-
摘要:
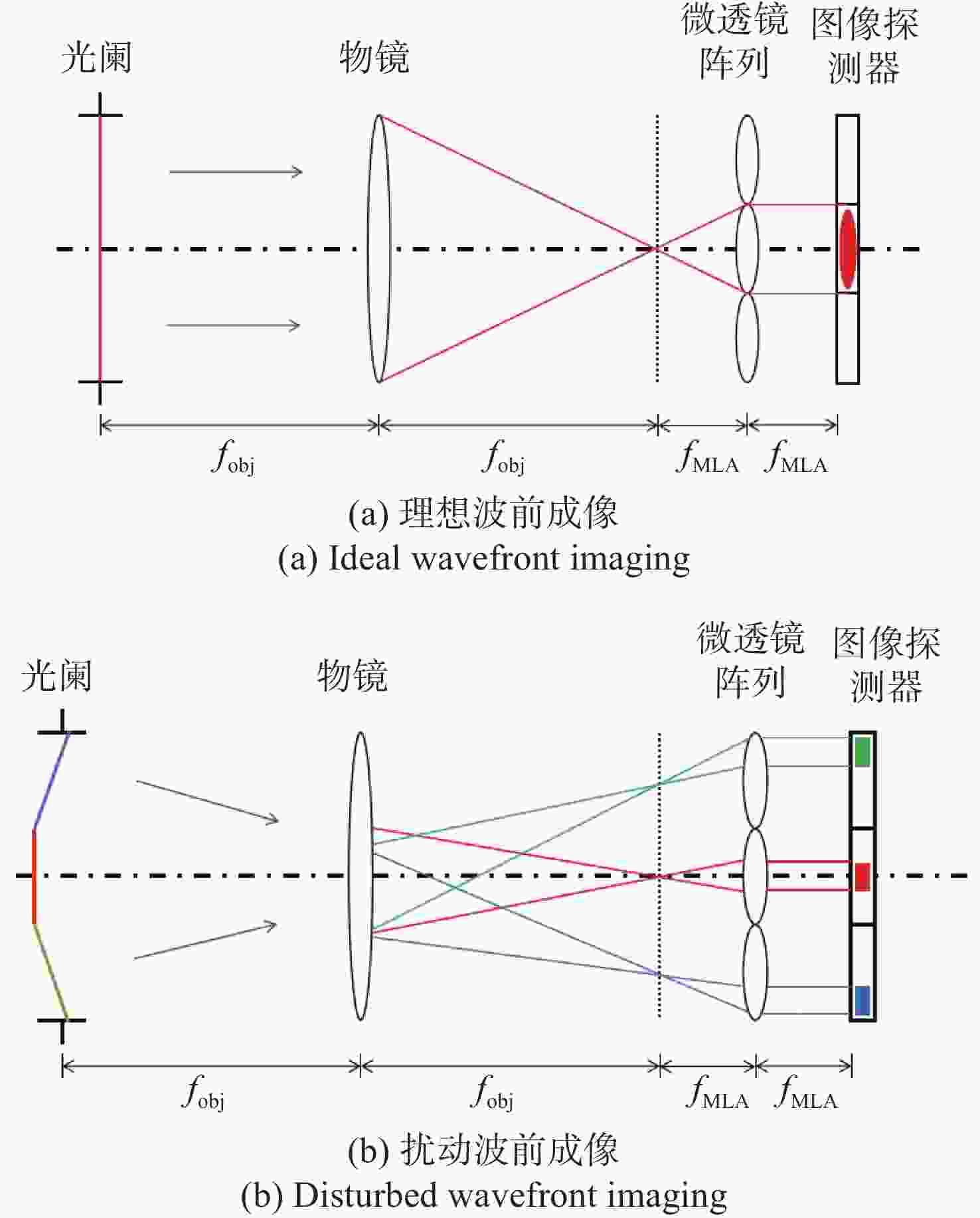
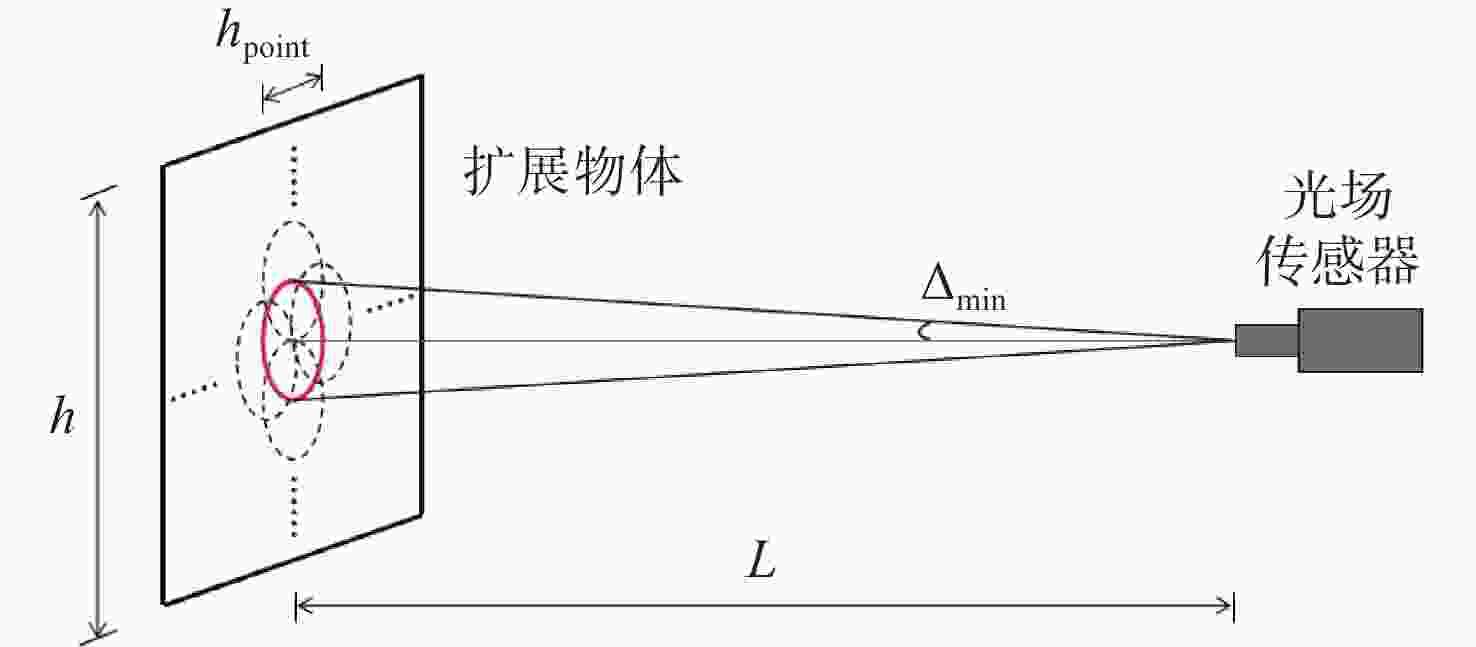
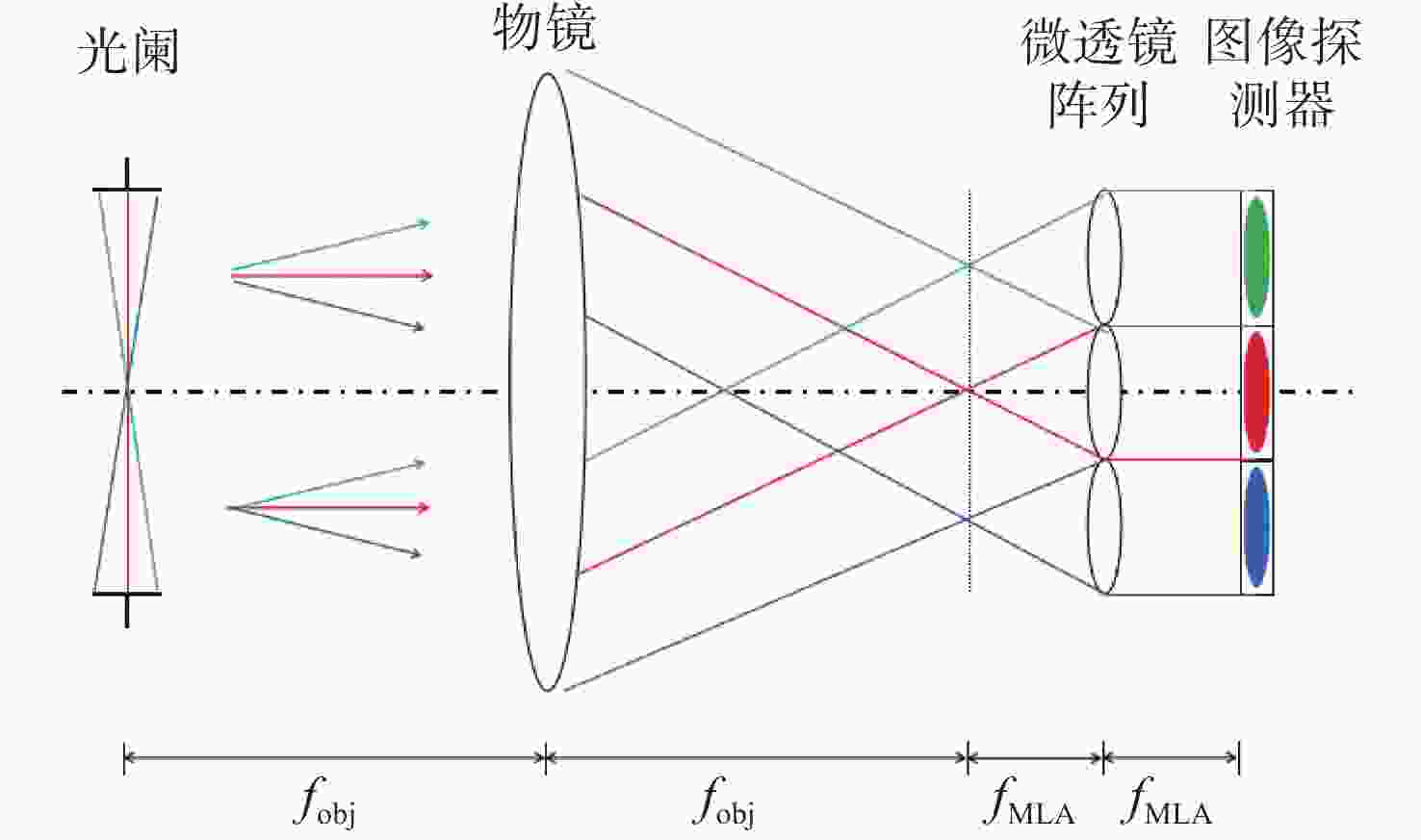
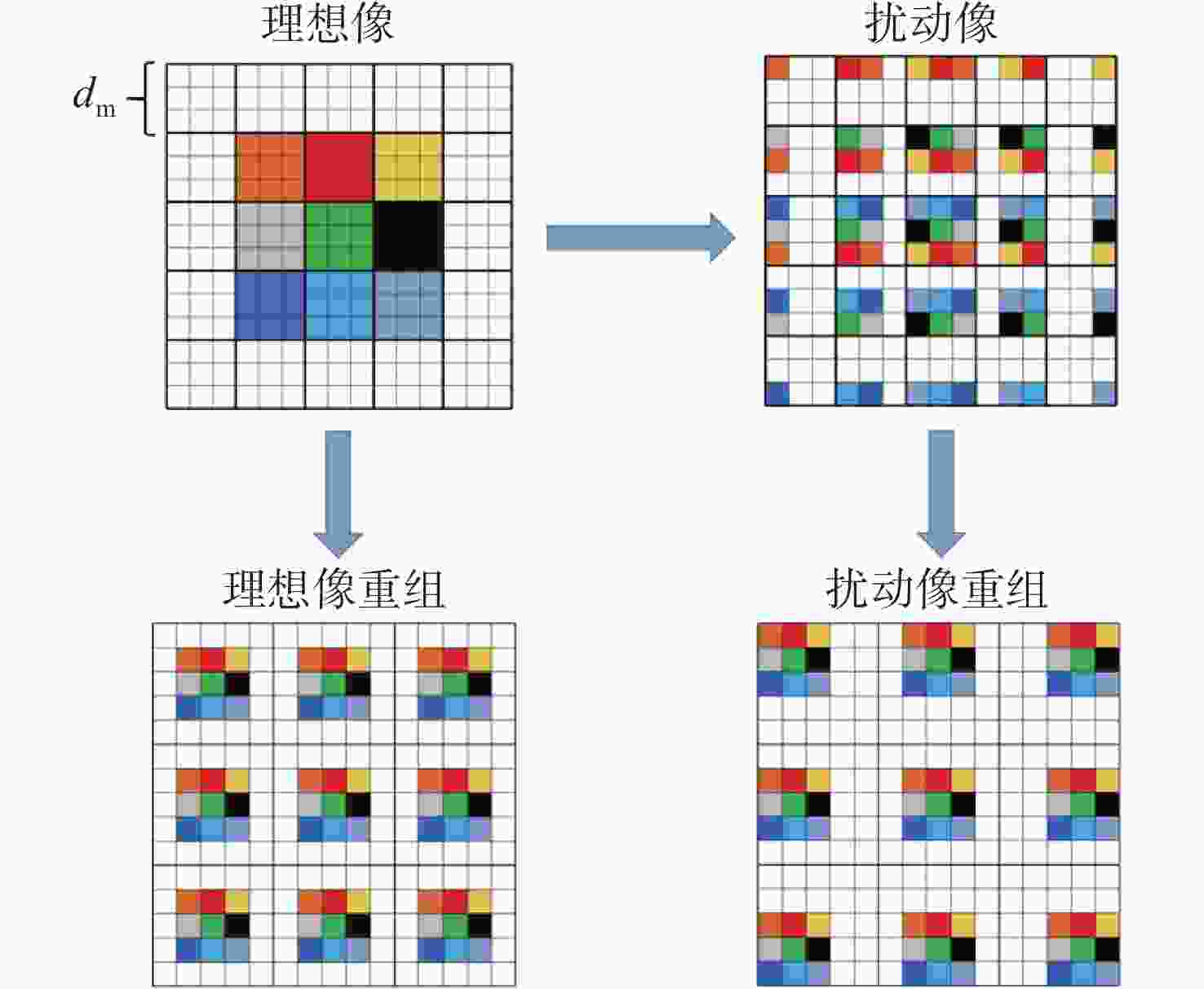
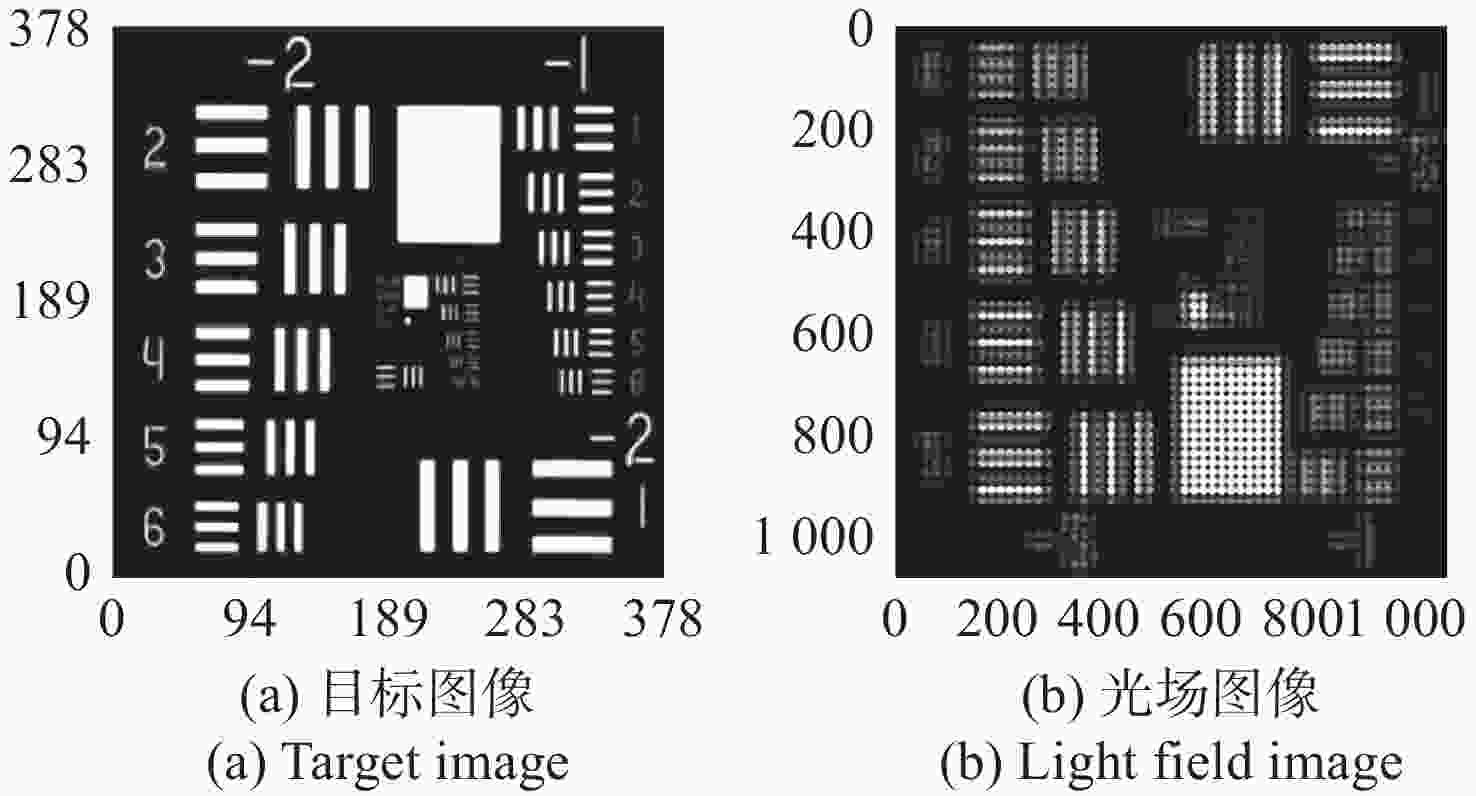
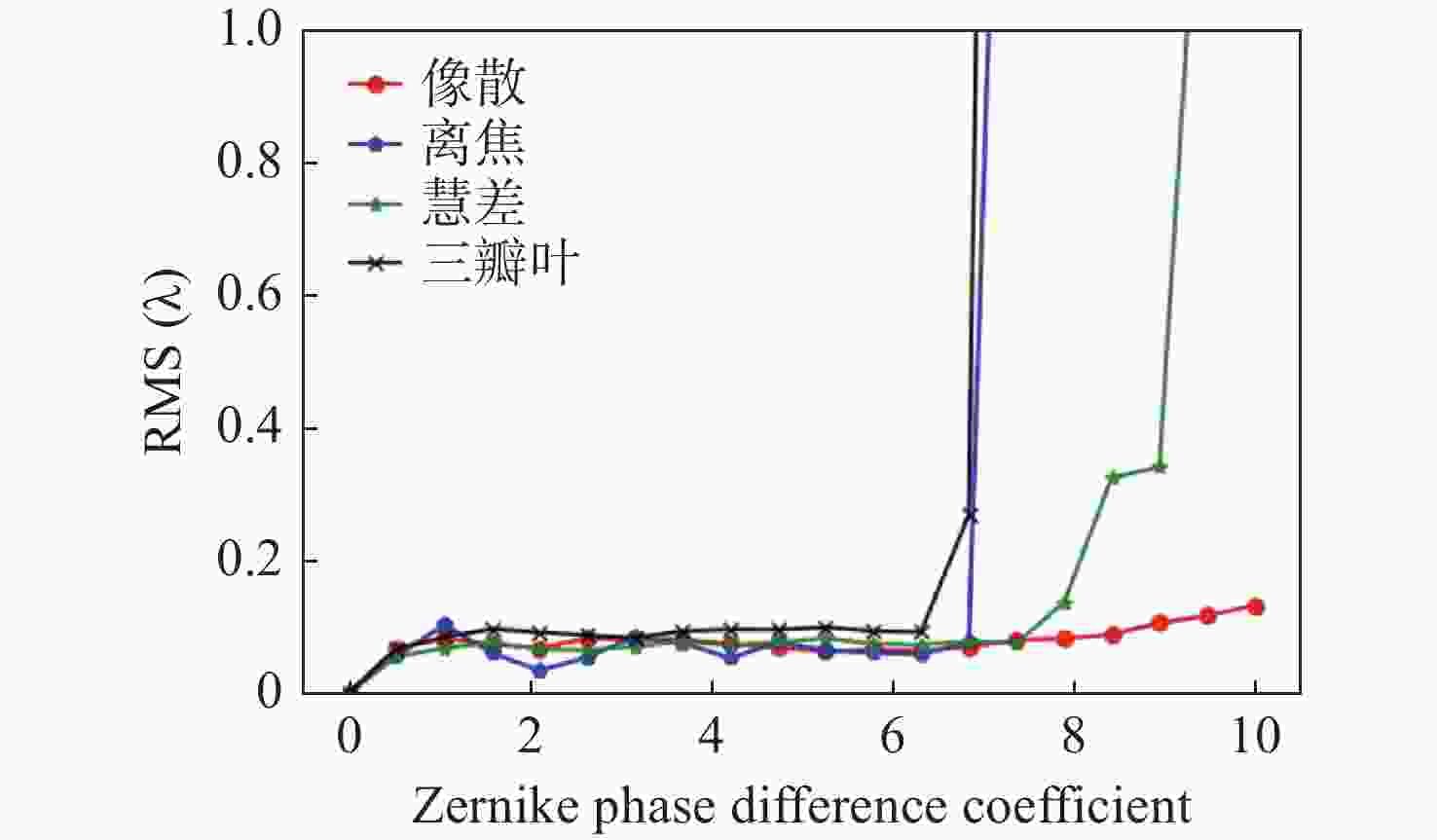
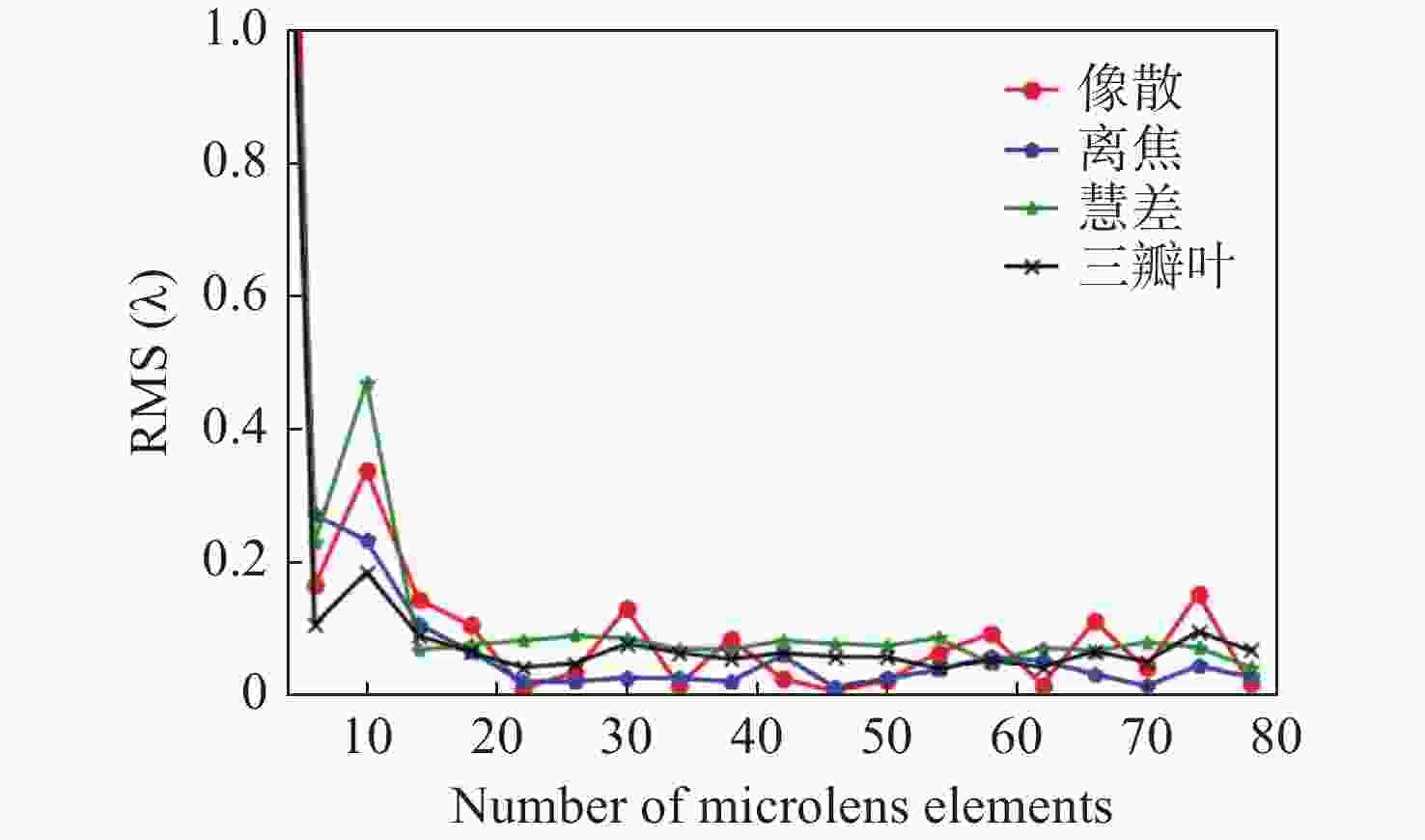
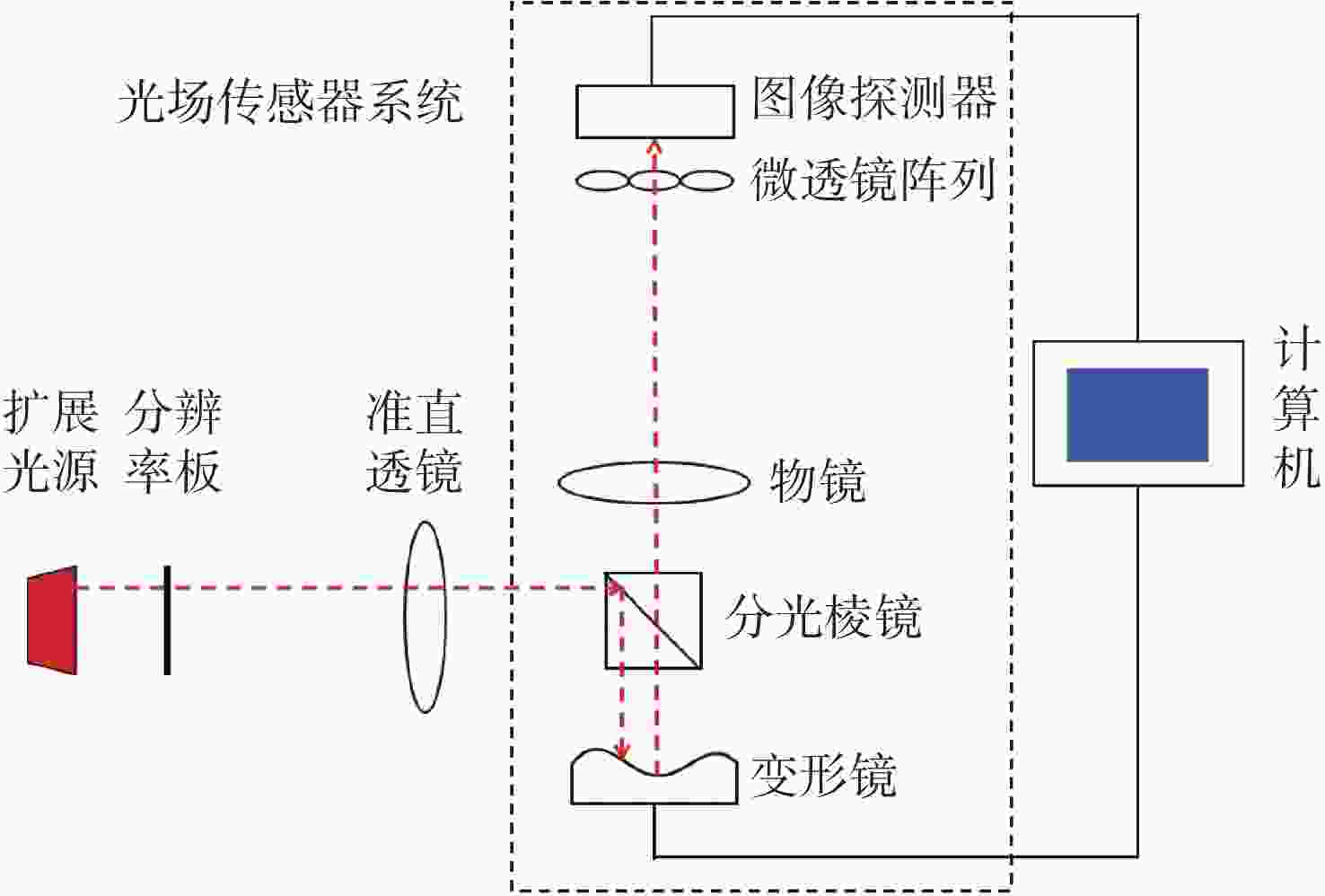
针对强湍流环境下自适应光学系统无理想点信标波前探测的难题,本文提出利用光场传感器(Plenoptic sensor)对扩展信标进行光场信息探测。对扩展信标的光场成像原理、波前位相重建算法、误差影响规律进行研究,利用等效法将扩展信标看做数个离散点的集合,简化扩展信标在光场传感器上的成像过程,然后将光场图像按照特定方式重新进行排列组合。通过图像互相关法和Zernike模式法实现0°视场的波前重建。针对不同输入像差系数、单列微透镜单元数和噪声等误差影响因素进行仿真研究,结果表明:当输入像差在6.5 λ以内时,波前重建精度约为0.08 λ,对于图像分辨率为
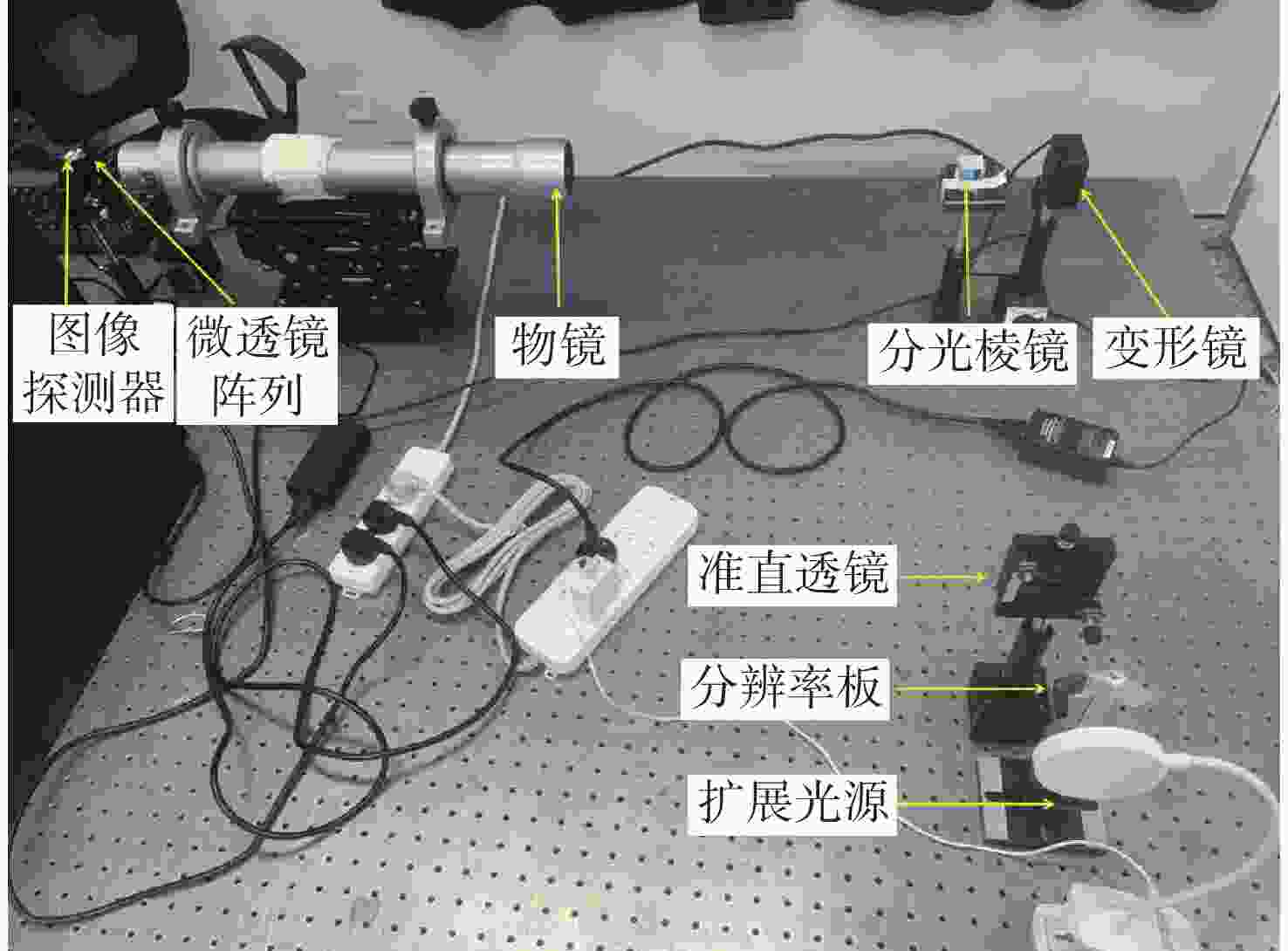
1080 ×1080 、像元尺寸为5.5 μm的图像探测器,单列微透镜单元数在40~50之间时波前重建精度最高,此外,系统噪声几乎不影响精度。最后,搭建了扩展信标波前探测系统,通过探测扩展信标对0°视场的4种像差波前进行重建,实验系统的波前重建精度约为0.04 λ,基本满足自适应光学系统的波前检测要求。Abstract:Aiming at the wavefront detection without an ideal point beacon in the adaptive optical system under the strong turbulent environment, we proposed a method to detect the optical field information of extended beacons using a Plenoptic sensor. The optical field imaging principle, wavefront phase reconstruction algorithm, and error influence rule of extended beacons were studied. The imaging process of the extended beacon on the optical field sensor was simplified through the equivalence method, and the optical field images were rearranged in a specific way. The image cross-correlation and Zernike mode methods were used to realize the wavefront reconstruction of the 0° field of view. Simulation studies were conducted on error-influencing factors such as different input aberration coefficients, the number of single-row microlens elements, and noise. The results show that when the input aberration is less than 6.5 λ, the wavefront reconstruction accuracy is about 0.08 λ. For the image detector with an image resolution of 1080×1080 and pixel size of 5.5 μm, the wavefront reconstruction accuracy is the highest when the number of single row microlens units is between 40 and 50, and the system noise hardly affects the accuracy. Finally, an extended beacon wavefront detection system was built to reconstruct the four aberrant wavefronts of 0° field of view by detecting the extended beacon. The wavefront reconstruction accuracy of the experimental system is about 0.04 λ, which meets the wavefront detection requirements of the adaptive optical system.
-
Key words:
- strong turbulence /
- plenoptic sensor /
- extended beacons /
- wave front reconstruction
-
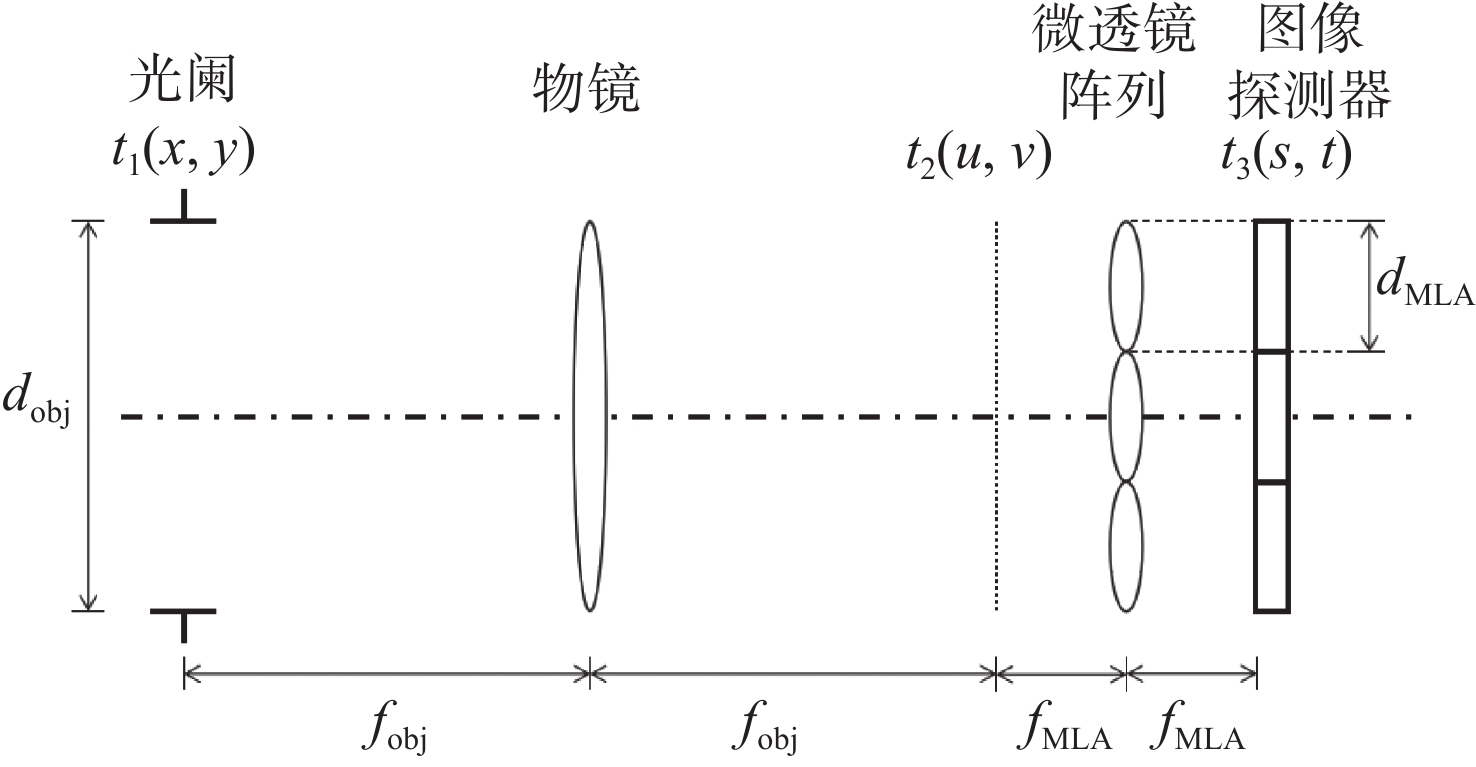
表 1 仿真系统结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of simulation system
(Unit: mm) 参数 值 系统通光口径 8.503 物镜焦距 1000 微透镜单元口径 0.1 微透镜焦距 11.76 探测器宽度 6 像元尺寸 0.0055 表 2 各像差对应的重建波前RMS误差
Table 2. RMS error of the reconstructed wavefront corresponding to each aberration
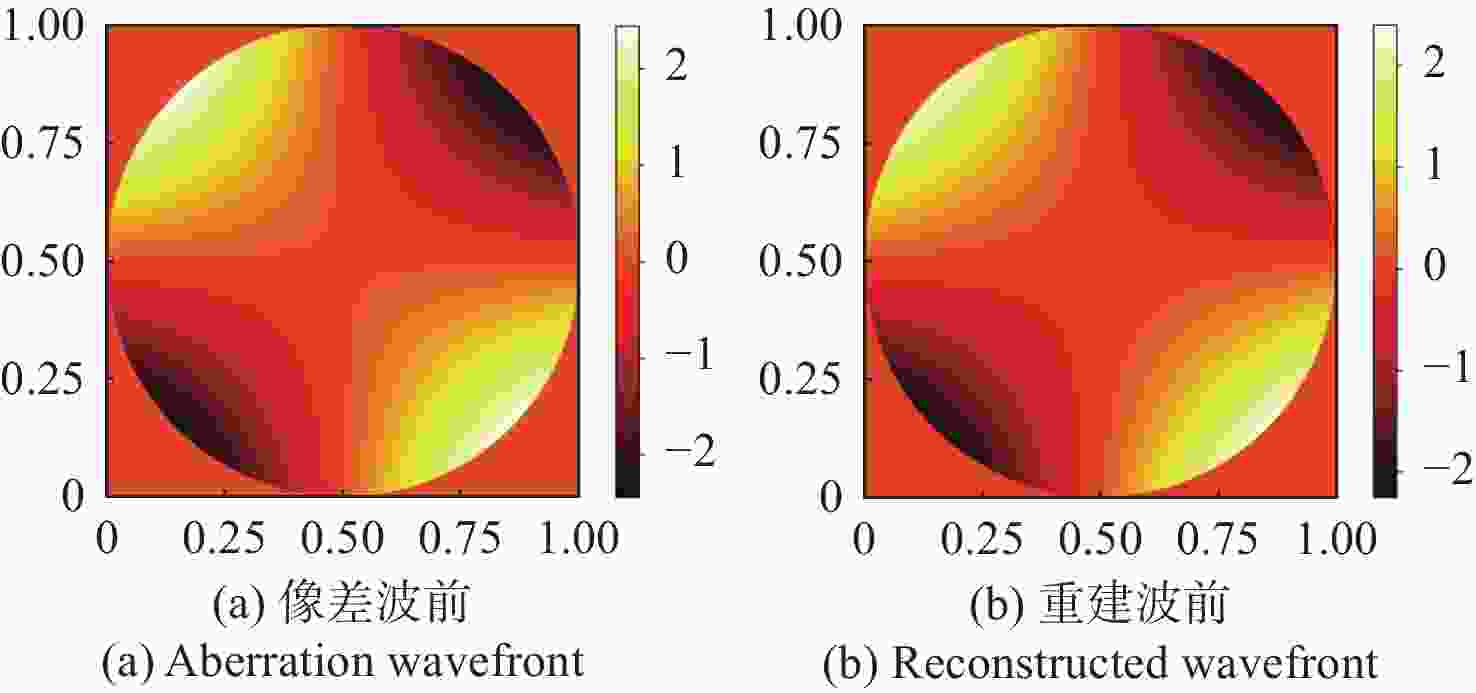
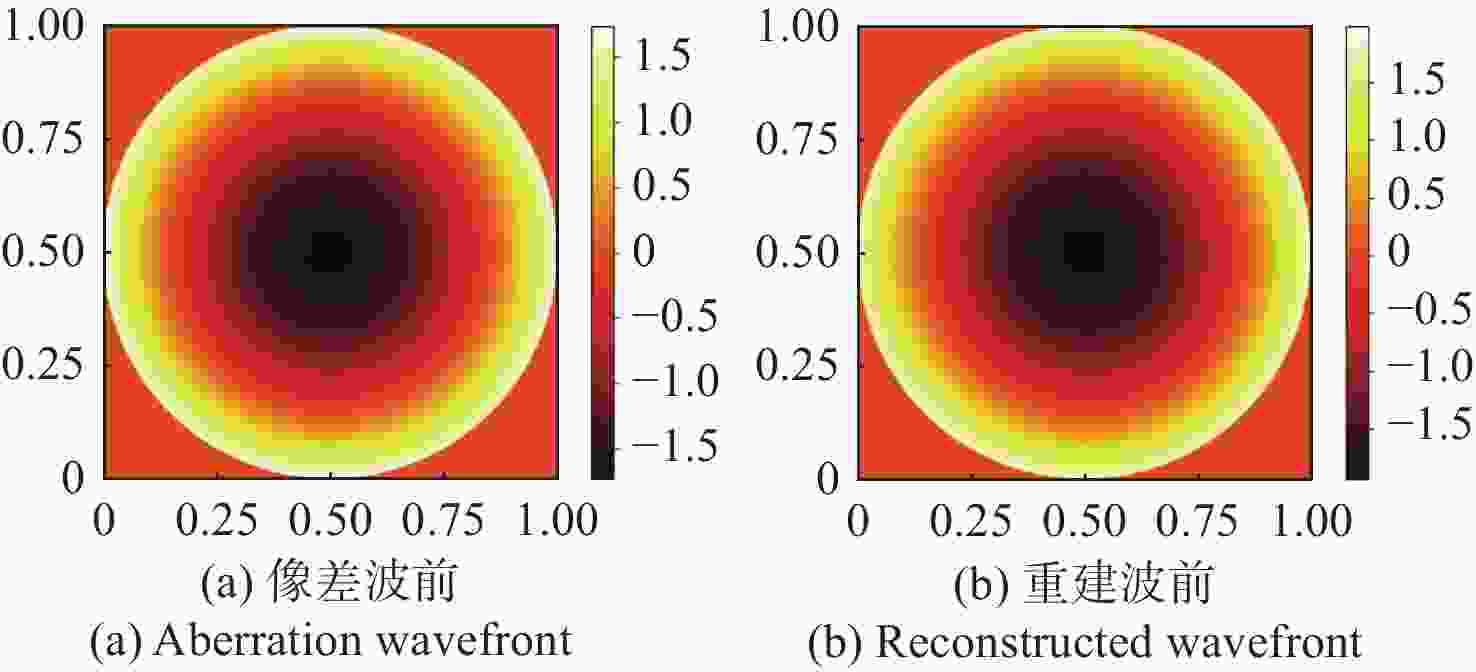
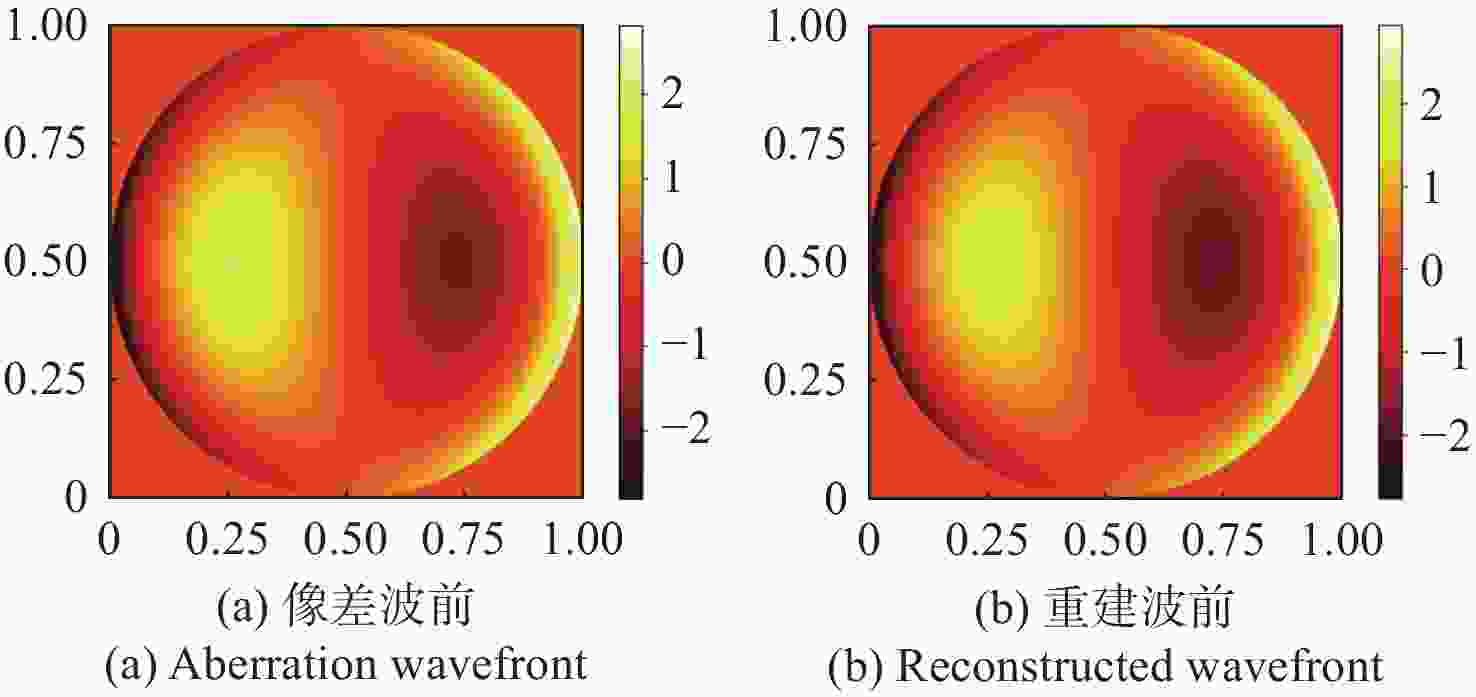
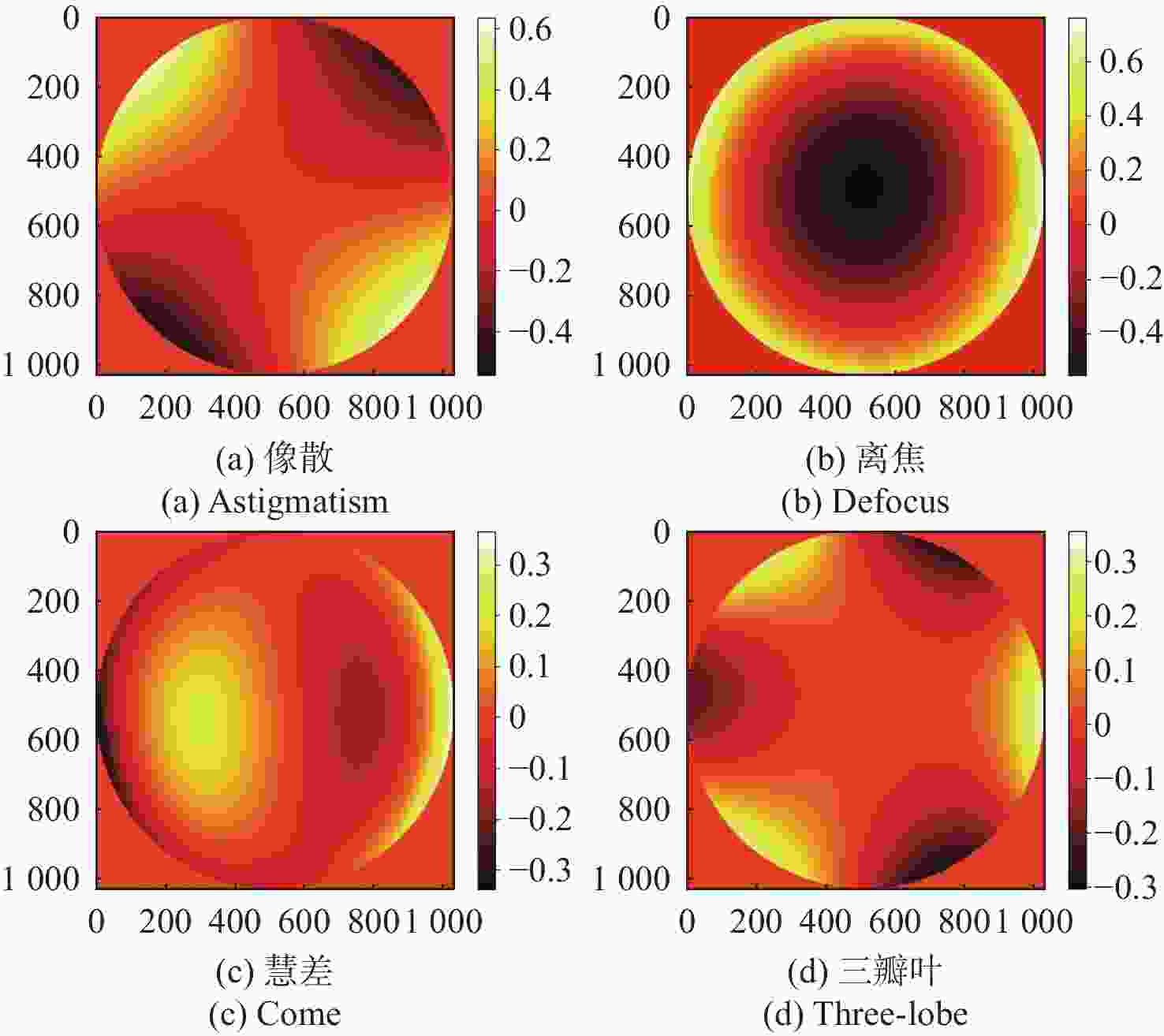
像差 重建波前残差RMS(λ) 像散 0.0893 离焦 0.1102 慧差 0.0576 三瓣叶 0.0758 表 3 不同噪声下的重建波前残差
Table 3. RMS error of the reconstructed wavefront for each aberration under different types of noise
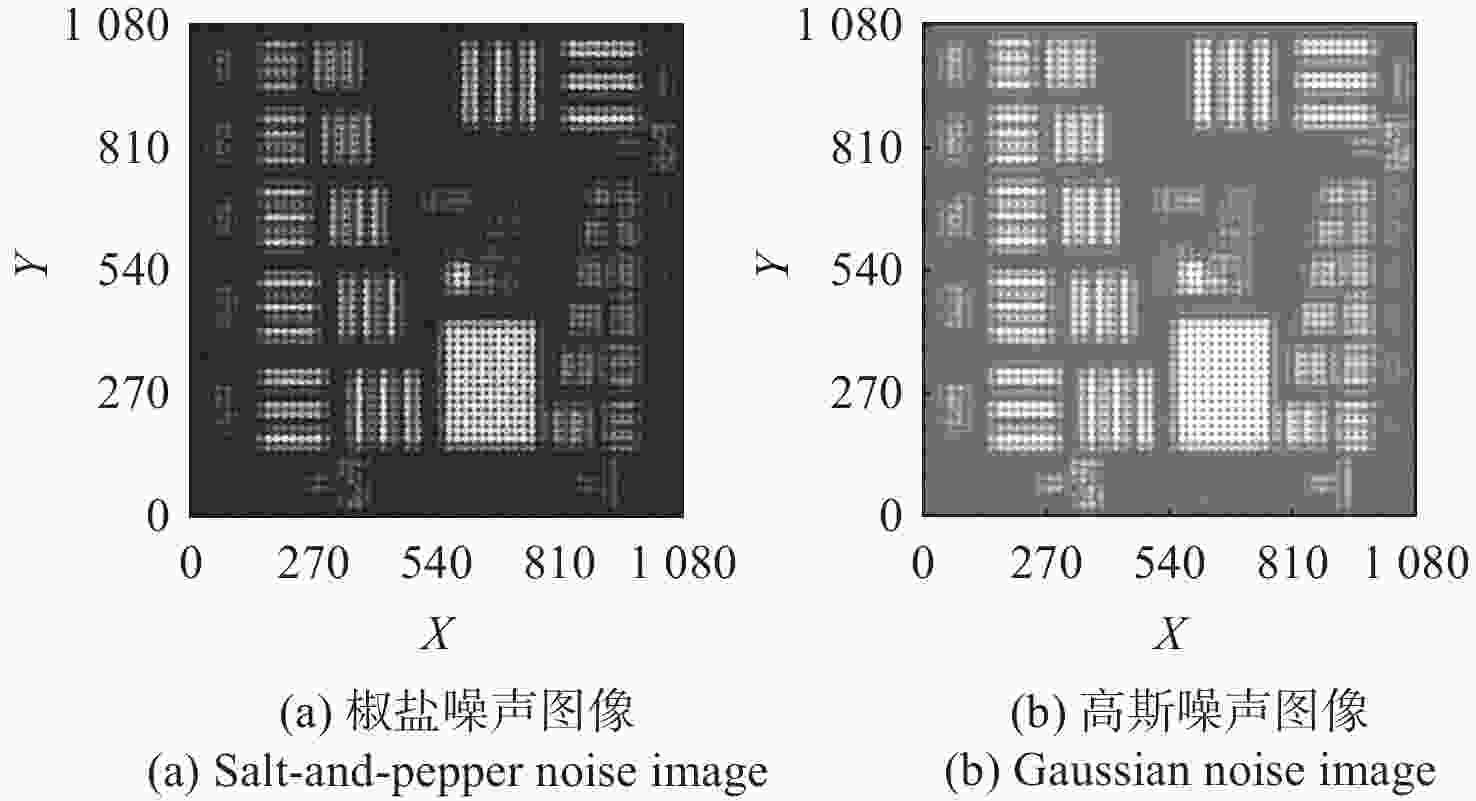
像差 椒盐噪声重建波前残差RMS(λ) 高斯噪声重建波前残差RMS(λ) 像散 0.0850 0.0932 离焦 0.1213 0.1151 慧差 0.0587 0.0606 三瓣叶 0.0723 0.0731 表 4 系统结构参数
Table 4. System structure parameters
(Unit: mm) 参数 参数值 系统通光口径 12 物镜焦距 560 微透镜单元口径 0.3 微透镜焦距 14 探测器宽度 3 像元尺寸 0.0029 表 5 几种像差的重建波前残差
Table 5. RMS errors of reconstructed wavefronts
像差 输入像差RMS(λ) 重建波前残差RMS(λ) 像散 0.2449 0.0436 离焦 0.3464 0.0532 慧差 0.1061 0.0308 三瓣叶 0.1060 0.0306 -
[1] BABCOCK H W. The possibility of compensating astronomical seeing[J]. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 1953, 65(386): 229-236. [2] SPRANGLE P, TING A, PENANO J, et al. Incoherent combining and atmospheric propagation of high-power fiber lasers for directed-energy applications[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2009, 45(2): 138-148. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2008.2002501 [3] CAMPBELL H I, GREENAWAY A H. Wavefront sensing: from historical roots to the state-of-the-art[J]. EAS Publications Series, 2006, 22: 165-185. doi: 10.1051/eas:2006131 [4] 朱沁雨, 陈梅蕊, 陆焕钧, 等. 微透镜阵列衍射效应对夏克一哈特曼波前探测器的影响分析[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(1):94-102. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0176ZHU Q Y, CHEN M R, LU H J, et al. Analysis of influence of diffraction effect of microlens array on Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(1): 94-102. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0176 [5] 王海铭, 权佳宁, 葛宝臻. 适用于近地面成像的自适应光学系统研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(4):843-852. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0230WANG H M, QUAN J N, GE B ZH. An adaptive optics system suitable for near-ground imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(4): 843-852. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0230 [6] KO J, DAVIS C C. Comparison of the plenoptic sensor and the Shack-Hartmann sensor[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(13): 3689-3698. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003689 [7] ADELSON E H, WANG J Y A. Single lens stereo with a plenoptic camera[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2): 99-106. doi: 10.1109/34.121783 [8] RODRÍGUEZ-RAMOS M J, CASTELLA F B, NAVA P F, et al. Wavefront and distance measurement using the CAFADIS camera[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7015: 70155Q. doi: 10.1117/12.789380 [9] LV Y, ZHANG X ZH, MA H T, et al. Large viewing field wavefront sensing by using a lightfield system[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8905: 89052T. doi: 10.1117/12.2035212 [10] JIANG P ZH, XU J P, LIANG Y H, et al. Plenoptic camera wavefront sensing with extended sources[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2016, 63(16): 1573-1578. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2016.1162336 [11] ESLAMI M, WU CH SH, RZASA J, et al. Using a plenoptic camera to measure distortions in wavefronts affected by atmospheric turbulence[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8517: 85170S. doi: 10.1117/12.943038 [12] WU CH SH, DAVIS C C. Modified plenoptic camera for phase and amplitude wavefront sensing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8874: 88740I. [13] WU CH SH, KO J, NELSON W, et al. Phase and amplitude wave front sensing and reconstruction with a modified plenoptic camera[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9224: 92240G. [14] WU CH SH, KO J, DAVIS C C. Determining the phase and amplitude distortion of a wavefront using a plenoptic sensor[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2015, 32(5): 964-978. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.32.000964 [15] WU CH SH, KO J, DAVIS C C. Plenoptic mapping for imaging and retrieval of the complex field amplitude of a laser beam[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(26): 29852-29871. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.029852 [16] WU CH SH, KO J, DAVIS C C. Complex wavefront sensing with a plenoptic sensor[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9979: 99790Y. [17] WU CH SH, KO J, DAVIS C C. Imaging through strong turbulence with a light field approach[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(11): 11975-11986. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.011975 [18] WU CH SH, KO J, DAVIS C C. Using a plenoptic sensor to reconstruct vortex phase structures[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(14): 3169-3172. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.003169 [19] WU CH SH, PAULSON D A, RZASA J R, et al. Comparison between the plenoptic sensor and the light field camera in restoring images through turbulence[J]. OSA Continuum, 2019, 2(9): 2511-2525. doi: 10.1364/OSAC.2.002511 [20] KO J, WU CH SH, DAVIS C C. Implementation of a rapid correction algorithm for adaptive optics using a plenoptic sensor[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9979: 99790O. [21] HU J T, CHEN T, LIN X D, et al. Improved wavefront reconstruction and correction strategy for adaptive optics system with a plenoptic sensor[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2021, 13(4): 1-8. [22] 王志冲. 强湍流下激光通信波前光场传感技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2022.WANG ZH CH. Research on plenoptic wavefront sensing technique of free space laser communication under strong turbulence[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. (in Chinese). [23] LARDIÈRE O, CONAN R, CLARE R, et al. Performance comparison of centroiding algorithms for laser guide star wavefront sensing with extremely large telescopes[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(31): G78-G94. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.000G78 [24] NOLL R J. Zernike polynomials and atmospheric turbulence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1976, 66(3): 207-211. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.66.000207 -





 下载:
下载: