Application of dual-wavelength nanosecond laser cleaning technology on stone artifacts
-
摘要:
传统的清洗方法不能对文物表面较小污染颗粒进行清洗,并且容易造成文物表面不可逆的损伤。为提高清洗污染物的能力,激光清洗技术逐渐应用于不同类型文物的清洗。本文研制了纳秒激光清洗系统并对故宫博物院的大理石模拟样品和大理石碎片进行清洗,清洗的对象是黑色结壳污染物。为了避免变黄效应,采用波长为
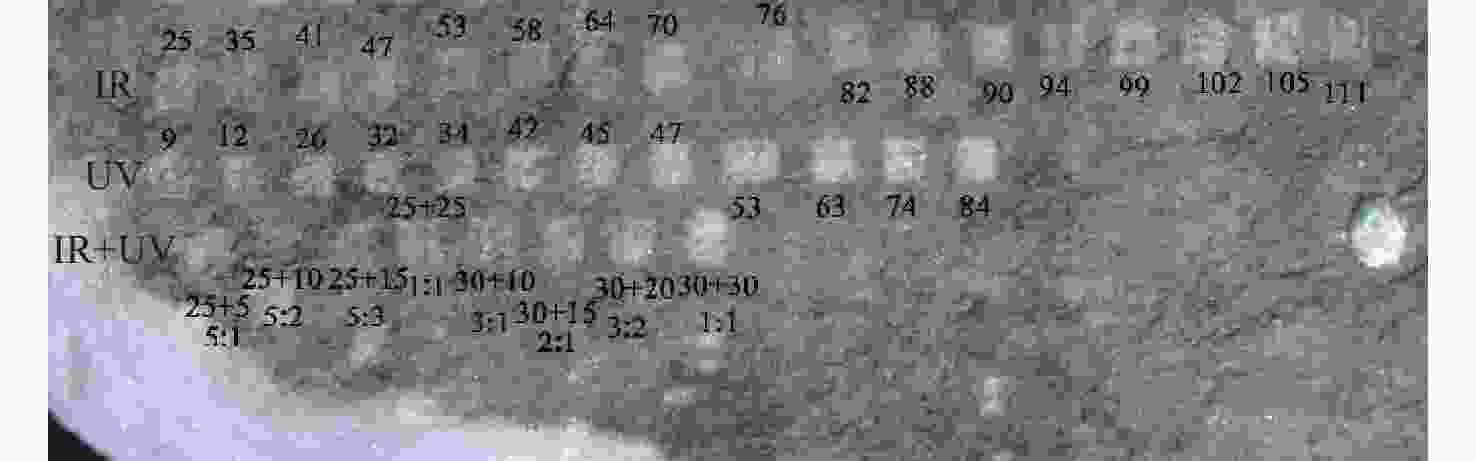
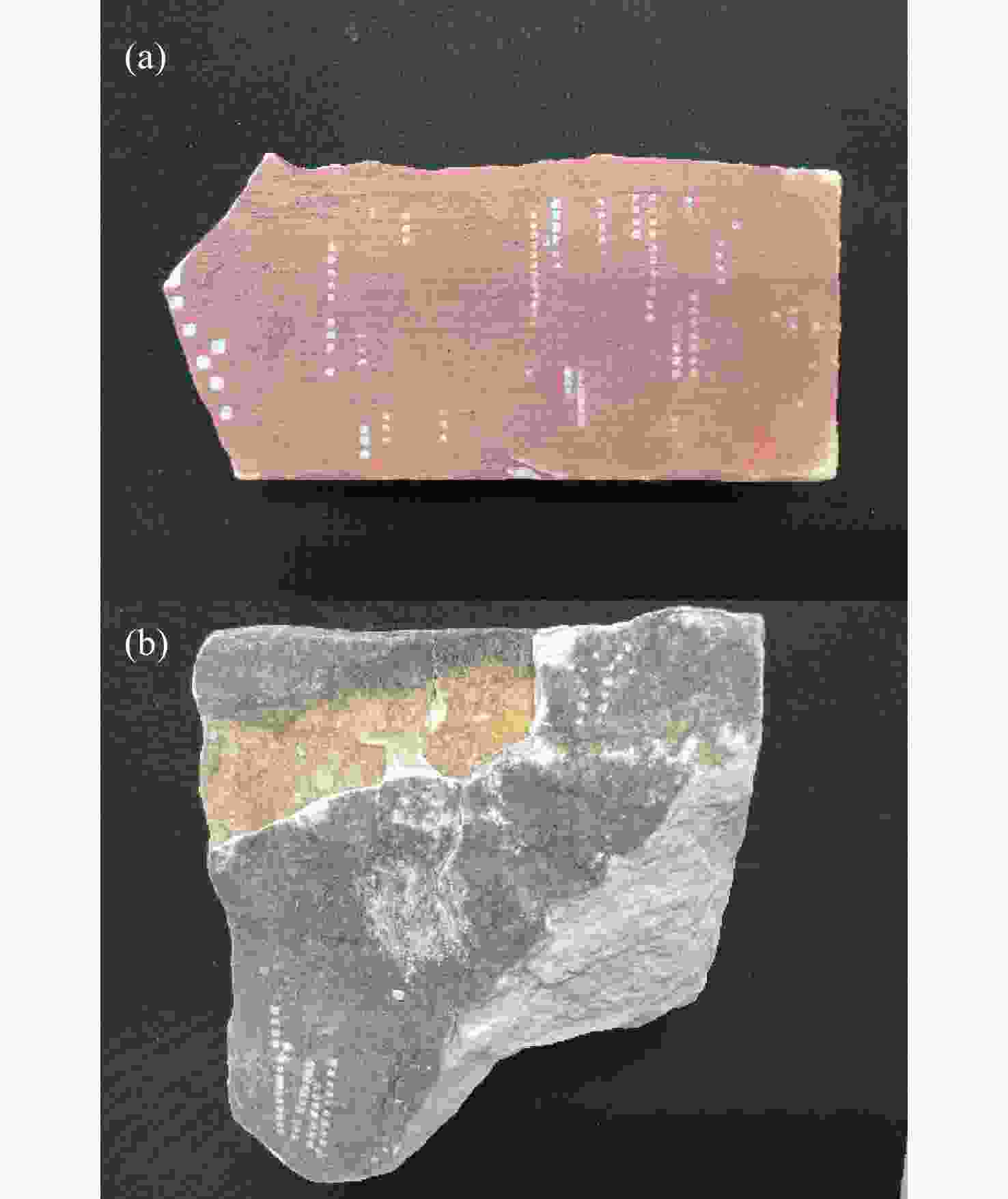
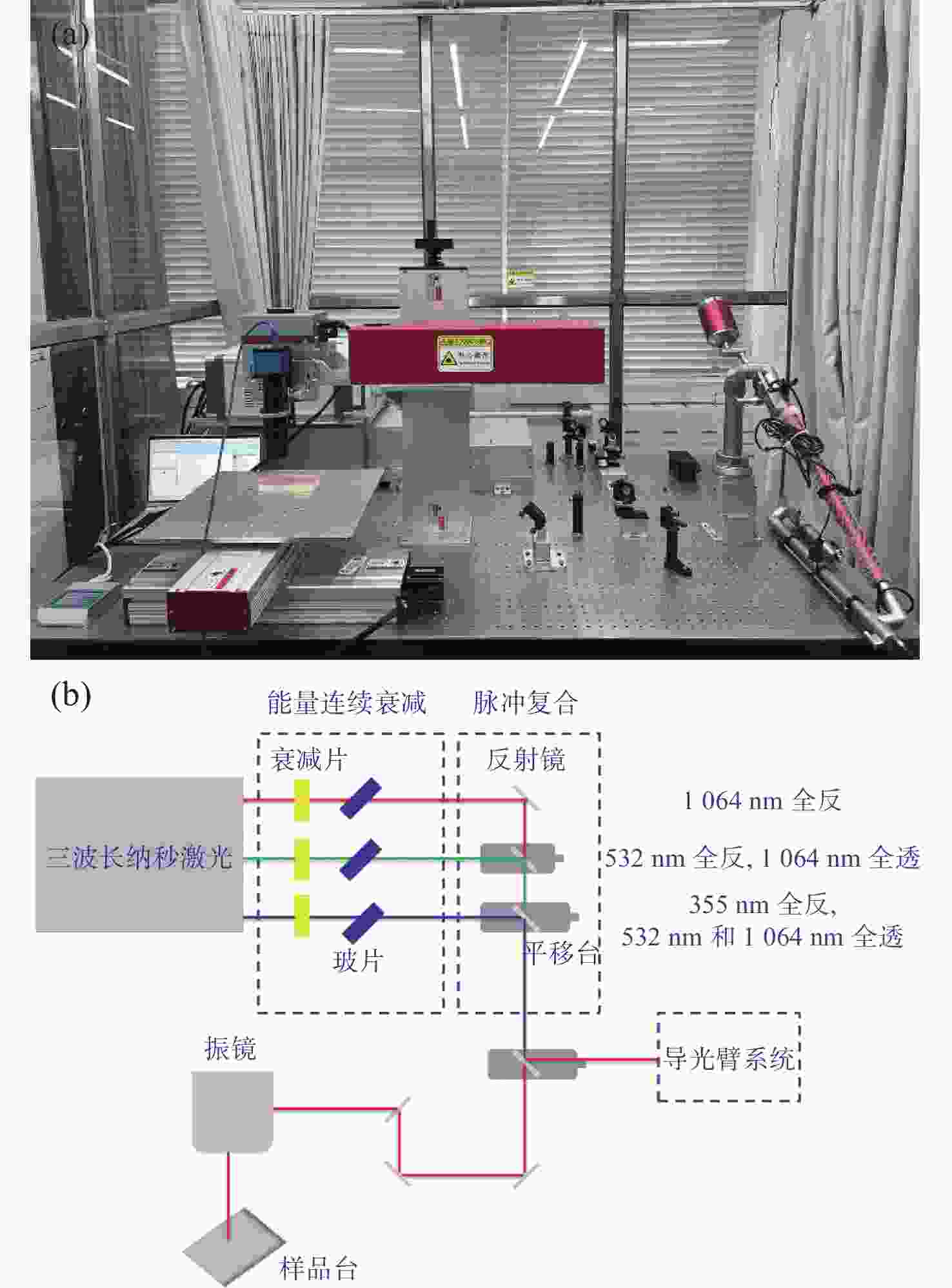
1064 nm近红外光与355 nm紫外相结合的方法对大理石模拟样本进行激光清洗。当两者的能量密度比值为3∶2时,显微观测系统的照片显示有较好的清洗效果。将此比值应用于大理石碎片样本,利用显微拉曼光谱仪对清洗效果进行分析。实验结果证实了激光清洗的优势,也为激光清洗大理石表面污染物提供参数和评价方法参考。本文研究也为激光清洗技术在其他石质文物表面的清洗提供借鉴。Abstract:Traditional cleaning methods can not clean small pollution particles on the surface of cultural relics. Moreover it can easily cause irreversible damage. In order to improve the ability to clean pollutants, laser cleaning technology has been gradually applied to the cleaning of different types of cultural relics. In this paper, we develop a nanosecond laser cleaning system to clean the simulated marble samples and marble fragments in the Palace Museum. The object of the cleanout is black crust pollutants. To avoid the yellowing effect, a dual wavelength combination of
1064 nm near-infrared and 355 nm ultraviolet light is used for laser cleaning of simulated marble samples. When the energy density ratio of these two wavelengths is 3∶2, photos from the microscopic observation system show a good cleaning effect. This ratio (3∶2) is then applied to marble fragments samples. The micro-Raman spectrometer is utilized to evaluate the cleaning effect. The experimental results confirm the advantages of laser cleaning and also provide reference parameters and evaluation methods for laser cleaning of pollutants on marble surface. At the same time, it also offer insights for the application of laser cleaning technology to the cleaning of other stone artifacts.-
Key words:
- laser cleaning technology /
- marble /
- dual-wavelength
-
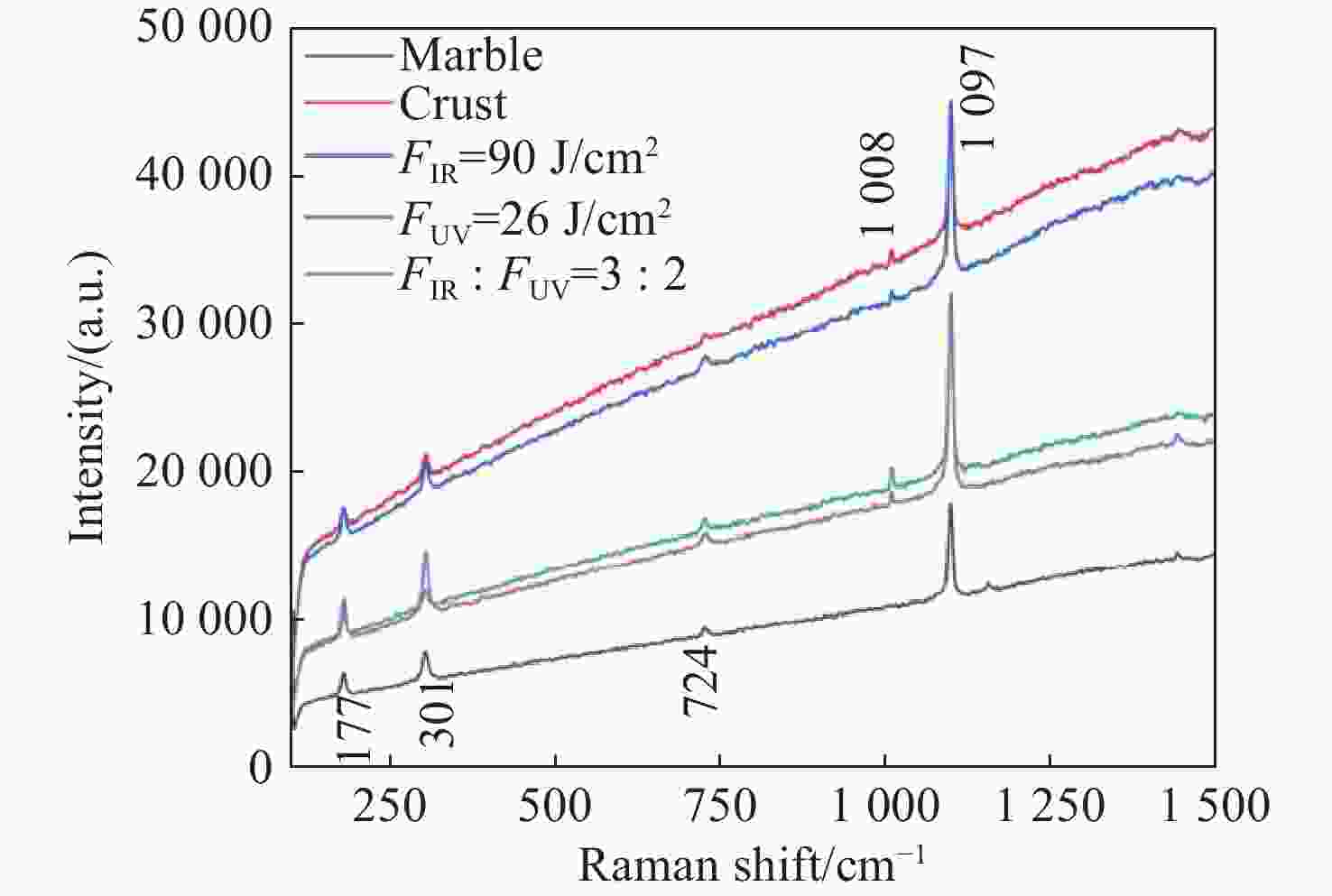
图 8 无污染物的大理石、有污染物大理石未经清洗、单独用
1064 nm近红外光清洗(FIR=90 J/cm2)、单独用355 nm紫外光清洗(FUV=26 J/cm2)及1064 -nm和355-nm(FIR/FUV=3/2)双波段激光清洗后的拉曼光谱Figure 8. Raman spectra of marble without crust, marble with crust, laser cleaning separately with
1064 nm (FIR=90 J/cm2), laser cleaning separately with 355 nm (FUV=26 J/cm2), laser cleaning with1064 nm and 355 nm (FIR/FUV=3/2) at the same time表 1
1064 nm激光清洗污染物不同部位的单脉冲能量、能量密度及损伤概率表Table 1. Single pulse energy, energy density, and damage probability for cleaning different parts of pollutants by
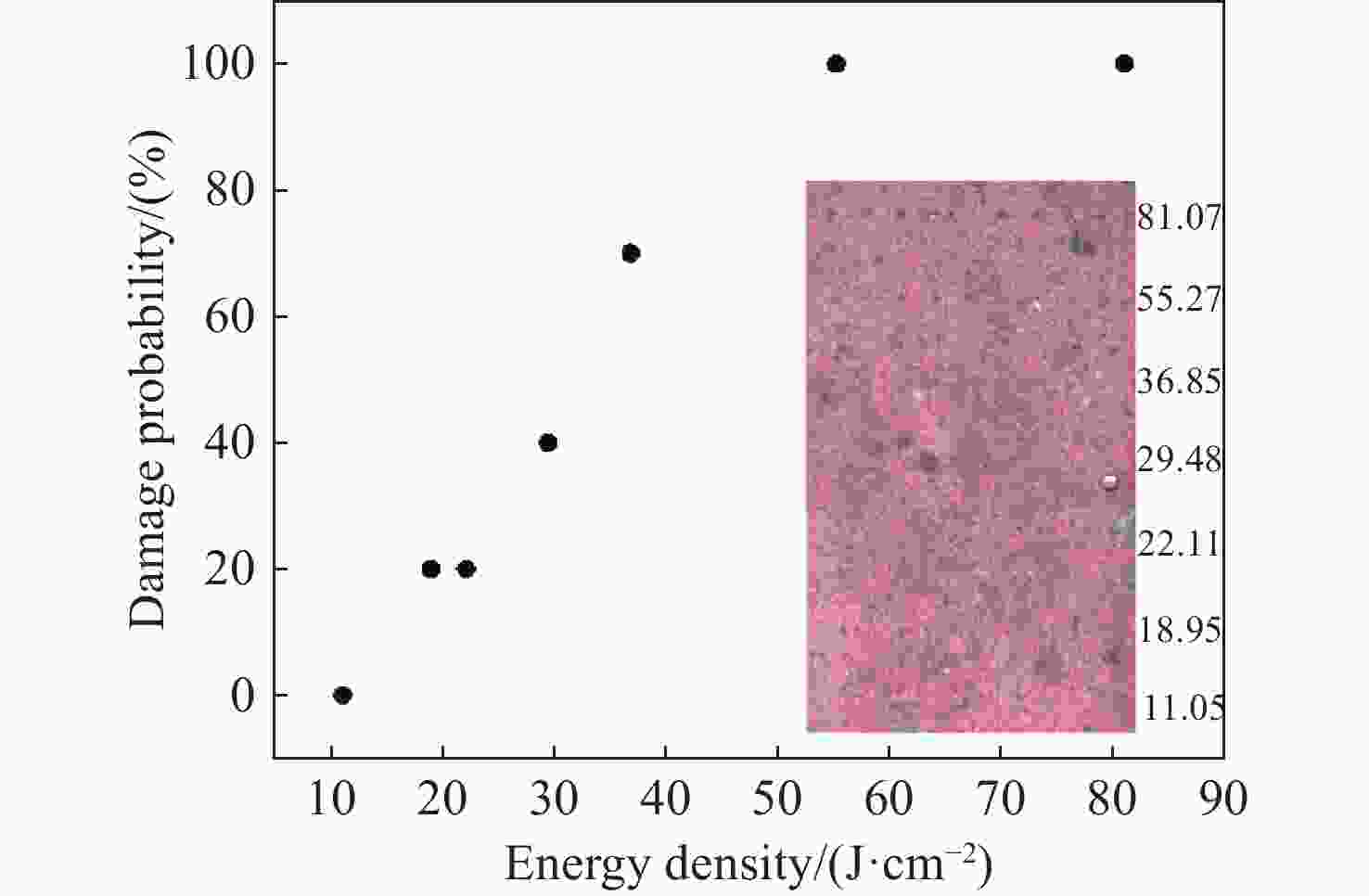
1064 -nm laser单脉冲能量(mJ) 能量密度(J·cm−2) 损伤概率(%) 0.89 52.06 100 0.73 42.7 100 0.46 26.91 90 0.28 16.38 90 0.09 5.26 70 0.07 4.09 60 0.06 3.51 60 0.05 2.92 40 0.04 2.34 0 表 2 355 nm激光清洗污染物不同部位的单脉冲能量、能量密度、损伤概率表
Table 2. Single pulse energy, energy density, and damage probability for cleaning different parts of pollutants by 355-nm laser
单脉冲能量/mJ 能量密度(J·cm−2) 损伤概率(%) 0.154 81.07 100 0.105 55.27 100 0.07 36.85 70 0.056 29.48 40 0.042 22.11 20 0.036 18.95 20 0.021 11.05 0 -
[1] 李晨毓, 曲亮, 刘晓龙, 等. 激光清洗技术在文物上的应用[J]. 中国文物科学研究,2021(1):52-60.LI C Y, QU L, LIU X L, et al. Application of laser cleaning technology in cultural relics[J]. China Cultural Heritage Scientific Research, 2021(1): 52-60. (in Chinese). [2] MAIMAN T H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby[J]. Nature, 1960, 187(4736): 493-494. doi: 10.1038/187493a0 [3] PAPLIAKA Z E, PHILIPPIDIS A, SIOZOS P, et al. A multi-technique approach, based on mobile/portable laser instruments, for the in situ pigment characterization of stone sculptures on the island of crete dating from venetian and ottoman period[J]. Heritage Science, 2016, 4: 15. doi: 10.1186/s40494-016-0085-2 [4] POULI P. Laser cleaning on stonework: principles, case studies, and future prospects[M]//GHERARDI F, MARAVELAKI P N. Conserving Stone Heritage: Traditional and Innovative Materials and Techniques. Cham: Springer, 2022: 75-100. [5] WEEKS C. The ‘Portail de la Mere Dieu’ of Amiens cathedral: its polychromy and conservation[J]. Studies in Conservation, 1998, 43(2): 101-108. [6] SIANO S, MARGHERI F, PINI R, et al. Cleaning processes of encrusted marbles by Nd: YAG lasers operating in free-running and Q-switching regimes[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(27): 7073-7079. doi: 10.1364/AO.36.007073 [7] OSTICIOLI I, MASCALCHI M, PINNA D, et al. Removal of Verrucaria nigrescens from Carrara marble artefacts using Nd: YAG lasers: comparison among different pulse durations and wavelengths[J]. Applied Physics A, 2015, 118(4): 1517-1526. doi: 10.1007/s00339-014-8933-y [8] ANDREOTTI A, COLOMBINI M P, DE CRUZ A. Er: YAG laser cleaning of a marble Roman urn[J]. Journal of the Institute of Conservation, 2020, 43(1): 12-24. doi: 10.1080/19455224.2019.1706593 [9] GRAMMATIKAKIS G, DEMADIS K D, MELESSANAKI K, et al. Laser-assisted removal of dark cement crusts from mineral gypsum (selenite) architectural elements of peripheral monuments at Knossos[J]. Studies in Conservation, 2015, 60(S1): S3-S11. [10] PRICE C A. Stone decay and preservation[J]. Chemistry in Britain, 1975, 11(10): 350-353. [11] LAZZARINI L, ASMUS J F. The application of laser radiation to the cleaning of statuary[J]. International Institute for Conservation of Historic and Artistic Works, 1973, 13(2): 39-49. doi: 10.1179/019713673806029486 [12] ASMUS J F, MURPHY C G, MUNK W H. Studies on the interaction of laser radiation with art artifacts[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1973, 41: 19-30. [13] LAZZARINI L, MARCHESINI L, ASMUS J F. Lasers for the cleaning of statuary: initial results and potentialities[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology, 1973, 10(6): 1039-1043. [14] ZANINI A, TRAFELI V, BARTOLI L. The laser as a tool for the cleaning of cultural heritage[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 364: 012078. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/364/1/012078 [15] PEREIRA-PARDO L, KORENBERG C. The use of erbium lasers for the conservation of cultural heritage. A review[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2018, 31: 236-247. doi: 10.1016/j.culher.2017.10.007 [16] POULI P, OUJJA M, CASTILLEJO M. Practical issues in laser cleaning of stone and painted artefacts: optimisation procedures and side effects[J]. Applied Physics A, 2012, 106(2): 447-464. doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6696-2 [17] TAM A C, LEUNG W P, ZAPKA W, et al. Laser-cleaning techniques for removal of surface particulates[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1992, 71(7): 3515-3523. doi: 10.1063/1.350906 [18] SIANO S, PINI R. Analysis of blast waves induced by Q-switched Nd: YAG laser photodisruption of absorbing targets[J]. Optics Communications, 1997, 135(4-6): 279-284. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(96)00666-9 [19] SIANO S, SALIMBENI R, PINI R, et al. Laser cleaning methodology for the preservation of the Porta del Paradiso by Lorenzo Ghiberti[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2003, 4(S1): 140-146. [20] POTGIETER-VERMAAK S S, GODOI R H M, VAN GRIEKEN R, et al. Micro-structural characterization of black crust and laser cleaning of building stones by micro-Raman and SEM techniques[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2005, 61(11-12): 2460-2467. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2004.09.010 [21] GIAKOUMAKI A, PHILIPPIDIS A, SIOZOS P, et al. Development of a methodology for the characterisation and assessment of biodeteriogens on archaeological surfaces by use of a portable LED-induced fluorescence instrument[J]. Heritage Science, 2022, 10: 204. doi: 10.1186/s40494-022-00827-x [22] TSEREVELAKIS G J, POULI P, ZACHARAKIS G. Listening to laser light interactions with objects of art: a novel photoacoustic approach for diagnosis and monitoring of laser cleaning interventions[J]. Heritage Science, 2020, 8: 98. doi: 10.1186/s40494-020-00440-w [23] 李悦, 张国霞, 蔡朝晴, 等. 大气压辉光放电结合圆柱约束增强激光诱导击穿光谱应用于土壤中稀土元素的检测[J]. 分析化学,2022,50(9):1384-1390.LI Y, ZHANG G X, CAI Z Q, et al. Atmospheric pressure glow discharge combined with cylindrical confinement enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for determination of rare earth in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 50(9): 1384-1390. [24] POULI P, FOTAKIS C, HERMOSIN B, et al. The laser-induced discoloration of stonework; A comparative study on its origins and remedies[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2008, 71(3): 932-945. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2008.02.031 [25] POULI P, FRANTZIKINAKI K, PAPAKONSTANTINOU E, et al. Pollution encrustation removal by means of combined ultraviolet and infrared laser radiation: the application of this innovative methodology on the surface of the Parthenon West Frieze[C]. Proceedings of Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks, Springer, 2005: 333-340. [26] TSEREVELAKIS G J, POZO-ANTONIO J S, SIOZOS P, et al. On-line photoacoustic monitoring of laser cleaning on stone: evaluation of cleaning effectiveness and detection of potential damage to the substrate[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2019, 35: 108-115. doi: 10.1016/j.culher.2018.05.014 [27] PAPANIKOLAOU A, TSEREVELAKIS G J, MELESSANAKI K, et al. Development of a hybrid photoacoustic and optical monitoring system for the study of laser ablation processes upon the removal of encrustation from stonework[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2020, 3(2): 190037. [28] 齐扬, 叶亚云, 王海军, 等. 激光清除石质文物表面污染物的作用机制[J]. 中国激光,2015,42(6):0603001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0603001QI Y, YE Y Y, WANG H J, et al. Mechanisms of laser cleaning of contamination on surface of stonework[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(6): 0603001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0603001 [29] 齐扬. 云冈石窟砂岩文物表面污物激光清除机理及应用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2015.QI Y. Study of mechanisms of laser cleaning of sandstone surface contaminants in Yungang grottoes and its applications[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2015. (in Chinese). [30] 张秉坚, 任瑛丽, 张西燕, 等. 激光技术与石质材料清洗[J]. 石材,2001,10(10):11-13.ZHANG B J, REN Y L, ZHANG X Y, et al. Laser technology and cleaning of stone materials[J]. Stone, 2001, 10(10): 11-13. (in Chinese). [31] 齐扬, 周伟强, 周萍, 等. 激光清洗石质文物工艺[J]. 江汉考古,2015,1(1):112-117.QI Y, ZHOU W Q, ZHOU P, et al. Laser cleaning technology for stone cultural relics[J]. Jianghan Archaeology, 2015, 1(1): 112-117. (in Chinese). [32] 齐扬, 周伟强, 陈静, 等. 激光清洗云冈石窟文物表面污染物的试验研究[J]. 安全与环境工程,2015,22(2):32-38.QI Y, ZHOU W Q, CHEN J, et al. Laser cleaning of contaminants on the surface of Yungang Grottoes[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(2): 32-38. (in Chinese). [33] 叶亚云, 齐扬, 秦朗, 等. 激光清除石质文物表面污染物[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(9):0903005. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0903005YE Y Y, QI Y, QIN L, et al. Laser cleaning of contaminants on the surface of stone relics[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(9): 0903005. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0903005 [34] 张秉坚, 铁景沪. 大型石质文物表面清洗技术的现状和发展趋势[J]. 石材,2007,11(11):19-22.ZHANG B J, TIE J H. The current situation and development trend of surface cleaning technology for large stone cultural relics[J]. Stone, 2007, 11(11): 19-22. (in Chinese). [35] 刘菊, 张秉坚. 地衣对石材的破坏与激光清除技术[J]. 中国建材,2002,6(6):74-76.LIU J, ZHANG B J. Lichen damages to stone resources and laser removing technology[J]. China Building Materials, 2002, 6(6): 74-76. (in Chinese). [36] GRACIA M, GAVIÑO M, VERGÈS-BELMIN V, et al. Mössbauer and XRD study of the effect of Nd: YAG-1064 nm laser irradiation on hematite present in model samples[C]. Proceedings of Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks, Springer, 2005: 341-346. [37] DE OLIVEIRA C, VERGÈS-BELMIN V, LAFAIT J, et al. Contribution of goethite to laser-induced stone yellowing[J]. Applied Physics A, 2016, 122(4): 467. doi: 10.1007/s00339-016-9818-z [38] 程军杰, 曹智, 杨灿然, 等. 便携式远程激光诱导击穿光谱系统及其定量分析性能[J]. 应用化学,2022,39(9):1147-1152.CHENG J J, CAO Z, YANG C R, et al. Quantitative analysis with a portable remote laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy System[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2022, 39(9): 1147-1152. [39] BARTOLI L, POULI P, FOTAKIS C, et al. Characterization of stone cleaning by Nd: YAG lasers with different pulse duration[J]. Laser Chemistry, 2006, 2006: 081750. [40] 陈宝华, 吴泉英, 唐运海, 等. 产生环形激光的光学系统设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2023,16(6):1365-1375. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0045CHEN B H, WU Q Y, TANG Y H, et al. Design of an optical system for generating ring-shaped laser beam[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1365-1375. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0045 [41] POULI P, PAPAKONSTANTINOU E, FRANTZIKINAKI K, et al. The two-wavelength laser cleaning methodology; Theoretical background and examples from its application on CH objects and monuments with emphasis to the Athens acropolis sculptures[J]. Heritage Science, 2016, 4: 9. doi: 10.1186/s40494-016-0077-2 [42] ASMUS J F, SERACINI M, ZETLER M J. Surface morphology of laser-cleaned stone[J]. Lithoclastia, 1976, 2(1): 23-46. [43] BEADMAN K, SCARROW J. Laser cleaning Lincoln cathedral’s Romanesque frieze[J]. Journal of Architectural Conservation, 1998, 4(2): 39-53. doi: 10.1080/13556207.1998.10785215 [44] ARMANI E, CALCAGNO G, MENICHELLI C, et al. The church of the Maddalena in Venice: the use of laser in the cleaning of the façade[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2000, 1(S1): S99-S104. [45] CALCAGNO G, PUMMER E, KOLLER M. St. Stephen’s church in Vienna: criteria for Nd: YAG laser cleaning on an architectural scale[J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2000, 1(S1): S111-S117. [46] SIANO S, GIUSTI A, PINNA D, et al. The conservation intervention on the Porta della Mandorla[C]. Proceedings of Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks, Springer, 2005: 171-178. [47] PAPANIKOLAOU A, SIOZOS P, PHILIPPIDIS A, et al. Towards the understanding of the two wavelength laser cleaning in avoiding yellowing on stonework: a micro-Raman and LIBS study[C]. Lasers in the Conservation of Artworks XI, NCU Press, 2017: 95-104. -





 下载:
下载: