-
摘要:
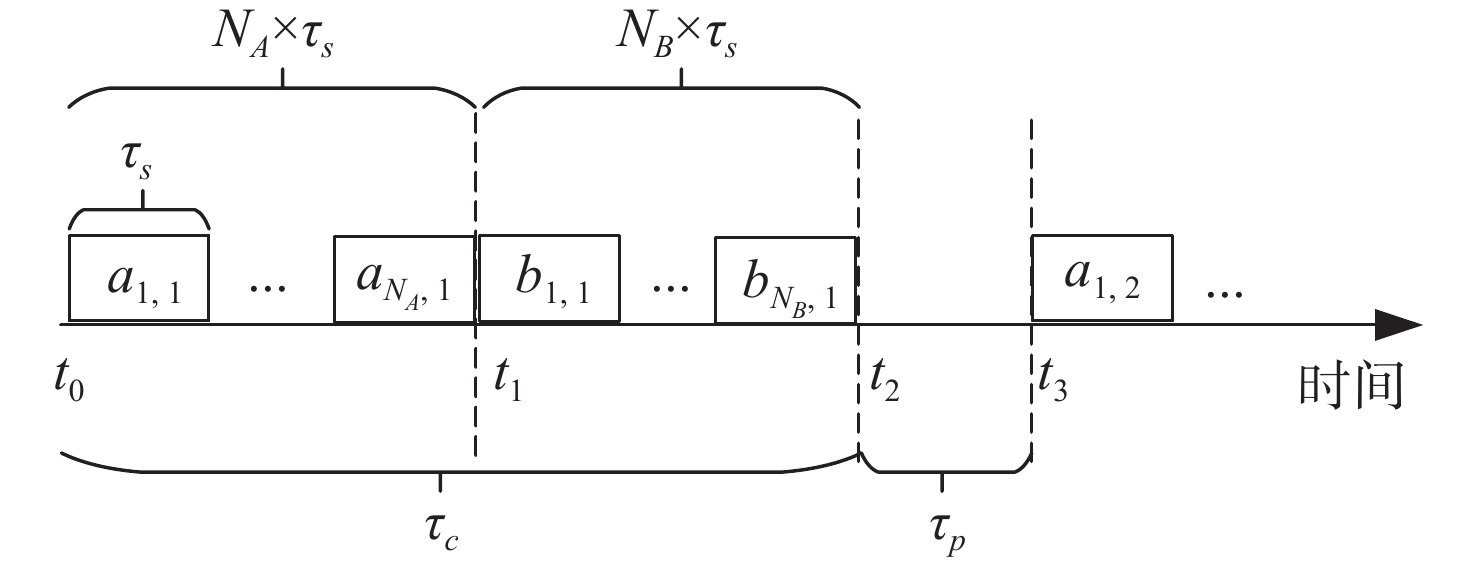
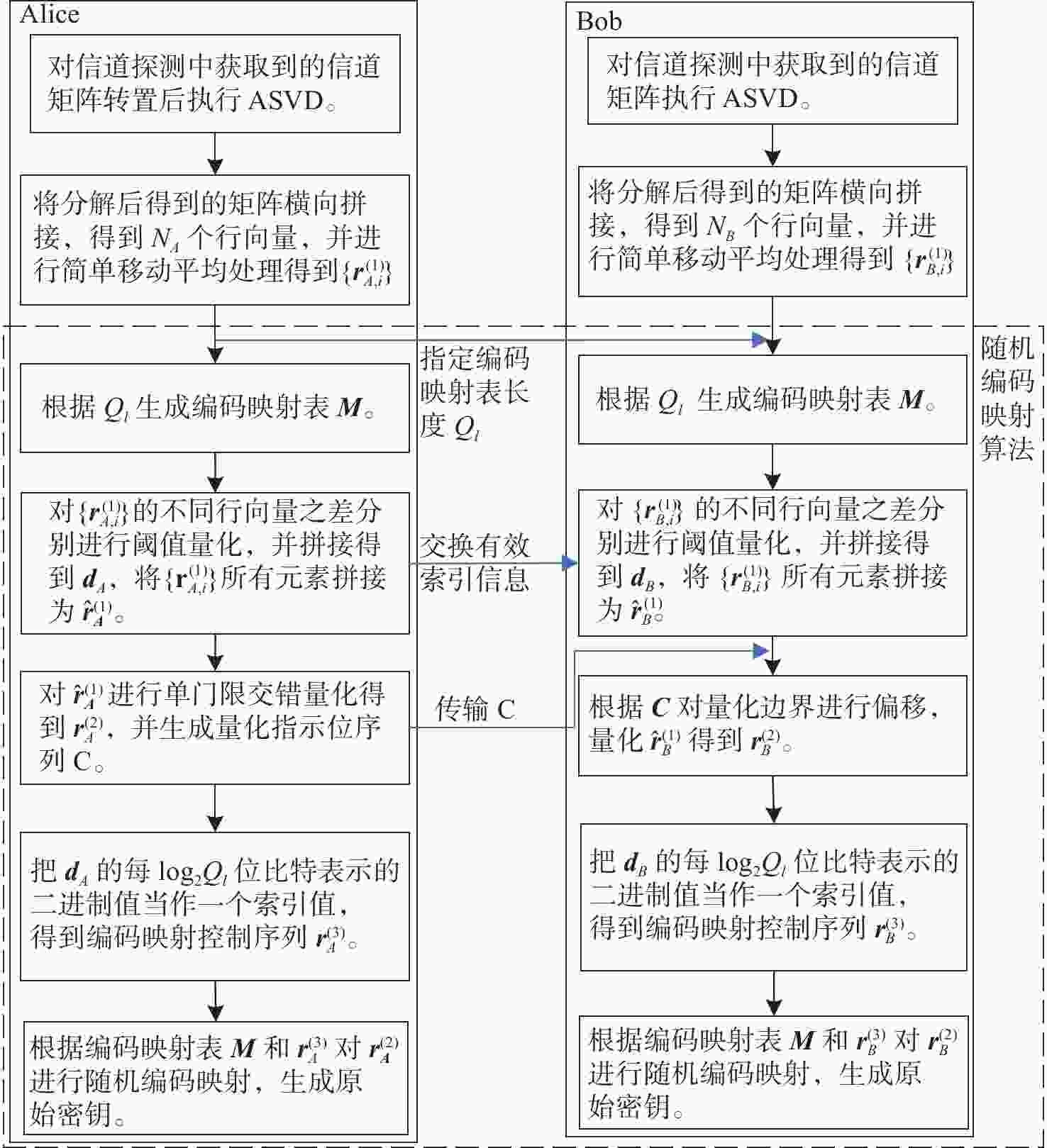
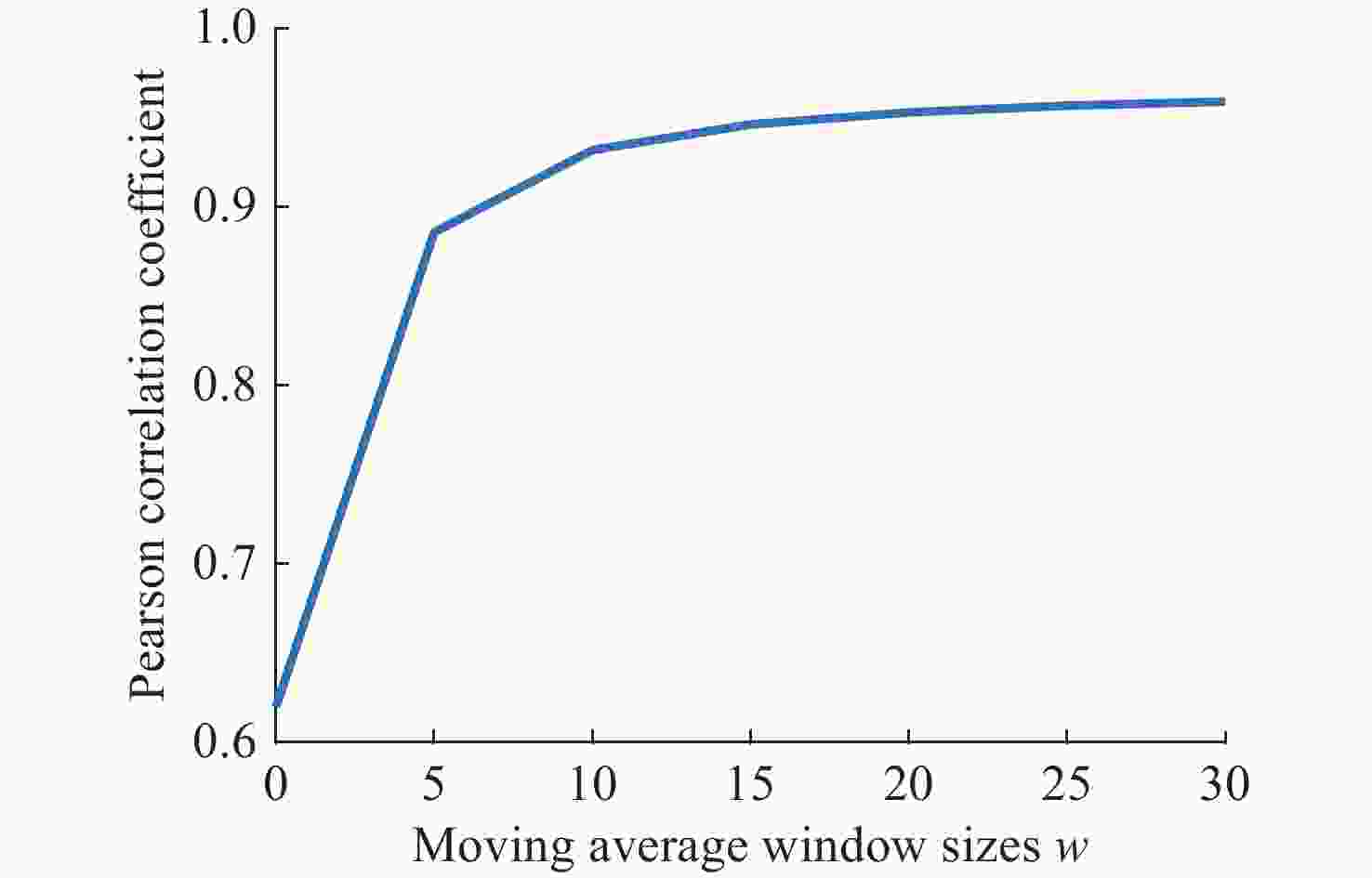
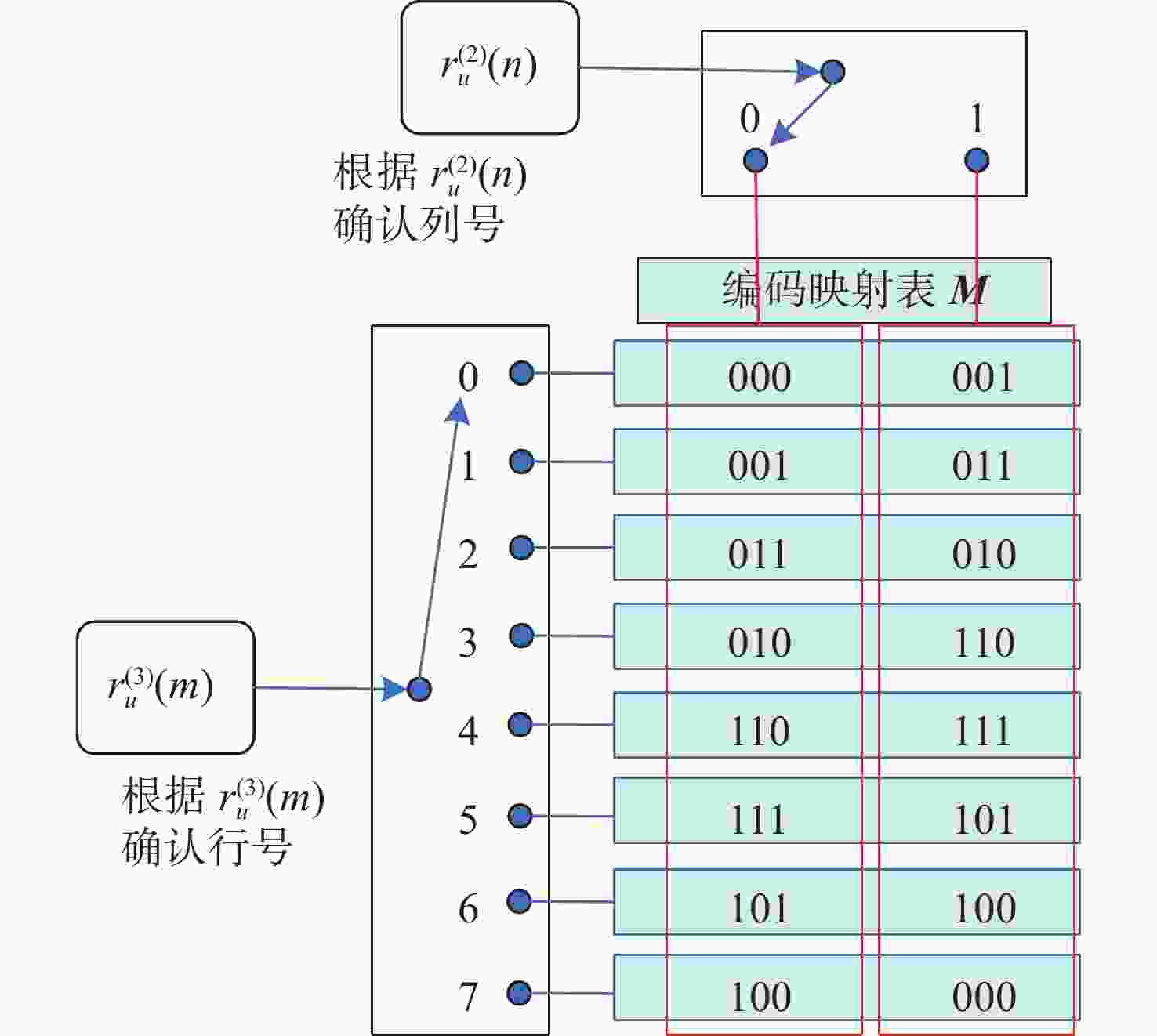
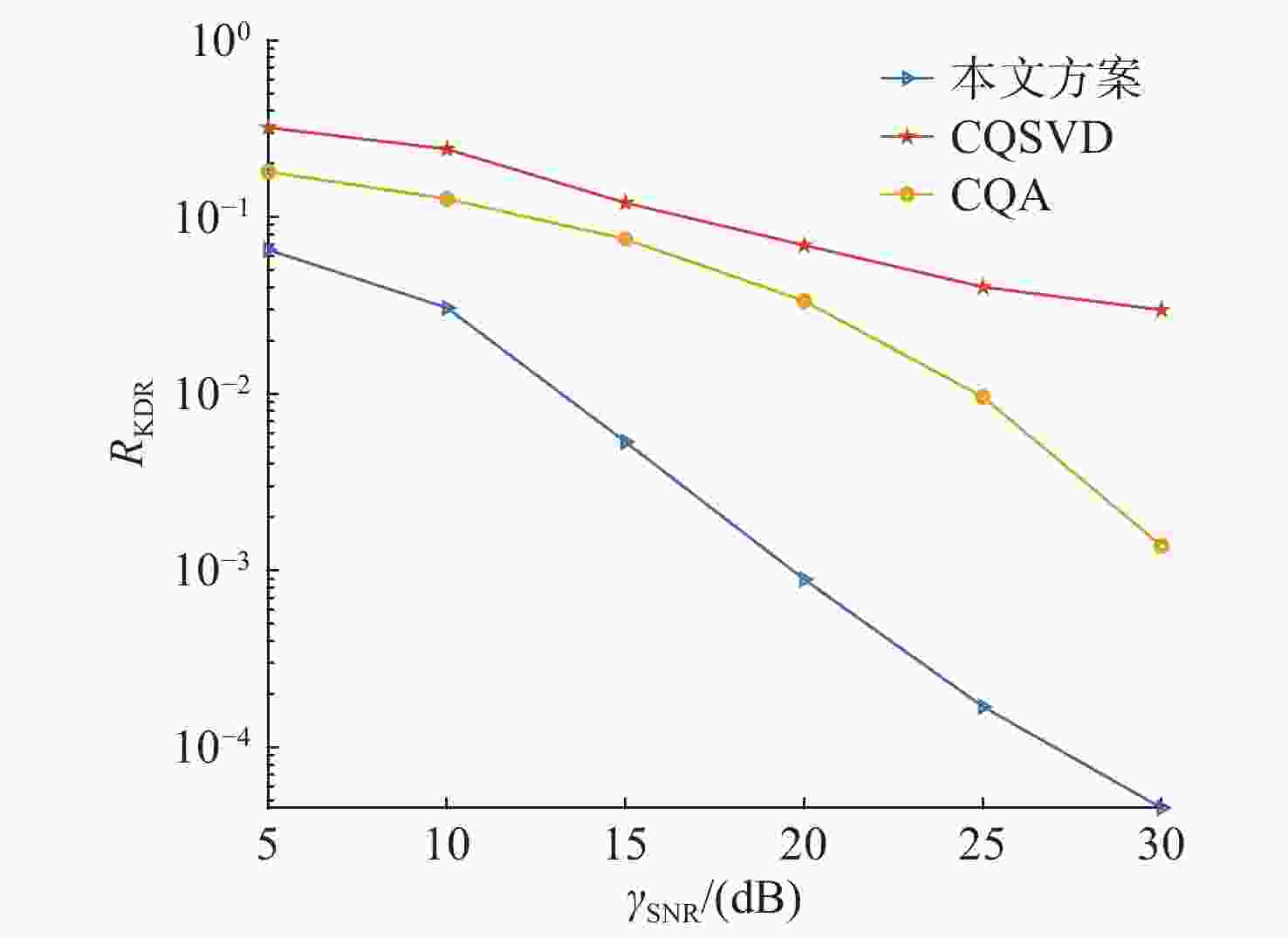
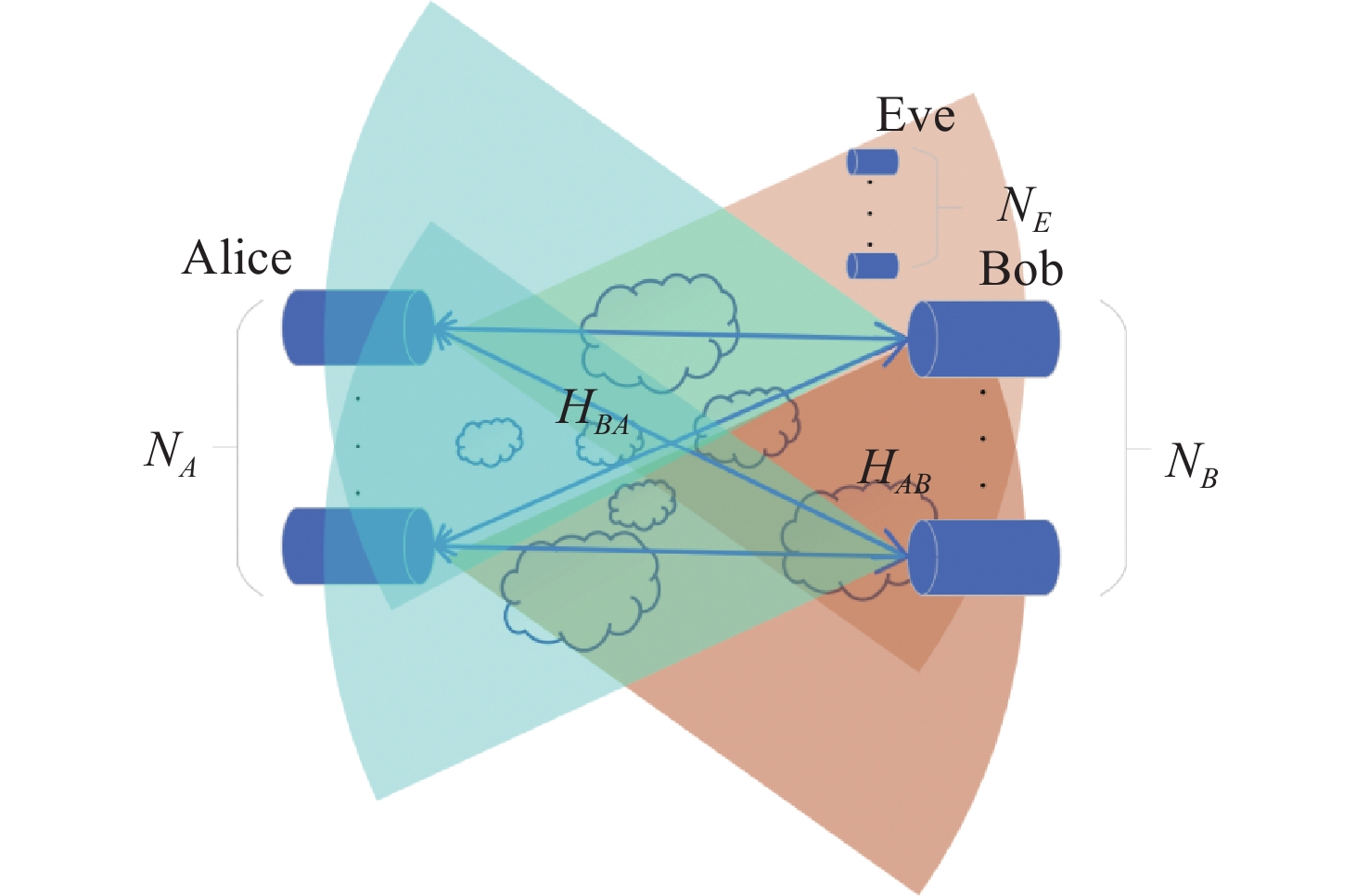
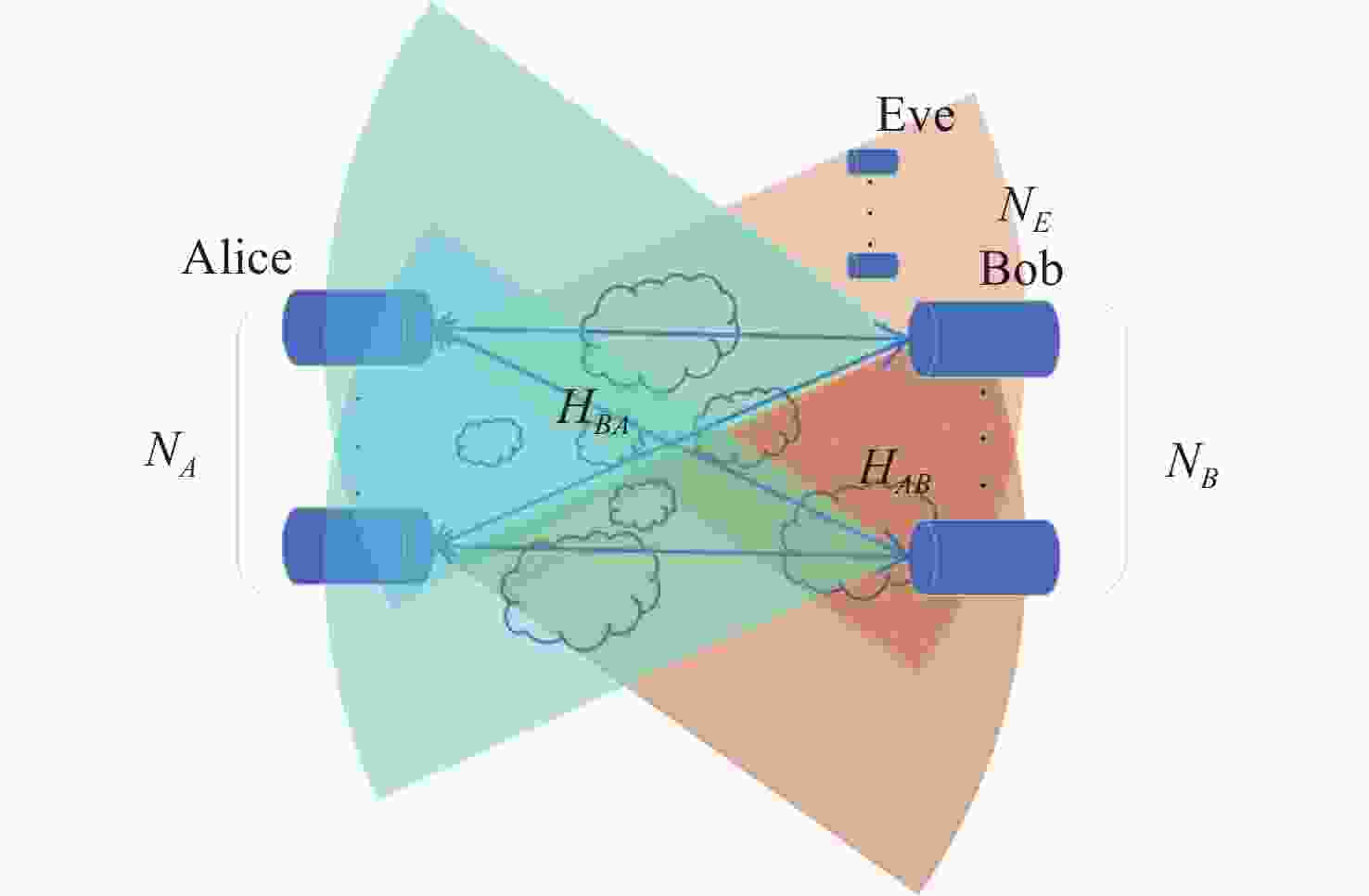
基于信道随机特征的共享密钥提取是实现大气光信道物理层安全的一种有效手段。密钥生成速率和不一致率是关注焦点。利用大气湍流光信道随机特征作为共享随机源,提出多输入-多输出(multiple-input multiple-output, MIMO)大气光信道环境下的密钥提取方案。采用另类奇异值分解法来分解信道矩阵,通过简单移动平均提升合法双方获得的信道特征序列间的相关性,并对移动平均后的信道特征序列进行单门限交错量化。合法双方基于分集差分值生成编码映射控制随机序列,实现对信道特征序列的单门限交错量化结果的编码映射。实验结果表明,本文方案的原始密钥不一致率在信噪比为30 dB时能够达到4.5×10−5,且生成的随机比特序列可通过美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)的随机性测试。本文结果对MIMO大气光信道密钥提取有一定参考价值。
Abstract:Shared secret-key extraction from random channel characteristics is an effective approach to ensuring the physical layer security of atmospheric optical channels. The secret-key generation rate and disagreement rate are two issues that attract a lot of attention. Using the random characteristics of atmospheric turbulent optical channels as a shared source of randomness, a secret-key extraction scheme for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) atmospheric optical channels is proposed. The alternative singular value decomposition is used to decompose the channel matrix; the correlation between the two channel characteristic sequences obtained by the two legitimate parties is enhanced through a simple moving average, and the single-threshold interleaved quantization is performed on the channel characteristic sequences after moving average. The two legitimate parties generate random controlling sequences for coding mapping based on differential diversity values, in order to implement encoding mapping for the single threshold interleaved quantization results of the channel characteristic sequences. The experimental results show that our scheme’s initial key disagreement rate can reach 4.5×10−5 at a signal-to-noise ratio of 30 dB, and that the generated random bit sequences have passed the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) randomness test. The results are useful in the implementation of secret-key extraction from atmospheric MIMO optical channels.
-
Key words:
- MIMO /
- optical channel /
- atmospheric turbulence /
- secret-key extraction /
- quantization
-
表 1 NIST随机性测试结果
Table 1. NIST randomness test results
Test Average P-value 频率 0.066882 块内频率 0.058146 游程 0.350485 最大游程 0.213309 二进制矩阵秩 0.065429 离散傅立叶变换 0.534971 非重叠字匹配 0.739913 重叠字匹配 0.911413 线性复杂度 0.739918 串行 0.122325 0.035174 累积和 0.064229 0.067324 -
[1] 王潋, 周媛媛, 周学军, 等. 泡沫覆盖不规则海面的非均匀空-水信道量子密钥分发[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2019,12(6):1362-1375. doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1362WANG L, ZHOU Y Y, ZHOU X J, et al. Quantum key distribution based on heterogeneous air-water channels with foam-covered irregular sea surfaces[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1362-1375. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1362 [2] 向磊, 陈纯毅, 姚海峰, 等. 双向大气湍流光信道瞬时衰落相关特性测量[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2019,12(5):1100-1108. doi: 10.3788/co.20191205.1100XIANG L, CHEN CH Y, YAO H F, et al. Measurement of instantaneous-fading correlation in bidirectional optical channels through atmospheric turbulence[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(5): 1100-1108. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20191205.1100 [3] CHEN CH Y, YANG H M. Shared secret key generation from signal fading in a turbulent optical wireless channel using common-transverse-spatial-mode coupling[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(13): 16422-16441. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.016422 [4] CHEN CH Y. Sample-grouping-based vector quantization for secret key extraction from atmospheric optical wireless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(11): 8905-8918. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3170724 [5] WANG L, AN H N, ZHU H J, et al. MobiKey: mobility-based secret key generation in smart home[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7590-7600. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2986399 [6] 黄开枝, 金梁, 钟州. 5G物理层安全技术——以通信促安全[J]. 中兴通讯技术,2019,25(4):43-49.HUANG. K ZH, JIN L, ZHONG ZH. 5G physical layer security technology: enhancing security by communication[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2019, 25(4): 43-49. (in Chinese) [7] HUANG L, GUO D K, XIONG J, et al. An improved CQA quantization algorithm for physical layer secret key extraction[C]. Proceeding of the 2020 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), IEEE, 2020: 829-834. [8] TANG J, WEN H, SONG H H, et al. Secure MIMO-SVD communications against eavesdroppers with any number of antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11077-11089. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3007430 [9] PREMNATH S N, GOWDA P L, KASERA S K, et al. Secret key extraction using Bluetooth wireless signal strength measurements[C]. 2014 Eleventh Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), IEEE, 2014: 293-301. [10] 高玉威, 熊俊, 郭登科, 等. 面向无人机空地通信的无线信道密钥生成技术研究[J]. 密码学报,2022,9(1):76-87.GAO Y W, XIONG J, GUO D K, et al. Design of key generation schemes for aerial communication scene of UAVs[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2022, 9(1): 76-87. (in Chinese). [11] FURQAN H M, HAMAMREH J M, ARSLAN H. Secret key generation using channel quantization with SVD for reciprocal MIMO channels[C]. 2016 International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), IEEE, 2016: 597-602. [12] WALLACE J W, SHARMA R K. Automatic secret keys from reciprocal MIMO wireless channels: measurement and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2010, 5(3): 381-392. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2010.2052253 [13] ZHAN F R, YAO N M, GAO ZH G, et al. Efficient key generation leveraging wireless channel reciprocity for MANETs[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 103: 18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.11.014 [14] YANG L, GAO Y S, ZHANG J Q, et al. A channel perceiving attack and the countermeasure on long-range IoT physical layer key generation[J]. Computer Communications, 2022, 191: 108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2022.04.027 [15] LU Y J, WU F, HUANG Q Y, et al. Telling secrets in the light: an efficient key extraction mechanism via ambient light[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 186-198. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3023930 -





 下载:
下载: