-
摘要:
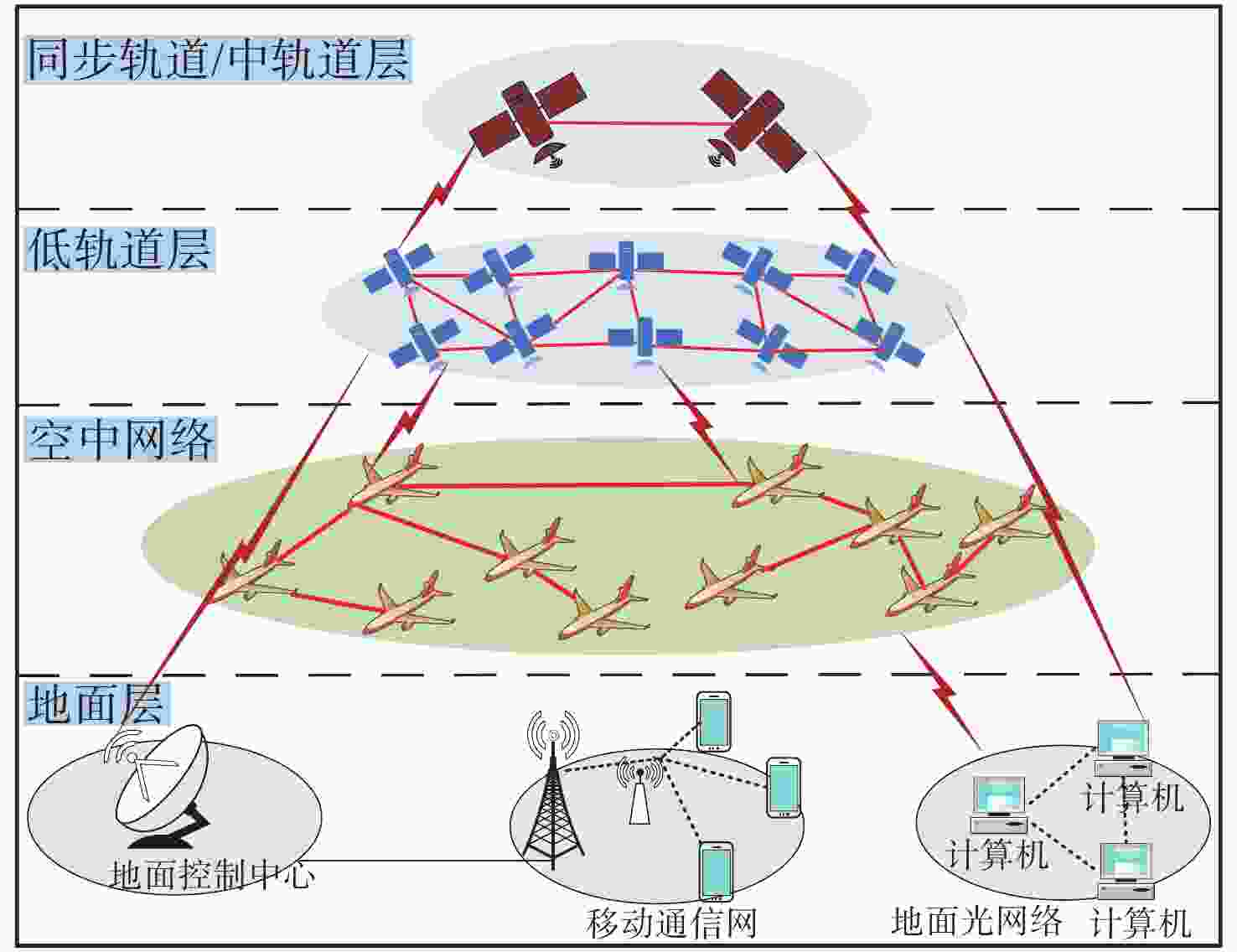
激光通信是以光波为载体实现信息传输的通信技术,具有高速率、高带宽、小尺寸、抗干扰和保密性好等优势,具备实现空间信息网络高速传输和安全运行的关键能力。本世纪以来,国内外主要研究机构致力于研究激光通信技术在实现组网过程中所需要解决的一系列问题,包括一点对多点同时激光通信、节点内多路信号全光交换与转发、节点动态随遇接入、网络动态拓扑结构设计等关键技术,并开展了众多演示验证实验,部分研究成果已经投入应用。本文在对空间激光通信组网技术进行分析探讨的基础上,概述了国内外激光通信组网技术的发展现状,重点对卫星星座、卫星中继和航空网络等领域中激光通信组网技术的应用情况和发展现状进行了分析和总结,对国内相关研究技术方案、实验验证情况等进行了综述,最后对激光通信组网技术与应用的发展趋势进行了预测。
Abstract:Laser communication utilizes light waves as the transmission medium. It offers many advantages, including high data rates, expansive bandwidth, compactness, robust interference resistance, and superior confidentiality. It has the critical capability to enable high-speed transmission and secure operation of space information networks. Prominent research institutions have committed to studying a series of challenges that need to be solved in the process of networking laser communication technology, including point-to-multipoint simultaneous laser communication, all-optical switching and forwarding of multi-channel signals within nodes, node dynamic random access, and network topology design. Numerous demonstration and verification experiments have been conducted, with a subset of these research results finding practical applications. Based on the analysis and discussion of space laser communication networking technology, this paper summarizes the development of laser communication networking technology both domestically and internationally, focusing on the application of laser communication networking technology in the fields of satellite constellations, satellite relays, and aviation networks. Furthermore, it presents a review of pertinent domestic research methodologies, experimental validations, and technical solutions. Finally, it predicts the development trend of laser communication networking technology and applications.
-
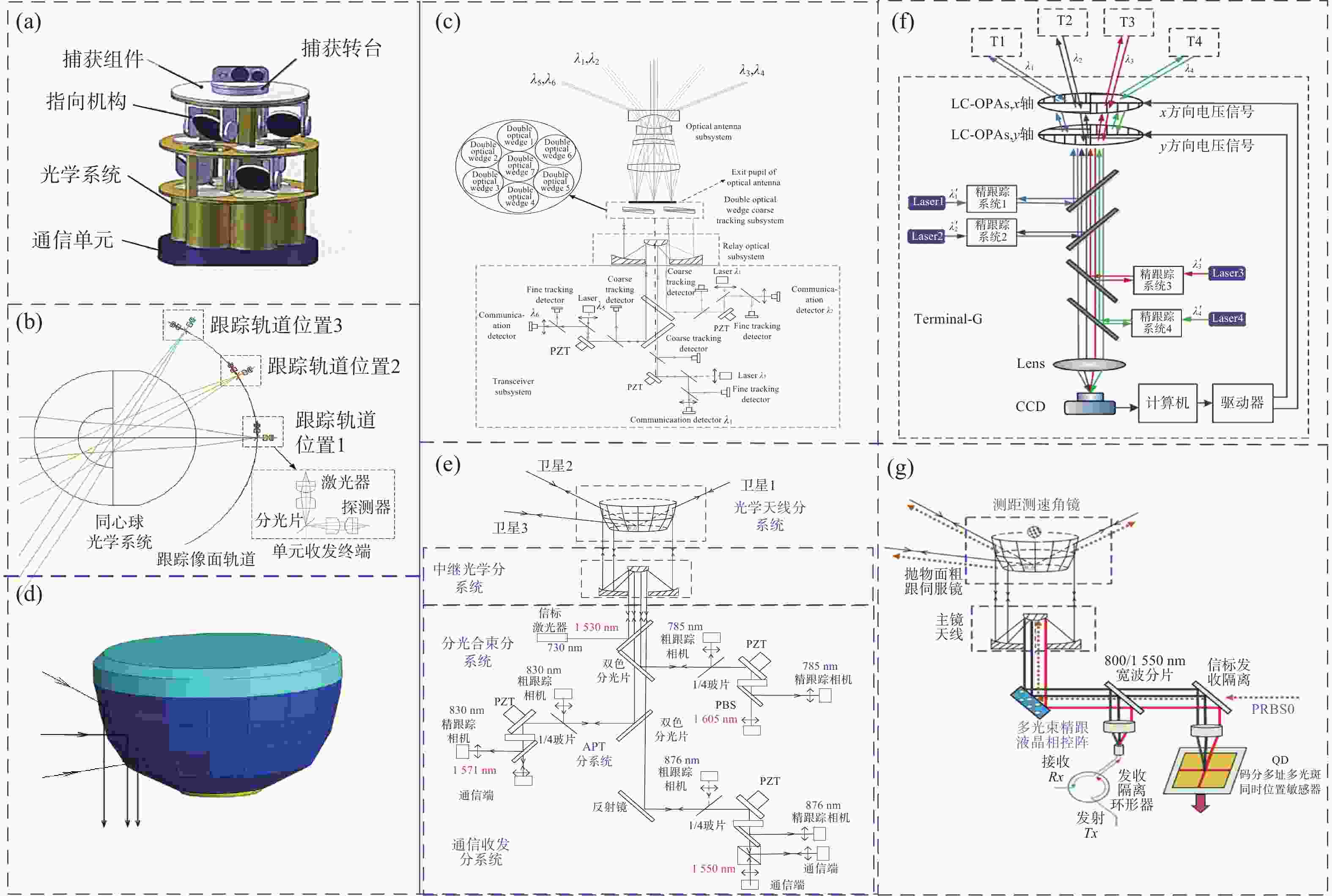
图 5 “一点对多点”激光通信系统原理图。(a)多分光镜叠加型天线结构[24]、(b)同心球面透镜天线结构[24]、(c)双光楔棱镜结构[23]、(d)旋转抛物面天线结构[25]、(e)基于旋转抛物面结构的一对多同时激光通信系统[25]、(f)四个波束的跟踪系统结构[26]、(g)一对多卫星间激光测通传一体化系统[27]
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of point-to-multipoint laser communication system. (a) Multi-beam splitter superimposed antenna structure[24]; (b) concentric spherical lens antenna structure scheme[24]; (c) double light wedge prism[23]; (d) rotating parabolic antenna structure scheme[25]; (e) a point-to-multipoint simultaneous laser communication system based on a rotating paraboloid structure[25]; (f) four-beam tracking system[26]; (g) the integrated laser measurement and transmission system between point-to-multipoint satellites[27]
图 9 节点内全光交换技术研究进展。(a)WC-OCS和格式转换的三节点FSO网络的实验系统示意图[29];(b)单泵浦FWM实验设置图[30];(c)基于WOCS的光交换原理[31]
Figure 9. Research progress on nodal all-optical switching technology. (a) Schematic diagram of the 3-node FSO network with the simultaneous WC-OCS and format conversion[29], (b) experimental setup diagram of single-pump FWM[30], and (c) optical switching principle diagram based on WOCS[31]
表 1 一点对多点激光通信方案的性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of performance parameters of point-to-multipoint laser communication schemes
参数 HAWK终端 球形转台 硅基光学
相控阵液晶光学相控阵 特殊光机结构
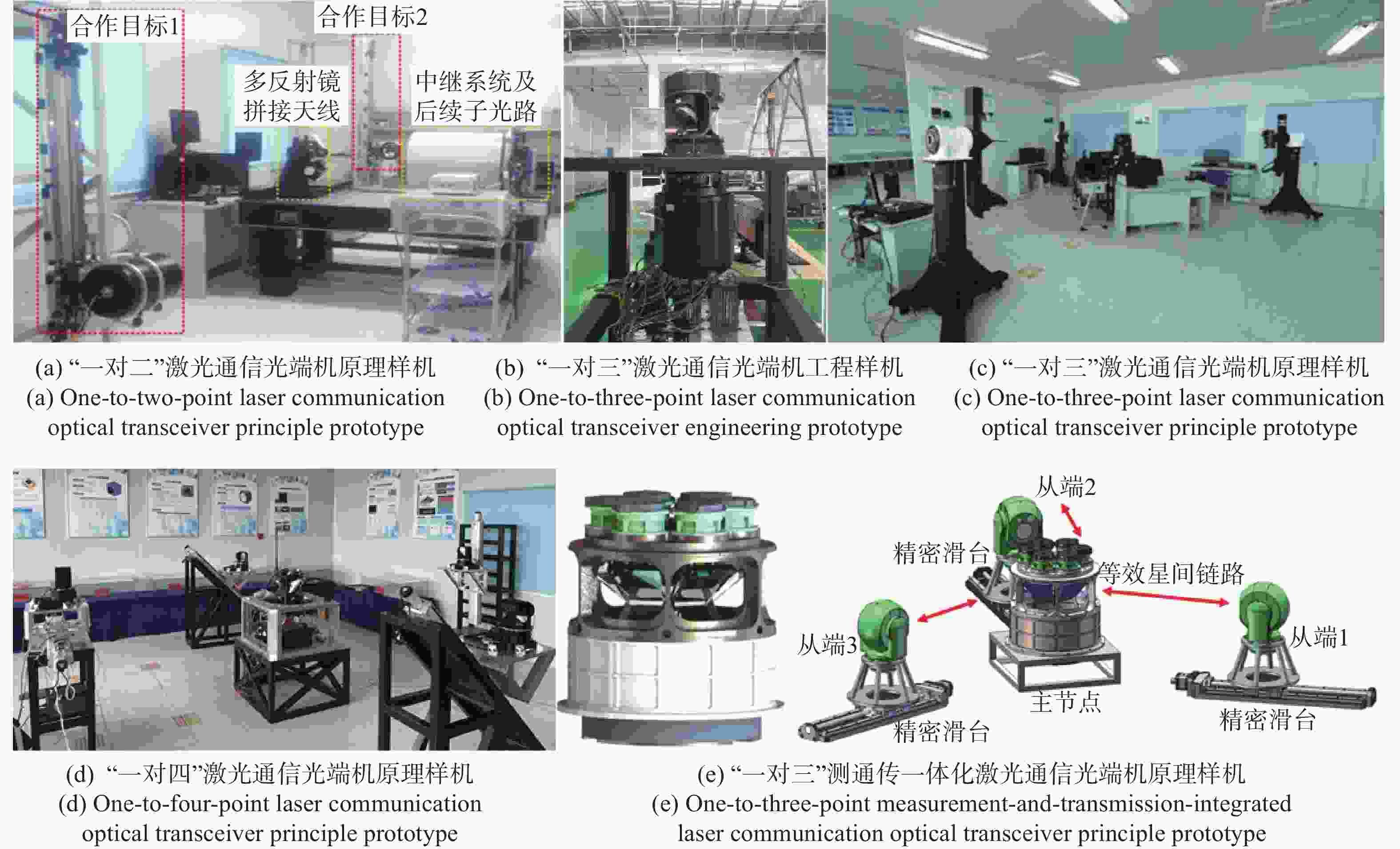
(旋转抛物面)目前水平 规划参数 工作模式 一对一×4 一对一×4 一对多 一对多 一对多 一对四 数据传输速率/Gbps 7 2.5 70 25 100+ 10 通信光束发散角/μrad 80 100 68 - - 50 偏转最大角度 方位角:0−360° ±5°(内框) 50°(单孔径) ±25°(单孔径) ±45°(单孔径) 方位角360°,俯仰角15° 平均切换时间 - <30 s 200 ms <10 ms <5 ms <30 s 传输距离 50 km 100 km 54 m 1000 km系统功耗 110 w 1000 w- <80 W <30 W <150 W 系统体积 279 mm×256 mm×546 mm Φ250 mm - 175 mm×125 mm×50 mm - Φ300 mm×750 mm 系统质量 13 kg 25 kg - 1 kg 45 kg 跟踪精度 - 20~30 μrad - 20 μrad 3 μrad 通光孔径 31 mm 150 mm 3 mm 25 mm 等效收发口径≥85 mm 功耗 2.9 W 5 W 72.53 μW <3 W 转向机构 无 二轴四框架 无 无 无 二维摆镜 表 2 一对多同时激光通信光端机参数对照表
Table 2. Parameter comparison table of point-to-multipoint simultaneous laser communication optical terminals
参数 “一对二”原理
验证装置“一对三”原理样机 “一对三”工程样机 “一对四”原理样机 “一对三”测通传
一体化原理样机通信光波长 1550 nm/1064 nm1550 nm/1530 nm、1561 nm/1605 nm;1530 nm1605 nm/1571 nm/1550 nm1550 nm/1530 nm1550 nm通信速率 1−2.5 Gbps 2.5 Gbps 2.5 Gbps 1 Gbps−10 Gbps 10 Gbps 通信距离(等效) 50 km 100~ 1000 km100~ 1000 km1000 km1000 km通信光束散角 100 µrad 300 μrad(主)
40 μrad(从)200 μrad(主)
40 μrad(从)80 μrad(主)
80 μrad(从)50 μrad(主、从) 信标光束散角 - 1 mrad(主、从) 2 mrad(主、从) 2 mrad(主、从) 300 μrad(主、从) 通信范围 360°(方位)
38°(俯仰)360°(方位)
30°(俯仰)360°(方位)
30°(俯仰)360°(方位)
30°(俯仰)360°(方位)
30°(俯仰)通信光发射功率 1 W 5 W(主)
2 W(从)5 W(主)
2 W(从)5 W(主)
2 W(从)4 W(主、从) 状态 完成实验室原理验证 完成实验室原理验证 完成野外演示验证 完成实验室原理验证 正在进行实验室原理验证 表 3 卫星星座激光通信组网典型案例
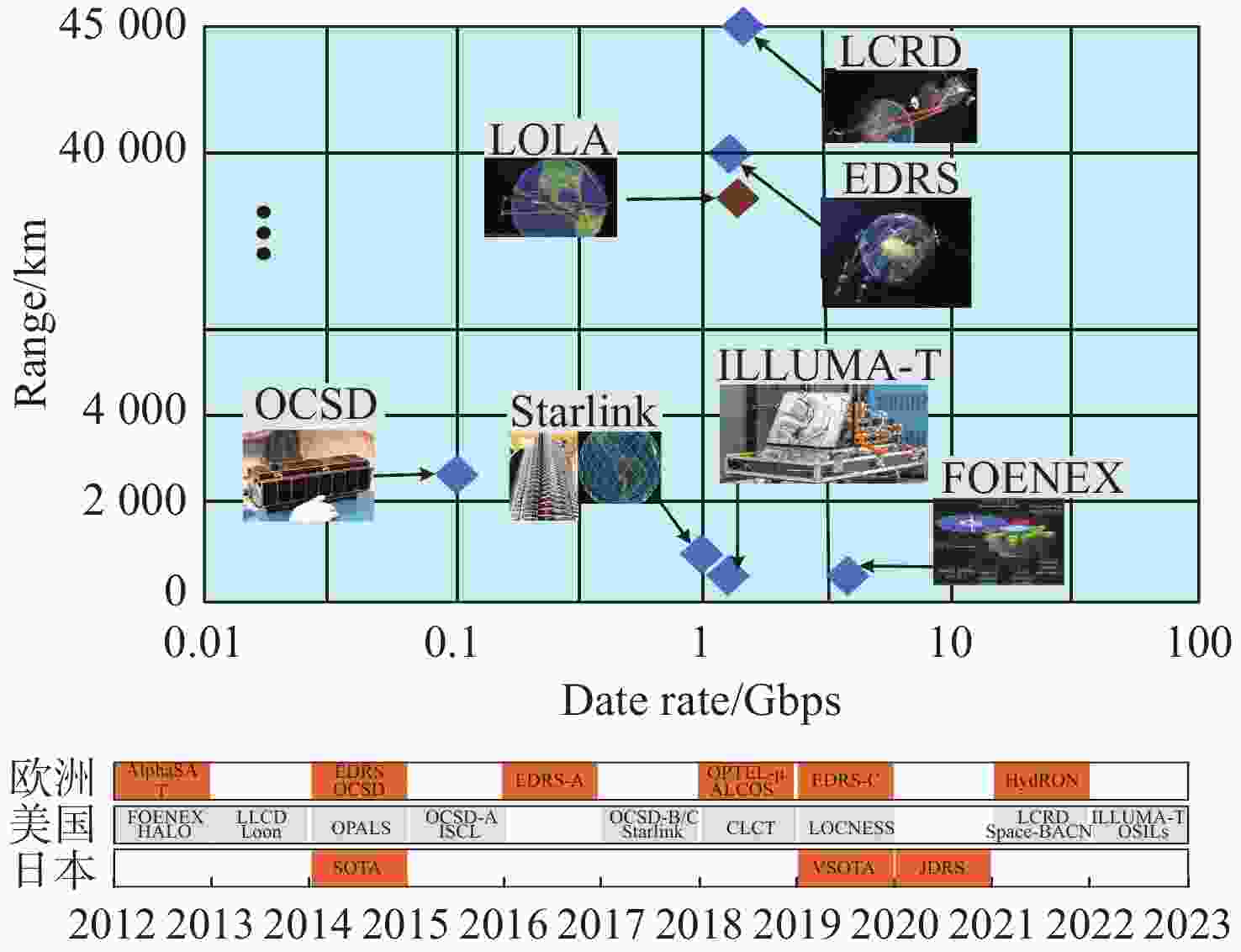
Table 3. Typical cases of laser communication networking in satellite constellations
系统 HALO AlphaSAT Starlink Transport Layer Space-BACN 搭载平台 LEO-GEO LEO-GEO LEO LEO GEO-LEO 年份 2012 2012 2017 2019 2021 国家 美国 欧洲 美国 美国 美国 通信速率 4200 Gbps100 Mbps 1 Gbps 200 Gbps 100 Gbps 链路距离/km - 36000 km1204 km3000 ~7000 km10000 km表 4 卫星中继激光通信组网典型案例
Table 4. Typical cases of satellite relay laser communication networking
系统 EDRS HICALI LCRD LOCNESS JDRS 搭载平台 Sentinel1-Alpha GEO-LEO GEO-Ground GEO-Ground GEO-LEO 年份 2014 2021 2019 2019 2020 国家 欧洲 日本 美国 美国 日本 通信速率 1.8 Gbps 10 Gbps 2.88 Gbps/622 Mbps 10/100 Gbps 1.8 Gbps 工作波长 1064 nm1541.35 nm1550 nm- 1540 nm/1560 nm链路距离 45000 km45000 km38000 km73395 km45000 km通信光功率 2.2 W 2.5 W 0.5 W - - 光学口径 135 mm 150 mm 108 mm 220 mm 150 mm 调制/解调方式 BPSK/零差相干探测 DPSK DPSK/16PPM - RZ-DPSK-DD/IM-DD/直接探测 质量 50 kg 50 kg 69 kg - 50 kg左右 功耗 160 W 160 W 130 W - - 表 5 航空平台激光通信组网典型案例
Table 5. Typical cases of laser communication networking on aviation platforms
系统 ORCLE ORCA Falcon FOENEX Loon Aquila Ultra Air 搭载平台 Aircraft Aircraft Aircraft Aircraft H-A-P(stratospheric) Aircraft Aircraft 年份 2008 2008 2011 2012 2015 2016 2021 国家 美国 美国 美国 美国 美国 美国 美国 通信速率 155 Mpbs 2.5 Gbit/s 2.5 Gbit/s 6 Gbps 130 Mpbs 1 Gbps 10 Gbps 链路距离 25 km 18 km 132 km 230 km 100 km 17 km 4500 km通信光功率 0.5 W 0.2 W 10 W 0.5 W 0.1 W 1 W 15.85 W 光学口径 5.08 cm 2.54 cm 3.05 cm 10.75 cm - - - 调制/解调方式 OOK OOK OOK FM/IM OOK QPSK - -
[1] 姜会林, 安岩, 张雅琳, 等. 空间激光通信现状、发展趋势及关键技术分析[J]. 飞行器测控学报,2015,34(3):207-217.JIANG H L, AN Y, ZHANG Y L, et al. Analysis of the status Quo, development trend and key technologies of space laser communication[J]. Journal of Spacecraft TT& C Technology, 2015, 34(3): 207-217. (in Chinese). [2] HEMMATI H. Deep Space Optical Communications[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. [3] KAUSHAL H, KADDOUM G. Optical communication in space: challenges and mitigation techniques[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(1): 57-96. [4] HEMMATI H, BISWAS A, DJORDJEVIC I B. Deep-space optical communications: future perspectives and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2011, 99(11): 2020-2039. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2011.2160609 [5] THRUN S, MONTEMERLO M, DAHLKAMP H, et al. Stanley: the robot that won the DARPA Grand Challenge[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2006, 23(9): 661-692. doi: 10.1002/rob.20147 [6] SUN L, DU Q H. Physical layer security with its applications in 5G networks: a review[J]. China Communications, 2017, 14(12): 1-14. doi: 10.1109/CC.2017.8246483 [7] RADHAKRISHNAN R, EDMONSON W W, AFGHAH F, et al. Survey of inter-satellite communication for small satellite systems: physical layer to network layer view[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(4): 2442-2473. [8] BILGI M, YUKSEL M. Multi-element free-space-optical spherical structures with intermittent connectivity patterns[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM Workshops 2008, IEEE, 2008: 1-4. [9] VELAZCO J E, GRIFFIN J, WERNICKE D, et al. High data rate inter-satellite omnidirectional optical communicator[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd Annual AIAA/USU, 2018: 354-2305. [10] 高世杰, 吴佳彬, 刘永凯, 等. 微小卫星激光通信系统发展现状与趋势[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(6):1171-1181. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0033GAO SH J, WU J B, LIU Y K, et al. Development status and trend of micro-satellite laser communication systems[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(6): 1171-1181. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0033 [11] SEARCY P, MATSUMORI B A. Five advantages of managed optical communications array (MOCA) technology over other Lasercomm approaches[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11678: 116780Y. [12] 李全超. 基于万向节的机载高精度光电平台机构研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2022.LI Q CH. Research on mechanism of aerial high-precision optoelectronic platform based on universal joint[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. (in Chinese). [13] YOU Q, CHEN D G, XIAO X, et al. 10 Gb/s free space optical interconnect with broadcasting capability enabled by a silicon integrated optical phased array[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(12): 120602. doi: 10.3788/COL202119.120602 [14] HAN R L, SUN J F, HOU P P, et al. Multi-dimensional and large-sized optical phased array for space laser communication[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(4): 5026-5037. doi: 10.1364/OE.447351 [15] 李盈祉. 硅基光学相控阵芯片的研制及应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023.LI Y ZH. Research and application of silicon-based optical phased array chip[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese). [16] 许剑华, 汪相如, 黄子强, 等. 基于液晶光学相控阵的空间激光通信PID跟踪方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(2):021202.XU J H, WANG X R, HUANG Z Q, et al. PID tracking method of space laser communication based on liquid crystal optical phased array[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(2): 021202. (in Chinese). [17] 曹汉, 张士元, 穆全全, 等. 基于光控取向技术的液晶光阀系统[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,44(3):10-14.CAO H, ZHANG SH Y, MU Q Q, et al. Liquid crystal light valve system based on photoalignment[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 44(3): 10-14. (in Chinese). [18] SEARCY P, MATSUMORI B A. MOCA technology and product update with analytical results[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2022, 11993: 1199303. [19] PRESBY H M, TYSON J A. Point-to-multipoint free-space wireless optical communication system: US, 6445496B1[P]. 2002-09-03. [20] SPARROLD S W, UPTON E L, OKOROGU A O. Free space point-to-multipoint optical communication system and apparatus: US, 6912360B1[P]. 2005-06-28. [21] 史蒂芬·G·兰伯特. 自由空间光通信网络及用于中继节点的方法: 美国, 106341184A[P]. 2017-01-18.LAMBERT S G. Free space optical communications network and method for relay nodes: US, 106341184A[P]. 2017-01-18. (in Chinese). [22] M·D·马可夫斯基, G·D·科尔曼, W·J·小斯尔卡科, 等. 用于自由空间光通信的激光继电器: 美国, 105284064A[P]. 2016-01-27.MARKOVSKI M D, COLEMAN G D, SIERKACZKO W J, et al. Laser relay for free space optical communications: US, 105284064A[P]. 2016-01-27. (in Chinese). [23] 江伦, 胡源, 王超, 等. 一点对多点同时空间激光通信光学系统研究[J]. 光学学报,2016,36(5):0506001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0506001JIANG L, HU Y, WANG CH, et al. Optical system in one-point to multi-point simultaneous space laser communications[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(5): 0506001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0506001 [24] 姜会林, 胡源, 宋延嵩, 等. 空间激光通信组网光端机技术研究[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2011,32(5):52-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2011.05.013JIANG H L, HU Y, SONG Y S, et al. Research on space laser communication network[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2011, 32(5): 52-59. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2011.05.013 [25] 姜会林, 胡源, 丁莹, 等. 空间激光通信组网光学原理研究[J]. 光学学报,2012,32(10):1006003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.1006003JIANG H L, HU Y, DING Y, et al. Optical principle research of space laser communication network[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(10): 1006003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.1006003 [26] 郭鸿儒. 基于液晶光学相控阵的多用户捕跟方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019.GOU H R. Multi-user acquisition tracking method based on liquid crystal optical phased array[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019. (in Chinese). [27] 陈帅. 基于码分多址的多信标光单探测器同时识别技术研究[D]. 长春理工大学, 2024.CHEN SH. Research on Simultaneous Recognition Technology of Multiple Beacon Light Single Detector Based on Code Division Multiple Access[D].Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2024. (in Chinese). [28] HUANG X N, SUH Y, DUAN T, et al. Simultaneous wavelength and format conversions based on the polarization-insensitive FWM in free-space optical communication network[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2019, 11(1): 6500210. [29] 郏帅威, 汪伟, 谢小平, 等. 空间激光通信网络中的全光数据合路技术研究[J]. 遥测遥控,2022,43(4):70-79. doi: 10.12347/j.ycyk.20211227001JIA SH W, WANG W, XIE X P, et al. Research on the all-optical data aggregation technology in the space laser communication network[J]. Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2022, 43(4): 70-79. (in Chinese). doi: 10.12347/j.ycyk.20211227001 [30] 陆红强, 汪伟, 黄新宁, 等. 下一代空间激光骨干网络全光处理技术[J]. 遥测遥控,2022,43(6):56-63. doi: 10.12347/j.ycyk.20220318001LU H Q, WANG W, HUANG X N, et al. All-optical processing techniques for next-generation laser-based space backbone-networks[J]. Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2022, 43(6): 56-63. (in Chinese). doi: 10.12347/j.ycyk.20220318001 [31] 孟佳成, 谢宁波, 白兆峰, 等. 面向卫星互联网的星载光交换技术[J]. 天地一体化信息网络,2022,3(2):47-55.MENG J CH, XIE N B, BAI ZH F, et al. Spaceborne optical switching technology for satellite internet[J]. Space- Integrated- Ground Information Networks, 2022, 3(2): 47-55. (in Chinese). [32] 中国科学院. 西安光机所星载光交换技术成功在轨验证[EB/OL]. (2023-11-08). https://www.cas.cn/syky/202310/t20231008_4973365.shtml.Chinese Academy of Sciences. Xi'an institute of optics and mechanics successfully validates on-orbit optical switching technology[EB/OL]. (2023-11-08). https://www.cas.cn/syky/202310/t20231008_4973365.shtml. (in Chinese) [33] 付强, 姜会林, 王晓曼, 等. 空间激光通信研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国光学,2012,5(2):116-125.FU Q, JIANG H L, WANG X M, et al. Research status and development trend of space laser communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(2): 116-125. (in Chinese). [34] 高铎瑞, 谢壮, 马榕, 等. 卫星激光通信发展现状与趋势分析(特邀)[J]. 光子学报,2021,50(4):0406001.GAO D R, XIE ZH, MA R, et al. Development current status and trend analysis of satellite laser communication (invited)[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 0406001. (in Chinese). [35] 杨成武, 谌明, 刘向南, 等. 小卫星激光通信终端技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 遥测遥控,2021,42(3):1-7.YANG CH W, CHEN M, LIU X N, et al. Current status and development trends of minisatellite laser communication terminal technology[J]. Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2021, 42(3): 1-7. (in Chinese). [36] HEINE F, SÁNCHEZ-TERCERO A, MARTIN-PIMENTEL P, et al. In orbit perfomance of tesat LCTs[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 10910: 109100U. [37] HAAN H, SIEMENS C. Airborne optical communication terminal: first successful link from Tenerife to the GEO Alphasat[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11133: 1113306. [38] ROSE T S, ROWEN D W, LALUMONDIERE S, et al. Optical communications downlink from a 1.5 U CubeSat: OCSD program[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11180: 111800J. [39] 郑运强, 刘欢, 孟佳成, 等. 空基激光通信研究进展和趋势以及关键技术[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(6):20210475. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210475ZHENG Y Q, LIU H, MENG J CH, et al. Development status, trend and key technologies of air-based laser communication[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(6): 20210475. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210475 [40] PULLIAM J, ZAMBRE Y, KARMARKAR A, et al. TSAT network architecture[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Military Communications Conference, IEEE, 2008: 1-7. [41] ZHI H, JIANG X J, WANG J F. Multicolour photometry of LEO mega-constellations Starlink and OneWeb[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 530(4): 5006-5015. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae693 [42] RAINBOW J. SpaceX launches OneWeb Gen 2 technology demonstrator[EB/OL]. (2023-08-01). https://spacenews.com/spacex-launches-oneweb-gen-2-technology-demonstrator/. [43] HAUSCHILDT H, ELIA C, JONES A, et al. ESAs ScyLight programme: activities and status of the high throughput optical network "HydRON"[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11180: 111800G. [44] VASKO C A, ARAPOGLOU P D, ACAR G, et al. Optical high-speed data network in space-an update on HydRON's system concept[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications, IEEE, 2022: 7-13. [45] SDA. Space development agency next-generation space architecture request for information (SDA-SN-19-0001)[R]. Washington: Defense Pentagon, 2019. [46] 许连杰, 刘亮亮, 庞鸿锋, 等. 美国“扩散型作战人员太空架构”系统建设进展及关键技术分析[J]. 中国航天,2023(9):47-54.XU L J, LIU L L, PANG H F, et al. Development and key technology analysis of US proliferated warfighter space architecture[J]. Aerospace China, 2023(9): 47-54. (in Chinese). [47] DARPA. DARPA’s Mandrake 2 satellites: communicating at the speed of light[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://breakingdefense.com/2022/08/darpas-mandrake-2-satellites-communicating-at-the-speed-of-light/. [48] SDA. SDA layered network of military satellites now known as “proliferated warfighter space architecture”[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://www.sda.mil/sda-layered-network-of-military-satellites-now-known-as-proliferated-warfighter-space-architecture/. [49] United States Government. Space development agency successfully launches tranche 0 satellites[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/3348974/space-development-agency-successfully-launches-tranche-0-satellites/. [50] U. S. Department of Defense. Space development agency makes awards for 126 satellites to build tranche 1 transport layer[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://www.defense.gov/News/Releases/Release/Article/2948229/space-development-agency-makes-awards-for-126-satellites-to-build-tranche-1-tra/. [51] ERWIN S. Space Development Agency issues draft solicitation for 100 satellites[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://spacenews.com/space-development-agency-issues-draft-solicitation-for-100-satellites/. [52] ERWIN S. DARPA selects companies for inter-satellite laser communications project[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://spacenews.com/darpa-selects-companies-for-inter-satellite-laser-communications-project/. [53] 科技日报. 基于激光通信互联 遥感小卫星星座建成[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://www.xinhuanet.com/tech/20230116/46f74613b1e94a80af9091ded3ac8cf6/c.html.Science and Technology Daily. Remote sensing small satellite constellation established based on laser communication interconnection[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02. https://www.xinhuanet.com/tech/20230116/46f74613b1e94a80af9091ded3ac8cf6/c.html. (in Chinese). [54] Laser Light Communications. HALO communications system[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02). https://proceedings.kaconf.com/papers/2016/clq/2_3.pdf. [55] PULTAROVA T. Starlink satellites: facts, tracking and impact on astronomy[EB/OL]. (2025-03-03). https://www.space.com/spacex-starlink-satellites.html. [56] CHAUDHRY A U, YANIKOMEROGLU H. Laser inter-satellite links in a starlink constellation[J]. arXiv: 2103.00056, 2021. [57] POSCH M. Starlink’s inter-satellite laser links are setting new record with 42 million GB per day[EB/OL]. (2024-03-03). https://hackaday.com/2024/02/05/starlinks-inter-satellite-laser-links-are-setting-new-record-with-42-million-gb-per-day/. [58] RIGOLLE M. LeoSat—a new satellite paradigm[EB/OL]. (2023-08-05). http://www.satmagazine.com/story.php?number=1365559905. [59] JEWETT R. Mynaric to roll out next-generation optical link terminal[EB/OL]. (2023-08-05). https://www.satellitetoday.com/innovation/2021/08/26/mynaric-to-roll-out-next-generation-optical-link-terminal/. [60] JEWETT R. Mynaric to supply Raytheon with optical terminals for SDA program[EB/OL]. (2023-08-05). https://www.satellitetoday.com/government-military/2023/06/22/mynaric-to-supply-raytheon-with-optical-terminals-for-sda-program/. [61] ERWIN S. Boeing unveils WGS-11 design with new military payload[EB/OL]. (2025-03-04). https://spacenews.com/boeing-unveils-wgs-11-design-with-new-military-payload/. [62] HEINE F, MARTIN-PIMENTEL P, KAEMPFNER H, et al. Alphasat and sentinel 1A, the first 100 links[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications, IEEE, 2015: 1-4. [63] RIDGEWAY B. Laser communications relay demonstration (LCRD) overview[EB/OL]. (2023-08-06). https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/stmd/tech-demo-missions-program/laser-communications-relay-demonstration-lcrd-overview/. [64] 董全睿, 陈涛, 高世杰, 等. 星载激光通信技术研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(6):1260-1270. doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1260DONG Q R, CHEN T, GAO SH J, et al. Progress of research on satellite-borne laser communication technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1260-1270. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1260 [65] ISRAEL D J, EDWARDS B L, STAREN J W. Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD) update and the path towards optical relay operations[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, IEEE, 2017: 1-6. [66] GILLMER S R, SMEATON C V, BURNSIDE J W, et al. Demonstration of a modular, scalable, laser communication terminal for human spaceflight missions[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11816: 118160E. [67] SEAS A, ROBINSON B, SHIH T, et al. Optical communications systems for NASA's human space flight missions[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11180: 111800H. [68] ISRAEL D J, SHAW H. Next-generation NASA earth-orbiting relay satellites: fusing optical and microwave communications[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference, IEEE, 2018: 1-7. [69] PARK E A, CORNWELL D, ISRAEL D. NASA's next generation ≥ 100 Gbps optical communications relay[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Aerospace Conference, IEEE, 2019: 1-9. [70] WITTING M, HAUSCHILDT H, MURRELL A, et al. Status of the European data relay satellite system[C]. Proceedings of 2012 International Conference on Space Optical Systems and Applications, 2012: 9-12. [71] PERDIGUES J M, SODNIK Z, HAUSCHILDT H, et al. The ESA's optical ground station for the EDRS-A LCT in-orbit test campaign: upgrades and test results[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10562: 105622V. [72] HILL J. Airbus to commence service on EDRS-C satellite[EB/OL]. (2023-08-06). https://www.satellitetoday.com/launch/2020/07/17/airbus-to-commence-service-on-edrs-c-satellite/. [73] JEWETT R. Inmarsat, addvalue debut inter-satellite data relay system linking LEO and GEO[EB/OL]. (2023-08-06). https://www.satellitetoday.com/mobility/2020/11/23/inmarsat-addvalue-debut-inter-satellite-data-relay-system-linking-leo-and-geo/. [74] ANDREWS L C, PHILLIPS R L, BAGLEY Z C, et al. Hybrid optical/radio frequency (RF) communications[M]//MAJUMDAR A K. Advanced Free Space Optics (FSO): A Systems Approach. New York: Springer, 2015. [75] YOUNG D W, HURT H H, SLUZ J E, et al. Development and demonstration of laser communications systems[J]. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 2015, 33(2): 122-138. [76] KUMAR K D, PONSEELAN A J, PRABHA D D, et al. A study on Google project loon-opportunities and challenges[J]. International Journal of Emerging Technology and Innovative Engineering, 2020, 6(3): 206-214. [77] NEWTON C. Facebook’s drone test flight ended with part of the wing snapping off[EB/OL]. (2023-08-07). https://www.theverge.com/2016/12/16/13983868/facebook-drone-crash-aquila-wing-failure-ntsb-report. [78] WU SH Q, LI SH Q, LIN Y X, et al. Performance analysis of hybrid FSO/RF transmission assisted airborne free-space optical communication system[J]. Journal of Communications and Information Networks, 2022, 7(3): 252-258. doi: 10.23919/JCIN.2022.9906939 [79] 赵尚宏, 魏军, 李勇军, 等. 航空光通信与网络技术[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2020.ZHAO SH H, WEI J, LI Y J, et al. Aviation Optical Communication and Networking Technology[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 2020. (in Chinese). [80] SHEKHAR S, BOGAERTS W, CHROSTOWSKI L, et al. Roadmapping the next generation of silicon photonics[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 751. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44750-0 [81] ERWIN S. Mynaric selected by DARPA to design next-generation optical terminals[EB/OL]. (2023-08-07). https://spacenews.com/mynaric-selected-by-darpa-to-design-next-generation-optical-terminals/. -





 下载:
下载: