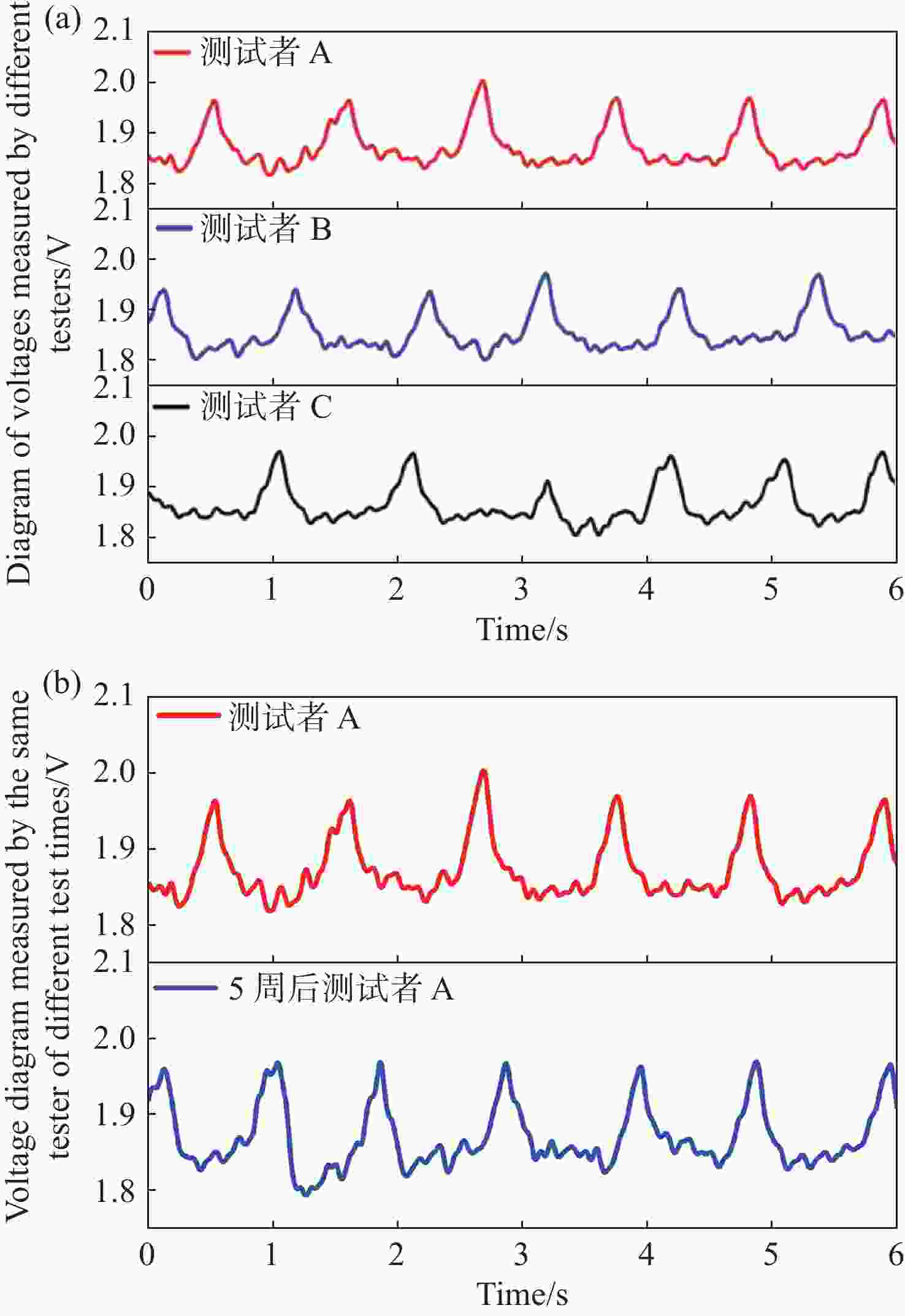
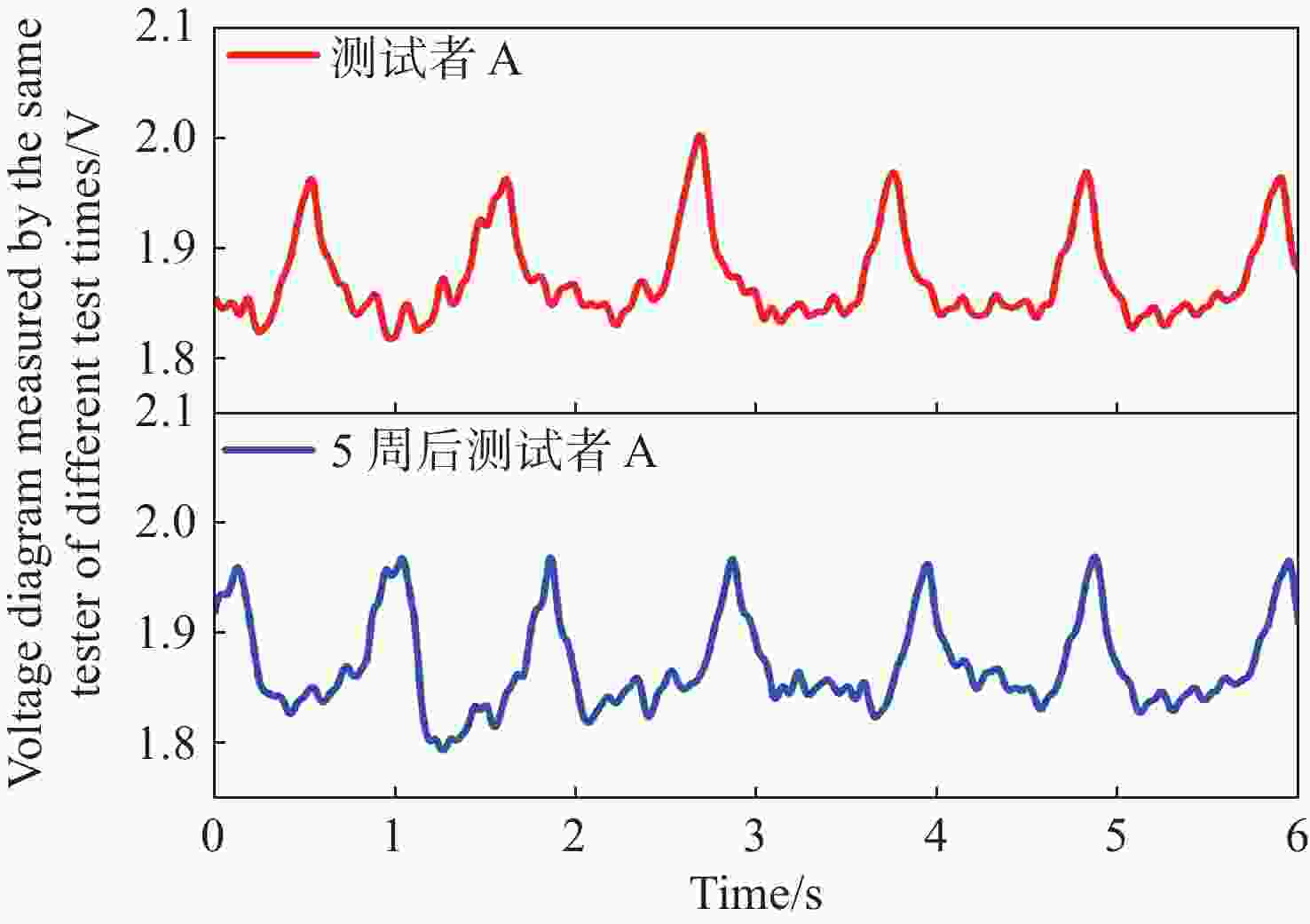
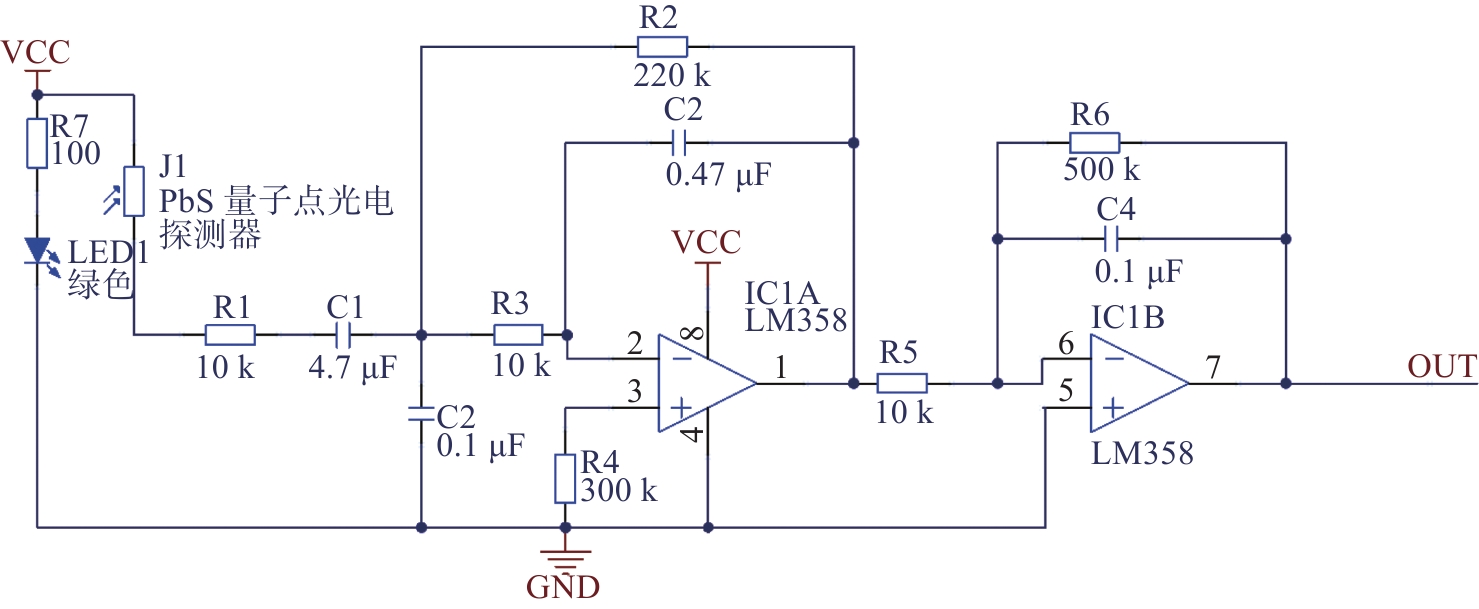
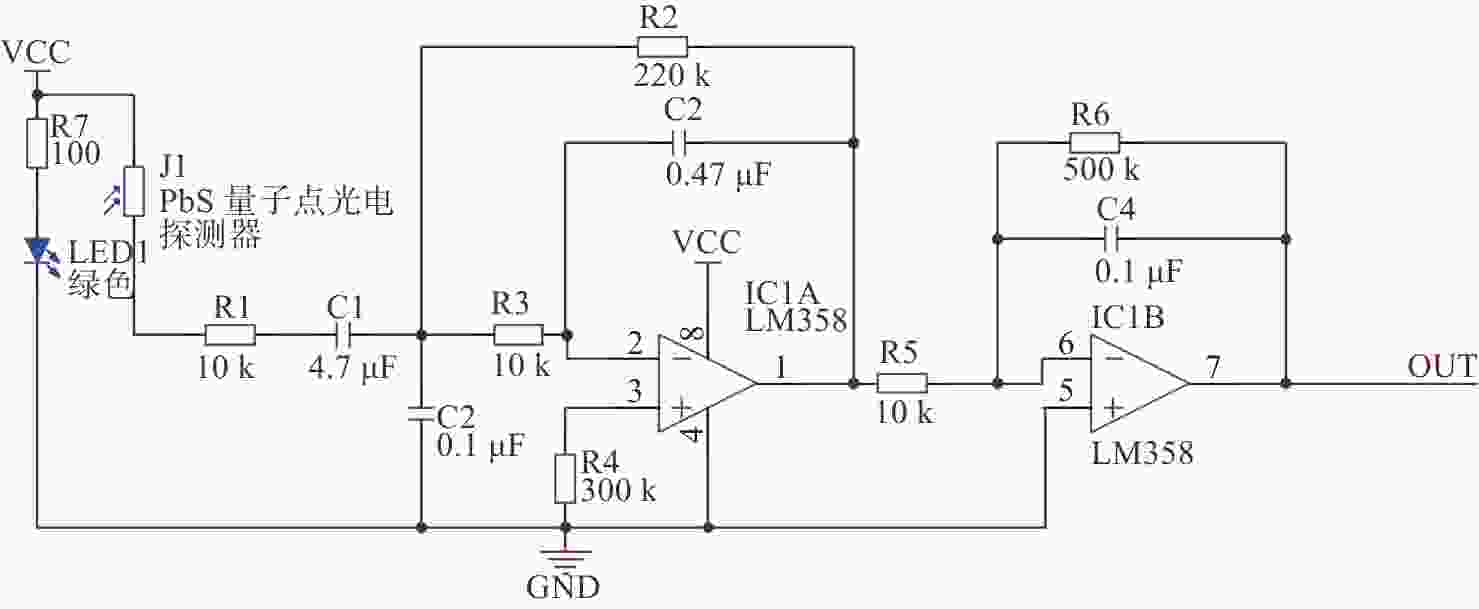
-
摘要:
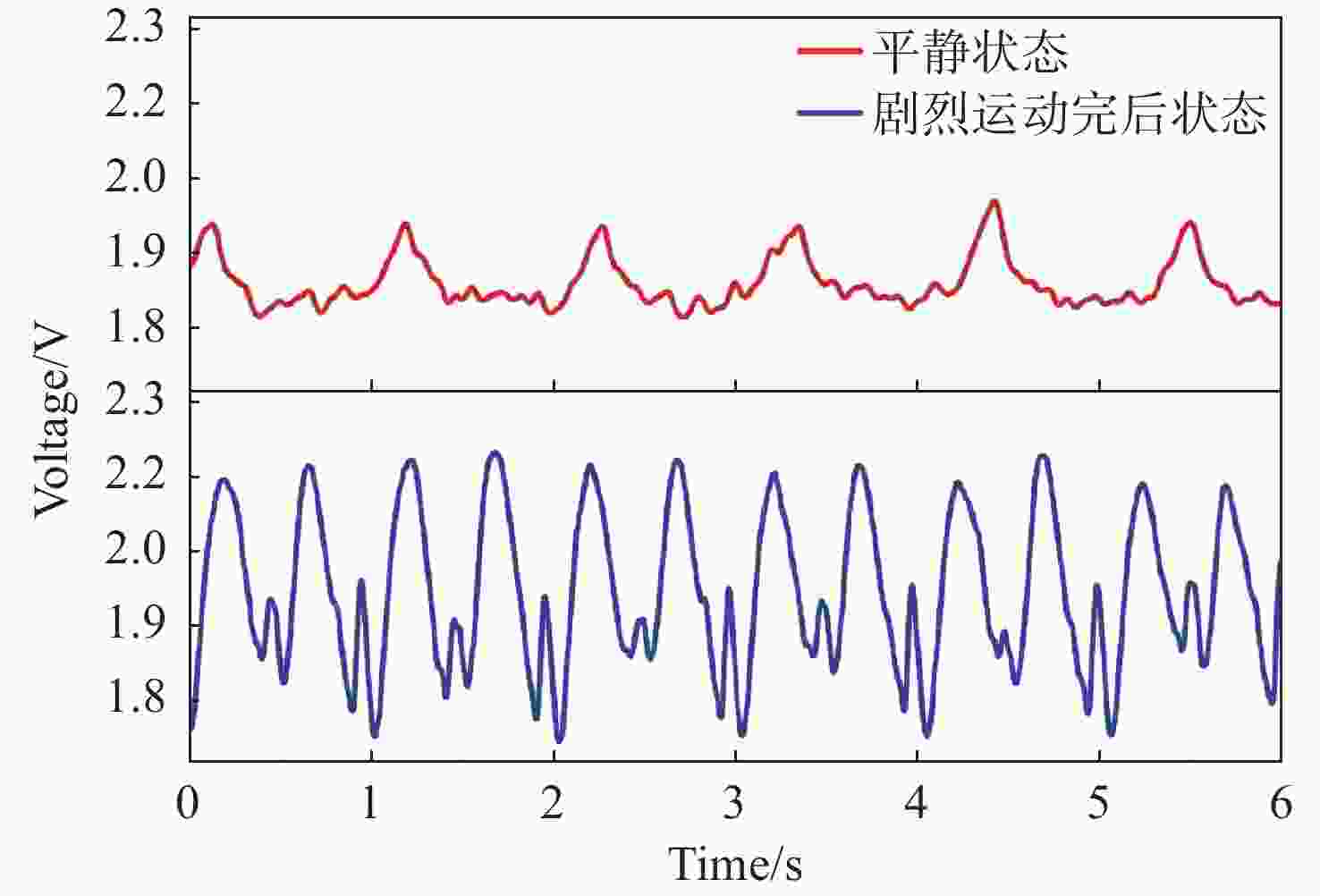
脉搏蕴含人体丰富的血流信息,检测脉搏并推导出人体心血管系统健康状态正成为研究的热点。本文利用热注射法合成得到尺寸为3 nm的PbS量子点,在金叉指电极表面通过旋涂的方法构筑PbS量子点光电探测器。基于已制备的PbS量子点光电探测器研制了数据可视化的脉搏检测系统。运用光电容积脉搏波描记法,对同一测试者不同运动状态以及不同测试者同一运动状态进行测量,经过电路处理将测得的数据显示在电子显示屏上。结果表明,探测器在15.2 μW·cm−2光强度照射下,其响应度(
R )和探测率(D *)在−3 V偏压下分别为0.33 A/W和1.33×1012 Jones。将其应用于测量脉搏电路中,系统能够有效接收并测得人体脉搏信号。上述结果表明基于PbS量子点光电探测器的脉搏检测系统在灵敏度、稳定性以及可靠性均满足应用要求。-
关键词:
- 硫化铅量子点 /
- 光电探测器 /
- 光电容积脉搏波描记法 /
- 脉搏波测量
Abstract:As the pulse contains rich blood flow information of the human body, detecting the pulse and deducing the health status of human cardiovascular system are becoming a hot spot. In this study, PbS quantum dots with a size of 3 nm were synthesized using the hot injection method, and a PbS quantum dot photodetector was constructed on the surface of gold forked finger electrode through spin coating. Based on the prepared PbS quantum dot photodetector, a data visualization pulse detection system was developed. Using the optoelectronic capacitance pulse wave recording method, the same tester was measured under different exercise states and different testers were measured under the same exercise state. The measured data was displayed on the electronic display screen through circuit processing. The results show that under the illumination of 15.2 μW·cm−2 light intensity, its responsivity (
R ) and light detection rate (D *) are 0.33 A/W and 1.33×1012 Jones under −3 V bias voltage, respectively. When used in a pulse measurement circuit, the system can effectively receive and measure the human pulse signal. It can be concluded that the pulse detection system based on the PbS quantum dot photodetector meets the application requirements regarding sensitivity, stability, and reliability.-
Key words:
- PbS QDs /
- photoelectric detector /
- photoplethysmography /
- pulse detection sensor
-
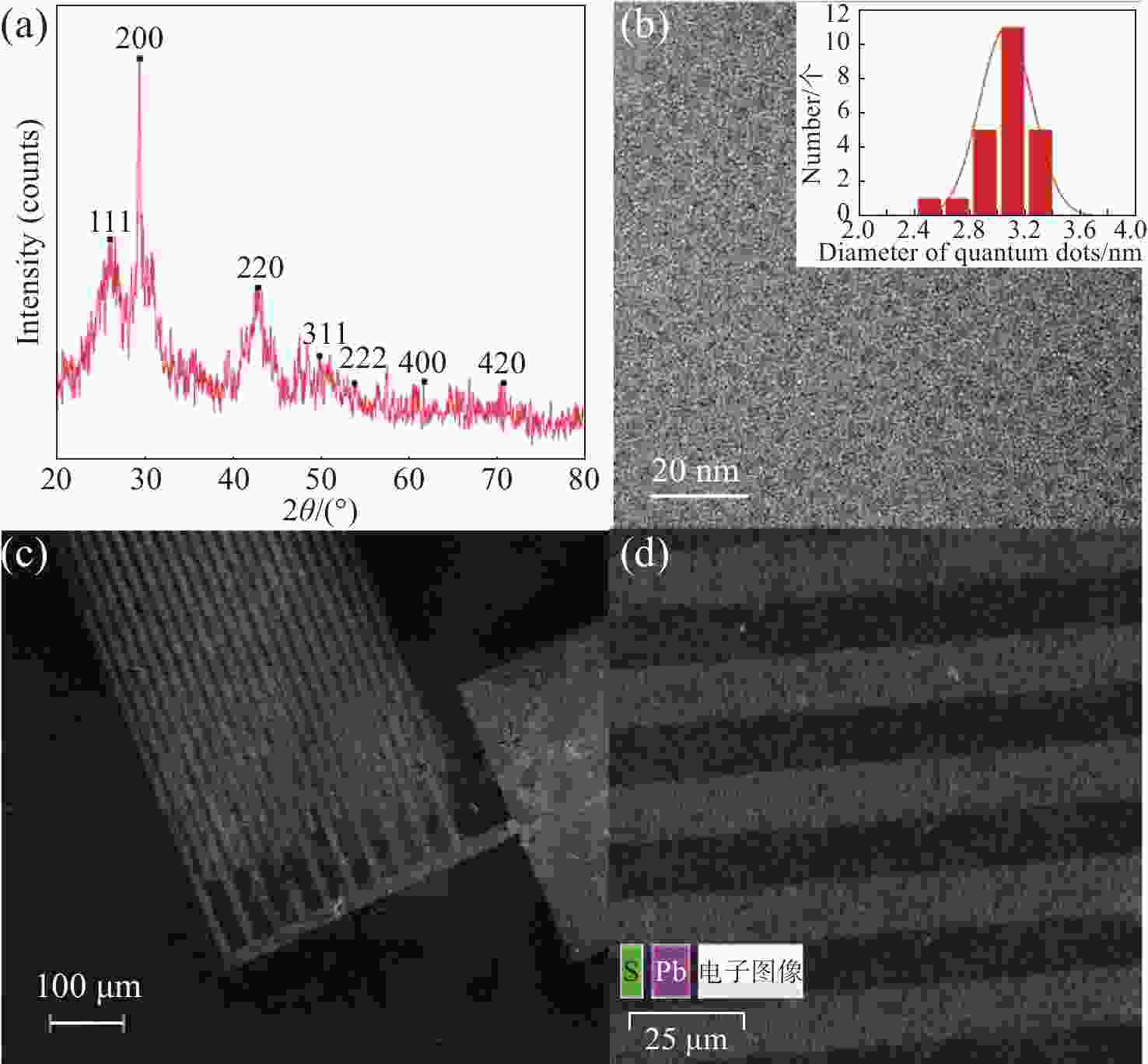
图 2 PbS光电探测器的各项测试结果。(a) 所制备材料的XRD数据图;(b) PbS量子点的TEM图,插图为PbS量子点的直径大小分布直方图;(c) PbS光电探测器的SEM图;(d) PbS光电探测器的SEM-EDS图
Figure 2. Performance test results of photodetector. (a) XRD data of PbS quantum dots; (b) TEM of PbS quantum dots, the illustration is a histogram showing the distribution of diameter sizes of PbS quantum dots, (c) SEM of PbS photodetectors, (d) SEM-EDS of PbS photodetector
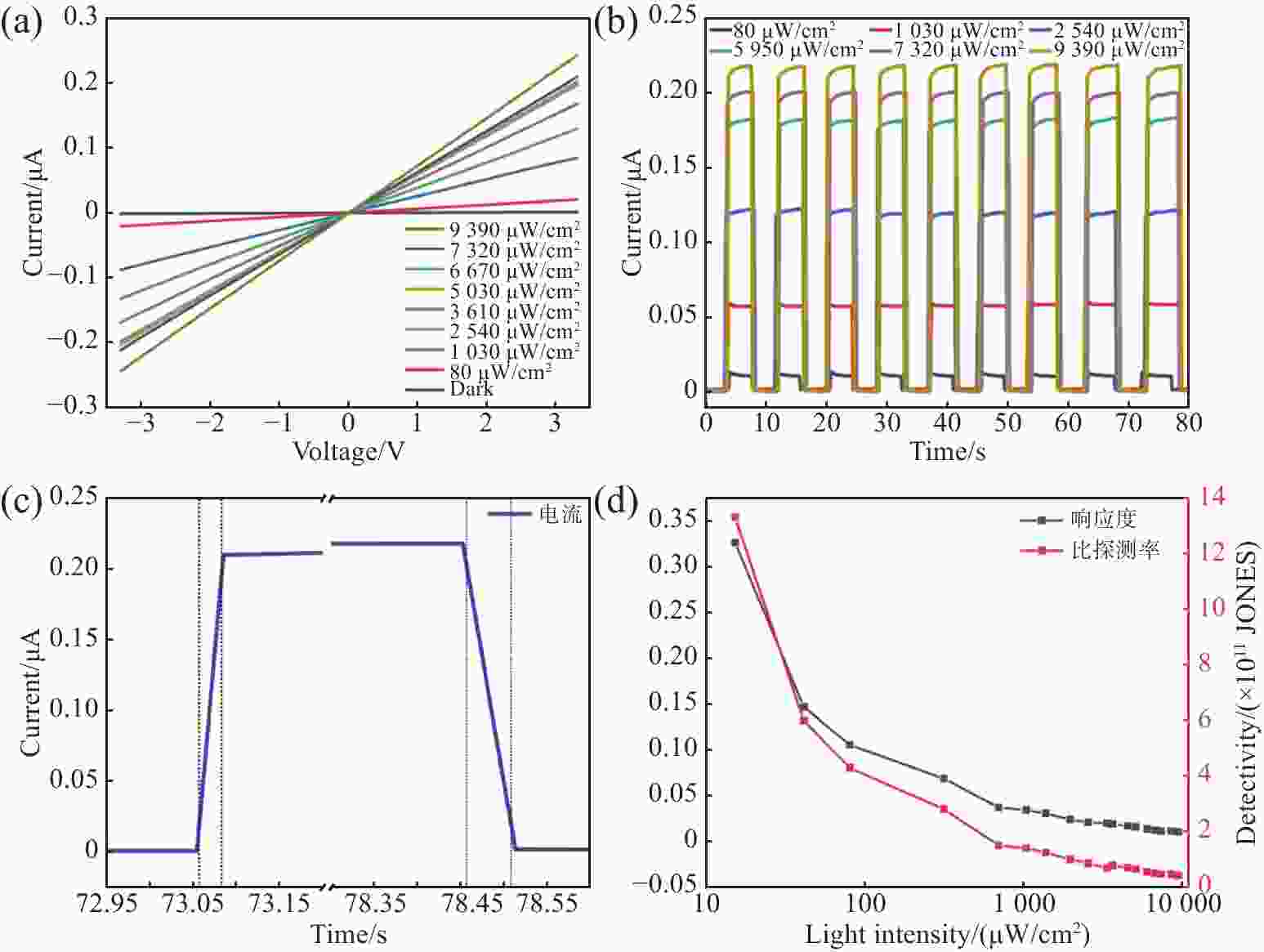
图 3 (a) PbS量子点光电探测器在不同光功率密度下的电流-电压(I-V)图;(b) −3 V偏压下PbS量子点光电探测器在不同光功率密度下的电流-时间(I-T)图;(c) PbS量子点光电探测器在
9390 μW·cm−2光强下的响应时间图;(d) PbS光电探测器件在不同光功率密度下的响应度曲线图和比探测率曲线图Figure 3. (a) Current-voltage (I-V) diagram of PbS quantum dot photodetector at different optical power densities; (b) current-time (I-T) diagram of PbS quantum dot photodetector at different optical power densities when bias is −3 V; (c) response time of PbS quantum dot photodetector at
9390 μW·cm−2 light intensity, (d) responsivity curve and specific detection rate curve of PbS photodetector at different optical power densities表 1 两种系统脉搏检测结果统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of pulse test results of the two systems
(Unit: times/minute) 名称 第一次测试 第二次测试 第三次测试 PbS量子点光电探测器 63 73 68 gladstone 64 70 73 -
[1] ARNOLD C G, WALKER J R, METTER E J, et al. Pulse oximeter plethysmograph waveform and automated oscillometric sphygmomanometer for ankle-brachial index measurement[J]. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2021, 40: 162-165. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.10.042 [2] FINE J, BRANAN K L, RODRIGUEZ A J, et al. Sources of inaccuracy in photoplethysmography for continuous cardiovascular monitoring[J]. Biosensors, 2021, 11(4): 126. doi: 10.3390/bios11040126 [3] CHOI S H, KIM S Y, PARK S H, et al. Diagnostic performance of CT, gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI, and PET/CT for the diagnosis of colorectal liver metastasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2018, 47(5): 1237-1250. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25852 [4] JUNG H, KIM D, LEE W, et al. Performance evaluation of a wrist-worn reflectance pulse oximeter during sleep[J]. Sleep Health, 2022, 8(5): 420-428. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2022.04.003 [5] WANG J, ZHU Y R, WU Z Y, et al. Wearable multichannel pulse condition monitoring system based on flexible pressure sensor arrays[J]. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2022, 8(1): 16. [6] 陈星池, 赵海, 李晗, 等. 近红外可穿戴设备中脉搏波的呼吸率检测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(6):1297-1306. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162406.1297CHEN X C, ZHAO H, LI H, et al. Detection of respiratory rate using pulse wave on near infrared wearable devices[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(6): 1297-1306. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162406.1297 [7] 张丽娜, 周润景, 武佩, 等. 基于心电、脉搏波信号的动脉硬化无创检测[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2016,33(4):631-638,644. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160105ZHANG L N, ZHOU R J, WU P, et al. Study on non-invasive detection of atherosclerosis based on electrocardiogram and pulse wave signals[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 33(4): 631-638,644. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.20160105 [8] MOÇO A, VERKRUYSSE W. Pulse oximetry based on photoplethysmography imaging with red and green light: Calibratability and challenges[J]. Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing, 2021, 35(1): 123-133. doi: 10.1007/s10877-019-00449-y [9] CHARLTON P H, PILT K, KYRIACOU P A. Establishing best practices in photoplethysmography signal acquisition and processing[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2022, 43(5): 050301. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ac6cc4 [10] MOÇO A V, STUIJK S, DE HAAN G. New insights into the origin of remote PPG signals in visible light and infrared[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 8501. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26068-2 [11] 吴育东, 钟舜聪, 伏喜斌. 基于光电容积脉搏波的血压测量实验研究[J]. 机电工程,2017,34(8):865-869. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2017.08.010WU Y D, ZHONG S C, FU X B. Blood pressure measurement based on photoelectric volume pulse wave[J]. Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, 2017, 34(8): 865-869. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4551.2017.08.010 [12] MAEDA Y, SEKINE M, TAMURA T, et al. Comparison of reflected green light and infrared photoplethysmography[C]. 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE, 2008: 2270-2272. [13] HUANG Y T, LIANG H F, ZHANG Y L, et al. Vertical tip-to-tip interconnection p–n silicon nanowires for plasmonic hot electron-enhanced broadband photodetectors[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2021, 4(2): 1567-1575. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c03048 [14] 朱晓秀, 葛咏, 李建军, 等. 量子点增强硅基探测成像器件的研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(1):62-74. doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0062ZHU X X, GE Y, LI J J, et al. Research progress of quantum dot enhanced silicon-based photodetectors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(1): 62-74. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/co.20201301.0062 [15] HOU B, KIM B S, LEE H K H, et al. Multiphoton absorption stimulated metal chalcogenide quantum dot solar cells under ambient and concentrated irradiance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(39): 2004563. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202004563 [16] HU A Q, TIAN H J, LIU Q L, et al. Graphene on self-assembled ingan quantum dots enabling ultrahighly sensitive photodetectors[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2019, 7(8): 1801792. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801792 [17] TANG J F, SIE Y D, TSENG Z L, et al. Perovskite quantum dot–ZnO nanowire composites for ultraviolet–visible photodetectors[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(5): 7237-7245. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.2c01145 [18] TETSUKA H, NAGOYA A, TAMURA S I. Graphene/nitrogen-functionalized graphene quantum dot hybrid broadband photodetectors with a buffer layer of boron nitride nanosheets[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(47): 19677-19683. doi: 10.1039/C6NR07707B [19] DONG R, BI C, DONG Q F, et al. An ultraviolet-to-NIR broad spectral nanocomposite photodetector with gain[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2014, 2(6): 549-554. doi: 10.1002/adom.201400023 [20] 许峻峰. 硫化铅量子点薄膜光电器件的性能提升[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2018.XU J F. Performance enhancement of PbS quantum dots based thin-film optoelectronic devices[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese). [21] LUO M T, CHEN R, ZHU Z W, et al. A broadband photodetector based on PbS quantum dots and graphene with high responsivity and detectivity[J]. Nanomaterials, 2023, 13(13): 1996. doi: 10.3390/nano13131996 [22] CHEN H, CHEN J. High performance near-infrared photodetector based on PbS quantum dots and graphene[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2022, 339: 113508. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2022.113508 [23] SONI A K, JOSHI R, NINGTHOUJAM R S. Hot Injection Method for Nanoparticle Synthesis: Basic Concepts, Examples And Applications[M]//TYAGI A K, NINGTHOUJAM R S. Handbook on Synthesis Strategies for Advanced Materials. Singapore: Springer, 2021: 383–434. [24] WU C Y, ZHU H N, WANG M, et al. Controlled synthesis of GaSe microbelts for high-gain photodetectors induced by the electron trapping effect[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(16): 5375-5379. doi: 10.1039/D0TC01120G -





 下载:
下载: