-
摘要:
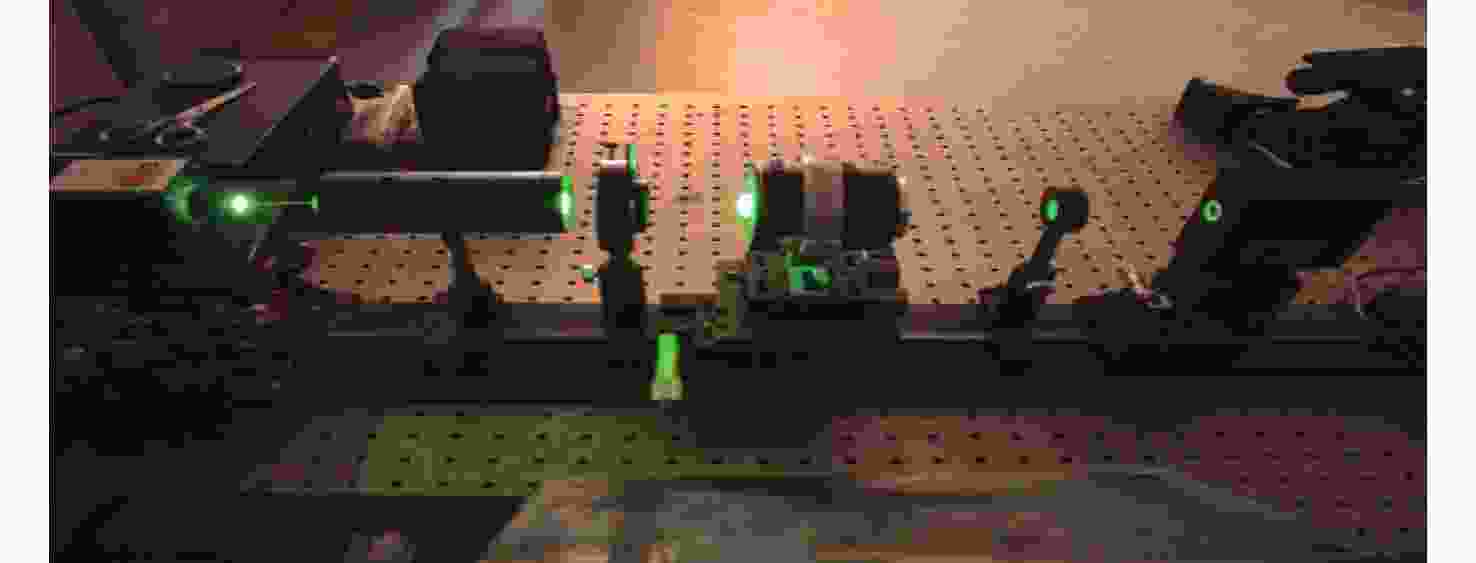
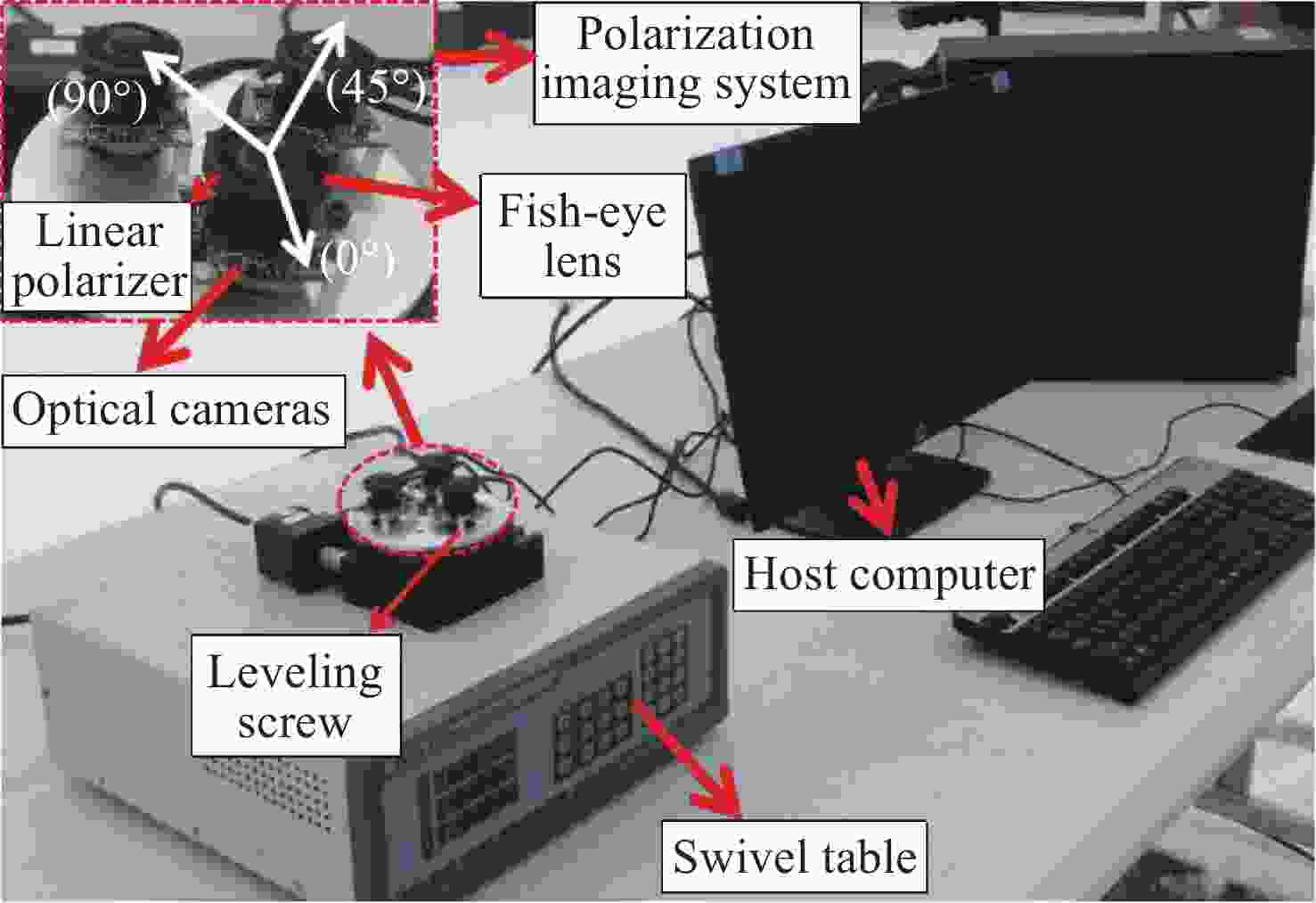
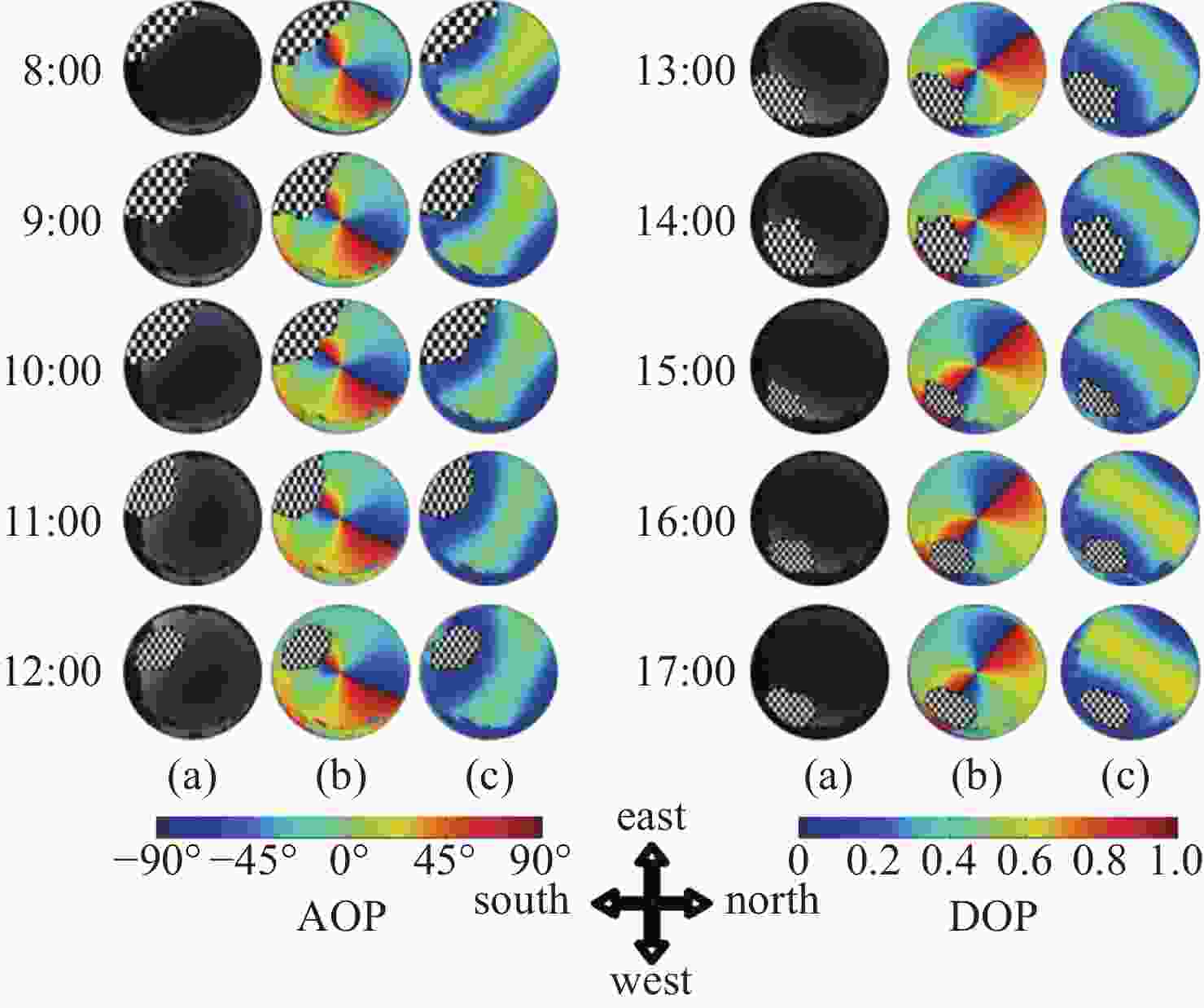
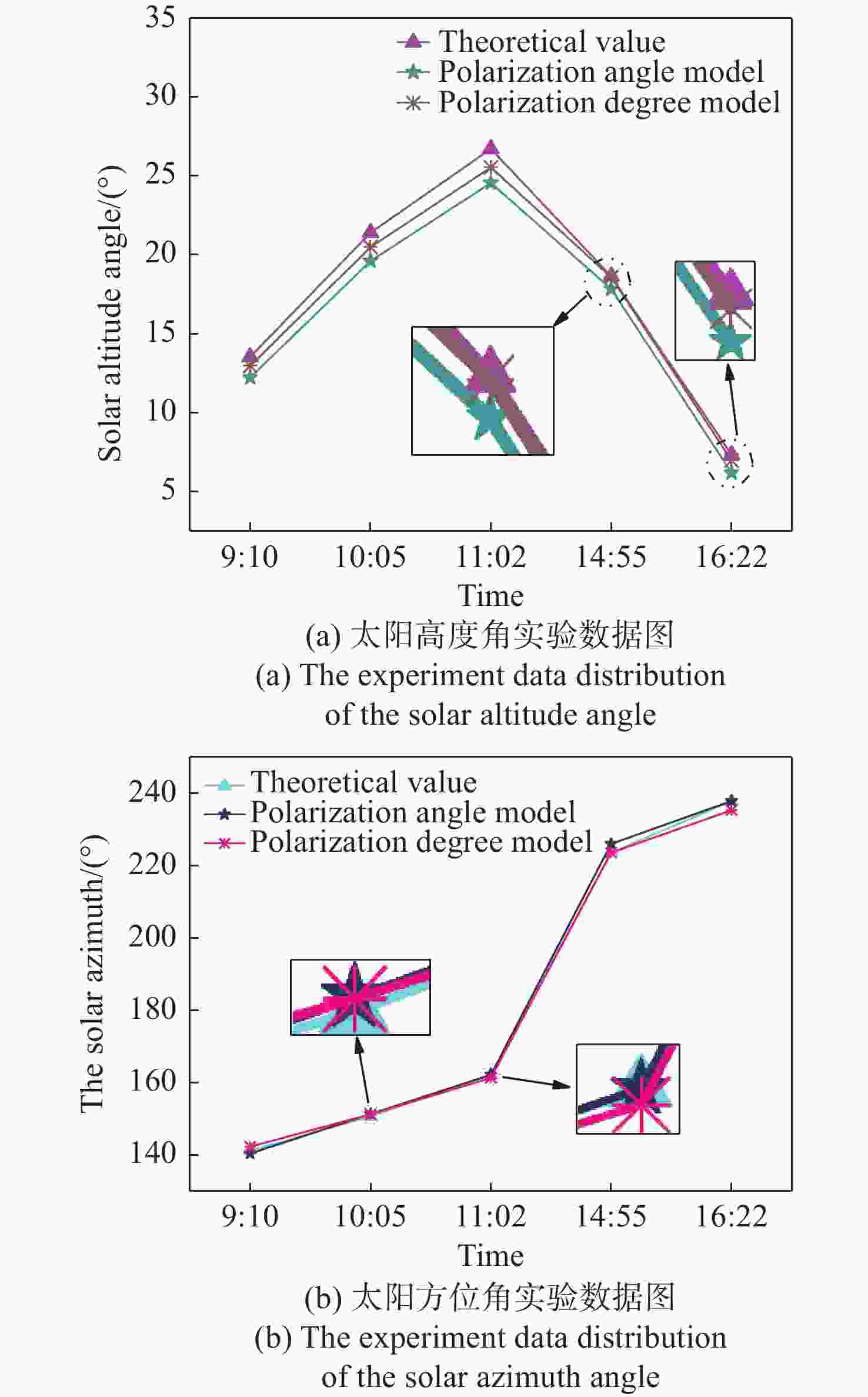
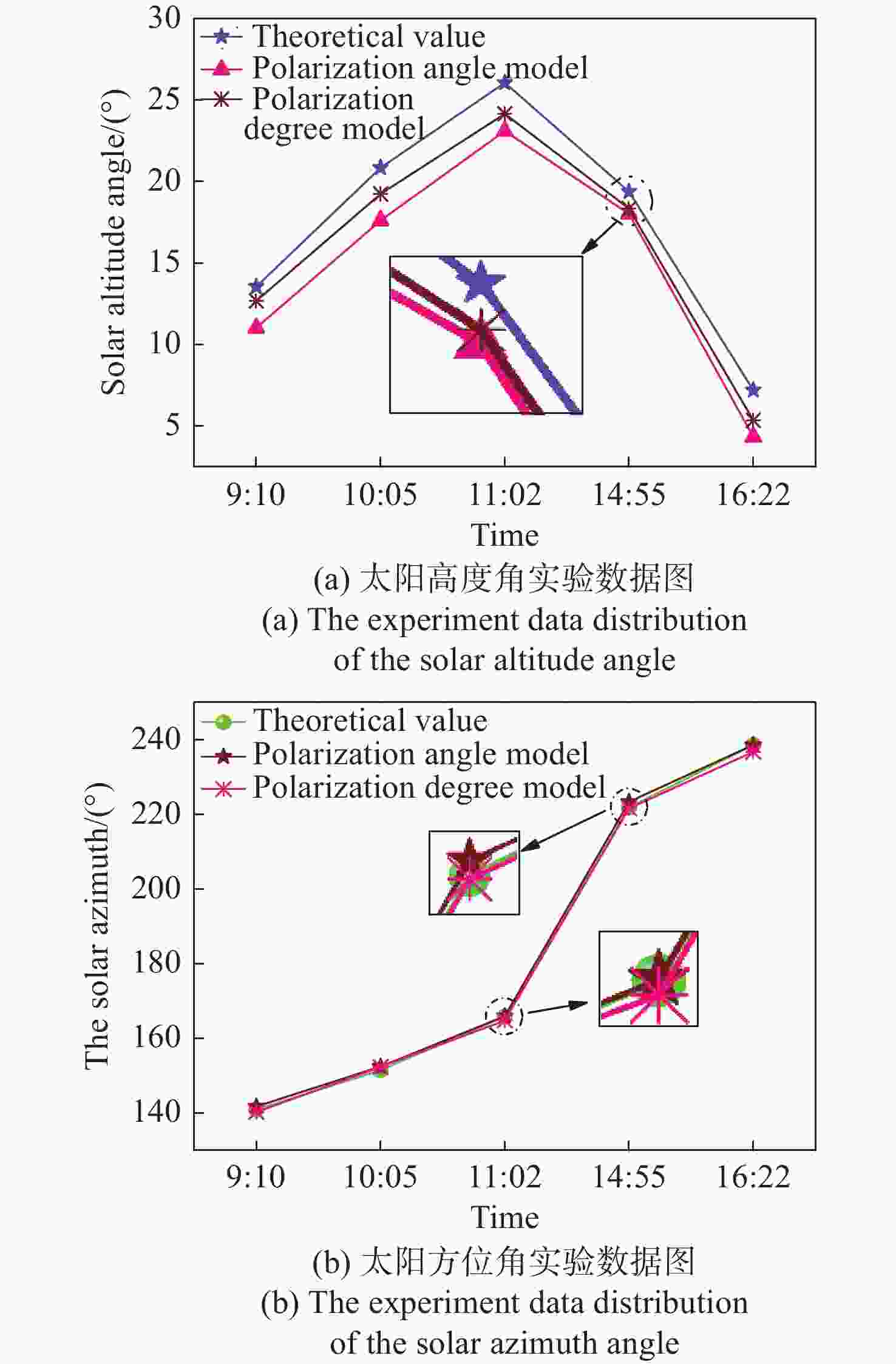
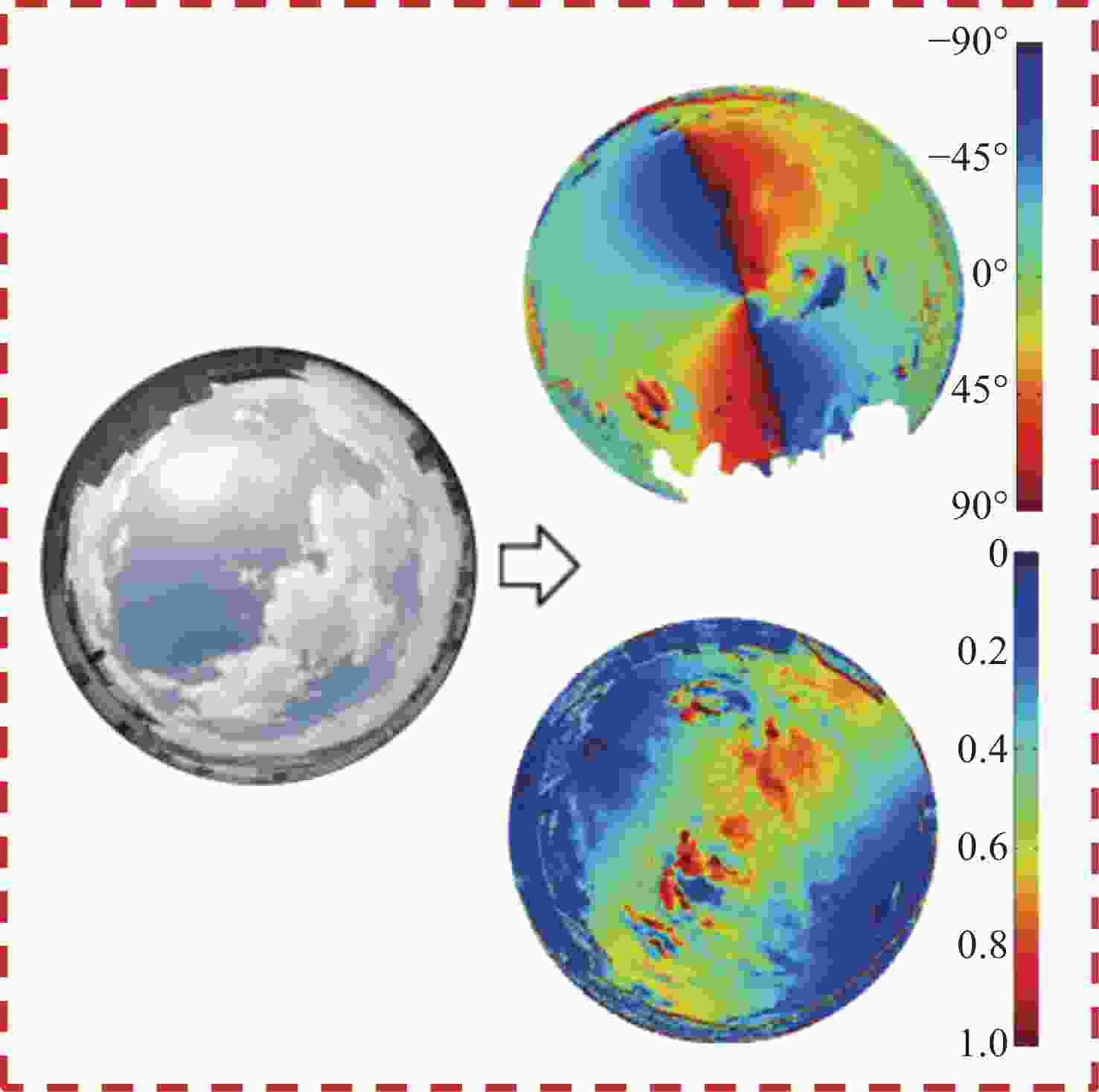
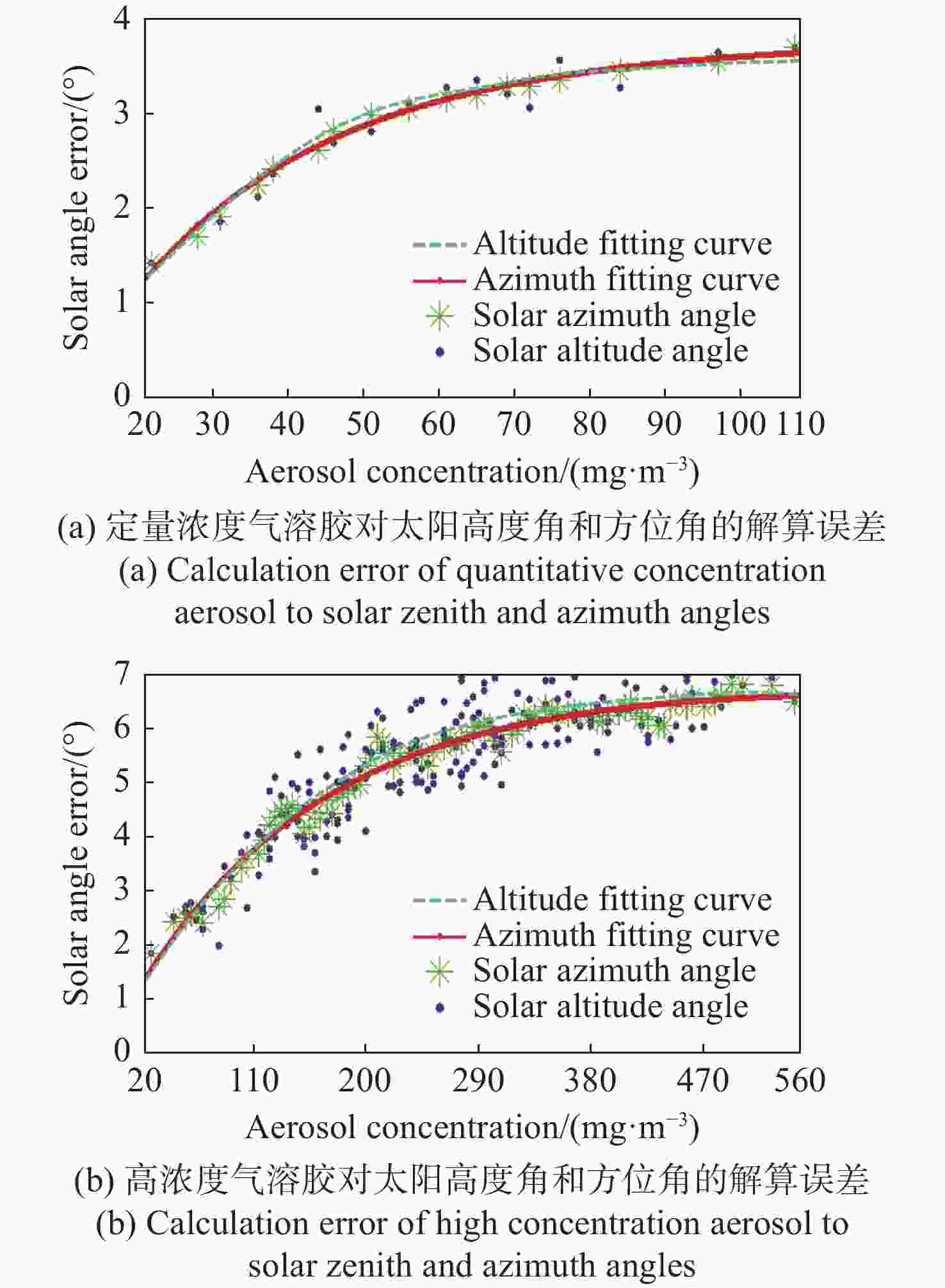
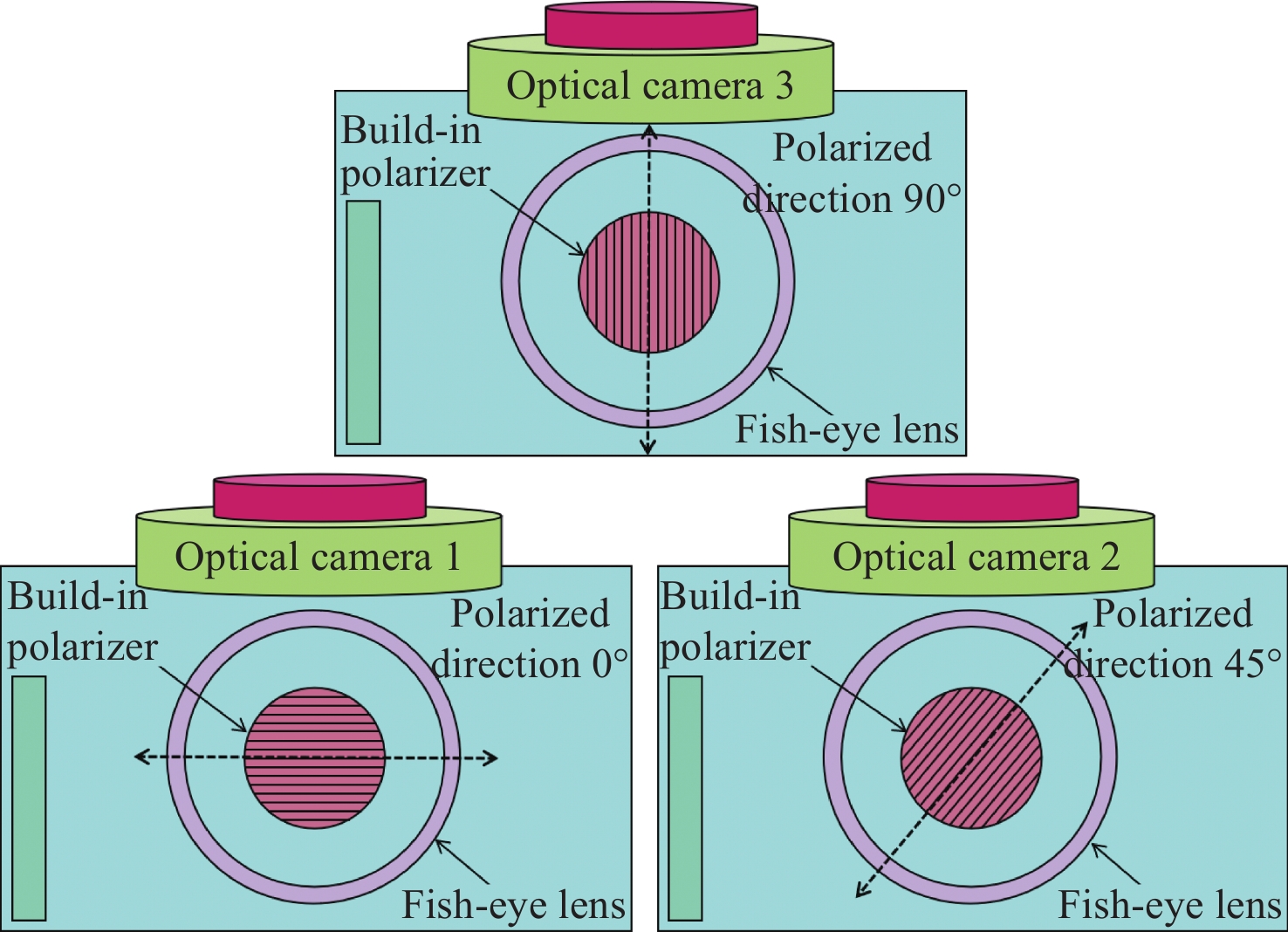
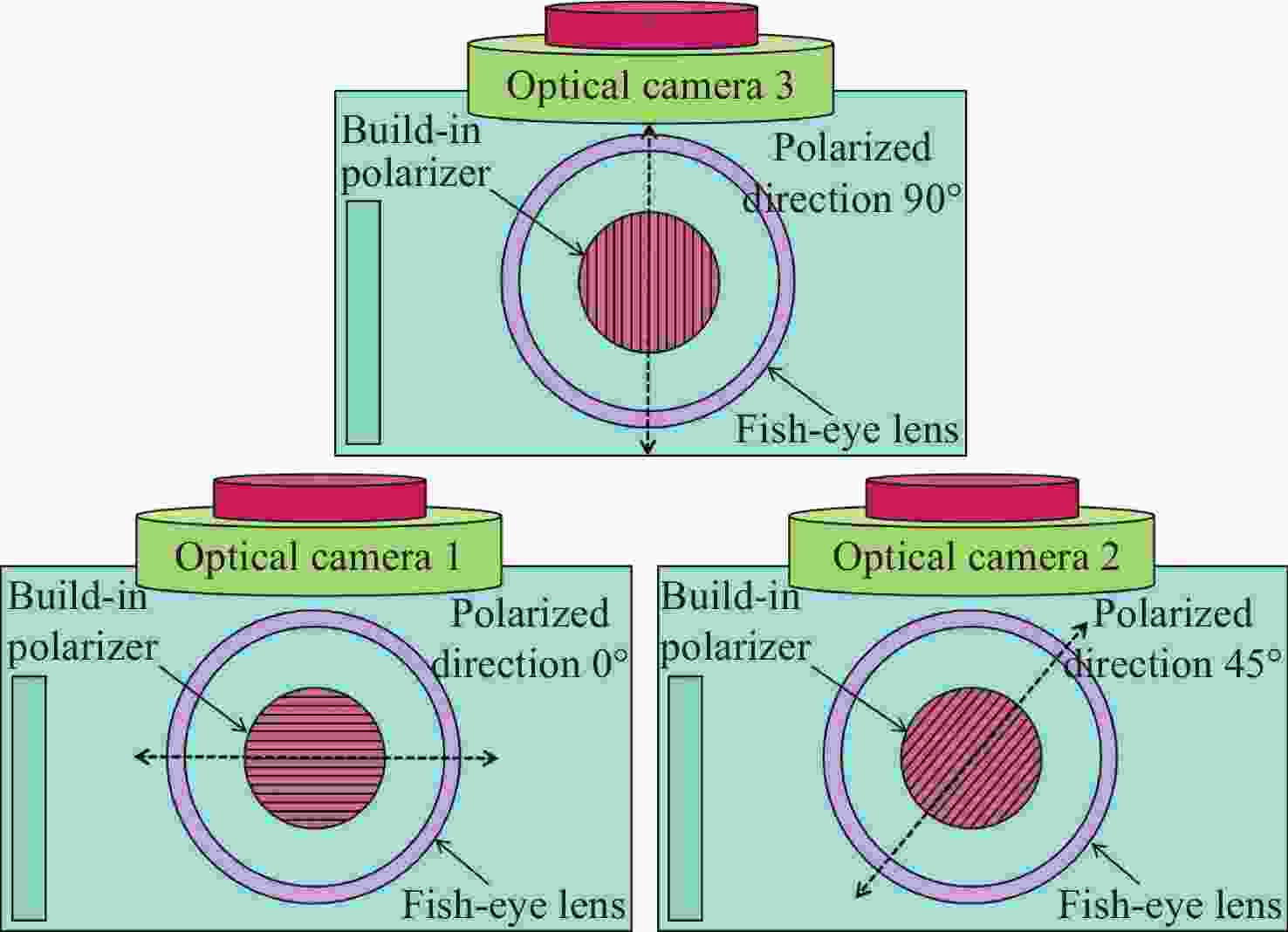
针对偏振光导航对天空中特征点精确位置信息的需求,提出一种基于全天域偏振模式成像系统对太阳位置进行精确检测的方法。与传统的基于光斑的太阳位置检测方法相比,该方法利用大气中固有的偏振信息完成对太阳位置的精确测量,具有检测方法简单、精度高且适用范围广等特点。搭建的光学采集系统由三个微小型的大视场摄像头模组和偏振片构成,使得结构更加紧凑,体积更小,高度更低。从原理出发,仿真分析太阳位置求解算法,采用搭建的光学采集系统对本算法在3种天气(晴天、遮挡、气溶胶)环境下进行验证。结果显示:当天气晴朗时,在同一天不同时刻,测量的太阳高度角和方位角的精度分别为0.024°和0.03°;当太阳被高层建筑物遮挡时,太阳的高度角和方位角的测量精度分别为0.08°和0.05°;当太阳被树木的枝叶遮挡时,太阳的高度角和方位角的测量精度分别为0.3°和0.1°。研究发现当气溶胶的浓度超过一定量时就会破坏偏振光的Rayleigh分布模式,进而会影响太阳位置的检测精度。实验结果表明,这种新型的检测方法不仅能够满足偏振光导航对太阳位置精确信息的需求,还能为喜欢探索宇宙奥秘的爱好者提供一种新的探索思路。
Abstract:Aiming at the requirement of polarized light navigation for accurate position information of feature points in the sky, an accurate detection method for the solar position of imaging system based on all sky polarization mode is proposed. Compared with the traditional detection method of the solar position based on spot, we use the inherent polarization information in the atmosphere to complete the accurate measurement of the solar position, which has the characteristics of simple, high accuracy and wide application range. The optical acquisition system consists of three micro large-field-of-view camera modules and polarizers, which makes the structure more compact, smaller and lower in height. Starting from the principle, the algorithm of solving the solar position is simulated first, and then the algorithm is verified in three weather environments (sunny, occluded, and aerosol) using the optical acquisition system. It can be seen that when the weather is clear, the sun is detected at different times of the same day, and the accuracy of the measured sun's altitude and azimuth are 0.024° and 0.03° respectively; when the sun is blocked by high-rise buildings, the accuracy of the measured sun's altitude and azimuth are 0.08° and 0.05°; when the sun is blocked by the branches and leaves of trees, the accuracy of the measured sun's altitude and azimuth are 0.3° and 0.1° respectively. Only when the aerosol concentration exceeds a certain amount will the Rayleigh distribution mode of polarized light be destroyed, which will affect the detection accuracy of solar position. The experimental results show that this new detection method can not only meet the needs of polarized light navigation for the solar position, but also provide a new way of exploration for fans who like to explore the mysteries of the universe.
-
Key words:
- atmospheric optics /
- atmospheric polarization mode /
- solar position /
- optical CCD
-
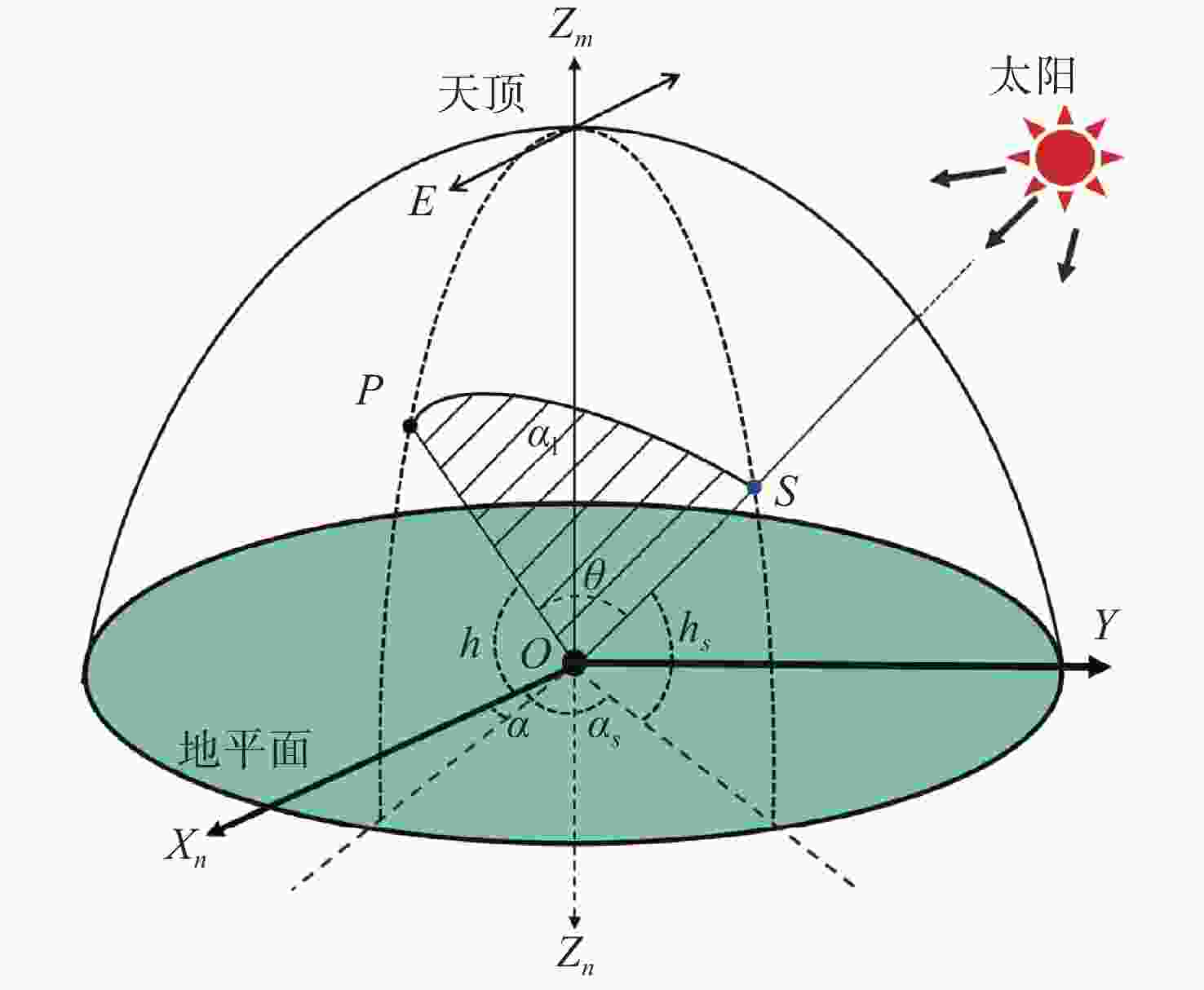
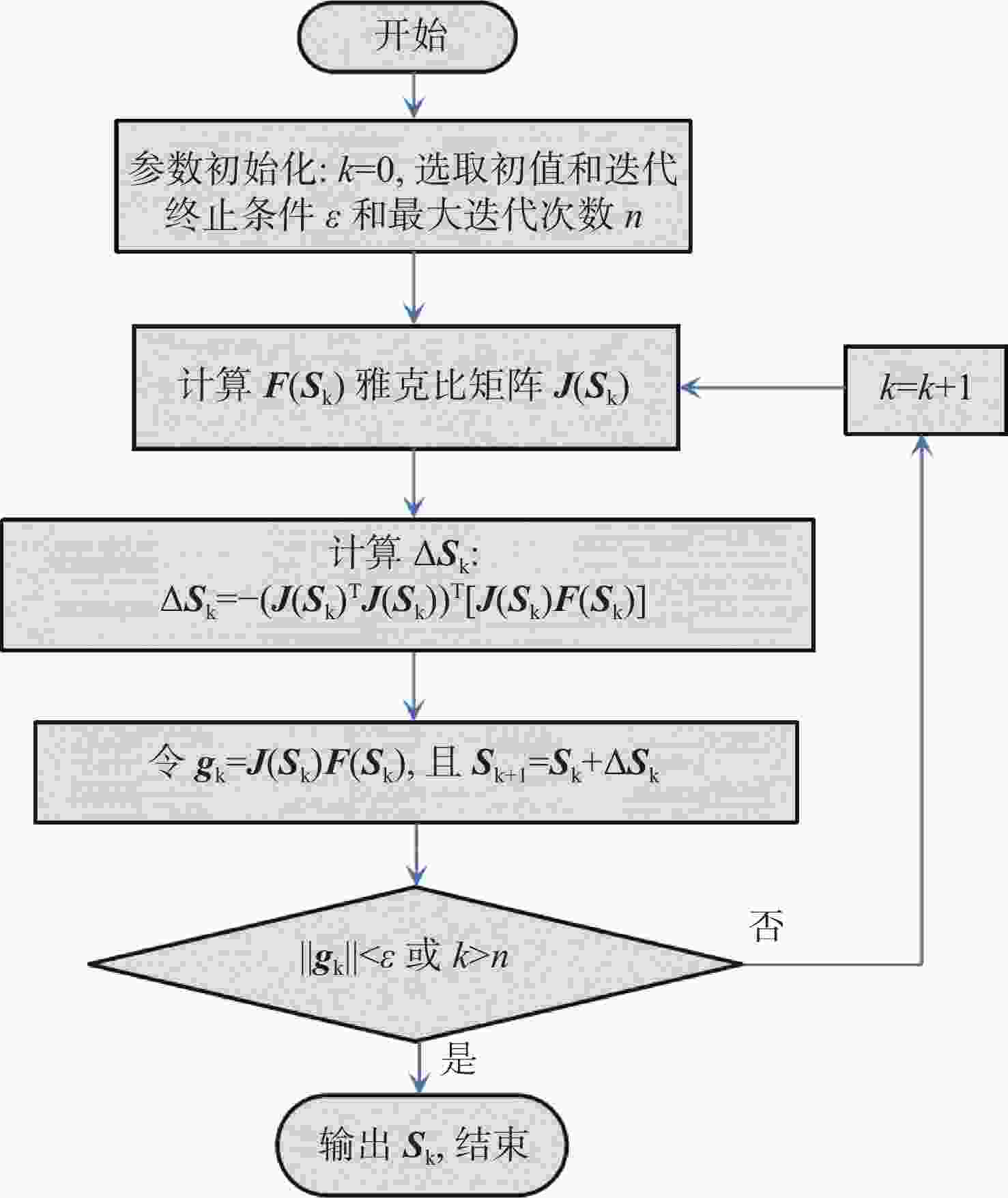
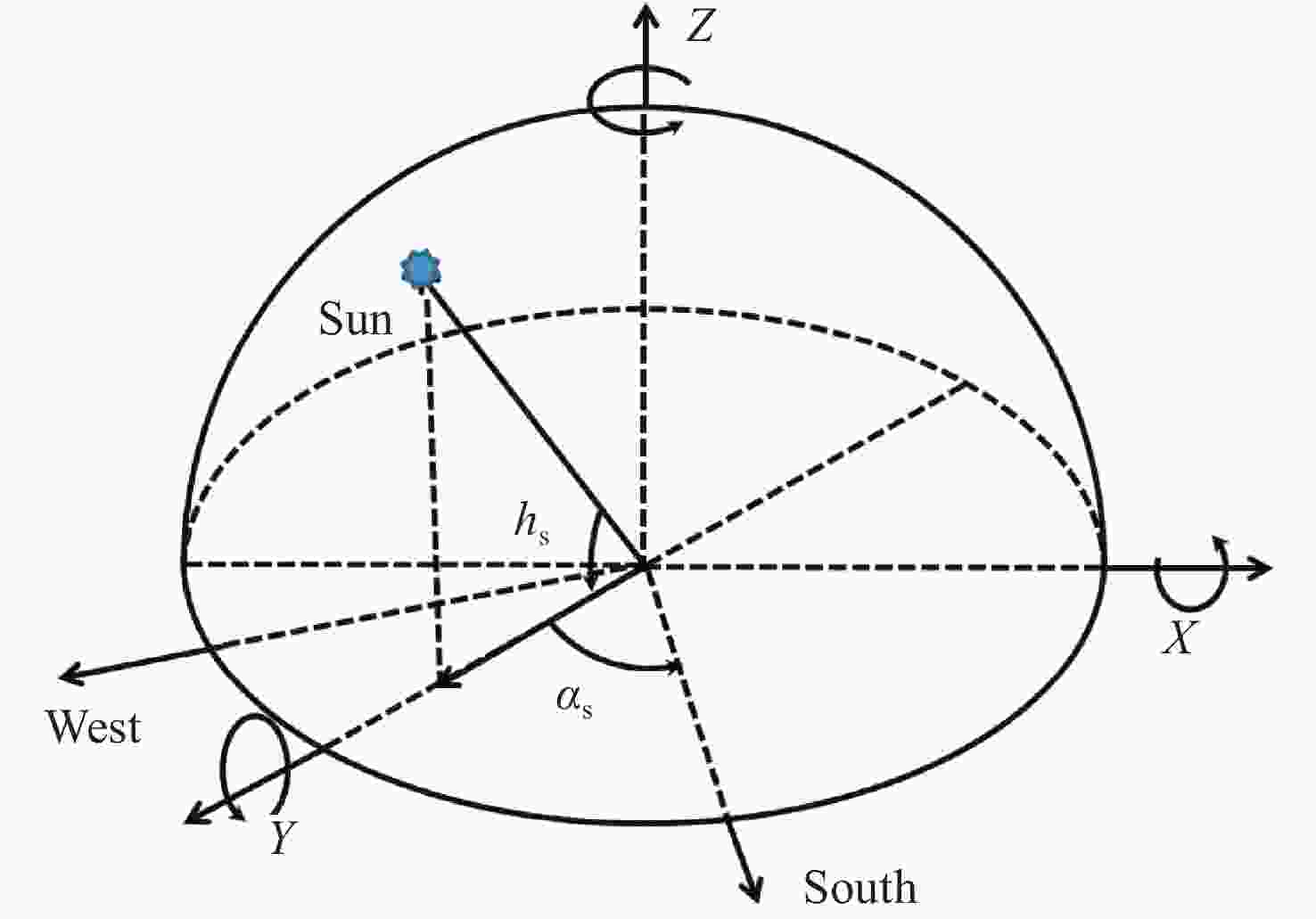
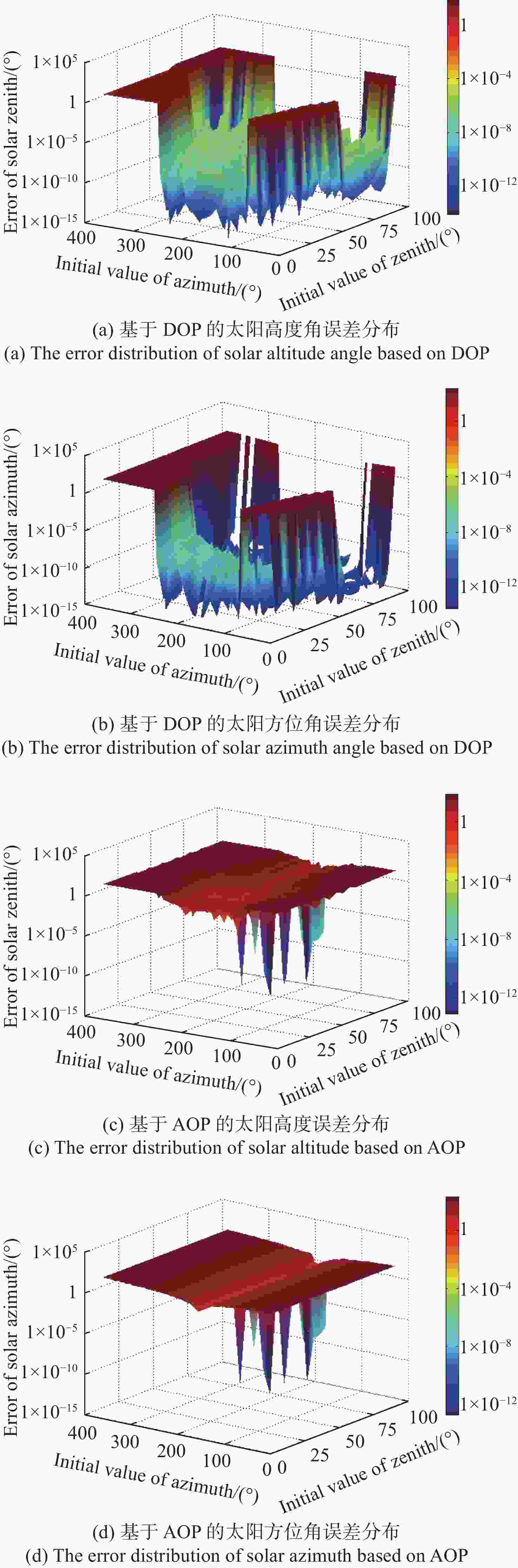
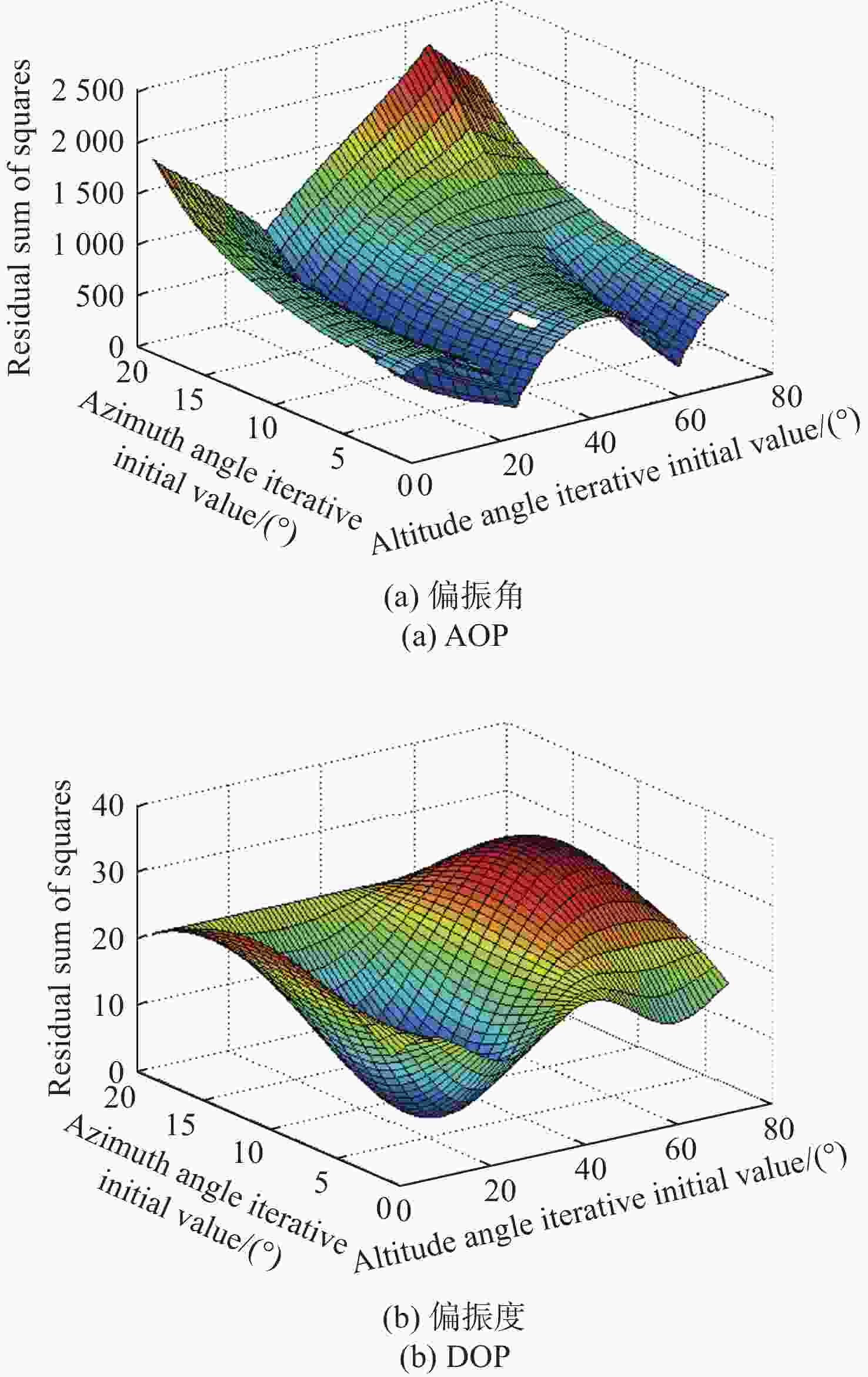
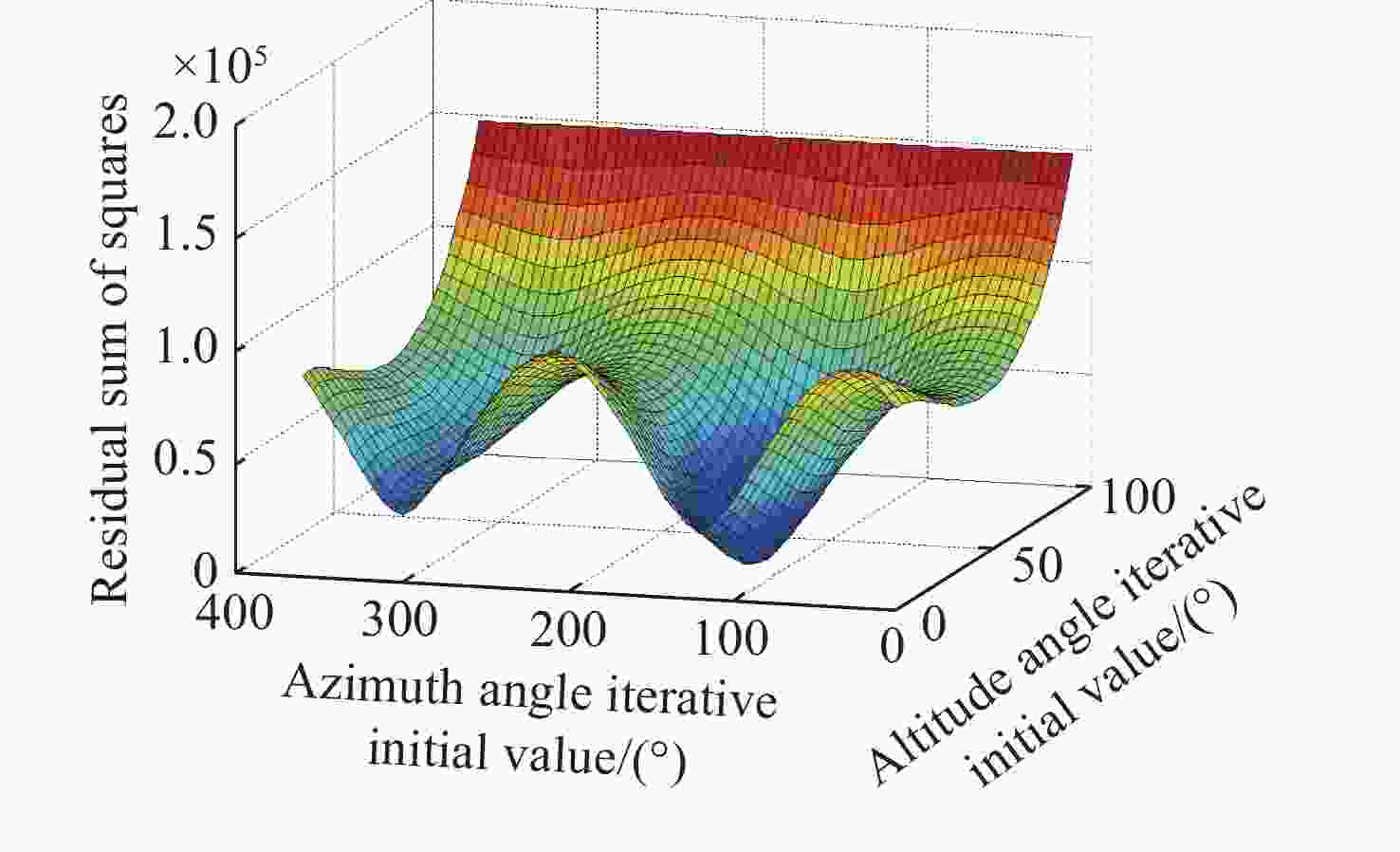
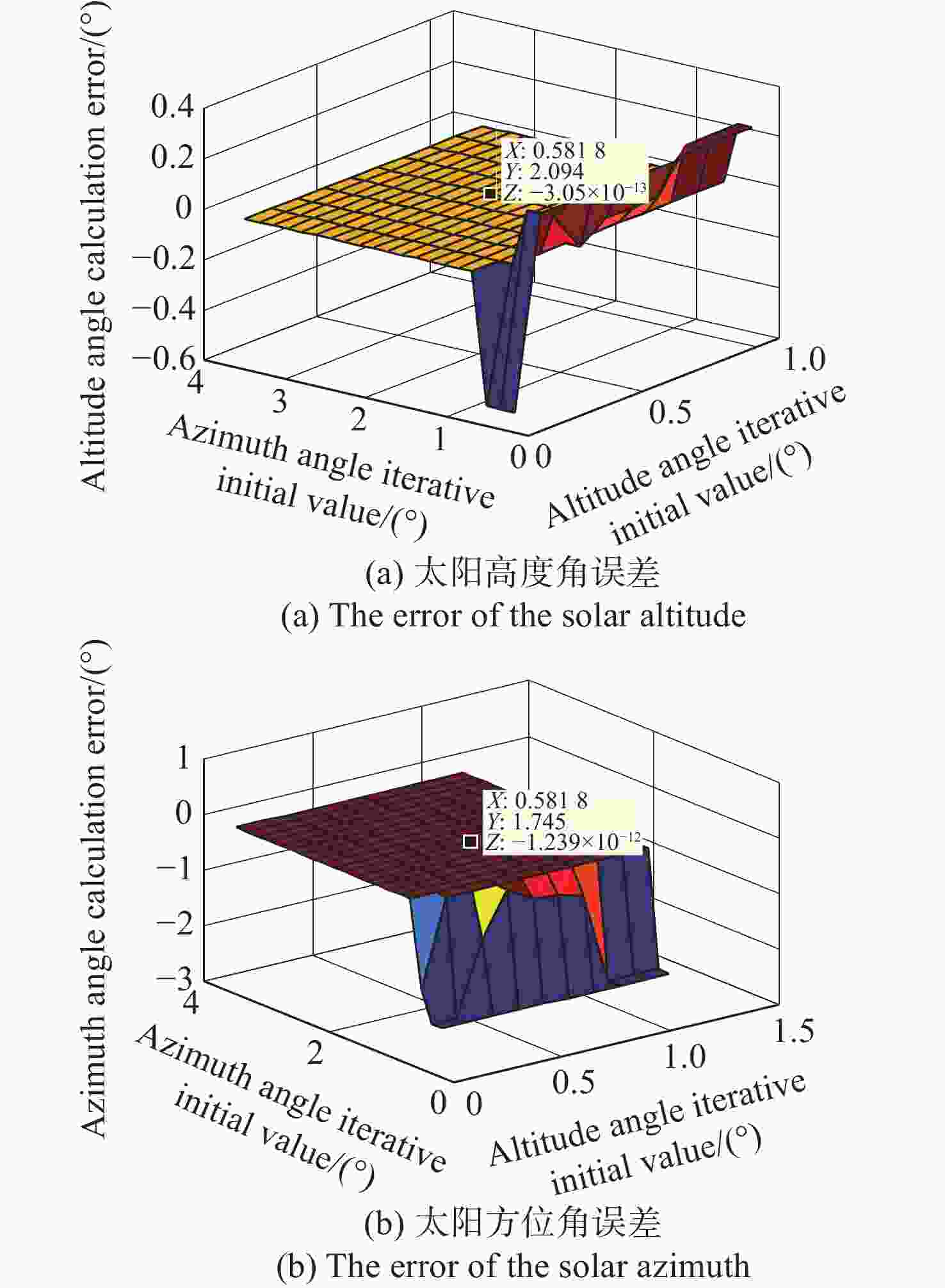
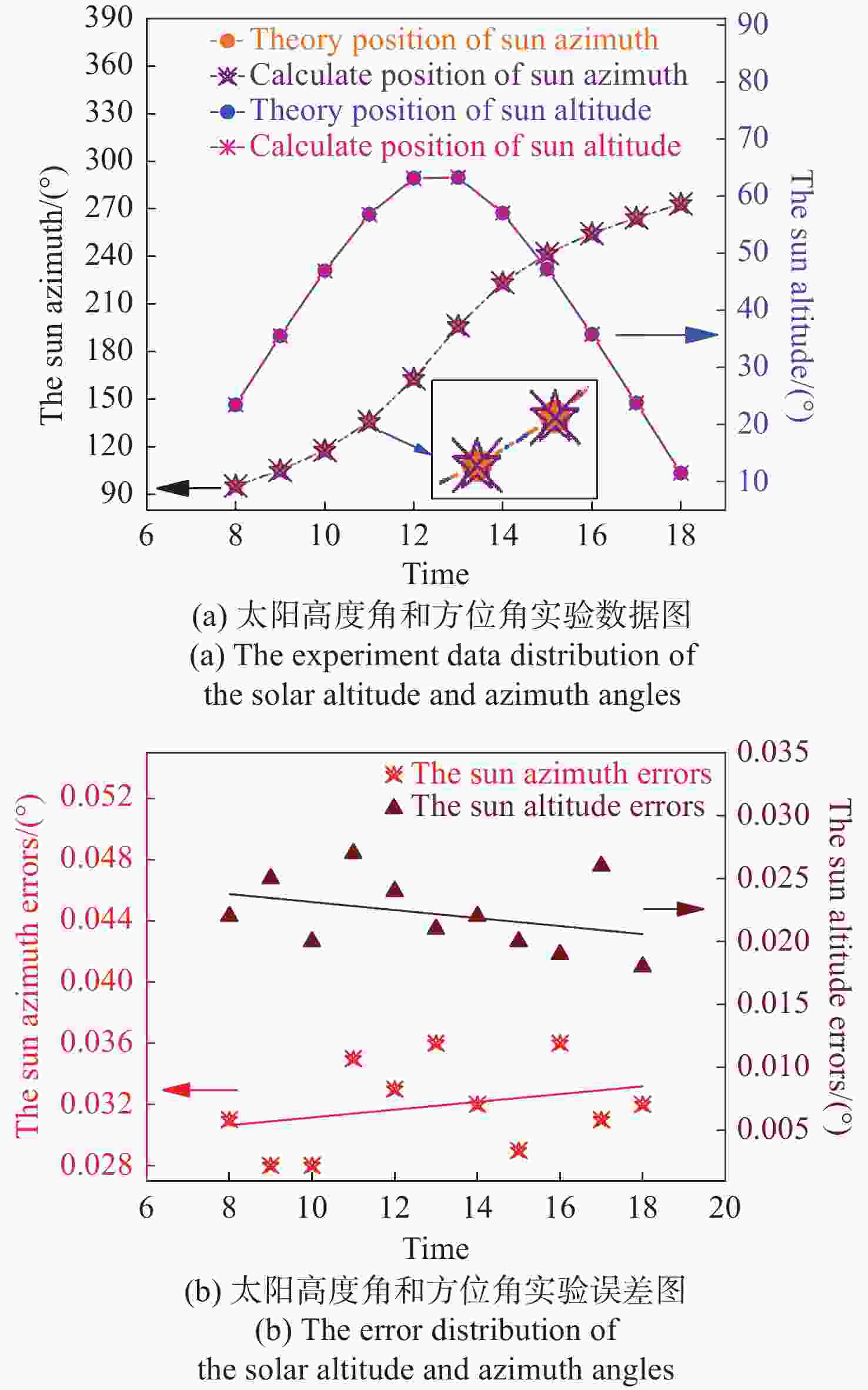
太阳位置的多次迭代算法 计算太阳的空间位置:$ {\boldsymbol{S}} = \left( {{h_{\rm{s}}},{\alpha _{\rm{s}}}} \right) $ 当 $ k = {\text{0}} $时 选取初始值 $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_{\text{0}}} $ 选择迭代终止条件 $ \varepsilon $>0,且为一个很小的常数 确定最大迭代次数 计算雅可比矩阵: 使用公式(11)计算雅克比矩阵 $ {\boldsymbol{J}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}} \right) $ 将$ \Delta \left( {{{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}} \right) $代入式(9)中的雅克比矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{J}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}} \right) $ $ {{\boldsymbol{g}}_k} = {\boldsymbol{J}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}} \right){\boldsymbol{F}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{S}}_k}} \right),{{\boldsymbol{S}}_{k + {\text{1}}}} = {{\boldsymbol{S}}_k} + \Delta {{\boldsymbol{S}}_k} $ 如果 $ \left\| {{{\boldsymbol{g}}_k}} \right\| \lt \varepsilon $,或者 $ k \gt n $,迭代停止 输出 $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_k} $ 结束 通过式(10)计算 $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_{k + {\text{1}}}} $ 迭代继续 如果 $ \left\| {{{\boldsymbol{g}}_k}} \right\| \geqslant \varepsilon $,或者 $ k \leqslant n $ 令$ k = k + {\text{1}} $ 计算雅克比矩阵 ... 直到 $ \left\| {{{\boldsymbol{g}}_k}} \right\| \lt \varepsilon $,$ k \gt n $,然后计算 $ {{\boldsymbol{S}}_k} $ 结束 计算 $ {h_{\rm{s}}} $,$ {\alpha _{\rm{s}}} $ 表 1 实验数据表
Table 1. Experiment data list
时间 太阳的理论位置 基于改进的偏振角
模型计算的太阳位置误差 $\alpha_s $ hs $\alpha_s $ hs $\alpha_s $ hs 8:00 95.333 23.450 95.365 23.472 0.031 0.022 9:00 105.216 35.529 105.189 35.554 −0.028 0.025 10:00 117.819 46.959 117.791 46.939 −0.028 −0.020 11:00 135.892 56.827 135.857 56.800 −0.035 −0.027 12:00 162.984 63.167 163.018 63.143 0.033 −0.024 13:00 196.214 63.255 196.178 63.276 −0.036 0.021 14:00 223.550 57.040 223.519 57.063 −0.032 0.022 15:00 241.809 47.232 241.838 47.212 0.029 −0.020 16:00 254.509 35.826 254.545 35.807 0.036 −0.019 17:00 264.438 23.757 264.469 23.783 0.031 0.026 18:00 273.160 11.486 273.192 11.504 0.032 0.018 -
[1] WANG X H, WANG J P, ZHANG CH W. Research of an omniberaing sun locating method with fisheye picture based on transform domain algorithm[C]. Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing in Signal Processing and Pattern Recognition, Springer, 2006: 1169-1174. [2] 刘鹏, 吴瑞梅, 杨普香, 等. 基于计算机视觉技术的茶叶品质随机森林感官评价方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2019,39(1):193-198.LIU P, WU R M, YANG P X, et al. Study of sensory quality evaluation of tea using computer vision technology and forest random method[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(1): 193-198. (in Chinese). [3] ZHANG W J, CAO Y, ZHANG X ZH, et al. Angle of sky light polarization derived from digital images of the sky under various conditions[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(3): 587-595. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.000587 [4] LU H, ZHAO K CH, WANG X CH, et al. Real-time imaging orientation determination system to verify imaging polarization navigation algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(2): 144. doi: 10.3390/s16020144 [5] 杨菁华. 基于无人机机载异类传感器的高超声速目标定位关键技术[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018.YANG J H. Research on key technology of hypersonic target location based on airborne heterogeneous sensors of UAV[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018. (in Chinese). [6] 杨江涛, 王健安, 王银, 等. 基于大气偏振模式的三维姿态角解算方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(22):221107.YANG J T, WANG J A, WANG Y, et al. Calculation method of three-dimensional attitude angle based on atmospheric polarization pattern[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(22): 221107. (in Chinese). [7] 顾敬桥, 李高杰, 胡鹏伟, 等. 基于大气多次散射的波浪水下偏振模式研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1324-1332. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0223GU J Q, LI G J, HU P W, et al. The polarization mode of underwater waves based on atmospheric multiple scattering[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1324-1332. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0223 [8] 杨江涛, 王健安, 王银, 等. 基于柔性材料的亚波长金属光栅偏振器的关键技术研究[J]. 中国激光,2020,47(11):1113004. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.1113004YANG J T, WANG J A, WANG Y, et al. Sub-wavelength metal-grating polarizer fabricated on a flexible substrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(11): 1113004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.1113004 [9] YANG J T, WANG J A, WANG Y, et al. Algorithm design and experimental verification of a heading measurement system based on polarized light/inertial combination[J]. Optics Communications, 2021, 478: 126402. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126402 [10] TANG J, ZHANG N, LI D L, et al. Novel robust skylight compass method based on full-sky polarization imaging under harsh conditions[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(14): 15834-15844. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.015834 [11] ZHAO H J, XING J, GU X F, et al. Polarization imaging in atmospheric environment based on polarized reflectance retrieval[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2019, 17(1): 012601. doi: 10.3788/COL201917.012601 [12] 张卫国. 海面太阳耀光背景下的偏振探测技术[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):231-236. doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0231ZHANG W G. Application of polarization detection technology under the background of sun flare on sea surface[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 231-236. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20181102.0231 [13] LAMBRINOS D. Navigation in desert ants: the robotic solution[J]. Robotica, 2003, 21(4): 407-426. doi: 10.1017/S0263574703005058 [14] YANG J T, XU X Y, CHEN X, et al. Polarized light compass-aided inertial navigation under discontinuous observations environment[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(11): 19665-19683. doi: 10.1364/OE.459870 [15] 王威, 褚金奎, 崔岩, 等. 基于矢量辐射传输的大气偏振建模[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(5):0513001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0513001WANG W, CHU J K, CUI Y, et al. Modeling of atmospheric polarization pattern based on vector radiative transfer[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(5): 0513001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0513001 [16] 褚金奎, 陈文静, 王洪青, 等. 基于偏振光传感器的移动机器人导航实验[J]. 光学 精密工程,2011,19(10):2419-2426. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111910.2419CHU J K, CHEN W J, WANG H Q, et al. Mobile robot navigation tests with polarization sensors[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2011, 19(10): 2419-2426. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111910.2419 [17] 褚金奎, 张然, 王志文, 等. 仿生偏振光导航传感器研究进展[J]. 科学通报,2016,61(23):2568-2577. doi: 10.1360/N972015-01163CHU J K, ZHANG R, WANG ZH W, et al. Progress on bio-inspired polarized skylight navigation sensor[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(23): 2568-2577. (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N972015-01163 [18] 李逸博, 高隽, 王昕, 等. 独立通道偏振罗盘信息检测方法及传感器设计[J]. 光电工程,2015,42(7):12-18.LI Y B, GAO J, WANG X, et al. Independent channel measurement method of polarization compass information and the design of sensor[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2015, 42(7): 12-18. (in Chinese). [19] 甘鑫, 高欣健, 钟彬彬, 等. 基于有限样本的大气偏振模式生成方法[J]. 光电工程,2021,48(5):200331.GAN X, GAO X J, ZHONG B B, et al. A few-shot learning based generative method for atmospheric polarization modelling[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2021, 48(5): 200331. (in Chinese). [20] 范之国, 陈曼丽, 王波, 等. 基于大气偏振模式的三维姿态信息获取[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(6):1248-1256. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162406.1248FAN ZH G, CHEN M L, WANG B, et al. Three-dimensional attitude information obtained by the skylight polarization pattern[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(6): 1248-1256. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162406.1248 -





 下载:
下载: