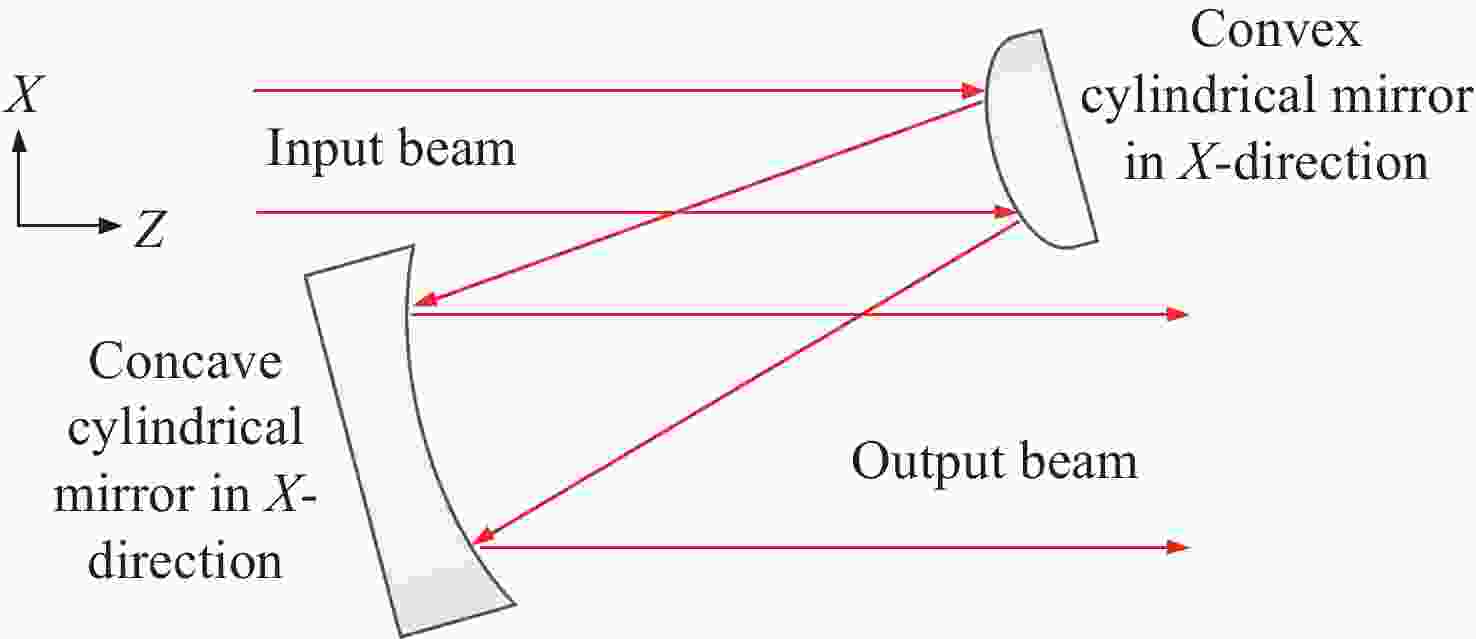
-
摘要:
针对高能激光器出光过程中出现的大量离焦和0°像散低阶像差现象,提出了基于哈特曼波前传感器和二维整形光路的
XY 离焦像差校正方法。首先,通过对Zernike多项式的离焦项和0°像散项进行线性组合得到XY 离焦像差的表达式,该XY 离焦像差系数的大小可直接表征X 离焦和Y 离焦的波前PV值。同时,通过微调高能激光器中二维整形光路中的镜子间距,可实现激光器输出光束XY 离焦波面的补偿。因此,首先利用哈特曼波前传感器提取出光束的XY 离焦像差系数大小,而后再根据XY 离焦像差系数的大小实时闭环微调二维整形光路中的镜子间距,从而实现XY 离焦像差的校正,改善输出光束的光束质量。实验结果表明,该方法可有效地将高能激光器输出光束XY 离焦量的PV值由5.2 μm和1.1 μm校正到0.5 μm以下,相应的光束质量β 因子由3.1降到1.8,光束质量得到明显改善。Abstract:A method for correcting
XY defocus aberrations, based on Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor and two-dimensional beam-shaping light path, was presented due to the large percentage of defocus and 0° astigmatism aberrations with large PV values in high-energy laser beam. The first step is to derive an expression forXY defocus aberrations by linearly combining the defocus and 0° astigmatism terms of Zernike polynomials. The coefficients directly characterize the wavefront peak-to-valley (PV) values ofX andY defocus. At the same time, compensation forXY defocus wavefronts of the laser beam can be achieved by fine-tuning the mirror spacing in the two-dimensional shaping optics of the high-energy laser. Therefore, the Hartmann wavefront sensor is used to extract the coefficients ofXY defocus aberrations from the laser beam. The computer dynamically adjusts the mirror spacing in the two-dimensional shaping optics based on these coefficient values to correctXY defocus aberrations and improve the beam quality of the output laser beam. The results of the experiment showcase a significant decrease in PV value ofXY defocus aberrations from 5.2 μm and 1.1 μm to less than 0.5 μm, as well as a decrease inβ factor from 3.1 to 1.8, resulting in substantial improvement in beam quality.-
Key words:
- high energy laser /
- beam quality /
- aberration correction /
- beam shaping /
- matrix optics
-
图 6 整形光路中凸柱面镜和凹柱面镜相对共焦间距不同偏移量时的XY离焦量变化曲线。(a)X方向整形光路;(b)Y方向整形光路
Figure 6. The XY defocus variation curves with the relatively different deviation of the co-focal distance of the convex cylindrical mirror and the concave cylindrical mirror in the (a) X-direction and (b) Y-direction shaping optical path
-
[1] 王艳茹, 王建忠, 冉铮惠, 等. 高能激光光束质量 β因子的影响因素分析[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(2):353-360. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0137WANG Y R, WANG J ZH, RAN ZH H, et al. Analysis of effects on the beam quality β factor of high power laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(2): 353-360. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0137 [2] 刘泽金, 周朴, 许晓军. 高能激光光束质量通用评价标准的探讨[J]. 中国激光,2009,36(4):773-778. doi: 10.3788/CJL20093604.0773LIU Z J, ZHOU P, XU X J. Study on universal standard for evaluating high energy beam quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009, 36(4): 773-778. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL20093604.0773 [3] 王启晗, 姚强强, 冯驰. 热透镜焦距和球差影响光束质量的分析模型[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2018,55(8):081402.WANG Q H, YAO Q Q, FENG CH. Analytical model for thermal focal length and spherical aberration on beam quality[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(8): 081402. (in Chinese). [4] 牛志峰, 郭建增, 周小红. 变形镜受热变形引起的波前畸变仿真及补偿[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2015,27(1):011010. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20152701.11010NIU ZH F, GUO J Z, ZHOU X H. Simulation and compensation of wavefront aberration caused by deformable mirror thermal deformation[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2015, 27(1): 011010. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20152701.11010 [5] 胡小川, 彭家琪, 张彬. 变形镜热形变及其对光束质量的影响分析[J]. 中国激光,2015,42(1):0102003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0102003HU X CH, PENG J Q, ZHANG B. Thermal distortion of deformable mirror and its influence on beam quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(1): 0102003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0102003 [6] RODDIER F. Curvature sensing and compensation: a new concept in adaptive optics[J]. Applied Optics, 1988, 27(7): 1223-1225. doi: 10.1364/AO.27.001223 [7] JEONG T M, KO D K, LEE J. Method of reconstructing wavefront aberrations from the intensity measurement[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(24): 3507-3509. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.003507 [8] 潘国涛, 闫钰锋, 于信, 等. 矩形大口径激光光束质量评价光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):306-317.PAN G T, YAN Y F, YU X, et al. Design of optical system for quality evaluation of a large rectangular aperture laser beam[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 306-317. (in Chinese). [9] LAI B H, DONG L ZH, CHEN SH Q, et al. Hybrid adaptive optics system for a solid-state zigzag master oscillator power amplifier laser system[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(9): 091402. doi: 10.3788/COL201614.091402 [10] YU X, DONG L ZH, LAI B H, et al. Automatic low-order aberration correction based on geometrical optics for slab lasers[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(6): 1730-1739. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.001730 [11] 余江川, 田博宇, 钟哲强, 等. 大遮拦比薄管激光环域像差校正方法[J]. 中国激光,2020,47(9):0905001. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0905001YU J CH, TIAN B Y, ZHONG ZH Q, et al. Method for annular aberration correction of large-aperture thin-wall tube lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(9): 0905001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0905001 [12] 李国会, 杜应磊, 徐宏来, 等. 双变形镜对Yb: YAG板条激光器光束质量校正技术[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(8):20210800.LI G H, DU Y L, XU H L, et al. Correction of beam quality correction of Yb: YAG laser with double deformable mirrors[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(8): 20210800. (in Chinese). [13] 赵宪宇, 薛栋林, 程强. 哈特曼原理子口径斜率扫描检测及误差研究[J]. 红外与激光工程,2019,48(8):0813003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0813003ZHAO X Y, XUE D L, CHENG Q. Research on Hartmann principle based on sub-aperture slope scanning detection and error[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(8): 0813003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0813003 [14] 朱沁雨, 陈梅蕊, 陆焕钧, 等. 微透镜阵列衍射效应对夏克—哈特曼波前探测器的影响分析[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):94-102. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0176ZHU Q Y, CHEN M R, LU H J, et al. Analysis of influence of diffraction effect of microlens array on Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 94-102. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0176 [15] YANG P, LIU Y, YANG W. Adaptive mode optimization of a continuous-wave solid-state laser using an intracavity piezoelectric deformable mirror[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 278(2): 377-381. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2007.06.043 [16] 王海铭, 权佳宁, 葛宝臻. 适用于近地面成像的自适应光学系统研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(4):843-852. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0230WANG H M, QUAN J N, GE B ZH. An adaptive optics system suitable for near-ground imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(4): 843-852. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0230 [17] YANG P, NING Y, LEI X, et al. Enhancement of the beam quality of non-uniform output slab laser amplifier with a 39-actuator rectangular piezoelectric deformable mirror[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(7): 7121-7130. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.007121 [18] 张天宇, 王钢, 张熙, 等. 基于焦面复制方法的自适应光学系统静态像差校正技术[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(3):545-551. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0182ZHANG T Y, WANG G, ZHANG X, et al. Staticaberration correction technique for adaptive optics system based on focal-plane copy approach[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(3): 545-551. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0182 [19] LIU G L, YANG H F, RAO CH H, et al. Experimental verification of combinational-deformable-mirror for phase correction[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2007, 5(10): 559-562. [20] 张雨东, 饶长辉, 李新阳. 自适应光学及激光操控[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2016: 17-26.ZHANG Y D, RAO CH H, LI X Y. Adaptive Optics and Laser Manipulation[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2016: 17-26. (in Chinese) [21] MAHAJAN V N. Zernike circle polynomials and optical aberrations of systems with circular pupils[J]. Applied Optics, 1994, 33(34): 8121-8124. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.008121 [22] 郭建增, 刘铁根, 王振华, 等. 基于整形光路的低阶像差校正方法[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2012,24(8):1797-1800. doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122408.1797GUO J Z, LIU T G, WANG ZH H, et al. Method for lower order aberration correction based on beam shaping[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2012, 24(8): 1797-1800. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20122408.1797 [23] 石顺祥, 张海兴, 刘劲松. 物理光学与应用光学[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2000: 380-390.SHI SH X, ZHANG H X, LIU J S. Physical Optics and Applied Optics[M]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Electronic Science and Technology Press, 2000: 380-3906. (in Chinese) [24] 卢亚雄, 吕百达. 矩阵光学[M]. 大连: 大连理工大学出版社, 1989: 48-82.LU Y X, LV B D. Matrix Optics[M]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 2000: 380-3906. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: