-
摘要:
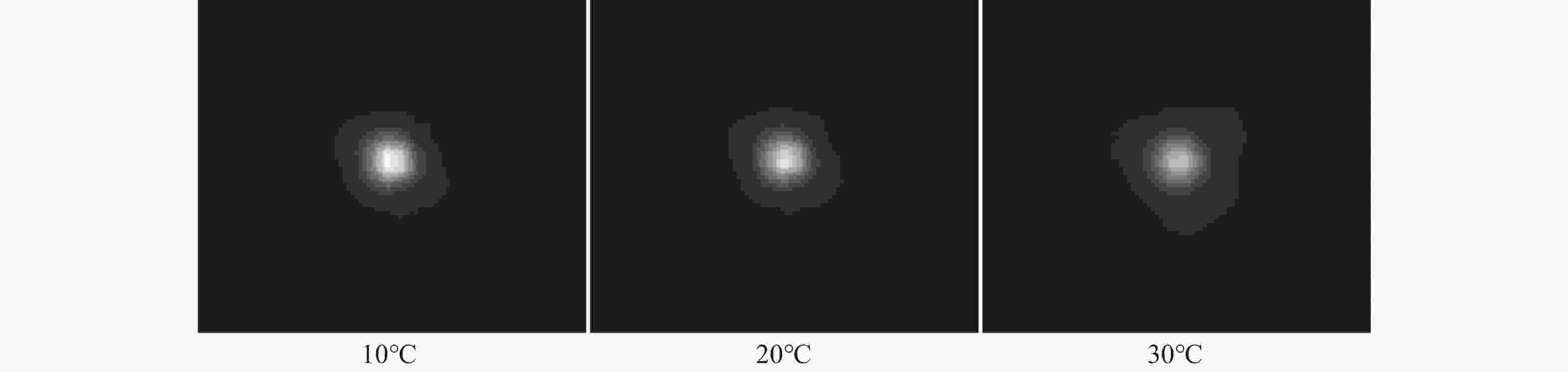
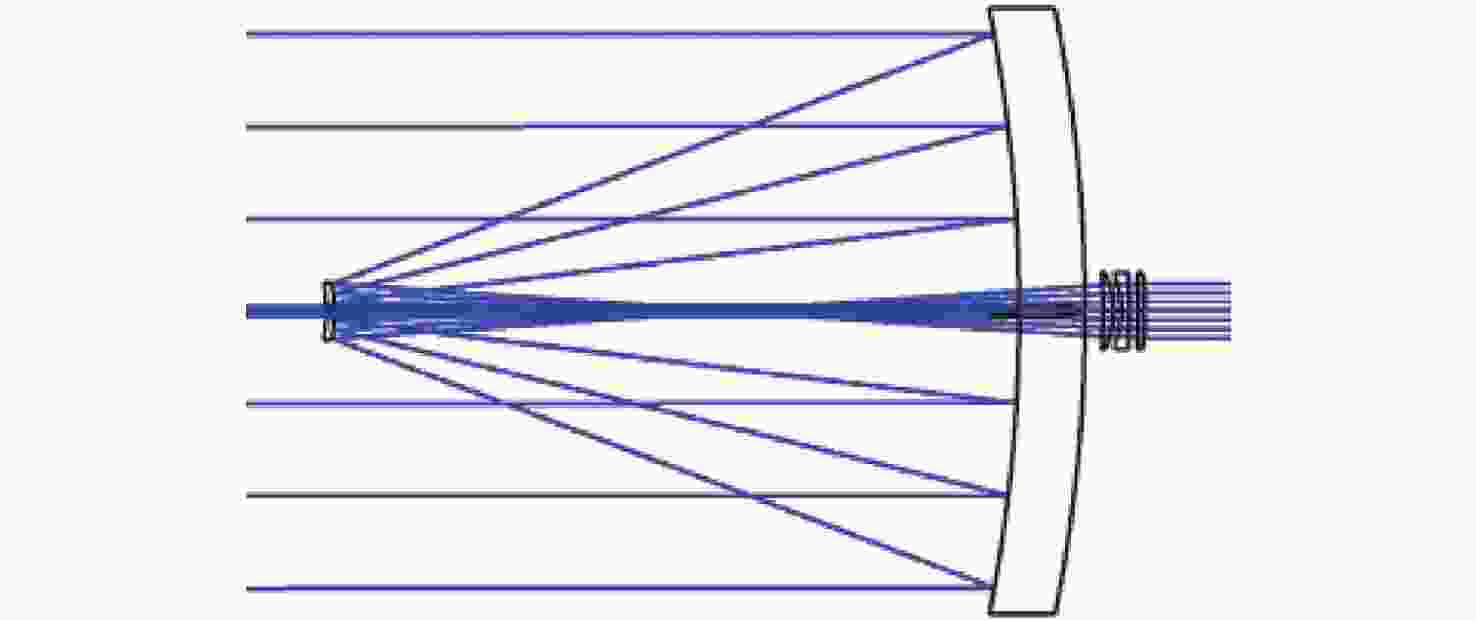
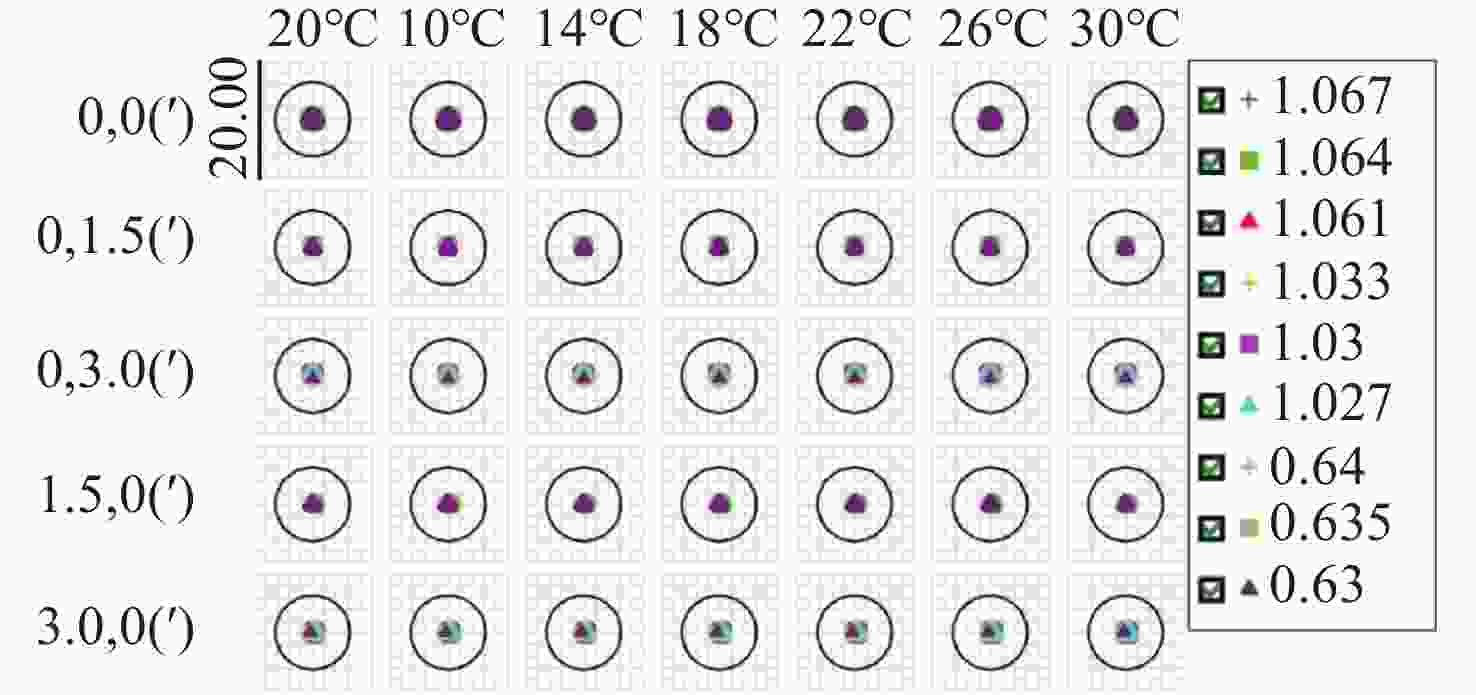
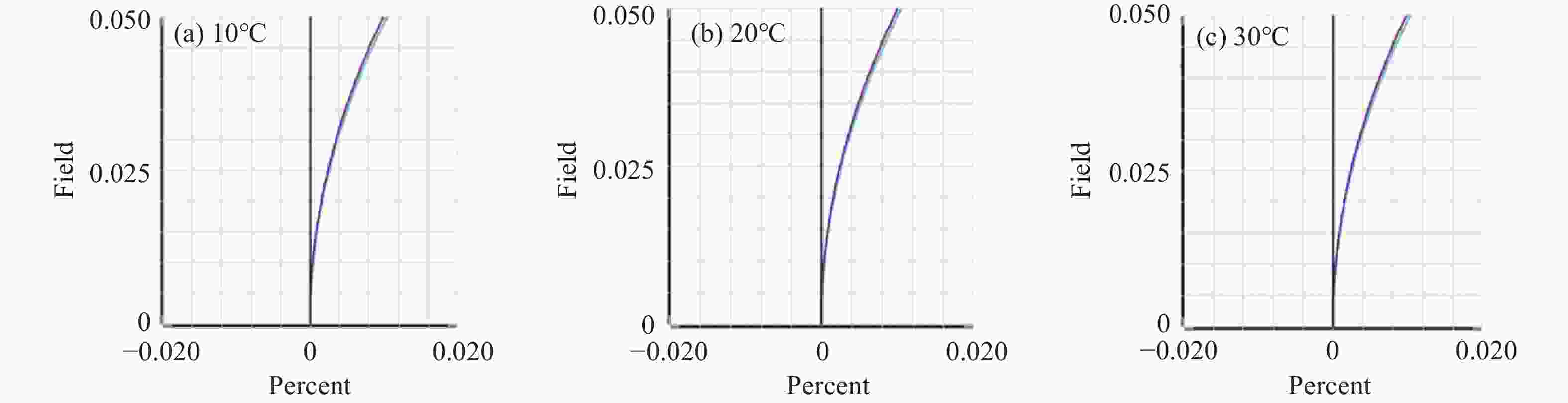
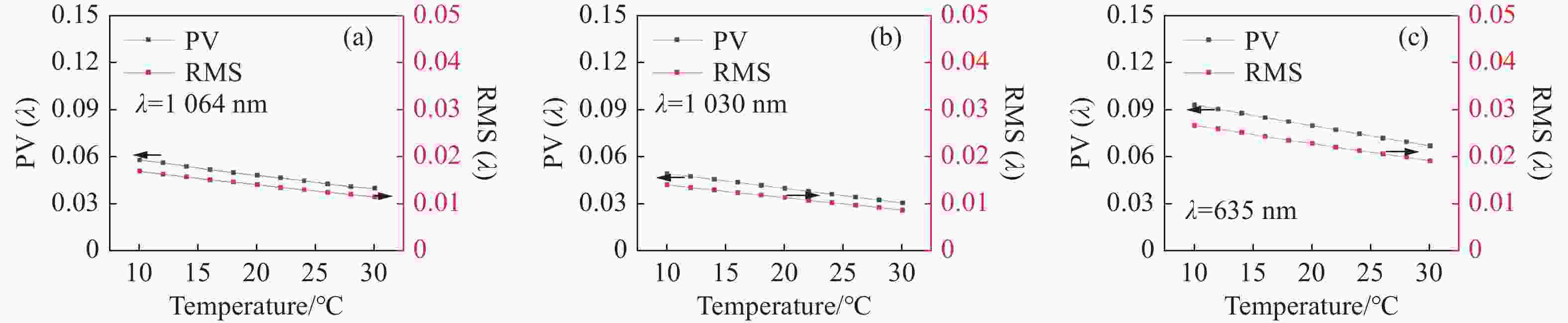
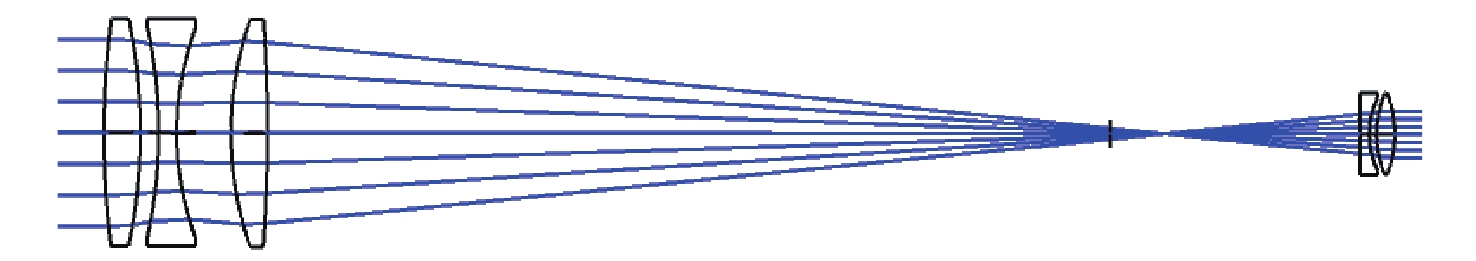
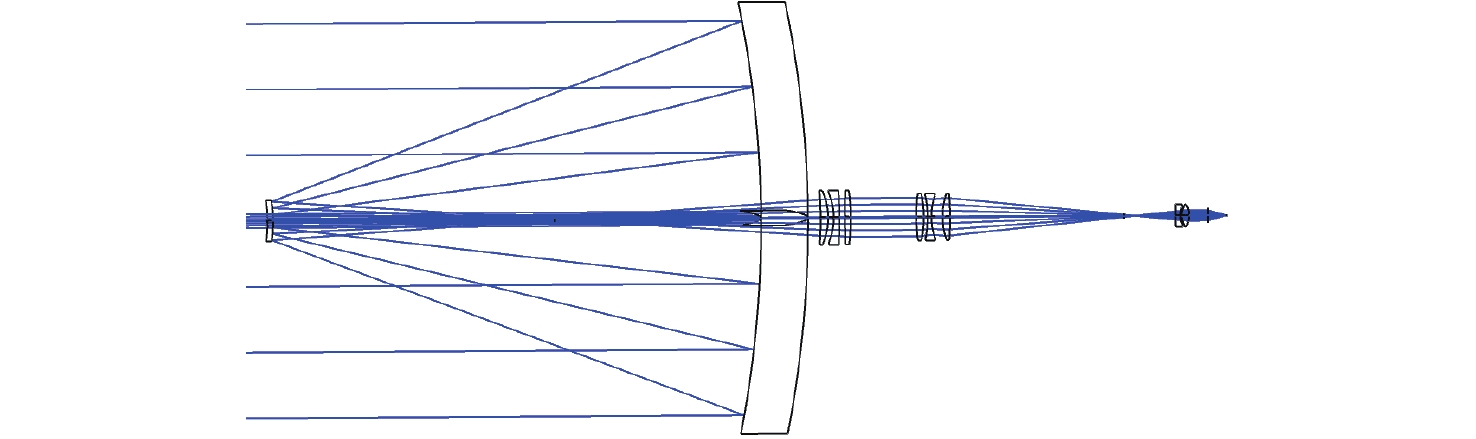
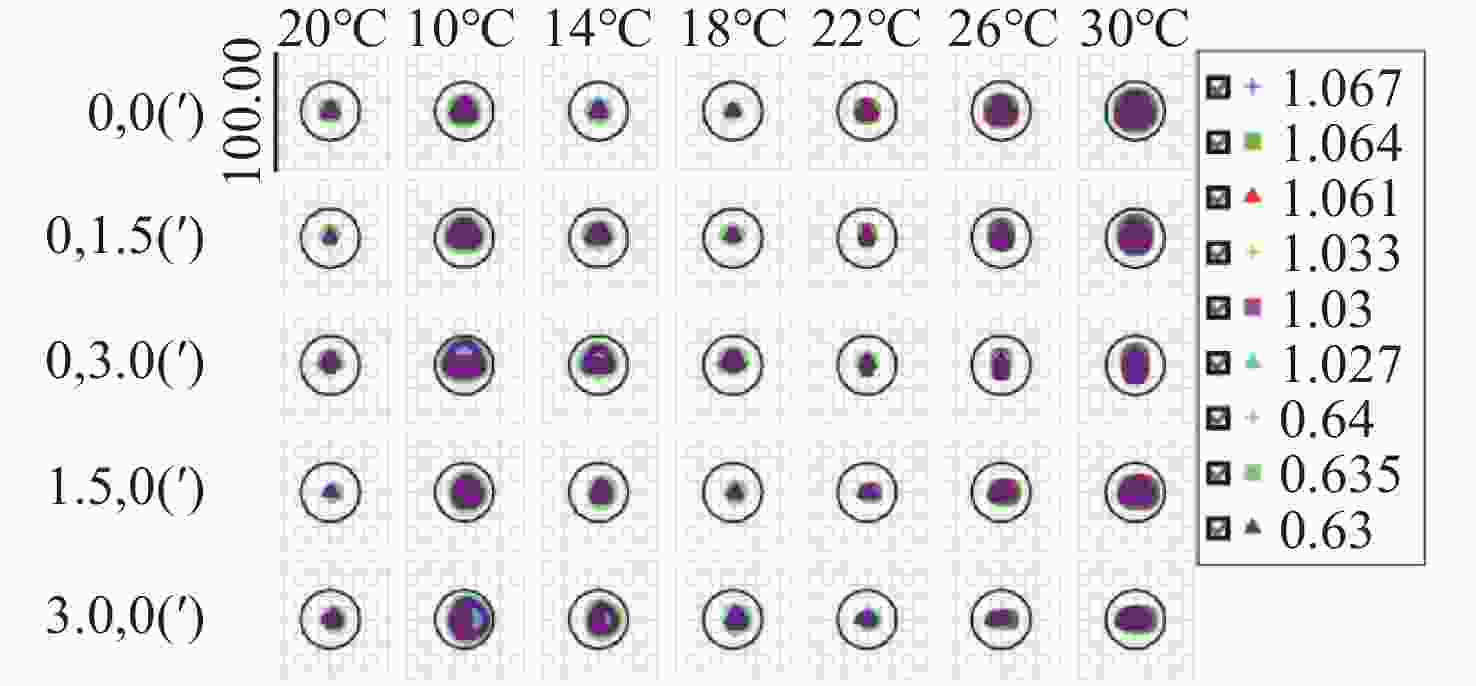
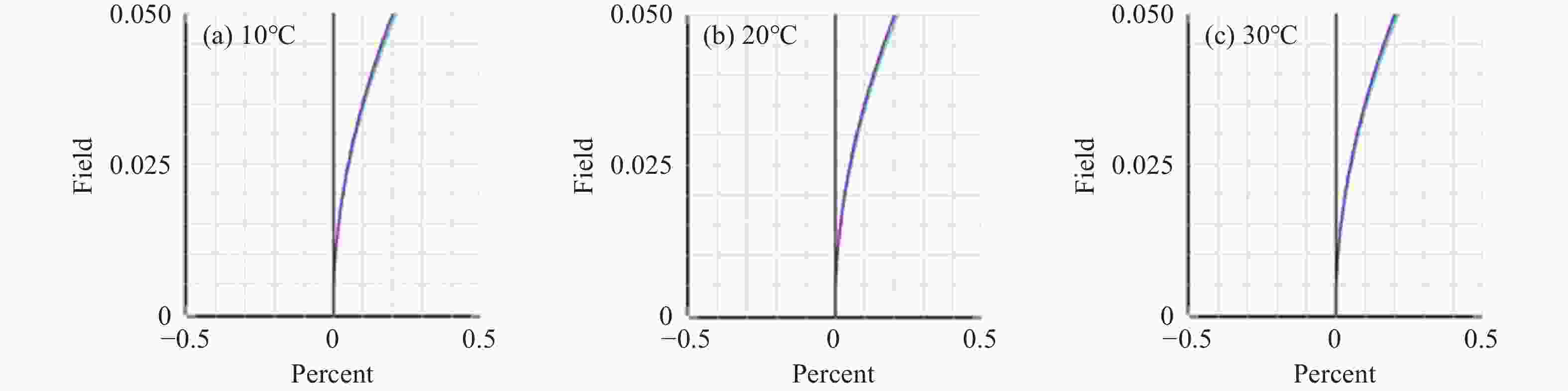
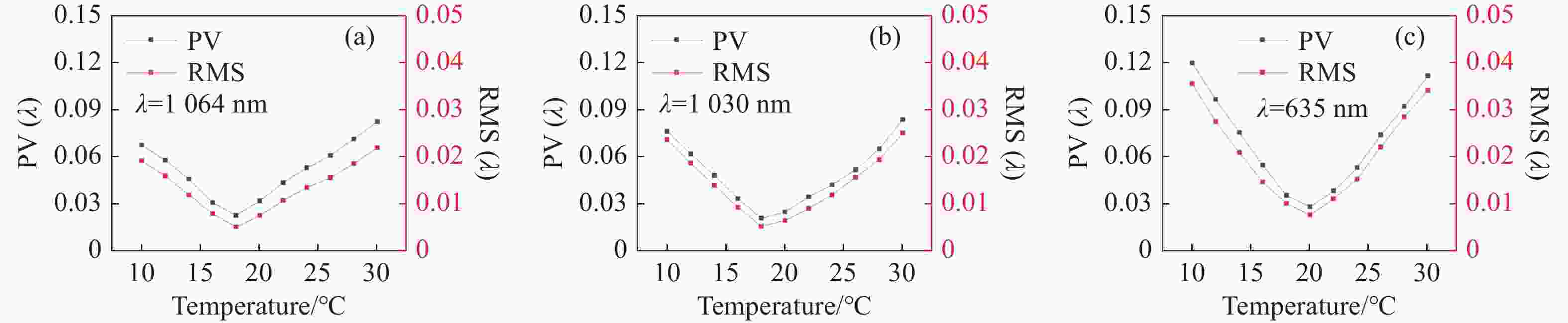
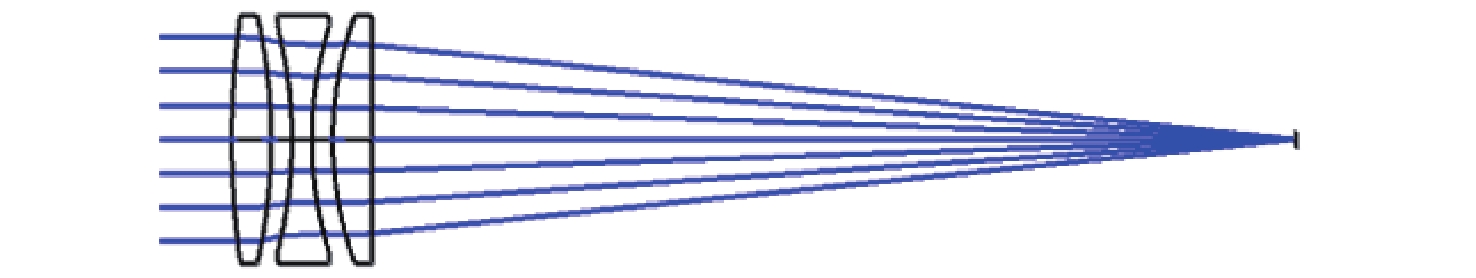
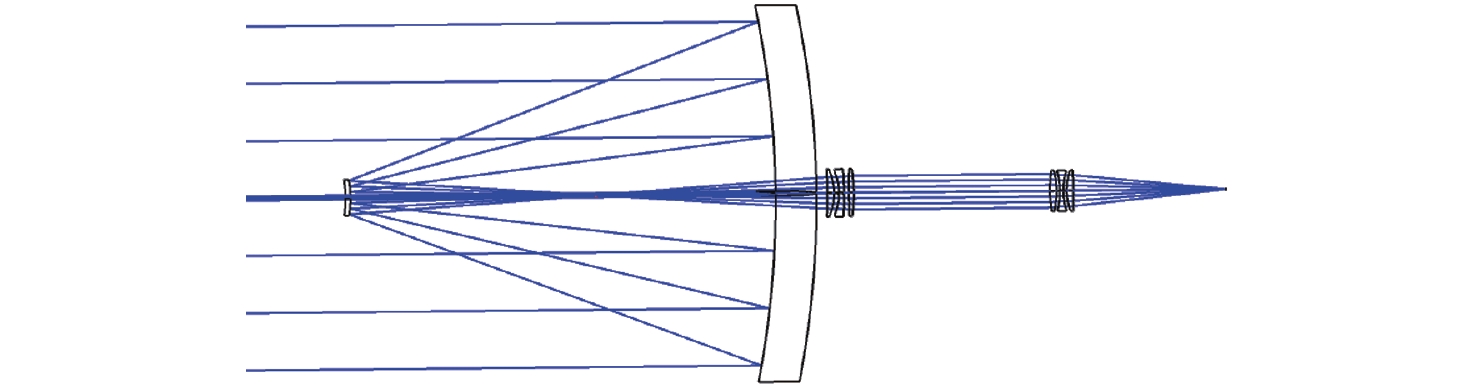
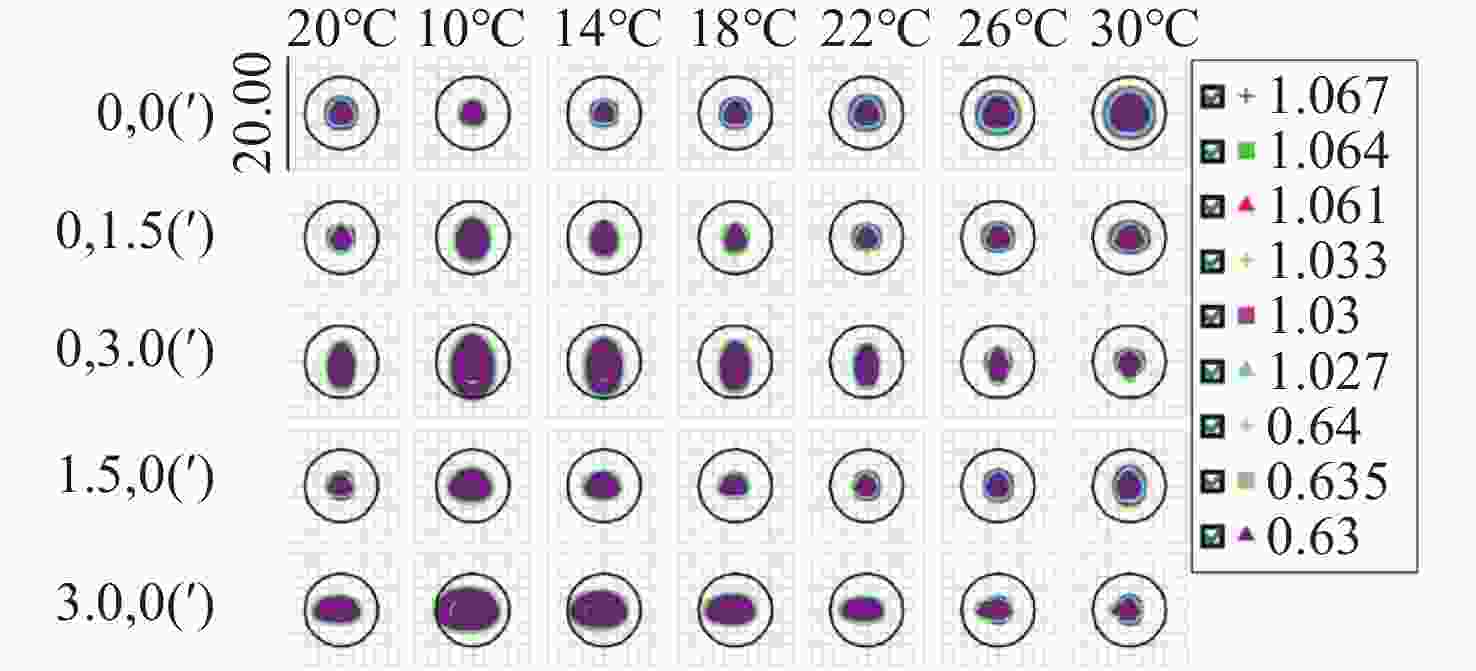
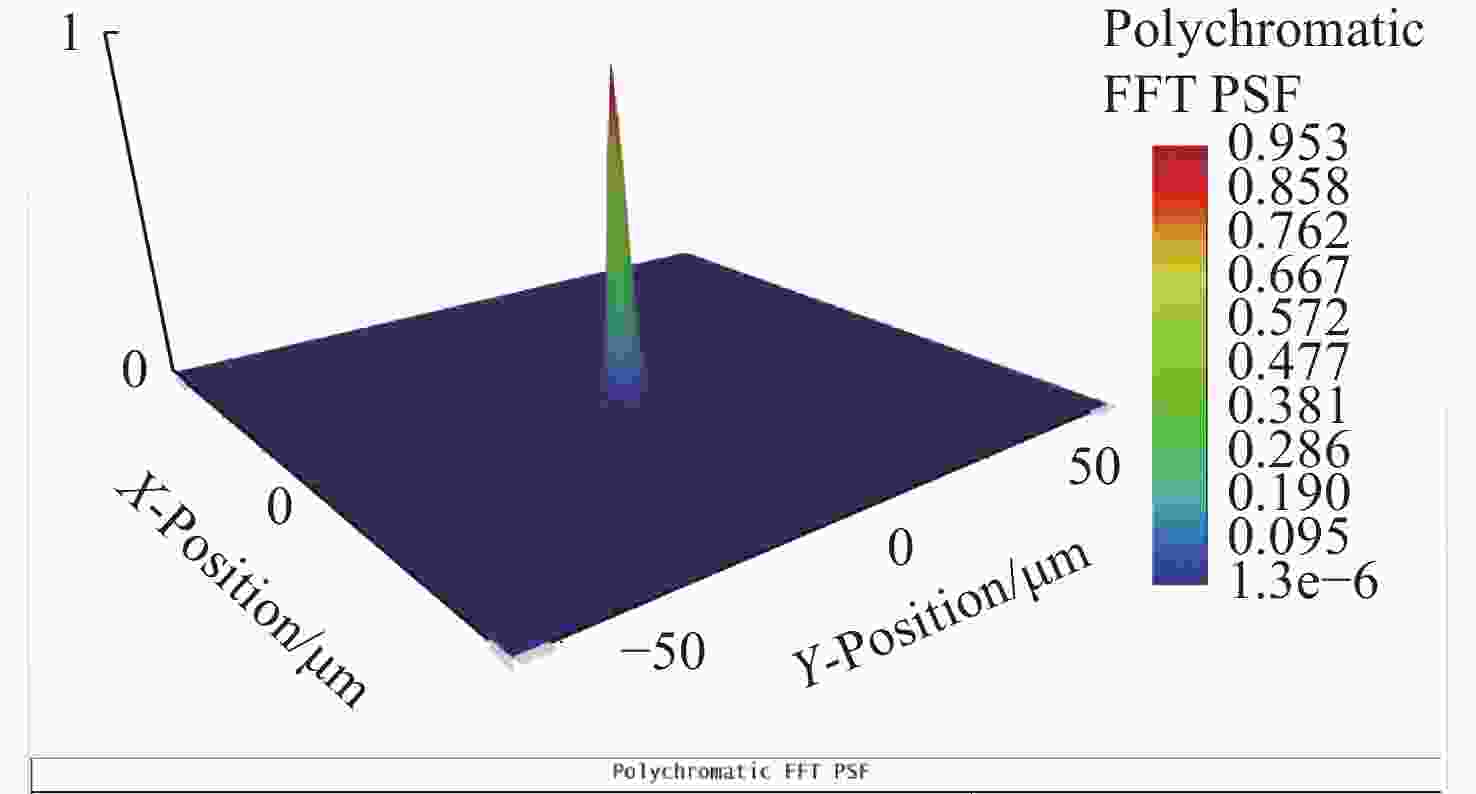
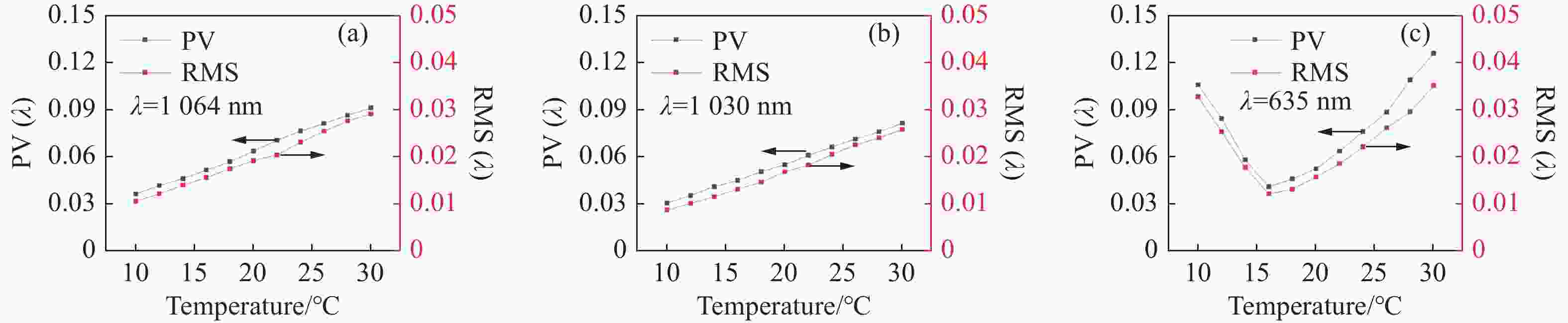
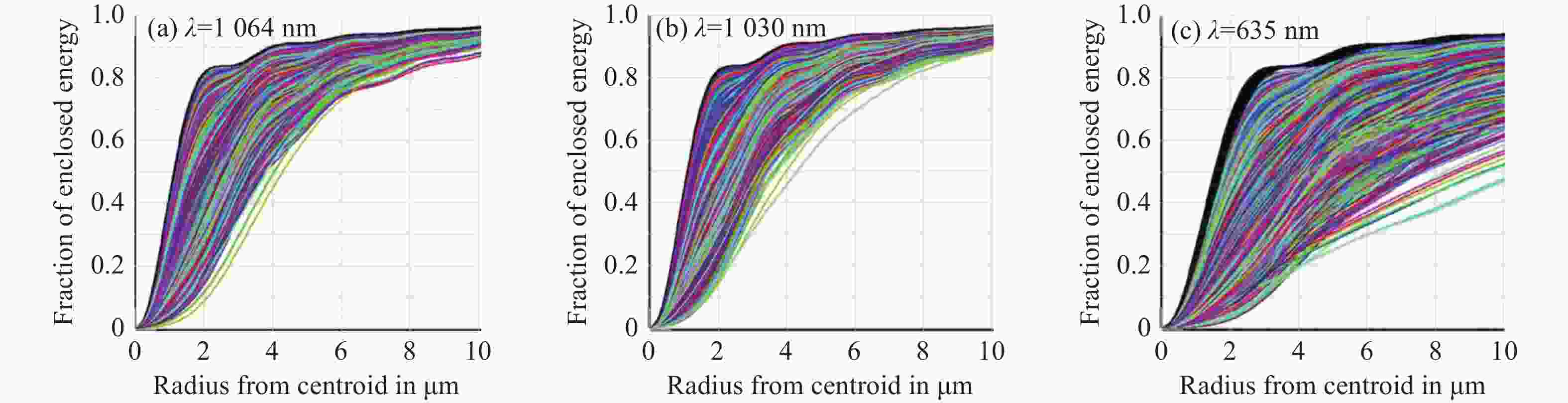
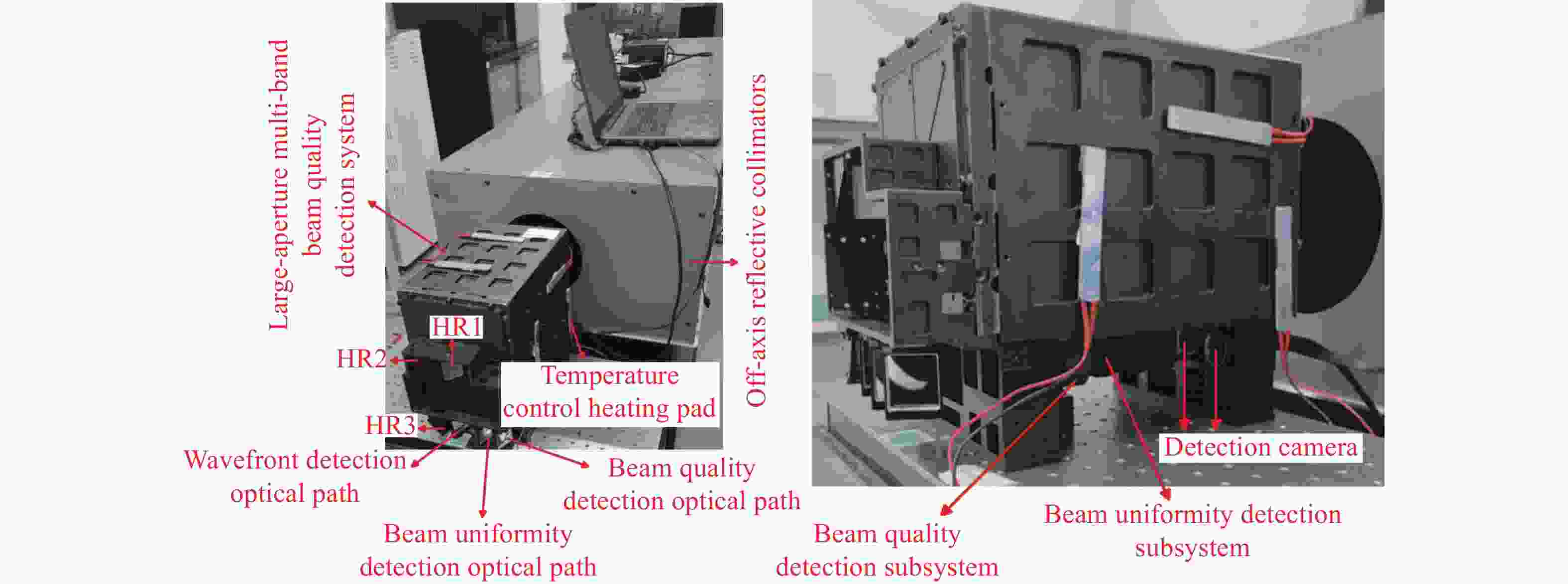
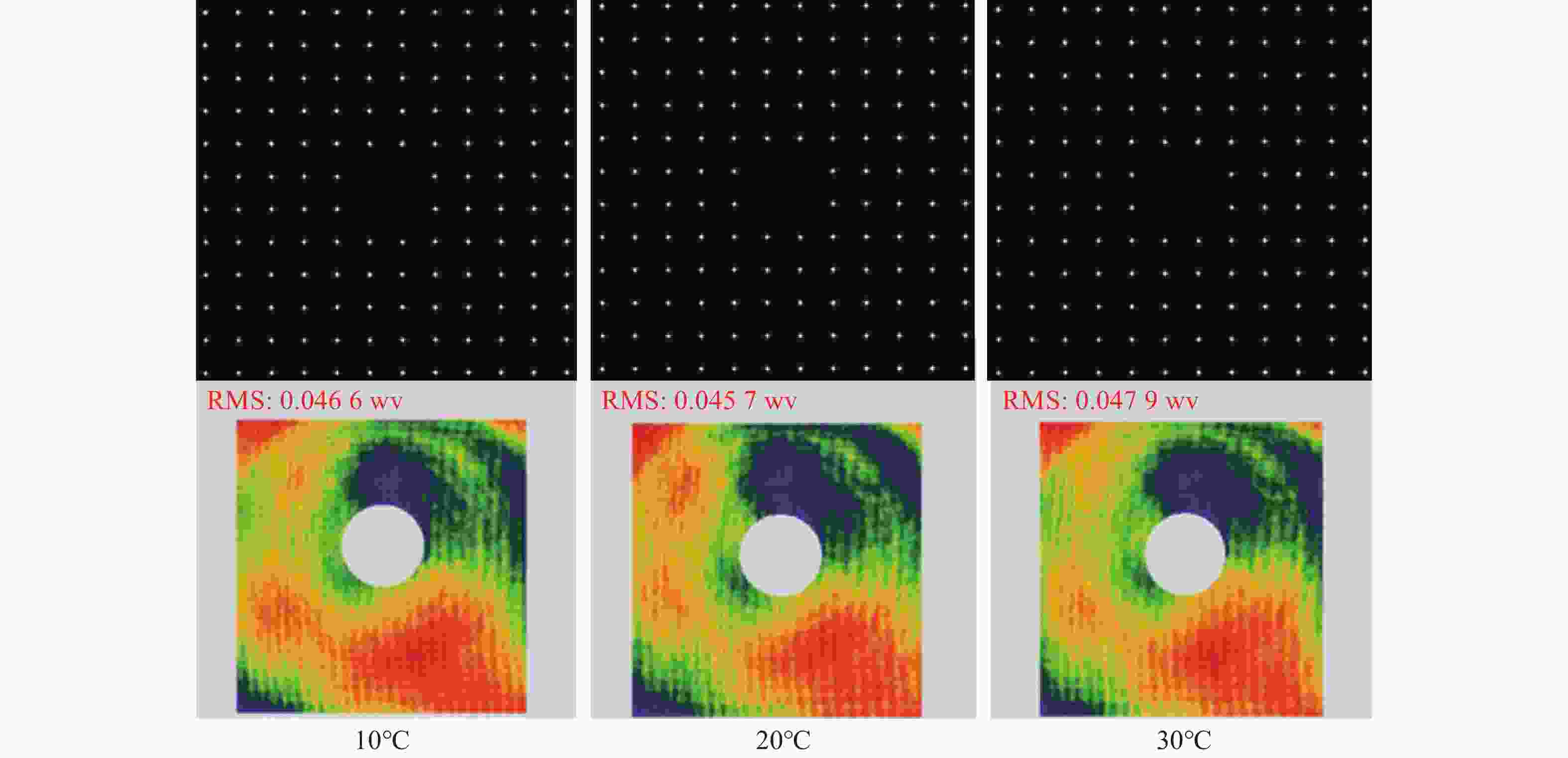
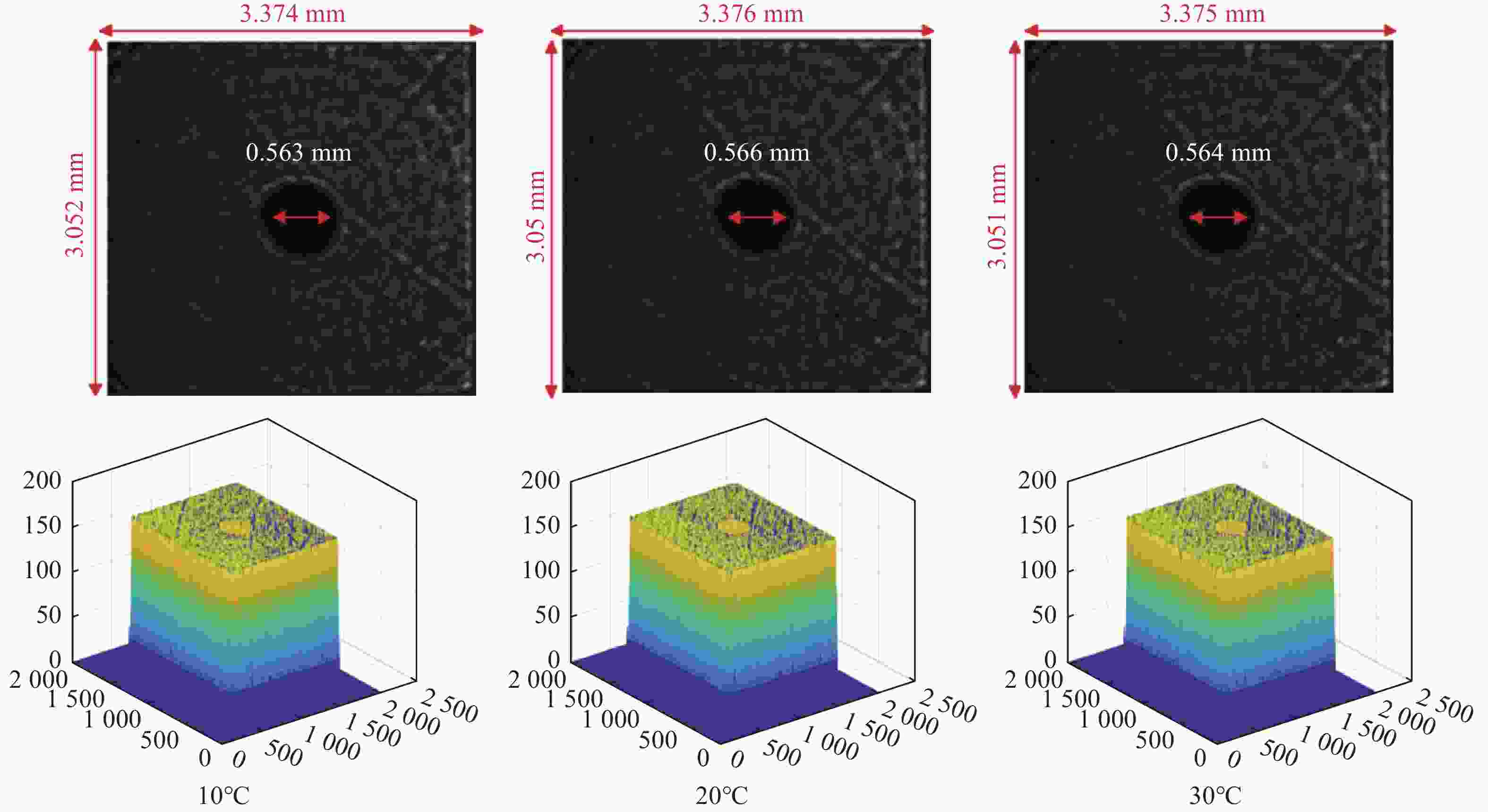
光谱合成技术是实现高能激光输出的重要技术途径,如何在高功率输出的前提下,保证高光束质量的激光输出已成为当前光谱合成技术最迫切要解决的问题。本文针对155 mm×140 mm矩形口径、(1 064±3)nm、(1030±3)nm和(635±5)nm波段光束的参数检测问题,设计了大口径多波段多参数检测系统。波前检测单元基于开普勒的望远结构,在构建变形镜与微透镜共轭关系的同时,压缩光束口径以匹配探测器尺寸。前组物镜采用卡塞格林结构,以解决大口径、多波段的色差校正难题;后组镜采用三片式复消色差折射镜组,补偿色差的同时,兼顾无热化设计,用以补偿前组物镜的残余热差和后组镜热差。经波前检测单元后进行分光探测,实现光束质量和光束均匀性检测。为了提高系统的环境适应性,采用光学被动无热化方法对系统进行了20 °C±10 °C的无热化设计。最后,对系统进行装调测试,采用泽尼克波前复原方法对波前探测相机采集的光斑图像进行波前复原,测得10 °C~30 °C下系统波前的RMS值优于0.0524λ(λ=632.8 nm),光束均匀性优于0.893,光束质量
β 因子优于1.26倍衍射极限。Abstract:Spectral synthesis technology is an important technical approach to achieving high-energy laser output. Ensuring high-quality laser output under the premise of high-power output has become the most urgent goal in further developing spectral synthesis technology. Aiming at the challenge of parameter detection for 155 mm × 140 mm rectangular aperture, (1064 ± 3) nm, (1030 ± 3) nm, and (635 ± 5) nm band beams, we design a large-aperture multi-band multi-parameter detection system. The wavefront detection unit is based on Kepler’s telescopic structure, the conjugate relationship between the deformable mirror and the microlens is constructed, at the same time, the compressed beam matches the detector size. The front group objective lenses adopt a Cassegrain structure to solve the problem of color difference correction in large-aperture and multi-band. The rear group of mirrors adopts a three-piece apochromatic refractor group, which compensates for the color difference while accounting for the non-thermal design. It can be used for compensation to the residual thermal difference of the front group of objectives and the thermal difference of the rear group of mirrors. After passing through the wavefront detection unit, the beam quality and beam uniformity can be measured. In order to improve the environmental adaptability of the system, it was designed through an optical passive anthermic method at 20 °C±10 °C. Finally, the system was installed and tested, and the wavefront spot image collected by the wavefront detection camera was restored using the Zernike wavefront restoration method. The measured RMS value of the wavefront of the system is better than 0.0524λ (λ=632.8 nm), the beam uniformity is better than 0.893, and the beam quality
β factor is better than 1.26 times the diffraction limit at 10 °C−30 °C. -
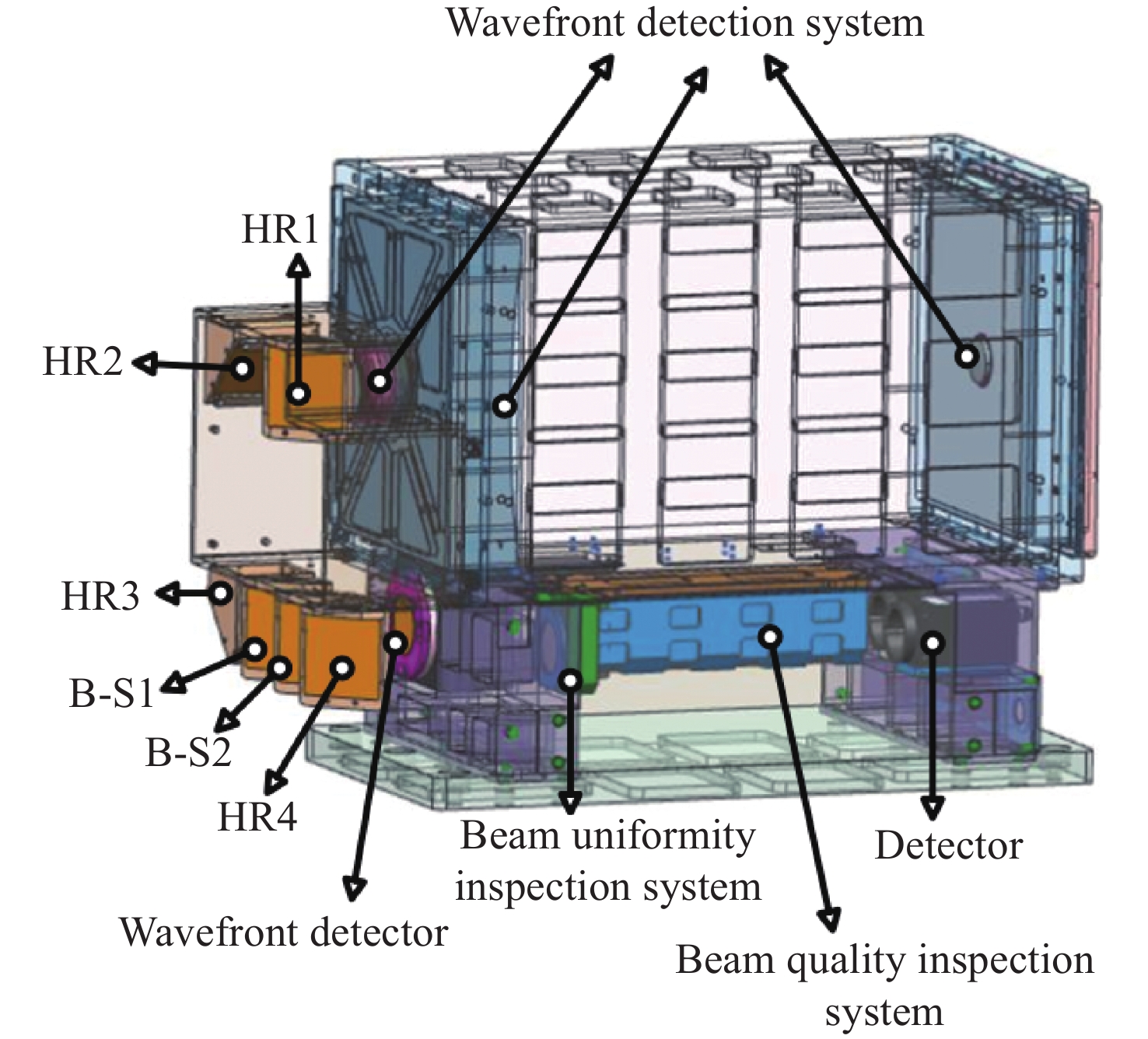
表 1 大口径多波段光束质量检测系统机械结构技术指标
Table 1. Technical index of mechanical structure of large-aperture multi-band beam quality detection system
指标 数值 系统整体尺寸 360 mm×200 mm×300 mm(长×宽×高) 系统重量 ≤25 kg 表 2 波前检测系统技术指标
Table 2. Technical index of the wavefront detection system
指标 数值 视场 ±3' 波段 (1064±3) nm、(1030±3) nm、(635±5) nm 口径 155 mm×140 mm 缩束倍率 1∶10.2 畸变 ≤1% 装调精度(RMS波前) ≤λ/15 工作环境 20 °C±10 °C 10 °C~30 °C光学系统设计结果波前PV值和RMS值的波动范围 PV≤λ/10,
RMS≤λ/20公差指标(RMS波前) ≤λ/8 表 3 波前检测系统透镜相关系数
Table 3. Lens parameters of wavefront detection system
表面类型 曲率半径/mm 厚度/mm 材料 标准面 −576.126 −260.000 MIRROR 标准面 −69.040 150.000 MIRROR 标准面 Infinity 141.761 — 标准面 −192.097 4.000 H-ZPK5 标准面 −35.350 2.998 — 标准面 −33.460 3.000 H-F4 标准面 −236.455 3.000 — 标准面 −376.700 3.000 H-LAF3B 标准面 −116.680 30.000 — 表 4 波前检测系统公差数据
Table 4. Tolerance of wavefront detection system
No. 光圈数 厚度/mm 透镜偏心/mm 透镜倾斜/(´) 折射率 阿贝误差% 镜1 3 0.05 0.01 0.6 0.001 0.3 镜2 3 0.05 0.01 0.6 0.001 0.3 镜3 3 0.05 0.03 1.5 0.001 0.3 镜4 3 0.05 0.03 1.5 0.001 0.3 镜5 3 0.05 0.03 1.5 0.001 0.3 表 5 波前检测系统λ1、λ2、λ3波段蒙特卡洛分析结果
Table 5. Monte Carlo analysis results for λ1、λ2、λ3 in wavefront detection system
指标 数值 λ1 λ2 λ3 蒙特卡洛分析/% 90 90 90 RMS波前 0.0931λ1 0.0922λ2 0.1303λ3 表 6 光束均匀性检测系统技术指标
Table 6. Technical index of beam uniformity detection system
指标 数值 缩束倍率 1:4.5 畸变 ≤1% 均匀性检测指标 ≥0.8 10 °C~30 °C光学系统设计结果波前
PV值和RMS值的波动范围PV≤λ/10,RMS≤λ/20 公差指标(RMS波前) ≤λ/8 表 7 光束均匀性检测子系统透镜数据
Table 7. Lens parameters of beam uniformity detection subsystem
表面类型 曲率半径/mm 厚度/mm 材料 标准面 98.136 4.000 H-LAF3B 标准面 −61.232 2.000 — 标准面 −54.883 2.000 H-F4 标准面 32.964 5.984 — 标准面 38.503 4.000 H-ZPK5 标准面 −172.545 92.637 — 标准面 Infinity 27.515 — 标准面 557.963 1.000 H-F4 标准面 9.375 0.800 — 标准面 11.436 2.000 H-ZPK5 标准面 −12.687 10.000 — 表 8 光束均匀性检测系统λ1、λ2、λ3波段蒙特卡洛分析结果
Table 8. Monte Carlo analysis results for λ1、λ2、λ3 in beam uniformity detection system
指标 数值 λ1 λ2 λ3 蒙特卡洛分析/% 90 90 90 RMS波前 0.1101λ1 0.1172λ2 0.1439λ3 表 9 光束质量检测系统技术指标
Table 9. Technical index of beam quality detection system
指标 数值 光束质量β因子 β≤1.3 10 °C~30 °C光学系统设计结果波前PV值和RMS值的波动范围 PV≤λ/10,RMS≤λ/20 表 10 光束质量检测子系统透镜数据
Table 10. Lens parameters of beam quality detection subsystem
表面类型 曲率半径/mm 厚度/mm 材料 标准面 88.158 4.000 H-LAF3B 标准面 −54.625 2.090 — 标准面 −44.584 2.000 H-F4 标准面 37.738 2.121 — 标准面 35.877 4.000 H-ZPK5 标准面 −779.682 93.327 — -
[1] 崔宇龙, 周智越, 黄威, 等. 中红外光纤激光技术研究进展与展望[J]. 光学学报,2022,42(9):0900001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0900001CUI Y L, ZHOU ZH Y, HUANG W, et al. Progress and prospect of mid-infrared fiber laser technology[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 0900001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0900001 [2] 王辉华, 林龙信, 叶辛, 等. 国外新型电驱动高能激光技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 红外与激光工程,2023,52(1):20220283. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220283WANG H H, LIN L X, YE X, et al. Status and development trend of overseas new type electric drive high-energy laser technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(1): 20220283. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220283 [3] KALISKY Y Y, KALISKY O. The status of high-power lasers and their applications in the battlefield[J]. Optical Engineering, 2010, 49(9): 091003. doi: 10.1117/1.3484954 [4] 顾勇刚, 牛健, 杨坚, 等. 激光在医疗领域中的应用[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(2):283-295. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0017GU Y G, NIU J, YANG J, et al. Application of laser in the medical field[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 283-295. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0017 [5] LV F R, LIU Y K, GAO SH J, et al. Research on bandwidth improvement of fine tracking control system in space laser communication[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(11): 1179. doi: 10.3390/photonics10111179 [6] 刘立培, 陈皓, 杨仁人, 等. 基体预热对激光熔覆制备M2钢熔覆层表面硬度均匀性的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2023: 1-24.LIU L P, CHEN H, YANG R R, et al. Effect of substrate preheating on the uniformity of surface hardness of M2 cladding layer prepared by laser cladding[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023: 1-24. (in Chinese). [7] 李苏, 张占辉, 韩善果, 等. 激光技术在材料加工领域的应用与发展[J]. 精密成形工程,2020,12(4):76-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2020.04.008LI S, ZHANG ZH H, HAN SH G, et al. Application and development of laser technology in the field of material processing[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2020, 12(4): 76-85. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2020.04.008 [8] 周子超, 崔文达, 奚小明, 等. 高功率光纤激光器纤芯温度在线测量技术及其应用研究进展[J]. 光学学报,2023,43(17):1714006. doi: 10.3788/AOS230988ZHOU Z C, CUI W D, XI X M, et al. Real-time temperature measurement of high-power fiber laser core and its applications[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(17): 1714006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS230988 [9] 曲锐. 机载多波段共孔径动态成像光学系统研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2023.QU R. Research on airborne multi-band common aperture dynamic imaging optical system[D]. Xi’an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi’an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanins, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023. (in Chinese). [10] 苏春轩. 板条固体激光器自适应光学优化控制技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2021.SU CH X. Optimal control adaptive optics system for solid-state slab lasers[D]. Chengdu: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese). [11] 李霄. 板条激光放大器相干合成技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2011.LI X. Study on coherent beam combination technology of slab lasers[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2011. (in Chinese). [12] 马士青. 基于自适应光学的混合腔板条固体激光器光束质量控制技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院光电技术研究所), 2021.MA SH Q. Research on beam quality control technology of hybrid-cavity slab solid-state laser based on adaptive optics[D]. Chengdu: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese). [13] SCHULZE C, FLAMM D, DUPARRÉ M, et al. Beam-quality measurements using a spatial light modulator[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(22): 4687-4689. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004687 [14] NIEDERRITER R D, GOPINATH J T, SIEMENS M E. Measurement of the M2 beam propagation factor using a focus-tunable liquid lens[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(8): 1591-1598. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.001591 [15] DU Y ZH, FU Y Q, ZHENG L X. Complex amplitude reconstruction for dynamic beam quality M2 factor measurement with self-referencing interferometer wavefront sensor[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(36): 10180-10186. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.010180 [16] 张成栋. 激光光束质量诊断与测量研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2017.ZHANG CH D. Diagnosis and measurement of laser beam quality[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2017. (in Chinese). [17] 张禹, 杨忠明, 刘兆军, 等. 大口径多光谱通道波前测量系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(8):20190559. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20190559ZHANG Y, YANG ZH M, LIU ZH J, et al. Design of large aperture multi-spectra channel wavefront measurement system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(8): 20190559. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20190559 [18] 潘国涛, 闫钰锋, 于信, 等. 矩形大口径激光光束质量评价光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学,2022,15(2):306-317. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0130PAN G T, YAN Y F, YU X, et al. Design of optical system for quality evaluation of a large rectangular aperture laser beam[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(2): 306-317. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0130 [19] 李晶. 基于次镜像移补偿的航空折反式光学系统降敏与无热化技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2023.LI J. Research on desensitization and athermal technology of aerial catadioptric optical system based on the secondary mirror image motion compensation[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023. (in Chinese). [20] 张大庆. 基于卡式结构的红外光学系统设计[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009.ZHANG D Q. Design of infrared optical system based on gassegrain-type[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese). [21] CHEN ZH ZH, XU Y T, GUO Y D, et al. 8.2 kW high beam quality quasi-continuous-wave face-pumped Nd: YAG slab amplifier[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(16): 5011-5015. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.005011 [22] ALLIK T H, DIXON R E, PROFFITT R P, et al. Beam uniformity analysis of infrared laser illuminators[J]. Optical Engineering, 2015, 54(2): 026103. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.54.2.026103 -





 下载:
下载: