Research progress of hydroxy-plane laser-induced fluorescence detection based on ultraviolet laser
-
摘要:
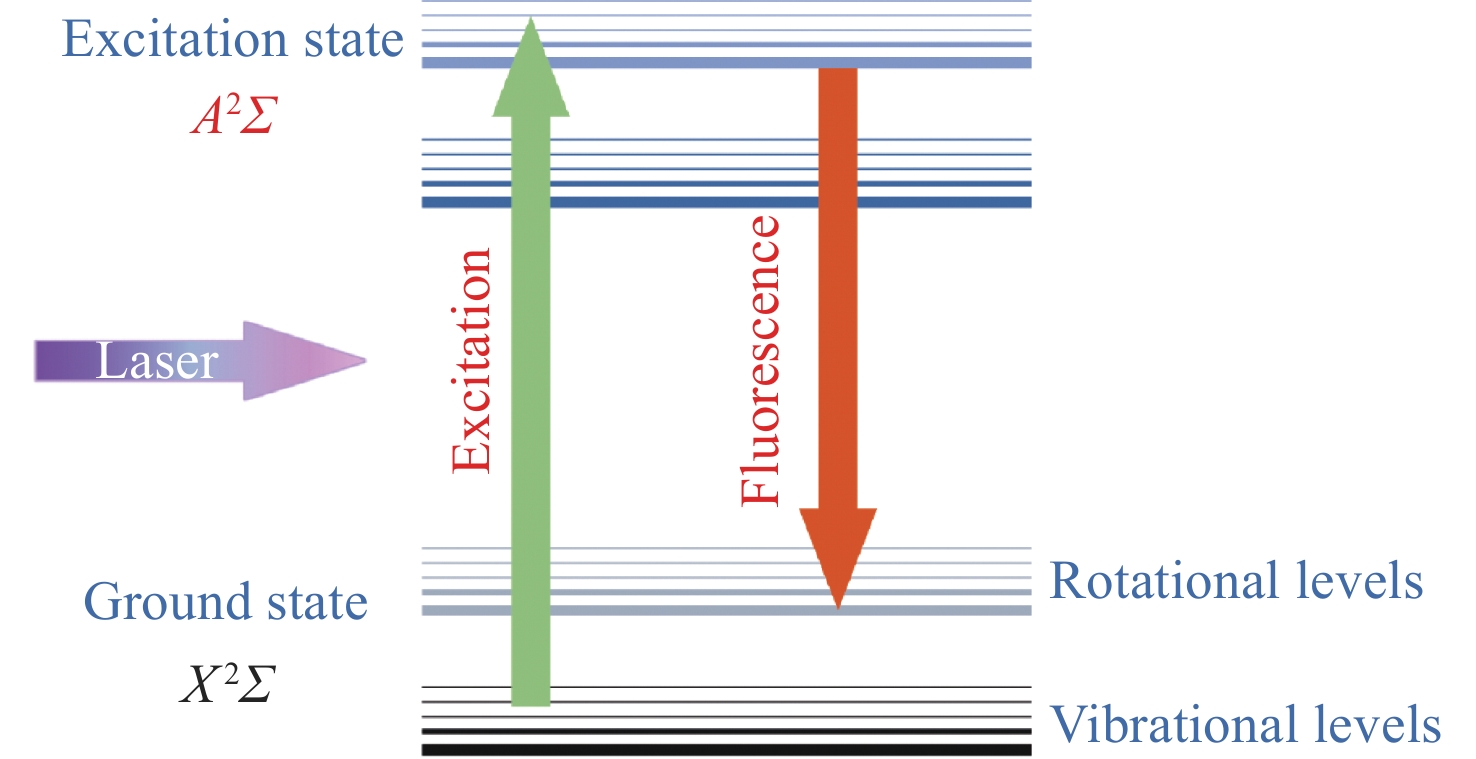
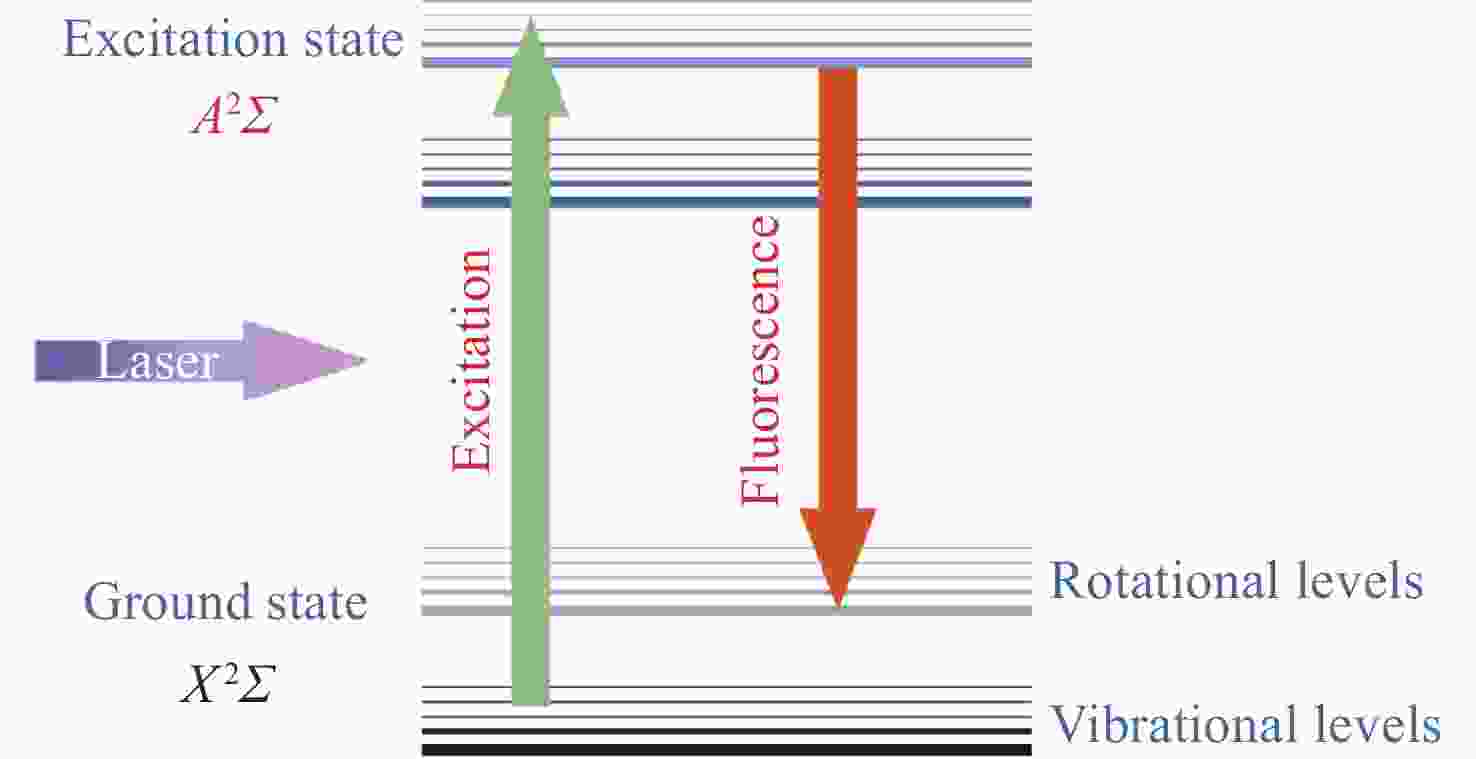
羟基(OH)是一种广泛存在于燃烧反应过程中的产物,在燃烧诊断技术中,基于羟基的二维空间分布常用于表征火焰的锋面结构,同时羟基也是表征火焰温度、火焰面密度和热释放速率等特征的重要参数。对燃烧火焰中的羟基进行有效探测是探究燃烧动力学演变过程,揭示火焰随机事件产生机理的重要支撑。平面激光诱导荧光(PLIF)技术作为一种光学测量方法,具有时空分辨率高、无干扰、可进行组份选择等优点,已成功用于对本生灯火焰、湍流火焰、旋流火焰和超声速火焰等多种燃烧火焰进行结构观测,为建立燃烧模型提供了重要参考。本文从PLIF探测的基本原理开始,梳理了PLIF技术在燃烧诊断领域的发展历程和研究现状,介绍了基于染料激光、光参量振荡和钛宝石三倍频方式实现的PLIF紫外光源技术,并对不同技术路线的特点进行了讨论,最后对用于OH-PLIF的紫外激光技术发展进行了展望。
Abstract:Hydroxyl (OH) is a widely existing product in the combustion reaction process. In combustion diagnosis technology, the two-dimensional spatial distribution based on hydroxyl is commonly used to characterize the structure of the flame front. Hydroxyl is an important parameter in characterizing the flame temperature, flame surface density, and heat release rate. The effective detection of hydroxyl in combustion flame is an important support for exploring the evolution of combustion dynamics and revealing the mechanism of random flame events. Planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF) has several advantages as an optical measurement method: high spatial and temporal resolution, non-intrusiveness, and component selection. PLIF has successfully observed the structure of various combustion flames, such as Bunsen burner flame, turbulent flame, swirl flame, and supersonic flame, which provides an important reference for establishing combustion models. This paper starts with the basic principle of PLIF detection, followed by the development history and research status of PLIF technology in the field of combustion diagnosis. Then, it introduces the PLIF ultraviolet light source technology based on dye laser, optical parametric oscillation, and Ti:sapphire tripling-frequency, and discusses the characteristics of different technical routes. Finally, it prospects the development of UV laser technology for OH-PLIF.
-
Key words:
- combustion /
- planar laser-induced fluorescence /
- laser /
- Hydroxyl
-
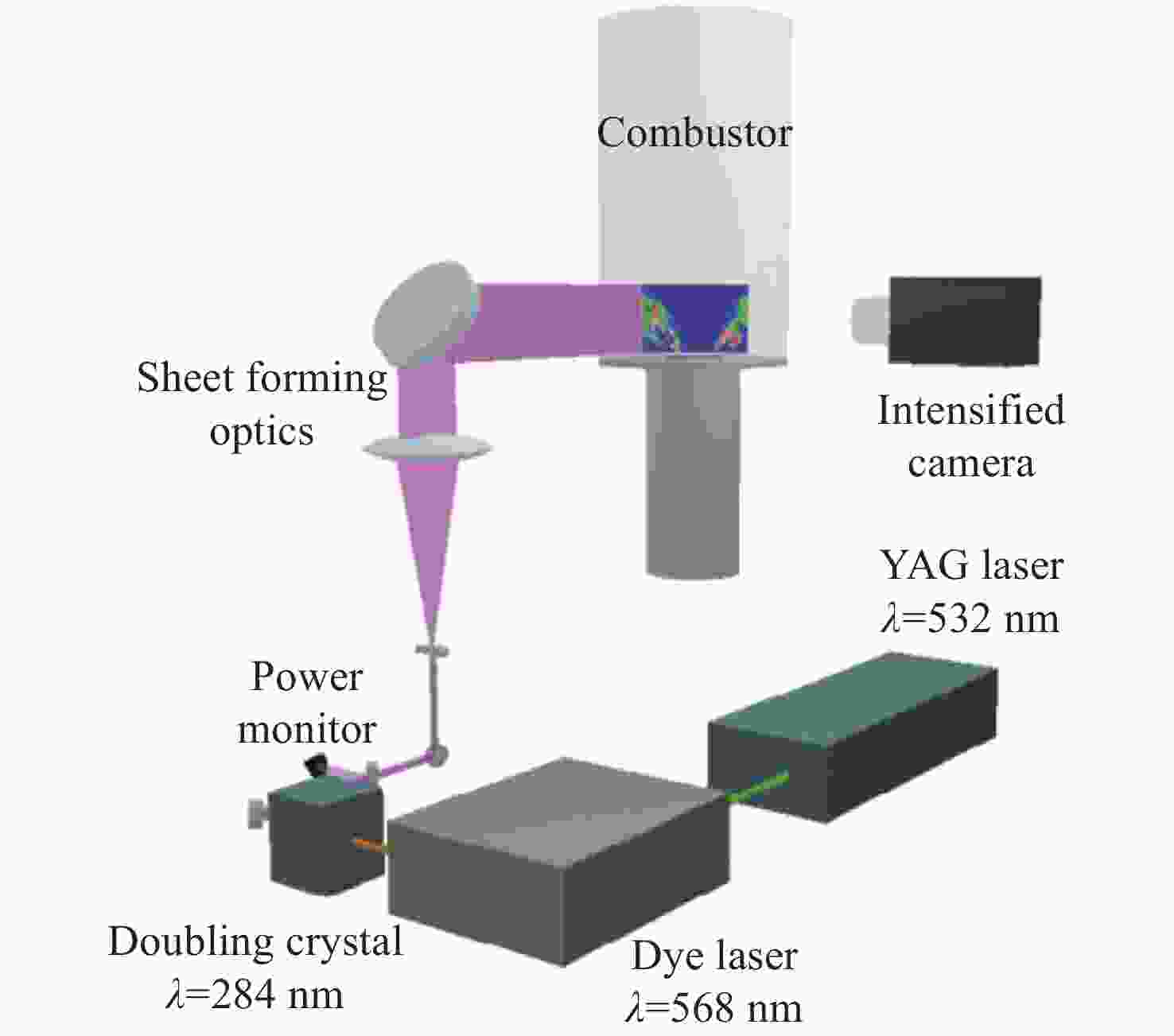
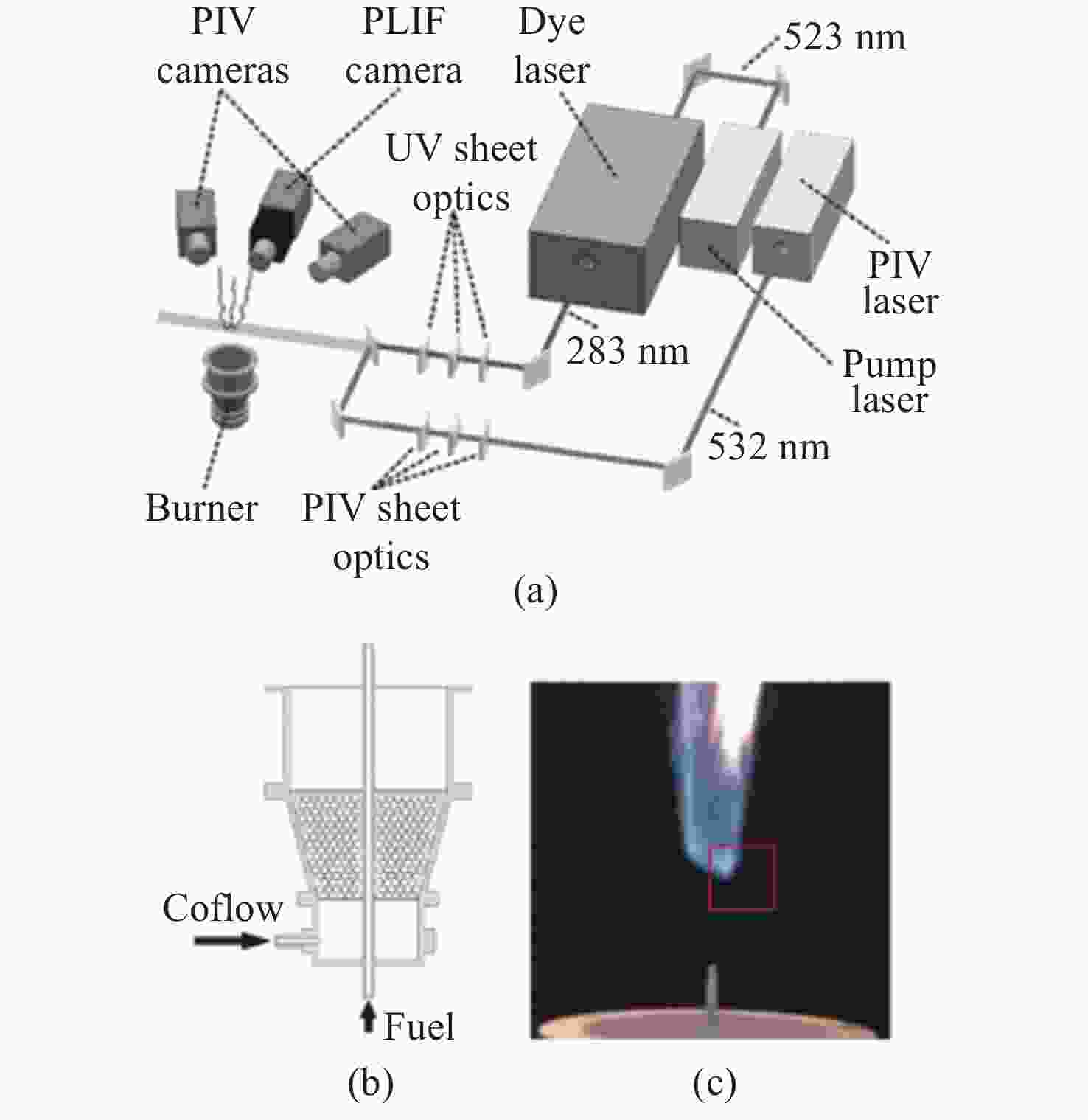
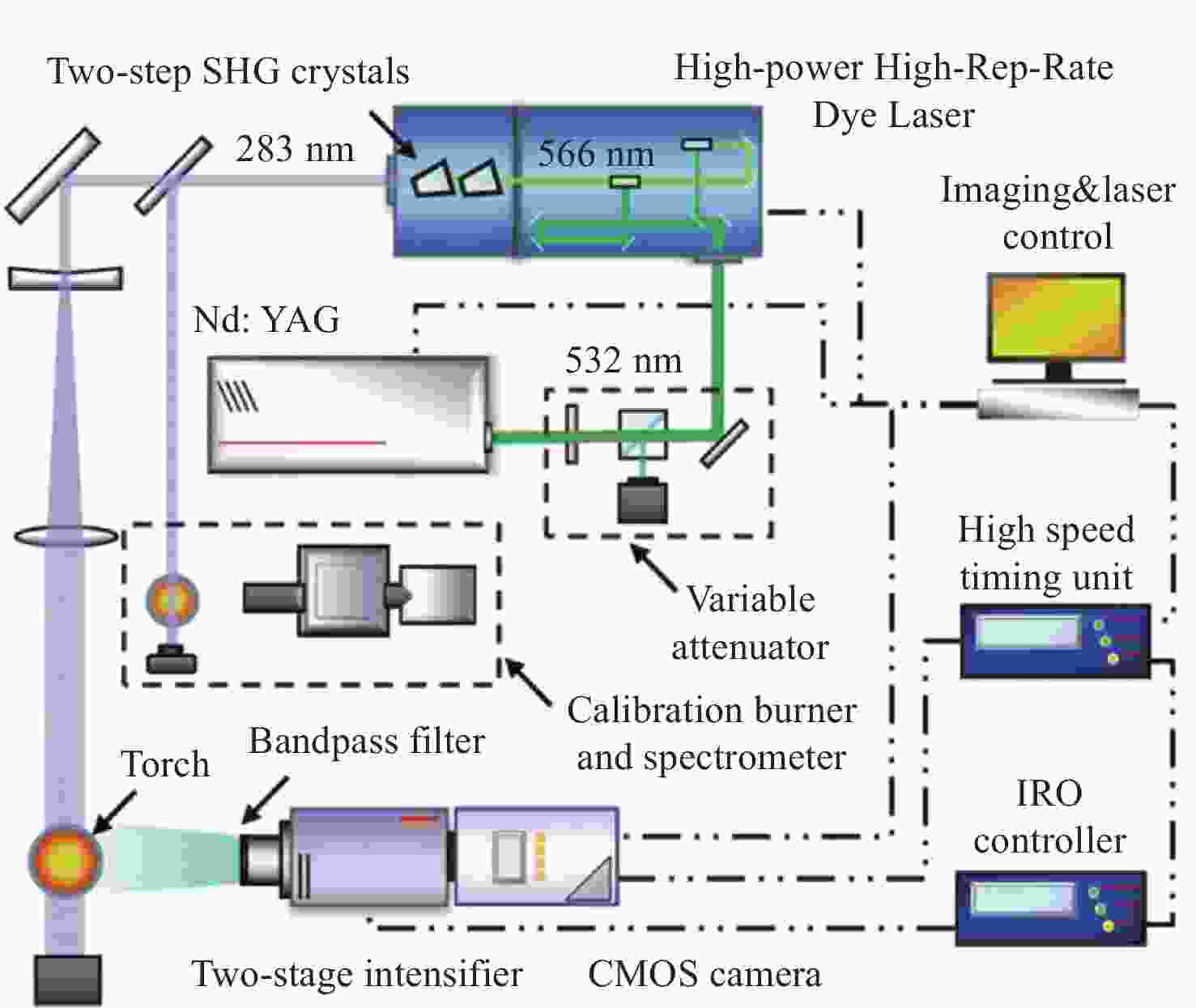
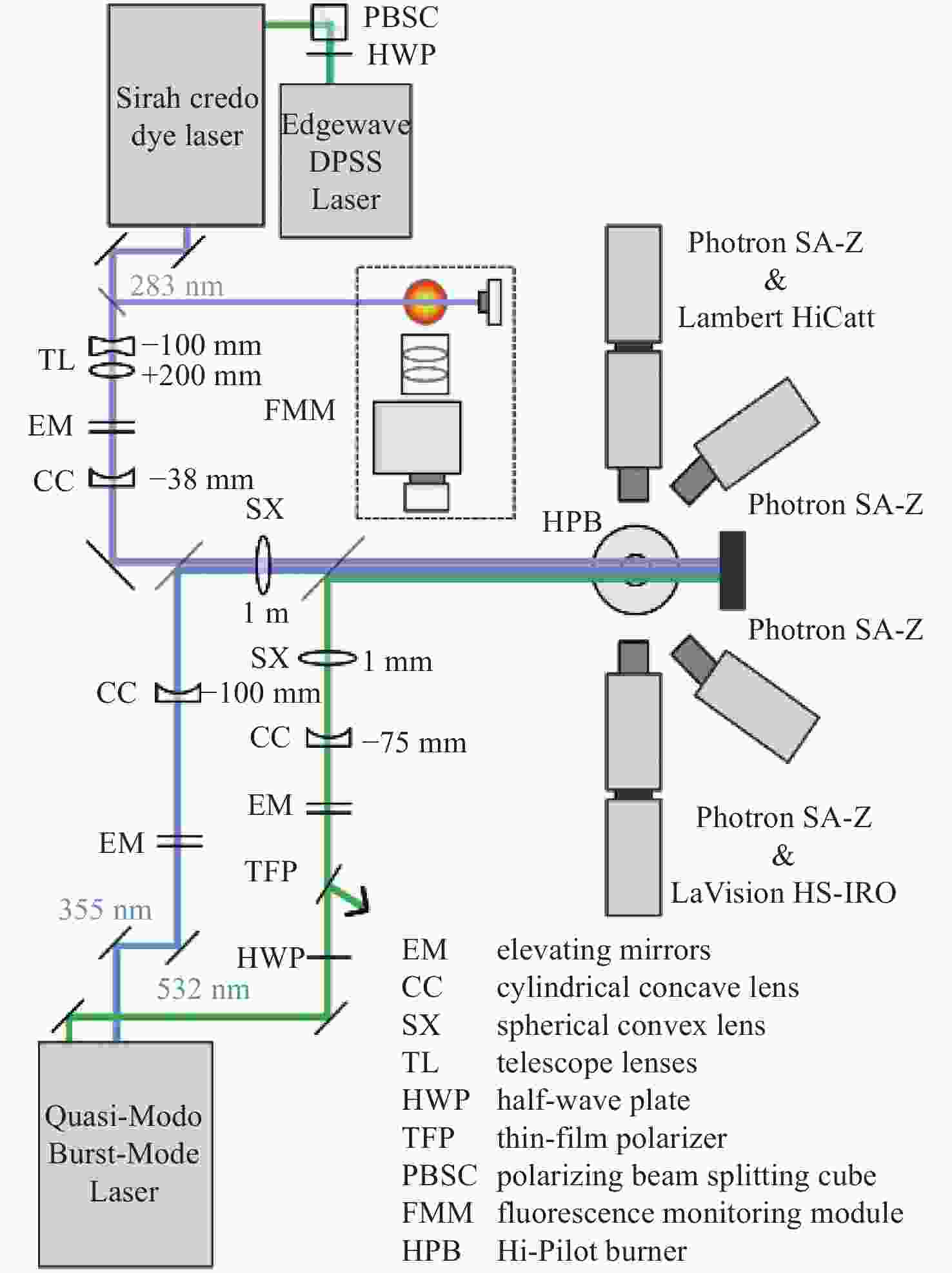
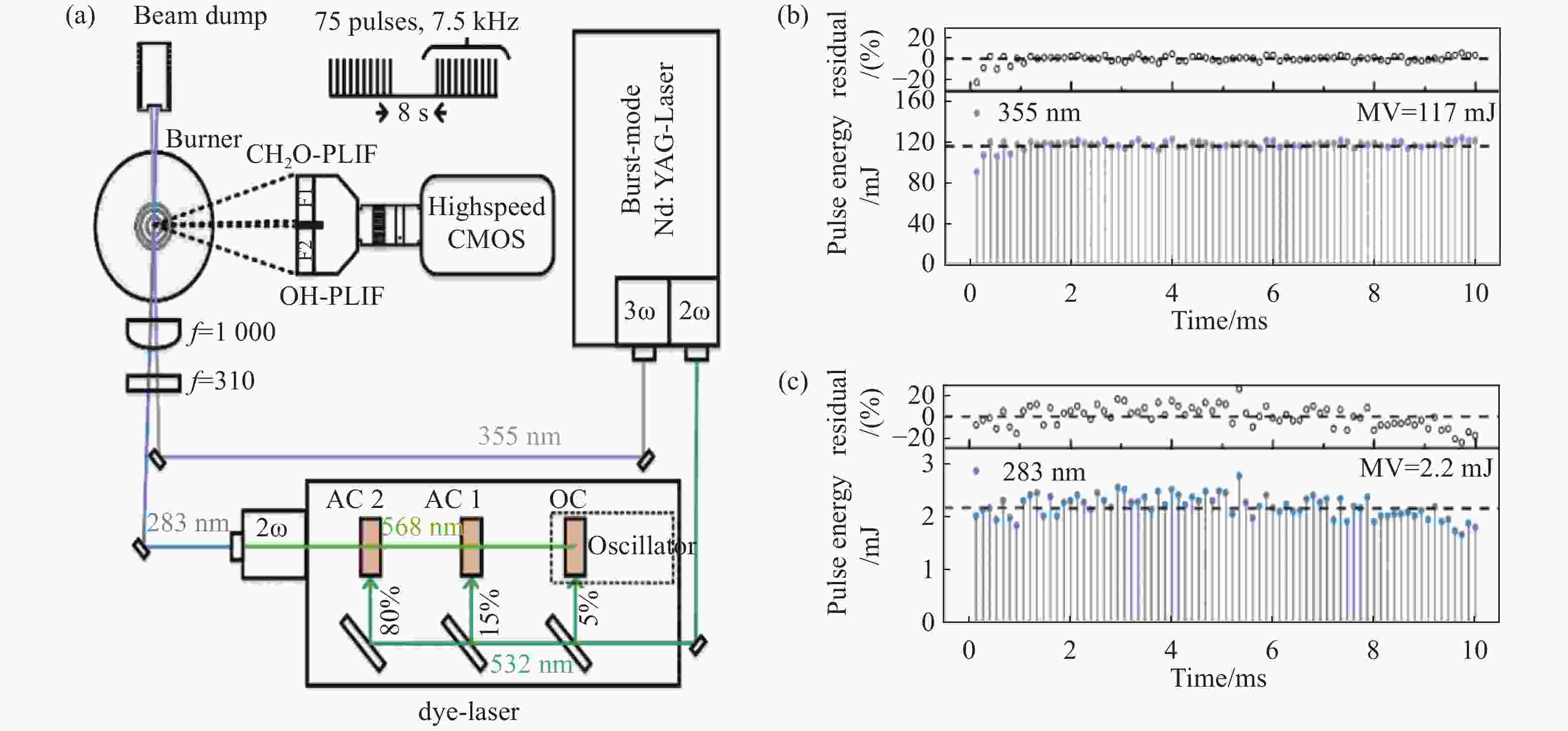
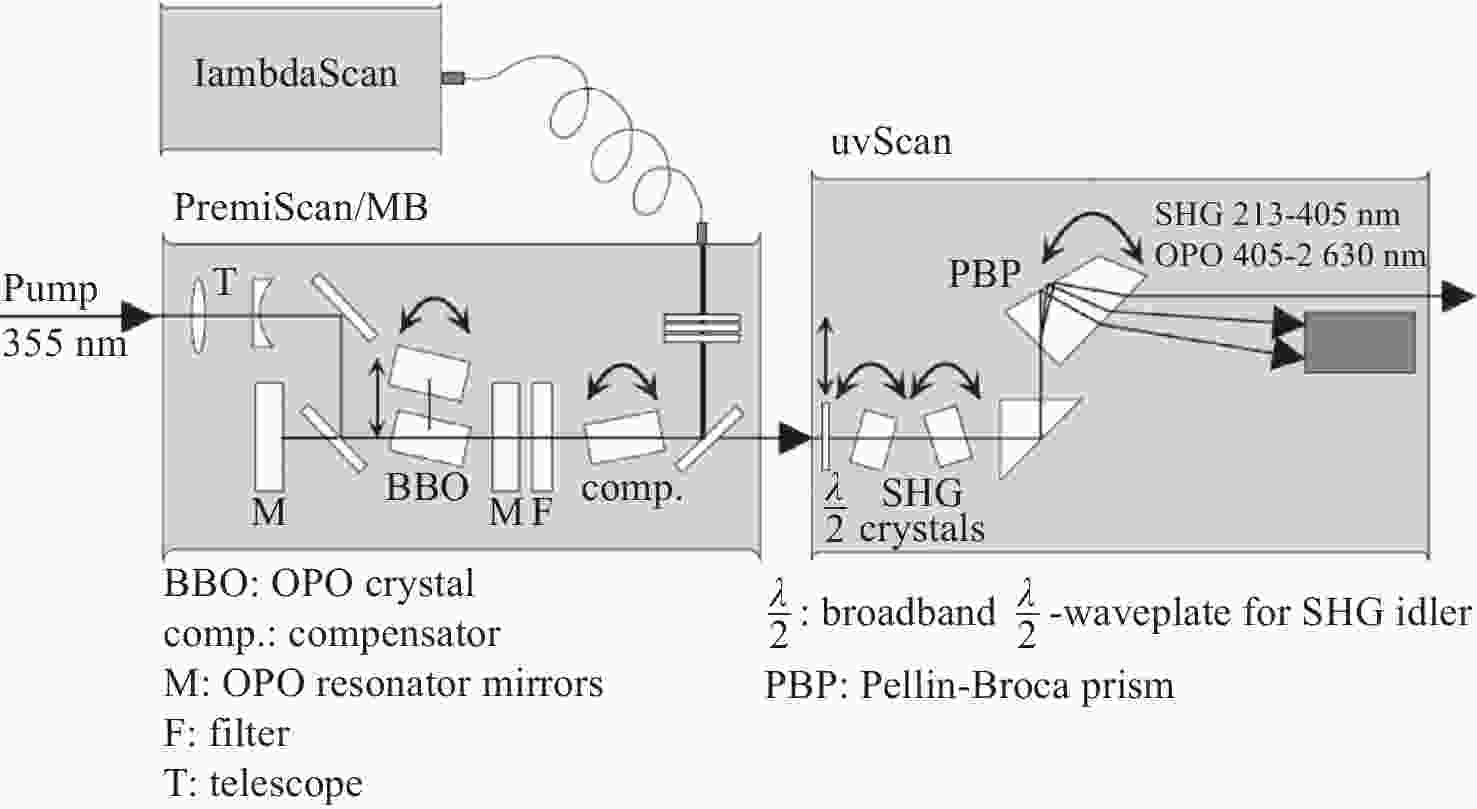
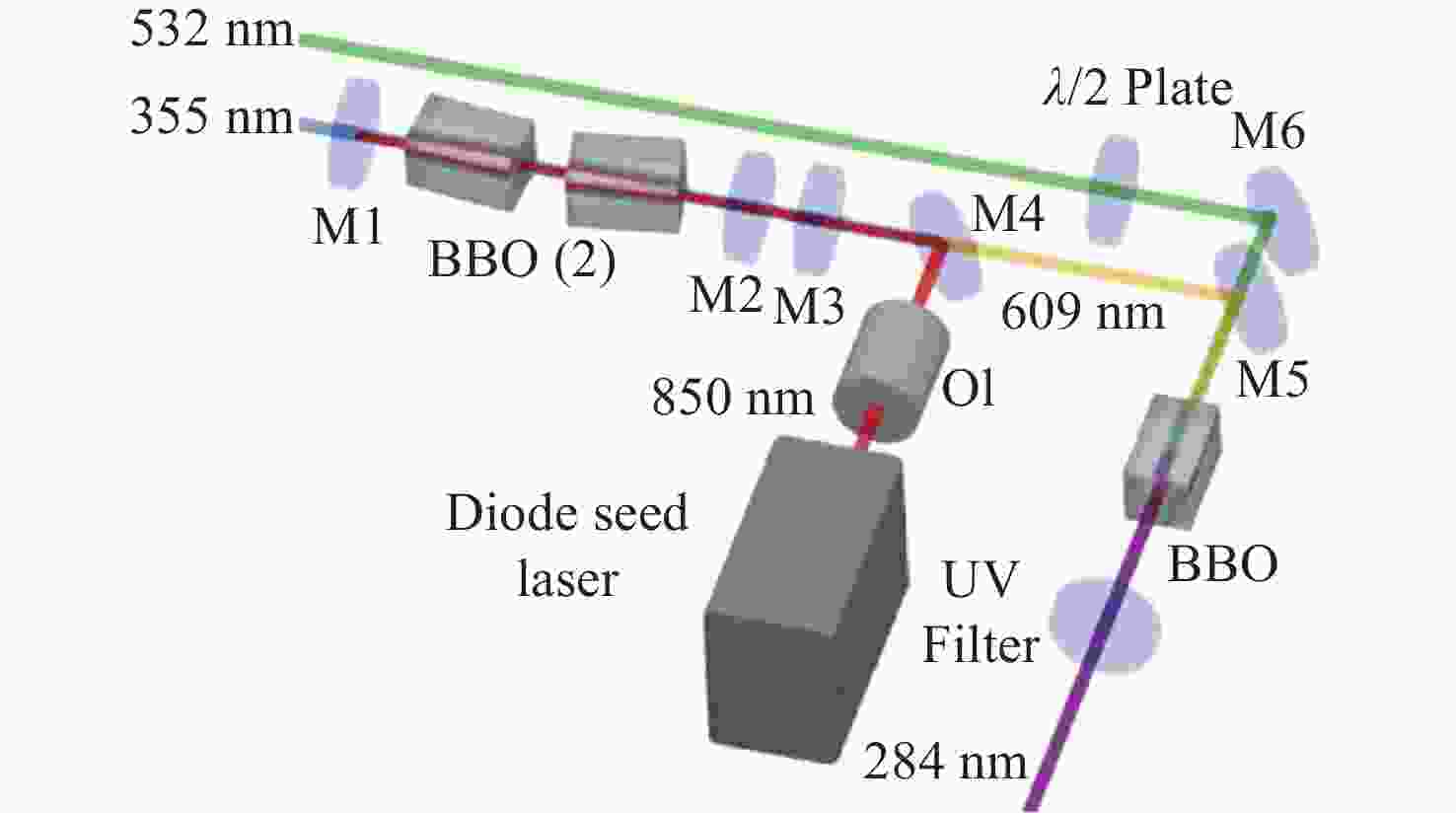
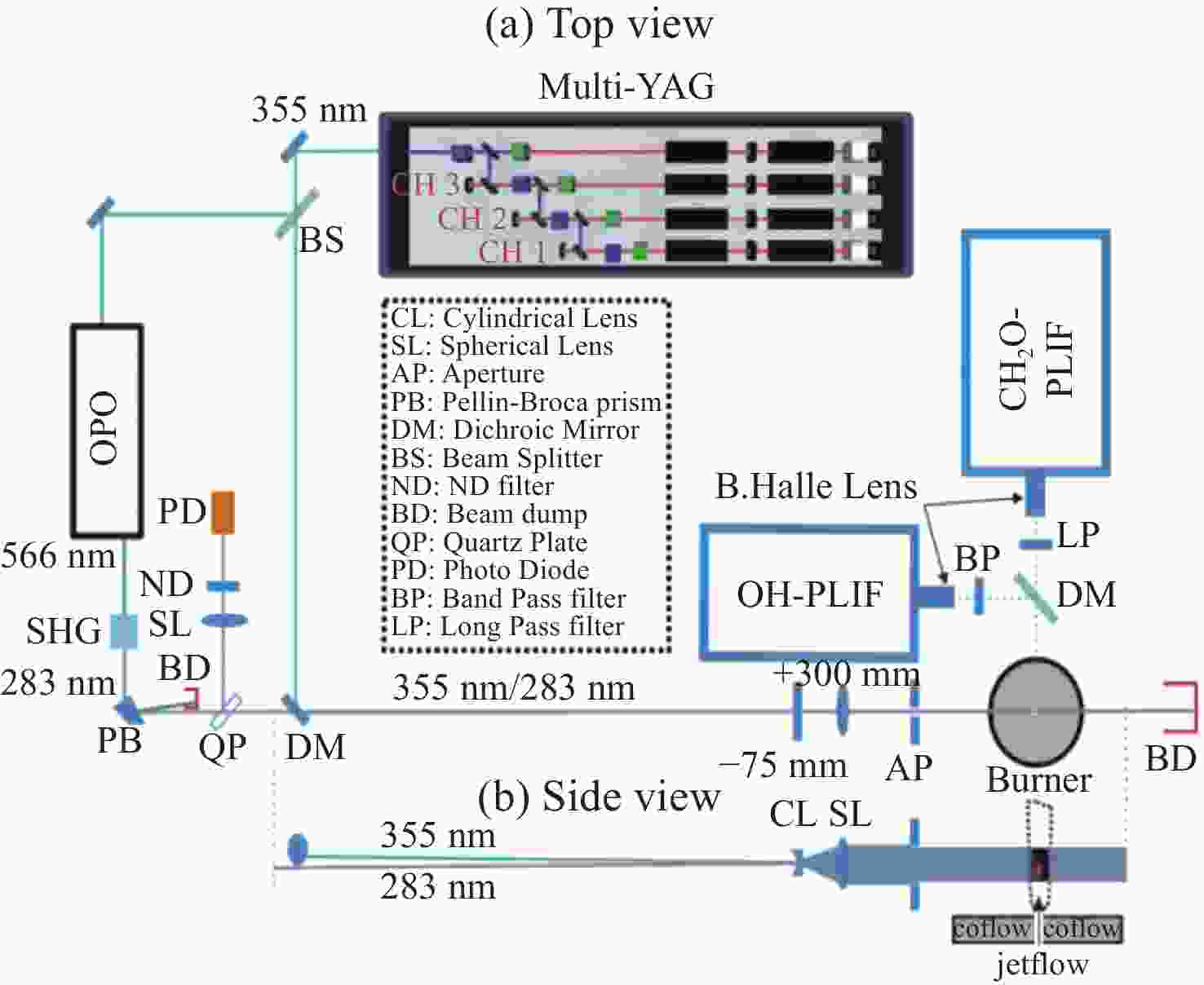
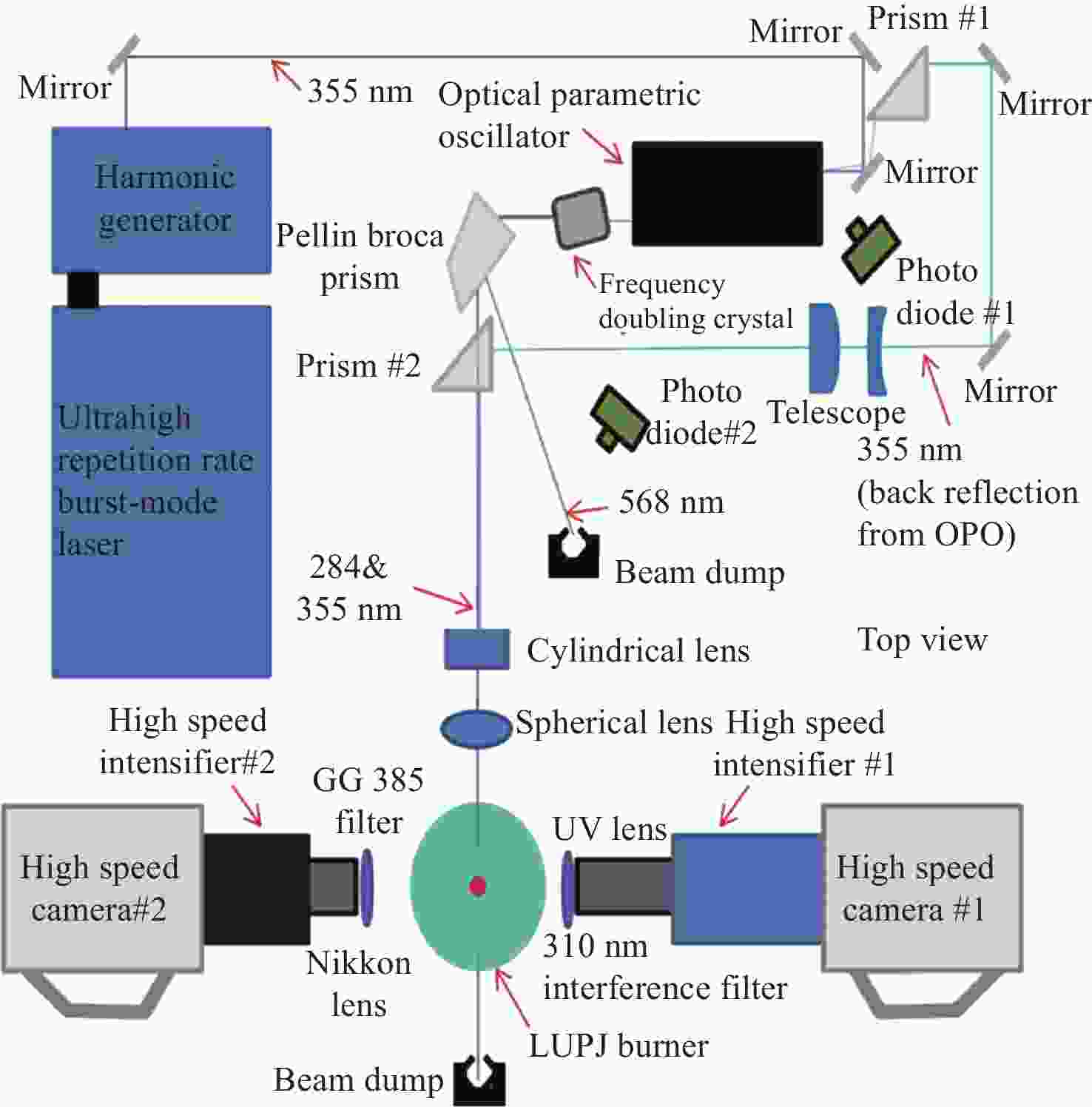
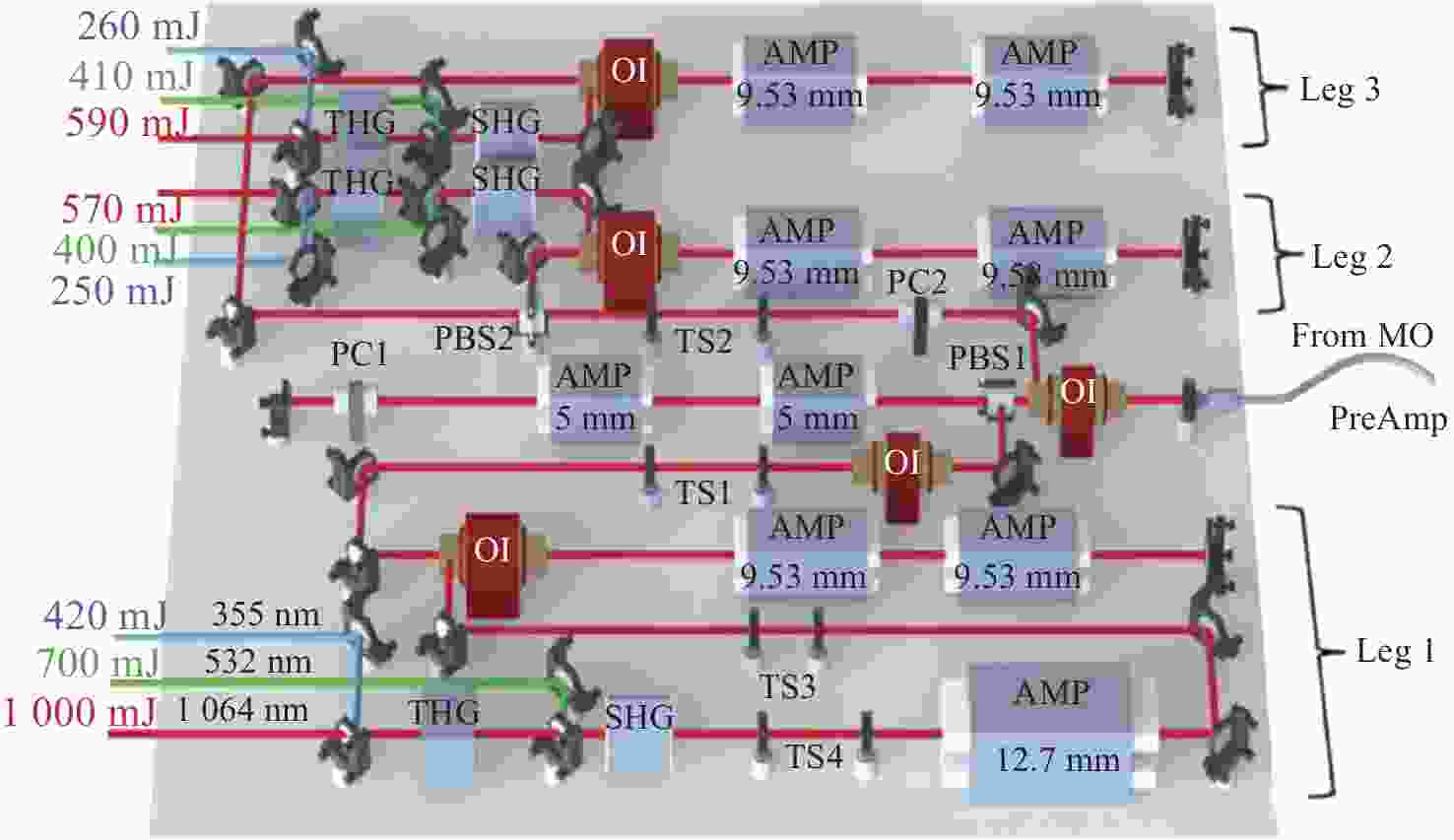
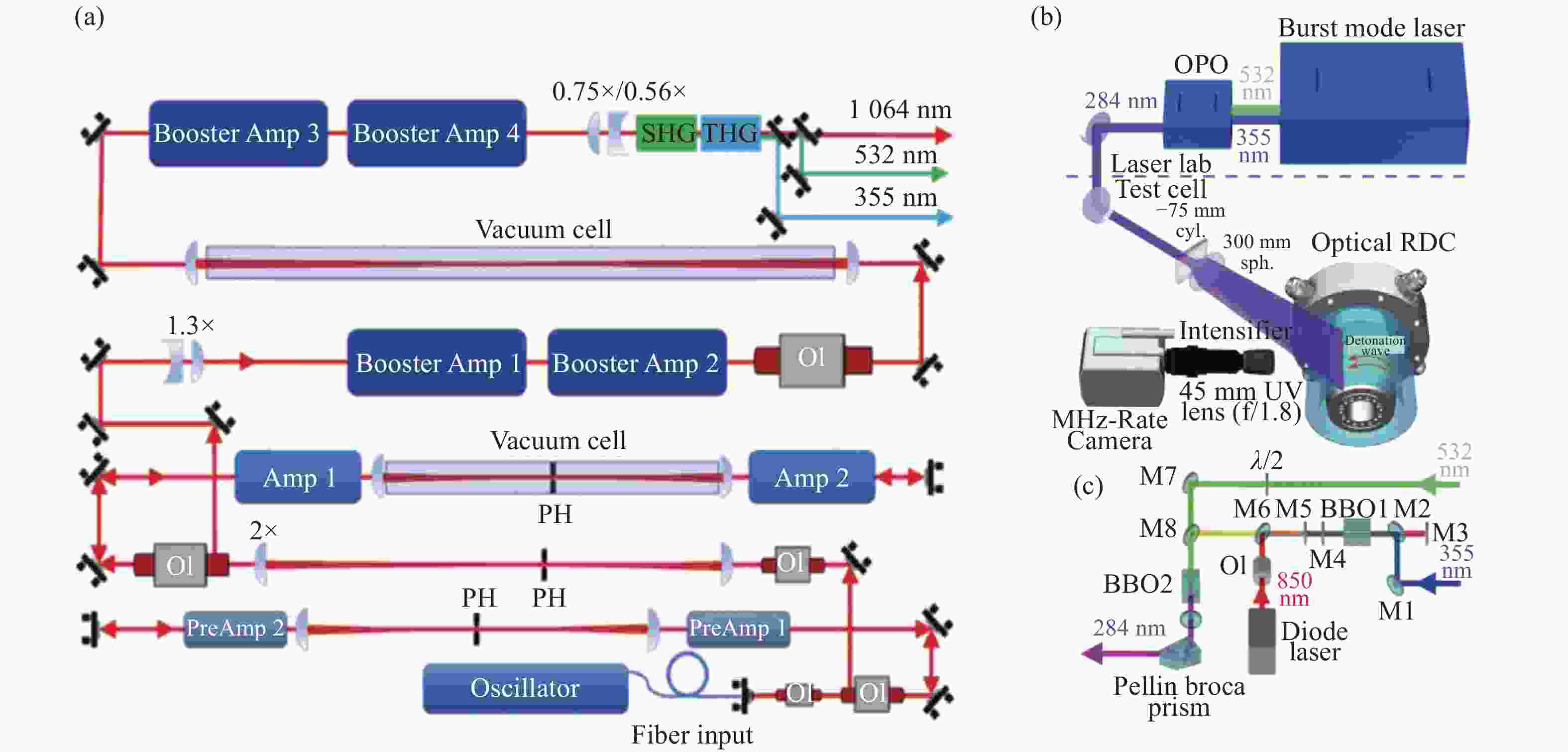
图 16 高速OH-PLIF实验装置示意图。(a) MHz泵浦源光路[57];(b)基于OPO-burst OH-PLIF的旋转爆震燃烧实验装置[57];(c) OPO光路图[58]
Figure 16. Schematic diagram of the high-speed OH-PLIF experimental setup. (a) MHz pump source optical path[57]; (b) OPO-burst OH-PLIF based rotary burst combustion experimental setup; (c) OPO optical path diagram[58]
表 1 用于OH-PLIF的紫外激光器性能对比
Table 1. Performance Comparison of UV Lasers for OH-PLIF
Year Operation mode Repetition frequency Wavelength Output power Pulse energy Conversion efficiency 2007[18] Rhodamine +SHG 10 Hz 283.92 nm 0.06 W 6 mJ - 2007[43] Rhodamine 5G+BBO SHG 2.5 kHz
5 kHz283 nm 130 mW
110 mW50 μJ
22 μJ0.7%
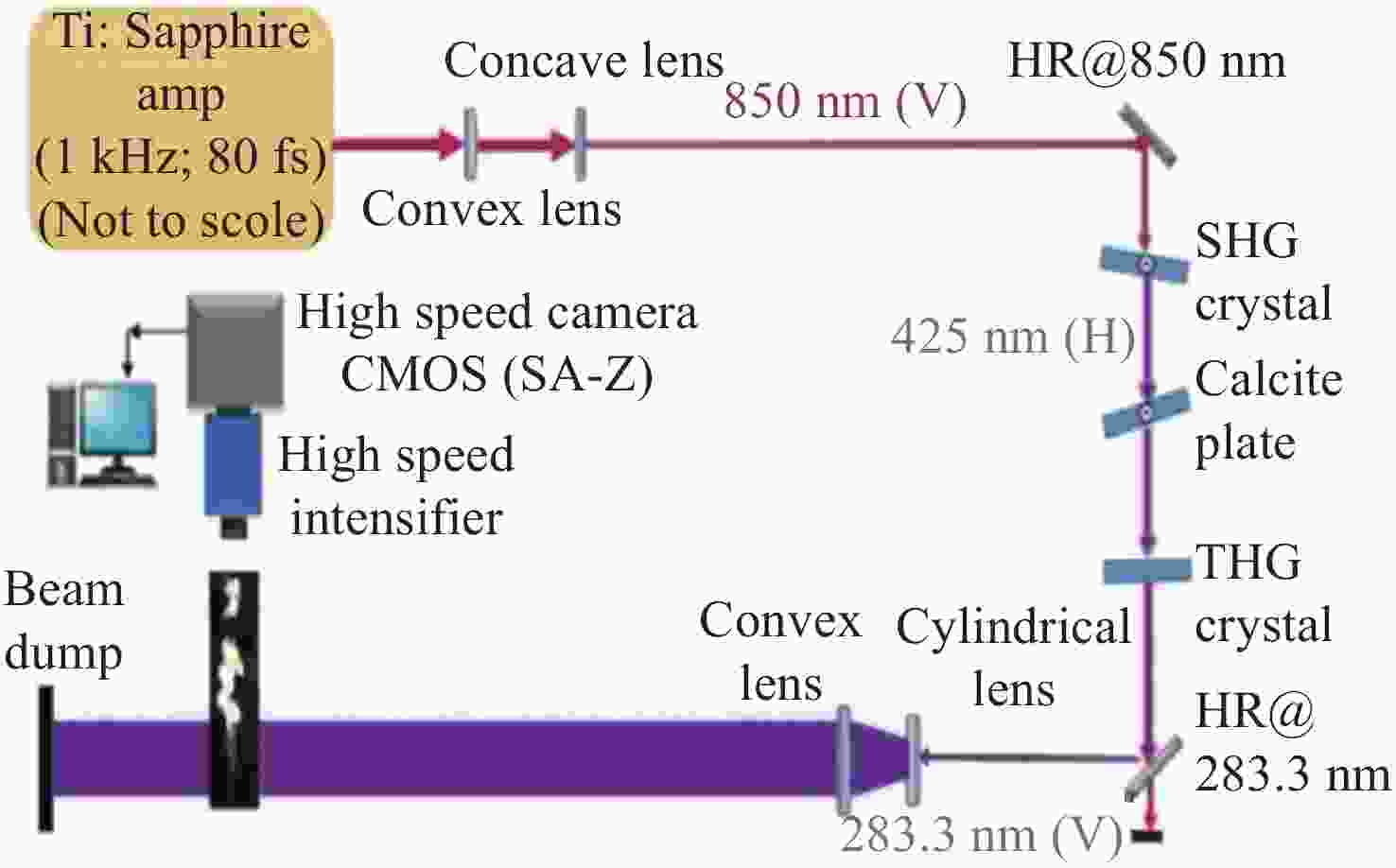
0.6%2009[44] Rhodamine 6G+SHG 1.5 kHz 283 nm 0.82 W 0.54 mJ 1.6% 2009[45] Rhodamine 6G+BBO SHG 5 kHz 283.2 nm 0.5 W 100 μJ 2.6% 2010[46] Rhodamine 6G+BBO SHG 10 kHz 283.2 nm 1.4 W 140 μJ 3.5% 2014[47] Rhodamine 6G+2*BBO SHG+MOPA 50 kHz 283 nm 7 W 0.14 mJ 3.5% 2018[48] Burst/Rhodamine 6G+SHG 20 kHz 283 nm 1.8 W 90 μJ 2.8% 2018[49] Burst/Rhodamine 6G+MOPA+BBO SHG 7.5 kHz 282.985 nm 16.5 W 2.2 mJ - 2018[11] Rhodamine 590+SHG - 283 nm - 12 mJ - 2020[51] Dye laser+SHG 10 kHz 283.9 nm 1.6 W 0.16 mJ - 2009[52] Burst/Seeding OPO+BBO SHG - 282.97 nm 0.2 W - - 2017[53] Burst/Seeding OPO+BBO SFG 10 kHz 284.005 nm - 3 mJ - 2017[54] Burst/Multi-YAG+OPO+SHG 50 kHz 283 nm - 2 mJ 1.25% 2017[55] Burst/OPO+BBO SHG 50 kHz 284 nm - 350 μJ 0.7% 2018[56] OPO+SFG 10 kHz 284 nm - 5 mJ 0.7% 2020[58] Burst/Seeding OPO+BBO SFG 1 MHz 284 nm - 400 μJ 0.6% 2020[59] fs Ti:sapphire+ BBO THG 1 kHz 283 nm - 90 μJ 4.5% 2023[60] ns Ti:sapphire+LBO SHG+BBO THG 1 kHz 283 nm 0.56 W 0.56 mJ 2.8% -
[1] 武国华, 于欣, 彭江波, 等. 超燃冲压发动机羟基/煤油-PLIF同步测量研究[J]. 推进技术,2024,45(1):2210098.WU G H, YU X, PENG J B, et al. Simultaneous measurements of OH/Kerosene-PLIF in scramjet[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2024, 45(1): 2210098. (in Chinese). [2] JOO S, KWAK S, LEE M C. Effect of fuel line acoustics on the flame dynamics of H2/CH4 syngas in a partially premixed gas turbine combustor[J]. Fuel, 2021, 285: 119231. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119231 [3] 尚勇, 何旭, 刘福水, 等. 燃烧光学可视化技术在内燃机测试中的应用研究[J]. 小型内燃机与车辆技术,2016,45(5):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0630.2016.05.001SHANG Y, HE X, LIU F SH, et al. Research on the application of combustion optical visualization technology in the test of internal combustion engine[J]. Small Internal Combustion Engine and Vehicle Technique, 2016, 45(5): 1-7. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0630.2016.05.001 [4] 王健儒, 晁侃, 陆贺建. 大型分段式固体火箭发动机点火瞬态过程研究[J]. 固体火箭技术,2017,40(2):141-145. doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2017.02.002WANG J R, CHAO K, LU H J. Investigation of ignition transient in large segmented SRM[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2017, 40(2): 141-145. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2017.02.002 [5] 寇志海, 王清印, 李广超, 等. 航空发动机高温壁面热电偶测温技术应用[J]. 热能动力工程,2023,38(1):202-210.KOU ZH H, WANG Q Y, LI G CH, et al. Thermocouple measurement technology for high temperature wall in aero-engine[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2023, 38(1): 202-210. (in Chinese). [6] WRBANEK J D, FRALICK G C. Thin film physical sensor instrumentation research and development at nasa glenn research center[C]. Proceedings of the 52nd International Instrumentation Symposium, 2006: 168-177. [7] SOBCZYK J. Experimental study of the flow field disturbance in the vicinity of single sensor hot-wire anemometer[J]. EPJ Web of Conferences, 2018, 180: 02094. doi: 10.1051/epjconf/201818002094 [8] 苏铁, 陈爽, 杨富荣, 等. 双色平面激光诱导荧光瞬态燃烧场测温实验[J]. 红外与激光工程,2014,43(6):1750-1754. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.06.010SU T, CHEN SH, YANG F R, et al. Investigation of temperature of transient combustion using two-line PLIF[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(6): 1750-1754. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.06.010 [9] PAUL P H, NAJM H N. Planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging of flame heat release rate[J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1998, 27(1): 43-50. doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(98)80388-3 [10] ZHOU B, KIEFER J, ZETTERBERG J, et al. Strategy for PLIF single-shot HCO imaging in turbulent methane/air flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2014, 161(6): 1566-1574. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.11.019 [11] 李红, 李博, 高强, 等. OH/CH2O基于PLIF测量得到的火焰面密度比较研究[J]. 燃烧科学与技术,2018,24(6):523-527.LI H, LI B, GAO Q, et al. Plane laser-induced fluorescence for flame surface density calculation of OH/CH2O: A comparative study[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2018, 24(6): 523-527. (in Chinese). [12] RASMUSSEN C C, DHANUKA S K, DRISCOLL J F. Visualization of flameholding mechanisms in a supersonic combustor using PLIF[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2007, 31(2): 2505-2512. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2006.08.007 [13] KARIUKI J, DOWLUT A, YUAN R, et al. Heat release imaging in turbulent premixed methane–air flames close to blow-off[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2015, 35(2): 1443-1450. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2014.05.144 [14] FIALA T, SATTELMAYER T. Heat release and UV–Vis radiation in non-premixed hydrogen–oxygen flames[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2015, 56(7): 144. doi: 10.1007/s00348-015-2013-8 [15] CIARDIELLO R, PATHANIA R S, HELOU I E, et al. Lean blow-off investigation in a linear multi-burner combustor operated in premixed and non-premixed modes[J]. Applications in Energy and Combustion Science, 2022, 9: 100041. doi: 10.1016/j.jaecs.2021.100041 [16] KARIUKI J, DOWLUT A, BALACHANDRAN R, et al. Heat release imaging in turbulent premixed ethylene-air flames near blow-off[J]. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 2016, 96(4): 1039-1051. doi: 10.1007/s10494-016-9720-y [17] MULLA I A, DOWLUT A, HUSSAIN T, et al. Heat release rate estimation in laminar premixed flames using laser-induced fluorescence of CH2O and H-atom[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2016, 165: 373-383. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.12.023 [18] STRAKEY P A, WOODRUFF S D, WILLIAMS T C, et al. OH-PLIF measurements of high-pressure, hydrogen augmented premixed flames in the simval combustor[C]. 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, AIAA, 2007: 11867-11880. [19] MILLER J D, ENGEL S R, TROGER J W, et al. Characterization of a CH planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging system using a kHz-rate multimode-pumped optical parametric oscillator[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(14): 2589-2600. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.002589 [20] BOHON M D, GUIBERTI T F, ROBERTS W L. PLIF measurements of non-thermal NO concentrations in alcohol and alkane premixed flames[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2018, 194: 363-375. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2018.05.024 [21] SCHULZ C, SICK V, HEINZE J, et al. Laser-induced-fluorescence detection of nitric oxide in high-pressure flames with A-X(0, 2) excitation[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(15): 3227-3232. doi: 10.1364/AO.36.003227 [22] PALMER J L, MCMILLIN B K, HANSON R K. Multi-line fluorescence imaging of the rotational temperature field in a shock-tunnel free jet[J]. Applied Physics B, 1996, 63(2): 167-178. doi: 10.1007/BF01095269 [23] HEINZE J, MEIER U, BEHRENDT T, et al. PLIF thermometry based on measurements of absolute concentrations of the OH radical[J]. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 2011, 225(11-12): 1315-1341. [24] 于欣, 杨超博, 彭江波, 等. 基于紫外可调谐激光吸收光谱技术的甲烷/空气平面预混火焰温度测量研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2016,36(4):1027-1032.YU X, YANG CH B, PENG J B, et al. Temperature measurement of CH4/air premix flat flame based on the absorption spectroscopy technology of UV tunable laser[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(4): 1027-1032. (in Chinese). [25] GRISCH F, ORAIN M. Role of planar laser-induced fluorescence in combustion research[J]. Journal of Aerospace Lab, 2009(1): 1-14. [26] YIP B, MILLE M F, LOZANO A, et al. A combined OH/acetone planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging technique for visualizing combusting flows[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 1994, 17(5): 330-336. doi: 10.1007/BF01874413 [27] SEITZMAN J M, MILLER M F, ISLAND T C, et al. Double-pulse imaging using simultaneous OH/acetone PLIF for studying the evolution of high-speed, reacting mixing layers[J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1994, 25(1): 1743-1750. doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(06)80823-4 [28] BRESSON A, BOUCHARDY P, MAGRE P, et al. OH/acetone PLIF and CARS thermometry in a supersonic reactive layer[C]. 10th AIAA/NAL-NASDA-ISAS International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies Conference, AIAA, 2001: 1759. [29] ELBAZ A M, ROBERTS W L. Experimental study of the inverse diffusion flame using high repetition rate OH/acetone PLIF and PIV[J]. Fuel, 2016, 165: 447-461. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.096 [30] RANKIN B A, FUGGER C A, RICHARDSON D R, et al. Evaluation of mixing processes in a non-premixed rotating detonation engine using acetone PLIF[C]. 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, AIAA, 2016: 1198. [31] 严浩, 张少华, 余西龙, 等. OH与CH2O双组分平面激光诱导荧光对旋流燃烧室火焰结构与脉动特征的研究[J]. 航空动力学报,2019,34(4):894-907.YAN H, ZHANG SH H, YU X L, et al. Flame structure and dynamics characters inVestigation by OH and CH2O planar laser-induced fluorescence in the swirl combustor[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2019, 34(4): 894-907. (in Chinese). [32] 陈晓丽, 金川, 苏秋成, 等. 基于激光诱导荧光法的同轴射流火焰中羟基自由基、甲醛、发热率与一氧化氮的二维可视化测量[J]. 分析测试技术与仪器,2021,27(3):182-188.CHEN X L, JIN CH, SU Q CH, et al. Two-dimensional visualization measurement of hydroxyl radical, formaldehyde, heat release rate and nitric oxide in co-flow jet flame based on planar laser induced fluorescence technology[J]. Analysis and Testing Technology and Instruments, 2021, 27(3): 182-188. (in Chinese). [33] 梁剑寒, 李韵, 孙明波, 等. 超声速燃烧火焰放热区结构CH-PLIF成像技术[J]. 国防科技大学学报,2019,41(1):27-33. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201901005LIANG J H, LI Y, SUN M B, et al. CH-PLIF imaging of flame heat-release structures in supersonic combustion[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2019, 41(1): 27-33. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201901005 [34] 吴戈, 李韵, 万明罡, 等. 平面激光诱导荧光技术在超声速燃烧火焰结构可视化中的应用[J]. 实验流体力学,2020,34(3):70-77. doi: 10.11729/syltlx20190168WU G, LI Y, WAN M G, et al. Visualization of flame structure in supersonic combustion by planar laser induced fluorescence technique[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 34(3): 70-77. (in Chinese). doi: 10.11729/syltlx20190168 [35] 关小伟, 刘晶儒, 黄梅生, 等. PLIF法定量测量甲烷-空气火焰二维温度场分布[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2005,17(2):173-176.GUAN X W, LIU J R, HUANG M SH, et al. Two-dimensional temperature field measurement in a methane-air flame by PLIF[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2005, 17(2): 173-176. (in Chinese). [36] 曹春丽, 徐胜利, 刘二伟. 双波长NO-PLIF法测量运动激波前后温度场的实验研究[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报,2012,42(12):977-983. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2012.12.005CAO CH L, XU SH L, LIU E W. Temperature measurement on moving shock wave by two-wavelength NO-PLIF method[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 2012, 42(12): 977-983. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2012.12.005 [37] 宋东先, 谢辉, 邹庆武, 等. 单线双示踪粒子PLIF测温技术的开发[J]. 小型内燃机与车辆技术,2015,44(4):1-5,55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0630.2015.04.001SONG D X, XIE H, ZOU Q W, et al. The development of single-line two tracers PLIF temperature measurement technology in an optical engine[J]. Small Internal Combustion Engine and Vehicle Technique, 2015, 44(4): 1-5,55. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0630.2015.04.001 [38] 梁帅, 张周, 丁海春, 等. 用PLIF测量GDI发动机滚流平面的混合气浓度[J]. 内燃机学报,2018,36(6):481-490.LIANG SH, ZHANG ZH, DING H CH, et al. Mixture distribution measurement in the tumble plane of a GDI engine via PLIF method[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2018, 36(6): 481-490. (in Chinese). [39] 任晓光, 王兰红, 董全, 等. 基于PLIF技术的天然气喷射流场摩尔浓度特性[J]. 内燃机学报,2020,38(5):417-425.REN X G, WANG L H, DONG Q, et al. Concentration characteristics in the flow field of a natural gas injection based on PLIF[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2020, 38(5): 417-425. (in Chinese). [40] SCHMIDT J B, JIANG N, GANGULY B N. Nitric oxide PLIF measurement in a point-to-plane pulsed discharge in vitiated air of a propane/air flame[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2014, 23(6): 065005. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/23/6/065005 [41] 余响林, 王世敏, 许祖勋, 等. 光电功能性有机染料及其应用研究进展[J]. 染料与染色,2004,41(2):63-66,80.YU X L, WANG SH M, XU Z X, et al. Progress on the study of photoelectrical functional organic dyes and their applications[J]. Dyestuffs and Coloration, 2004, 41(2): 63-66,80. (in Chinese). [42] 李海鹏, 韩奎, 沈晓鹏, 等. 半花菁衍生物分子第一超极化率频率色散效应的理论研究[J]. 光学学报,2005,25(5):655-660. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2005.05.018LI H P, HAN K, SHEN X P, et al. Theoretical studies on frequency-dispersion effect of first hyperpolarizabilities of hemicyanine derivatives[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2005, 25(5): 655-660. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2005.05.018 [43] KITTLER C, DREIZLE A. Cinematographic imaging of hydroxyl radicals in turbulent flames by planar laser-induced fluorescence up to 5 kHz repetition rate[J]. Applied Physics B, 2007, 89(2): 163-166. [44] BOXX I, HEEGER C, GORDON R, et al. Simultaneous three-component PIV/OH-PLIF measurements of a turbulent lifted, C3H8-Argon jet diffusion flame at 1.5kHz repetition rate[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2009, 32(1): 905-912. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2008.06.023 [45] BOXX I, STÖHR M, CARTER C, et al. Sustained multi-kHz flamefront and 3-component velocity-field measurements for the study of turbulent flames[J]. Applied Physics B, 2009, 95(1): 23-29. doi: 10.1007/s00340-009-3420-4 [46] BOXX I, ARNDT C M, CARTER C D, et al. High-speed laser diagnostics for the study of flame dynamics in a lean premixed gas turbine model combustor[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2012, 52(3): 555-567. doi: 10.1007/s00348-010-1022-x [47] HAMMACK S, CARTER C, WUENSCHE C, et al. Continuous hydroxyl radical planar laser imaging at 50 kHz repetition rate[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(23): 5246-5251. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.005246 [48] HAMMACK S D, CARTER C D, SKIBA A W, et al. 20 kHz CH2O and OH PLIF with stereo PIV[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(5): 1115-1118. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001115 [49] PAN R C, RETZER U, WERBLINSKI T, et al. Generation of high-energy, kilohertz-rate narrowband tunable ultraviolet pulses using a burst-mode dye laser system[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(5): 1191-1194. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001191 [50] RETZER U, PAN R C, WERBLINSKI T, et al. Burst-mode OH/CH2O planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging of the heat release zone in an unsteady flame[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 18105-18114. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.018105 [51] FUGGER C A, HSU P S, JIANG N B, et al. 10-kHz simultaneous dual-plane stereo-PIV and OH-PLIF imaging[J]. Applied Physics B, 2020, 126(10): 167. doi: 10.1007/s00340-020-07522-4 [52] SJÖHOLM J, KRISTENSSON E, RICHTER M, et al. Ultra-high-speed pumping of an optical parametric oscillator (OPO) for high-speed laser-induced fluorescence measurements[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2009, 20(2): 025306. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/20/2/025306 [53] HALLS B R, HSU P S, JIANG N B, et al. kHz-rate four-dimensional fluorescence tomography using an ultraviolet-tunable narrowband burst-mode optical parametric oscillator[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(8): 897-902. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000897 [54] LI Z M, ROSELL J, ALDÉN M, et al. Simultaneous burst imaging of dual species using planar laser-induced fluorescence at 50 kHz in turbulent premixed flames[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(6): 1363-1367. doi: 10.1177/0003702816678866 [55] WANG Z K, STAMATOGLOU P, LI Z M, et al. Ultra-high-speed PLIF imaging for simultaneous visualization of multiple species in turbulent flames[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(24): 30214-30228. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.030214 [56] ROY S, JIANG N B, HSU P S, et al. Development of a three-legged, high-speed, burst-mode laser system for simultaneous measurements of velocity and scalars in reacting flows[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(11): 2704-2707. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.002704 [57] FELVER J, SLIPCHENKO M N, BRAUN E L, et al. High-energy laser pulses for extended duration megahertz-rate flow diagnostics[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(16): 4583-4586. doi: 10.1364/OL.400831 [58] HSU P S, SLIPCHENKO M N, JIANG N B, et al. Megahertz-rate OH planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging in a rotating detonation combustor[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(20): 5776-5779. doi: 10.1364/OL.403199 [59] JAIN A, PARAJULI P, WANG Y J, et al. Hydroxyl radical planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging in flames using frequency-tripled femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(17): 4690-4693. doi: 10.1364/OL.400930 [60] ZHANG ZH L, YANG A L, WANG J, et al. OH planar laser-induced fluorescence imaging system using a kilohertz-rate 283 nm UV Ti: sapphire laser[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(8): 1915-1920. doi: 10.1364/AO.484749 [61] 叶景峰, 张振荣, 李国华, 等. 激光激励煤油荧光光谱实验研究[C]. 中国力学大会2011暨钱学森诞辰100周年纪念大会论文集, 中国力学学会, 2011: 1-5.YE J F, ZHANG ZH R, LI G H, et al. The experiment study of laser induced kerosene fluorescence[C]. Review of the Chinese Conference on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics-2001 in Memorial of Tsien-Shen's 100th Anniversary, The Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2011: 1-5. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: