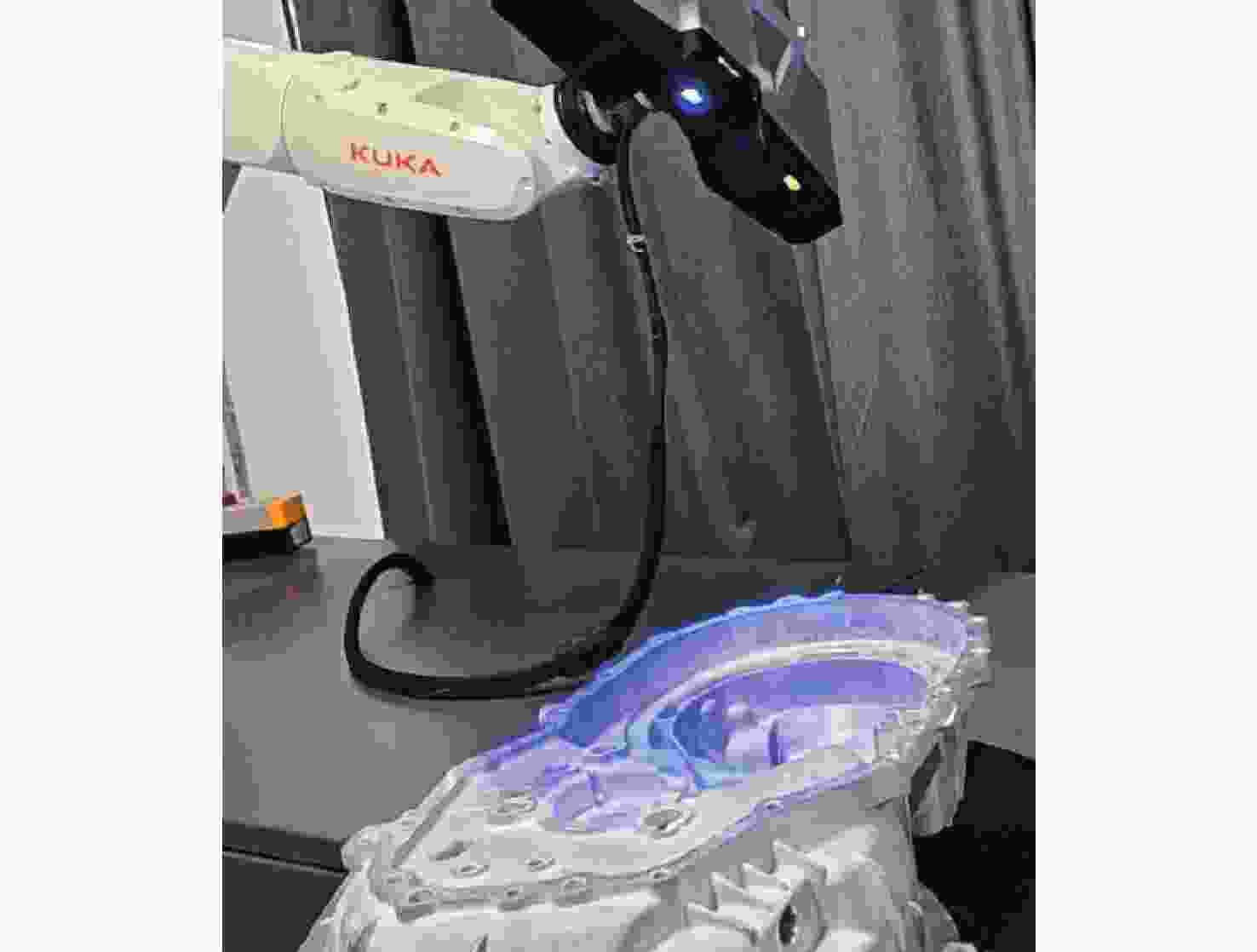
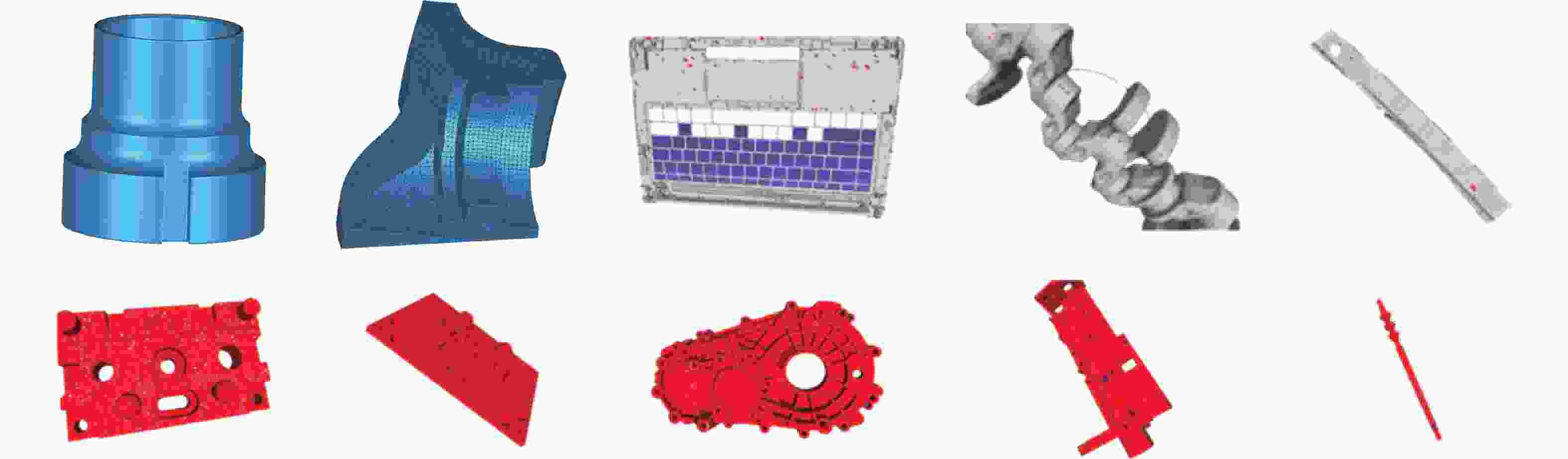
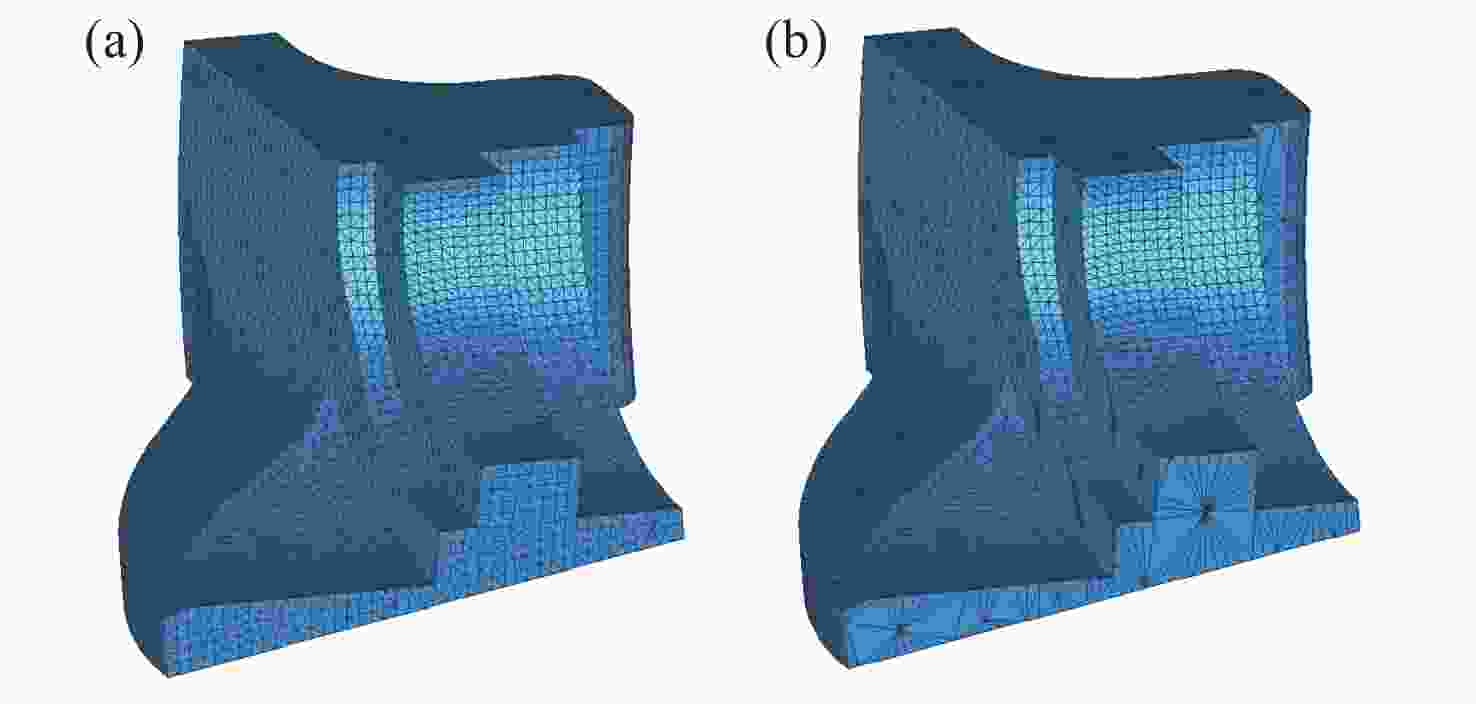
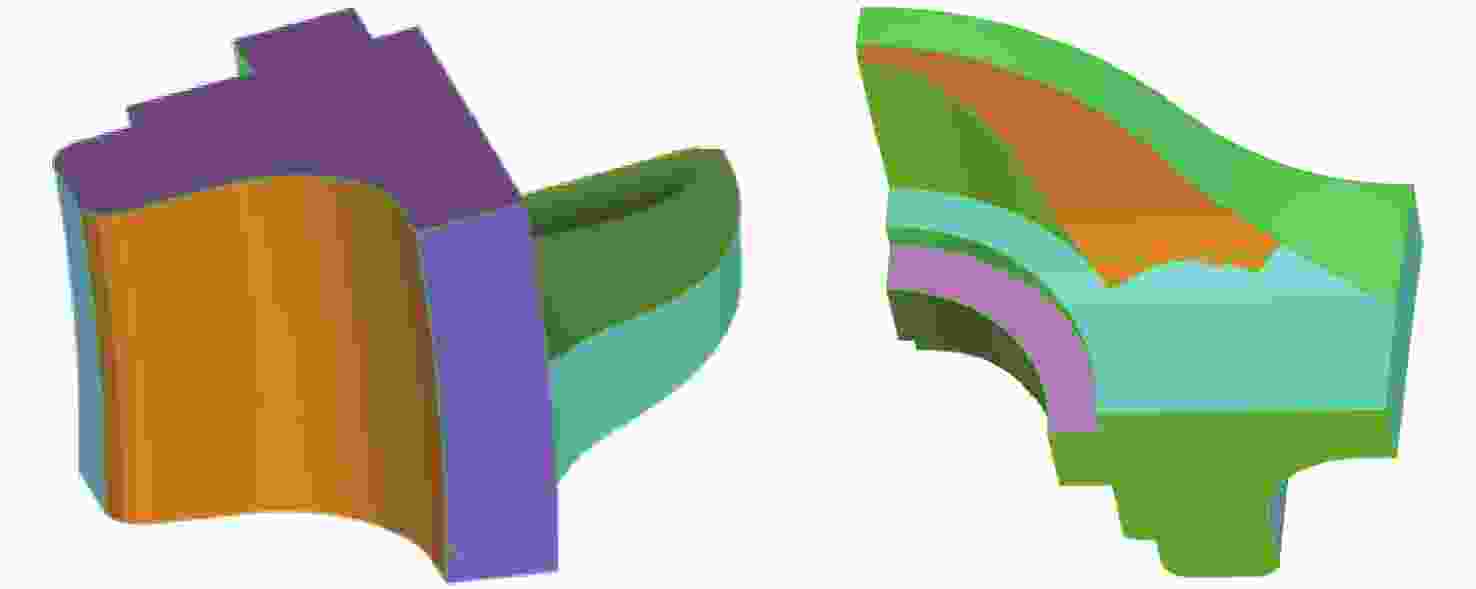
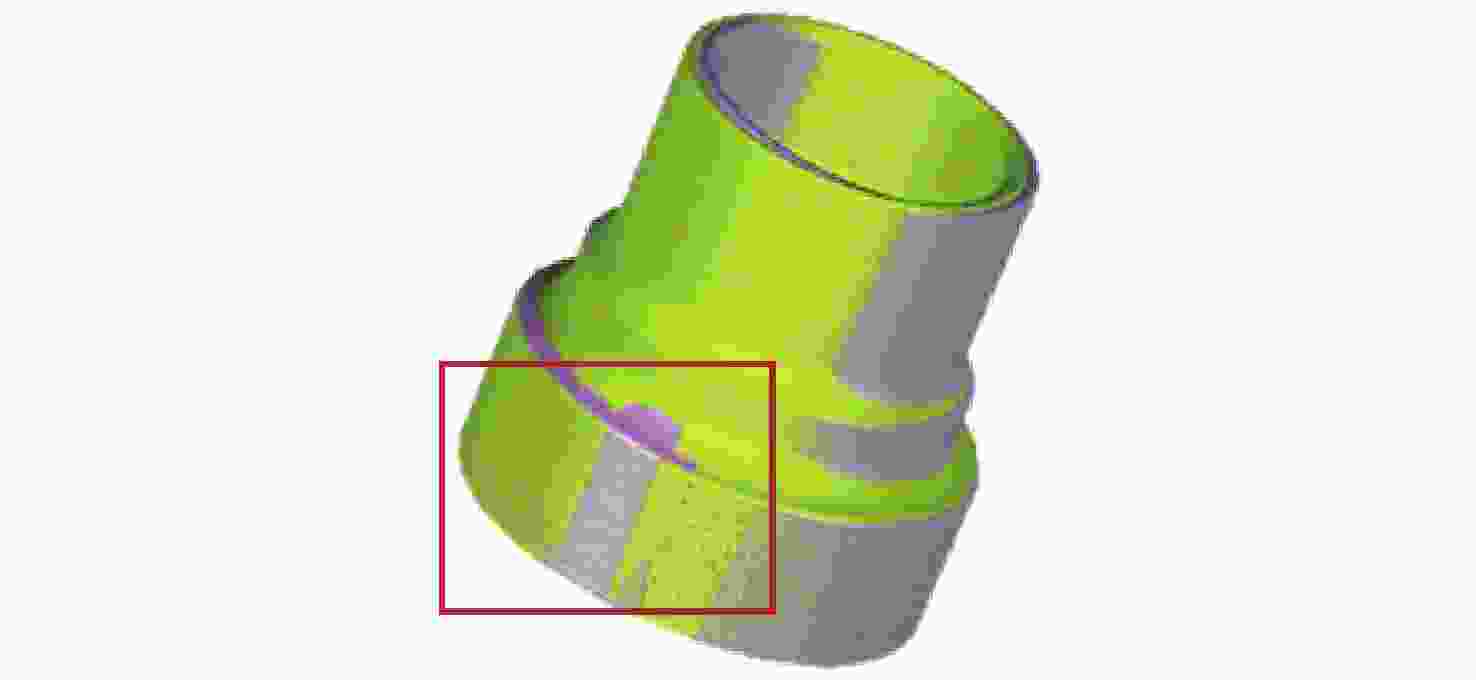
Segmentation method for enhanced features in automatic registration of triangular mesh model of mechanical parts
-
摘要:
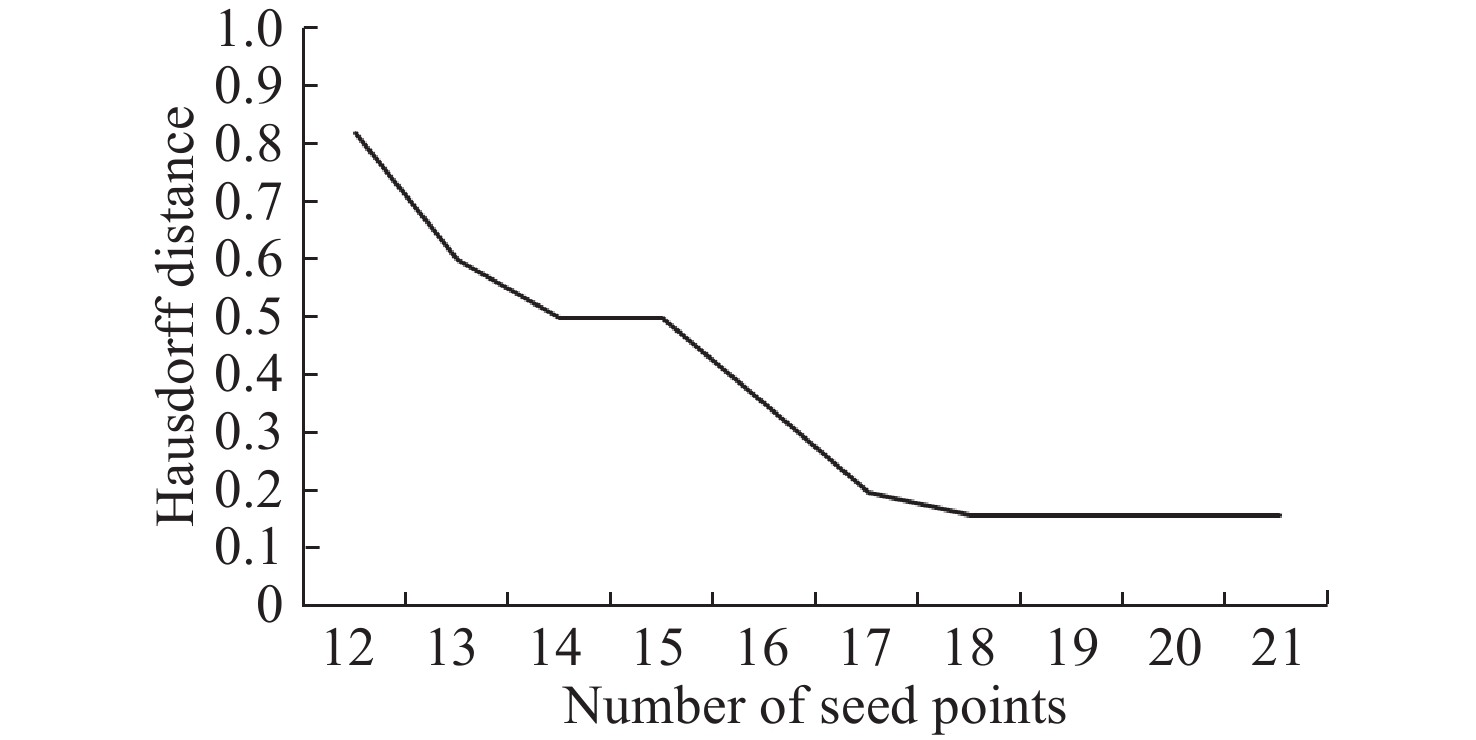
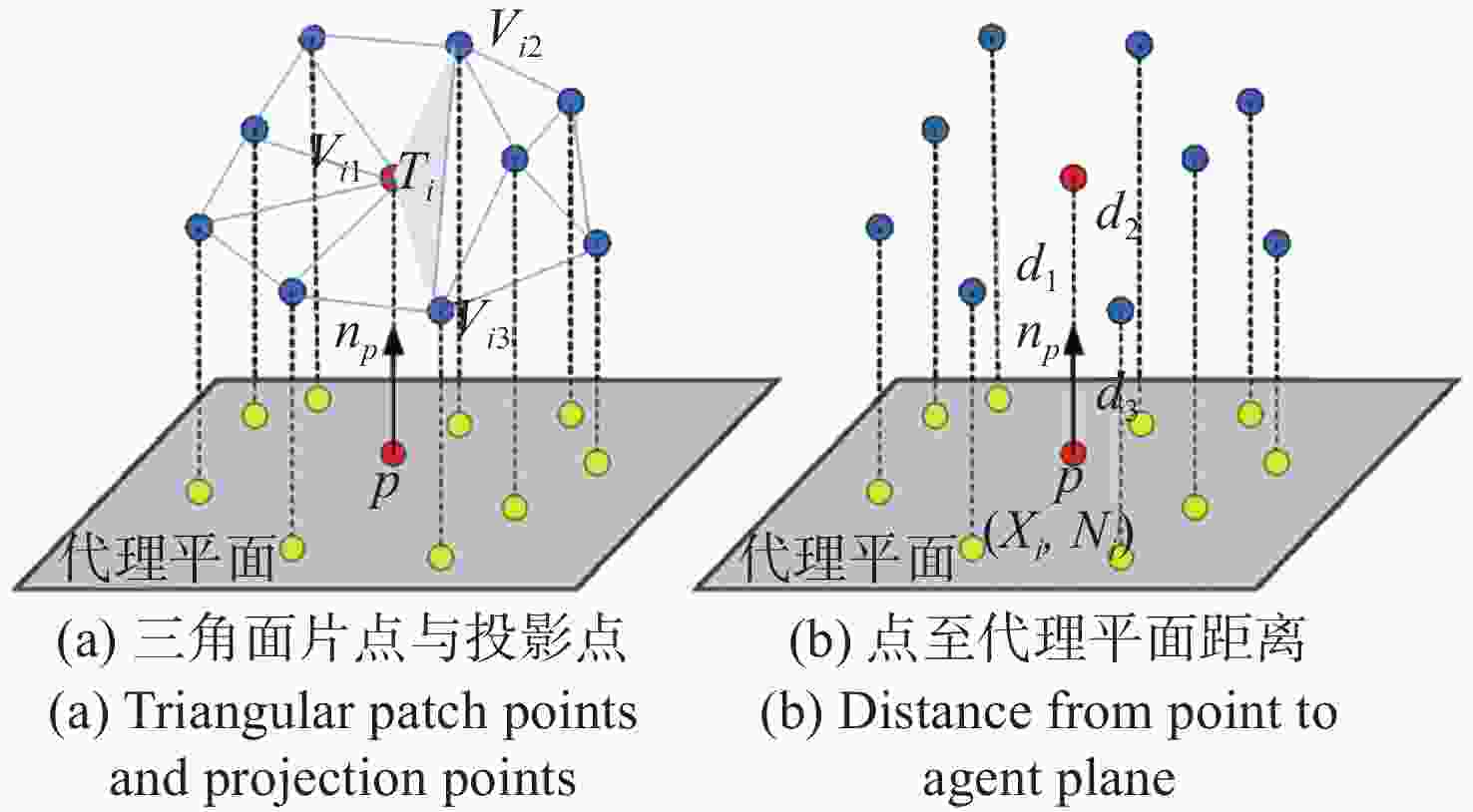
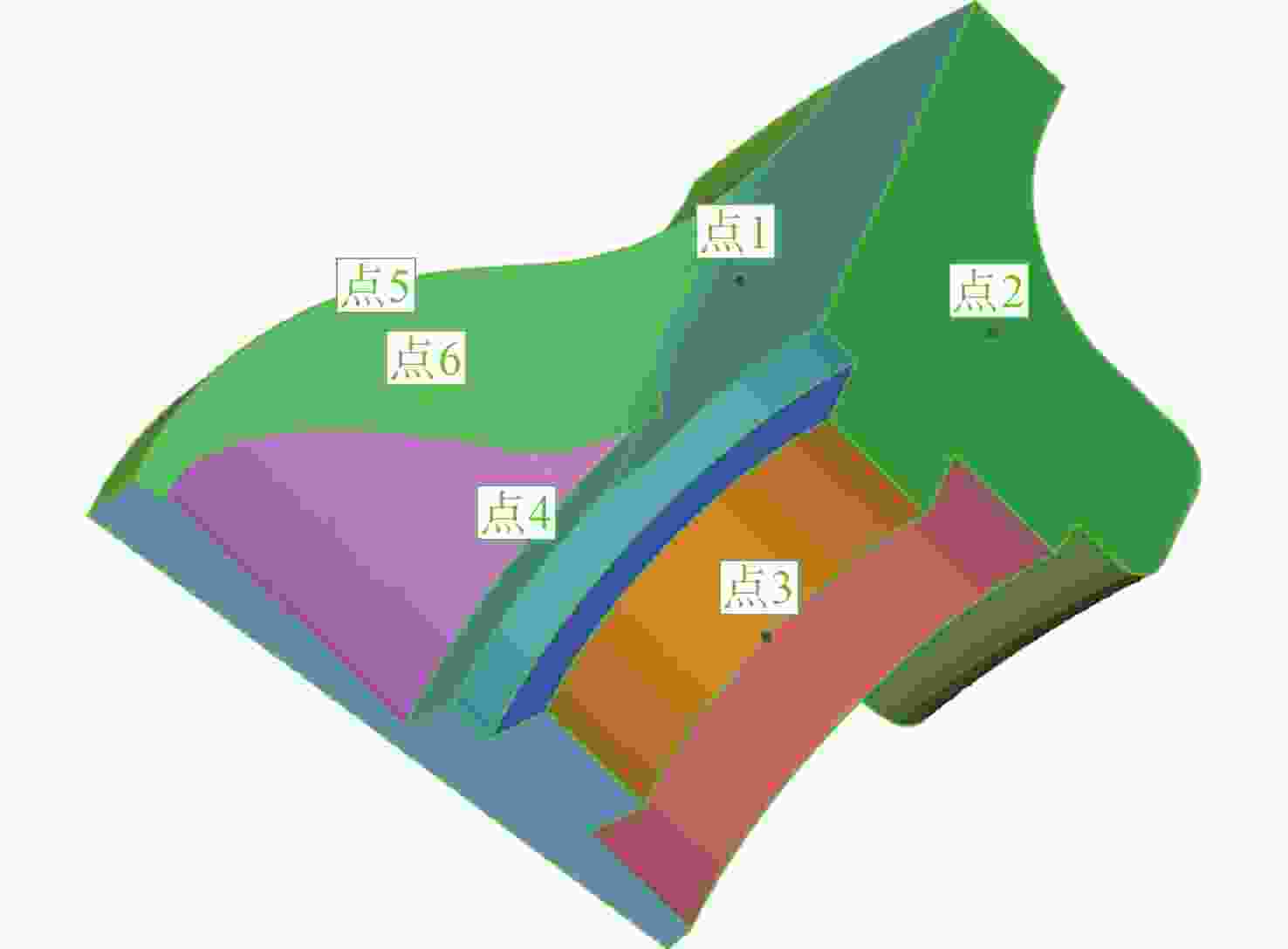
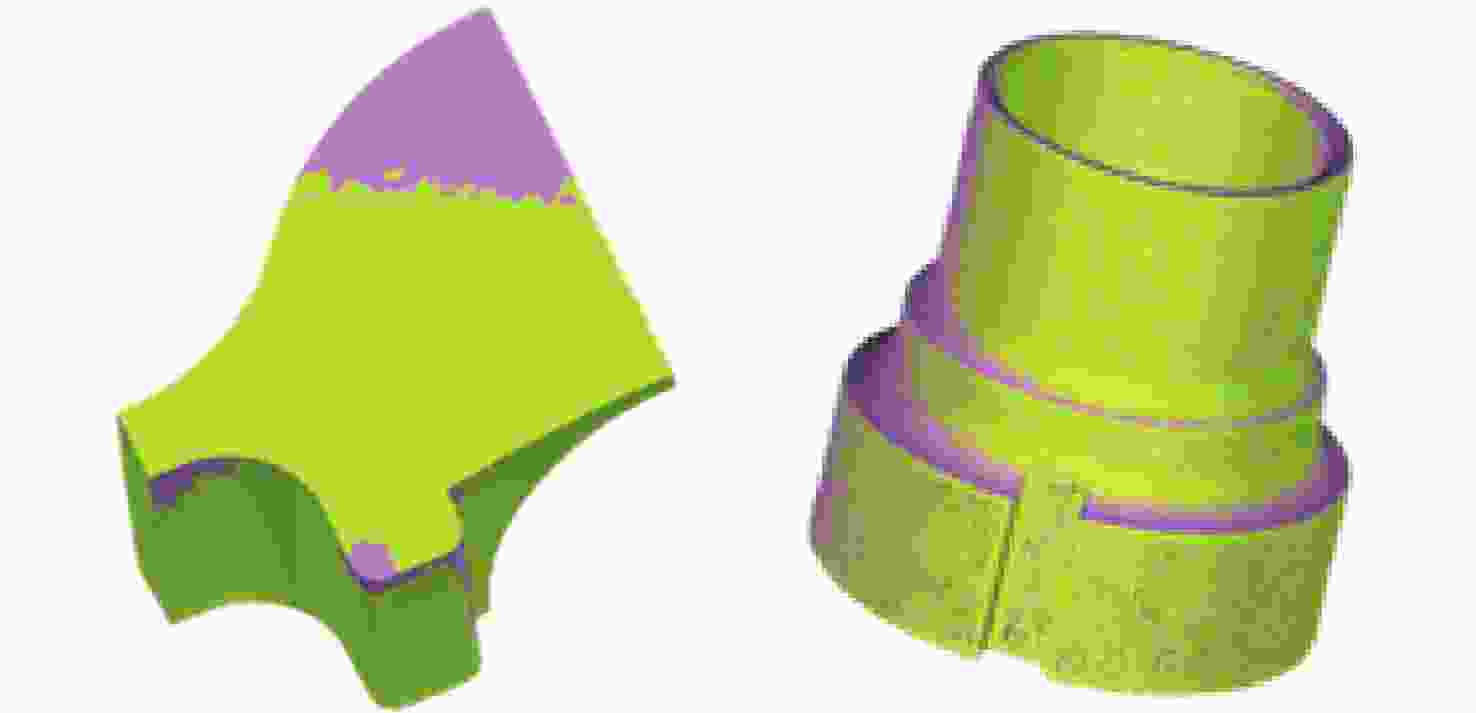
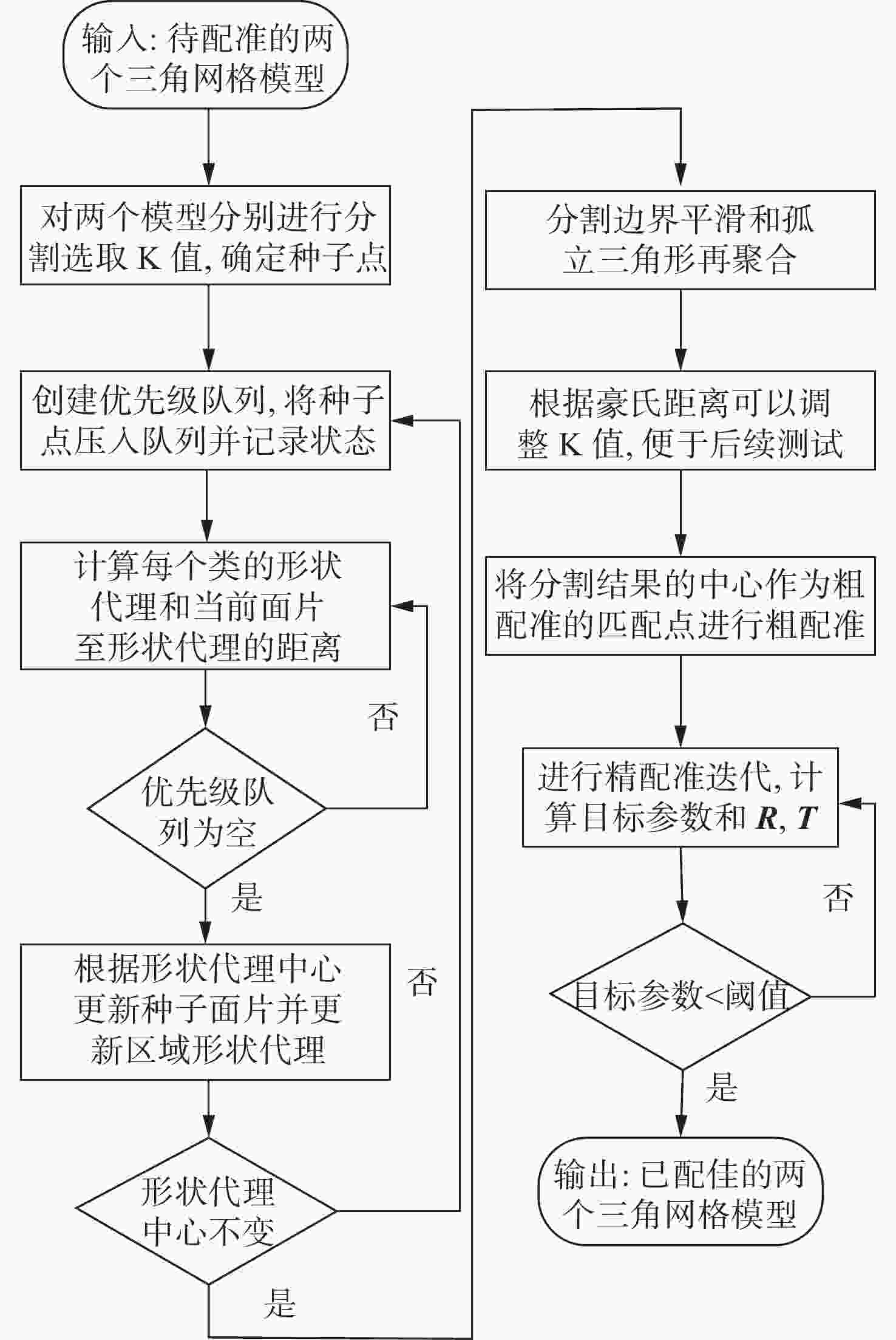
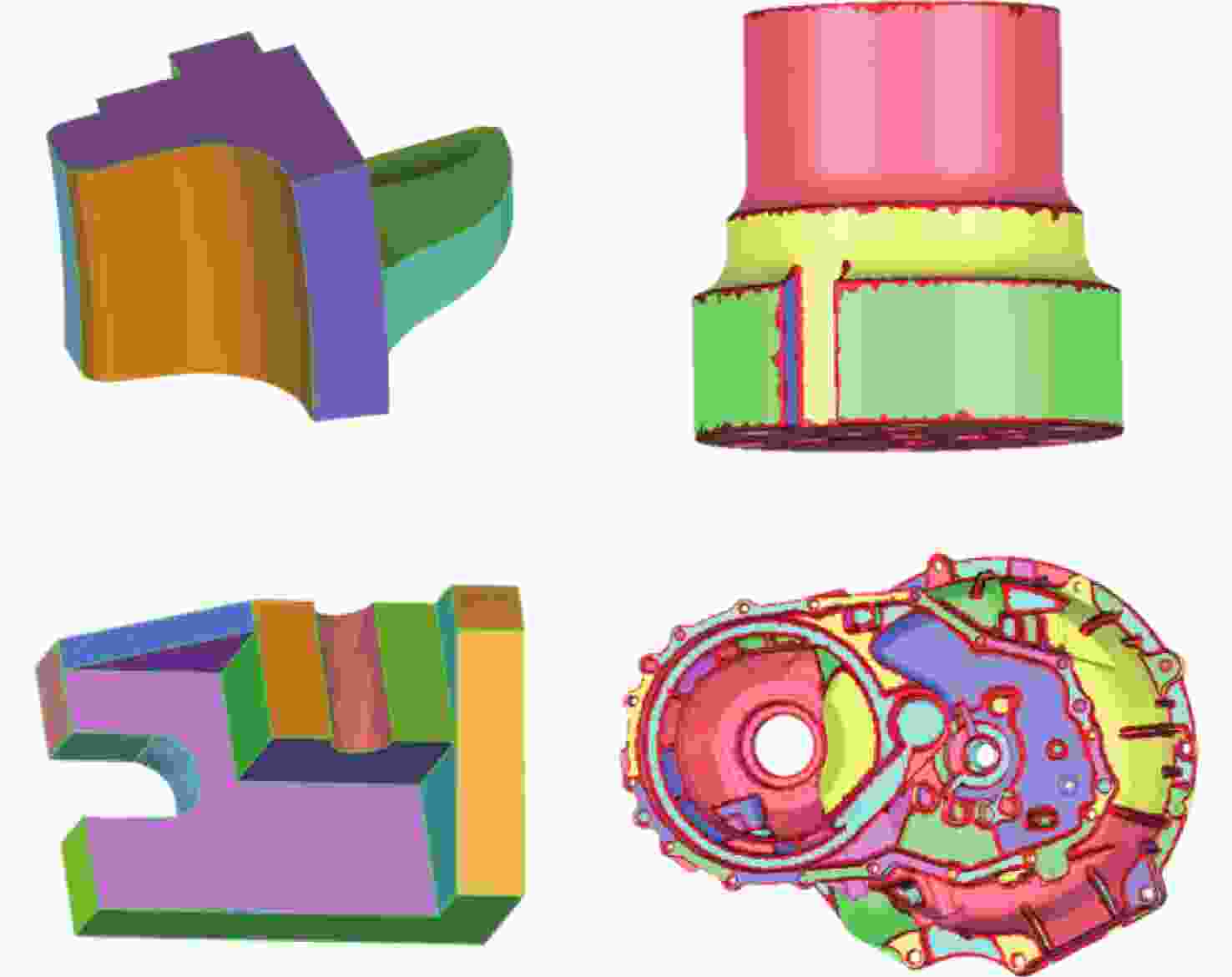
三角网格模型配准是工业自动化检测软件中的重要一环,其配准精度对检测机械零件的形位公差有重要影响。针对三角网格模型的自动配准精度低、鲁棒性差的问题,本文提出一种面向机械零件三角网格模型自动配准中增强特征的分割方法。首先,确定三角网格模型特征分割的K值,通过拉普拉斯矩阵确定种子点进行迭代初始化。其次,本文采用合适的区域形状代理和代价函数以加速该过程,并通过多源迭代聚类得到特征分割结果。最终,在三角网格模型特征分割结果的基础上进行基于奇异值分解法的粗配准,之后再根据EM-ICP进行精配准。与传统的特征描述子粗配准结合ICP精配准的方法进行对比,结果表明,本文方法的配准误差下降了25.2%,自动配准时间缩短了62.6%,有效地提高了三角网格模型自动配准的精度和效率。
Abstract:Triangular mesh model registration is an important part of industrial automation detection software. The registration accuracy has an important influence on mechanical parts' shape and position tolerance. Aiming to solve the problems of low accuracy and poor robustness of the automatic registration of triangular mesh models, we propose a segmentation method for enhanced features in the automatic registration of triangular mesh models for mechanical parts. First, the K value of the feature segmentation of the triangular mesh model was determined, and the Laplacian matrix determined the seed points for iterative initialization. Second, the appropriate region shape agent and cost function were used to accelerate the process and perform multi-source iterative clustering to obtain the intended feature segmentation results. Finally, based on the feature segmentation results of the triangular mesh model, the coarse registration based on the singular value decomposition method was performed, then the fine registration was performed according to the EM-ICP. The experimental results show that the proposed method reduces registration error by 25.2% and shortens the automatic registration time by 62.6%, compared with the traditional feature descriptor coarse registration combined with ICP fine registration method. This effectively improves the accuracy and efficiency of the automatic registration of the triangular mesh model.
-
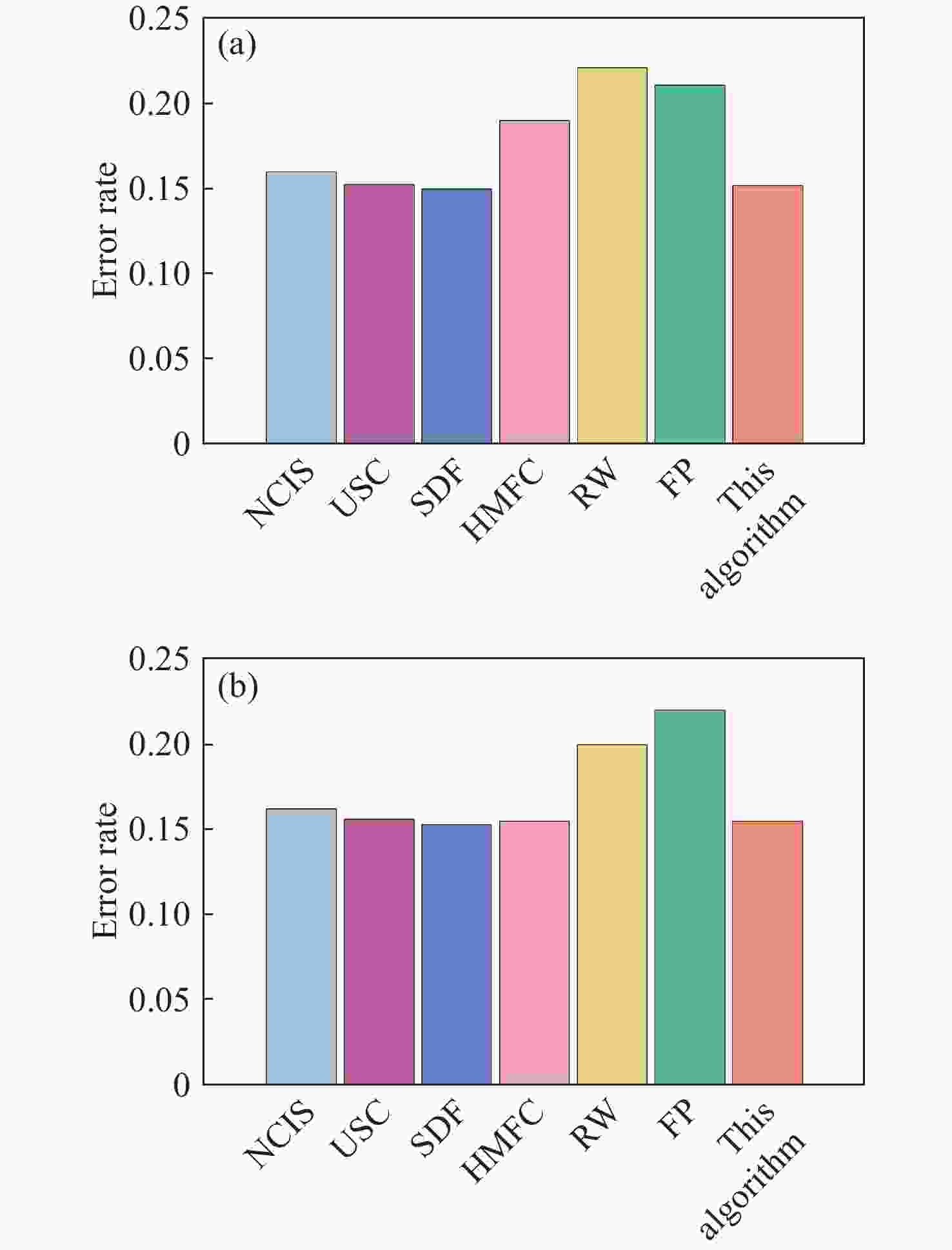
表 1 自动配准RMSE和耗时结果
Table 1. RMSE and time-consuming results of automatic registration
模型
序号模型面片
数量特征描述子方法
RMSE(mm)本文方法
RMSE(mm)特征描述
子方法耗时/s本文方法
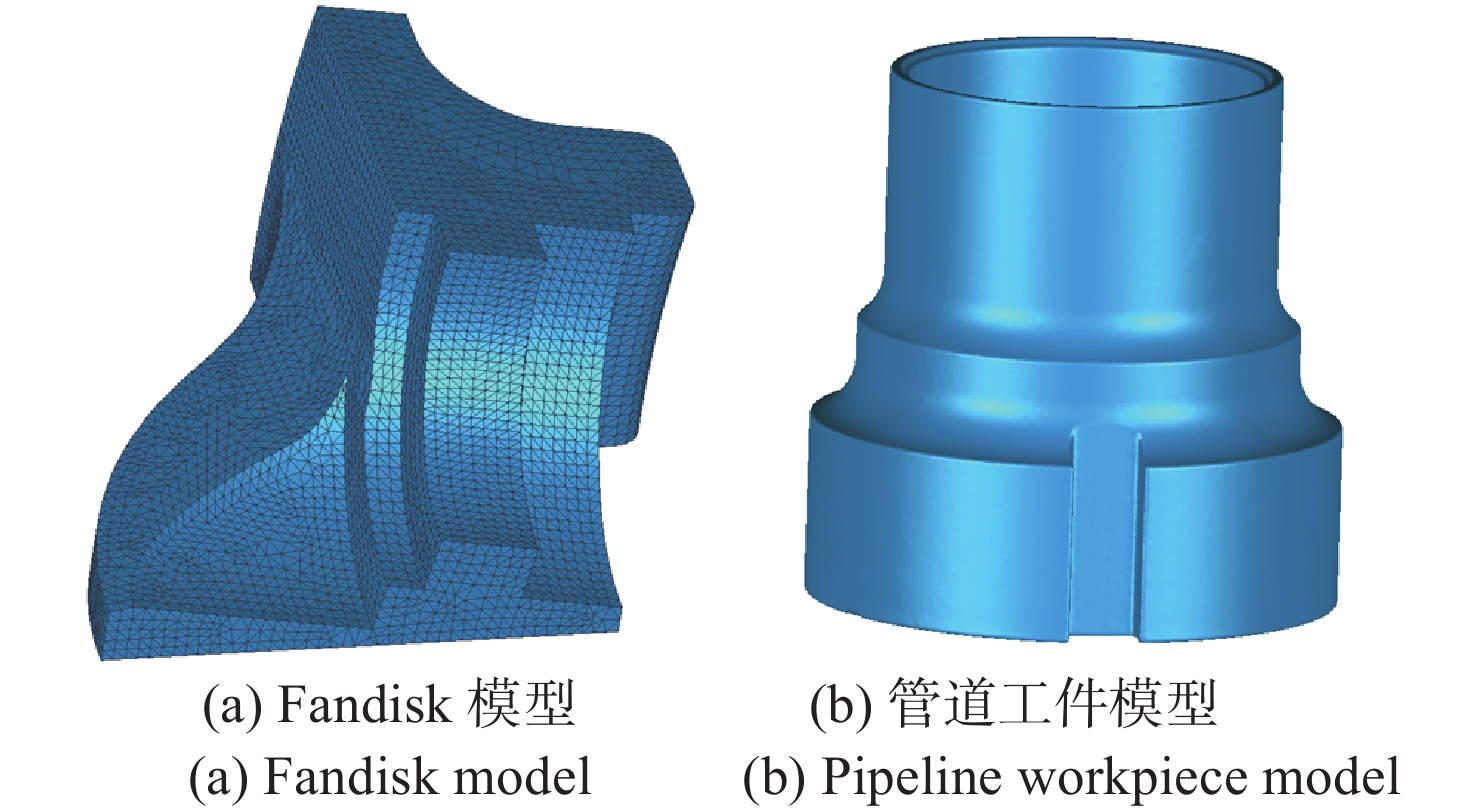
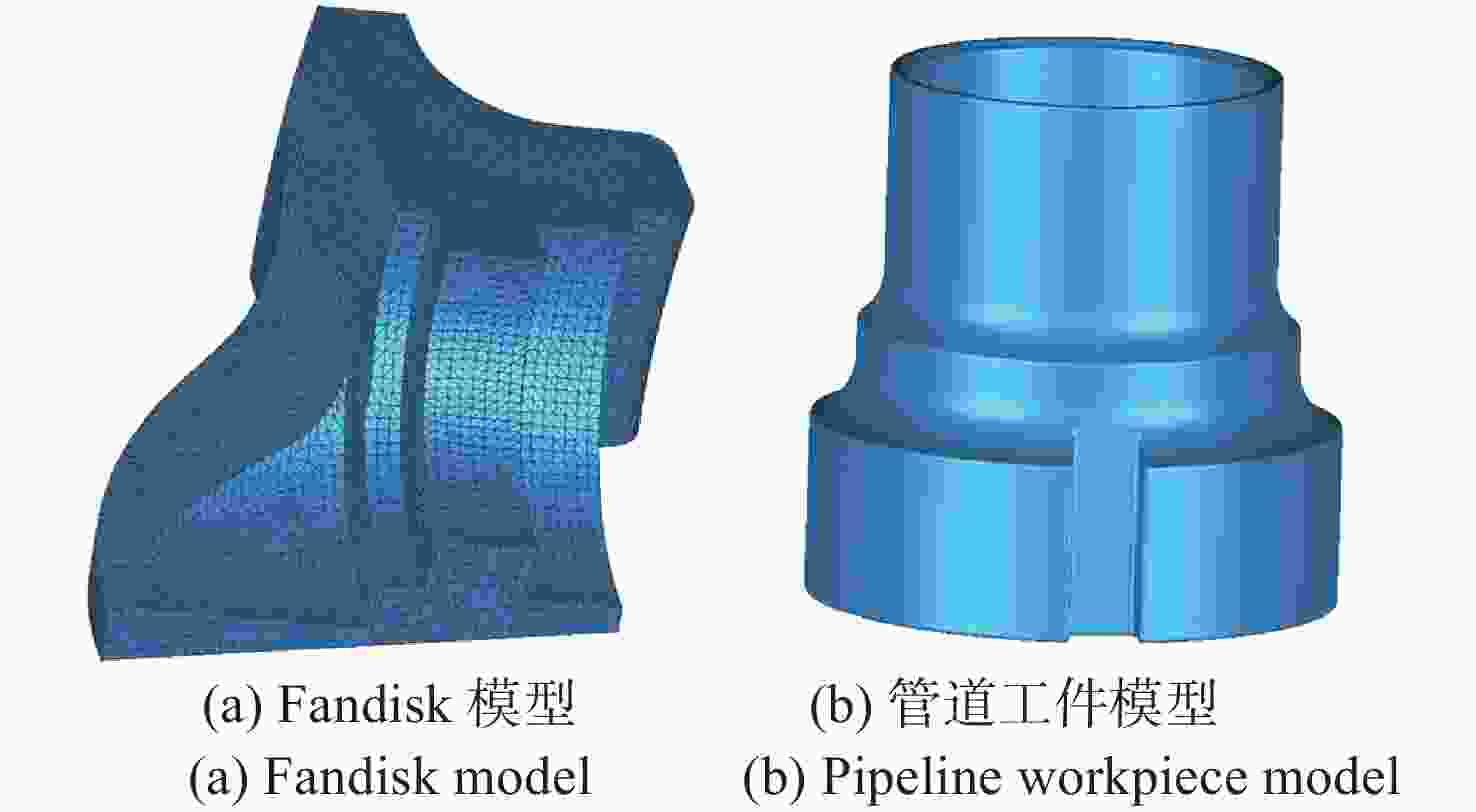
耗时/s1 7401766 0.695 0.249 83.43 29.76 2 34946 0.002 0.002 6.73 0.13 3 14764242 0.387 0.386 197.46 50.48 4 29686649 \ 0.296 \ 113.42 5 13262362 0.473 0.473 208.32 47.32 6 1920009 0.254 0.253 26.54 7.75 7 1794486 0.086 0.085 30.66 8.47 8 4418964 0.858 0.375 50.37 15.93 9 5081628 0.572 0.572 63.20 18.62 10 13136277 0.418 0.418 147.81 46.68 均值 9150133 0.416 0.311 90.50 33.86 -
[1] 周晓东, 张雅超, 谭庆昌, 等. 基于结构光视觉技术的圆柱度测量新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版),2017,47(2):524-529.ZHOU X D, ZHANG Y CH, TAN Q CH, et al. New method of cylindricity measurement based on structured light vision technology[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 524-529. (in Chinese). [2] RAFFAELI R, MENGONI M, GERMANI M, et al. Off-line view planning for the inspection of mechanical parts[J]. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing, 2013, 7(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1007/s12008-012-0160-1 [3] PHAN N D M, QUINSAT Y, LAVERNHE S, et al. Scanner path planning with the control of overlap for part inspection with an industrial robot[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 98(1-4): 629-643. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2336-8 [4] 杨鹏程, 杨朝, 孟杰, 等. 基于法向量和面状指数特征的文物点云棱界配准方法[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(3):654-662. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0156YANG P CH, YANG ZH, MENG J, et al. Aligning method for point cloud prism boundaries of cultural relics based on normal vector and faceted index features[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(3): 654-662. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0156 [5] JUNIOR E M O, SANTOS D R, MIOLA G A R. A new variant of the ICP algorithm for pairwise 3D point cloud registration[J]. American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences, 2022, 85(1): 71-88. [6] YANG J L, LI H D, CAMPBELL D, et al. Go-ICP: a globally optimal solution to 3D ICP point-set registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(11): 2241-2254. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2513405 [7] LIAN W, ZHANG L, YANG M H. An efficient globally optimal algorithm for asymmetric point matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(7): 1281-1293. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2603988 [8] LIU Y L, WANG CH, SONG ZH J, et al. Efficient global point cloud registration by matching rotation invariant features through translation search[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Springer, 2018: 448-463. [9] 刘跃生, 陈新度, 吴磊, 等. 混合稀疏迭代最近点配准[J]. 光学 精密工程,2021,29(9):2255-2267. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212909.2255LIU Y SH, CHEN X D, WU L, et al. Sparse mixture iterative closest point registration[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(9): 2255-2267. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212909.2255 [10] 林森, 张强. 应用邻域点信息描述与匹配的点云配准[J]. 光学 精密工程,2022,30(8):984-997. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223008.0984LIN S, ZHANG Q, et al. Point cloud registration using neighborhood point information description and matching[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(8): 984-997. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223008.0984 [11] GARLAND M, WILLMOTT A, HECKBERT P S. Hierarchical face clustering on polygonal surfaces[C]. Proceedings of the 2001 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics, ACM, 2001: 49-58. [12] THEOLOGOU P, PRATIKAKIS I, THEOHARIS T. Unsupervised spectral mesh segmentation driven by heterogeneous graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 397-410. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2544311 [13] SHI J B, MALIK J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(8): 888-905. doi: 10.1109/34.868688 [14] CHAHHOU M, MOUMOUN L, EL FAR M, et al. Segmentation of 3D meshes usingp-spectral clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(8): 1687-1693. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.2297314 [15] DONG Q J, WANG Z X, LI M Y, et al. Laplacian2Mesh: Laplacian-based mesh understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2023.3259044. [16] LEI H, AKHTAR N, SHAH M, et al. Mesh convolution with continuous filters for 3-D surface parsing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3281871. [17] LAVOUÉ G, DUPONT F, BASKURT A. A new CAD mesh segmentation method, based on curvature tensor analysis[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2005, 37(10): 975-987. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2004.09.001 [18] BHOLOWALIA P, KUMAR A. EBK-means: A clustering technique based on elbow method and K-means in WSN[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2014, 105(9): 17-24. [19] COHEN-STEINER D, ALLIEZ P, DESBRUN M. Variational shape approximation[C]. Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH 2004 Papers, ACM, 2004: 905-914. [20] LIANG Y Q, HE F ZH, ZENG X T. 3D mesh simplification with feature preservation based on whale optimization algorithm and differential evolution[J]. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 2020, 27(4): 417-435. doi: 10.3233/ICA-200641 [21] DU T, INALA J P, PU Y W, et al. InverseCSG: Automatic conversion of 3D models to CSG trees[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37(6): 213. [22] BORJI A, CHENG M M, HOU Q B, et al. Salient object detection: a survey[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(2): 117-150. doi: 10.1007/s41095-019-0149-9 [23] ATTENE M, FALCIDIENO B, SPAGNUOLO M. Hierarchical mesh segmentation based on fitting primitives[J]. The Visual Computer, 2006, 22(3): 181-193. doi: 10.1007/s00371-006-0375-x [24] SHAPIRA L, SHAMIR A, COHEN-OR D. Consistent mesh partitioning and skeletonisation using the shape diameter function[J]. The Visual Computer, 2008, 24(4): 249-259. doi: 10.1007/s00371-007-0197-5 [25] KATZ S, TAL A. Hierarchical mesh decomposition using fuzzy clustering and cuts[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2003, 22(3): 954-961. doi: 10.1145/882262.882369 [26] LAI Y K, HU S M, MARTIN R R, et al. Rapid and effective segmentation of 3D models using random walks[J]. Computer Aided Geometric Design, 2009, 26(6): 665-679. doi: 10.1016/j.cagd.2008.09.007 [27] YANG H, SHI J N, CARLONE L. TEASER: fast and certifiable point cloud registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(2): 314-333. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2020.3033695 [28] RODRIGUES R S V, MORGADO J F M, GOMES A J P. A contour-based segmentation algorithm for triangle meshes in 3D space[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2015, 49: 24-35. [29] CHEN X B, GOLOVINSKIY A, FUNKHOUSER T. A benchmark for 3D mesh segmentation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(3): 73. -





 下载:
下载: