Coronary artery angiography image vessel segmentation method based on feature pyramid network
-
摘要:
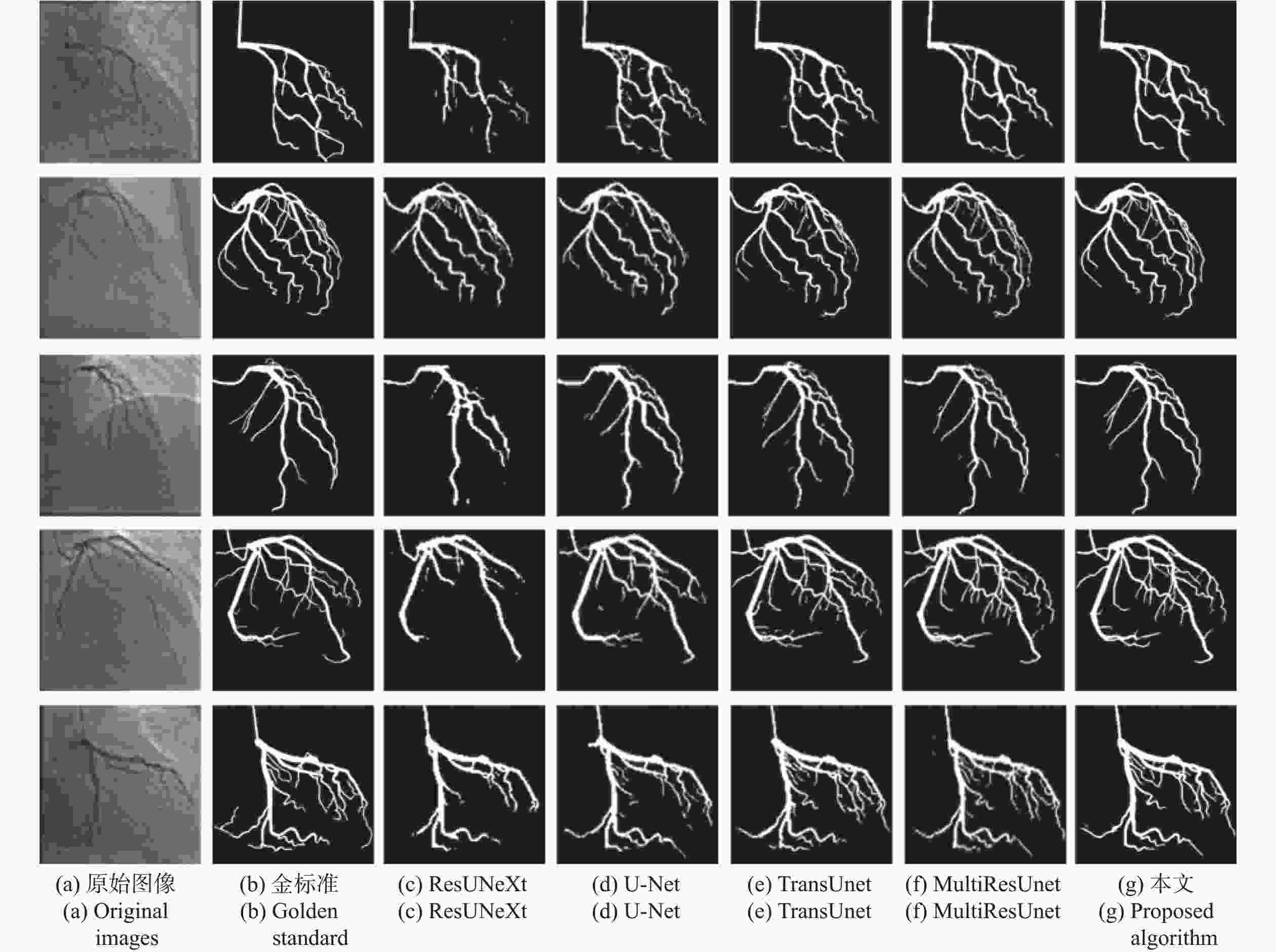
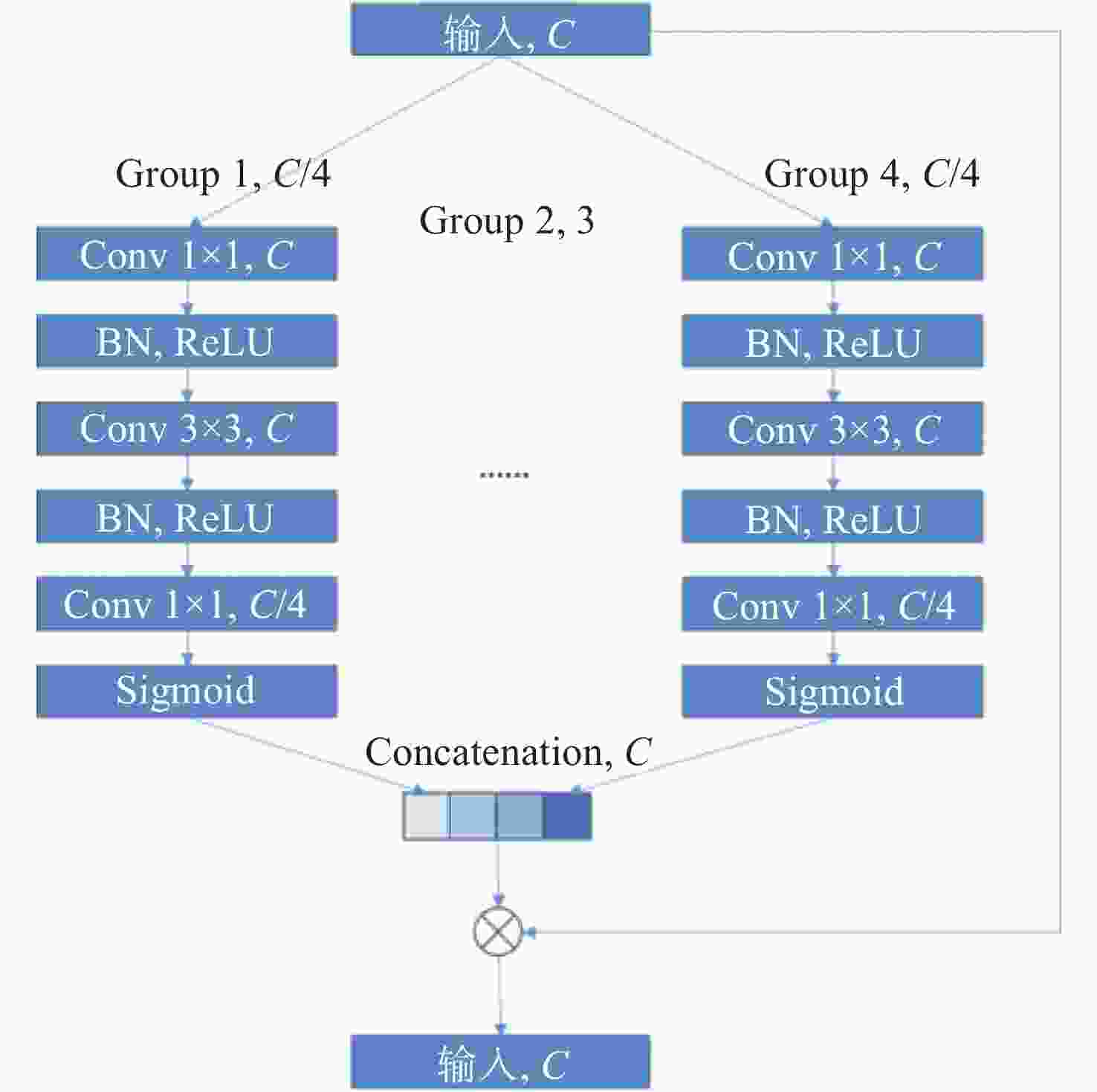
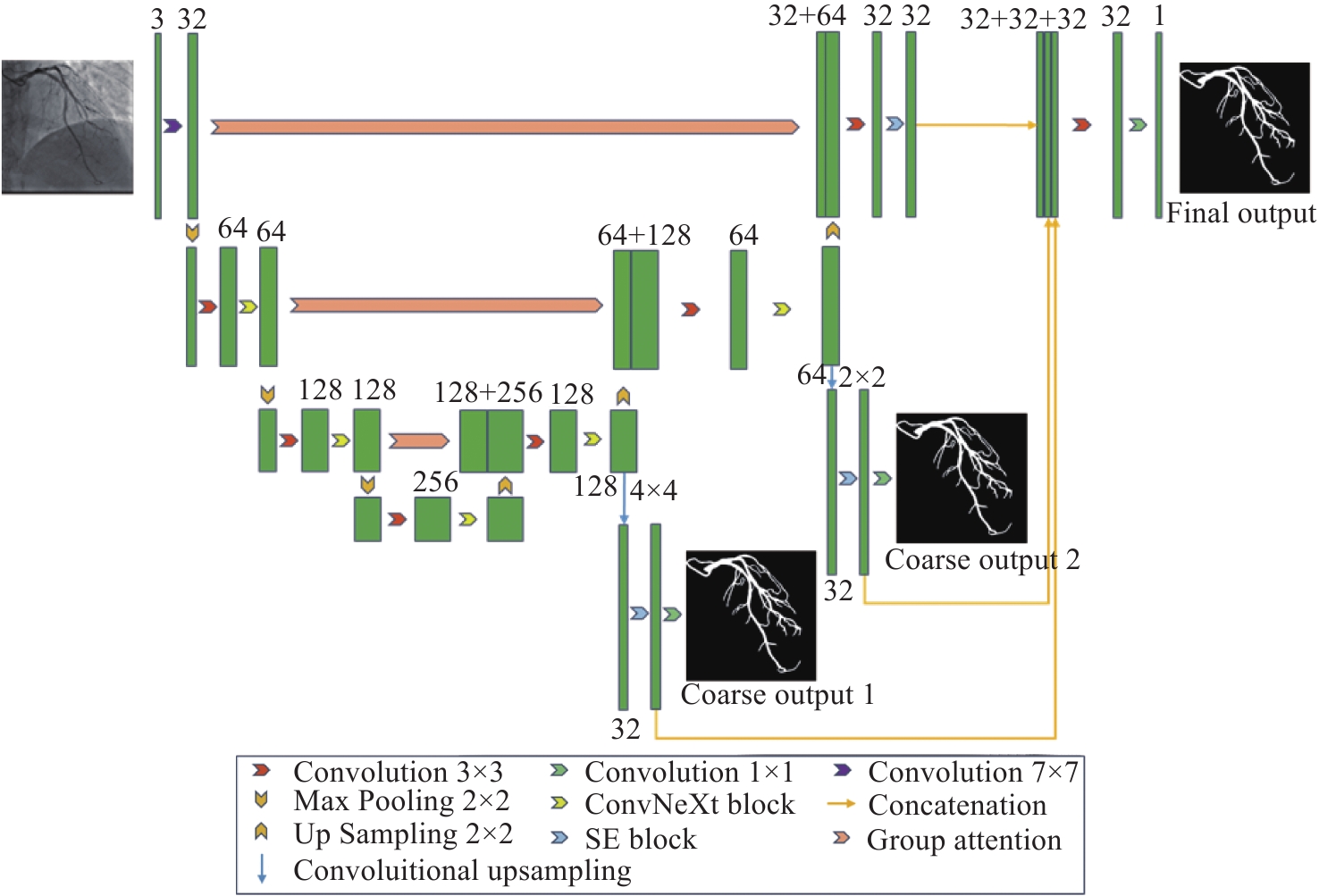
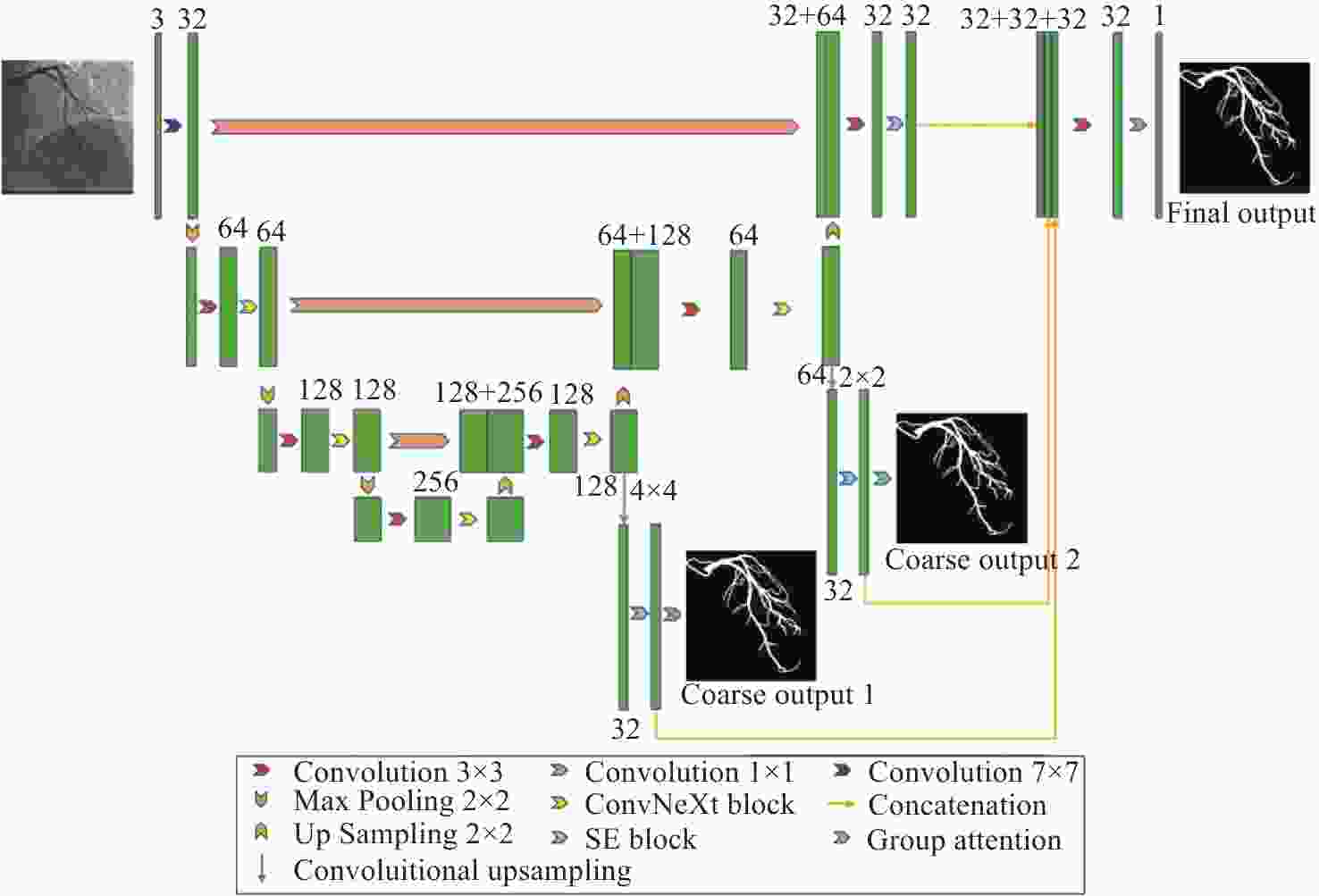
针对冠脉造影图像照明不均、血管结构与背景区域对比度低、冠脉血管拓扑结构复杂等分割难点,建立了一个冠脉造影血管分割标注数据集,并在此基础上提出了一种基于特征图金字塔的冠脉造影图像血管分割模型。本文模型以U-Net网络为基础进行改进和优化,首先,将U-Net编码部分的第一个卷积层修改为一个7×7的卷积层,并提高每一层的感受野,在编解码层中引入修改后的ConvNeXt block,使得网络提取更深层次特征的能力有所提升;其次,设计分组注意力机制模块GA,并将其引入到U-Net跨连接处,对编码部分提取的特征进行增强,弥补编解码器间存在的语义差距;最后,在U-Net解码器处设计了一个特征图金字塔级联模块PFC,融合各尺度的特征图,并在PFC中每一层中加入SE注意力机制模块,用于筛选特征图中的有效信息,网络损失函数为PFC模块各层输出的加权,以监督网络各层的特征提取。本文模型在测试集上的测试结果如下:Dice系数为0.8843,Jaccard系数为0.7926。实验结果表明,相比其他常用方法,本文模型在冠脉血管分割上具有较强的鲁棒性,在低对比度下能够有效抑制噪声,对冠脉血管具有更好的分割效果。
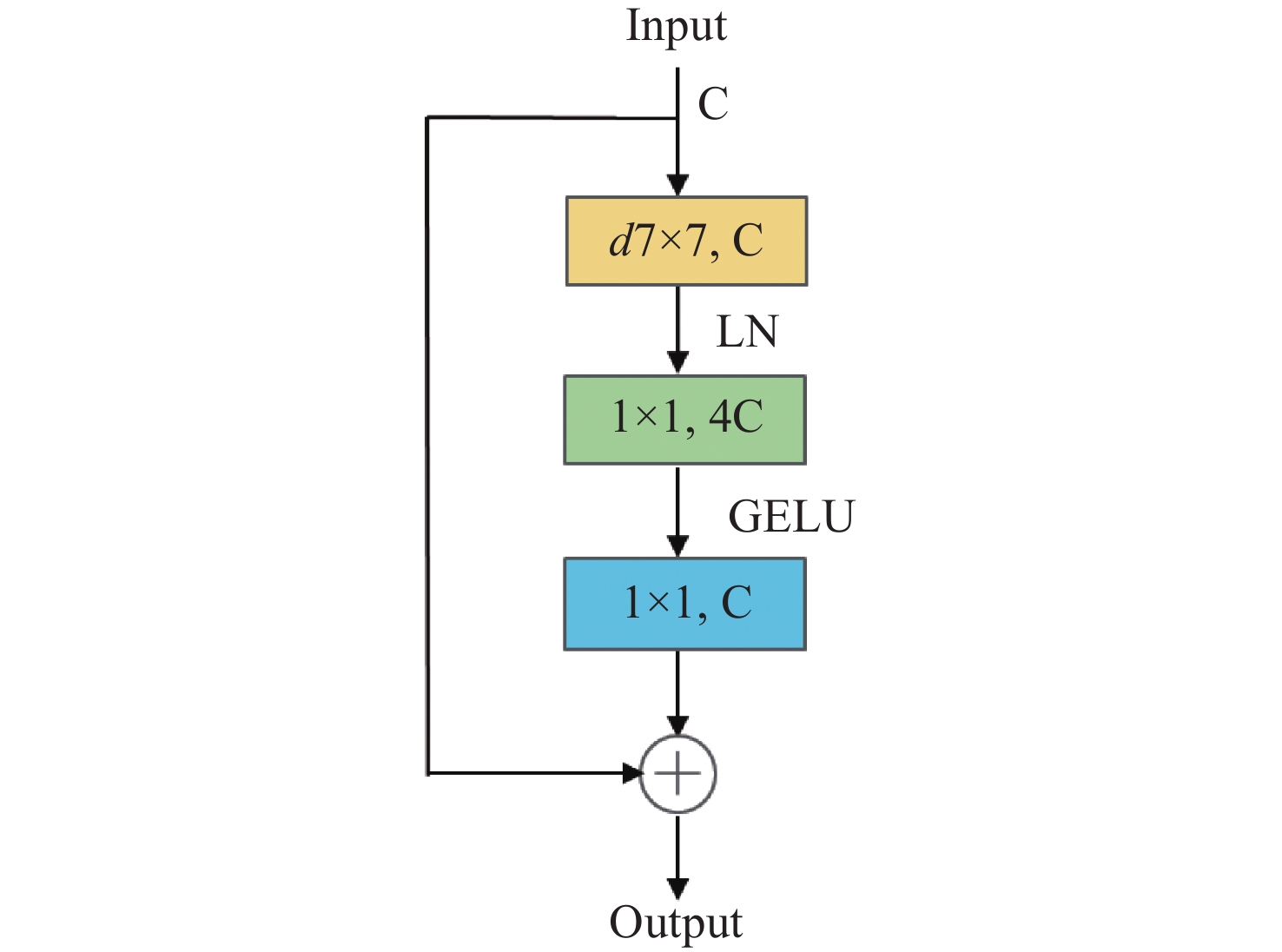
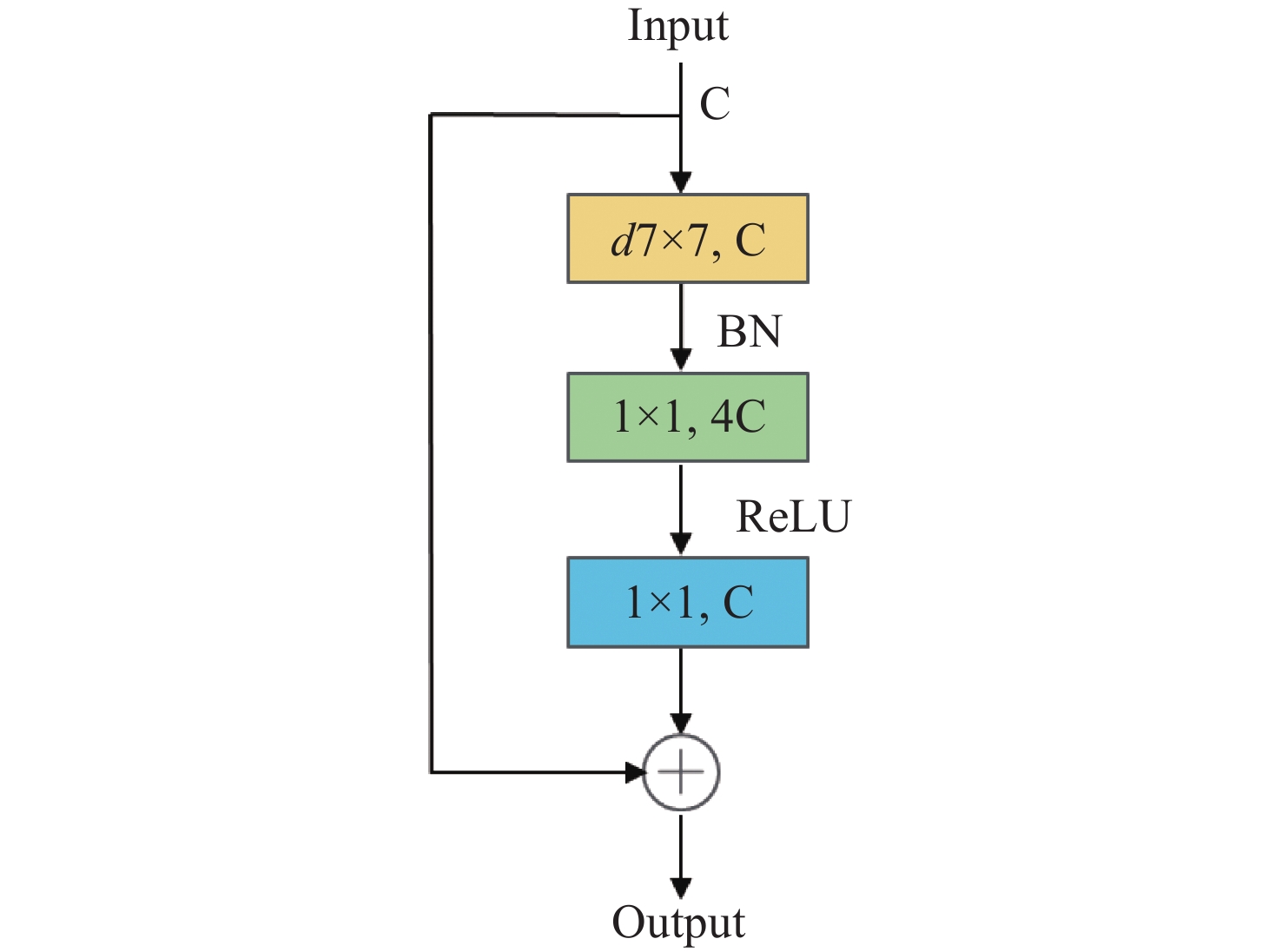
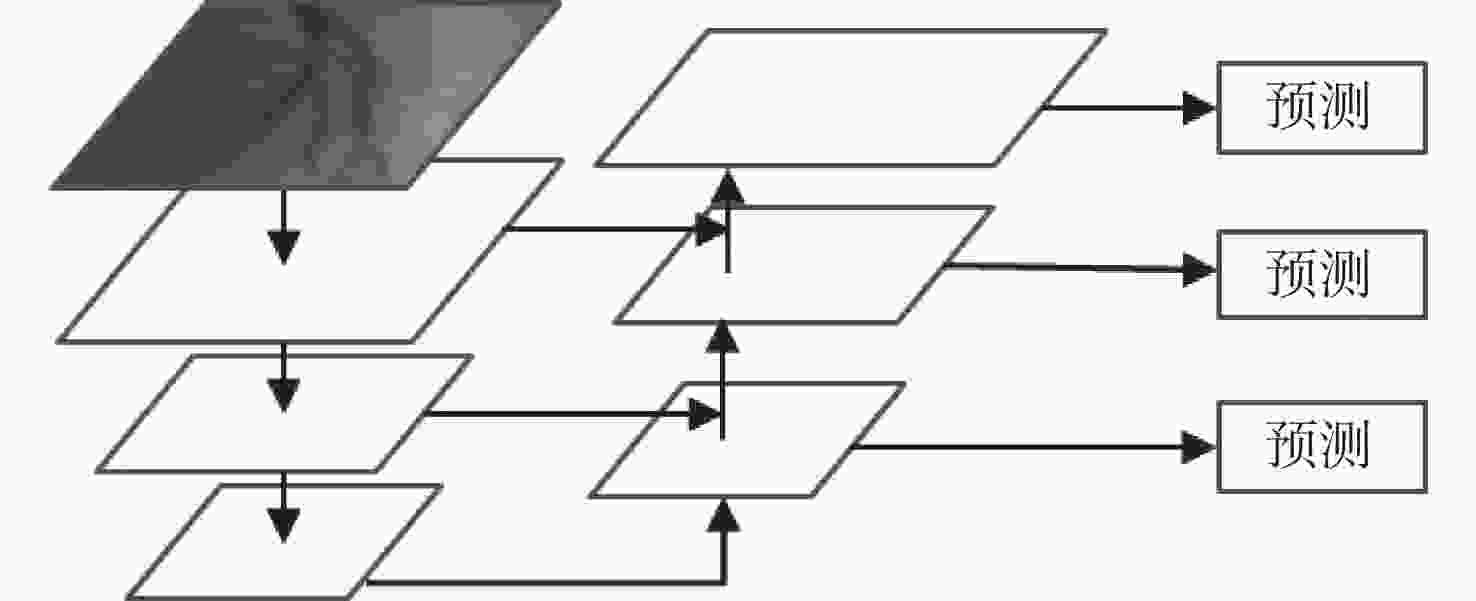
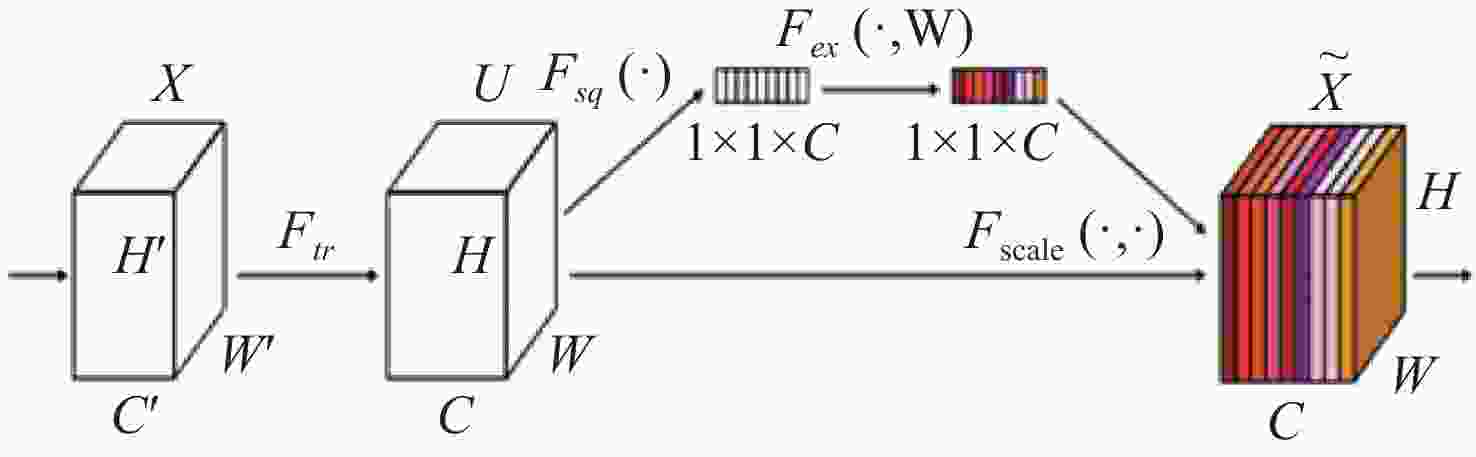
Abstract:To address issues such as uneven illumination in coronary angiography images, low contrast between vascular structures and background regions, and the complexity of coronary vascular topology, we establish a coronary angiography vascular segmentation annotation dataset. Additionally, we propose a coronary angiography image vascular segmentation model based on the feature map pyramid. On the basis of the U-Net architecture, this model was improved and optimized. First, the first convolutional layer in the U-Net encoding part was replaced with a 7×7 convolutional layer to increase the receptive field of each layer. Modified ConvNeXt blocks were added to the encoding and decoding layers to enhance the network's ability to extract deeper-level features. Second, a Group Attention (GA) mechanism module was designed and incorporated at the U-Net skip connection to strengthen the features extracted from the encoding part, addressing semantic gaps between the encoder and decoder. Finally, a Pyramid Feature Concatenation (PFC) module was designed at the U-Net decoder, which fused features from different scales. Squeeze-and-Excitaton (SE) attention mechanisms were added to each layer of the PFC to filter out effective information from the feature maps. The loss function of the network is weighted based on the outputs of the PFC module at each layer, serving to supervise the feature extraction process across different layers of the network. The test results of this model on the test set are as follows: the Dice coefficient is 0.8843 and the Jaccard coefficient is 0.7926. Experimental results indicate that this model is highly robust in coronary vascular segmentation, more effectively suppressing noise under low contrast and achieving better segmentation results for coronary vessels when compared to other methods.
-
Key words:
- coronary angiography /
- vessel segmentation /
- feature pyramid network /
- attention mechanism /
- U-Net
-
表 1 各模块对性能的影响
Table 1. Each module’s impact on performance
网络 Jaccard Dice BaseNet 0.6476±0.0098 0.7861±0.0073 BaseNet+Conv.7×7 0.6606±0.0119 0.7956±0.0086 BaseNet+ConvNeXt block 0.7104±0.0065 0.8307±0.0044 BaseNet+修改后的 ConvNeXt block 0.7234±0.0044 0.8395±0.0030 BaseNet+PFC 0.7036±0.0088 0.8260±0.0061 BaseNet+PFC+SE 0.7104±0.0043 0.8260±0.0061 BaseNet+PFC+SE+加权Loss 0.7364±0.0062 0.8482±0.0041 BaseNet+GA 0.7044±0.0028 0.8266±0.0019 BaseNet+Conv.7×7 +PFC+SE +修改后的ConvNeXt block+GA+加权Loss 0.7926±0.0058 0.8843±0.0036 表 2 不同算法测试结果
Table 2. Test results for different algorithms
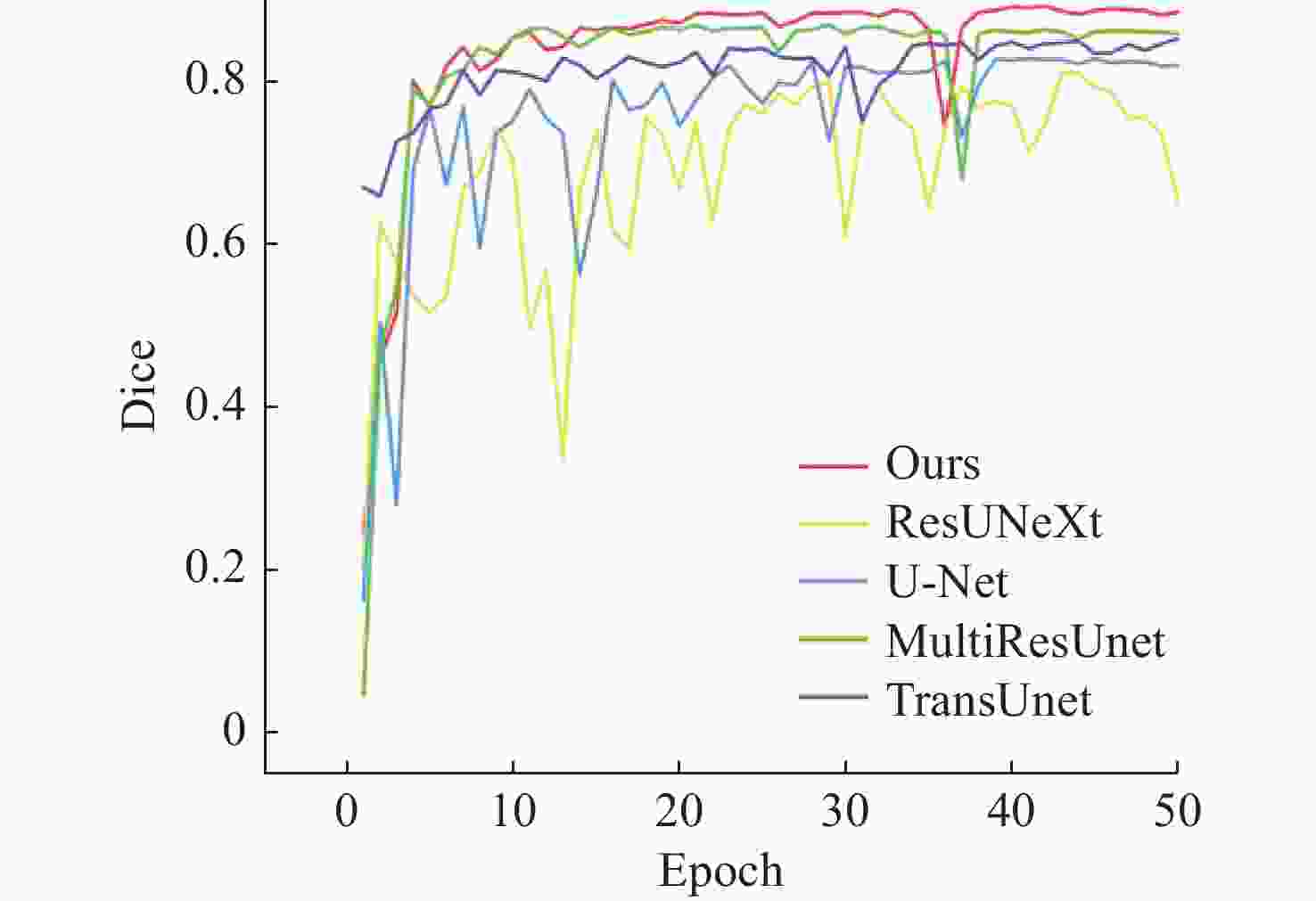
网络 Jaccard Dice AUC Accuracy Precision Sensitivity Specificity U-Net 0.7116 0.8315 0.9733 0.9706 0.8769 0.7908 0.9888 ResUNeXt 0.6849 0.8130 0.8741 0.9683 0.8847 0.7526 0.9901 TransUnet 0.7421 0.8519 0.9884 0.9748 0.8628 0.8416 0.9873 MultiResUnet 0.7664 0.8677 0.9842 0.9761 0.8775 0.8583 0.9879 Ours 0.7926 0.8843 0.9913 0.9783 0.9008 0.8597 0.9904 -
[1] WANG H, NAGHAVI M, ALLEN C, et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015[J]. The Lancet, 2016, 388(10053): 1459-1544. [2] JIANGPING S, ZHE Z, WEI W, et al. Assessment of coronary artery stenosis by coronary angiography: a head-to-head comparison with pathological coronary artery anatomy[J]. Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions, 2013, 6(3): 262-268. [3] FLEMING R M, KIRKEEIDE R L, SMALLING R W, et al. Patterns in visual interpretation of coronary arteriograms as detected by quantitative coronary arteriography[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 1991, 18(4): 945-951. [4] WIJNS W, SERRUYS P W, REIBER J H, et al. Quantitative angiography of the left anterior descending coronary artery: correlations with pressure gradient and results of exercise thallium scintigraphy[J]. Circulation, 1985, 71(2): 273-279. [5] GARRONE P, BIONDI-ZOCCAI G, SALVETTI I, et al. Quantitative coronary angiography in the current era: principles and applications[J]. Journal of Interventional Cardiology, 2009, 22(6): 527-536. [6] BLONDEL C, MALANDAIN G, VAILLANT R, et al. Reconstruction of coronary arteries from a single rotational X-ray projection sequence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25(5): 653-663. [7] SHECHTER G, DEVERNAY F, COSTE-MANIÈRE E, et al. Three-dimensional motion tracking of coronary arteries in biplane cineangiograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2003, 22(4): 493-503. [8] SUN ZH, ZHOU Y. Assessing cardiac dynamics based on X-ray coronary angiograms[J]. J. Multim., 2013, 8(1): 48-55. [9] FELFELIAN B, FAZLALI H R, KARIMI N, et al. Vessel segmentation in low contrast X-ray angiogram images[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), IEEE, 2016: 375-379. [10] CHEN Y, ZHANG Y D, YANG J, et al. Curve-like structure extraction using minimal path propagation with backtracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(2): 988-1003. [11] JIN M X, LI R, JIANG J, et al. Extracting contrast-filled vessels in X-ray angiography by graduated RPCA with motion coherency constraint[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 63: 653-666. [12] BANKHEAD P, SCHOLFIELD C N, MCGEOWN J G, et al. Fast retinal vessel detection and measurement using wavelets and edge location refinement[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e32435. [13] LI Y L, ZHOU SH J, WU J H, et al. A novel method of vessel segmentation for X-ray coronary angiography images[C]. 2012 Fourth International Conference on Computational and Information Sciences, IEEE, 2012: 468-471. [14] SOARES J V B, LEANDRO J J G, CESAR R M, et al. Retinal vessel segmentation using the 2-D gabor wavelet and supervised classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2006, 25(9): 1214-1222. [15] FRANGI A F, NIESSEN W J, VINCKEN K L, et al. Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering[C]. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention— MICCAI’98, Springer, 1998: 130-137. [16] M’HIRI F, DUONG L, DESROSIERS C, et al. Vessel walker: coronary arteries segmentation using random walks and hessian-based vesselness filter[C]. 2013 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, IEEE, 2013: 918-921. [17] DEHKORDI M T, HOSEINI A M D, SADRI S, et al. Local feature fitting active contour for segmenting vessels in angiograms[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2014, 8(3): 161-170. [18] LAW M W K, CHUNG A C S. Efficient implementation for spherical flux computation and its application to vascular segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(3): 596-612. [19] ORLANDO J I, PROKOFYEVA E, BLASCHKO M B. A discriminatively trained fully connected conditional random field model for blood vessel segmentation in fundus images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 2017, 64(1): 16-27. [20] 郑跃坤, 葛明锋, 常智敏, 等. 基于残差网络的结直肠内窥镜图像超分辨率重建方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):1022-1033.ZHENG Y K, GE M F, CHANG ZH M, et al. Super-resolution reconstruction for colorectal endoscopic images based on a residual network[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1022-1033. (in Chinese). [21] 白瑞峰, 江山, 孙海江, 等. 基于编码解码结构的微血管减压图像实时语义分割[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):1055-1065.BAI R F, JIANG SH, SUN H J, et al. Real-time semantic segmentation of microvascular decompression images based on encoder-decoder structure[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 1055-1065. (in Chinese). [22] ZHAO H SH, SHI J P, QI X J, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2017: 6230-6239. [23] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. [24] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, Springer, 2015: 234-241. [25] IBTEHAZ N, RAHMAN M S. MultiResUNet: rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 121: 74-87. [26] PAN S W, ZHANG W, ZHANG W J, et al. Diagnostic model of coronary microvascular disease combined with full convolution deep network with balanced cross-entropy cost function[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 177997-178006. [27] XIAN ZH CH, WANG X Q, YAN SH D, et al. Main coronary vessel segmentation using deep learning in smart medical[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 8858344. [28] YANG S, KWEON J, KIM Y H. Major vessel segmentation on X-ray coronary angiography using deep networks with a novel penalty loss function[C]. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, MIDL, 2019. [29] JUN T J, KWEON J, KIM Y H, et al. T-Net: Nested encoder-decoder architecture for the main vessel segmentation in coronary angiography[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 128: 216-233. [30] LI L ZH, VERMA M, NAKASHIMA Y, et al. IterNet: retinal image segmentation utilizing structural redundancy in vessel networks[C]. 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), IEEE, 2020: 3645-3654. [31] LIU ZH, MAO H Z, WU CH Y, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2022: 11966-11976. [32] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2017: 936-944. [33] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 7132-7141. [34] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS, 2017: 5998-6008. [35] DIAKOGIANNIS F I, WALDNER F, CACCETTA P, et al. ResUNet-a: a deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 162: 94-114. [36] CHEN J N, LU Y Y, YU Q H, et al. TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation[J]. arXiv: 2102.04306, 2021. -





 下载:
下载: