.482580 [25] EYYUBOĞLU H T. Propagation analysis of Ince-Gaussian beams in turbulent atmosphere[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(11): 2290-2296. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.002290 [26] NARVÁEZ CASTAÑEDA E, GUERRA VÁZQUEZ J C, RAMÍREZ ALARCÓN R, et al. Ince-Gauss beams in a turbulent atmosphere: the effect of structural parameters on beam resilience[J]. Optics Continuum, 2022, 1(8): 1777-1794. doi: 10.1364/OPTCON.461875 [27] 卢芳. 阵列光束在湍流大气中的传输及目标散射回波特性[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2016.LU F. Propagation and target scattered characteristics of array beams in turbulent atmosphere[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2016. (in Chinese). [28] GRAYSHAN K J, VETELINO F S, YOUNG C Y. A marine atmospheric spectrum for laser propagation[J]. Waves in Random and Complex Media, 2008, 18(1): 173-184. doi: 10.1080/17455030701541154 [29] SUN B Y, LÜ H, WU D, et al. Propagation of a modified complex Lorentz–Gaussian-correlated beam in a marine atmosphere[J]. Photonics, 2021, 8(3): 82. doi: 10.3390/photonics8030082 [30] 杨天星. 海洋湍流相位屏模型及该模型下OAM光束传输特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2018.YANG T X. Study on the ocean turbulence phase screen model and the transmission characteristics of OAM beam under this model[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018. (in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: