Improved integral sliding mode control strategy for the segmented arc permanent magnet synchronous motor based on dual observer
-
摘要:
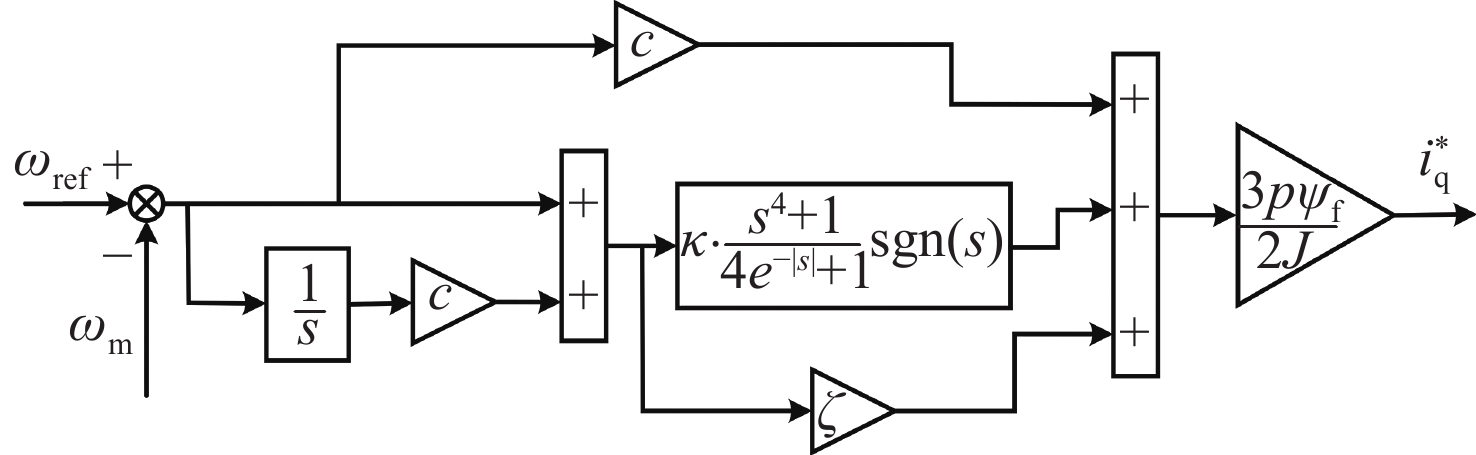
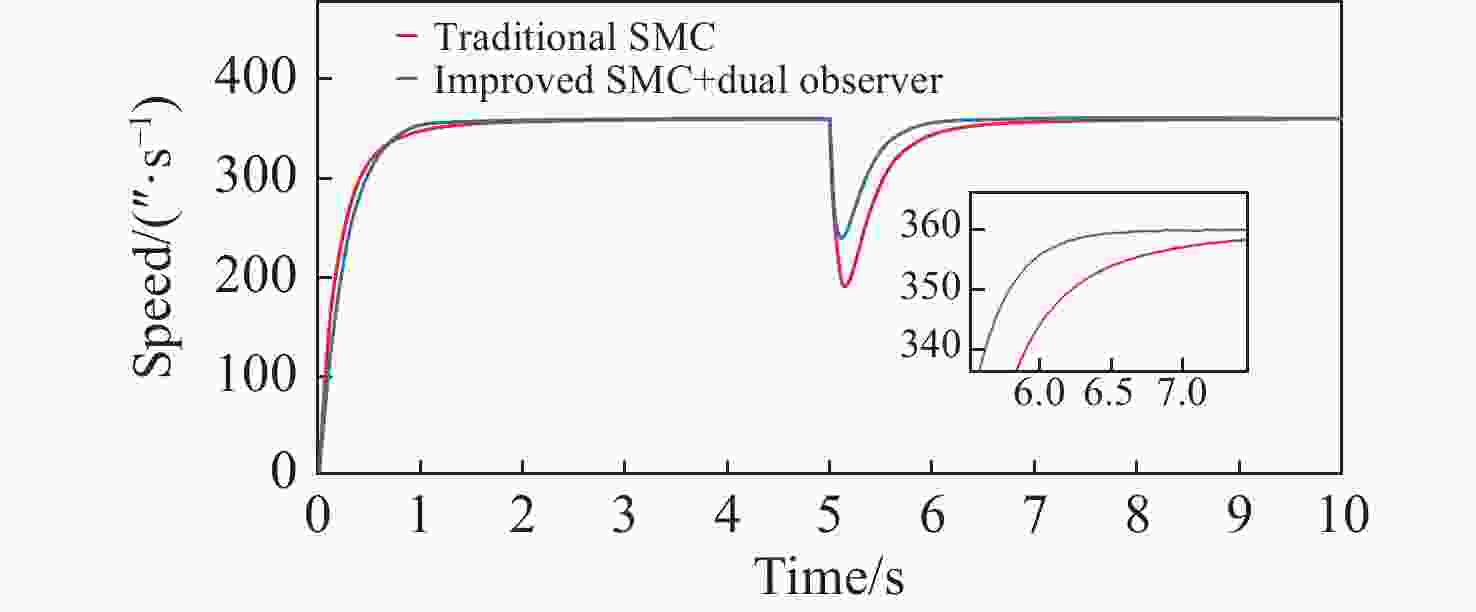
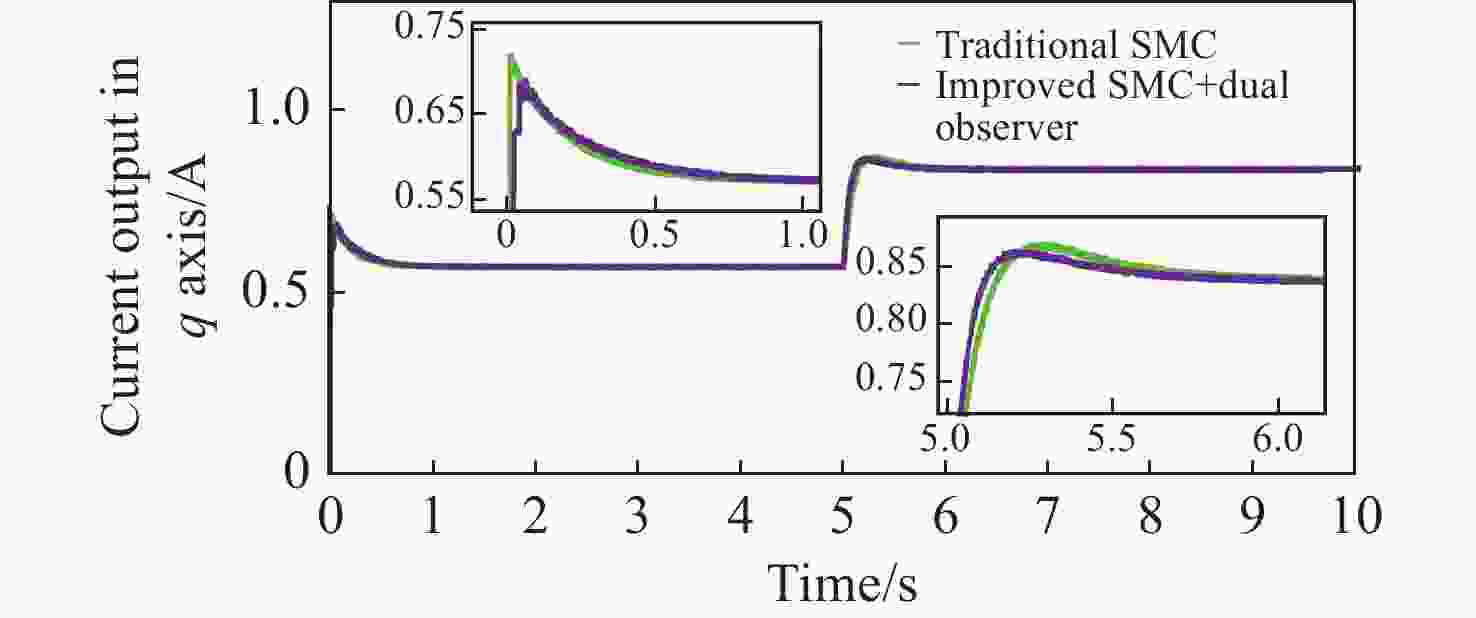
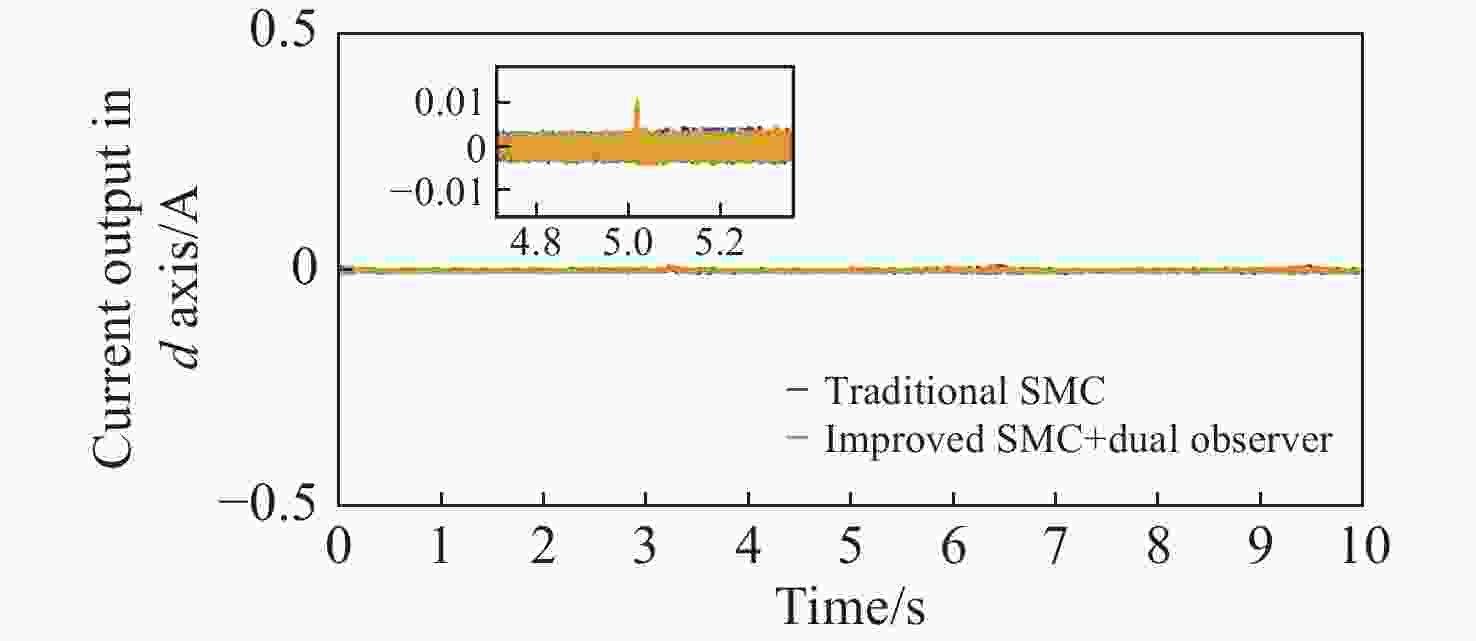
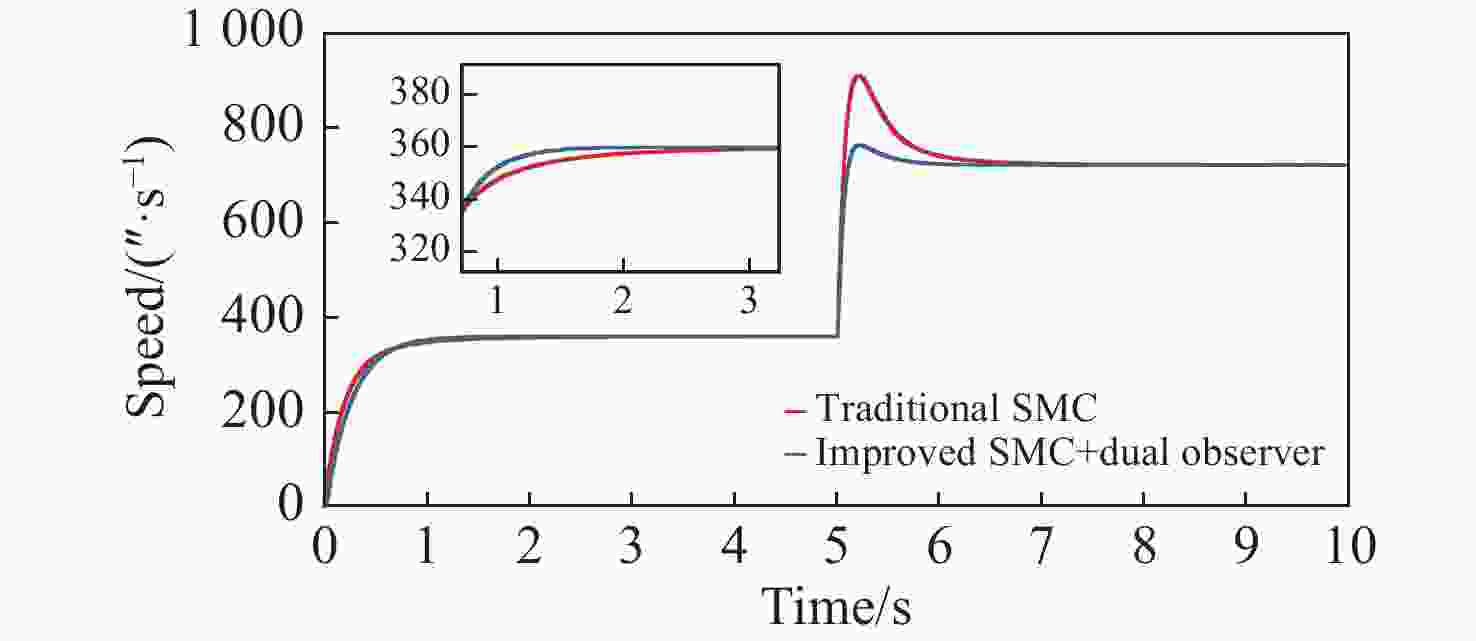
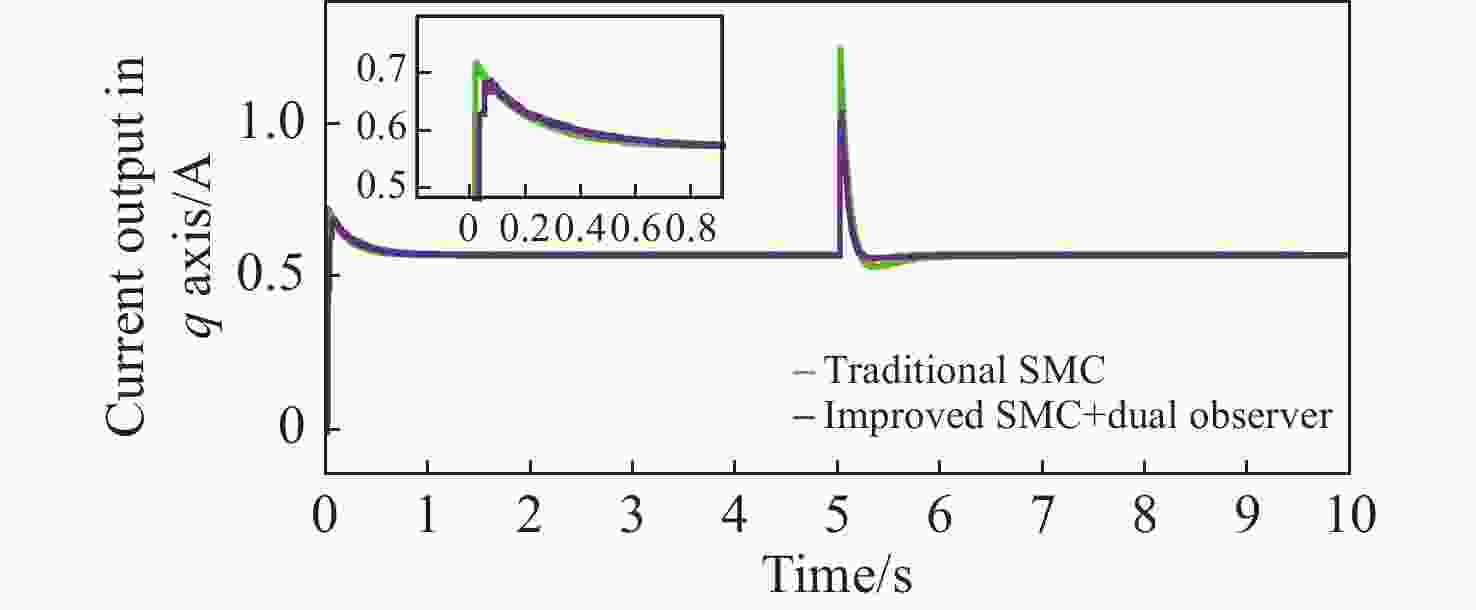
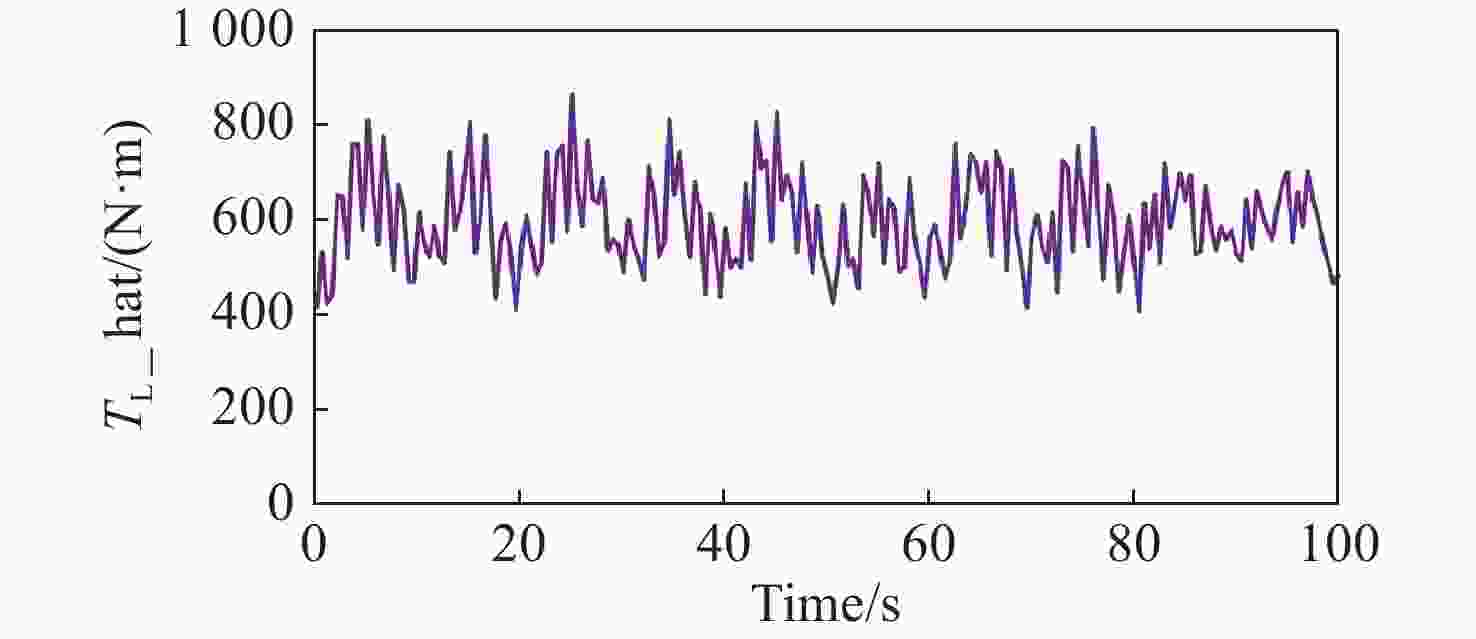
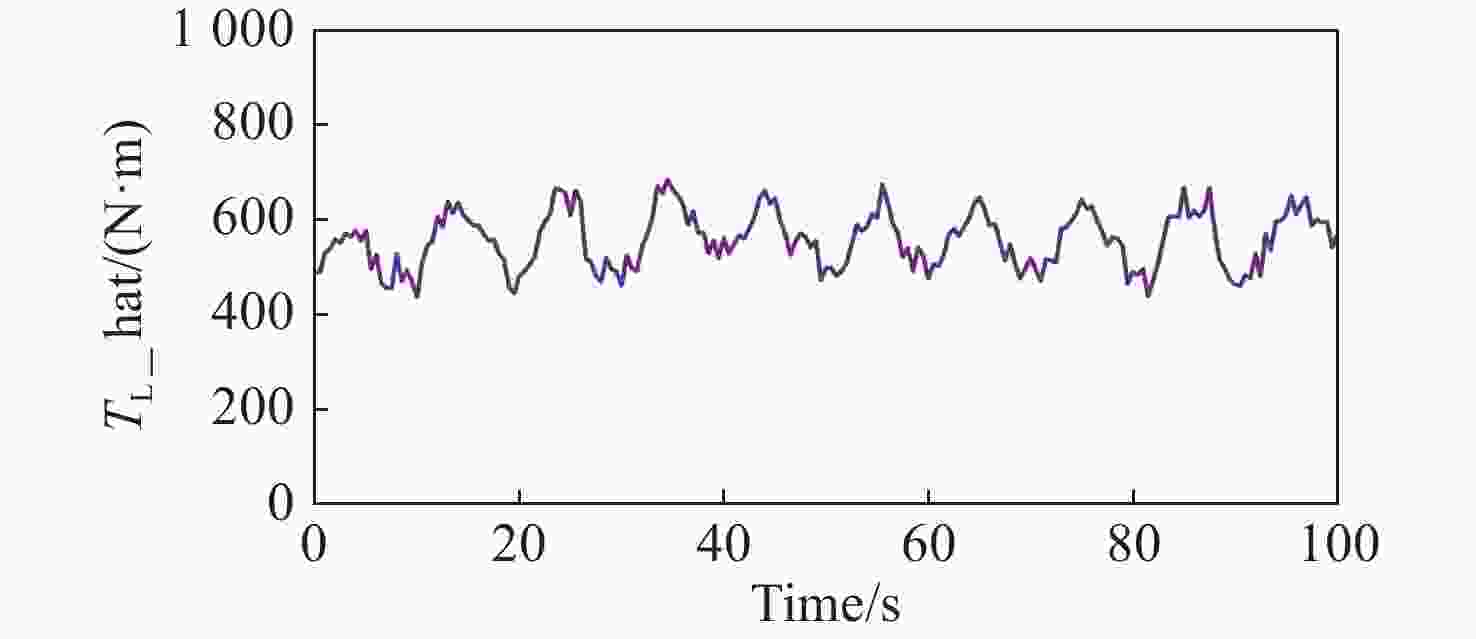
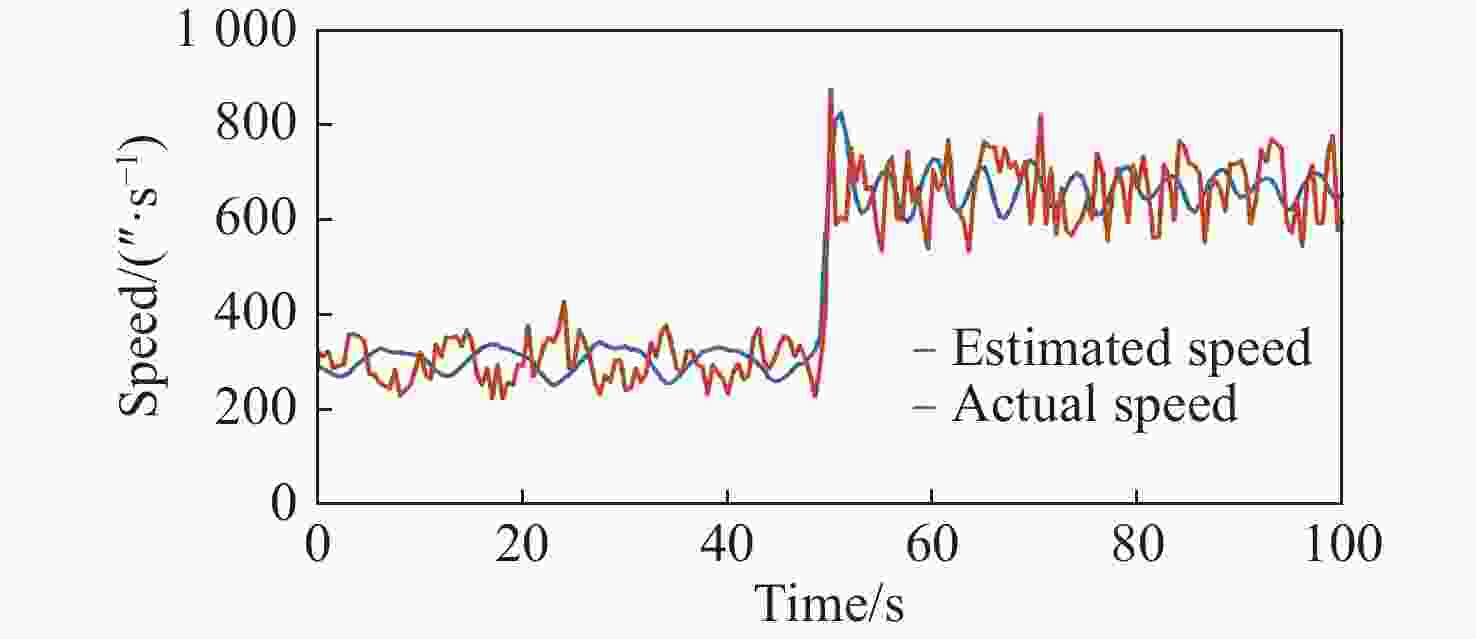
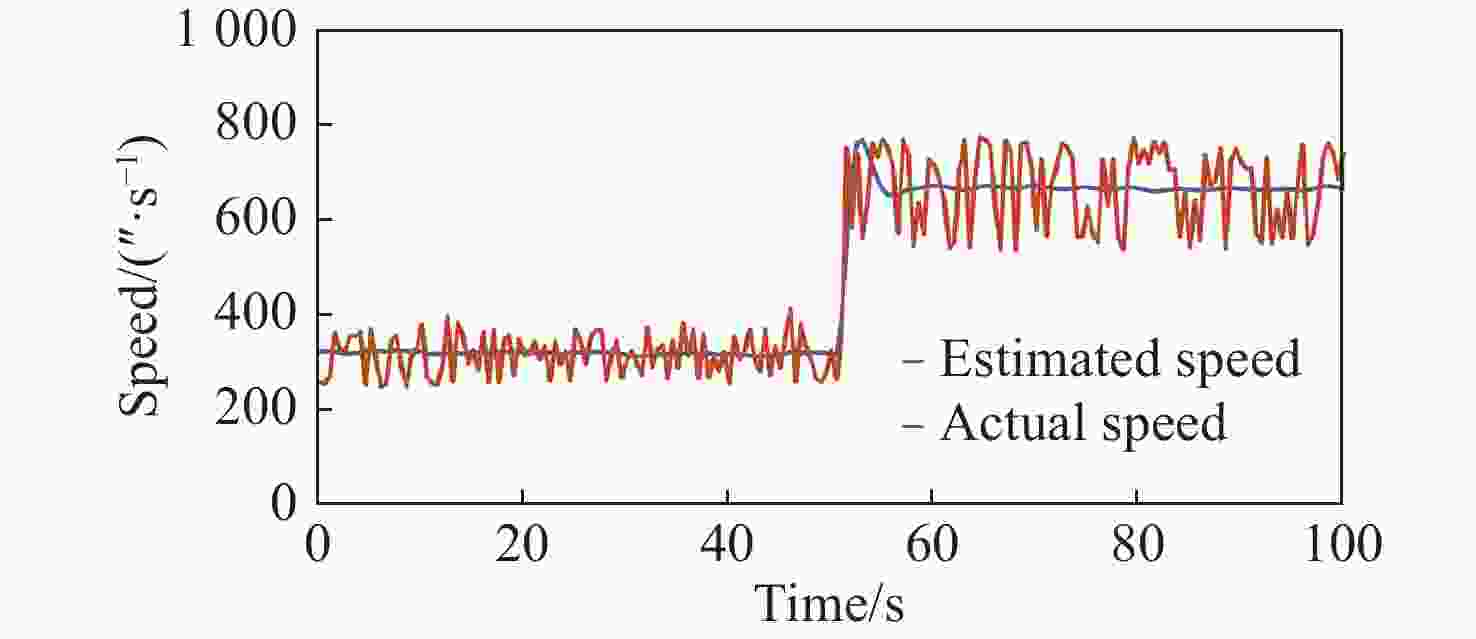
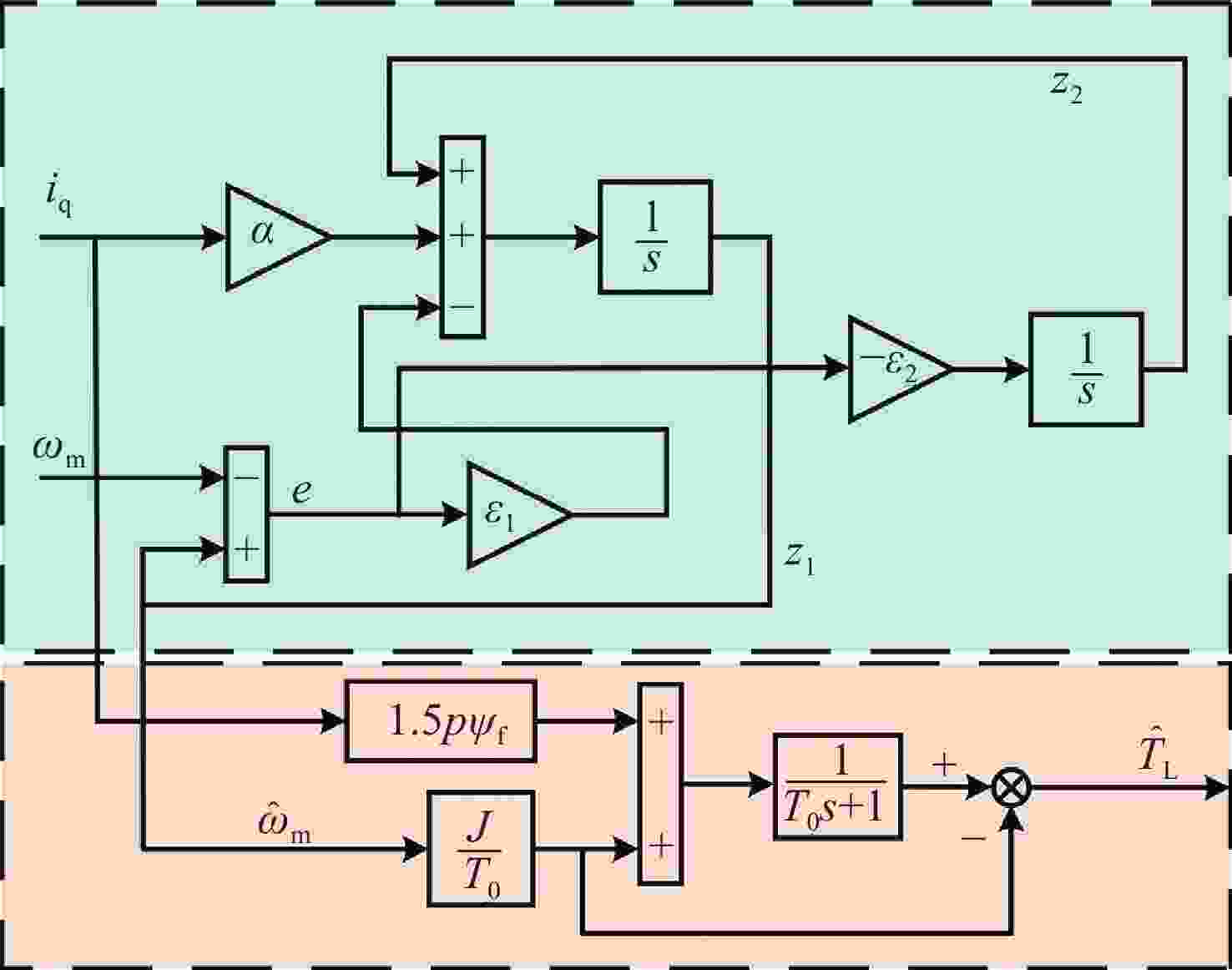
拼接弧线电机凭借其高转矩比和低速稳定运行等优点,为大口径天文望远镜观测提供了高性能驱动技术支持。电机运行过程中存在的如参数畸变、谐波等其他内外部干扰,都对提高电机性能提出了挑战。因此,本文提出一种基于新型趋近律的积分滑模控制器,同时结合扩张状态观测器与负载观测器的混合控制策略,旨在优化传统滑模控制并增强系统的抗干扰能力。传统趋近律参数较为繁杂且不能很好地抑制抖振,新型的趋近律简化了参数,有效克服了系统抖振。其次,采用扩张状态观测器对反馈转速进行估计,然后结合q轴电流信息和估计出的转速数据作为负载转矩观测器输入,进一步提高了负载观测性能,并将负载观测值转换为电流进行前馈补偿,用以提高电机的抗干扰性能。仿真和实验结果表明:所提出的双观测器方法能够有效观测电机的转速和负载值,显著增强了电机的抗负载扰动能力;同时,采用新型滑模速度控制器降低了电机转速超调量,并在一定程度上抑制了滑模抖振,为弧线电机在大口径天文望远镜的高精度观测应用提供了理论和实验支持。
-
关键词:
- 大型天文望远镜 /
- 拼接弧线永磁同步电机 /
- 双观测器 /
- 改进滑模控制
Abstract:With its high torque ratio and stable low-speed operation, the segmented arc permanent magnet synchronous motor (SAPMSM) provides high-performance drive technology support for large-aperture astronomical telescope observations. Improving the motor’s performance is challenging due to various internal and external interferences during its operation, such as parameter distortion, harmonics, etc. To this end, this paper proposes an integral sliding mode controller based on a new reaching law and a hybrid control strategy that combines an expanded state observer and a load observer, aiming to optimize the traditional sliding mode control and enhance the system’s anti-interference ability. The traditional reaching law has complicated parameters and cannot suppress chattering well. The new reaching law simplifies the parameters and effectively overcomes the system chattering. Second, an expanded state observer is used to estimate the feedback speed. Then, the q-axis current information and the estimated speed data are combined as the input of the load torque observer. This further improves the load observation performance and converts the load observation value into current for pre-processing. Feedback compensation is used to improve the motor’s anti-interference performance. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed dual observer method can effectively observe the motor's speed and load, significantly enhancing the motor’s ability to resist load disturbances. At the same time, the new sliding mode speed controller reduces the motor speed overshoot and suppresses the buffeting of the sliding mode to a certain extent, providing theoretical and experimental support for arc motors in high-precision observation applications of large-aperture astronomical telescopes.
-
表 1 拼接弧线电机参数
Table 1. Parameters of the SAPMSM
参数 数值 极对数$p$ 200 定子电阻${R_{\mathrm{s}}}/\Omega$ 20 d轴电感${L_{\text{d}}}/{\text{H}}$ 1.2 q轴电感${L_{\text{q}}}/{\text{H}}$ 1.2 转动惯量$J/({\text{Kg}} \cdot {{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}})$ 18000 永磁体磁链${\psi _{\text{f}}}/{\text{Wb}}$ 3.5 母线电压${U_{{\text{dc}}}}/{\text{V}}$ 300 -
[1] 霍银龙, 杨飞, 王富国. 大口径光学望远镜拼接镜面关键技术综述[J]. 中国光学(中英文),2022,15(5):973-982. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0109HUO Y L, YANG F, WANG F G. Overview of key technologies for segmented mirrors of large-aperture optical telescopes[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(5): 973-982. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0109 [2] SONG X L, CAO ZH J. Research on control strategy of hamiltonian theory for large telescope based on SAPMSM[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 31960-31967. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3368880 [3] 朱泳廷, 张泽. 基于音圈电机的柔性杆自抗扰LQR抑振控制算法研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2023,42(22):283-292.ZHU Y T, ZHANG Z. Algorithm for the LQR active disturbance rejection control of a flexible beam for vibration suppression based on voice coil motors[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(22): 283-292. (in Chinese). [4] ZHAO X M, GONG Y W, JIN H Y, et al. Adaptive super-twisting-based nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control of permanent magnet linear synchronous motor[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2023, 45(16): 3057-3066. doi: 10.1177/01423312231162782 [5] SUN Y P, LAN Y P, SHI X L, et al. Variable speed sliding mode control of magnetic suspension linear synchronous motor based on feedback linearization[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2023, 37(11): 5843-5853. doi: 10.1007/s12206-023-1023-3 [6] ZHOU N, DENG W X, YANG X W, et al. Continuous adaptive integral recursive terminal sliding mode control for DC motors[J]. International Journal of Control, 2023, 96(9): 2190-2200. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2022.2086928 [7] MOGHANNI-BAVIL-OLYAEI M R, KEIGHOBADI J, GHANBARI A, et al. Passivity-based hierarchical sliding mode control/observer of underactuated mechanical systems[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2023, 29(13-14): 3096-3111. doi: 10.1177/10775463221091035 [8] WU Y Q, YU J B, ZHANG ZH C. Output feedback regulation control for a class of cascade nonlinear systems by time-varying Kalman observer[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2019, 29(7): 2149-2170. doi: 10.1002/rnc.4485 [9] YUE B Y, CHENG Q M, CHENG Y M. Robustness improvement model predictive control strategy based on Luenberger observer for Y-type modular multilevel converter[J]. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 2023, 51(12): 5672-5690. doi: 10.1002/cta.3731 [10] LU E, LI W, YANG X F, et al. Anti-disturbance speed control of low-speed high-torque PMSM based on second-order non-singular terminal sliding mode load observer[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 88: 142-152. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2018.11.028 [11] LI ZH, FENG SH D, WANG J S, et al. Design of model-free position controller for PMSLM based on hyperlocal model[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2023, 105(4): 2361-2372. doi: 10.1007/s00202-023-01813-7 [12] SHU H Y, GUO CH, SONG Y T, et al. Design of model predictive controllers for PMSM drive system based on the extended Kalman filter observer[J]. International Journal of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles, 2019, 11(4): 378-394. doi: 10.1504/IJEHV.2019.102887 [13] SUN ZH Y, TAN C, LI B, et al. Dual model predictive control strategy of direct-drive PMSM based on sliding mode disturbance observer[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2024, 19(4): 527-534. doi: 10.1002/tee.24001 [14] LIU H X, MEI K Q, LIU L, et al. Fixed-time non-singular terminal sliding mode control for PMSM drive systems[J]. Journal of Power Electronics, 2024, 24(2): 258-268. doi: 10.1007/s43236-023-00727-8 [15] LIU L, LIU Y X, ZHOU L L, et al. Cascade ADRC with neural network-based ESO for hypersonic vehicle[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2023, 360(12): 9115-9138. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.09.019 [16] 张海洋, 许海平, 方程, 等. 基于负载转矩观测器的直驱式永磁同步电机新型速度控制器设计[J]. 电工技术学报,2018,33(13):2923-2934.ZHANG H Y, XU H P, FANG CH, et al. Design of a novel speed controller for direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous motor based on load torque observer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(13): 2923-2934. (in Chinese). [17] 王东辉, 孔国利, 陈书立. 采用滑模观测器的机载激光通信视轴精度控制[J]. 红外与激光工程,2022,51(3):20210460. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210460WANG D H, KONG G L, CHEN SH L. Precision control of airborne laser communication optical axis using sliding mode observer[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(3): 20210460. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210460 [18] ZHANG ZH C, LI L, WU Y Q. Disturbance-observer-based antiswing control of underactuated crane systems via terminal sliding mode[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 12(18): 2588-2594. [19] MA H F, LI Y M, XIONG ZH H. Discrete-time sliding-mode control with enhanced power reaching law[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(6): 4629-4638. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2864712 -





 下载:
下载: