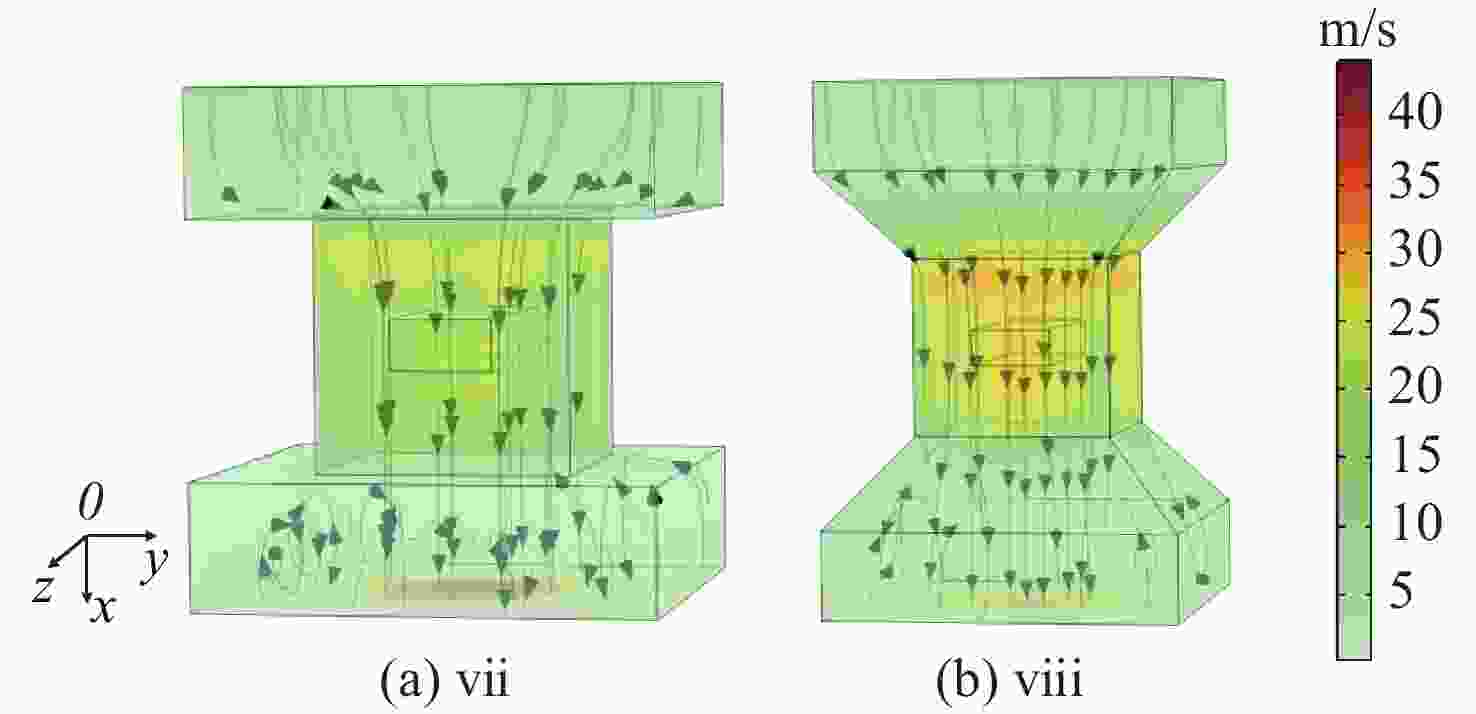
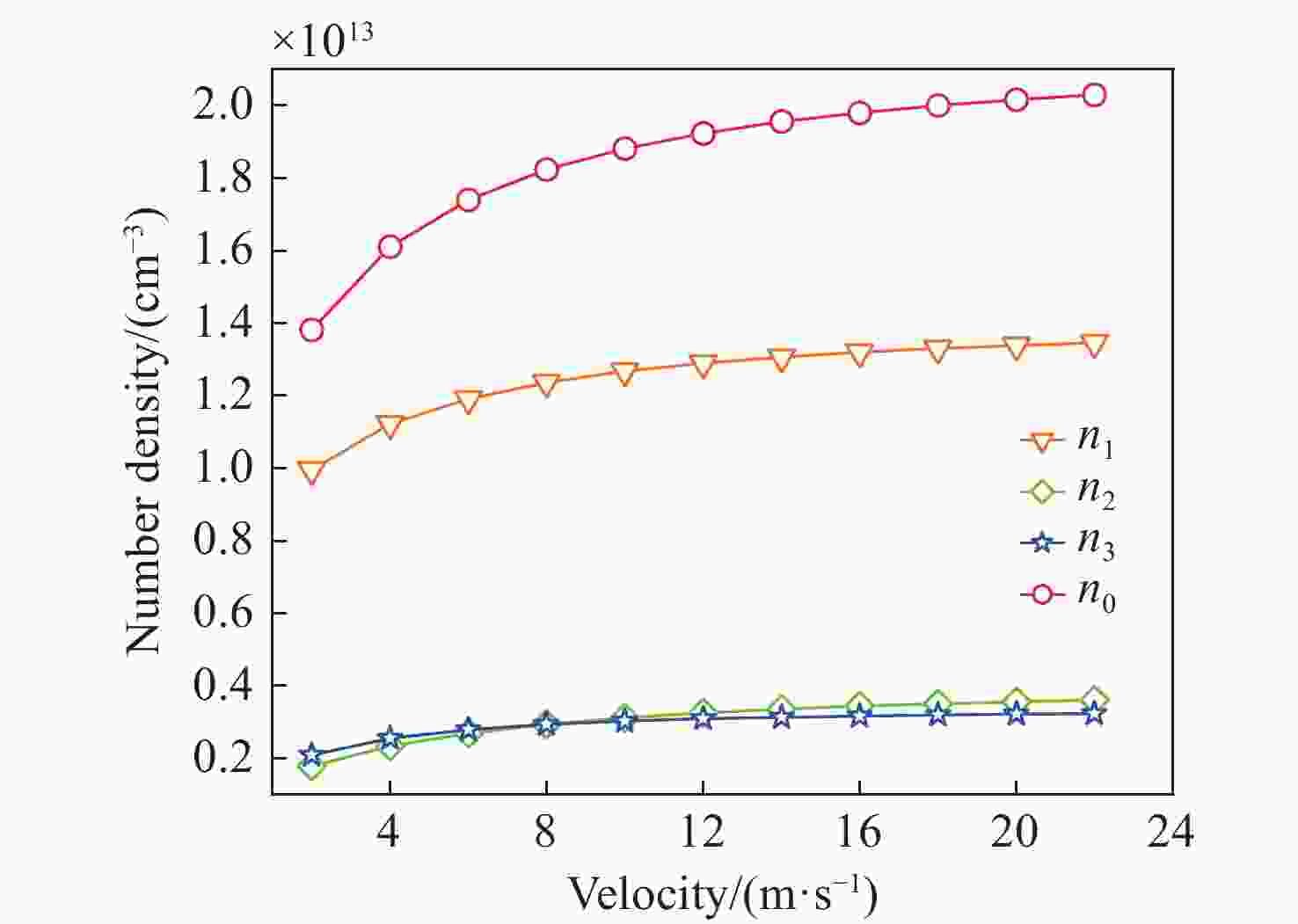
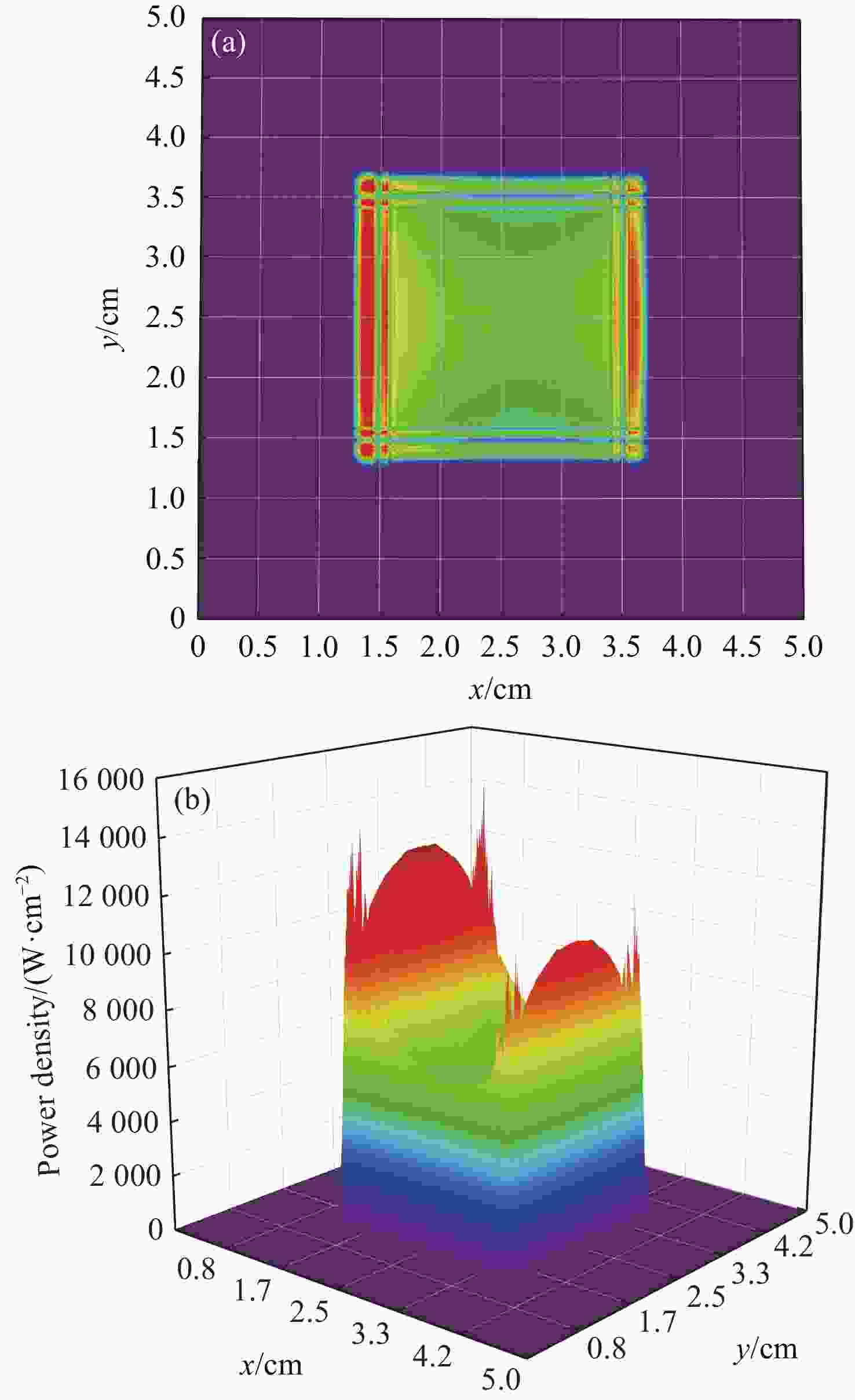
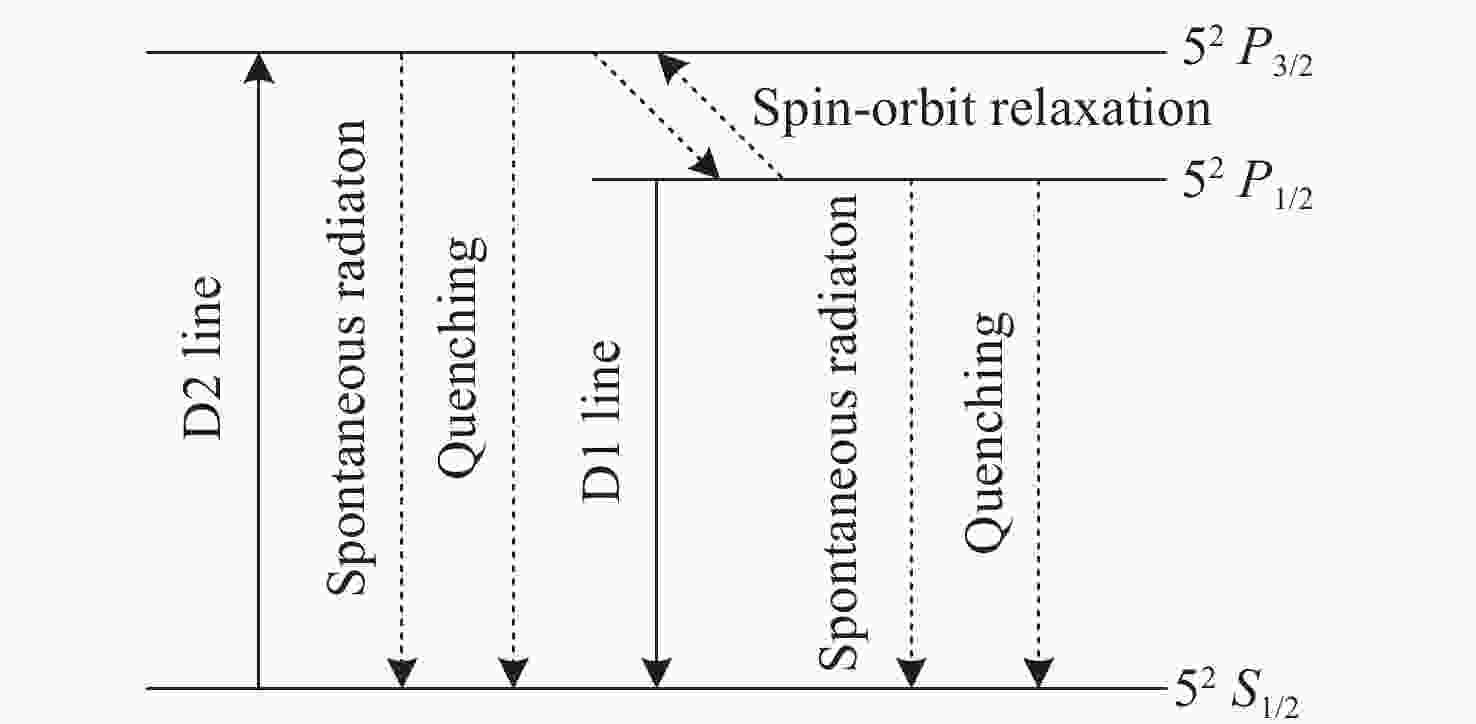
Influence of flow channel structure on characteristics of laser diode pumped flowing-gas rubidium vapor laser
-
摘要:
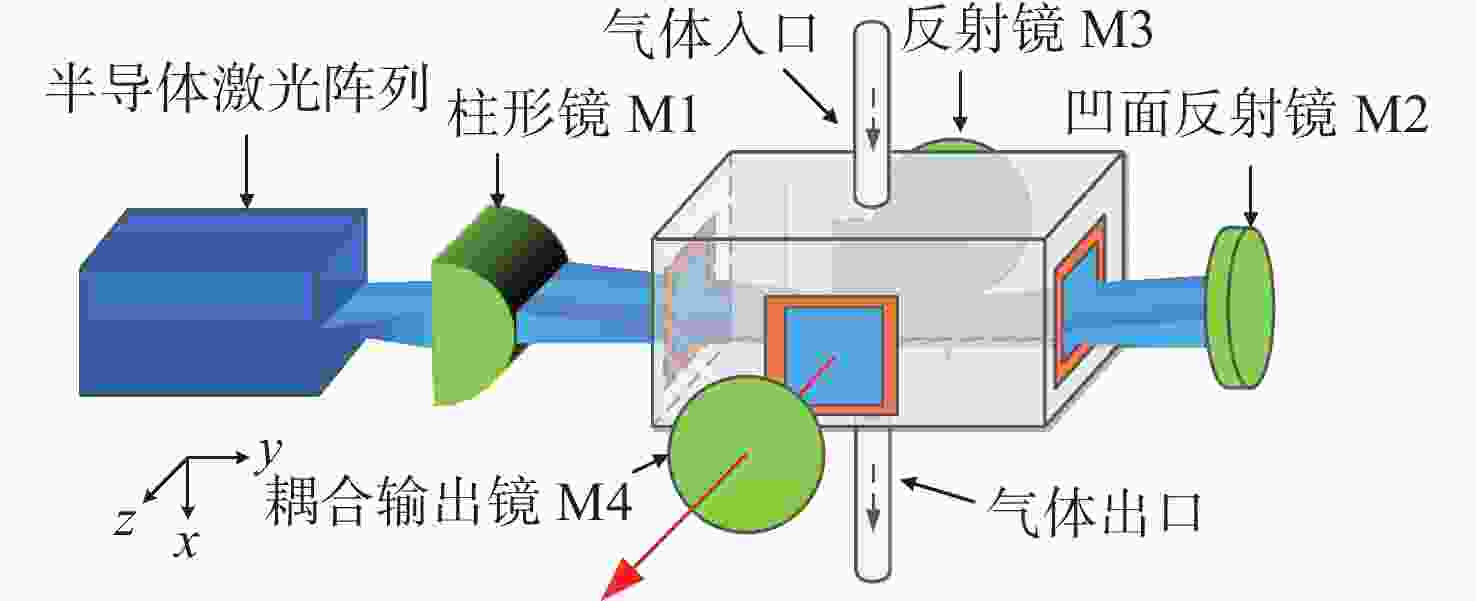
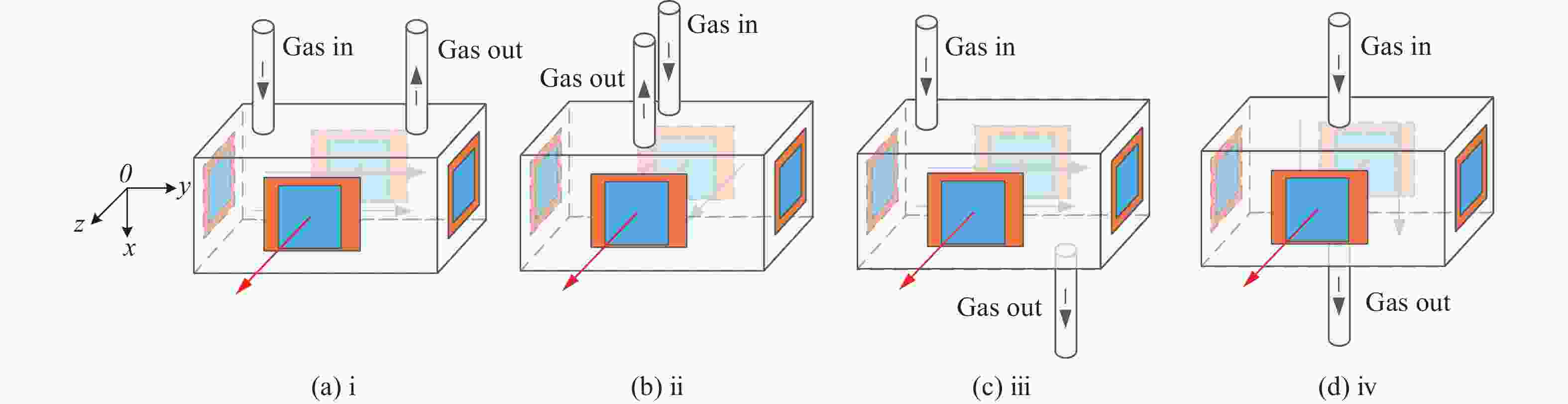
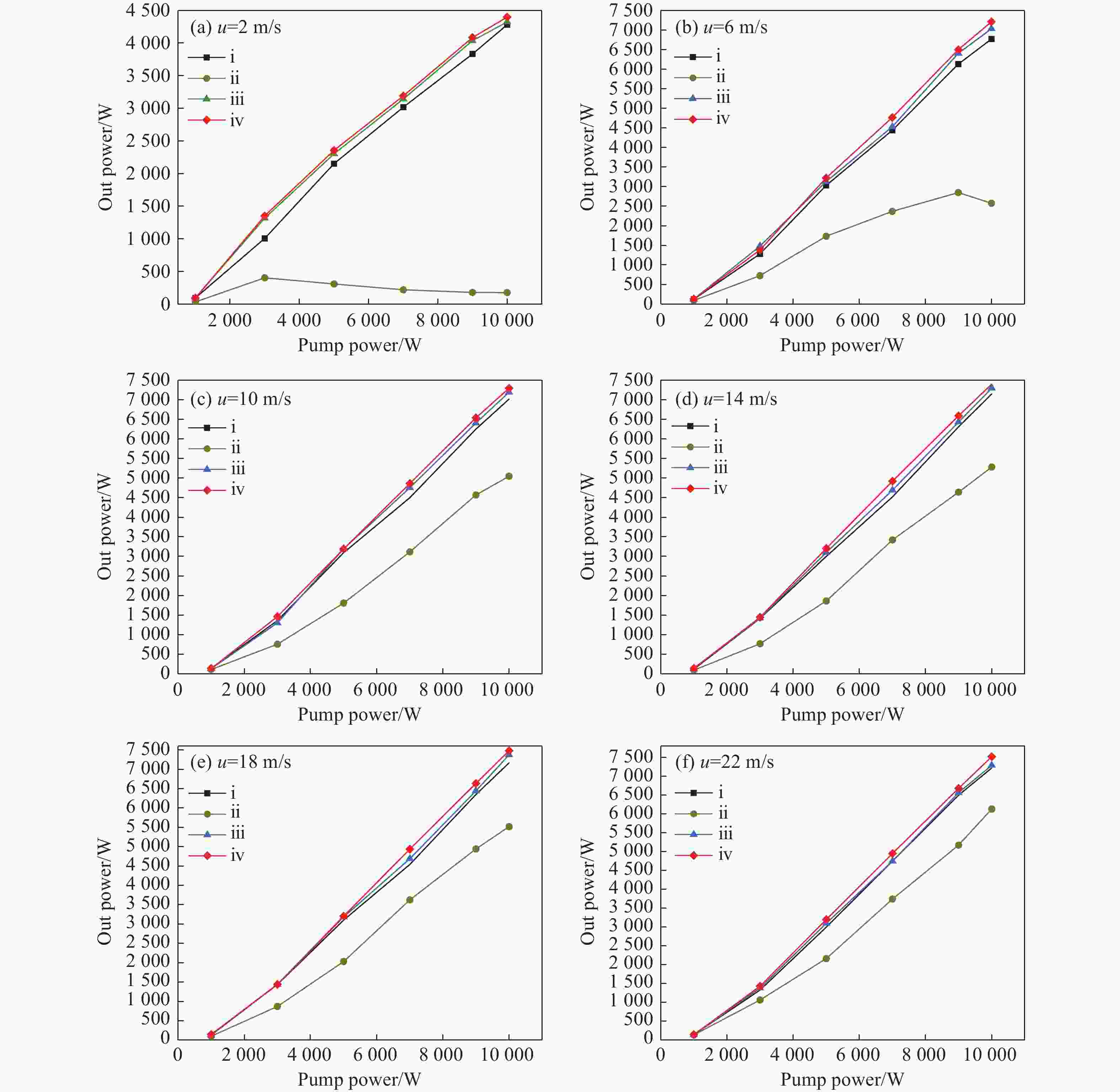
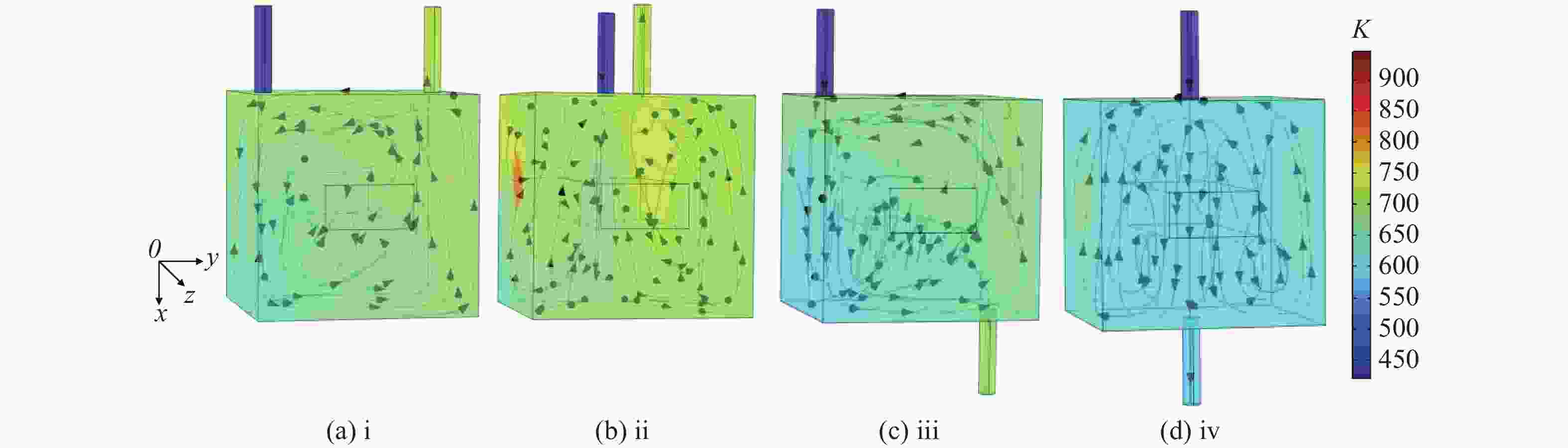
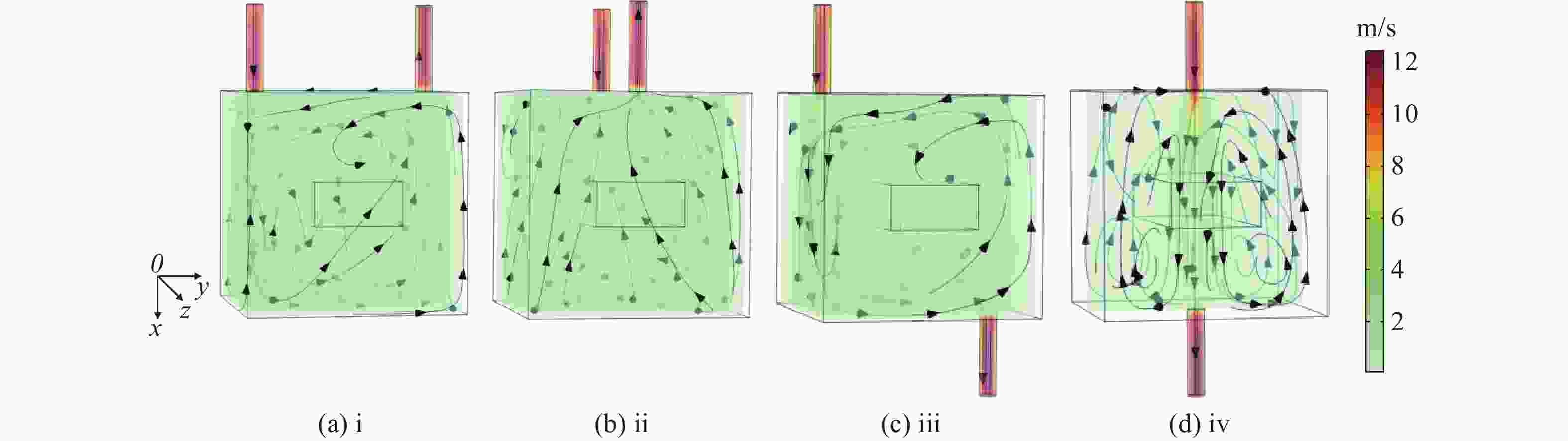
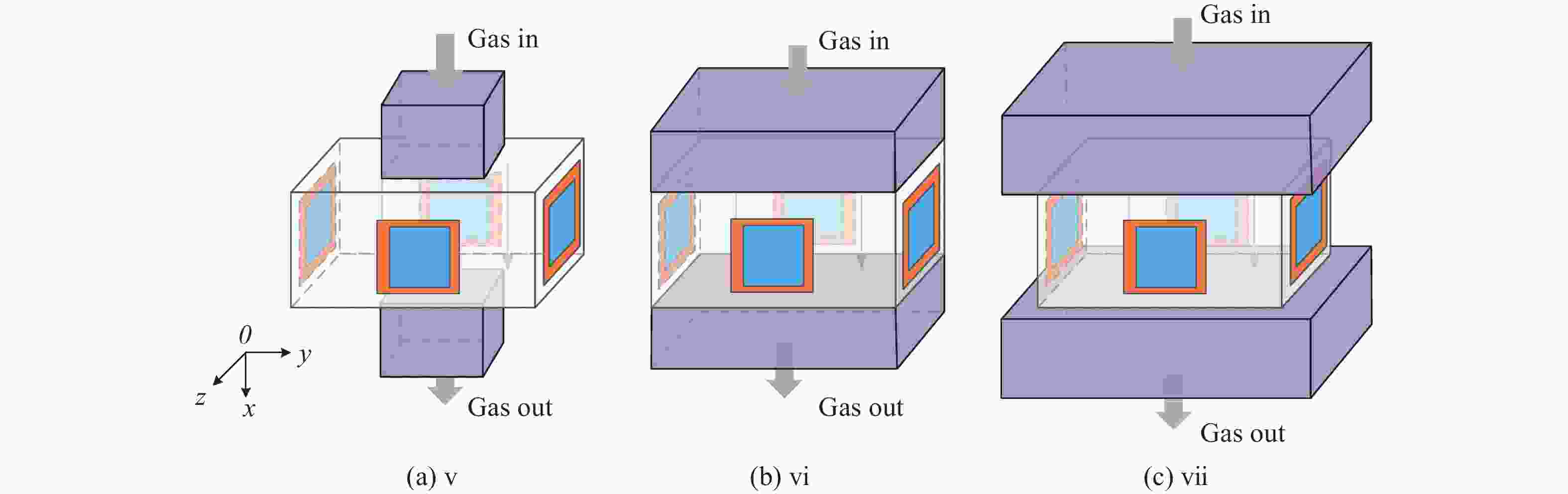
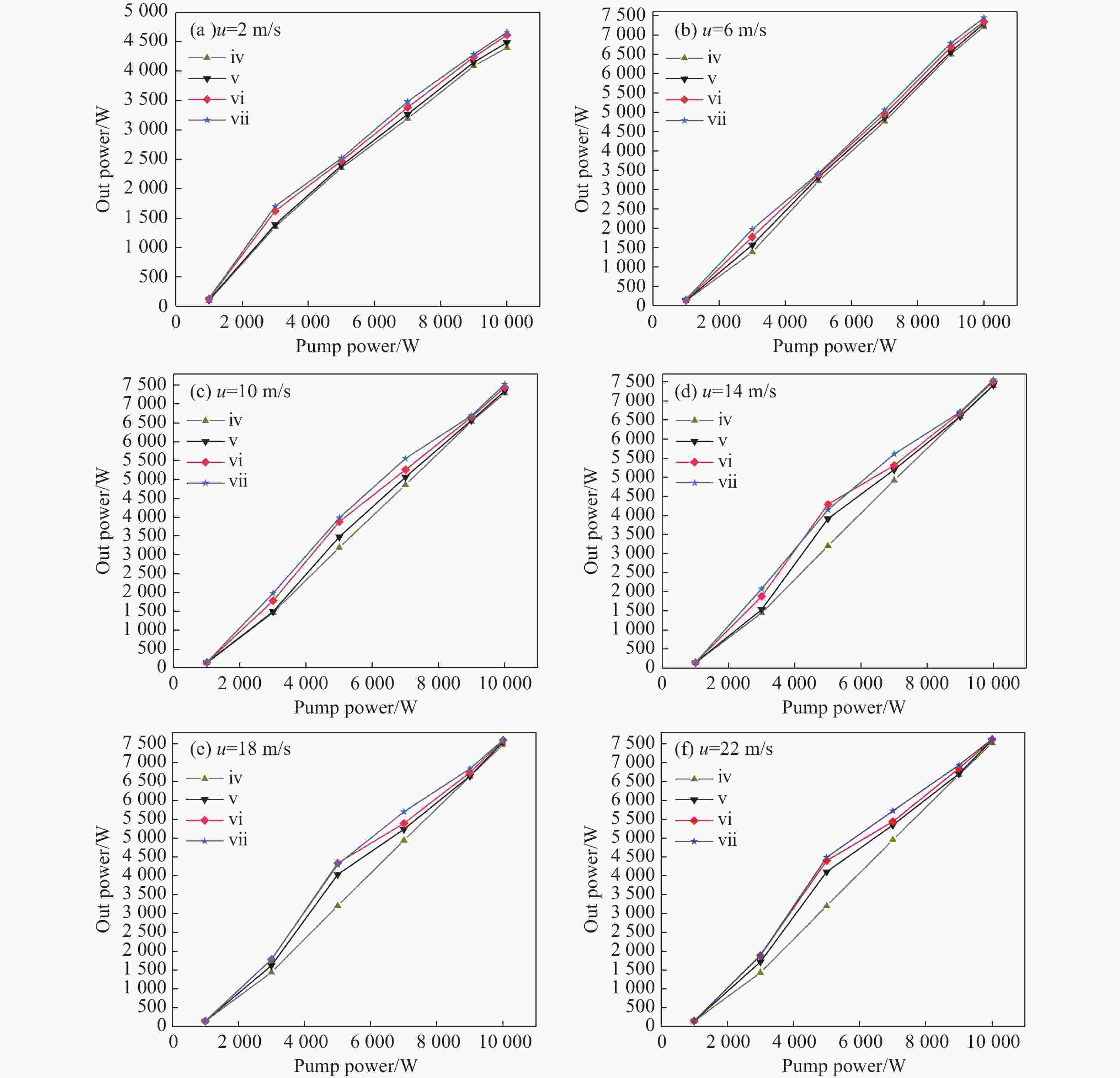
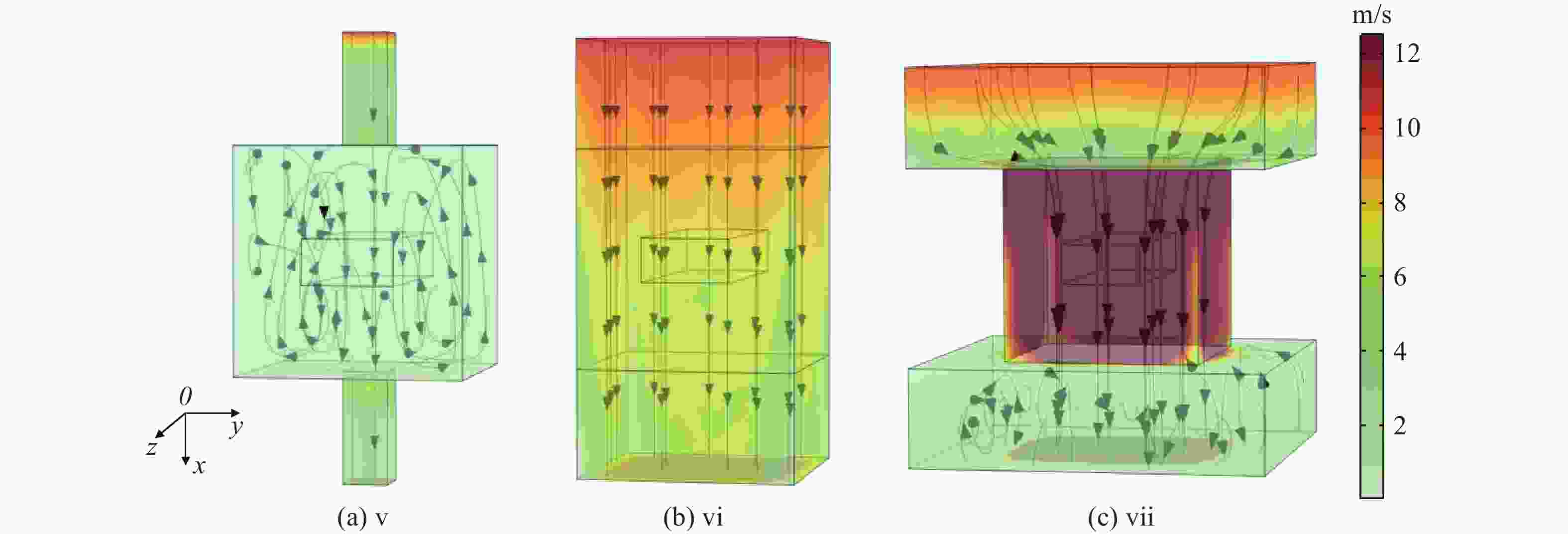
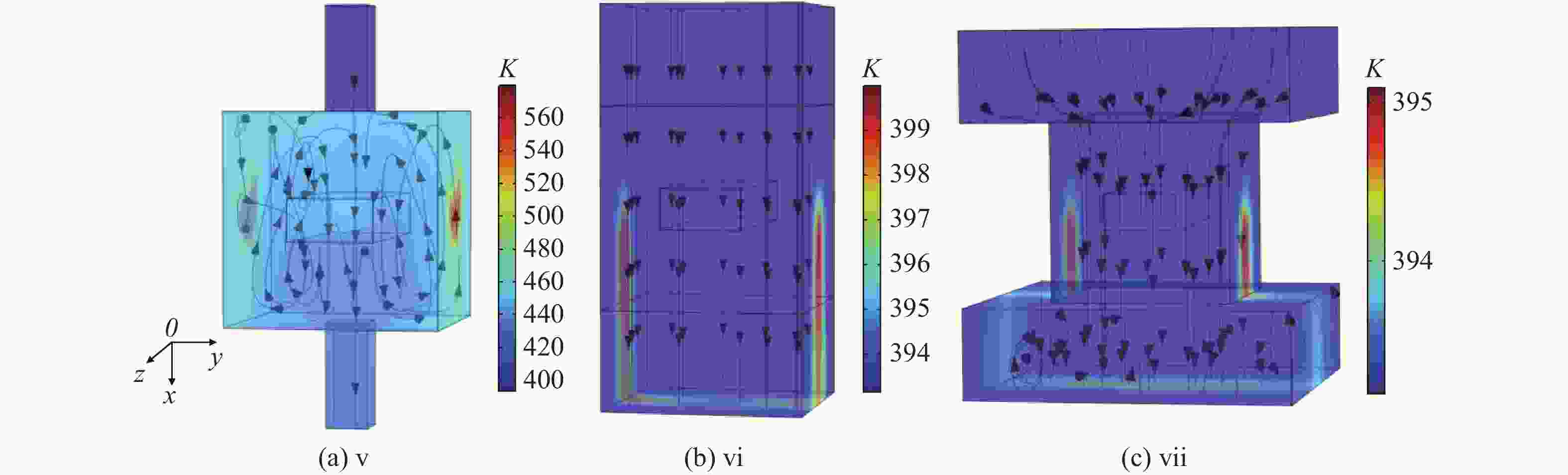
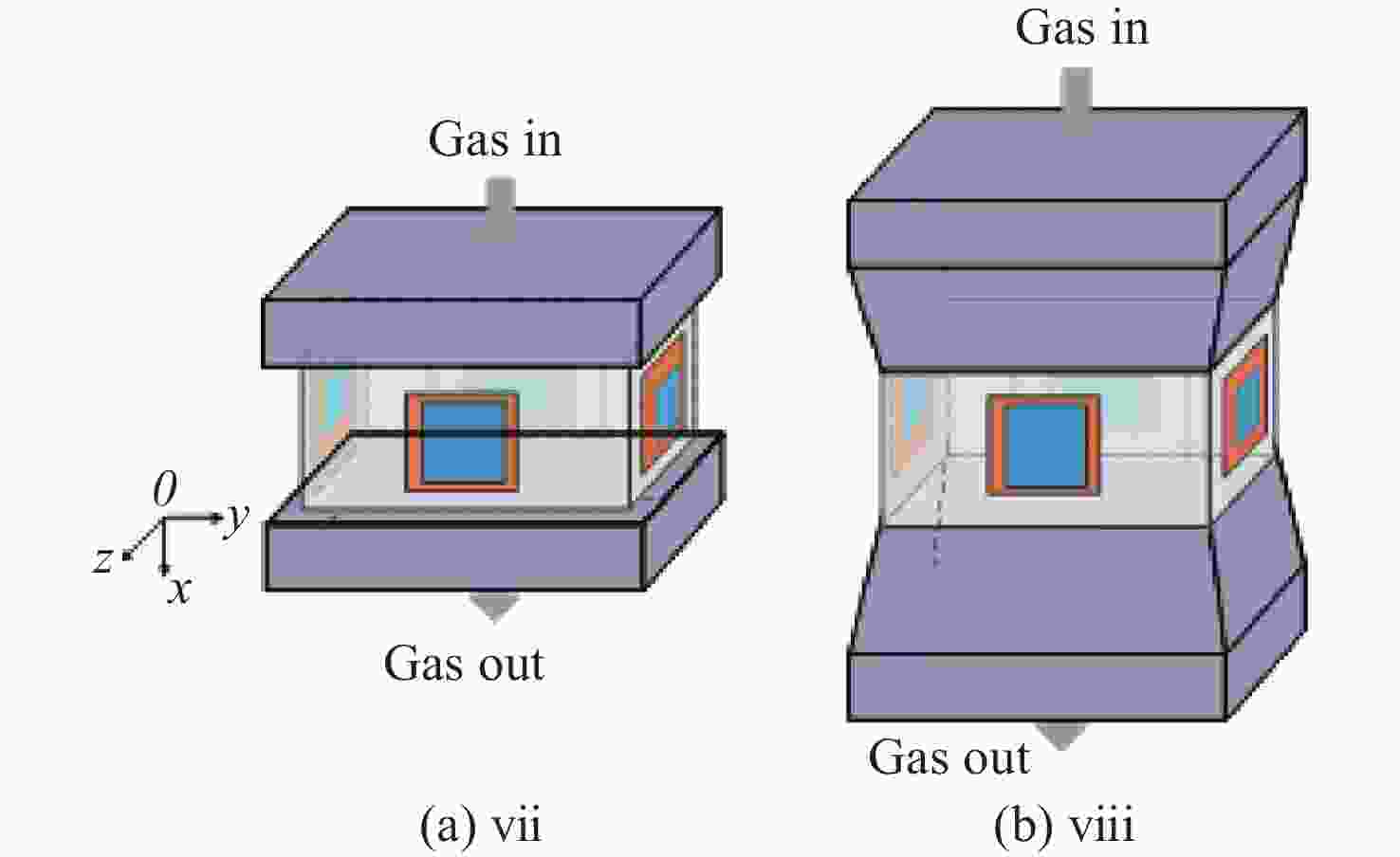
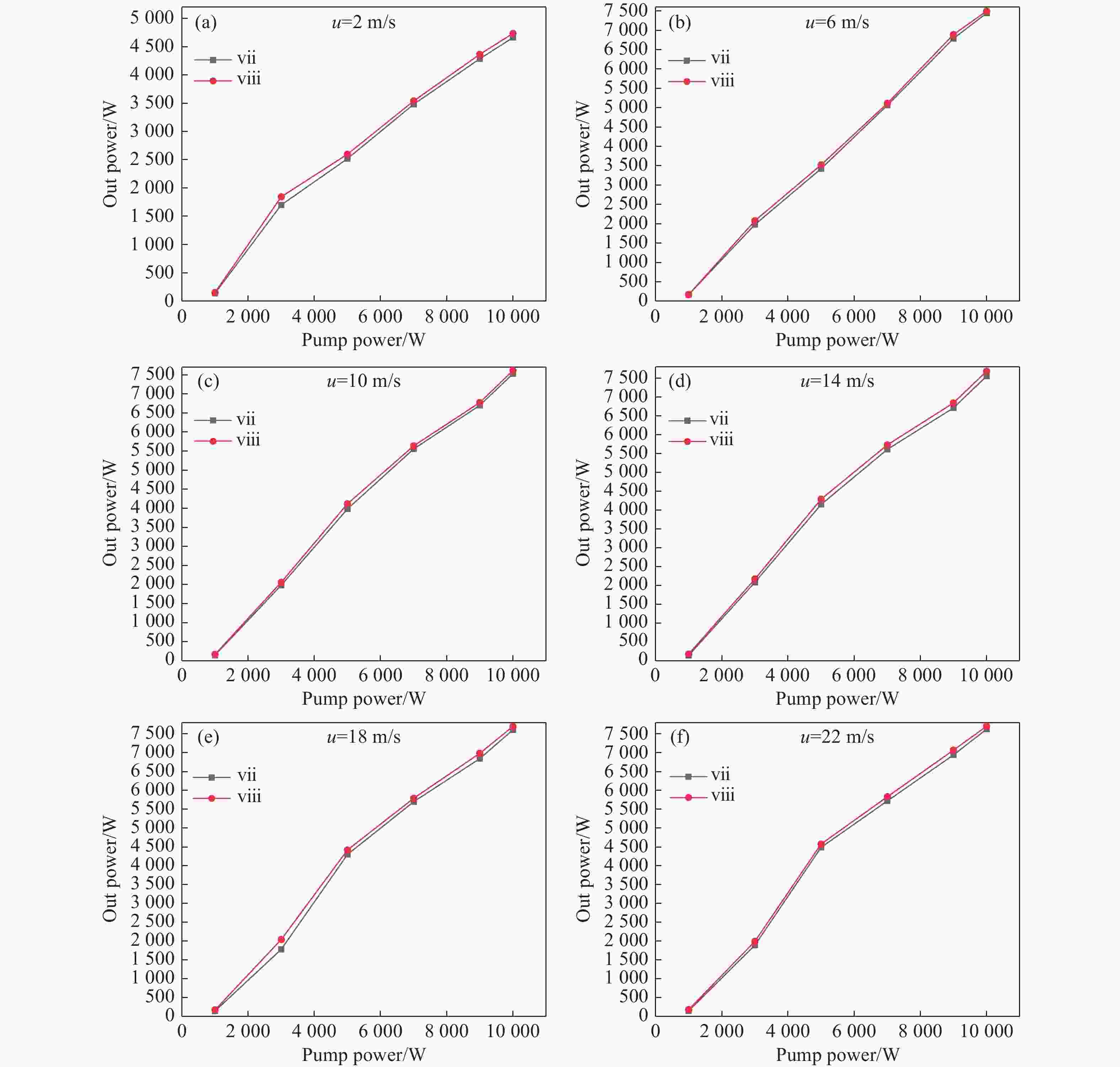
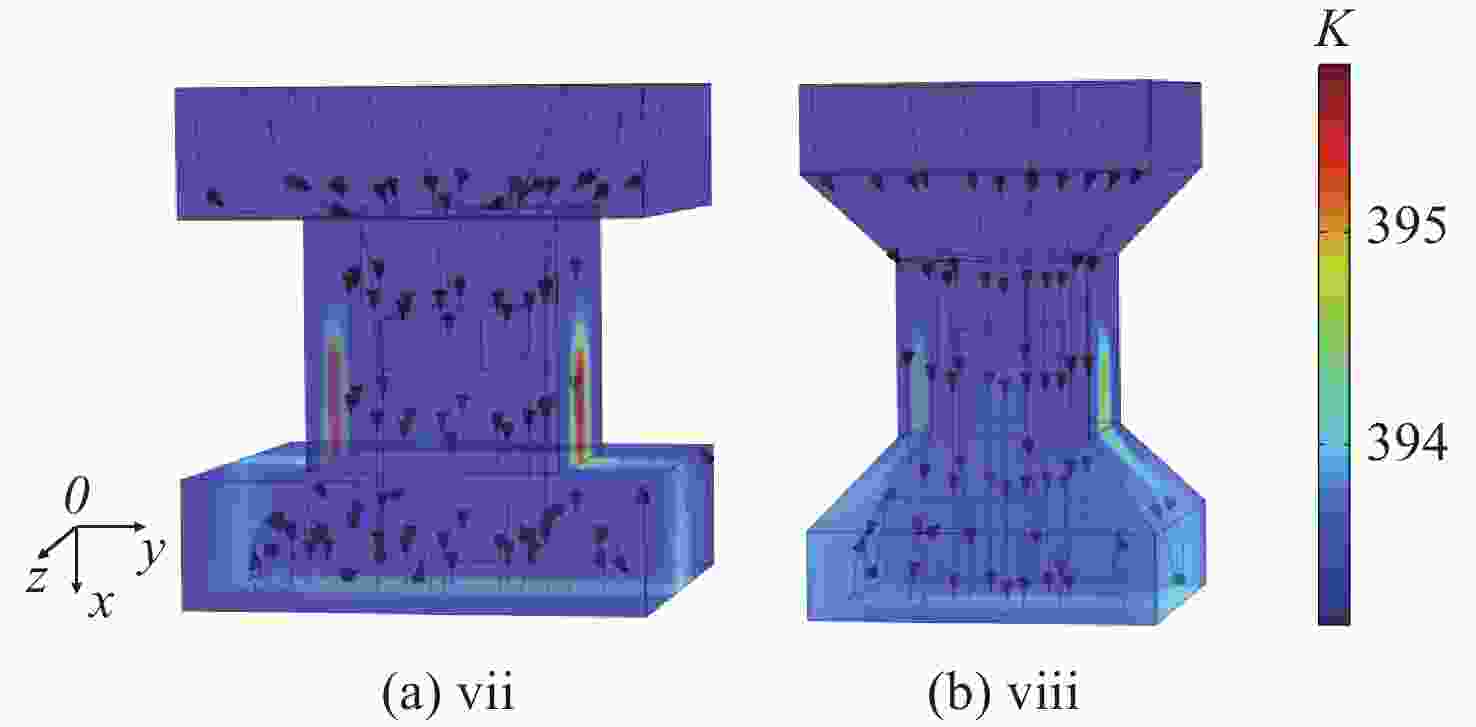
为研究气体流道结构对半导体泵浦流动碱金属蒸气激光器(FDPAL)输出性能的影响,本文结合FDPAL中气体传热、流体力学和激光动力学过程建立了FDPAL理论模型,以侧面泵浦Rb蒸气FDPAL(Rb-FDPAL)为仿真对象,分析气体流动方向、流道横截面积和流道形状等对Rb-FDPAL输出性能的影响。结果表明,采用横流方式,通过提高流道横截面积并将气体流道与蒸气池连接部位设置为砌体结构时,蒸气内涡流得到有效抑制,气体流速增加,蒸气池内热效应更小,Rb-FDPAL的激光输出功率和斜率效率更高,仿真结果与实验相符。
Abstract:In order to study the influence of the gas flow channel structure on the output performance of the flowing-gas diode pumped alkali vapor laser (FDPAL), we established the FDPAL theoretical model based on the gas heat transfer, fluid mechanics, and laser dynamics process in FDPAL using side pumping Rb vapor FDPAL (Rb-FDPAL) as the simulation object. The impacts of the gas flow direction, the cross-sectional area and the shape of the runner on the Rb-FDPAL’s output performance were analyzed. The results show that with the horizontal flow method and by increasing the cross-sectional area of the flow channel and setting a masonry structure as the connection between the gas flow channel and the steam pool, we effectively suppress the vortex in the vapor, increase the gas flow rate, and decrease the thermal effect of the steam pool. Rb-FDPAL's laser output power and slope efficiency are higher, and the simulation results are consistent with the experiment.
-
Key words:
- high power laser /
- gas laser /
- DPAL /
- gas flow
-
表 1 缓冲气体的恒压热容、粘滞系数和导热系数[22]
Table 1. Partial thermophysical properties of buffer gases
缓冲气体 恒压热容
(J·kg−1·K−1)粘滞系数
(Pa·s)导热系数
(W·m−1·K−1)氦 5193.2 3×10−8×T+1×10−5 0.0003×T+0.0897 乙烷 3.9×T+600.3 3×10−8×T+2×10−5 0.0002×T−0.035 表 2 循环流动Rb-FDPAL仿真参数
Table 2. Parameters of gas flowing diode pumped rubidium laser
参数 值 参数 值 泵浦光中心波长(nm) 780 蒸气池增益长度(cm) 5 泵浦光光斑大小(cm×cm) 5×0.2 反射镜M3反射率 99% 泵浦光线宽(GHz) 30 耦合输出镜M4反射率 50% 缓冲气体压强(atm) 1 流动气体初始温度(K) 393.15 表 3 不同流道结构的实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of the experimental results for different flow channel structures
-
[1] KRUPKE W F, BEACH R J, KANZ V K, et al. New class of cw high-power diode-pumped alkali lasers (DPALs) (Plenary Paper)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5448: 7-17. doi: 10.1117/12.547954 [2] KRUPKE W F. Diode pumped alkali lasers (DPALs)—A review (rev1)[J]. Progress in Quantum Electronics, 2012, 36(1): 4-28. doi: 10.1016/j.pquantelec.2011.09.001 [3] 季艳慧, 何洋, 万浩华, 等. 高功率循环流动型半导体泵浦碱金属蒸汽激光器研究进展(特邀)[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(12):20201080. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201080JI Y H, HE Y, WAN H H, et al. Research progress on the high power flowing-gas circulation diode-pumped alkali vapor laser (Invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(12): 20201080. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201080 [4] 陈毅, 孙俊杰, 于晶华, 等. 大能量碟片激光多通放大器腔体设计研究综述[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):996-1009. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0009CHEN Y, SUN J J, YU J H, et al. Review of the cavity-design of high-energy thin-disk laser multi-pass amplifiers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 996-1009. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0009 [5] 张世达, 耿乙迦. 碲化铋倏逝场锁模器件的超快光纤激光器[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(3):433-442. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0216ZHANG SH D, GENG Y J. Ultrafast fiber laser based on bismuth telluride evanescent field mode-locked device[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(3): 433-442. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0216 [6] 徐飞, 潘其坤, 陈飞, 等. 中红外Fe2+: ZnSe激光器研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(3):458-469. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0180XU F, PAN Q K, CHEN F, et al. Development progress of Fe2+: ZnSe lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 458-469. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0180 [7] ZHDANOV B V, EHRENREICH T, KNIZE R J. Highly efficient optically pumped cesium vapor laser[J]. Optics Communications, 2006, 260(2): 696-698. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2005.11.042 [8] BOGACHEV A V, GARANIN S G, DUDOV A M, et al. Diode-pumped caesium vapour laser with closed-cycle laser-active medium circulation[J]. Quantum Electronics, 2012, 42(2): 95-98. doi: 10.1070/QE2012v042n02ABEH014734 [9] GAO F, CHEN F, XIE J J, et al. Review on diode-pumped alkali vapor laser[J]. Optik, 2013, 124(20): 4353-4358. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.01.061 [10] ZHDANOV B V, ROTONDARO M D, SHAFFER M K, et al. Power degradation due to thermal effects in Potassium Diode Pumped Alkali Laser[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 341: 97-100. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2014.12.021 [11] WAICHMAN K, BARMASHENKO B D, ROSENWAKS S. Laser power, cell temperature, and beam quality dependence on cell length of static Cs DPAL[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2017, 34(2): 279-286. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.34.000279 [12] YACOBY E, WAICHMAN K, SADOT O, et al. Modeling of flowing-gas diode-pumped potassium laser with different pumping geometries: scaling up and controlling beam quality[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2017, 53(4): 1000107. [13] PIZA G A, STALNAKER D M, GUILD E M, et al. Advancements in flowing diode pumped alkali lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9729: 972902. [14] YACOBY E, AUSLENDER I, WAICHMAN K, et al. Analysis of continuous wave diode pumped cesium laser with gas circulation: experimental and theoretical studies[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 17814-17819. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.017814 [15] BARMASHENKO B D, ROSENWAKS S, WAICHMAN K. Kinetic and fluid dynamic processes in diode pumped alkali lasers: semi-analytical and 2D and 3D CFD modeling[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 8962: 89620C. [16] SHEN B L, HUANG J H, XU X Q, et al. Modeling of steady-state temperature distribution in diode-pumped alkali vapor lasers: analysis of the experimental results[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2017, 53(3): 1500207. [17] GAVRIELIDES A, SCHLIE L A, LOPER R D, et al. Unstable resonators for high power diode pumped alkali lasers[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10090: 100901M. [18] HUANG J H, SU CH Y, XU X Q, et al. Theoretical simulations on pulsed exciplex pumped Rb vapor laser[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 141: 107165. [19] YANG J, AN G F, GUO J W, et al. Study on a gas flowing diode pumped cesium laser[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 11890: 118900N. [20] 徐艳, 陈飞, 谢冀江, 等. 缓冲气体对碱金属蒸汽激光器工作特性的影响[J]. 红外与激光工程,2015,44(2):455-460. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.02.010XU Y, CHEN F, XIE J J, et al. Influence of buffer gas on performance of alkali vapor laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(2): 455-460. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.02.010 [21] ROTONDARO M D, PERRAM G P. Role of rotational-energy defect in collisional transfer between the 5 2P1/2, 3/2 levels in rubidium[J]. Physical Review A, 1998, 57(5): 4045-4048. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.57.4045 [22] LEMMON E W. Thermophysical properties of fluid systems[J]. NIST Chemistry WebBook, 2010. [23] SHU H, BASS M. Three-dimensional computer model for simulating realistic solid-state lasers[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(23): 5687-5697. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.005687 [24] WAICHMAN K, BARMASHENKO B D, ROSENWAKS S. CFD DPAL modeling for various schemes of flow configurations[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9251: 92510U. doi: 10.1117/12.2067019 [25] YAMAMOTO T, YAMAMOTO F, ENDO M, et al. Experimental investigation of gas flow type DPAL[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10254: 102540S. -





 下载:
下载: