-
摘要:
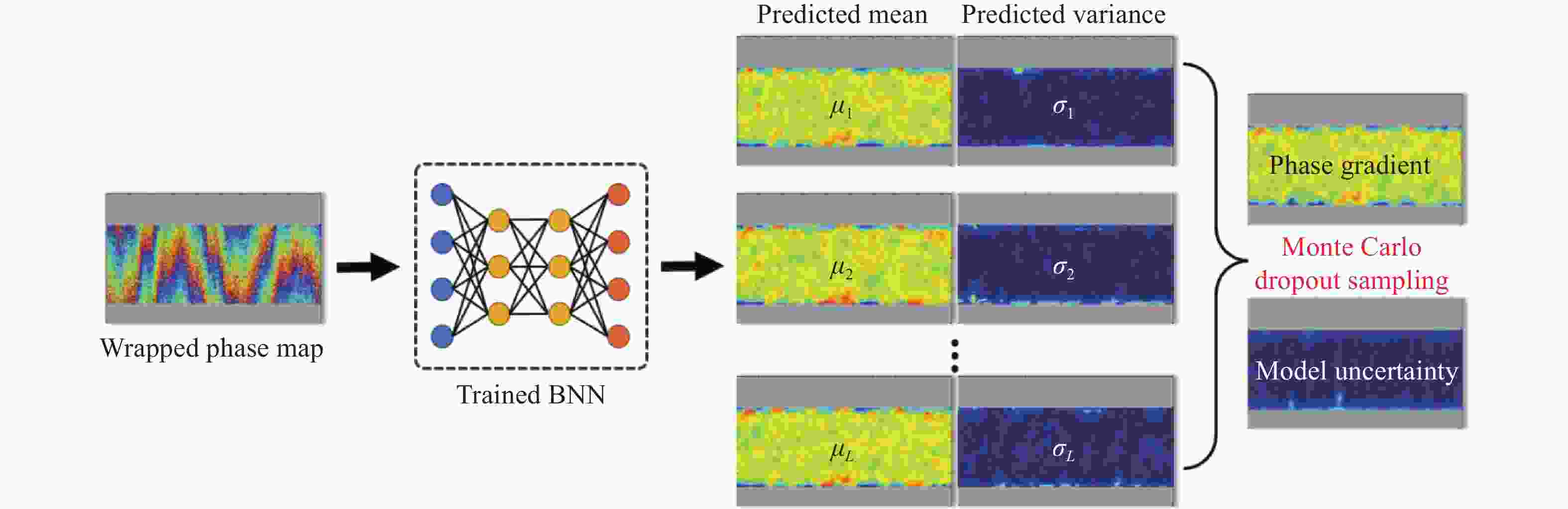
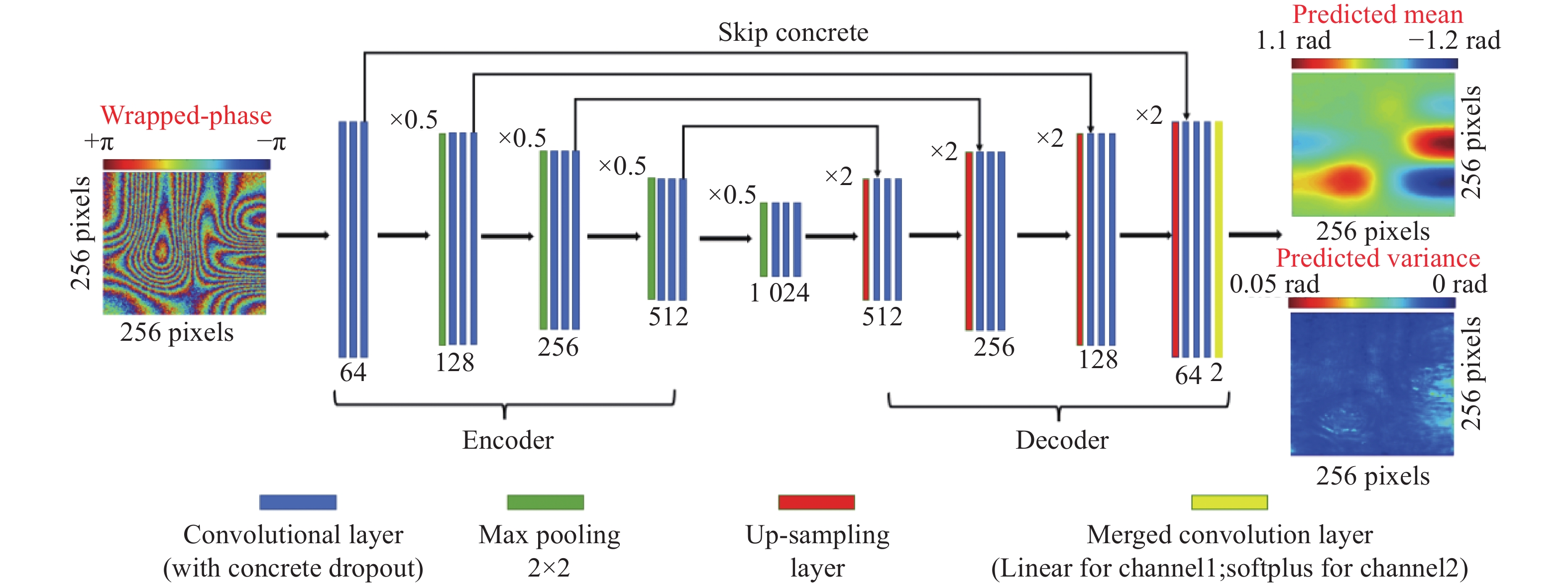
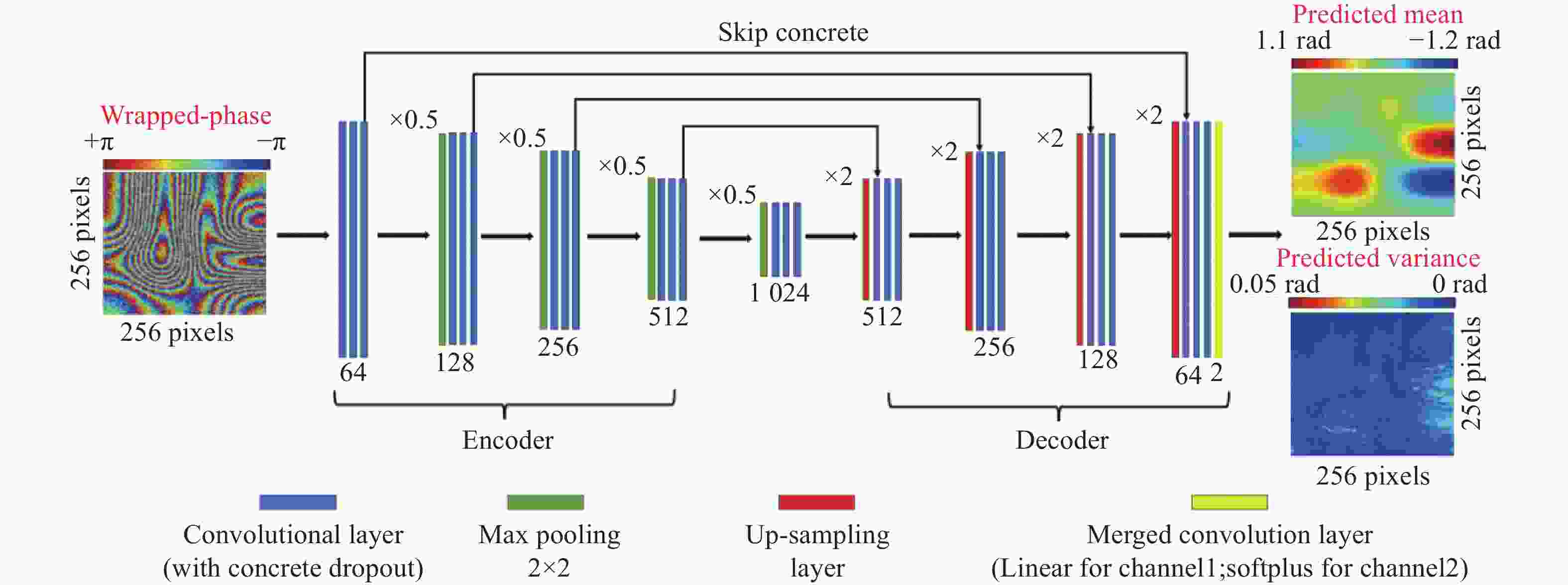
应变重构是相衬光学相干层析力学性能表征中的关键步骤,其需要准确计算出差分包裹相位的梯度分布。为了能够解决强噪声干扰下的相位梯度重构信噪比低的难题,提出了一种基于贝叶斯神经网络的相位梯度计算方法。首先,通过计算机模拟不同散斑噪声等级下的包裹相位图,并生成相应的理想相位梯度,以构建网络的训练集。其次,基于网络训练集采用贝叶斯推断理论学习强噪声环境下的包裹相位与相位梯度的“端到端”映射关系。最后,将相衬光学相干层析测量的差分包裹相位结果送入贝叶斯神经网络进行处理,实现高信噪比相位梯度预测。此外,通过借助贝叶斯神经网络的统计特性,以模型不确定度来定量评估相位梯度预测结果的可靠性。通过数值实验和三点弯曲力学加载实验对比分析了本文方法和主流矢量方法的性能。实验结果表明:在噪声较小的条件下,本文方法重构的相位梯度信噪比可提升8%;在噪声较强条件下,本文方法能成功恢复因相位条纹难以分辨而无法计算的相位梯度。此外,模型不确定度能够定量分析网络的相位梯度预测误差。可以预见,在样品形变复杂且先验信息未知的条件下,本工作为相衬光学相干层析提供了一种有效的应变重构方法,从而能实现高质量和高可靠的内部力学性能表征。
Abstract:Strain reconstruction is a vital component in the characterization of mechanical properties of phase-contrast optical coherence tomography (PC-OCT). It requires an accurate calculation for gradient distributions on the differential wrapped phase map. In order to address the challenge of low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in phase gradient calculation under severe noise interference, a Bayesian-neural-network-based phase gradient calculation is presented. Initially, wrapped phase maps with varying levels of speckle noise and their corresponding ideal phase gradient distributions are generated through a computer simulation. These wrapped phase maps and phase gradient distributions serve as the training datasets. Subsequently, the network learns the “end-to-end” relationship between the wrapped phase maps and phase gradient distributions in a noisy environment by utilizing a Bayesian inference theory. Finally, the wrapped phase measured by PC-OCT is processed by Bayesian neural network (BNN), and the high-quality distribution of phase gradients is accurately predicted by inputting the measured wrapped phase-difference maps into the network. Additionally, the statistical process introduced by BNN allows for the utilization of model uncertainty in the quantitative assessment of the network predictions’ reliability. Computer simulation and three-point bending mechanical loading experiment compare the performance of the BNN and the popular vector method. The results indicate that the BNN can enhance the SNR of estimated phase gradients by 8% in the presence of low noise levels. Importantly, the BNN successfully recovers the phase gradients that the vector method is unable to calculate due to the unresolved phase fringes in the presence of strong noise. Moreover, the BNN model uncertainty can be used to quantitatively analyze the prediction errors. It is expected that the contribution of this work can offer effective strain estimation for PC-OCT, enabling the internal mechanical property characterization to become high-quality and high-reliability.
-
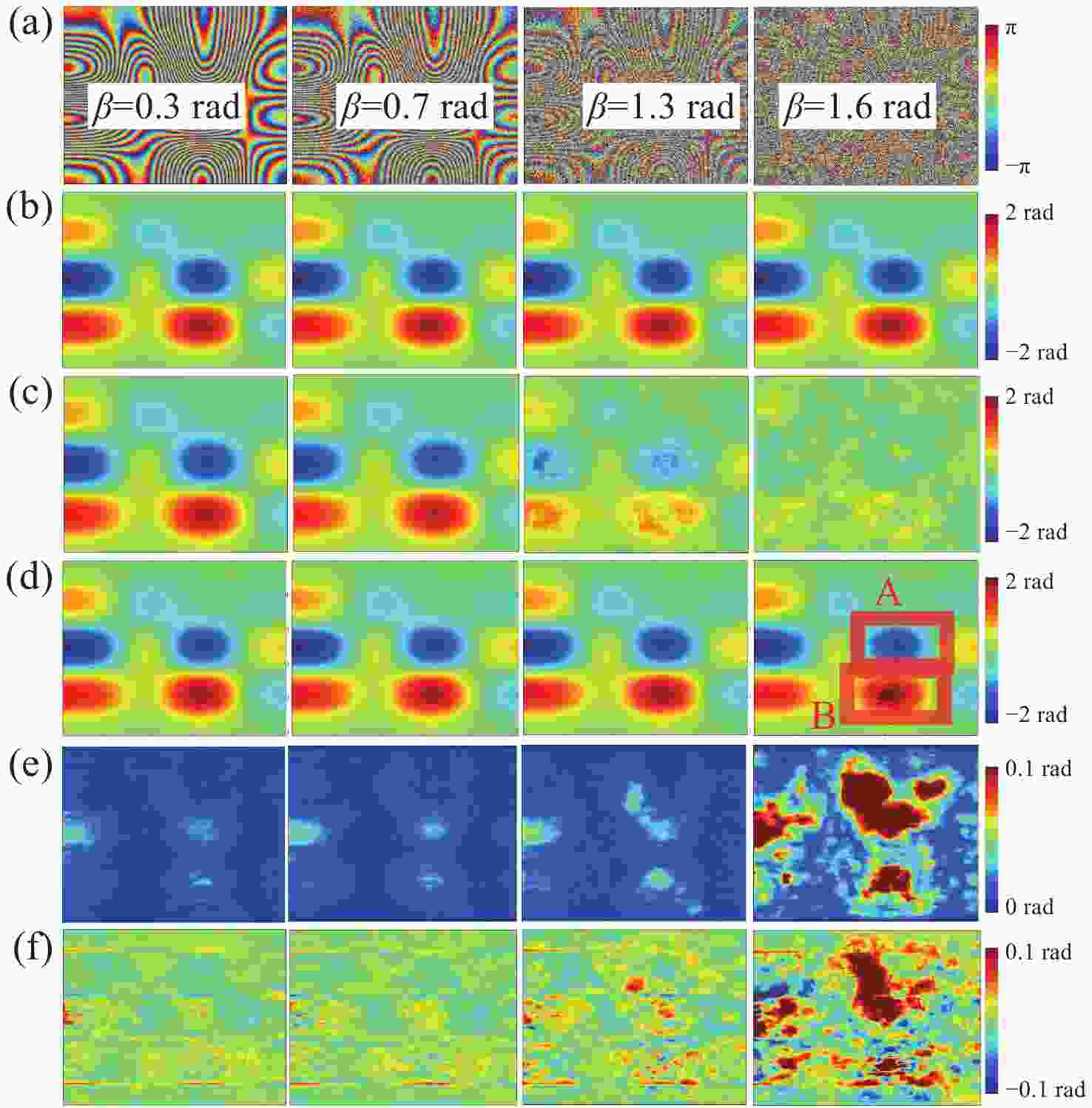
图 4 不同方法估计的相位梯度结果。(a)不同噪声等级的相位图;(b)理论相位梯度结果;(c)矢量法;(d)贝叶斯神经网络;(e)贝叶斯神经网络模型不确定度;(f)网络预测结果的误差分布
Figure 4. Phase gradient estimated using different methods. (a) Phase maps with different noise levels; phase gradient results obtained by (b) theorectical calculation; (c) vector method and (d) Bayesian neural network; (e) BNN model uncertainty; (f) error distributions of phase gradient by using BNN model
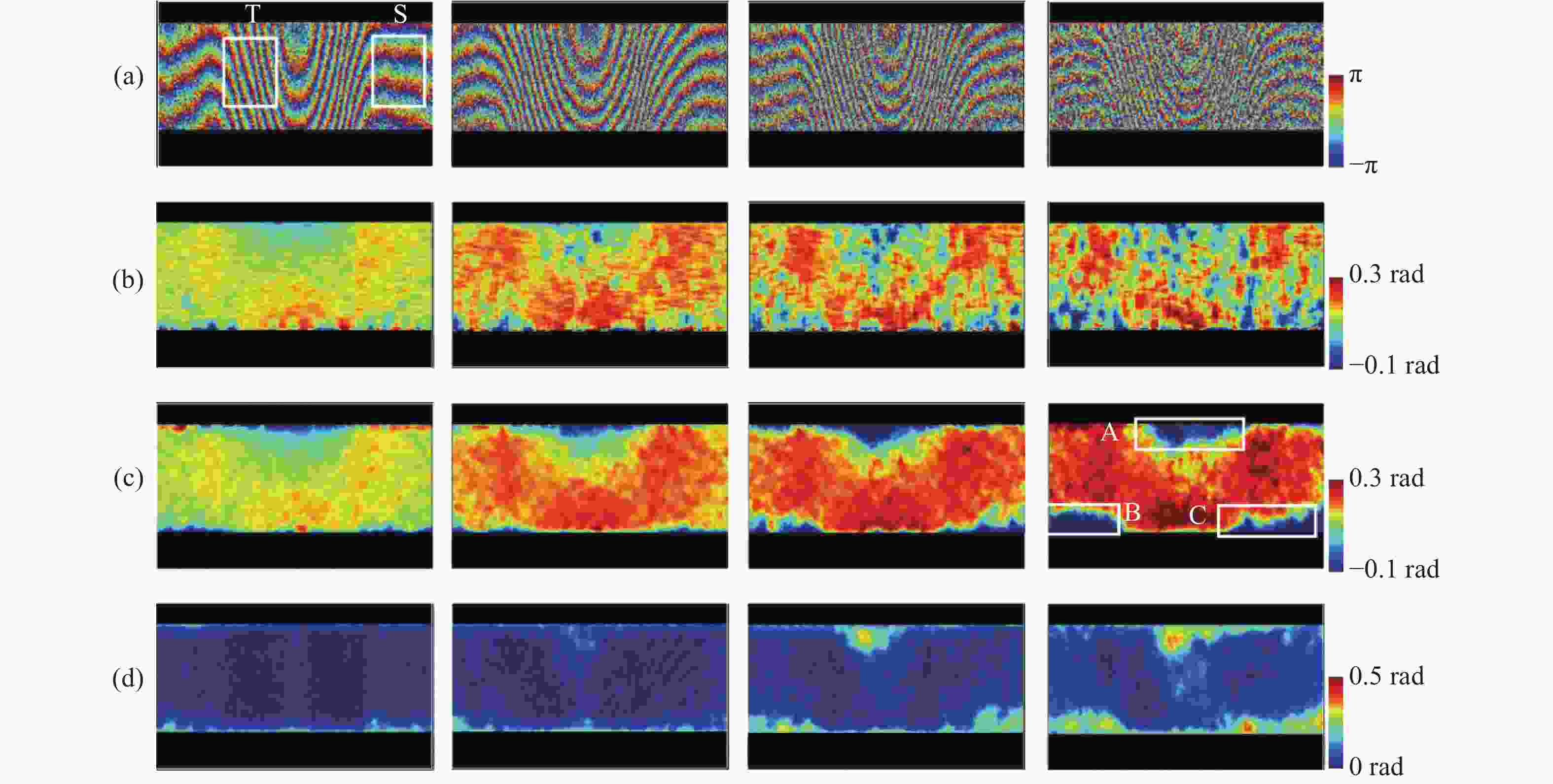
图 7 相位退相关实验结果。(a)-(b) 加载量分别为12 μm和14 μm对应的差分包裹相位;(c)-(d) 贝叶斯网络估计的相位梯度结果;(e)-(f) 贝叶斯网络的模型不确定度
Figure 7. Experimental results of phase decorrelation. (a)-(b) Wrapped phase-difference maps corresponding to the loading 12 μm and 14 μm, respectively; (c)-(d) results of phase gradient estimated using BNN; (e)-(f) BNN model uncertainty
-
[1] 吴哲, 陆冬筱, 李金华. 金纳米星诊疗剂的光热特性及其在光热治疗和光学相干层析成像中的应用研究[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):233-241. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0205WU ZH, LU D X, LI J H. Photothermal properties of gold nanostars therapeutic agent and its application in photothermal therapy and optical coherence tomography[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 233-241. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0205 [2] WANG X D, YUAN X, SHI L P. Optical coherence tomography-in situ and high-speed 3D imaging for laser materials processing[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2022, 11(1): 280. [3] FANG B, ZHONG SH C, ZHANG Q K, et al. Full-range line-field optical coherence tomography for high-accuracy measurements of optical lens[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(9): 7180-7190. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.2978313 [4] 谢胜利, 廖文建, 白玉磊, 等. 相衬光学相干层析在无损检测领域的应用[J]. 广东工业大学学报,2021,38(6):20-28.XIE SH L, LIAO W J, BAI Y L, et al. Phase-contrast optical coherence tomography in applications of non-destructive testing[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology, 2021, 38(6): 20-28. (in Chinese). [5] WU Z, WEI W B, GAO K, et al. Prototype system of noninterferometric phase-contrast computed tomography utilizing medical imaging components[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2021, 129(7): 074901. doi: 10.1063/5.0031392 [6] BAI Y L, CAI SH Y, XIE SH L, et al. Adaptive incremental method for strain estimation in phase-sensitive optical coherence elastography[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(16): 25327-25336. doi: 10.1364/OE.433245 [7] KENNEDY B F, HILLMAN T R, MCLAUGHLIN R A, et al. In vivo dynamic optical coherence elastography using a ring actuator[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(24): 21762-21772. [8] GRIMWOOD A, GARCIA L, BAMBER J, et al. Elastographic contrast generation in optical coherence tomography from a localized shear stress[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2010, 55(18): 5515-5528. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/18/016 [9] KENNEDY B F, KOH S H, MCLAUGHLIN R A, et al. Strain estimation in phase-sensitive optical coherence elastography[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2012, 3(8): 1865-1879. doi: 10.1364/BOE.3.001865 [10] ZAITSEV V Y, MATVEYEV A L, MATVEYEV L A, et al. Optimized phase gradient measurements and phase-amplitude interplay in optical coherence elastography[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2016, 21(11): 116005. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.21.11.116005 [11] MATVEYEV A L, MATVEEV L A, SOVETSKY A A, et al. Vector method for strain estimation in phase-sensitive optical coherence elastography[J]. Laser Physics Letters, 2018, 15(6): 065603. doi: 10.1088/1612-202X/aab5e9 [12] 朱新军, 赵浩淼, 王红一, 等. 基于轻型自限制注意力的结构光相位及深度估计混合网络[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):118-127. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0066ZHU X J, ZHAO H M, WANG H Y, et al. A hybrid network based on light self-limited attention for structured light phase and depth estimation[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 118-127. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0066 [13] GONTARZ M, DUTTA V, KUJAWIŃSKA M, et al. Phase unwrapping using deep learning in holographic tomography[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(12): 18964-18992. doi: 10.1364/OE.486984 [14] DE LA TORRE-IBARRA M H, RUIZ P D, HUNTLEY J M. Double-shot depth-resolved displacement field measurement using phase-contrast spectral optical coherence tomography[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(21): 9643-9656. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.009643 [15] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [16] 刘泽隆, 李茂月, 卢新元, 等. 高动态范围条纹结构光在机检测技术及应用进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):1-18.LIU Z L, LI M Y, LU X Y, et al. On-machine detection technology and application progress of high dynamic range fringe structured light[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 1-18. (in Chinese). [17] FENG SH J, ZUO CH, HU Y, et al. Deep-learning-based fringe-pattern analysis with uncertainty estimation[J]. Optica, 2021, 8(12): 1507-1510. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.434311 [18] LYU Z L, BAI Y L, HE ZH SH, et al. Super-resolution reconstruction of speckle phase in depth-resolved wavelength scanning interference using the total least-squares analysis[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2019, 36(5): 869-876. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.36.000869 [19] CHAKRABORTY S, GHOSH M. Applications of Bayesian neural networks in prostate cancer study[J]. Handbook of Statistics, 2012, 28: 241-262. [20] JOSPIN L V, LAGA H, BOUSSAID F, et al. Hands-on Bayesian neural networks-a tutorial for deep learning users[J]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2022, 17(2): 29-48. doi: 10.1109/MCI.2022.3155327 [21] LEMAY A, HOEBEL K, BRIDGE C P, et al. Improving the repeatability of deep learning models with Monte Carlo dropout[J]. npj Digital Medicine, 2022, 5(1): 174. doi: 10.1038/s41746-022-00709-3 -





 下载:
下载: