The influence factors and optimization of modulation transfer spectroscopy for laser frequency discrimination
-
摘要:
采用电光位相调制器对泵浦光进行位相调制,得到射频调制转移光谱 (MTS),并研究MTS光谱的类色散信号中心过零点斜率优化问题。通过改变泵浦光的调制频率,泵浦光与探测光的光斑大小,研究MTS光谱信号过零点斜率与二者之间的参数依赖关系,在泵浦光调制频率为~3.6 MHz(大约是自然线宽的0.69倍)时,得到最佳的MTS光谱信号。最后利用最优的MTS光谱将DL Pro @ 852 nm 激光频率锁定到铯原子D2线(F = 4) − (F = 5’)循环跃迁,在60 min采样时间内激光频率起伏约为170 kHz,与自由运转时激光器~11 MHz的频率起伏相比,频率起伏得到了显著改善。
Abstract:We use an electro-optical potential phase modulator to modulate the pump light to obtain radio frequency modulation transfer spectroscopy (MTS), and study the optimization problem of the zero-crossing slope of the center of the dispersive signal of the MTS spectrum. By changing the modulation frequency of the pump light, the spot size of the pump light and the probe light, we study the parameter dependence between the zero-crossing slope of the MTS spectral signal and the modulation frequency, and spot size. The optimal MTS spectral signal is obtained when the pump light modulation frequency is −3.6 MHz (about 0.69 times the natural linewidth). Finally, by using the optimal MTS spectrum, the DL Pro @ 852 nm laser frequency is locked to the cesium atom D2 line (F = 4) - (F = 5') cycle transition, and the laser frequency fluctuation is about 170 kHz in the 60 minutes sampling time, which is significantly improved compared with the frequency fluctuation of the laser −11 MHz during free running.
-
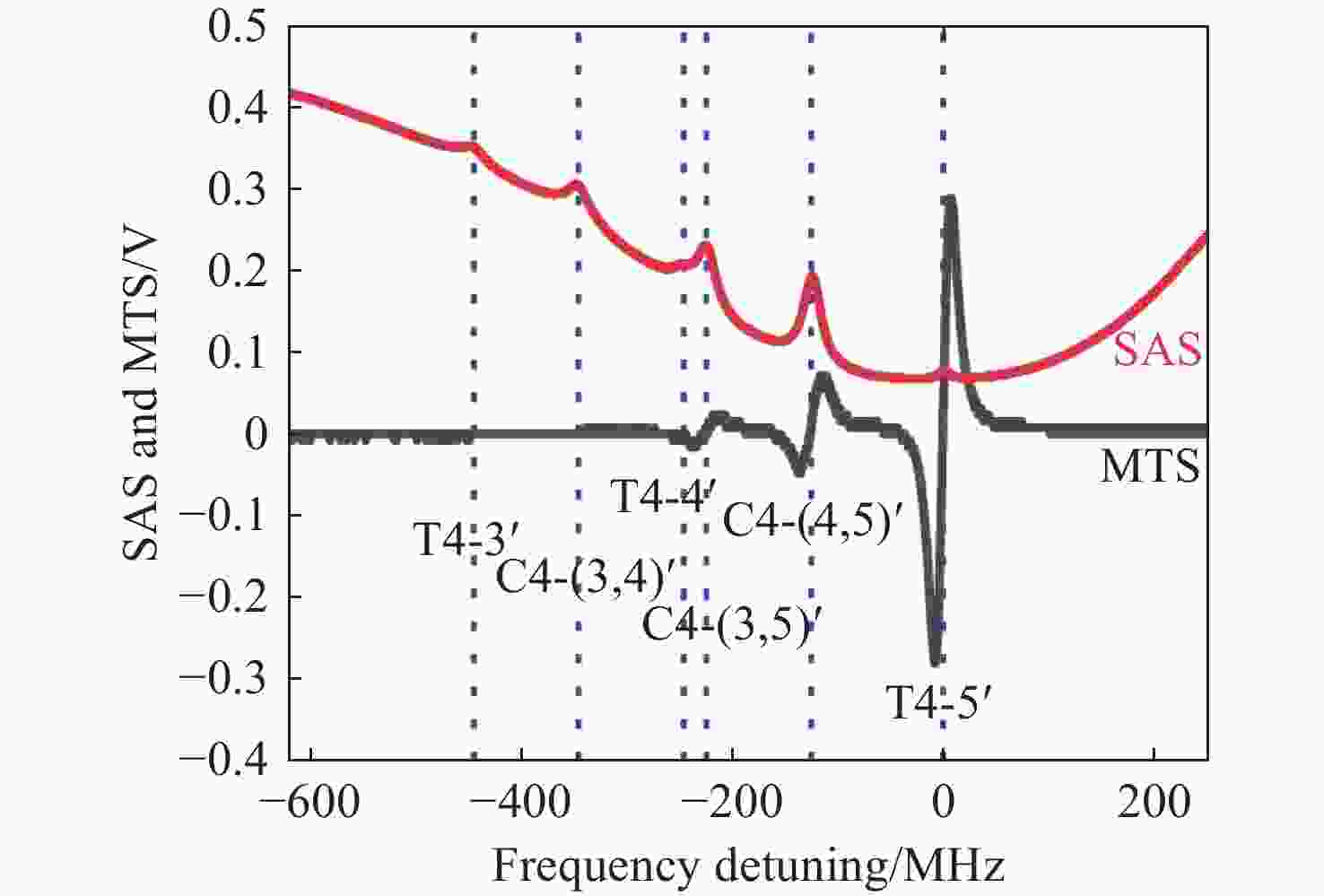
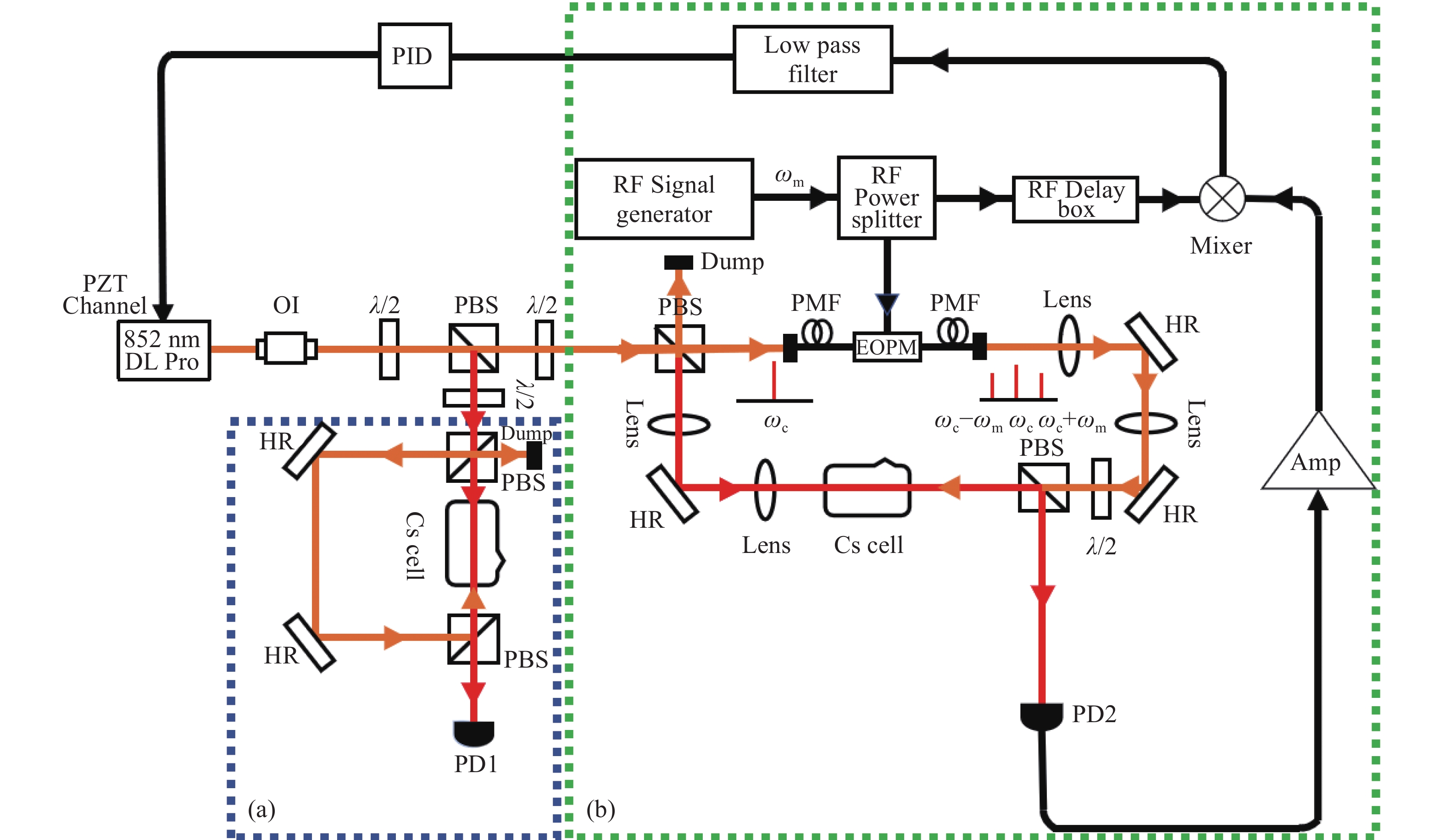
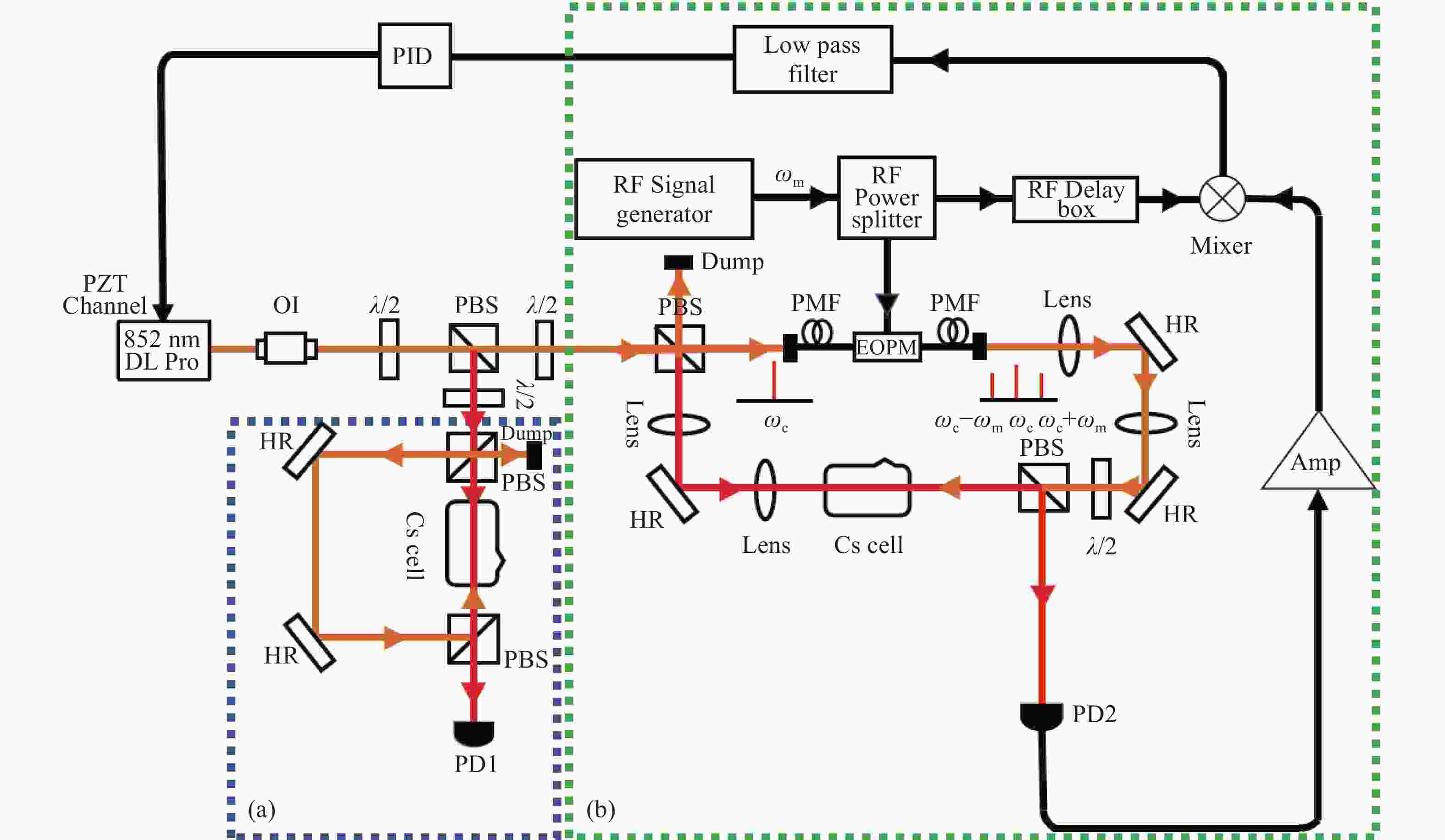
图 1 实验装置图。(a)铯原子气室饱和吸收光谱仪;(b)铯原子气室调制转移光谱仪。图1中,
$\omega_{\mathrm{m}} $ 为调制频率,$\omega_{\mathrm{c}} $ 是泵浦光频率,PMF为保偏光纤,PBS为偏振分束棱镜,EOPM为带输入输出单模保偏光纤的电光位相调制器,AMP为放大器,RF为射频,PID为比例-积分-差分放大器Figure 1. Diagram of experimental setup. (a) Cesium atomic gas chamber saturation absorption spectrometer; (b) Cesium atomic gas chamber modulation transfer spectrometer.
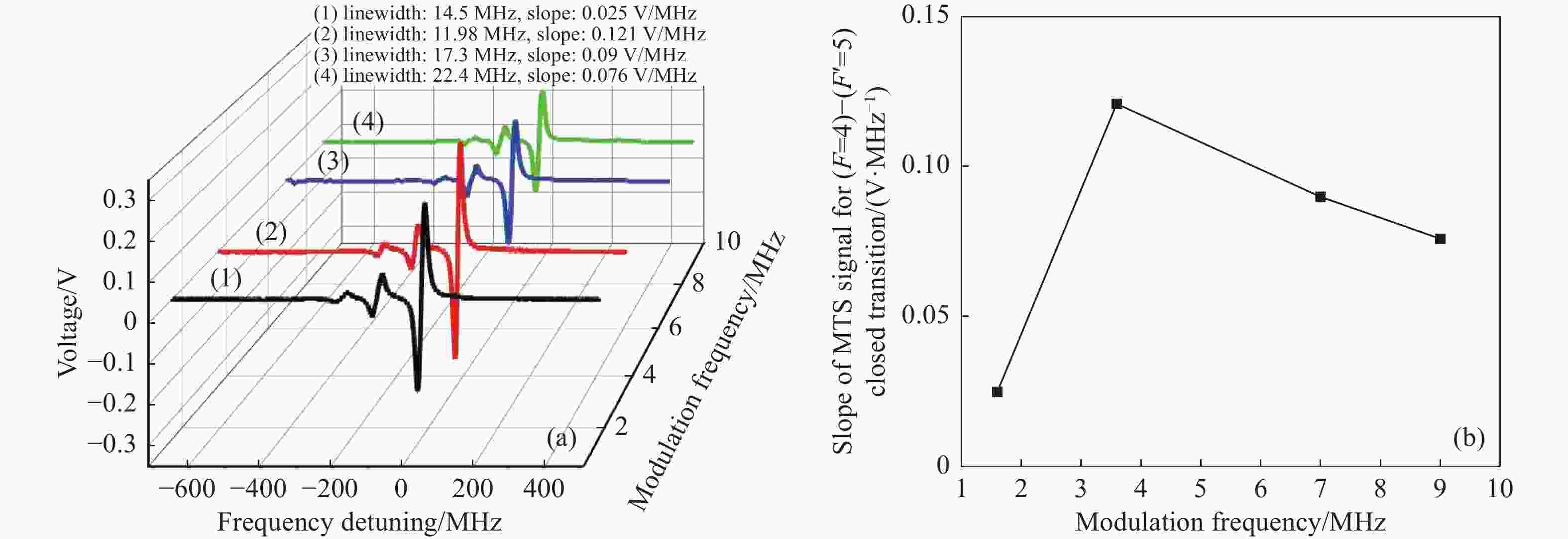
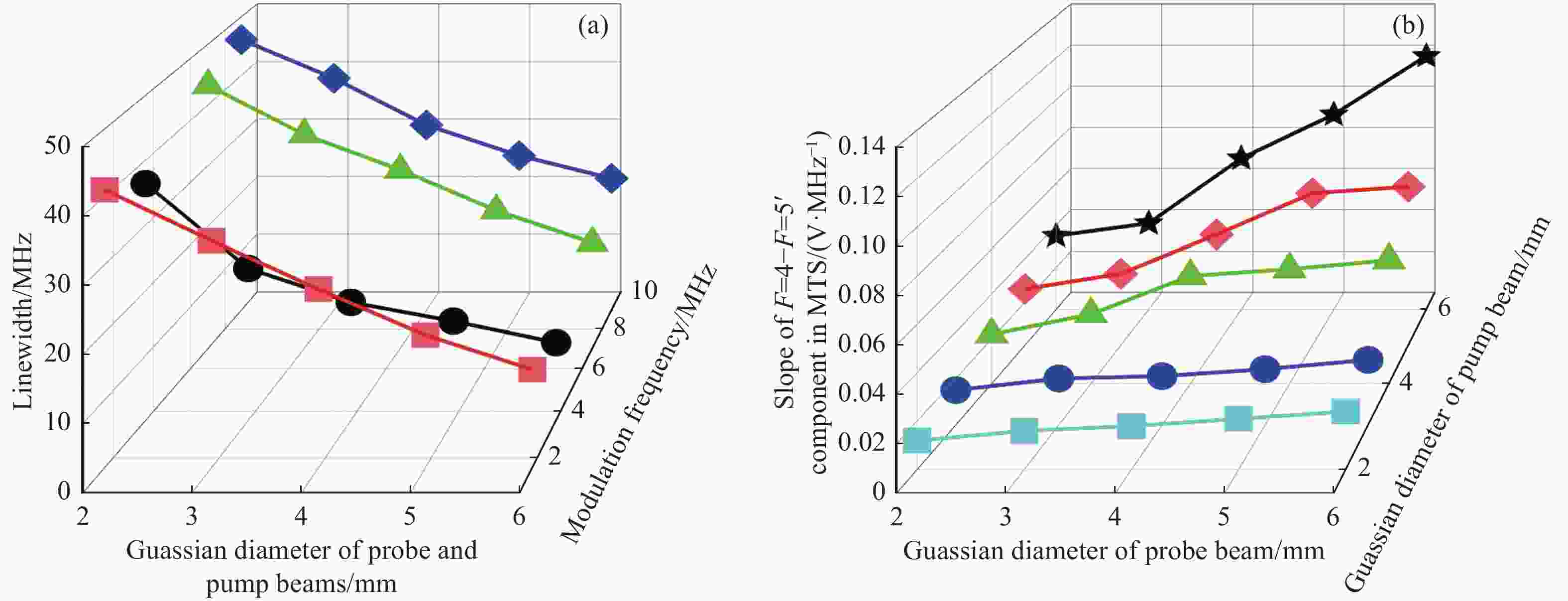
$ {\omega }_{m} $ is the modulation frequency, and$ {\omega }_{c} $ is the frequency of pump light. The upper and lower sidebands are at frequencies with$ {\omega }_{c}+{\omega }_{m} $ and$ {\omega }_{c}-{\omega }_{m} $ . Key to figure: λ/2: half-wave plate; PMF: polarization maintaining fiber; PBS: polarization beam splitter cube; EOPM: polarization-maintaining-fiber pig-tailed electro-optic phase modulator; PZT: piezoelectric tranducer; Amp: amplifier; RF: radio frequency; PID: proportional-integral-differential amplifier图 4 (a)调制频率、光斑大小对Cs原子D2线(F=4) - (F=5’)循环跃迁的调制转移光谱线宽的影响;(b)探测光与泵浦光光斑大小对Cs原子D2线(F=4) - (F=5’)循环跃迁的调制转移光谱过零点斜率的影响
Figure 4. (a) Effects of modulation frequency and spot size on the MTS linewidth of cesium (F=4) - (F=5’) cycling transition in D2 line; (b) influence of probe and pump beam sizes on the MTS slope of cesium (F=4) - (F=5’) cycling transition in D2 line
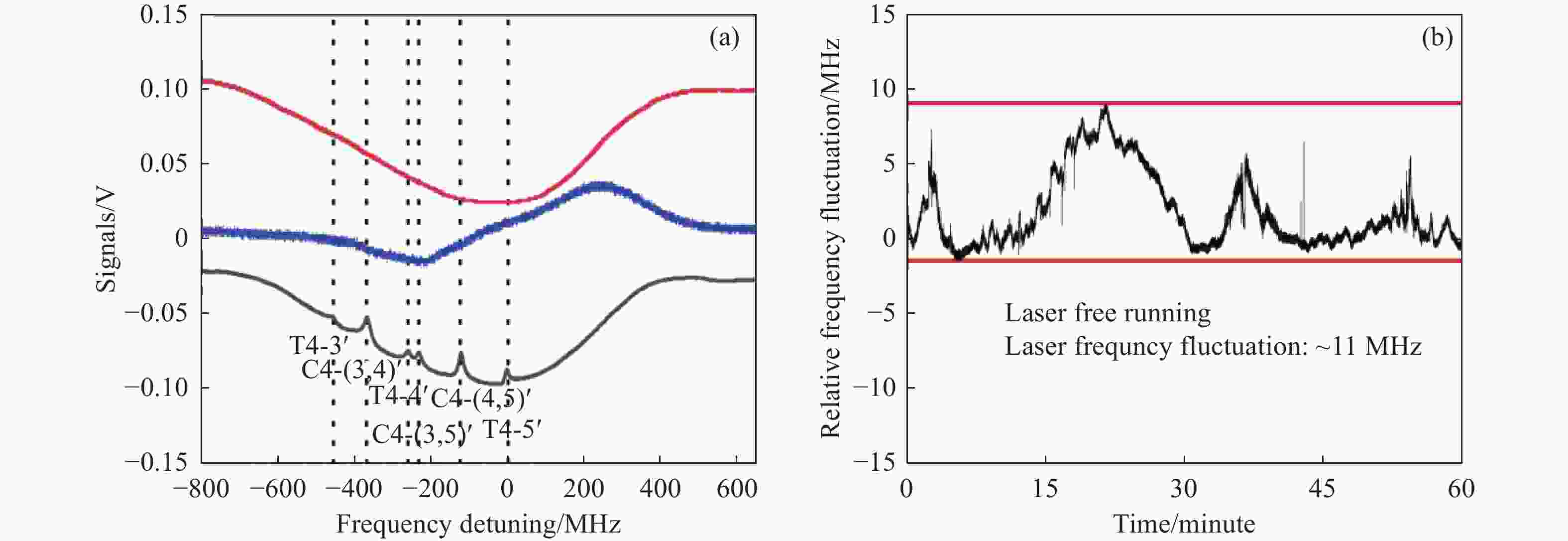
图 5 (a) Cs原子多普勒展宽的吸收光谱及其微分信号以及带多普勒背景的饱和吸收光谱。(b) DL Pro @ 852 nm光栅外腔半导体激光器自由运转时的典型频率起伏
Figure 5. (a) Cs atomic Doppler broaden absorption spectrum and its first order differential spectrum, and the saturated absorption spectrum with Doppler background. (b) Typical frequency fluctuation of DL Pro @ 852 nm in the free running case
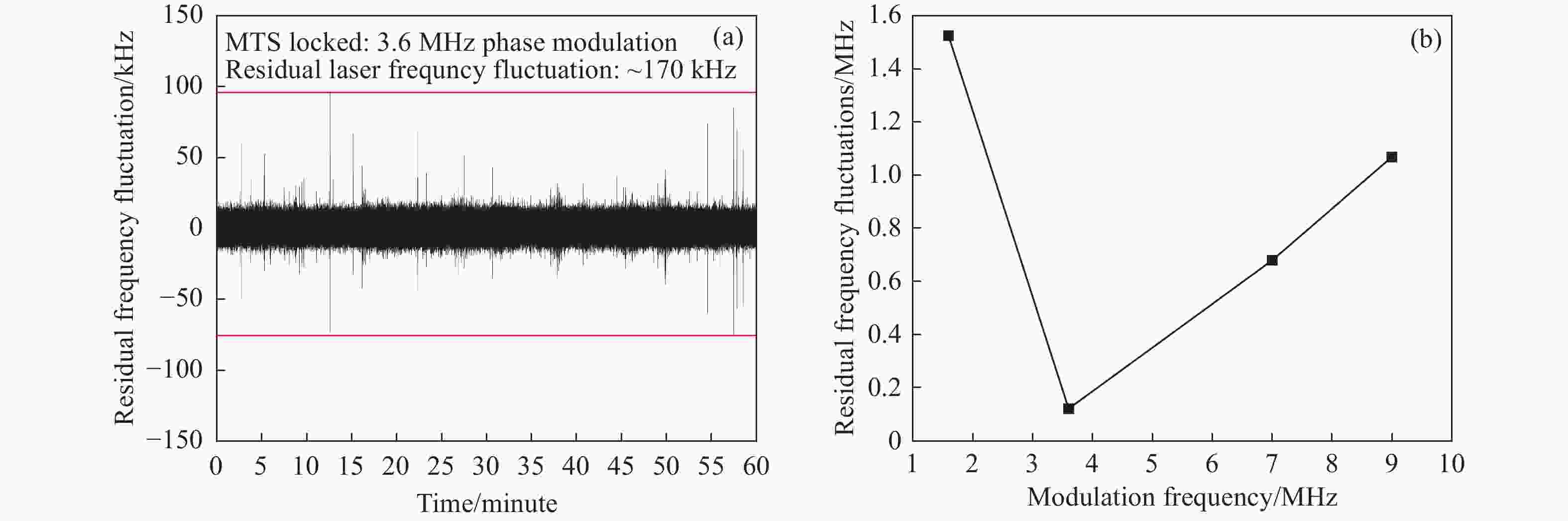
图 6 (a)调制频率为3.6 MHz时对激光器进行MTS锁频后的典型残余频率起伏;(b)不同调制频率下对激光器进行MTS锁频后的典型残余频率起伏
Figure 6. (a) Typical residual frequency fluctuations after MTS lock of the laser at a phase modulation frequency of 3.6 MHz; (b) typical residual frequency fluctuations after MTS lock of the laser at various phase modulation frequencies
-
[1] BJORKLUND G C. Frequency-modulation spectroscopy: a new method for measuring weak absorptions and dispersions[J]. Optics Letters, 1980, 5(1): 15-17. doi: 10.1364/OL.5.000015 [2] LEE S, MOON G, PARK S E, et al. Laser frequency stabilization in the 10−14 range via optimized modulation transfer spectroscopy on the 87 Rb D 2 line[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(4): 1020-1023. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.44.1251 [3] 刘瑞斌, 殷允嵩. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术相关物理机制研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2024,17(1):19-37. doi: 10.1364/OL.7.000537LIU Rui-bin, YIN Yun-song. Research progress on the related physical mechanism of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 19-37. (in Chinese). doi: 10.1364/OL.7.000537 [4] CAMY G, BORDÉ C J, DUCLOY M. Heterodyne saturation spectroscopy through frequency modulation of the saturating beam[J]. Optics Communications, 1982, 41(5): 325-330. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(82)90406-0 [5] TAKAMOTO M, HONG F L, HIGASHI R, et al. An optical lattice clock[J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7040): 321-324. doi: 10.1038/nature03541 [6] LUDLOW A D, ZELEVINSKY T, CAMPBELL G K, et al. Sr lattice clock at 1×10−16 fractional uncertainty by remote optical evaluation with a Ca clock[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5871): 1805-1808. doi: 10.1126/science.1153341 [7] 任颐杰, 颜昌翔, 徐嘉蔚. 增强吸收光谱技术的研究进展及展望[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1273-1292. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0246REN Y J, YAN CH X, XU J W. Development and prospects of enhanced absorption spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1273-1292. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0246 [8] 程军杰, 曹智, 杨灿然, 等. 便携式远程激光诱导击穿光谱系统及其定量分析性能[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(9):1447-1452.CHENG J J, CAO ZH, YANG C R, et al. Quantitative analysis with a portable remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(9): 1447-1452. (in Chinese). [9] MA L S, HALL J L. Optical heterodyne spectroscopy enhanced by an external optical cavity: toward improved working standards[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1990, 26(11): 2006-2012. doi: 10.1109/3.62120 [10] ZHANG J, WEI D, XIE CH D, et al. Characteristics of absorption and dispersion for rubidium D2 lines with the modulation transfer spectrum[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(11): 1338-1344. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.001338 [11] 刘涛, 李利平, 闫树斌, 等. 铯原子D2线调制转移光谱的实验研究[J]. 中国激光,2003,30(9):791-794. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2003.09.006LIU T, LI L P, YAN SH B, et al. Experimental investigation of modulation transfer spectrum of cesium D2 line[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2003, 30(9): 791-794. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0258-7025.2003.09.006 [12] LEE S, LEE S B, PARK S E, et al. Compact modulation transfer spectroscopy module for highly stable laser frequency[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2021, 146: 106698. [13] 杨舒涵, 乔顺达, 林殿阳, 等. 基于可调谐半导体激光吸收光谱的氧气浓度高灵敏度检测研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):151-157. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/26/4/044205YANG SH H, QIAO SH D, LIN D Y, et al. Research on highly sensitive detection of oxygen concentrations based on tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 151-157. (in Chinese). doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/26/4/044205 [14] ZHOU Z CH, WEI R, SHI CH Y, et al. Observation of modulation transfer spectroscopy in the deep modulation regime[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2010, 27(12): 124211. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/27/12/124211 [15] 贾豫东, 林志立, 欧攀, 等. 调制转移光谱光频率标准系统中电光参数的优化研究[J]. 物理学报,2011,60(12):124214. doi: 10.7498/aps.60.124214JIA Y D, LIN ZH L, OU P, et al. Optimization of electro-optical parameter of optical frequency standard system based on modulation transfer spectroscopy technique[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60(12): 124214. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.60.124214 [16] CHENG B, WANG ZH Y, WU B, et al. Laser frequency stabilization and shifting by using modulation transfer spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2014, 23(10): 104222. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/23/10/104222 [17] SHANG H, ZHANG T, MIAO J, et al. Laser with 10−13 short-term instability for compact optically pumped cesium beam atomic clock[J]. Optics express, 2020, 28(5): 6868-6880. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/27/7/074201 [18] YOSHITAKE S, AKIYAMA K, IRITANI M, et al. 1.55-μm-band practical frequency-stabilized semiconductor laser using C2H2 or HCN absorption lines[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1993, 1837: 124-133. doi: 10.1117/12.143666 [19] PISANI M, SASSI M P, ZUCCO M. High spectral purity CO2 laser stabilized using a molecular frequency reference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 1995, 44(2): 159-161. doi: 10.1109/19.377798 [20] BRUNER A, ARIE A, ARBORE M A, et al. Frequency stabilization of a diode laser at 1540 nm by locking to sub-Doppler lines of potassium at 770 nm[J]. Applied Optics, 1998, 37(6): 1049-1052. doi: 10.1364/AO.37.001049 [21] HALL J L, MA L SH, TAUBMAN M, et al. Stabilization and frequency measurement of the I2-stabilized Nd: YAG laser[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 1999, 48(2): 583-586. doi: 10.1109/19.769663 [22] GALZERANO G, SVELTO C, BAVA E, et al. High-frequency-stability diode-pumped Nd: YAG lasers with the FM sidebands method and Doppler-free iodine lines at 532 nm[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(33): 6962-6966. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.006962 [23] GUO R X, HONG F L, ONAE A, et al. Frequency stabilization of a 1319-nm Nd: YAG laser by saturation spectroscopy of molecular iodine[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(15): 1733-1735. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.001733 [24] LEONHARDT V, CAMP J B. Space interferometry application of laser frequency stabilization with molecular iodine[J]. Applied Optics, 2006, 45(17): 4142-4146. doi: 10.1364/AO.45.004142 [25] GALZERANO G, LAPORTA P. Absolute frequency stabilization of diode lasers around 0.94 μm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2007, 56(2): 365-368. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2007.891059 [26] MCCARRON D J, KING S A, CORNISH S L. Modulation transfer spectroscopy in atomic rubidium[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2008, 19(10): 105601. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/19/10/105601 [27] 洪毅, 侯霞, 陈迪俊, 等. 基于Rb 87调制转移光谱稳频技术研究[J]. 中国激光,2021,48(21):2101003. doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.2101003HONG Y, HOU X, CHEN D J, et al. Research on frequency stabilization technology of modulation transfer spectroscopy based on Rb87[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(21): 2101003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202148.2101003 [28] 宋微, 朱欣欣, 吴彬, 等. 基于调制转移光谱多参量相关的激光稳频特性研究[J]. 光子学报,2021,50(11):1114003. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20215011.1114003SONG W, ZHU X X, WU B, et al. Research on frequency stabilization characteristics of multi-parameter dependent laser source based on modulated transfer spectrum[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(11): 1114003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20215011.1114003 [29] 喻晓, 吕梦洁, 张旭, 等. 基于铷原子调制转移光谱技术的1560 nm光纤激光器频率锁定研究[J]. 中国激光,2022,49(3):0301002. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0301002YU X, LV M J, ZHANG X, et al. Research on frequency locking of 1560 nm fiber laser based on rubidium atomic modulation transfer spectroscopy technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(3): 0301002. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.0301002 -











 下载:
下载: