An autofocus algorithm for fusing global and local information in ferrographic images
-
摘要:
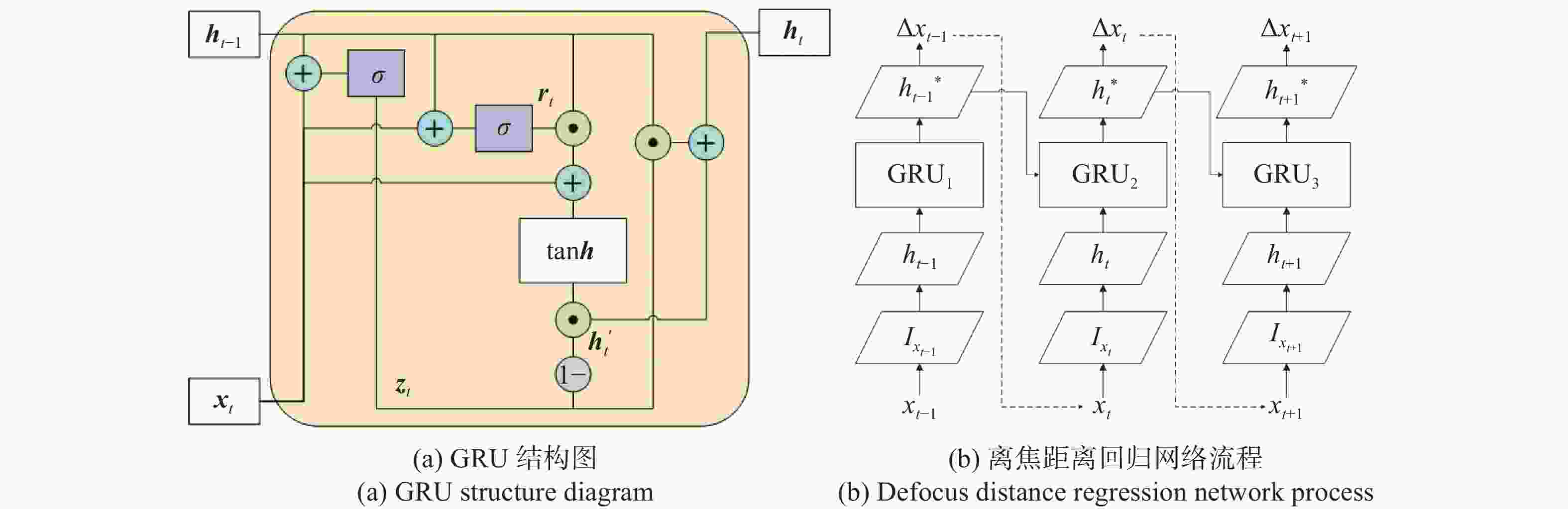
针对铁谱图像获取时人工对焦误差大、速度慢等问题,提出了一种融合全局信息和局部信息的铁谱图像自动对焦方法。此方法分为两个阶段:全局对焦阶段利用卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Networks,CNN)提取整幅图像的特征向量,并利用门控循环单元(Gate Recurrent Unit,GRU)融合对焦过程提取的特征,预测当前全局离焦距离,起到粗对焦的作用;局部对焦阶段提取磨粒的特征向量,利用GRU融合当前特征与前一轮对焦提取的特征,并依据最厚磨粒信息,预测当前磨粒离焦距离,起到精对焦的作用。同时,为了提高对焦准确率,提出了结合拉普拉斯梯度的对焦方向判定法。实验结果表明,此算法在测试集上的对焦误差为2.51 μm,当景深为2.0 μm时对焦准确率为80.1%,平均对焦时间为0.771 s。本文提出的自动对焦方法具有较好的性能,为铁谱图像自动准确采集提供了技术支持。
Abstract:To address the issues of large error and slow speed of manual focusing in ferrographic image acquisition, we propose an autofocus method for fusing global and local information in ferrographic images. This method includes two stages. In the first stage, the global autofocus stage, the feature vectors of the whole image is extracted by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) , and the features extracted in the focus process is fused by the Gate Recurrent Unit (GRU) to predict global defocusing distance, which serves as coarse focusing. In the local autofocus stage, the feature vector of the wear particle is extracted and the current features is fused with those extracted in the previous focusing process by GRU. The current defocusing distance is predicted by the resulting fused data based on the information of the thickest particle, which facilitates fine focusing. Moreover, we propose a determination method for autofocus direction using Laplacian gradient function to improve autofocus accuracy. Experimental results indicate an autofocus error of 2.51 μm on the test set and a focusing accuracy of 80.1% with a microscope depth of field of 2.0 μm. The average autofocus time is 0.771 s. The automatic ferrographic image acquisition system exhibits excellent performance and offers a practical approach for its implementation.
-
Key words:
- autofocus /
- ferrographic images /
- global information /
- local information /
- deep learning /
- gate recurrent unit
-
表 1 对焦过程中每一步的结果
Table 1. Results of each step in the focusing process
ith step dist (frame) Accdof-1 Accdof-3 Accdof-5 AT (s) 1 63.649±12.960 0.017±0.009 0.039±0.017 0.061±0.027 0.118±0.034 2 22.678±6.408 0.061±0.026 0.133±0.583 0.202±0.086 0.115±0.027 3 15.404±5.660 0.134±0.062 0.257±0.125 0.346±0.153 0.118±0.041 4 10.891±4.205 0.194±0.076 0.364±0.135 0.474±0.152 0.138±0.027 5 7.393±3.235 0.288±0.102 0.523±0.145 0.666±0.141 0.140±0.019 6 6.271±2.680 0.360±0.130 0.651±0.149 0.801±0.125 0.143±0.018 表 2 消融实验的结果
Table 2. Results of ablation experiments
消融实验序号 GRU Focus strategy LAF dist (frame) Accdof-1 Accdof-3 Accdof-5 消融实验1 √ √ 29.496±16.882 0.345±0.150 0.578±0.163 0.663±0.157 消融实验2 √ √ 81.259±71.561 0.032±0.047 0.068±0.092 0.111±0.123 消融实验3 √ 101.528±71.457 0.023±0.029 0.056±0.059 0.084±0.086 消融实验4 √ √ 28.046±20.225 0.253±0.146 0.484±0.202 0.626±0.216 本文算法 √ √ √ 6.271±2.680 0.360±0.130 0.651±0.149 0.801±0.125 表 3 不同自动对焦算法的结果
Table 3. Results of different autofocus algorithms
序号 算法 dist (frame) Accdof-1 Accdof-3 Accdof-5 AT (s) 1 整图全局搜索法 8.647 0.107 0.321 0.536 17.856 2 图像块全局搜索法 8.603 0.179 0.357 0.607 22.068 3 爬山法 12.926 0.286 0.464 0.500 1.459 4 HH-Net 27.177 0.036 0.179 0.429 0.119 5 Autofocus-RNN 31.839 0.321 0.429 0.571 0.419 6 本文算法 6.271 0.360 0.651 0.801 0.771 -
[1] ROYLANCE B J. Ferrography—then and now[J]. Tribology International, 2005, 38(10): 857-862. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2005.03.006 [2] WANG J Q, WANG X L. The segmentation of ferrography images: a brief survey[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2013, 770: 427-432. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.770.427 [3] 卿华, 王新军. 飞机油液监控技术[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2011.QING H, WANG X J. Aircraft oil Monitoring Technology[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2011. (in Chinese). [4] 叶一青, 易定容, 张勇贞, 等. 基于倾斜摄像头的显微自动对焦方法[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(12):1218001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1218001YE Y Q, YI D R, ZHANG Y ZH, et al. Microscopy autofocus method using tilt camera[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(12): 1218001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.1218001 [5] BATHE-PETERS M, ANNIBALE P, LOHSE M J. All-optical microscope autofocus based on an electrically tunable lens and a totally internally reflected IR laser[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(3): 2359-2368. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.002359 [6] ZHANG X, ZENG F, LI Y, et al. Improvement in focusing accuracy of DNA sequencing microscope with multi-position laser differential confocal autofocus method[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(2): 895-904. [7] 唐凌宇, 葛明锋, 董文飞. 全自动推扫式高光谱显微成像系统设计与研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(6):1486-1494. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0040TANG L Y, GE M F, DONG W F. Design and research of fully automatic push-broom hyperspectral microscopic imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1486-1494. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0040 [8] JANG J, YOO Y, KIM J, et al. Sensor-based auto-focusing system using multi-scale feature extraction and phase correlation matching[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(3): 5747-5762. doi: 10.3390/s150305747 [9] GUO K K, LIAO J, BIAN Z CH, et al. InstantScope: a low-cost whole slide imaging system with instant focal plane detection[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2015, 6(9): 3210-3216. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.003210 [10] GAN Y H, YE Z T, HAN Y B, et al. Single-shot autofocusing in light sheet fluorescence microscopy with multiplexed structured illumination and deep learning[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 168: 107663. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107663 [11] HOU S B, ZHANG H Y, MA B L, et al. Extended autofocusing in dual-wavelength digital holography[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(22): 5959-5968. doi: 10.1364/AO.494696 [12] 郭立强, 刘恋. 结合斜变换与方差的图像聚焦测度[J]. 光学 精密工程,2021,29(7):1731-1739. doi: 10.37188/OPE.2020.0555GUO L Q, LIU L. Image focus measure based on slant transform and variance[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(7): 1731-1739. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.2020.0555 [13] LIAO Y, XIONG Y H, YANG Y H. An auto-focus method of microscope for the surface structure of transparent materials under transmission illumination[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(7): 2487. doi: 10.3390/s21072487 [14] NOEK R, KNOERNSCHILD C, MIGACZ J, et al. Multiscale optics for enhanced light collection from a point source[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(14): 2460-2462. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.002460 [15] SHAJKOFCI A, LIEBLING M. Semi-blind spatially-variant deconvolution in optical microscopy with local point spread function estimation by use of convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2018. [16] FARNES S A R, TSAI D M, CHIU W Y. Autofocus measurement for electronic components using deep regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 11(4): 697-707. doi: 10.1109/TCPMT.2021.3060809 [17] GE Y H, LI B, ZHAO Y ZH, et al. HH-Net: image driven microscope fast auto-focus with deep neural network[C]. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Association for Computing Machinery, 2019: 180-185. [18] XIANG Y, HE ZH J, LIU Q, et al. Autofocus of whole slide imaging based on convolution and recurrent neural networks[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2021, 220: 113146. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2020.113146 [19] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[J/OL]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [20] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN SH Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2016. -






 下载:
下载: