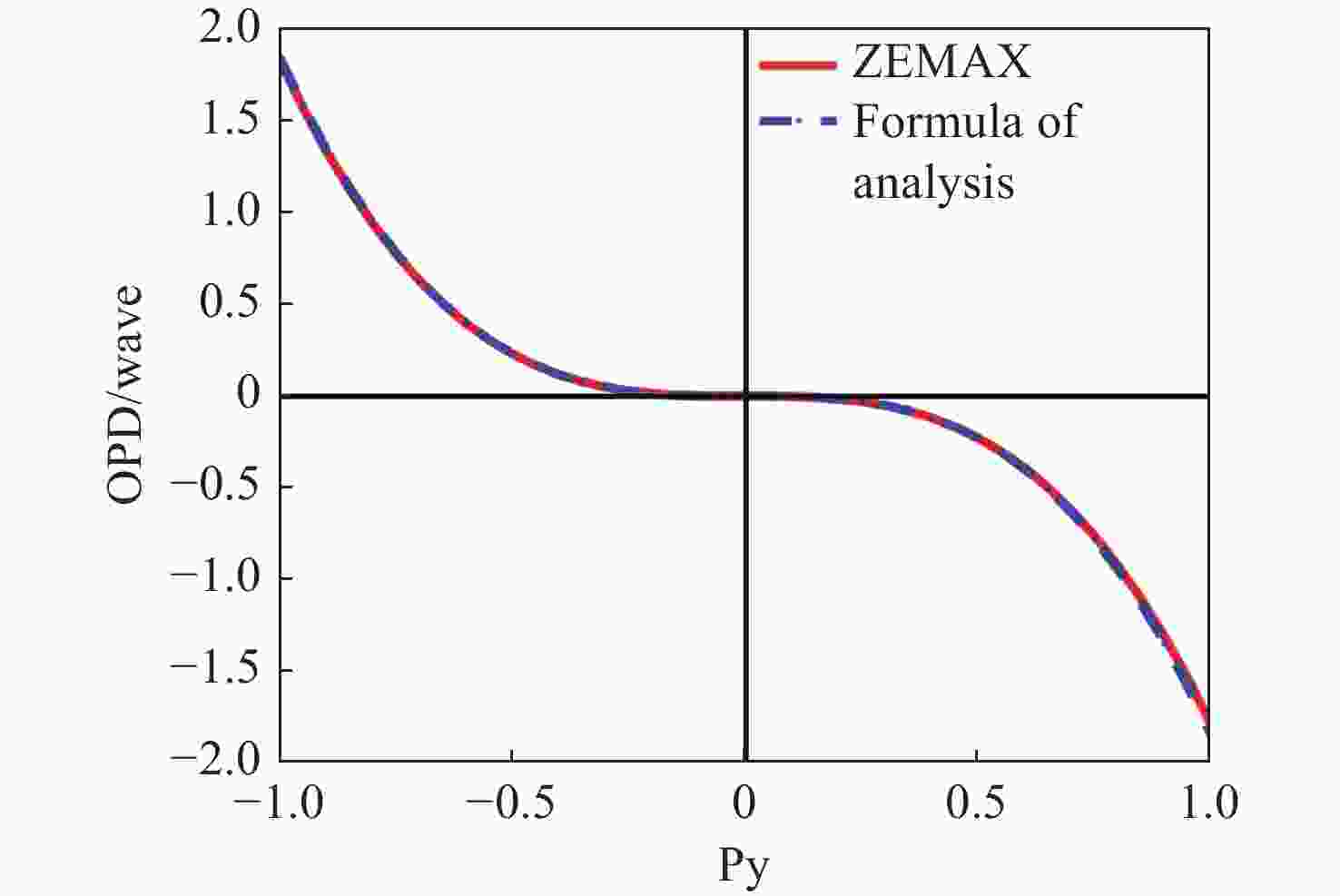
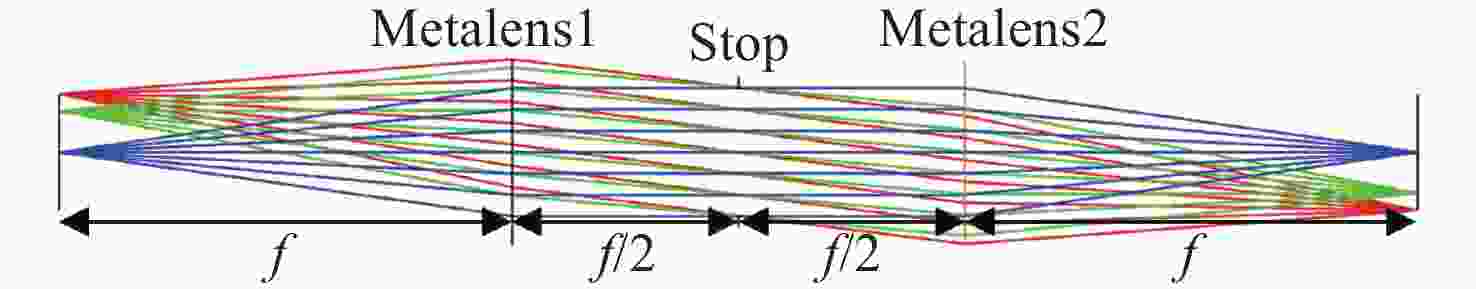
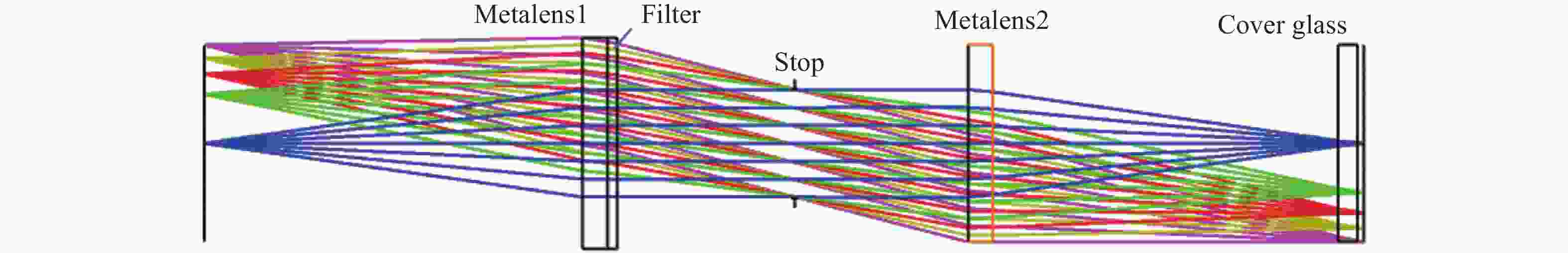
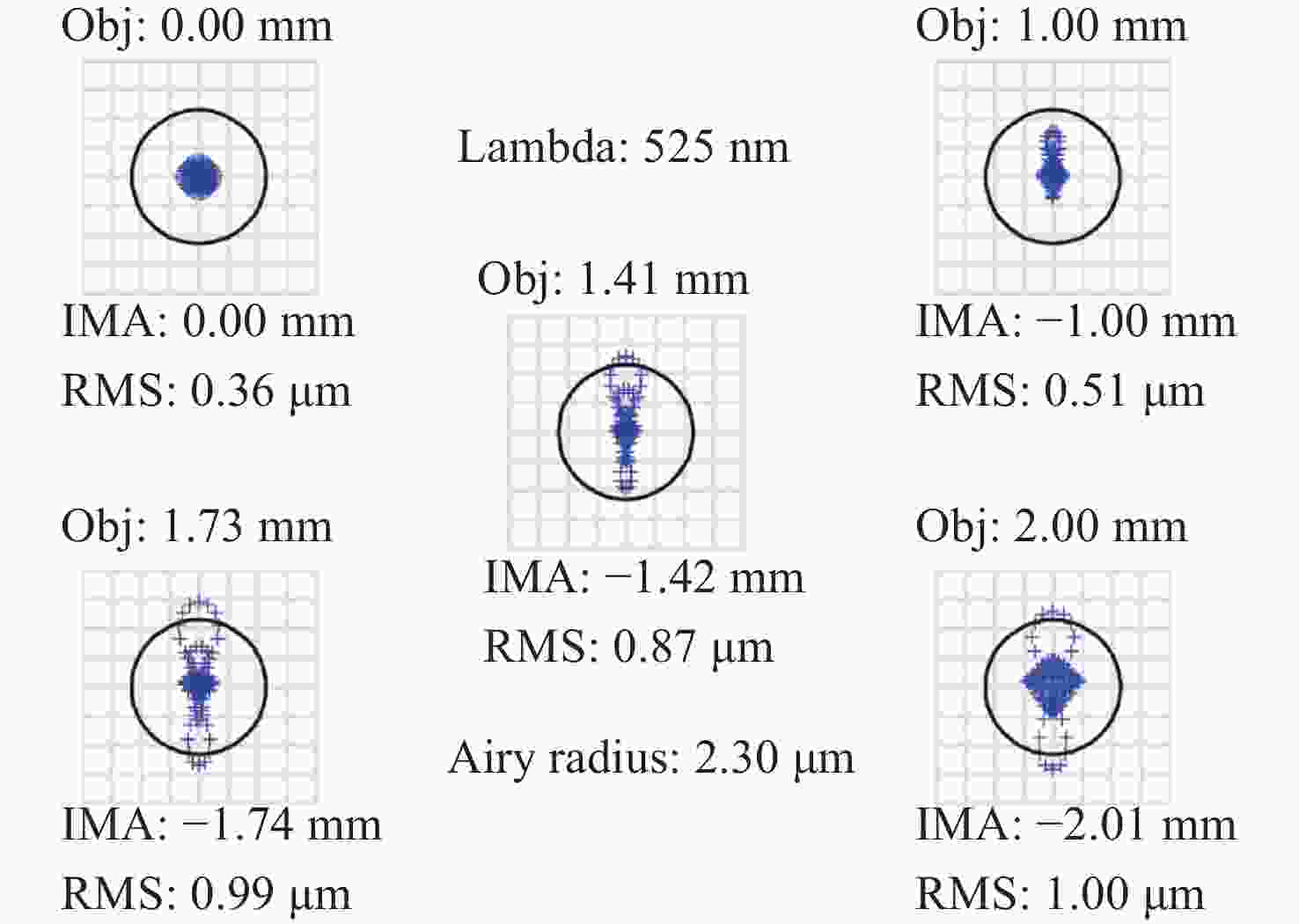
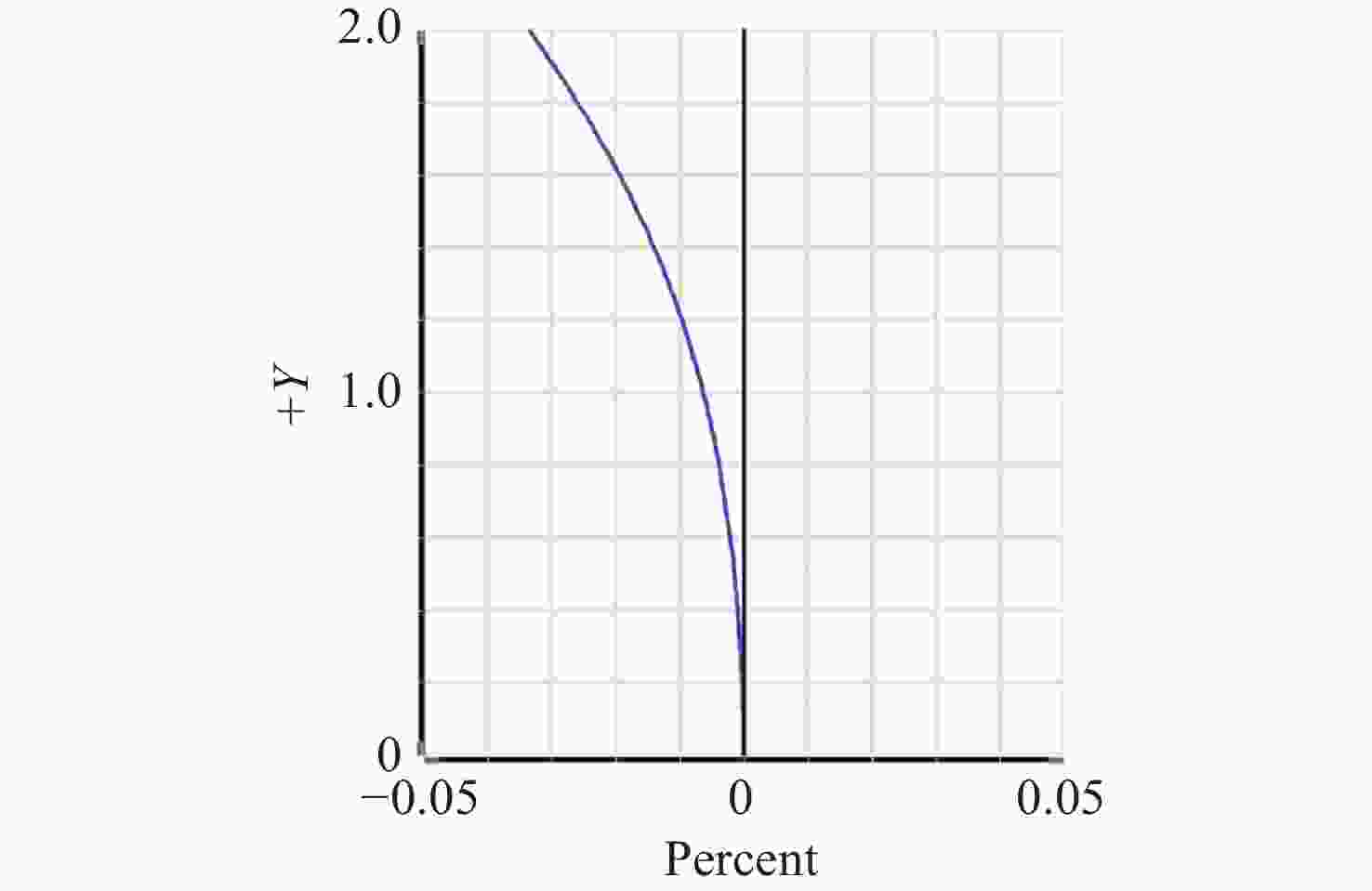
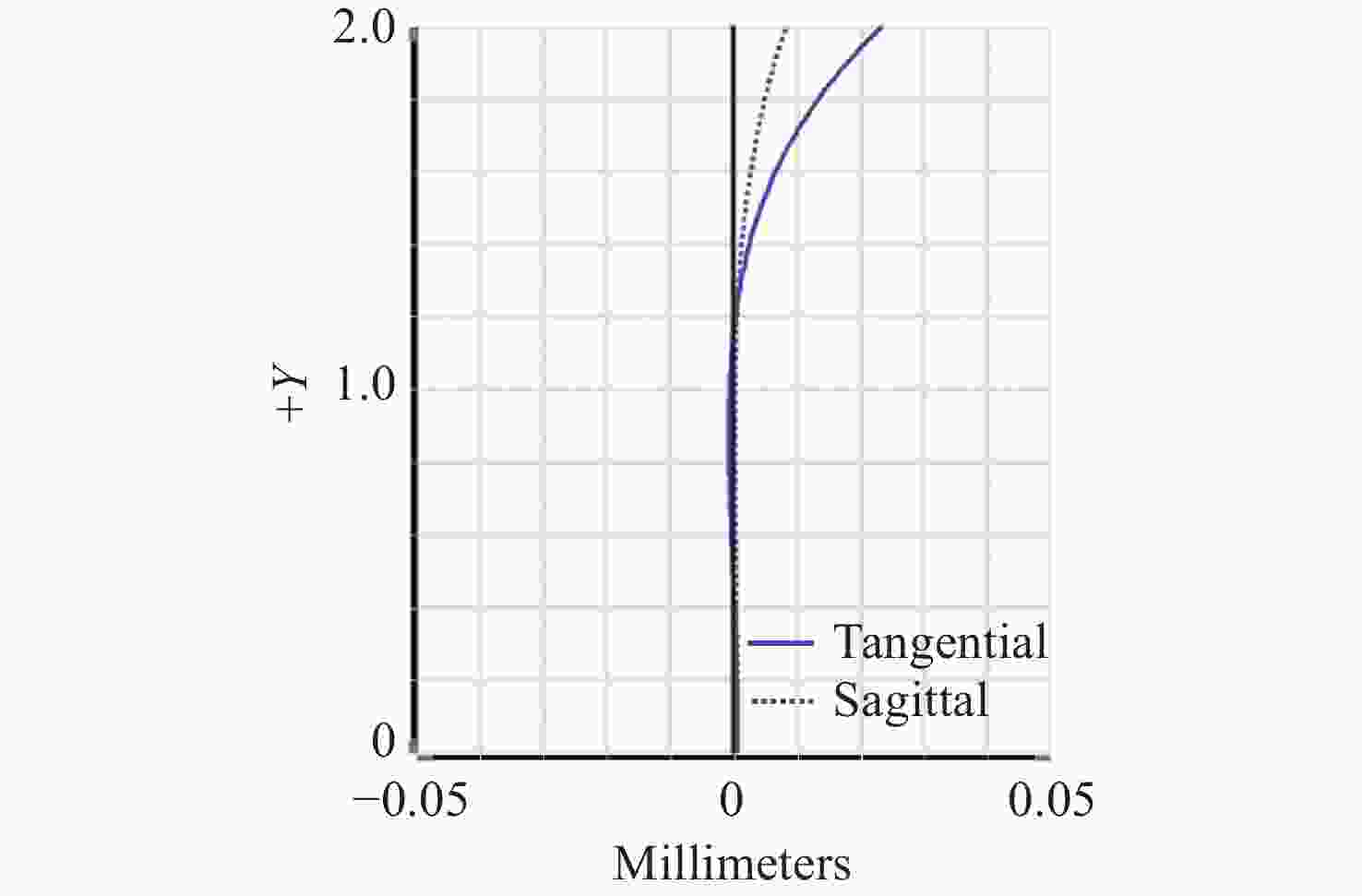
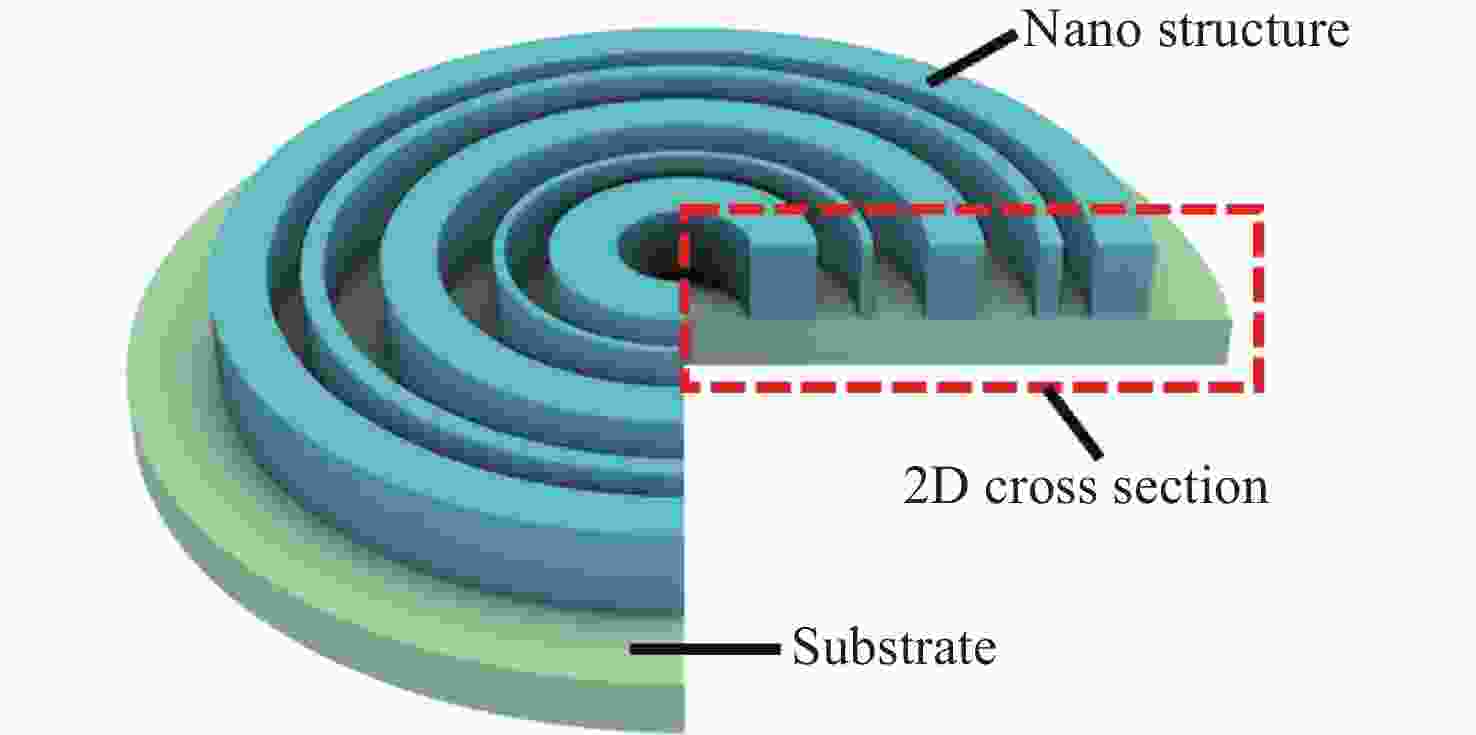
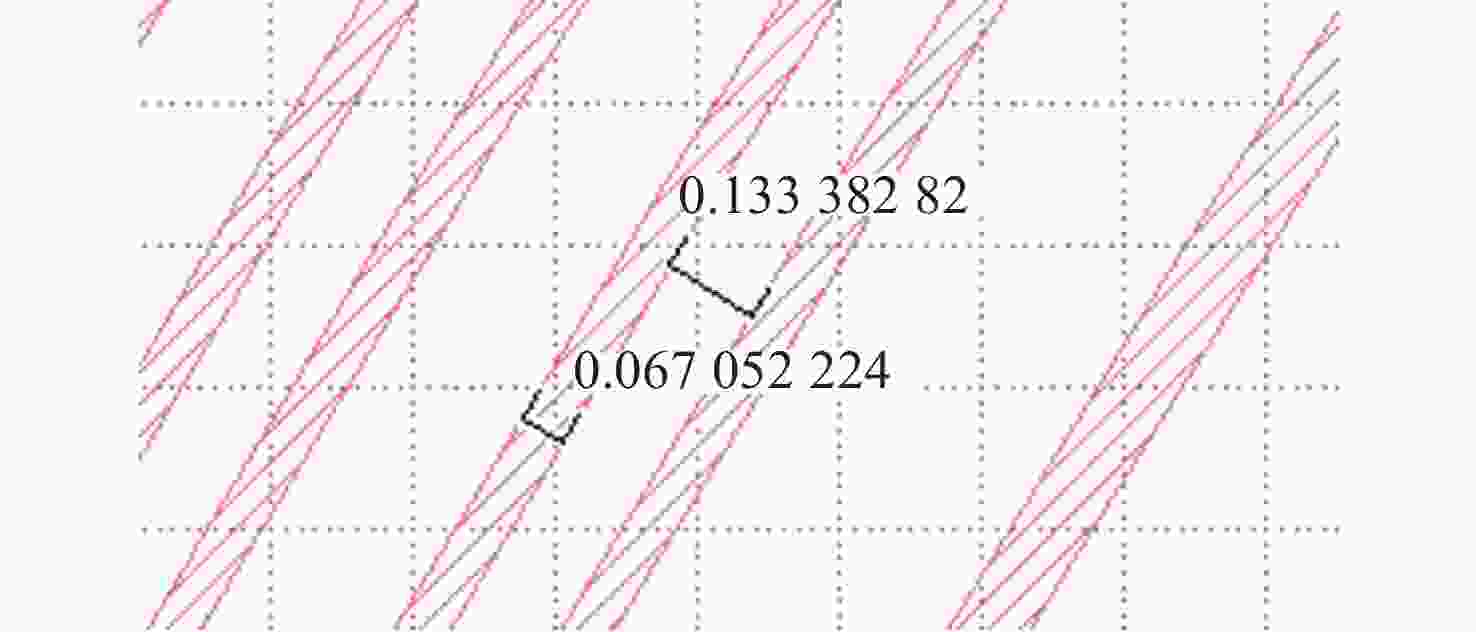
-
摘要:
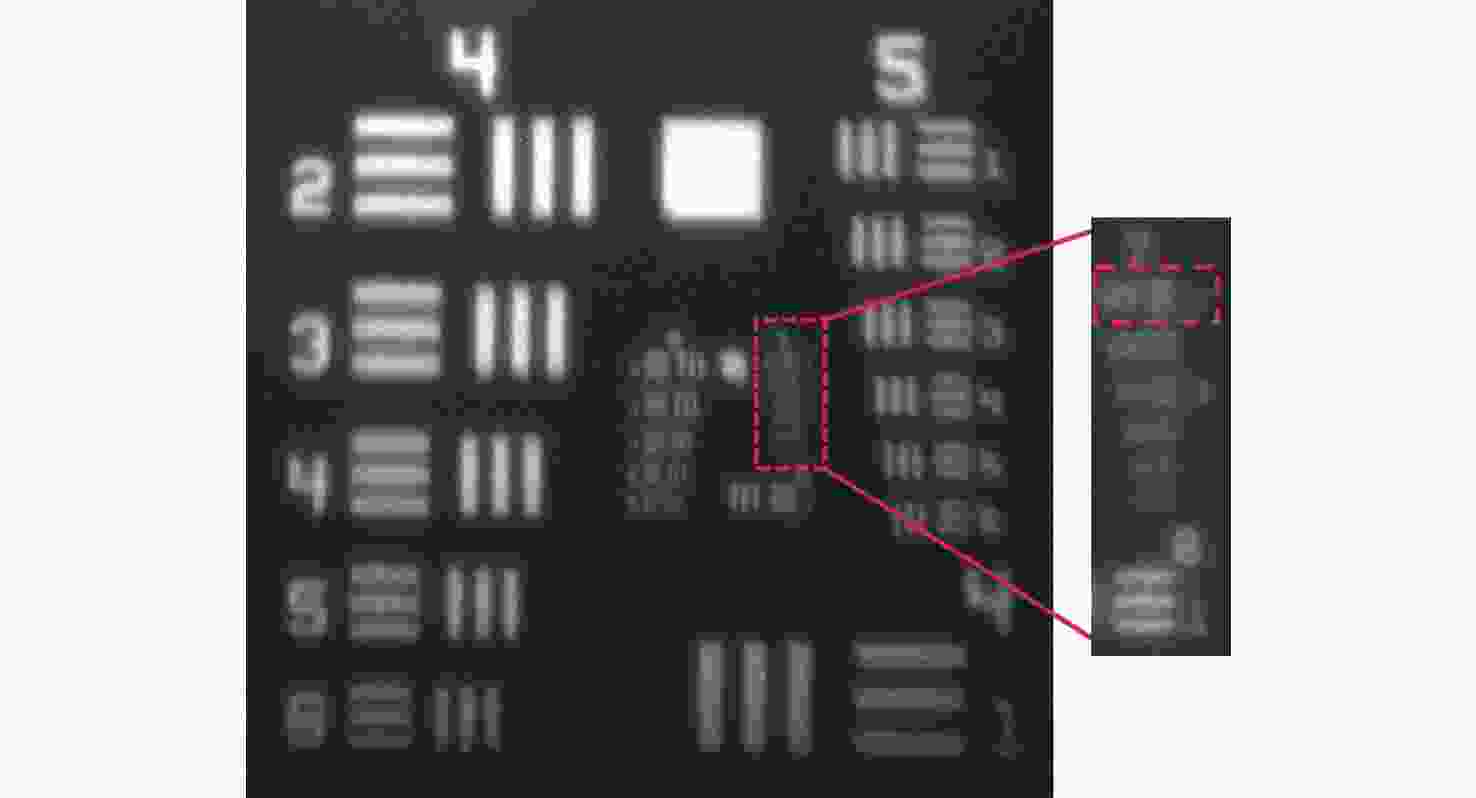
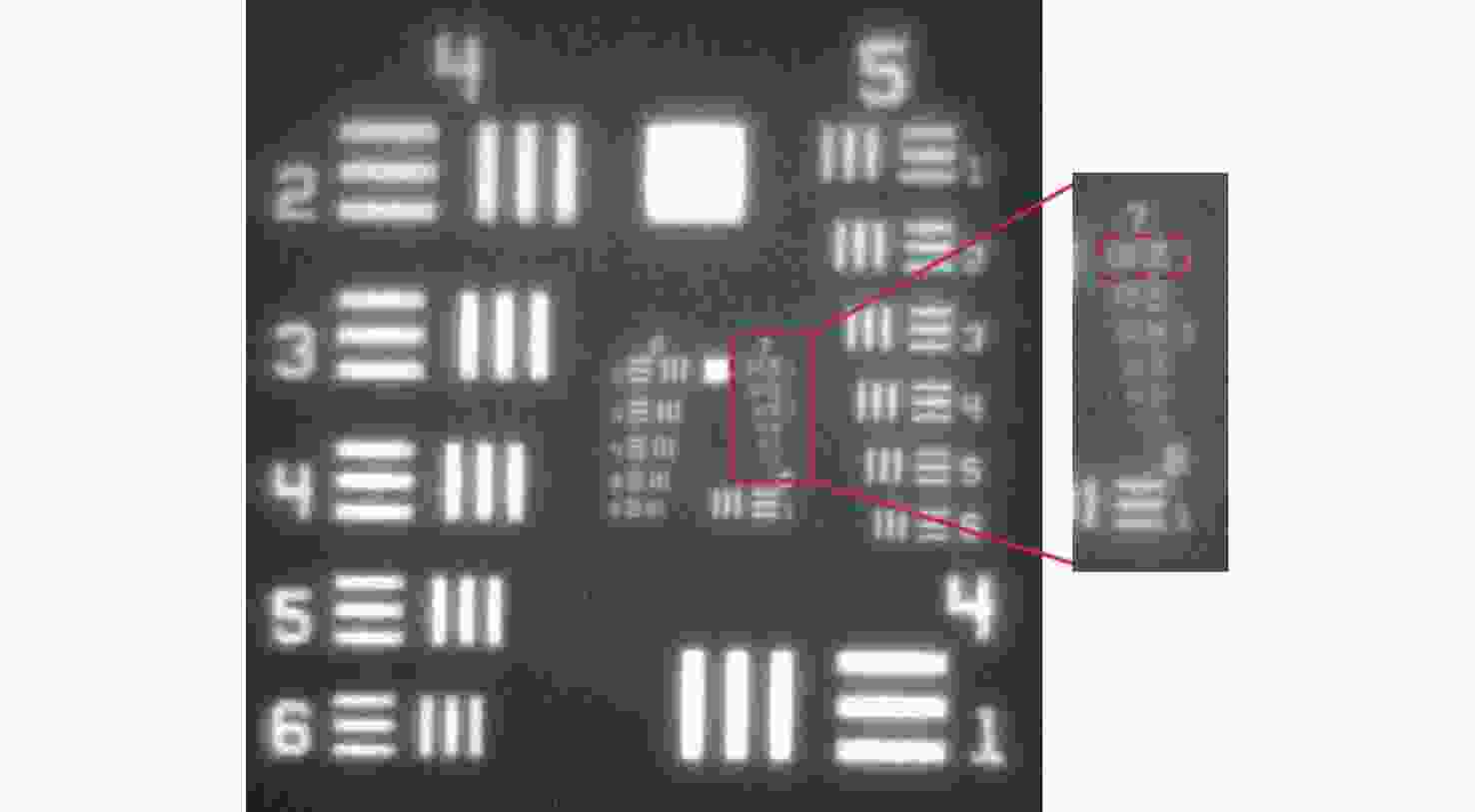
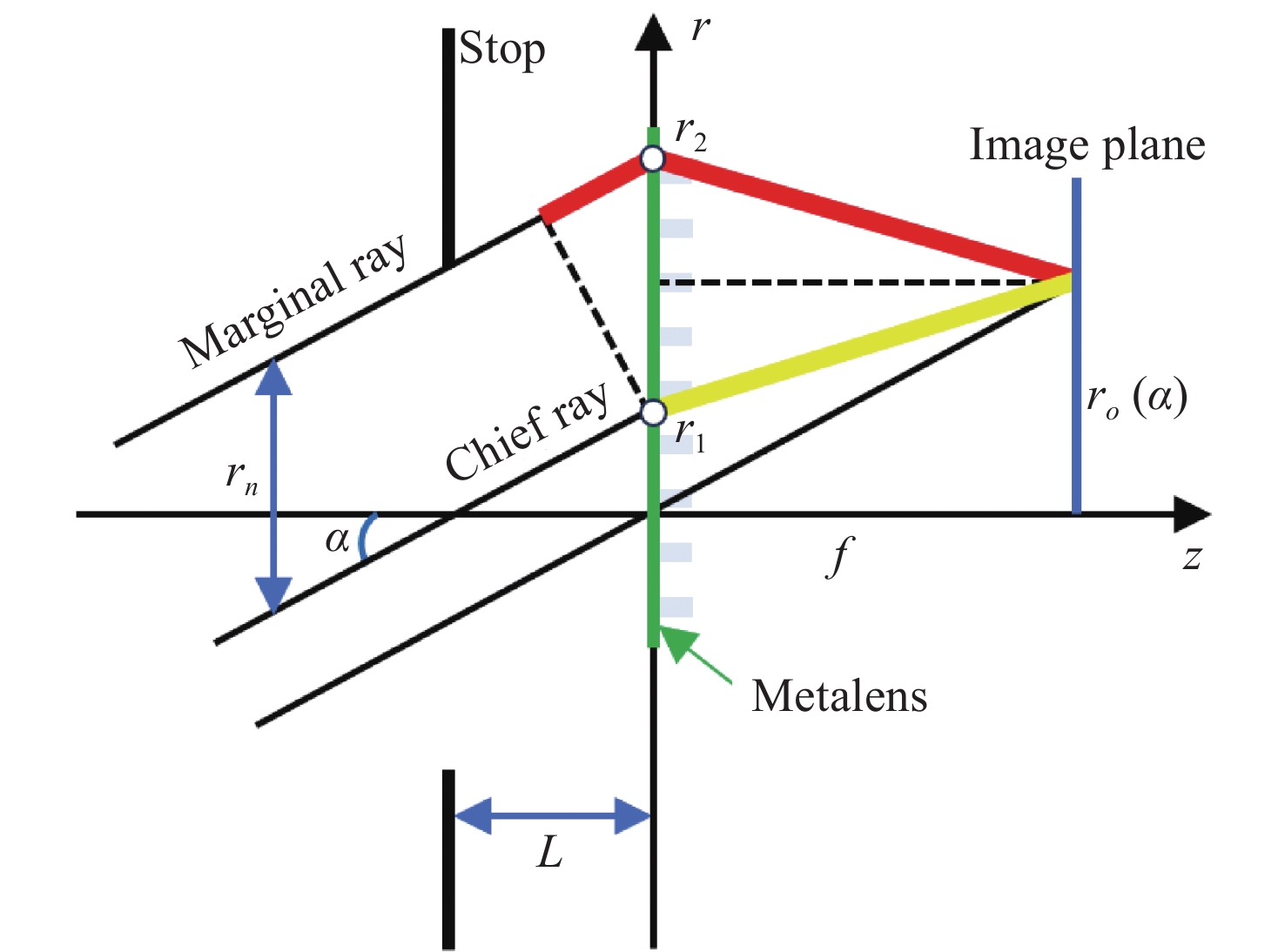
微型头戴式荧光显微镜可以对自由移动活体动物大脑中的神经活动进行实时成像,是近些年兴起的脑科学研究新仪器。然而,目前大多数微型荧光显微镜为了做到更小巧、更轻便,视场都比较小,这使得可用于观测的神经细胞数量受限,虽然有大视场系统的报道,但重量都比较大,对动物的自由行为会产生一定的影响。为了提高微型荧光显微镜成像性能,同时降低其重量,光学系统采用超轻、超薄、成像质量高的超构透镜。本文首先推导了双曲相位超构透镜的像差公式,并以此为指导,完成了一款视场为4 mm×4 mm、NA为0.14的微型荧光显微镜设计,实现了7种初级像差的校正。装配完成的样机重量仅为4.11 g,全视场范围内分辨率为7.8 μm,对自由移动小鼠大脑中的神经活动进行成像观测能够达到单细胞分辨率。
Abstract:The recent advent of miniature head-mounted fluorescence microscopes has revolutionized brain science research, enabling real-time imaging of neural activity in the brains of free-moving animals. However, the pursuit of miniaturization and reduced weight often results in a limited field of view, constraining the number of neurons observable. While larger field-of-view systems exist, their increased weight can impede the natural behaviors of the subjects. Addressing these limitations, a novel design utilizing a metalens schematic is proposed. This approach offers the benefits of being ultra-light, ultra-thin, and capable of high-quality imaging. By deriving the aberration formula specific to hyperbolic phase metalens and using it as a foundation, a design for a miniature fluorescence microscope was developed. This microscope boasts a 4 mm×4 mm field of view and a numerical aperture (NA) of 0.14, effectively correcting seven primary aberrations. The resulting prototype, weighing a mere 4.11 g, achieves a resolution of 7.8 μm across the entire field of view. This performance is sufficient to image neural activity in the brains of freely moving mice with single-cell resolution.
-
Key words:
- miniature fluorescence microscope /
- metalens /
- optical design /
- neuron science /
- aberration theory
-
表 1 光学系统设计参数
Table 1. Optical system design parameters
参数 指标要求 波段 512 nm~537 nm 数值孔径 0.14 视场 4 mm×4 mm 系统放大率 1× 表 2 图像传感器参数
Table 2. Parameters of image sensor
光学格式/in 像素尺寸/μm 成像区域尺寸/mm 分辨率 1/2.5(4:3) 2.2 5.70 × 4.28 2592 × 1944 -
[1] GRIENBERGER C, KONNERTH A. Imaging calcium in neurons[J]. Neuron, 2012, 73(5): 862-885. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.011 [2] YU H, SENARATHNA J, TYLER B M, et al. Miniaturized optical neuroimaging in unrestrained animals[J]. NeuroImage, 2015, 113: 397-406. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.070 [3] CHEN SH Y, WANG Z CH, ZHANG D, et al. Miniature fluorescence microscopy for imaging brain activity in freely-behaving animals[J]. Neuroscience Bulletin, 2020, 36(10): 1182-1190. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00561-z [4] 付强, 张智淼, 赵尚男, 等. 微型头戴式单光子荧光显微成像技术研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(5):1010-1021. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0007FU Q, ZHANG ZH M, ZHAO SH N, et al. Research progress of miniature head-mounted single photon fluorescence microscopic imaging technique[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1010-1021. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0007 [5] RYNES M L, SURINACH D A, LINN S, et al. Miniaturized head-mounted microscope for whole-cortex mesoscale imaging in freely behaving mice[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(4): 417-425. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01104-8 [6] GHOSH K K, BURNS L D, COCKER E D, et al. Miniaturized integration of a fluorescence microscope[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(10): 871-878. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1694 [7] CAI D J, AHARONI D, SHUMAN T, et al. A shared neural ensemble links distinct contextual memories encoded close in time[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7605): 115-118. doi: 10.1038/nature17955 [8] LIBERTI W A, PERKINS L N, LEMAN D P, et al. An open source, wireless capable miniature microscope system[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2017, 14(4): 045001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aa6806 [9] SKOCEK O, NÖBAUER T, WEILGUNY L, et al. High-speed volumetric imaging of neuronal activity in freely moving rodents[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(6): 429-432. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0008-0 [10] JACOB A D, RAMSARAN A I, MOCLE A J, et al. A compact head-mounted endoscope for in vivo calcium imaging in freely behaving mice[J]. Current Protocols in Neuroscience, 2018, 84(1): e51. doi: 10.1002/cpns.51 [11] AHARONI D, KHAKH B S, SILVA A J, et al. All the light that we can see: a new era in miniaturized microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2019, 16(1): 11-13. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0266-x [12] BAGRAMYAN A. Lightweight 1-photon miniscope for imaging in freely behaving animals at subcellular resolution[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2020, 32(15): 909-912. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2020.3004283 [13] DE GROOT A, VAN DEN BOOM B J G, VAN GENDEREN R M, et al. NINscope, a versatile miniscope for multi-region circuit investigations[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e49987. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49987 [14] YANNY K, ANTIPA N, LIBERTI W, et al. Miniscope3D: optimized single-shot miniature 3D fluorescence microscopy[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2020, 9: 171. [15] SHUMAN T, AHARONI D, CAI D J, et al. Breakdown of spatial coding and interneuron synchronization in epileptic mice[J]. Nature Neuroscience, 2020, 23(2): 229-238. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0559-0 [16] BAGRAMYAN A, TABOURIN L, RASTQAR A, et al. Focus-tunable microscope for imaging small neuronal processes in freely moving animals[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(7): 1300. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.418154 [17] WANG Y ZH, MA ZH T, LI W ZH, et al. Cable-free brain imaging for multiple free-moving animals with miniature wireless microscopes[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2023, 28(2): 026503. [18] SCOTT B B, THIBERGE S Y, GUO C Y, et al. Imaging cortical dynamics in GCaMP transgenic rats with a head-mounted widefield macroscope[J]. Neuron, 2018, 100(5): 1045-1058. e5. [19] GUO CH L, BLAIR G J, SEHGAL M, et al. Miniscope-LFOV: a large-field-of-view, single-cell-resolution, miniature microscope for wired and wire-free imaging of neural dynamics in freely behaving animals[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(16): 3918-3918. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg3918 [20] XU B B, LI H M, GAO SH L, et al. Metalens-integrated compact imaging devices for wide-field microscopy[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2020, 2(6): 066004. [21] TSENG E, COLBURN S, WHITEHEAD J, et al. Neural Nano-optics for high-quality thin lens imaging[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 6493. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26443-0 [22] LIU Y, YU Q Y, CHEN Z M, et al. Meta-objective with sub-micrometer resolution for microendoscopes[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(2): 106-115. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.406197 [23] AIETA F, GENEVET P, KATS M, et al. Aberrations of flat lenses and aplanatic metasurfaces[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(25): 31530-31539. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.031530 [24] YOUNG M. Zone plates and their aberrations[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1972, 62(8): 972-976. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.62.000972 [25] GROSS H. Handbook of Optical Systems (Volume 3: Aberration Theory and Correction of Optical Systems)[M]. Weinheim: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2007. [26] WANG CH M, LIN Y, HAN Y M, et al. Fabricable concentric-ring metalens with high focusing efficiency based on two-dimensional subwavelength unit splicing[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(20): 33596-33607. doi: 10.1364/OE.500688 [27] JIN ZH, LIN Y, WANG CH M, et al. Topologically optimized concentric-nanoring metalens with 1 mm diameter, 0.8 NA and 600 nm imaging resolution in the visible[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(6): 10489-10499. doi: 10.1364/OE.478680 -





 下载:
下载: