Vortex phase-shifting digital holography for micro-optical element surface topography measurment
-
摘要:
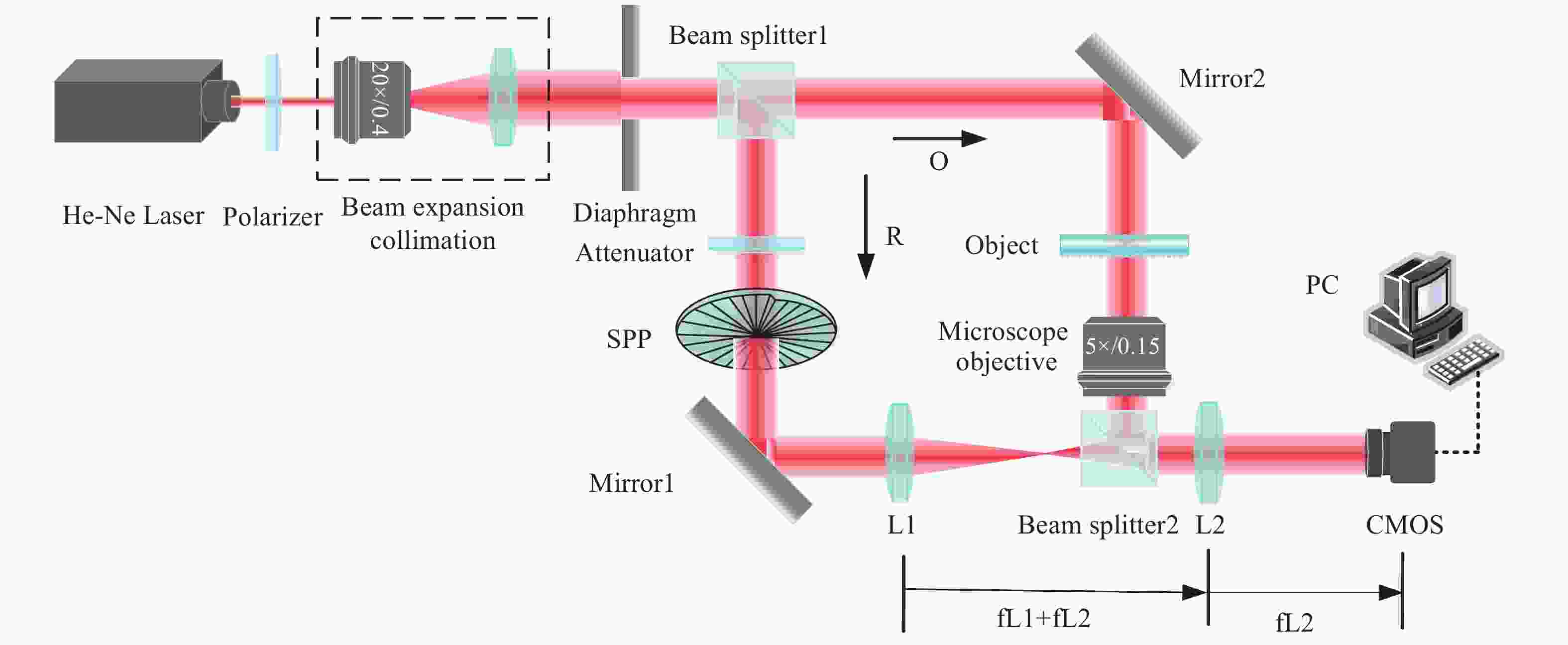
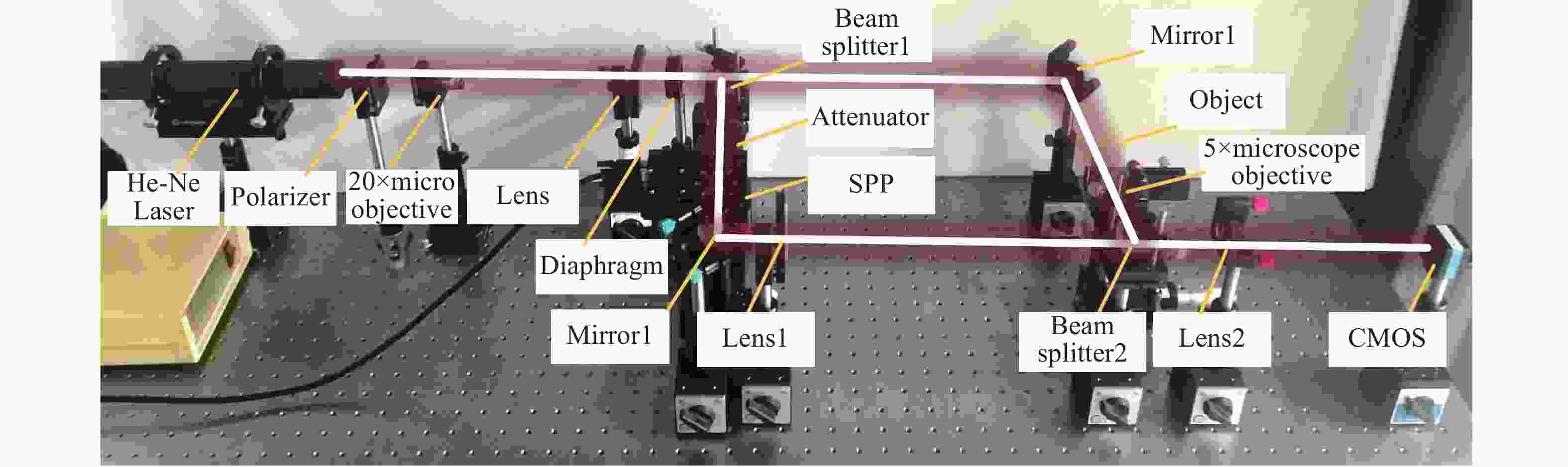
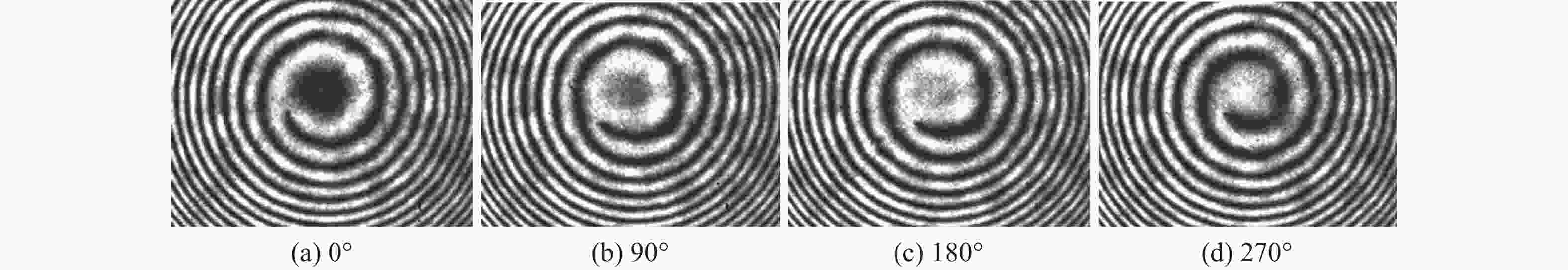
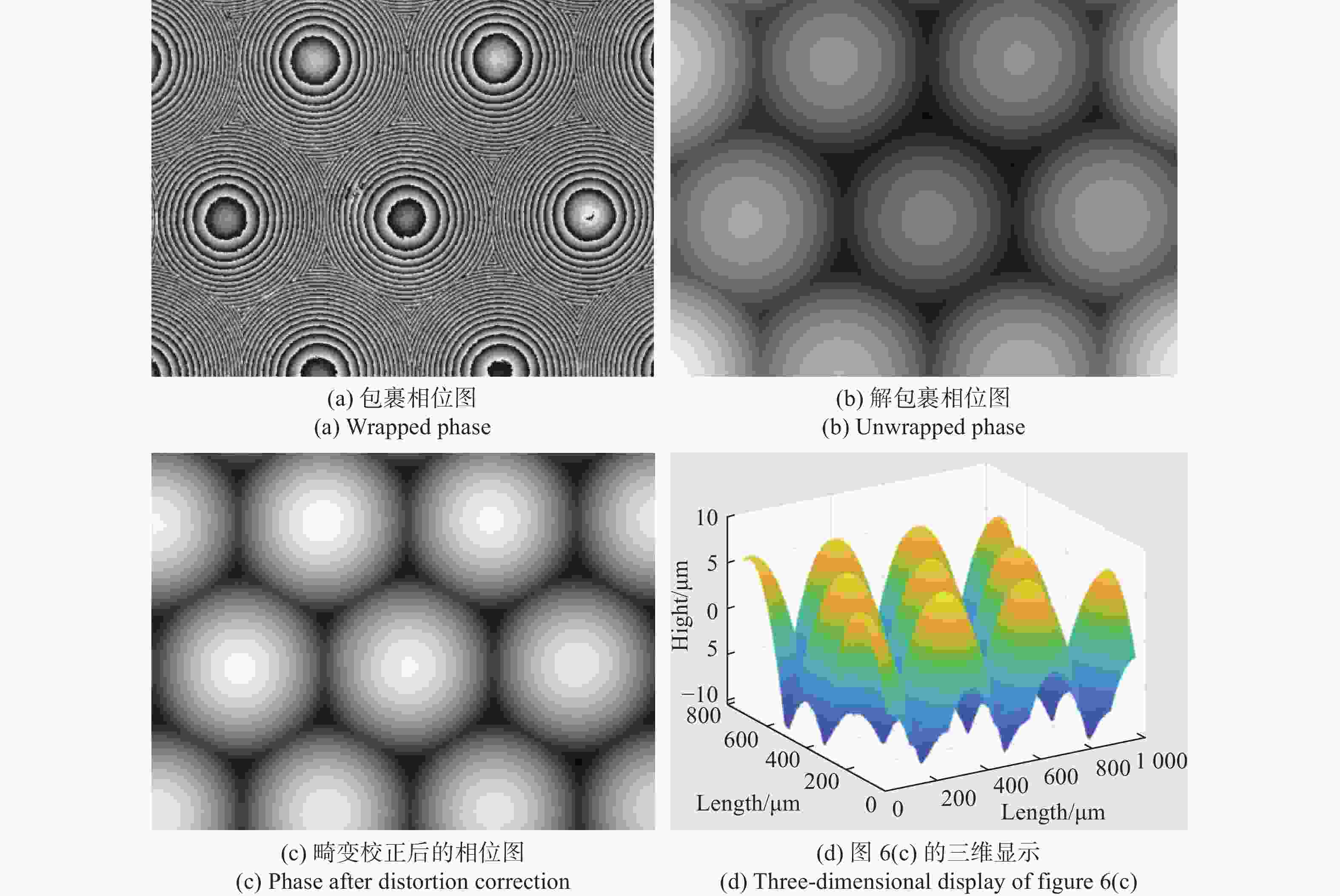
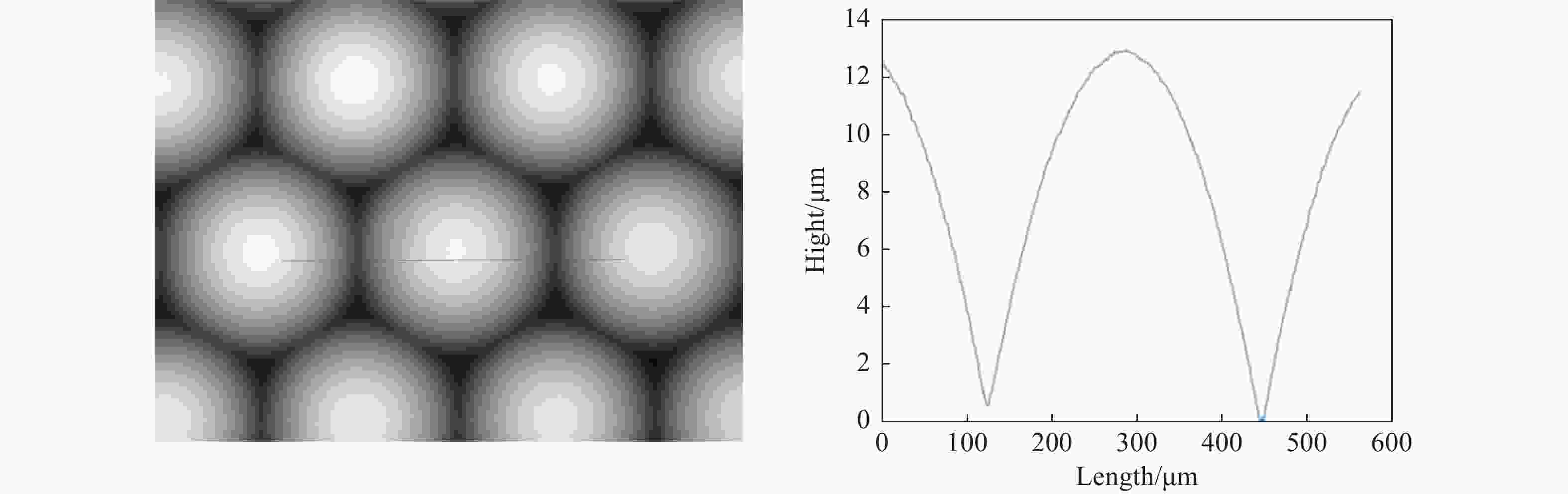
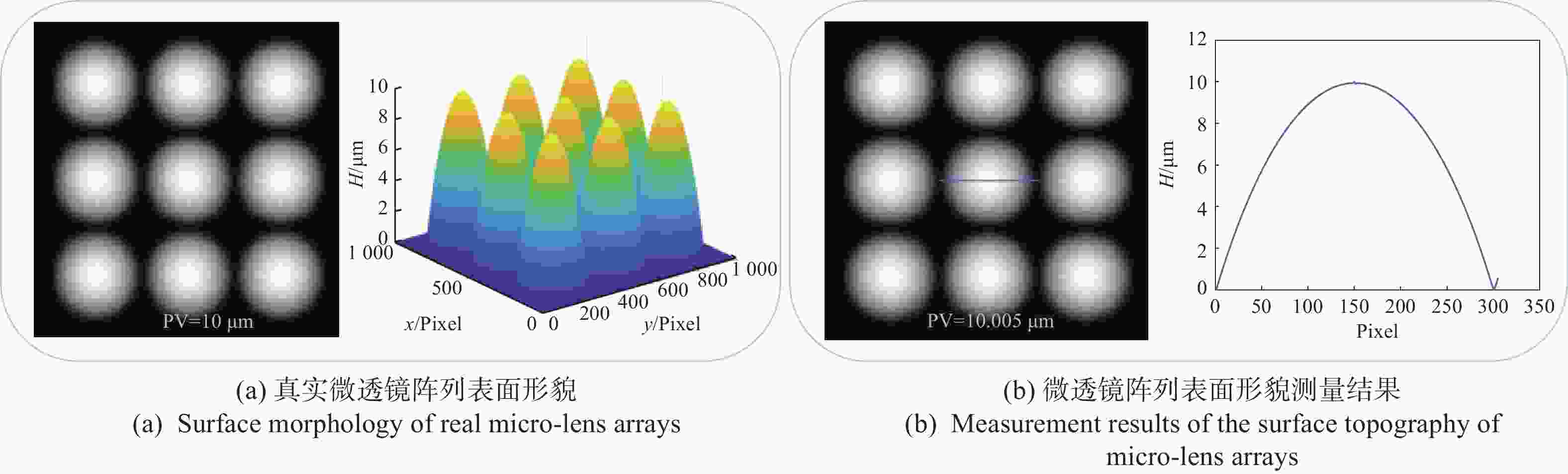
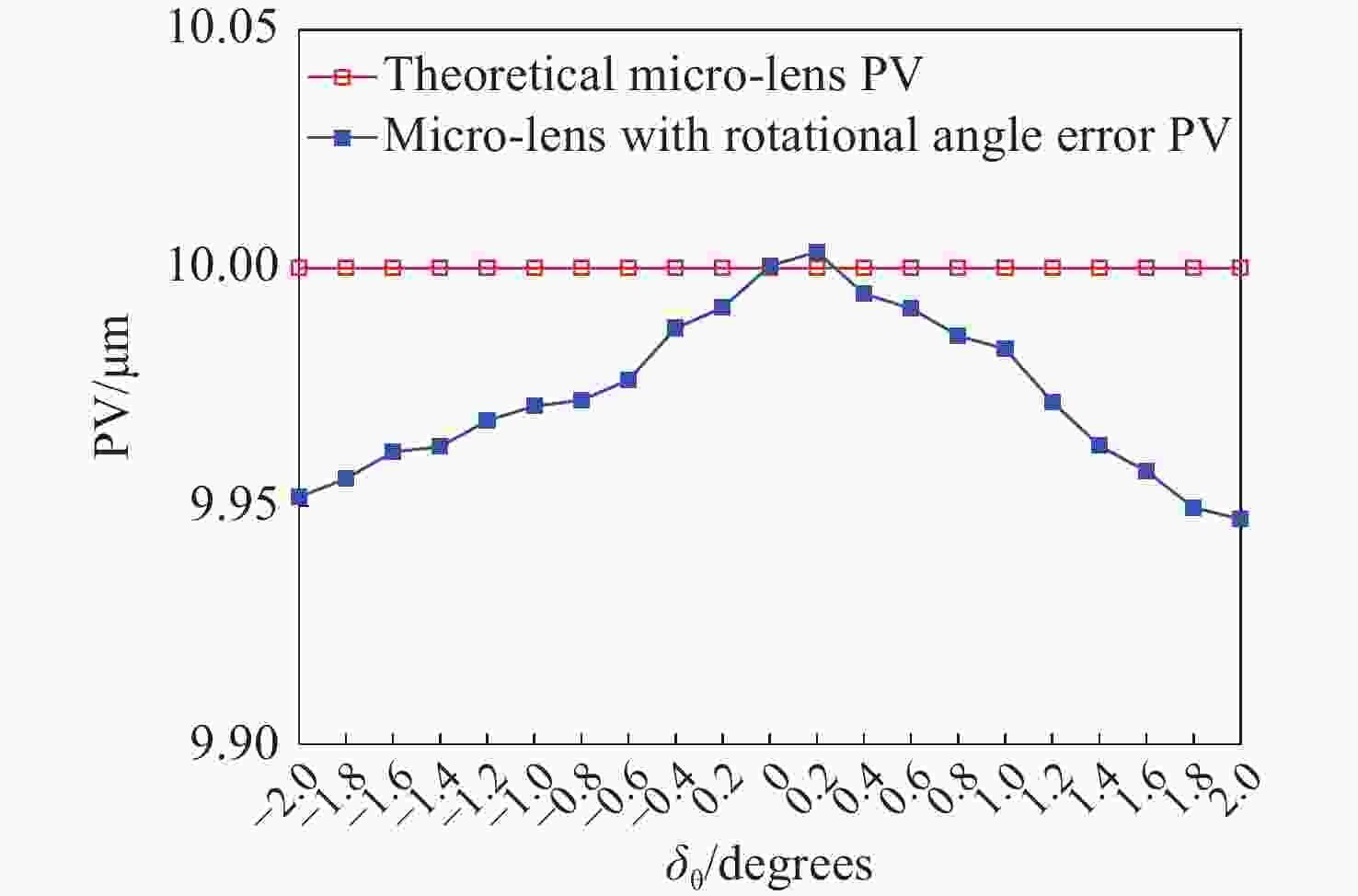
非接触、无损害的相移数字全息技术对微光学元件检测具有独特优势。因传统的相移数字全息技术需要对相移器进行精细控制和繁琐校准,同时其光路易受到机械振动干扰,导致全息再现像的质量降低。本文借助涡旋光特殊的相位分布,提出了一种基于涡旋相移数字全息的微光学元件表面形貌测量方法。该方法利用螺旋相位板调制涡旋相位,引入高精度相移。基于构建的涡旋相移数字全息显微实验装置,采用干涉极值法确定了相移干涉图之间的真实相移量,并对螺旋相位板的旋转角度与相移量的关系进行标定,实验验证了涡旋相移的可行性;对微透镜阵列进行了重复测量实验,将测试结果与ZYGO白光干涉仪的测试结果进行比较。结果表明:测量得到单个微透镜的平均纵向矢高为12.897 μm,平均相对误差为0.155%。所提方法可以实现对被测微光学元件表面形貌的高精度测量,具有易操作、稳定可靠、准确性高等优点。
Abstract:Non-destructive, non-contact phase-shifting digital holography technology has distinct advantages in identifying micro-optical components. As traditional phase-shifting digital holography technology requires fine control and cumbersome calibration of the phase shifter, furthermore, its optical path is susceptible to mechanical vibration interference, which reduces the quality of the holographically reproduced image. To solve the above problems, we propose a vortex phase-shifting digital holography for the micro-optical element surface measurement with the help of the special phase distribution of vortex light. The method utilizes a helical phase plate to modulate the vortex phase and introduce a high-precision phase shift. Based on the constructed vortex phase-shifting digital holographic microscopy experimental setup, the actual phase shifts between phase-shift interferograms were determined using the interferometric polarity method, the relationship between the rotation angle of the helical phase plate and the phase shift was calibrated, and the feasibility of the vortex phase shift was experimentally verified. Repeated measurement experiments were carried out on the micro-lens arrays, and the measurement results were compared with those of the ZYGO white light interferometer. The results indicate that a single micro-lens's average longitudinal vector height is 12.897 μm with an average relative error of 0.155%. The proposed method enables highly precise measurement of the surface topography of micro-optical elements. It offers the advantages of easy operation, high stability, and high accuracy.
-
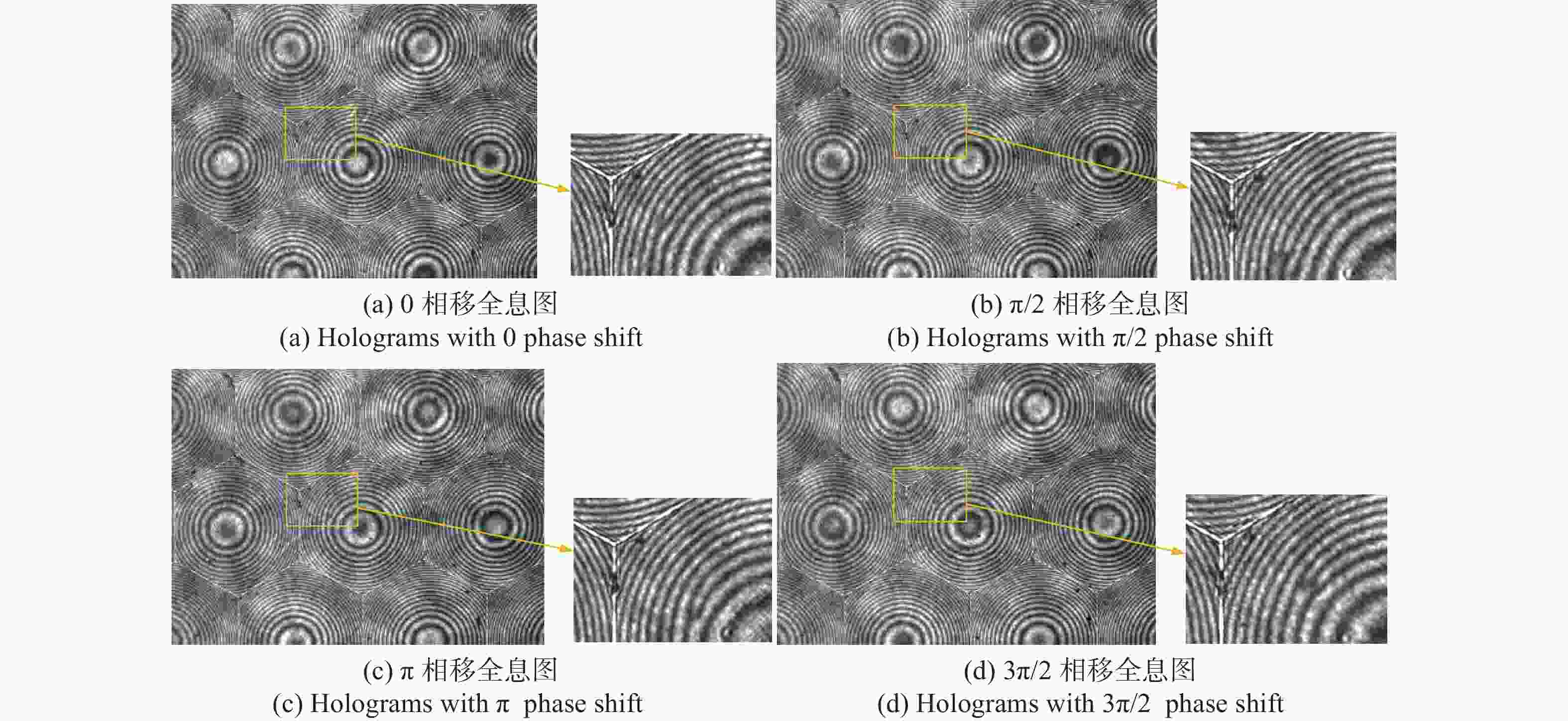
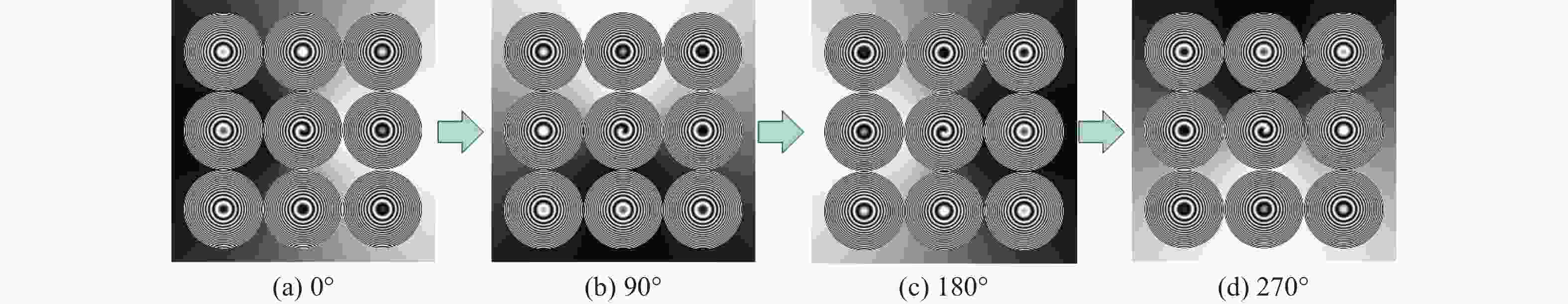
表 1 相移全息图的实际相移量和相移误差
Table 1. Actual phase shift and phase shift error in phase shift holograms
No. Theoretical Phase
Shift/radActual Phase
Shift/radPhase Shift
Error/rad1 0 0 0 2 0.5π 0.4992π −0.0008π 3 π 0.9963π −0.0037π 4 1.5π 1.4876π −0.0024π 表 2 测量微透镜阵列纵向矢高实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of the measured longitudinal vector height of micro-lens arrays
No. Vertical height of single
micro-lens/μmAbsolute
error/μmRelative
error/%1 12.906 0.011 0.085 2 12.917 0.000 0.000 3 12.920 0.003 0.023 4 12.898 0.019 0.147 5 12.921 0.004 0.031 6 12.875 0.042 0.325 7 12.897 0.020 0.155 8 12.860 0.057 0.441 9 12.871 0.046 0.356 10 12.903 0.014 0.108 -
[1] 王丹艺, 薛常喜, 李闯, 等. 基于微透镜阵列的电子内窥镜光学系统设计[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(2):0222003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0222003WANG D Y, XUE CH X, LI CH, et al. Design of electronic endoscope optical system based on microlens array[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(2): 0222003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0222003 [2] 李恒, 邵永红, 王岩, 等. 基于微透镜阵列和振镜扫描的光谱分辨多焦点多光子显微技术[J]. 中国激光,2010,37(5):1240-1244. doi: 10.3788/CJL20103705.1240LI H, SHAO Y H, WANG Y, et al. Spectrally resolved multifocal multiphoton microscopy using microlens array and galvo mirror scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2010, 37(5): 1240-1244. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL20103705.1240 [3] LIU G, SCOTT P D. Phase retrieval and twin-image elimination for in-line Fresnel holograms[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1987, 4(1): 159-165. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.4.000159 [4] 黄郑重, 曹良才. 面向高通量的多通道复用数字全息成像技术[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(6):1182-1193. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0070HUANG ZH Z, CAO L C. Multi-channel multiplexing digital holographic imaging for high throughput[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(6): 1182-1193. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0070 [5] 满天龙, 万玉红, 菅孟静, 等. 面向生物样品三维成像的光干涉显微技术研究进展[J]. 中国激光,2022,49(15):1507202. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1507202MAN T L, WAN Y H, JIAN M J, et al. Research progress in optical interference microscopy toward three-dimensional imaging of biological samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(15): 1507202. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.1507202 [6] KUMAR M, PENSIA L, KUMAR R. Highly stable vibration measurements by common-path off-axis digital holography[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 163: 107452. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.107452 [7] MACH M, PSOTA P, ŽÍDEK K, et al. On-chip digital holographic interferometry for measuring wavefront deformation in transparent samples[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(11): 17185-17200. doi: 10.1364/OE.486997 [8] LIU B C, FENG D Q, FENG F, et al. Maximum a posteriori-based digital holographic microscopy for high-resolution phase reconstruction of a micro-lens array[J]. Optics Communications, 2020, 477: 126364. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126364 [9] XIA P, WANG Q H, RI SH E. Random phase-shifting digital holography based on a self-calibrated system[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(14): 19988-19996. doi: 10.1364/OE.395819 [10] XIA P, RI SH E, INOUE T, et al. Dynamic phase measurement of a transparent object by parallel phase-shifting digital holography with dual polarization imaging cameras[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2021, 141: 106583. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2021.106583 [11] RODRIGUEZ-ZURITA G, MENESES-FABIAN C, TOTO-ARELLANO N I, et al. One-shot phase-shifting phase-grating interferometry with modulation of polarization: case of four interferograms[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(11): 7806-7017. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.007806 [12] CARRÉ P. Installation et utilisation du comparateur photoélectrique et interférentiel du Bureau International des Poids et Mesures[J]. Metrologia, 1966, 2(1): 13-23. doi: 10.1088/0026-1394/2/1/005 [13] NOBUKAWA T, MUROI T, KATANO Y, et al. Single-shot phase-shifting incoherent digital holography with multiplexed checkerboard phase gratings[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(8): 1698-1701. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001698 [14] 石侠, 朱五凤, 袁斌, 等. 非相干光照明数字全息实验研究[J]. 中国激光,2015,42(12):1209003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.1209003SHI X, ZHU W F, YUAN B, et al. Experimental study of the incoherent digital holography[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(12): 1209003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.1209003 [15] 钱晓彤, 田爱玲, 刘丙才, 等. 基于液晶空间光调制器的相移数字全息显微测量系统精度分析[J]. 光子学报,2022,51(4):0409003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225104.0409003QIAN X T, TIAN A L, LIU B C, et al. Precision analysis of phase shifting digital holography micromeasurement system based on LCSLM[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(4): 0409003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20225104.0409003 [16] 邓丽军, 黄星艳, 曾吕明, 等. 基于双色LED芯片的双波长像面数字全息显微术[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(1):0111004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0111004DENG L J, HUANG X Y, ZENG L M, et al. Dual-wavelength image-plane digital holographic microscopy based on Bi-color LED chips[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(1): 0111004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0111004 [17] LIM J, CHOI H, PARK N C. Phase-shift digital holography using multilayer ceramic capacitor actuators[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2022, 156: 107080. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2022.107080 [18] SHEN Y J, WANG X J, XIE ZH W, et al. Optical vortices 30 years on: OAM manipulation from topological charge to multiple singularities[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2019, 8(1): 90. [19] WANG Y L, WANG Y ZH, GUO ZH Y. OAM radar based fast super-resolution imaging[J]. Measurement, 2022, 189: 110600. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110600 [20] SHAW L A, PANAS R M, SPADACCINI C M, et al. Scanning holographic optical tweezers[J]. Optics Letters, 2017, 42(15): 2862-2865. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.002862 [21] XU L Y, REN Y, CHEN L L, et al. Azimuth measurement based on OAM phase spectrum of optical vortices[J]. Optics Communications, 2023, 530: 129170. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2022.129170 [22] FUJIMOTO I, SATO S, KIM M Y, et al. Optical vortex beams for optical displacement measurements in a surveying field[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2011, 22(10): 105301. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/22/10/105301 [23] SUN H B, WANG X H, SUN P. In-plane displacement measurement using optical vortex phase shifting[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(21): 5610-5613. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.005610 [24] WANG W P, HUANG S J, CHEN Y, et al. Three-dimensional refractive index measurement of special optical fiber based on optical vortex phase-shifting digital holographic microscopy[J]. Optical Engineering, 2019, 58(3): 034108. [25] ZHAO D E, JIA CH ZH, MA Y Y, et al. High-accuracy surface profile measurement based on the vortex phase-shifting interferometry[J]. International Journal of Optics, 2021, 2021: 6937072. [26] KOTLYAR V V, KOVALEV A A, SKIDANOV R V, et al. Simple optical vortices formed by a spiral phase plate[J]. Journal of Optical Technology, 2007, 74(10): 686-693. doi: 10.1364/JOT.74.000686 [27] DENG J, WANG H K, ZHANG F J, et al. Two-step phase demodulation algorithm based on the extreme value of interference[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(22): 4669-4671. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004669 -





 下载:
下载: